A genus of literary works. Genera and genres of literature
Read also
For millennia cultural development mankind has created countless literary works, among which some basic types can be distinguished, similar in the way and form of reflection of man's ideas about the world around him. These are three kinds (or types) of literature: epic, drama, lyrics.
What is the difference between each type of literature?
Epic as a kind of literature
Epos(epos - Greek, narration, story) is an image of events, phenomena, processes external to the author. Epic works reflect the objective course of life, human being in general. Using various artistic means, the authors of epic works express their understanding of the historical, socio-political, moral, psychological and many other problems that human society in general and each of its representatives in particular lives with. Epic works have significant pictorial capabilities, thereby helping the reader to learn about the world around him, to comprehend the deep problems of human existence.
Drama as a kind of literature
Drama(drama - Greek, action, action) is a kind of literature, the main feature of which is the scenic nature of works. Plays, i.e. dramatic works are created specifically for the theater, for staging on stage, which, of course, does not exclude their existence in the form of independent literary texts intended for reading. Like the epic, the drama reproduces the relationship between people, their actions, the conflicts that arise between them. But unlike the epic, which has a narrative nature, the drama has a dialogical form.
Associated with this features of dramatic works :
2) the text of the play consists of the conversations of the characters: their monologues (the speech of one character), dialogues (the conversation of two characters), polylogs (the simultaneous exchange of replicas of several participants in the action). That's why speech characteristic turns out to be one of the most important means of creating a memorable character of the hero;
3) the action of the play, as a rule, develops quite dynamically, intensively, as a rule, it is given 2-3 hours of stage time.
Lyrics as a kind of literature
Lyrics(lyra - Greek, a musical instrument, to the accompaniment of which poetic works, songs were performed) is distinguished by a special type of construction of an artistic image - it is an image-experience in which the individual emotional and spiritual experience of the author is embodied. Lyrics can be called the most mysterious kind of literature, because it is addressed to the inner world of a person, his subjective sensations, ideas, ideas. In other words, a lyric work primarily serves the individual self-expression of the author. The question arises: why the readers, i.e. other people refer to such works? The point is that the lyricist, speaking on his own behalf and about himself, surprisingly embodies universal human emotions, ideas, hopes, and the more significant the author's personality, the more important his individual experience is for the reader.
Each type of literature also has its own system of genres.
genre(genre - French genus, species) is a historically developed type of literary works that has similar typological features. The names of genres help the reader navigate the boundless sea of literature: someone loves detective stories, another prefers fantasy, and the third is a fan of memoirs.
How to determine What genre does a particular work belong to? Most often, the authors themselves help us in this, calling their creation a novel, story, poem, etc. However, some of the author's definitions seem unexpected to us: remember that A.P. Chekhov stressed that "The Cherry Orchard" is a comedy, and not a drama at all, but A.I. Solzhenitsyn considered One Day in the Life of Ivan Denisovich to be a story, not a story. Some literary critics call Russian literature a collection of genre paradoxes: a novel in verse "Eugene Onegin", a poem in prose " Dead Souls", Satirical chronicle" The history of one city. " There was a lot of controversy regarding "War and Peace" by L.N. Tolstoy. The writer himself said only about what his book is not: “What is“ War and Peace ”? This is not a novel, even less a poem, still less a historical chronicle. "War and Peace" is what the author wanted and could express in the form in which it was expressed. " And only in the XX century literary critics agreed to call ingenious creation L.N. Tolstoy's epic novel.
Each literary genre has a number of stable features, the knowledge of which allows us to assign a specific work to one or another group. Genres develop, change, die off and are born, for example, literally before our eyes arose new genre blog (web loq English network journal) - personal internet diary.
However, for several centuries there have been stable (they are also called canonical) genres
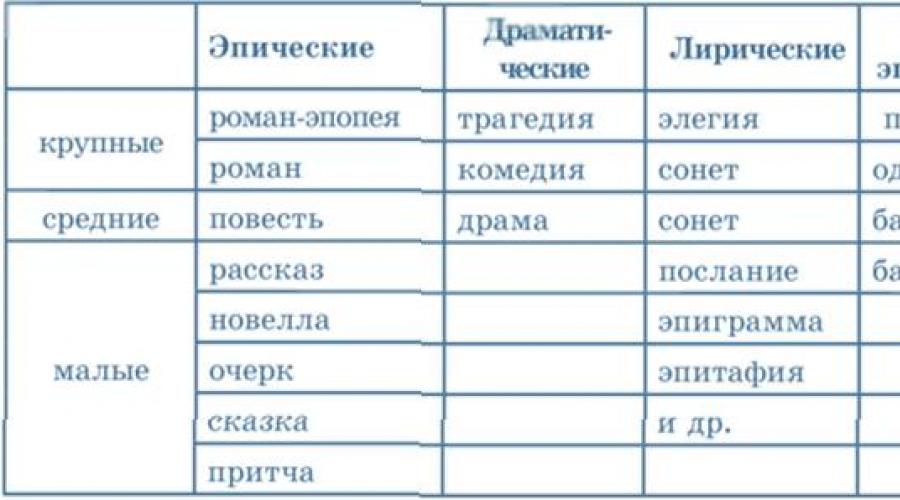
Literature literary works - see table 1).
Table 1.
Genres of literary works 
Epic genres of literature
Epic genres primarily differ in volume, according to this criterion they are divided into small ones ( sketch, story, short story, fairy tale, parable ), average ( story ), large ( novel, epic novel ).
Feature article- a small sketch from nature, the genre is both descriptive and narrative. Many essays are created on a documentary, life-based basis, often they are combined into cycles: classic pattern - « Sentimental journey across France and Italy "(1768) English writer Lawrence Stern, in Russian literature it is "A Journey from St. Petersburg to Moscow" (1790) by A. Radishchev, "Frigate Pallas" (1858) by I. Goncharov "" Italy "(1922) by B. Zaitsev and others.
Story- a small narrative genre, which usually depicts one episode, incident, human character, or an important incident in the life of the hero that influenced him further destiny("After the Ball" by L. Tolstoy). The stories are created both on a documentary, often autobiographical basis ("Matryonin Dvor" by A. Solzhenitsyn), and thanks to pure fiction ("The Lord from San Francisco" by I. Bunin).
The intonation and content of stories are very different - from comic, curious ( early stories A.P. Chekhov ") to deeply tragic (" Kolyma stories"V. Shalamov). Stories, like essays, are often combined into cycles ("Notes of a Hunter" by I. Turgenev).
Novella(novella ital. news) is in many ways akin to a story and is considered its kind, but it is distinguished by a special dynamism of the narrative, sharp and often unexpected turns in the development of events. Often, the narrative in a novel begins with the ending, is built according to the law of inversion, i.e. the reverse order, when the denouement precedes the main events ("Terrible revenge" by N. Gogol). This feature of the construction of the novel will later be borrowed by the detective genre.
