Racial, ethnic and national composition. Ethnic composition of the population of Russia
Ethnic population
The study of any country in geography is impossible without the knowledge of those peoples that they live. It is important to know and in what language this people speak, and what features of spiritual and material culture are distinguished from other peoples, which is the feature of his demographic behavior. Many sciences are engaged in the past and real peoples: archeology, geography, philosophy and other sciences. But there is also a special science - ethnography (ethnology), which is engaged in the study of the origin of the peoples, their main characteristics and properties, relationships between them.
The main concept in ethnography is the concept of ethnos.
Ethnos– (from Greek. éthnos - society, group, tribe, people) Historically established sustainable community of people who have a set of signs: the community of territory and language, relatively stable features of material and spiritual culture and psyche, as well as the consciousness of their unity and differences from others Education, i.e. self-awareness and self-configuration (according to Yu.V. Bromlo
From the listed signs of the ethnos, no one is absolutely necessary, to assign a group of people to a specific people. So, the same people can speak in two languages \u200b\u200b(for example, Belarusians speak Russian and in Belarusian languages). A. english language They say both the British and Australians, New Zealanders, Americans of the United States, Irish and others. Peoples. As for the community of the territory, this sign does not always act as a mandatory sign of the ethnos. For example, the Belarusians may also be considered that emigrants who moved to permanent place Residence in Canada, USA, Brazil. It is very difficult inside a large group of people to find the absolute similarity in clothes, food, socio-household behavior. People are always different. And there may be a capital resident of Moscow, according to the features of the material and spiritual culture, closer to Parisian or Londonz, than the same Russian, but living in the village behind the Urals. Rather, the community of territory is a prerequisite for its occurrence and existence.
Therefore, the most important element of ethnic identification of any group of people is ethnic self-consciousness.
Under ethnic self-conscious It is customary to understand the awareness of the person of his belonging to a certain people (ethnosu), and under self-confidencenotify in the word this ethnos.
Sometimes ethnic self-consciousness acquires hypertrophied forms, i.e. Representatives of a certain people consider themselves more "significant" in comparison with other nearby living peoples, while achieving the privileges of one people over another in many areas of life (in the sphere of power, economic structures, symbolism, etc.) such ethnic self-consciousness is called nationalism. The extremely aggressive form of nationalism is chauvinism, in which representatives of a certain ethnos use ethnic discrimination or violent assimilation to other peoples. At the same time, if these measures reach the destruction of people of another nationality, then there is a phenomenon as genocide.
Famous Russian scientist L.N. Gumilev believes that the ethnos is in the process of continuous development and transformation, has a stage of origin, development, aging and disappearance (now such peoples like Byzantines, Hellen, Romans, Gunns, Babylonians, and once they were the great peoples left We traces for their own great culture). From the moment of the origin until the moment of disappearance goes around 1200-1550 years, and the current "backward peoples", for example, the peoples of Africa or Oceania are only ethnic groups at their stage of youth or the opposite of old age, and civilized Europeans are Cvalleva, which can enjoy the accumulated culture of previous centuries of its development.
In our ethnography, it is customary to allocate three stages The formation of the ethnos (the so-called stadial or temporal types).
The earliest and simple stages of the development of the ethnic rod and tribe. Rod and tribe has the following signs: a certain territory; general signs of economic activity; Generic power. Ethnic self-consciousness in the members of the tribe is reflected in the presentation of the overall ancestor. The category of this historical and classic example served by Evenks, Nenets (Northern peoples living in the European north of our country) are still in the near the pre-revolutionary past. Examples modern period Some preserved tribes in hard-to-reach isolated places in the Indians of South America, Australia's Aboriginal, the peoples of Equatorial Africa.
With an increase in public division of labor, with the advent class society and the formation of states began to develop nationality - The second stage of the development of the ethnos. Nature can be perceived in two senses:
1. Stage of the development of an ethnos, which occupies an intermediate position between the tribe and the nation. In this case, this group of people has the following signs: a single territory, culture, primitive community of economic life and statehood; Ethnic self-consciousness is already expressed in the awareness of the generality of origin from a certain tribe.
2. Modern ethnic groups, lost tribal traits and not found nations.
The highest stages of the development of the ethnos is the nation.