The word "novella" has another meaning that future lawyers need to know. V Ancient Rome the phrase "novellae leges" (new laws), called the laws introduced after the official codification of law (after the release of the Code of Theodosius II in 438). The novels of Justinian and his successors, published after the second edition of the Code of Justinian, later formed part of the corpus of Roman laws (Corpus iuris civillis). V modern era a novel is a law submitted to parliament (in other words, a draft law).
Fairy tale- The oldest of the small epic genres, one of the main in the oral work of any nation. This is a small work of a magical, adventurous or everyday character, where fiction is clearly emphasized. Another important feature of a folk tale is its edifying nature: "A fairy tale is a lie, but there is a hint in it, a lesson for good fellows." It is customary to divide folk tales into magic ("The Tale of the Frog Princess"), everyday ("Porridge from the Ax") and tales about animals ("Zayushkina's hut").
With the development of written literature, literary tales appear in which traditional motives and symbolic possibilities of a folk tale are used. Danish writer Hans Christian Andersen (1805-1875), his wonderful "The Little Mermaid", "The Princess and the Pea", " The Snow Queen"," Persistent tin soldier"," Shadow "," Thumbelina "are loved by many generations of readers, both very young and quite mature. And this is far from accidental, because Andersen's tales are not only extraordinary, but sometimes even strange adventures of the heroes, they contain a deep philosophical and moral sense, enclosed in beautiful symbolic images.
Of the European literary tales of the 20th century, The Little Prince (1942) by the French writer Antoine de Saint-Exupery has become a classic. And the famous "Chronicles of Narnia" (1950 - 1956) by the English writer Cl. Lewis and "The Lord of the Rings" (1954-1955), also by the Englishman JR Tolkien, are written in the fantasy genre, which can be called a modern transformation of an ancient folk tale.
In Russian literature, unsurpassed, of course, are the tales of A.S. Pushkin: "Oh dead princess and seven heroes "," About the fisherman and the fish "," About Tsar Saltan ... "," About the golden cockerel "," About the priest and his worker Balda ". The replacement storyteller was P. Ershov, the author of The Little Humpbacked Horse. E. Schwartz in the XX century creates the form of a fairy tale play, one of them "The Bear" (another name is "An Ordinary Miracle") is well known to many thanks to the wonderful film directed by M. Zakharov.
Parable- also very Ancient folklore genre, but, unlike the fairy tale, the parables contained written monuments: the Talmud, the Bible, the Koran, a monument of Syrian literature "Teaching to Akhara". A parable is an instructive, symbolic work, distinguished by its sublimity and seriousness of content. Ancient parables, as a rule, are small in volume, they do not contain detailed story about the events or psychological characteristics of the character of the hero.
The purpose of the parable is edification or, as they once said, the teaching of wisdom. In European culture, the most famous are the parables from the Gospels: prodigal son, about the richer and Lazarus, about the unrighteous judge, about the insane richer and others. Christ often spoke allegorically to his disciples, and if they did not understand the meaning of the parable, he explained it.
Many writers turned to the genre of the parable, not always, of course, putting a high religious meaning into it, but rather trying to express some moralistic edification in an allegorical form, as, for example, L. Tolstoy in his late creativity... Carry it. V. Rasputin - Farewell to Mother ”can also be called a detailed parable, in which the writer speaks with alarm and sorrow about the destruction of the“ ecology of conscience ”of a person. The story "The Old Man and the Sea" by E. Hemingway is also considered by many critics to be a literary parable tradition. The famous modern Brazilian writer Paulo Coelho also uses the parable form in his novels and stories (the novel "The Alchemist").
The story- an average literary genre, widely represented in world literature. The story depicts several important episodes from the life of the hero, as a rule, one storyline and a small amount of actors. Stories are characterized by a large psychological saturation, the author focuses on the experiences and mood changes of the characters. Very often, the main theme of the story becomes the love of the protagonist, for example, "White Nights" by F. Dostoevsky, "Asya" by I. Turgenev, "Mitya's Love" by I. Bunin. Novels can also be combined into cycles, especially those written on autobiographical material: "Childhood", "Adolescence", "Youth" by L. Tolstoy, "Childhood", "In People", "My Universities" by A. Gorky. The intonations and themes of the stories are very diverse: tragic, addressed to acute social and moral issues("Everything flows" by V. Grossman, "House on the Embankment" by Y. Trifonov), romantic, heroic ("Taras Bulba" by N. Gogol), philosophical, parable ("Pit" by A. Platonov), mischievous, comic ("Three in a boat, not counting a dog "by the English writer Jerome K. Jerome).
novel(French gotap originally, in late middle ages, any work written in the Romance language, as opposed to those written in Latin) is a major epic work in which the narrative is focused on the fate of an individual person. The novel is the most complex epic genre, which is distinguished by an incredible number of themes and plots: love, historical, detective, psychological, fantastic, historical, autobiographical, social, philosophical, satirical, etc. All these forms and types of the novel are united by its central idea - the idea of personality, individuality of a person.
The novel is called the epic of private life, because it depicts the diverse connections between the world and man, society and personality. Surrounding man reality is presented in the novel in different contexts: historical, political, social, cultural, national, etc. The author of the novel is interested in how the environment affects a person's character, how he is formed, how his life develops, whether he managed to find his purpose and realize himself.
The origin of the genre is attributed by many to antiquity, these are Long's "Daphnis and Chloe", Apuleius's "Golden Donkey", the knightly novel "Tristan and Isolde".
In the works of the classics of world literature, the novel is represented by numerous masterpieces:
Table 2. Examples of classic novel foreign and Russian writers (XIX, XX centuries) 
Famous novels Russians writers XIX v
.:
In the XX century, Russian writers develop and multiply the traditions of their great predecessors and create no less remarkable novels:

Of course, none of these enumerations can pretend to be complete and complete objectivity, especially in contemporary prose. In this case, the most famous works, who glorified both the country's literature and the name of the writer.
Epic novel... In ancient times, there were forms of heroic epic: folklore sagas, runes, epics, songs. These are the Indian "Ramayana" and "Mahabharata", the Anglo-Saxon "Beowulf", the French "Song of Roland", the German "Song of the Nibelungs", etc. In these works in an idealized, often exaggerated form, the hero's feats were exalted. The later epic poems "Iliad" and "Odyssey" by Homer, "Shah-name" by Ferdowsi, while retaining the mythological character of the early epic, nevertheless, had a pronounced connection with real story, and the weave theme human destiny and the life of the people becomes one of the main in them. The experience of the ancients will be in demand in XIX-XX centuries, when writers try to comprehend the dramatic relationship between the era and the individual personality, talk about what tests are subjected to morality, and sometimes the human psyche at the time of the greatest historical upheavals. Let us recall the lines of F. Tyutchev: "Blessed is he who visited this world in its fateful moments." The poet's romantic formula in reality meant the destruction of all habitual forms of life, tragic losses and unrealized dreams.
The complex form of the epic novel allows writers to artistically explore these problems in their entirety and contradictions.
When we talk about the genre of an epic novel, of course, we immediately recall "War and Peace" by L. Tolstoy. Other examples can be named: “ Quiet Don"M. Sholokhov," Life and Fate "by V. Grossman," The Forsyte Saga "by the English writer Galsworthy; the book by the American writer Margaret Mitchell “ gone With the Wind»Also with great reason can be ranked in this genre.
The very name of the genre indicates a synthesis, a combination of two main principles in it: the novel and the epic, i.e. associated with the theme of the life of an individual and the theme of the history of the people. In other words, the epic novel tells about the fates of the heroes (as a rule, the heroes themselves and their fates are fictional, invented by the author) against the background and in close connection with epoch-making historical events. Thus, in War and Peace, these are the fates of individual families (Rostovs, Bolkonskys), favorite heroes (Prince Andrei, Pierre Bezukhov, Natasha and Princess Marya) at a turning point for Russia and all of Europe historical period the beginning of the 19th century, the Patriotic War of 1812. In Sholokhov's book - the events of the First World War, two revolutions and a bloody civil war tragically intrude into the life of a Cossack farm, the Melekhov family, the fate of the main characters: Grigory, Aksinya, Natalia. V. Grossman talks about the Great Patriotic War and its main event - the Battle of Stalingrad, about the tragedy of the Holocaust. Life and Fate also intertwines the historical and family theme: the author traces the history of the Shaposhnikovs, trying to understand why the fates of the members of this family developed so differently. Galsworthy describes the life of the Forsyte family during the legendary Victorian era in England. Margaret Mitchell is the central event in US history, the North-South Civil War, which drastically changed the lives of many families and the fate of the most famous heroine of American literature - Scarlett O'Hara.
Dramatic genres literature
Tragedy(tragodia Greek goat song) is a dramatic genre that originated in Ancient Greece... Emergence ancient theater and tragedies are associated with the worship of the cult of the god of fertility and wine, Dionysus. A number of holidays were dedicated to him, during which ritual magic games were played with mummers, satyrs, whom the ancient Greeks represented in the form of two-legged goat-like creatures. It is assumed that it was precisely this appearance of the satyrs who performed hymns to the glory of Dionysus that gave such a strange name to this serious genre in translation. Theatrical performance in Ancient Greece was given a magical religious significance, and theaters, built in the form of large open-air arenas, were always located in the very center of cities and were one of the main public places. Spectators sometimes spent the whole day here: eating, drinking, loudly expressing their approval or censure of the presented show. The heyday of the ancient Greek tragedy is associated with the names of three great tragedians: this is Aeschylus (525-456 BC) - the author of the tragedies "Chained Prometheus", "Oresteia", etc .; Sophocles (496-406 BC) - the author of "King Oedipus", "Antigone" and others; and Euripides (480-406 BC) - the creator of Medea, Troyanok, etc. Their creations will remain examples of the genre for centuries, they will try to imitate them, but they will remain unsurpassed. Some of them ("Antigone", "Medea") are staged on the stage today.
What are the main features of the tragedy? The main one is the presence of an insoluble global conflict: in ancient tragedy, this is the confrontation between fate, fate, on the one hand, and a person, his will, free choice, on the other. In the tragedies of later eras, this conflict took on a moral and philosophical character, as a confrontation between good and evil, loyalty and betrayal, love and hatred. It has an absolute character, the heroes embodying the opposing forces are not ready for reconciliation, compromise, and therefore there are often many deaths at the end of the tragedy. This is how the tragedies of the great English playwright William Shakespeare (1564-1616), remember the most famous of them: "Hamlet", "Romeo and Juliet", "Othello", "King Lear", "Macbeth", "Julius Caesar" and others.
In the tragedies of the 17th century French playwrights Corneille (Horace, Polyeuct) and Racine (Andromache, Britannica), this conflict received a different interpretation - as a conflict of duty and feeling, rational and emotional in the souls of the protagonists, that is ... acquired a psychological interpretation.
The most famous in Russian literature is the romantic tragedy "Boris Godunov" by A.S. Pushkin, based on historical material. In one of his best works, the poet sharply raised the problem of the "real trouble" of the Moscow state - a chain reaction of impostors and "terrible atrocities" that people are ready for for the sake of power. Another problem is the attitude of the people to everything that happens in the country. The image of the “silent” people in the finale of “Boris Godunov” is symbolic, and discussions continue to this day about what Pushkin wanted to say. The opera of the same name by M.P. Mussorgsky was written based on the tragedy, which has become a masterpiece of Russian opera classics.
Comedy(Greek komos - a cheerful crowd, oda - a song) - a genre that originated in Ancient Greece a little later tragedy(V century BC). The most famous comedian of that time is Aristophanes ("Clouds", "Frogs", etc.).
In comedy with the help of satire and humor, i.e. comic, moral vices are ridiculed: hypocrisy, stupidity, greed, envy, cowardice, complacency. Comedies are usually topical, i.e. are also addressed to social issues, exposing the shortcomings of the authorities. Distinguish between sitcoms and comedies of characters. In the first, a cunning intrigue, a chain of events ("The Comedy of Errors" by Shakespeare) are important, in the second - the characters of the characters, their absurdity, one-sidedness, as in the comedies "The Minor" by D. Fonvizin, "Bourgeois in the Nobility", "Tartuffe", belonging to the classics genre, the French comedy of the 17th century Jean Baptiste Moliere. In Russian drama, it turned out to be especially in demand satirical comedy with her sharp social criticism, for example, "The Inspector General" by N. Gogol, "Crimson Island" by M. Bulgakov. Many wonderful comedies were created by A. Ostrovsky ("Wolves and Sheep", "Forest", "Mad Money", etc.).
The genre of comedy is invariably popular with the public, perhaps because it affirms the triumph of justice: in the finale, vice must certainly be punished, and virtue must triumph.
Drama- a relatively "young" genre that appeared in Germany in the 18th century as lesedrama (German) - a play for reading. The drama is addressed to the everyday life of a person and society, everyday life, family relations. Drama is primarily interested in the inner world of a person, it is the most psychological of all dramatic genres. At the same time, it is the most literary of the stage genres, for example, the plays of A. Chekhov are largely perceived more as texts for reading, and not as theatrical performances.
Lyric genres of literature
The division into genres in the lyrics is not absolute, since the differences between genres in this case are conditional and not as obvious as in epic and drama. More often we distinguish lyric works by their thematic features: landscape, love, philosophical, friendly, intimate lyrics, etc. However, you can name some genres that have pronounced individual characteristics: elegy, sonnet, epigram, message, epitaph.
Elegy(elegos Greek. plaintive song) - a poem of medium length, as a rule, moral-philosophical, love, confessional content.
The genre originated in antiquity, and the elegiac distich was considered its main feature, i.e. dividing a poem into couplets, for example:
The longed-for moment has come: my work of many years is over, Why is an incomprehensible sadness secretly disturbing me?
A. Pushkin
In the poetry of the XIX-XX centuries, division into couplets is no longer such a strict requirement, now semantic signs that are associated with the origin of the genre are more significant. Essentially, the elegy goes back to the form of the Ancient funeral "lamentation", in which, mourning the deceased, at the same time recalled his extraordinary merits. This origin predetermined the main feature of the elegy - the combination of sorrow with faith, regret with hope, acceptance of being through sorrow. The lyrical hero of the elegy is aware of the imperfection of the world and people, his own sinfulness and weakness, but does not reject life, but accepts it in all its tragic beauty. A striking example is "Elegy" by A.S. Pushkin:
Crazy years faded fun
It's hard for me like a vague hangover.
But like wine is the sadness of days gone by
In my soul, the older the stronger.
My path is dull. Promises me labor and sorrow
The coming agitated sea.
But I don’t want to die, oh friends;
I want to live in order to think and suffer;
And I know I will enjoy
Between sorrows, worries and worries:
Sometimes I'll revel in harmony again,
I will shed tears over fiction,
And maybe - to my sad sunset
Love will shine with a farewell smile.
Sonnet(sonetto ital. song) - the so-called "solid" poetic form, which has strict rules of construction. The sonnet has 14 lines, divided into two quatrains (quatrains) and two three verses (tercets). In quatrains, only two rhymes are repeated, in tercets, two or three. The methods of rhyming also had their own requirements, which, however, varied.
The birthplace of the sonnet is Italy; this genre is also represented in English and French poetry. The coryphaeus of the genre is considered the Italian poet Petrarch of the XIV century. He dedicated all his sonnets to his beloved Donna Laura.
In Russian literature, the sonnets of A.S. Pushkin remain unsurpassed, beautiful sonnets were also created by the poets of the Silver Age.
Epigram(Greek epigramma, inscription) is a short, mocking poem, usually addressed to a specific person. Epigrams are written by many poets, sometimes increasing the number of their ill-wishers and even enemies. The epigram on Count Vorontsov turned around for A.S. Pushkin's hatred of this nobleman and, ultimately, the expulsion from Odessa to Mikhailovskoe:
Popu-my lord, half-merchant,
Half-sage, half-ignorant,
Half a scoundrel, but there is hope
That will be complete at last.
Mocking verses can be dedicated not only to a specific person, but also to a generalized addressee, as, for example, in the epigram of A. Akhmatova:
Could Biche like Dante create,
Went Laura to glorify the heat of love?
I taught women to speak ...
But, God, how to silence them!
There are even known cases of a kind of duel of epigrams. When the famous Russian lawyer A.F. Horses were appointed to the Senate, ill-wishers extended an evil epigram to him:
Caligula brought a horse to the Senate,
He stands dressed in velvet and gold.
But I will say, we have the same arbitrariness:
I read in the newspapers that Koni is in the Senate.
To which A.F. Horses, distinguished by an outstanding literary talent, replied:
(Greek epitafia, tombstone) - a poem-farewell to a deceased person, intended for a tombstone. Initially, this word was used literally, but later it received more figurative meaning... For example, I. Bunin has a lyrical miniature in prose "Epitaph", dedicated to parting with the road for the writer, but forever receding into the past Russian estate. Gradually, the epitaph is transformed into a dedication poem, a farewell poem ("Wreath for the Dead" by A. Akhmatova). Perhaps the most famous poem of this kind in Russian poetry is The Death of a Poet by M. Lermontov. Another example is the "Epitaph" by M. Lermontov, dedicated to memory Dmitry Venevitinov, poet and philosopher, who died at the age of twenty-two.
Lyro-epic genres of literature
There are works in which some of the features of lyrics and epics are combined, as evidenced by the very name of this group of genres. Their main feature is the combination of the narrative, i.e. a story about events, with the transfer of the feelings and experiences of the author. It is customary to refer to lyric-epic genres poem, ode, ballad, fable .
Poem(poeo Greek. I create I create) is a very famous literary genre. The word "poem" has many meanings, both direct and figurative. In ancient times, poems were called large epic works, which today are considered epics (the above-mentioned poems of Homer).
V literature XIX-XX centuries, a poem is a large poetic work with a detailed plot, for which it is sometimes called a poetic story. The poem has characters, a plot, but their purpose is somewhat different than in a prose story: in the poem they help the lyrical self-expression of the author. This is probably why romantic poets loved this genre so much (Ruslan and Lyudmila by early Pushkin, Mtsyri and Demon by M. Lermontov, Cloud in Pants by V. Mayakovsky).
Oh yeah(oda Greek song) - a genre represented mainly in the literature of the 18th century, although it also has ancient origins... The ode goes back to the ancient genre of dithyramba - a hymn that glorifies folk hero or a winner Olympic Games, i.e. an outstanding person.
Poets of the 18th-19th centuries created odes on different cases... This could have been an appeal to the monarch: M. Lomonosov dedicated his odes to Empress Elizabeth, G. Derzhavin to Catherine P. Glorifying their deeds, the poets simultaneously taught the empresses and inspired them with important political and civic ideas.
Significant historical events could also be the subject of glorification and admiration in an ode. G. Derzhavin after the capture of the Russian army under the command of A.V. Suvorov of the Turkish fortress Izmail wrote the ode "Thunder of victory, sound!", Which for some time was an unofficial anthem Russian Empire... There was a kind of spiritual ode: "Morning Meditation on God's Greatness" by M. Lomonosov, "God" by G. Derzhavin. Civil, political ideas could also become the basis of the ode ("Liberty" by A. Pushkin).
This genre has a pronounced didactic nature; it can be called a poetic sermon. Therefore, it is distinguished by the solemnity of syllable and speech, the unhurried narrative. An example is the famous excerpt from "Ode on the day of her Majesty Empress Elizabeth Petrovna's accession to the All-Russian throne in 1747" by M. Lomonosov, written in the year when Elizabeth approved the new charter of the Academy of Sciences, significantly increasing funds for its maintenance. The main thing for the great Russian encyclopedist is the enlightenment of the young generation, the development of science and education, which, in the poet's conviction, will become the guarantee of Russia's prosperity.
Ballad(balare provence - dance) enjoyed particular popularity at the beginning of the 19th century, in sentimental and romantic poetry. This genre originated in French Provence as a folk dance of love content with obligatory choruses-repetitions. Then the ballad migrated to England and Scotland, where it acquired new features: now it is a heroic song with a legendary plot and heroes, for example, the famous ballads about Robin Hood. The only thing that remains unchanged is the presence of refrains (repetitions), which will also be important for ballads written later.
The poets of the 18th and early 19th centuries fell in love with the ballad for its special expressiveness. If we use an analogy with epic genres, the ballad can be called a poetic novella: it requires an unusual love, legendary, heroic plot that captures the imagination. Often, fantastic, even mystical images and motives are used in ballads: let us recall the famous "Lyudmila" and "Svetlana" by V. Zhukovsky. No less famous are A. Pushkin's "Song of the Prophetic Oleg", M. Lermontov's "Borodino".
In Russian lyrics of the 20th century, a ballad is a romantic love poem, often accompanied by musical accompaniment. Ballads are especially popular in "bardic" poetry, the anthem of which can be called the ballad of Yuri Vizbor, beloved by many.
Fable(basnia lat. story) - a short story in verse or prose of a didactic, satirical nature. Since ancient times, elements of this genre have been present in the folklore of all peoples as tales about animals, and then transformed into anecdotes. The literary fable took shape in Ancient Greece, its founder is Aesop (V century BC), after his name the allegorical speech began to be called "Aesopian language". In a fable, as a rule, there are two parts: a plot and a moralizing one. The first contains a story about some funny or ridiculous incident, the second - morality, a lesson. The heroes of fables are often animals, under the masks of which there are quite recognizable moral and social vices that are ridiculed. The great fabulists were Lafontaine (France, 17th century), Lessing (Germany, 18th century) In Russia, I.A. Krylov (1769-1844). The main advantage of his fables is alive, vernacular, a combination of cunning and wisdom in the author's intonation. The plots and images of many of I. Krylov's fables look quite recognizable even today.
By the genus of literature called epic, lyrics and drama. Epos- this is narrative works... Epic genres are epic, epic novel, novel, story, story, short story, essay. In oral folk art, the epic includes the genres of epics, fairy tales, and anecdotes. Lyrics- these are mainly poetic works that express the emotional state of their authors. Lyric genres: elegy, ode, sonnet, ballad, message, epigram, madrigal. Drama- these are works based mainly on the dialogues of the heroes, according to which theater performances... Dramatic genres: tragedy, comedy, drama, melodrama, vaudeville, farce.
First division of literature
For the first time theoretically literary genera was isolated by the ancient Greek philosopher and scientist Aristotle, who lived in the 4th century BC. He created a large scientific work called "Poetics", where he pointed out that poetry is imitation. Imitation exists in three forms, which are called the kinds of literature.
The emergence of the genus of literature is directly related to the emergence of art. Art emerged at the earliest stages of the development of human society. The famous art critic A.N. Veselovsky said that literary genera were formed from primitive ritual songs, which were performed in connection with three main events in human life: the birth of a child, marriage and death.
The ritual songs were sung by the chorus and expressed collective emotion, i.e. the emotional state of members of a tribe or clan. Emotions were expressed in emotional exclamations that were emitted by the participants in the ceremony. From these exclamations, the lyrics arose, which subsequently separated from the rite and turned into an independent genus.
How to distinguish between the types of literature
There were singers in the choir. They performed parts, from which later appeared lyric-epic, and then heroic poems, which laid the foundation for the epic. The choir members often engaged in ritual dialogue. A drama was formed on the basis of this dialogue.
According to the time of occurrence, literary births appeared at different times. First came the lyrics, later the epic, the drama was formed at a very late stage. Distinctive features childbirth are emotion, appreciation, attitude for lyrics, storytelling for an epic, dialogue and action for drama. It should be remembered that within each of the genera there are elements of a different kind. For example, in the epic there are elements of dialogue, which are characteristic of the kind of drama.
Description of the presentation for individual slides:
1 slide
Slide Description:
Literary birth and genres (theory of literary criticism)
2 slide