Nation There can also be two values:
§ The highest stage of the development of the ethnos, characterized by the presence of statehood, the community of ethnic territory, economic life, appearance and distribution literary languagerecognizing as a state, the presence of ethnic self-consciousness;
§ Citizens of citizens of one state.
Ethnic community is in constant motion: their number changes, the age of age is changing, some generality disappear, others are born. All those processes that lead to a change or some individual elements, or an ethnic volume as a whole called ethnic processes. They are ethnoaming or ethno-separative.
At the stage of the appearance and formation of states, ethno-variable processes were most common. Specialists mainly allocate two such processs: consolidation and assimilation. Consolidation is a merger of groups close in the language and culture of groups in a larger ethnic community or inclusion in the ethnic community of the group close to him. So, from the related tribes of Krivich, Radmichi and Dregovichi formed subsequently such people as Belarusians. Ethnic assimilation is the process of "dissolution" of a previously independent ethnos or some part of its part in the other, usually larger ethnos. It can be natural and violent. With natural assimilation, due to a long stay in someone else's country, immigrants assimilate the language, culture, stereotype of the behavior of people of the country of residence. The main path at the same time - inter-ethnic marriages. An example of violent assimilation may be beolation of Belarusians in the time of joining the Belarusian lands to the Commonwealth, when our population was satisfied polish language, catholic faith, Polish schools.
Today there is no accurate determination the number of peoples, however, the most frequently meeting amount of the number of peoples is 2000-2500, which are at various stages of development. The greatest distribution among geographers was distributed classification of peoples in numbers and language.
In terms of population The grouping of peoples was proposed by Brook S.I. The largest peoples whose number exceeds 100 million people. Are: Chinese, Hinduscans, US Americans, Bengalts, Russians, Brazilians, Japanese, Punjabs. These 8 peoples account for about 41% of the total population of the Earth. Peoples with a number from 50 to 100 million are about 17% of the population. There are 12 such peoples today. But most of all (more than 180) peoples have a number from 1 to 5 million people. Although in the aggregate they account for only 8% of the population of the Earth.
The most common is linguistic classification of peoples in the world (based on kinship languages). Taxonomic ranks of the peoples of the world, adopted in the linguistic classification of peoples such:
§ Subgroup
§ Division
In the linguistic classification of the peoples of the world, it is customary to allocate the following families: indo-European, Sino-Tibetan, Niger Congo Family, Semitskaya, Berber, Kushitskaya, Chadskaya, Austrasezia, Dravidian, Altai, Ural-Yukagirskaya, Austro-Azia, Parataya, Nilo-Sakhakkaya, North Caucasian, Carvela, Family Miao-Yao, Australian, Eskimo Aleutskaya, Chukotsko-Kamchatka, Papuass family, families indian peoples, Andaman.
Some nations occupy an isolated position, i.e. Do not enter into any named family (Aina, Basque, Nivhi, Borishi, Wike, Kusund).
The study of ethnic composition refers to the most important aspects of the geography of the population, since Russia is a polyethnic state, and representatives of more than 160 peoples live in it. The ethnic factor determines the significant territorial differences in demographic processes, the age of age and the size of the family, the mobility of the population, the forms of management and settlement. The ethnic composition of the population significantly affects public and political processes in the country.
Ethnos - historically established sustainable community of people possessing, as a rule, by a single language, common features of spiritual and material culture, ethnic territory, self-consciousness recorded in self-regulation (ethnonym).
In ethnology - science on ethnic groups - there are different theories explaining the emergence of ethnic groups. The most common of them is Primordialism, instrumentalism and constructivism.
For supporters of Primordialism, ethnicity is a fundamental part of the identity of a person - unconditional and unchanged. Ethnicity by Primordialists is understood as objectively existing historical educationHaving natural or public background. The formation of ethnic groups is a long historical process in which the most important factors are the community of language and territory.
In the mid-1970s. In Western Ethnology, a different approach to ethnosu appeared - instrumentalism. The followers of this direction believe that ethnicity is used in society as a tool in the struggle for welfare and power. Ethnicity was understood not as the objective property of a person, but as a sense of solidarity of a group of people who form in certain circumstances. Instrumentalists consider an ethnic group of ethnic myths that are created by the elite of society to achieve certain goals. Supporters of this approach are not looking for objective grounds for the occurrence of ethnic groups, but identify the functions that ethnic groups and ethnicity are played in society.