Slide Description:
3 slide

Slide Description:
Literary genus- a group of literary works, singled out according to a number of common features.
4 slide

Slide Description:
Lyrics is a kind of literature that reflects life through the image of individual states, thoughts, feelings, impressions and experiences of a person. Salient feature- poetic speech, rhythm, lack of plot, small size.
5 slide

Slide Description:
Epic - is a coherent story about certain events, as close as possible to objectivity. The epic is characterized by the reproduction of an action that unfolds in space and time. Specific trait the epic is that the author (or narrator) himself reports the events and their details as something past and remembered, at the same time resorting to descriptions of the setting of the action and the appearance of the characters, and sometimes to reasoning. The epic narration is conducted on behalf of the narrator, a kind of mediator between the portrayed and the listener (reader).
6 slide

Slide Description:
Drama is a kind of literature that reflects life in the actions (actions and experiences) of people. Intended for performance on stage. The action is shown through the conflict that lies at the center of the dramatic work, defining everything structural elements dramatic action. A dramatic conflict that reflects specific historical and universal contradictions, revealing the essence of time, social relations, is embodied in the behavior and actions of the heroes, and, above all, in dialogues, monologues, remarks.
7 slide

Slide Description:
Lyroepics is one of the four types of literature in the traditional classification. In lyroepic works art world the reader observes and evaluates from the outside as a plot narration, but at the same time the events and characters receive a certain emotional assessment of the narrator.
8 slide

Slide Description:
9 slide

Slide Description:
Epic (ancient Greek “word, narration” + “I create”) is a generic designation of large epic and similar works: An extensive narration in verse or prose about outstanding national-historical events. A complex, long history of something, including a series of major events. A novel is a work in which the narrative is focused on the fate of an individual in the process of its formation and development. According to Belinsky's definition, the novel is an "epic of private life" (for example, "Oblomov" by A. Goncharov, "Fathers and Sons" by I. Turgenev). The story is the "average" genre of the epic kind of literature. By volume, as a rule, less romance, but more of a story, a short story. If in a novel the center of gravity lies in the integral action, in the actual and psychological movement of the plot, then in the story the main weight is often transferred to the static components of the work - positions, states of mind, landscapes, descriptions, etc. (eg "Steppe"). The novella is a small prose genre, comparable in volume to the story (which sometimes gives rise to their identification - there is a point of view on the novella as a kind of story), but differs from it in a sharp centripetal plot, often paradoxical, lack of descriptiveness and compositional rigor (for example. , stories by A. Chekhov, N. Gogol, " Dark woods"I. Bunina). Story - a small epic genre form fiction- small in volume of the depicted phenomena of life, and hence in the volume of the text, a prose work.
10 slide

Slide Description:
Basnya is a poetic or prosaic literary work of a moralizing, satirical nature. At the end of the fable, there is a short didactic conclusion - the so-called morality. Actors usually there are animals, plants, things. The fable ridicules the vices of people. Fable is one of the oldest literary genres. Byliny (stáriny) - heroic-patriotic songs-legends telling about the exploits of heroes and reflecting the life of Ancient Russia in the 9th-13th centuries; a kind of oral folk art, which is characterized by a song-epic way of reflecting reality. The main plot of the epic is any heroic event, or a remarkable episode of Russian history (hence popular name epics - "old", "old-fashioned", implying that the action in question took place in the past). A literary tale - an epic genre: a fiction-oriented work closely related to folk tale, but, unlike it, belonging to a specific author, which did not exist orally before publication and did not have options.
11 slide

Slide Description:
A myth is a legend that conveys people's ideas about the world, a person's place in it, about the origin of all that exists, about gods and heroes. Legend (from the middle-lat. "Reading", "readable", "collection of liturgical excerpts for the daily service") is one of the varieties of fabulous prose folklore. A written legend about some historical event or person. V figuratively refers to the glorious, admirable events of the past, reflected in fairy tales, stories, etc. As a rule, contains additional religious or social pathos. An essay is one of all varieties of a small form of epic literature - a story, which differs from its other form, a short story, in the absence of a single, acute and quickly resolving conflict and in a more developed descriptive image. Both differences depend on the peculiarities of the problematic of the essay. Essay literature does not touch upon the problems of the formation of the character of a personality in its conflicts with the established social environment, as is inherent in the novel (and the novel), but the problems of the civil and moral state of the “environment” (usually embodied in individuals) - “moral descriptive” problems; it has a great cognitive variety. Essay literature usually combines the features of fiction and journalism.
12 slide

Slide Description:
13 slide

Slide Description:
14 slide

Slide Description:
1. Ode - a genre of praises, solemn lyric poems, glorifying heroic feat... Goes back to the traditions of classicism. For example the ode "Liberty". 2. Elegy - a genre of romantic poetry, a poem permeated with sadness, sad thoughts about life, destiny, your dream. For example, "The daylight has gone out ...". 3. Message - an appeal to another person. A genre unrelated to a specific tradition. Pushkin's messages are based on the combination of the beginning of the personal with the beginning of the public, civic. In terms of its scope, it is broader than a specific life situation... For example "To Chaadaev". 4. An epigram is a satirical poem addressed to a specific person. For example "on Vorontsov". 5. Song - The genre goes back to the traditions of oral folk art. For example "song Western Slavs". 6. Romance - for example "I am here, Inesilla ...". 7. Sonnet - for example "Stern Dante did not despise advice ...".
Epos - (gr. story, narration) - one of three types of literature, narrative genus. Genre varieties epic: fairy tale, short story, novella, story, essay, novel, etc. Epos reproduces objective reality external to the author in its objective essence. The epic uses a variety of ways of presentation - narration, description, dialogue, monologue, author's digressions. Epic genres are enriched and improved. Methods of composition, means of depicting a person, the circumstances of his life, everyday life are developing, a multilateral image of the picture of the world and society is achieved.
A fictional text is like a kind of fusion of narrative speech and the statements of the characters.
Everything told is given only through the narration. Epos very freely masters reality in time and space. He knows no limits in the volume of the text. Epic also includes epic novels.
Epic works include Honoremp de Balzac's novel Father Goriot, Stendhal's novel Red and Black, and Leo Tolstoy's epic novel War and Peace.
|
Lyrics - (Greek lyre, a musical instrument, to the accompaniment of which poetic works were performed) - one of the types of literature. Lyric works characterized by a special type of artistic image - image-experience. Unlike the epic and drama, where the image is based on many-sided image of a person, his character in complex relationships with people, in a lyric work before us is a holistic and concrete state of human character. The perception of personality does not require either an outline of events or a prehistory of the character. Lyrical image reveals the individual spiritual world of the poet, but at the same time it must be socially significant, carry a common human principle. It is important for us both that this experience was felt by this poet in certain circumstances, and that this experience could be experienced at all in these circumstances. That is why a lyrical work always contains fiction. Circumstances can be widely deployed in a lyrical work (Lermontov "When the yellowing cornfield is worried ...") or reproduced in a minimized form (Block "Night, street, lamp, pharmacy ..."), but they always have a subordinate meaning, play the role of a "lyrical situation" necessary for the emergence of an image-experience. Lyric poem in principle, this is a moment of human inner life, a snapshot of it, therefore, the lyrics are mainly written in the present tense, in contrast to the epic, where the past tense dominates. The main means of creating an image-experience in the lyrics is the word, the emotional coloring of speech, in which the experience becomes vitally convincing for us. Vocabulary, syntax, intonation, rhythm, sound - this is what characterizes poetic speech. Lyrical emotion- a clot of spiritual experience of a person. For lyrics is characterized by a conversation about the beautiful, the proclamation of ideals human life... In the lyrics, there may be satire, grotesque, but the bulk of lyric poems still belongs to another area. Principle lyrical kind: as short and as complete as possible. |
Drama - (Old-Greek action, action) - one of the types of literature. Unlike the lyrics and like the epic, the drama reproduces, first of all, the external world for the author - actions, relationships of people, conflicts. Unlike the epic, it has not a narrative, but a dialogical form. In it, as a rule, there are no internal monologues, author's characteristics of the characters and direct author's comments on the depicted. In the "Poetics" of Aristotle about drama it is spoken of as an imitation of action by action, not by story. This provision has not become obsolete until now. For dramatic works, acute conflict situations are characteristic, prompting the characters to verbal and physical actions. Author's speech can sometimes be in drama, but is of an auxiliary nature. Sometimes the author briefly comments on the lines of his characters, makes indications of their gestures and intonation.
Drama closely related to theatrical art and must meet the needs of the theater.
Drama considered as the crown of literary creativity. Examples dramas is the play "The Thunderstorm" by Ostrovsky, "At the Bottom" by Gorkov.
novel - large epic form, the most typical genre of bourgeois society.
Name "novel" arose in the Middle Ages and initially referred only to the language in which the work was written. The most widespread language of medieval Western European writing was, as you know, the literary language of the ancient Romans - Latin. In the XII-XIII centuries. AD, along with plays, stories, stories written in Latin and prevailing mainly among the privileged estates of society, the nobility and the clergy, stories and stories written in Romance languages and existed mainly among the democratic strata of society that do not know Latin, among the commercial bourgeoisie, artisans, villans. These works, in contrast to Latin, and began to be called: conte roman - romance story, story. And then the adjective acquired an independent meaning. This is how a special name arose for narrative works. Later it became part of the language and over time lost its original meaning. Roman began to call a work in any language, but not any, but only large in size, differing in some features of the subject matter, compositional construction, plot development, etc. In modern times, especially in the 18th-19th centuries, this type of works became the leading genre of fiction of modern times.
Despite the exceptional prevalence of this genre, its boundaries are still not clear and definite enough. Along with the works bearing this name, we meet in the literature of the last centuries large narrative works, which are called stories. Some writers give their great epic works the title of a poem (suffice it to recall Gogol, his "Dead Souls").
The most famous novels of Russian literature are "War and Peace" by Tolstoy, "Quiet Don" by Sholokhov.
The story - a broad, vague genre term that does not lend itself to a single definition. In its historical development as the very term “ story”, And the material he embraces has come a long historical path; it is absolutely impossible to speak of the story as a single genre in the ancient and new literature. The ambiguity of this term is complicated by two more specific circumstances. Firstly, for our term there are no exactly corresponding terms in Western European languages: German "Erzählung", French "conte", partly "nouvelle", English "tale", "story", etc. story and “story”, part of “fairy tale”. The term story in its definite opposition to the terms "story" and "novel" is a specifically Russian term.
Secondly, story- one of the oldest literary terms, which changed its meaning at different historical moments. It is also necessary to distinguish between the change in the meaning of the term story from changes in the corresponding phenomena themselves. The historical development of the term reflects, of course, 19 (with some only delay), the movement of the genre forms themselves. It is no coincidence that the terms "story" and "novel" appear in our country later than the story, and it is no coincidence that at a certain stage this latter is applied to works that are essentially stories.
Story - a narrative epic genre with a focus on a small volume and on the unity of an artistic event.
Story however, as a rule, it is devoted to a specific fate, speaks of a separate event in a person's life, grouped around a specific episode. This is how it differs from the story, as a more expanded form, which usually describes several episodes, a segment of the hero's life. Chekhov's story "I Want to Sleep" tells about a girl who sleepless nights brought to a crime: she strangles the one that prevents her from falling asleep infant... The reader learns about what happened to this girl before only from her dream, about what will happen to her after the crime has been committed is generally unknown. All the characters, except for the girl Varka, are very fluently outlined. All the events described prepare the central one - the murder of the baby. Story small in volume.
But it's not about the number of pages (there are stories that are small in volume and relatively long stories), and not even in the number of plot events, but in the author's attitude to the utmost brevity. So, Chekhov's story "Ionych" is close in content not even to a story, but to a novel (almost the entire life of the hero is traced). But all the episodes are presented very briefly, the author's goal is the same - to show the spiritual degradation of Doctor Startsev. According to Jack London, "a story is ... a unity of mood, situation, action."