And the third, the most common approach to ethnicity is constructivism. Ethnic group in constructivism - the community of people forming on the basis of cultural self-determination towards other communities. In this approach, the most important factors The ethnic volume is considered to be ethnic self-consciousness and language as a symbol, on the basis of which an understanding of ethnic differences of one ethnos from the other occurs. For constructivism, it is important how objectively the general historical origin Representatives of a particular ethnos, presentation or myth about the general historical fate of the ethnos.
Among the domestic ethnologists in the field of the theory of ethnos, the most significant works L. N. Gumileva, Yu.V. Bromleus, N.N. Cheboksaro, G.E. Markova, V.V. Pimenova, V.A. Tishkova, S.A. Harutyunova.
As part of any, even enough consolidated, peoples, there are groups, culture and life of which retain some features (they have their own dialects, cult rites). Such ethnic groups are called subethnas. They are often formed with a long separation of the part of the people from the main ethnic array.
The main role in the formation of ethnic groups is played by ethnic processes. The union of ethnic groups is carried out in the form of consolidation and assimilation. Consolidation is manifested in the merger of ethnic groups close on the language and culture of ethnic groups in a larger community. The consolidation process is manifested in smoothing cultural and linguistic differences between ethnic groups, strengthening the uniformity of the ethnic. Assimilation is the "dissolution" of one people in another, the loss of ethnic self-consciousness, which is especially characteristic of ethnic minorities and is due to the numerical and socio-cultural inequality of ethnic groups.
Along with this, there are separation ethnic processes that lead to the disintegration of the ethnos or separation of its part. They are associated with migrations or with the division of the ethnic territory by interstate borders.
The ethnic composition of the population is determined by the results of the censuses of the population, including questions about ethnicity, determined by self-consciousness. During the census of the population in the USSR in 1989, the ethnicity was largely determined by the native language.
According to the last Soviet census, 1989, Russians were only half of the population of the country (145 million from 286 million); Other major peoples were Ukrainians (44 million), Uzbeks (17 million), Belarusians (10 million), Kazakhs (8 million), Azerbaijanis (7 million), etc. - only 20 peoples with more than 1 million people.
After the collapse of the USSR, Russia has become more ethnically homogeneous: about 80% are Russian.
Ethnogeographic position of Russia. To deeper to understand the specifics of ethnic processes and the problems of interethnic relations in Russia, you need to consider our country on a broader background.
Under the ethnogeographic position, the position of the country in relation to the place of residence of other peoples,
155
diving relationship with these peoples (friendship, female, etc.) and their prospects.
The greatest importance for Russia has its nearest environment. The territory of the former Soviet Union, located at the junction of Europe and Asia, treated cultural scientists to various "cultural worlds" (or even to different civilizations).
In western parts former USSR Undoubtedly prevailed European influence.
Estonia and Latvia (previously under the authority of the Germans, and then, until the XVIII century, the Swedes) were a kind of "continuation of the Protestant Northern Europe. Lithuania, Western parts of Belarus and Ukraine, who have belonged to Poland for a long time (and in some extent complete), - continuation of the Catholic world. Orthodox Moldova, historically and culturally connected with Romania, is the continuation of the Orthodox "Balkan World".
Such a complex region, as the Caucasus, forming an independent integrity on the world map, at the same time is very strongly connected with the front Asia, the Middle and Middle East: they owned the Romans, Parfyan, Byzantines, Turks, Persians, and only from the XIX century. - Russian.
The interest of modern Iran to the current independent Azerbaijan is determined, in particular, by the fact that out of 17 million Azerbaijanis more than half live in Iran (in early XIX. c., After the last Russian-Persian war, the state border shared almost in half the ethnic territory of Azerbaijanis). And for Turkey, the fate of Georgian Muslims is important (in Adjara), as well as very close to them in the language and culture of Azerbaijanis (Languages \u200b\u200bTurkish and Azerbaijani differ little from each other). Turkey traditionally supported Caucasian Highlanders, resisted Russia. It was to Turkey that emigrated hundreds of thousands of Abkhaz, Shapsov, Circassians and other Caucasian peoples (as well as hundreds of thousands crimean Tatars).