The small volume of the story also determines its stylistic unity. The narration is usually conducted from one person. It can be an author, a storyteller, or a hero. But in the story, much more often than in the "large" genres, the pen is, as it were, transferred to the hero, who tells his own story. Often we have before us - a tale: the story of a certain fictional person with his own pronounced speech manner (the stories of Leskov, in the 20th century - Remizov, Zoshchenko, Bazhov, etc.).
Feature article - close to a documentary story about a real event or person; the role of fiction in the essay is minimal (see, for example, the physiological essays of the "natural school").
Parable - a short story of a moral character, akin to a fable; contains a lesson in an allegorical, allegorical form. It differs from the fable in the depth and significance of meaning, in the breadth of generalization. Illustrates an important idea related not only to the private life of a person, but also to the universal laws of being.
Poem - a large poetic work by a plot-narrative organization; a story or a novel in verse; a multi-part work in which epic and lyrical beginnings merge together.
Ballad - a narrative song (or poem) with a dramatic development of the plot, the basis of which is an extraordinary case, one of the types of lyric-epic poetry.
Poem - a small work created according to the laws of poetic speech. WITH. there is lyrical, journalistic, etc. “The lyric poem expresses a direct feeling, excited in the poet by a well-known phenomenon of nature or life, and the main thing here is not the feeling itself, not in passive perception, but in the internal reaction to the impression that is received from the outside "( ON. Dobrolyubov).
Elegy - a lyrical work with a sad mood. It can be a plaintive, mournful poem about unrequited love, a reflection on death, on the fleeting nature of life, or there can be sad memories of the past. Most often, elegies are written in the first person. Elegy (Latin elegia from the Greek elegos, a plaintive flute melody) is a genre of lyrics that describes a sad, pensive or dreamy mood, this sad meditation, the poet's meditation about a rapidly flowing life, about losses, parting with his native places, with loved ones, about that joy and sadness are intertwined in the heart of a person ... In Russia, the flowering of this lyric genre refers to the beginning of the 19th century: elegies wrote K. Batyushkov, V. Zhukovsky, A. Pushkin, M. Lermontov, N. Nekrasov, A. Fet; in the twentieth century - V. Brusov, I Annensky, A. Blok and others.
Arose in ancient poetry; originally it was called crying over the deceased. Elegy was based on the life ideal of the ancient Greeks, which was based on the harmony of the world, proportionality and balance of being, incomplete without sadness and contemplation, these categories passed into the modern elegy. Elegy can embody both life-affirming ideas and disappointment. The poetry of the 19th century continued to develop the elegy in its "pure" form; in the lyrics of the 20th century, elegy is found rather as a genre tradition, as a special mood. In modern poetry, an elegy is a plotless poem of a contemplative, philosophical and landscape nature.
Epigram – short poem making fun of a person.
Message - 1) the prose genre of Old Russian literature of didactic or political content in the form of a letter to a real or fictitious person. The “sense of authorship” was different in the genre of sermon and in the genre of the chronicle, in the genre of the message and in the genre of the story. The former presuppose an individual author and often signed the names of their authors ... ”(DS Likhachev). 2) a poetic work in the form of a letter, a letter in verse to a real, fictitious person or group of persons. The content is varied - from philosophical reflections to satirical pictures. A.S. Pushkin "Message to Siberia". V.V. Mayakovsky "Message to proletarian poets". THE FOLLOWINGhistory- this is a message about how the fate of the characters developed after the completion of the work.
Song - a small lyric work intended for singing; usually couplet (stanza). 1) NS. the main form of folk lyrics. In ancient times it is associated with dance and facial expressions. Types of song: everyday, lyric, burlak, urban, revolutionary peasant, soldier's, polyphonic, dance, solo, author's, folk song. “In traditional folklore, the lyrics of a song and its melody were created at the same time. The literary song served only as a basis for subsequent, often different musical adaptations "( S. Lazutin
Oh yeah - a solemn poem. Initially, in ancient Greek poetry, it was a lyric poem on various topics, performed by a chorus. V odes the ancient Greek poet Pindar (c. 518–442 BC) kings and aristocrats, who, according to the poet, were honored with the favor of the gods, are sung. Special development genre odes received in the poetry of European classicism. The solemn ode is the main genre of creativity of the founder of French classicism F. Malerba (1555-1628). The theme of his odes is the glorification of the absolutist power in France. A stage in the development of the genre of ode is the work of J. J. Rousseau.
In Russia Oh yeah, which "glorifies high, noble, sometimes tender matter" (V. K. Trediakovsky), was the main genre of classicism poetry. Exemplary works of this genre belong to M.V. Lomonosov, famous authors of odes were his poetic heir V.P. Petrov and opponent A.P. Sumarokov, the best works of this genre belong to G.R.Derzhavin. In addition to the solemn (pindaric) odes, in Russian. poetry was a moral ode (Horatian), love (anacreontic) and spiritual (transcription of psalms).
Sonnet (Italian sonetto, from Provence sonet - song) - a type (genre) of lyrics, the main feature of which is the volume of the text. The sonnet always consists of fourteen lines. Other rules for composing a sonnet (each stanza ends with a dot, not a single word is repeated) are not always observed. The fourteen lines of the sonnet are arranged in two ways. It can be two quatrains and two tercets, or three quatrains and distich. It was assumed that in quatrains there are only two rhymes, and in tercets there can be either two rhymes or three.
The idea of the comic goes back to ancient rituals, playful, festive and cheerful folk laughter. This is "the fantasy of the mind, which is given complete freedom." Comic is also called life changes, which contain inconsistency with the generally accepted norm, illogism.
A constant subject of comedy is the unfounded pretense of the ugly to think itself beautiful, petty - sublime, inert, dead - alive. All the elements of the comic image are taken from life, from real subject, faces. They are not transformed by creative imagination. Types of comic - irony, humor, satire. The high types of comedy differ in meaning (the greatest example in literature is Don Quixote M. de
Cervantes, laughter at the highest in a person) and funny, playful views (puns, friendly cartoons). Comedy is associated not only with the denial of the obsolete, but also with the spirit of affirmation, expressing the joy of being and the eternal renewal of life.
Tragedy - a dramatic work depicting deep, most often insoluble contradictions in life. Their consequences end with the death of the hero. Conflicts of reality are conveyed to tragedies in an extremely tense form. This, acting on the audience, awakens the strength of their feelings and gives rise to emotional uplift (catharsis - purification). Tragedy originated in Ancient Greece from a religious and cult rite of worship of the god of viticulture and winemaking Dionysus. In honor of Dionysus, festivities were organized, solemn processions with the singing of praises. Actions were played out, the participants of which were Dionysus fans dressed in goatskins and the choir sang (leading figure). These games, these "songs of the goats" marked the beginning tragedies as one of the varieties of drama.
The very word " tragedy"Means" song of the goats. " " Tragedy is an imitation of an important and complete action, which has a certain volume, produced by speech, sweetened in different ways in its various parts, produced in action and accomplishing through compassion and fear the purification of such passions. As for the characters, there are four points to keep in mind: the first and most important, that they are noble. The second point is that the characters are suitable ...
The third point is for the characters to be believable ... The fourth point is that the character is consistent. The dignity of verbal expression is to be clear and not be low. The clearest expression, of course, consists of common words, but it is low. An expression that is noble and free from triviality is one that uses unusual words. And I will call unusual glossa, metaphor, lengthening and everything that deviates from the common one ”(Aristotle“ Poetics ”).
One of the main genres (types) dramas as a kind of literature along with tragedy and comedy. Like comedy, the drama mainly reproduces the private life of people, but its main goal is not to ridicule morals, but to portray the personality in its dramatic relationship with society.
At the same time, like the tragedy, drama tends to recreate acute contradictions, but at the same time these contradictions are not so intense and allow for the possibility of a successful resolution.
As an independent genre drama developed in the second half of the 18th century. from the educators. Drama 19-20 centuries is predominantly psychological. Selected varieties dramas merge with related genres, using their means of expressiveness, for example, the techniques of tragicomedy, farce, theater of masks.
Literary genus is a set of works of art united general style presentation characteristic storylines... The genus of a literary work is lyrics, epic or drama. The most famous examples of each of them are described in this article.
Drama
Translated from this word means "action". In modern Russian, the term has acquired a different meaning. But this will be discussed below. Drama is a literary family that originated in Antiquity. The first dramatic works belonged to the ancient Greek authors Aeschylus, Sophocles and Euripides. This literary genus of works combines works of two types: comedy, tragedy.
Drama reached its perfection in the sixteenth century. French authors strictly adhered to certain provisions established by the ancient Greeks. Namely: the unity of time and place, the duration of events is no more than twenty-four hours.