The Caucasus is the place of the "joint" of the Christian and Muslim world, with the numerical predominance of the latter. Of all the peoples of the Caucasus, Christians are only Armenians, Georgians and Ossetians, almost all the others are Muslims.
Central Asia - a meeting place for such different culturesAs Parfyan and Turkic, Arab and Chinese, Iranian and Mongolian and many others. Muslim religion prevails here (and relatively small Orthodox Russian communities). In this area, the culture of settlement farmers always interacted (their descendants are most of the Tajiks and Uzbeks) and nomads (Turkmen, Kyrgyz, Kazakhs). Here lives a few Chinese (Dungan is the Chinese-Muslims) and Belukhi (immigrants from Belukhistan - at the junction of Iran, Afghanistan and Pakistan). In the area, like in the Caucasus, government boundaries cut ethnic territories: several million Tajiks live in Northern Afghanistan and about 2 million Uzbeks (which makes the penetration of Afghan civil workers in Tajikistan and Uzbekistan), in Iran - about a million Turkmen, in Iran China is about a million Kazakhs.
Especially the "butt", "transitional" position in modern Kazakhstan, the whole northern part of which is settled by the Russians. There are a little less than half of the entire population of the republic, and some of them appeared on this territory earlier than the Kazakhs. Many Germans (expelled in 1941 from the territory of the European part of Russia, Ukraine and Baltic), in the south - Uzbeks, Dungan, Uigur (Muslim Turkic people, the main part of which lives in the west of China) and others. Therefore, any manifestations are especially dangerous for Kazakhstan. interethnic tension. Apparently, in modern boundaries, this country can only exist with the "transparency" of these borders and a very "soft" national policy.
The extreme north of Russia is sometimes called part of the "fourth world".
In other words, it is the edge of peoples whose lifestyle is mainly associated with the assignment (hunting, fishing, gathering) or with pasture reindeer herding. In total, Russia has 26 of these peoples with a total number of 180 thousand people.
If you compare the ranges of the settlement of these peoples with a map of the natural living conditions of the population, it turns out that they live
157
in territories with "unfavorable" natural conditions. This once again indicates the conventions of any human ratings: the card was made up from the point of view of the resident of Central Russia, for which, for example, life on Taimyr is not at all attractive. But for the Nenets, the indigenous inhabitants of this area, this is exactly the nature to which they adapted for many centuries. In other conditions, the "best" from the point of view of the Europeans, they could not live, because they would not have the opportunity to engage in their traditional economy - pasture reindeer herding (and if they survived in other conditions, they would have become completely different people).
Currently, the extreme north for the economy of Russia performs the functions of "storeroom natural resources", primarily minerals. From here comes most of the oil and gas, all diamonds, gold, many other non-ferrous metals. Industrial development of the territory destroys the natural basis of the lives of these peoples: displays the deer of pastures, fishing places. Therefore, a very acute problem is the protection of the natural environment in these areas: otherwise, small nations will simply disappear from the face of the earth.
Transformation factors of the ethnic structure of Russia in the post soviet period. Changes in the ethnic composition of the population of Russia in the post-Soviet period occur under the action of several factors: differences in natural motion among various ethnic groups, processes of external migration, due to political conflicts after the collapse of the USSR and labor migrations, changes in ethnic self-consciousness among representatives of various ethnic groups.
Higher rates of the natural growth of the peoples of the North Caucasus, compared with other ethnic groups of Russia, influenced the growth, both their absolute numbers and relative weight in the ethnic structure of the country's population.
External ethnic migrations in the post-Soviet time also became one of the weighty factors of the change in the ethnic structure of the population of Russia. In the early 1990s Ethnic emigrations to Germany and Israel significantly reduced the absolute and relative number of Germans and the Jews of our country.
At the same time, the return migrations of the Russian-speaking population from former republics USSR compensated for demographs
158.
file decline in the population of Russia. The collapse of the USSR, social conflicts and economic difficulties in Transcaucasia served as one of the main reasons for mass immigration to Russia Armenians and Azerbaijanis. Also, the education of the CIS countries led to the return of the title ethnic groups of the former Union republics from the Russian Federation to their countries.
In the period from 1989 to 2002, the number of title ethnic groups of those former republics of the USSR increased, where ethnic and social conflicts were held. More than three times the number of Tajiks, Armenians, Azerbaijanis and Georgians rose.
The 2010 census data show that the active growth in the number of representatives of the Caucasus countries in the period 2002-2010. stopped. The number of Georgians and Azerbaijanis in Russia decreased compared with 2002, the number of Armenians increased by 4.6%.
The new trend was the increase in the number of title ethnic groups of Central Asian countries, which is a consequence of active labor migration from Central Asia To Russia, which was intensified in the first decade of the XXI century. (Table 2).
Researchers believe that the change in ethnic self-consciousness, especially in families, where there are representatives of the Russian and other ethnos, led to a significant decrease in the number of Germans in Russia in the period from 2002 to 2010, similar processes of changes in ethnic identity occur in mixed Russian-Mordovian and Russian-Ukrainian families.
2010 census was recorded in Russia 22 of the most numerous ethnos, the number of which in Russia exceeds 400 thousand people; In 2002, such ethnic groups were 23, and 1989 - 17. Due to the increasing population of the population by 2002, the Azerbaijanis, Kabardians, Darginians, Kumyki, Ingush, Lezgins and Yakuts, were included in this group, and dropped out due to a decrease in Numerous - Jews. In the period from 2002 to 2010, the Germans came out of this group due to a decrease in the number, all other ethnic groups retained the number more than 400 thousand people.
The number of seven peoples in Russia exceeds 1 million people: Russians, Tatars, Ukrainians, Bashkirs, Chuvashi, Chechens and Armenians. In this group in the post-Soviet period there were changes: in 2002, Chechens and Armenians entered the group, and came out of it
Changing the number of title ethnic groups of the republics of the former USSR,
as well as Germans and Jews in Russia in 1989-2010.
| Ethnic groups | Number, thousand people. | Changing the number of ethnic groups, thousand people. | Changing the number of ethnic group,% |
||||
| 1989 | 2002 | 2010 | 1989-2002 | 2002-2010 | 1989-2002 | 2002-2010 | |
| The population of the Russian Federation | 147021,9 | 145166,7 | 142856,5 | -1855,2 | -2310,2 | 98,7 | 98,4 |
| Russians | 119865,9 | 115889,1 | 111016,9 | -3976,8 | -4872,2 | 96,7 | 95,8 |
| Ukrainians | 4362.9 | 2943,0 | 1928,0 | -1419,9 | -1015,0 | 67,5 | 65,5 |
| Belorus | 1206,2 | 808,0 | 521,4 | -398,2 | -286,6 | 67,0 | 64,5 |
| Uzbeks | 126,9 | 122,9 | 289,9 | -4 | 167,0 | 96,8 | 235,9 |
| Kazakh | 635,9 | 140,0 | 647,7 | -495,9 | 507,7 | 22,0 | 462,6 |
| Georgians | 130,7 | 197,9 | 157,8 | 67,2 | -40,1 | 151,4 | 79,7 |
| Azerbaijanis | 335,9 | 621,8 | 603,1 | 285,9 | -18,7 | 185,1 | 97,0 |
| Lithuanians | 70,4 | 45,6 | 31,4 | -24,8 | -14,2 | 64,8 | 68,9 |
| Moldovans | 172,7 | 172,3 | 156,4 | -0,4 | -15,9 | 99,8 | 90,8 |
| Latvian | 46,8 | 28,5 | 19 | -18,3 | -9,5 | 60,9 | 66,7 |
| Kyrgyz | 41,7 | 31,8 | 103,4 | -9,9 | 71,6 | 76,3 | 325,2 |
| Tajiks | 38,2 | 120,1 | 200,3 | 81,9 | 80,2 | 314,4 | 166,8 |
| Armenians | 532,4 | 1130,5 | 1182,4 | 598,1 | 51,9 | 212,3 | 104,6 |
| Turkmen | 39,7 | 33,1 | 36,9 | -6,6 | 3,8 | 83,4 | 111,5 |
| Estonians | 46,4 | 28,1 | 17,9 | -18,3 | -10,2 | 60,6 | 63,7 |
| Jews | 536,8 | 229,9 | 156,8 | -306,9 | -73,1 | 42,8 | 68,2 |
| Germans | 842,3 | 597,2 | 394,1 | -245,1 | -203,1 | 70,9 | 66 |
table 2
Source: Census of the USSR and the Russian Federation, the results of which are posted on the site www.demoscope.ru
about
CD
CD
iQ.