Examples of dramatic works
In the drama of Sophocles "Oedipus the King" it comes about a man who, by perfect coincidence, once killed his father, and then, ironically, married his mother. The audience of the first production knew the plot. But even if they were unfamiliar with the story of Oedipus, they would recognize him short biography... Nevertheless, the drama is designed in such a way that its action covers the whole day. All events take place in the palace of the king.
Moliere, Racine and Corneille adopted the traditions of ancient playwrights. Their creations also follow the above principles. And, finally, it is worth giving an example of which every schoolchild is familiar - “Woe from Wit”. Chatsky arrives at Famusov's house. She learns that Sophia is in love with a selfish and narrow-minded person. The hero of Griboyedov conducts conversations with other characters in the comedy. He expresses extraordinary thoughts. As a result, Famusov's entourage decides that Chatsky is a little out of his mind. He, in turn, leaves the house of a relative with the words “Carriage to me, carriage!”. All this happens during the day.
None of the heroes go anywhere outside the Famusov mansion. Because drama is a literary genus of works of art in which everything that happens takes place during the day. It is worth mentioning one more feature of such compositions. Namely, they do not contain the words of the author. Only dialogues. Whether it's a comedy or a tragedy.
Epos
This term can be found as a masculine noun in literary dictionary... And in this encyclopedic edition it will be said that the epic is nothing more than a work that tells about the events that took place in the past.

Epic examples
The famous "Odyssey" is a striking example. In his essay, Homer describes at length and in detail the events that once took place. He talks about the journey of his hero, not forgetting to mention other characters and describe their life and everyday life in sufficient detail. How does an epic differ from a drama? First of all, the fact that the narration is conducted on behalf of the author. The next difference is impartiality.
Homer's works are written in the form of poetry. In the eighteenth century, new trends began to develop in literature: a type of prose appeared that had the characteristics of an epic. An example is Tolstoy's novel War and Peace. The events span a rather impressive time span. In the novel great amount characters.

Another example of epic prose is Galsworthy's novel The Forsyte Saga. This book tells about representatives of several generations of a large family.
Lyrics
What literary genus does any of the poems of Annensky, Fet, Tyutchev belong to? Of course, to the lyrics. The works of this literary kind are characterized by sensuality and emotionality. Unlike the epic, here the feelings of the hero are conveyed extremely vividly, and even somewhat subjectively.
Examples of lyric works
In Ancient Greece, not only was born dramatic art... Antiquity is the heyday of other trends in literature. The first lyric authors are Terpander. This ancient greek poet he read out his creations to the sounds of a string guitar. To the accompaniment read poetry and Alkey - the author, who preferred political topics. Sappho's poetry has also survived to this day.

In the Middle Ages, which is usually called "gloomy", it was created myriad romantic ballads by troubadours from France. Their plots were subsequently used more than once by later authors. Lyrics as received special development during the Renaissance. In the thirteenth century appeared new type troubadours. No longer French, but Italian. After all, it was in Italy that lyric poetry flourished.
In the nineteenth century, lyricism penetrated all His features are present in the works of Shelley, Byron, Coleridge. Lyricism also inspired Russian poets - Pushkin, Zhukovsky, Ryleev, etc. Then interest in lyrics faded for a while: its place was taken by epic prose. And, finally, the beginning of the twentieth century in Russia was marked by the emergence of a whole galaxy of talented lyricists. Among them are Pasternak, Blok, Akhmatova, Tsvetaeva, Yesenin.
In everyday speech
The literary genus, as we found out, is a collection of works of art that have characteristic features. It can be lyrics, epic or drama. In modern speech, each of these terms has a slightly different meaning.
Film drama is a genre characterized by tragedy. Lyrics is usually understood as love poetry. In literary terminology, these concepts have a different meaning. What literary genus is characterized by tragedy, sentimentality? Drama or lyrics. But at the same time, a dramatic work can be a comedy. And the composition of a lyricist is not necessarily a story about his unrequited love or homesickness.