160.
belarusians and Mordva. The same picture has been preserved according to the 2010 census.
In accordance with the linguistic classification of languages, the peoples of Russia belong mainly to the four language families: Indo-European (81.3% of the population), Altai (8.9)%), Ural (1.7%) and Caucasian (3.6%), Which, in turn, are divided into groups. About 4% of Russian residents, according to the 2010 census, did not indicate their nationality.
The largest largest Slavic group of the Indo-European family is 79.5% of the population of Russia.
The number of the most numerous among the Slavic peoples - Russians - in 2010. 111.02 million people., It is 77.7% of the population of Russia. The number of Russians compared to 1989 by 2010 decreased by 8.85 million people in Russia. This happened mainly due to the natural loss, which was not able to compensate for the migration influx of Russians from the near abroad, which was active in the first decade after the collapse of the USSR and amounted to more than 3 million people at that time.
Russians are resets everywhere, but their main part is focused within the main strip of settlement. The most mononational are the central and northwestern regions of the European part, where the Russian state originated. Here, the share of Russians in the population exceeds 93%. As a result of long-term migrations, the Russians settled in the areas of residence of other nations of Russia, and now in most republics and in almost all autonomous districts, the Russian population is numerically prevalent.
The area of \u200b\u200bresettlement of the Russian ethnos does not coincide with the state borders of Russia. With the collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991, outside the Russian Federation, about 25 million remained outside the Russian Federation (about 17% of all Russian USSR) of ethnic Russians, at various times moved from Russia or born in a new place. Distinctive features of the Russian population of the former republics of the USSR is that most of them are mostly urban residents and in Soviet times traditionally have a higher, compared with the title population of the Union republics, social status.
Most Russians outside Russia live in Ukraine. According to the population census, 1989, there were 11 million people, or 22% of the country's population, and on the last Ukrainian census (2001) - million people. (17.3% of the population of Ukraine). Russians in Ukraine live in eastern areas where heavy industry is developed, as well as in the central and southern regions.
Many Russians and Kazakhstan: In 1989, Mary, or 38% of the population was recorded, on the Kazakhstan census 2009 - million or 24% of the population (the main reason for reducing the number of Russians in Kazakhstan, the migration outflow in Russia). A significant part of Russian Kazakhstan is the descendants of migrants of the royal time, who spared the fertile lands of Northern Kazakhstan, or those who came in the 1950s. Develop virgin and sealing lands in the same areas. In 2009, the Russians constituted a significant proportion of the population in the North Kazakhstan, East Kazakhstan, Karaganda, Kustanai, Pavlodar and Akmola regions.
In Belarus, after the collapse of the USSR, 1.3 million Russians were, according to the 2009 census, their number declined to 785 thousand, in Uzbekistan, in 1989, 1.6 million lived in various data on the beginning of the 2000s. - 1.2 million; In Kyrgyzstan - 0.9 million, according to the 2009 census, 0.4 million.
The special situation was formed in Latvia, where in 1989, from the total population of 2.6 million people. A little less than 1 million were Russians. The Government of Latvia seeks to preserve a number of advantages for the indigenous population and limit the rights of "migrants", which, above all, concerns citizenship and the possibility of learning in Russian. There was a similar situation in Estonia, although Russians are less than (0.5 million, or 30%).
In other republics of the former USSR, the number of Russians that found them were heated from 50 thousand (Armenia) to 500 thousand (Moldova), and their share in the population is significantly less.
TO slavic group Indo-European Family also includes million Ukrainians, 521 thousand Belarusians and 47 thousand Poles. Much of Ukrainians live in cross-border areas
Chernozem and in the Krasnodar Territory. Agrarian resettlement end XIX. - The beginning of the XX century. Formed an increased proportion of Ukrainians in the population of Primorsky Krai, the northern regions of the new development were the main focus of migrations - from Vorkuta to Magadan. The most massive migration was migration to oil and gas-producing regions of Western Siberia: in the population of the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug, the share of Ukrainians in 1989 amounted to 17%, Khanty-Mansiysk - 12% at the average Russian level - 3%. Currently, due to external migrations and changes in ethnic identity, the share of Ukrainians in the population of Russia decreased to 1%, and in these regions to 9.4% and 6%, respectively.
The Indo-European family also includes the peoples of the German Group - Germans (394 thousand), living mainly in the south of Western Siberia, and the Jews (156 thousand), which live mainly in large cities of the European part of the country (in the population of the Jewish JSC, their share is less than 1 %). The number of these peoples over the past 20 years has decreased significantly due to emigration to Germany and Israel.
Armenians were allocated to a separate language group, the number of which in Russia for the 1990s. It has grown more than twice and amounted to 1.13 million in 2002, by 2010 the active growth in the number of Armenians in Russia ceased, and their number was 1.18 million. Most Armenians live in the North Caucasus.
The largest people of the Iranian group in Russia are Ossetians (528 thousand). In the languages \u200b\u200bof the Iranian group, Tajiks are spoken (of them in Russia 200 thousand), living in the North Caucasus Tatha (1.6 thousand) and mountain Jews (0.7 thousand). The number of peoples of the Baltic Group (Latvians (19 thousand), Lithuanians (31 thousand) in Russia are relatively small; more Moldovan (156 thousand), whose language relates to the Romance group.
Altai language family is represented by several groups, the largest of which is Turkic. The cultural ranges of the peoples of the Turkic Group are located in the Urals-Volga region, in Siberia, in the North Caucasus. This group includes the second largest people of Russia - Tatars (5.3 million). In Tatarstan, there are 38% of all Tatars of Russia, there are significant share of their share in Bashkiria, in the regions of the Volga region and in the south of Western Siberia. The same group includes Chuvashi (1.44 million) living on the Middle Volga, Bashkirs (1.58 million), inventing the south of the pre-Urals.
In the North Caucasus, the Turkic peoples include Kumyki (503 thousand) and Nogai (104 thousand), living mainly in Dagestan, as well as Karachai (218 thousand) and Balcarians (113 thousand). In Siberia and the Far East, the Turkic Group is represented by Yakuts (478 thousand), Tuvintsy (264 thousand), significantly smaller in numbers of Khakasami (73 thousand), Altaites (74 thousand), Shorets (13 thousand), as well as Living at the extreme north of the Dolgans (8 thousand).
From the Turkic peoples of the near abroad in Russia, most of the Kazakhs (648 thousand) are focused on border areas with Kazakhstan regions of the Ural Volga region and the south of Western Siberia. Central Asian peoples are represented by Uzbeks (290 thousand), Kirgizami (103 thousand) and Turkmen (37 thousand). Noticeably above the number of people living in Russia - 603 thousand, highly wide and the range of their settlement: less than 1/3 live in the border North Caucasus region.
The Mongolian group of the Altai language family is represented by two related peoples - Buryats (461 thousand) and Kalmyks (183 thousand), which, from the south of Siberia, on the Lower Volga in the XVII century. To the Tungus-Manchur group of the same family include the small peoples of Siberia and the Far East - Evenks (38 thousand), Even (22 thousand) and the Amur peoples (Nanachi, Ulch, etc.). Koreans (153 thousand) constitute a separate language seven.The main part of them lives in the Far East.
The peoples of the Ural family live mainly in the north of the European part of Russia, in the Volga-Vyatka district and Ural. In the Finno-Ugric group, the largest and most widely zeal ethnic groups are Mordva (744 thousand), the number of which is constantly reduced due to assimilation. This group also includes Udmurts (552 thousand), Markets (548 thousand), Komi (228 thousand), Komi-Permyaki (94 thousand) and Karelia (61 thousand). The number of Karel decreased almost a third over the past 30 years due to fast-reaching assimilation, their share in the Republic of Karelia is less than 7%. In Russia, there are 18 thousand Estonians and 20 thousand Finns, quite a bit of Hungarians, Episses and Saamov, also related to this language group. In the Urals Finno-Ugric peoples are Khanty (31 thousand) and Mansi (12 thousand), whose share in its autonomous district decreased to 1.5% after
mass migration of the Slavic population during the development of the largest oil and gas fields. The South African Group of the Ural family includes nonsense residents (45 thousand), small seglocks (3.6 thousand) and Nganasans (0.9 thousand).
The peoples of the North Caucasian language family are represented by two groups. Adygey residents (125 thousand) and the Kabardians related to them (517 thousand), Circassians (73 thousand) and abazines (43 thousand) live themselves in the north-western part. All of them belong to the Abkhaz-Adyg group. It also includes those who live mainly in the Transcaucasus Abkhaz. The Nakho-Dagestan group unites the peoples of the southeastern part of the region. The largest people of the North Caucasus - Chechens (1.43 million); Close to them in the language of Ingush 445 thousand. In the Dagestan subgroup, the largest people are Avars (912 thousand), then Darginians (589 thousand), Lezgins (474 \u200b\u200bthousand), Laktsy (179 thousand) and Tabasarana ( 146 thousand), in addition to them, Dagestan is inhabited by many ethnic groups and subethnos (Rutults, Aguly, Tsakhura, Udine, etc.).
The Chukchotskaya-Kamchatka language family is extremely small, it includes Chukchi (16 thousand), koryaki (8 thousand) and conferences (3 thousand). Even less in Russia, Eskimos (1.7 thousand) and Aleuts (0.5 thousand), combined into a separate family. The languages \u200b\u200bof two small peoples (Ketov and Nivkhov) do not apply to any of the existing language families and stand out as isolated.
Ethnic structure of the regions of Russia. Of the 83 regions - subjects of the Federation - 26 are national-territorial entities: 21 republic, 1 autonomous region, 4 autonomous districts.
Of the 21st of the Republic of Russia in 10 title nations make up more than half of all residents. This is most of the North Caucasus republics: Dagestan (more than 80%), Chechnya (95%), Ingushetia (94%), Kabardino-Balkaria (70%), North Ossetia (65%), Karachayevo-Cherkessia (53%), as well as Kalmykia (57%), Chuvashia (68%), Tatarstan (53%) and Tuva (82%). Minimum shares of title ethnic groups in Karelia (7.4%) and Khakassia (12%).
In autonomous districts, title peoples make up a minority of the population. Minimum values \u200b\u200bdue to the tributaries of the Novoselov in recent decades Have a Khanty-Mansiysk (2.1%) and Yamalo-Nenets (about 6%) of the district.
The dispersal of the placement of many nations, their intensive contacts between themselves and especially with Russian contributed to the process of assimilation ("dissolving" of some nations among others). Among the Finno-Ugric peoples, the ethnic territory of the Mordva is most dispersed: 45% of the Morder lives in the territory of Mordovia. Among the population of Mordovia Mordva is 40%, the rest of the population is mostly Russian, a little Tatars and the Chuvash. Even less, the share of the title nation in Karelia: there Karelia make up 7.4% of all residents. The number of Karelians and Mordov in recent decades has decreased due to assimilation among Russians.
The significance of the Russian language for the peoples of Russia. The Russian language, according to the 2002 census, own not only almost all Russians living in Russia (99.8%), but also representatives of other peoples. From 29 million people. Russia's non-Russian population 27 million people. They stated that they are owned by the Russian language. In total, 98.4% of Russia's population speak Russian.
Thus, the overwhelming majority of the Russian population can communicate among themselves in Russian. This is especially important for regions where nations speak different languages, for example, in Dagestan, where Russian fulfills the function of the language of interethnic communication. It is important for other republics, where the title peoples speak very different languages, for example, for Kabardino-Balkarikaria (where the Kabardian language belongs to the North Caucasian family, and Balkarsky - to the Turkic group of the Altai family).
In addition, the knowledge of the Russian language by representatives of non-Russian peoples allows them to join Russian culture (and through it to the world), to receive education not only at home, but also in any region of Russia, to participate in solving all-Russian problems.
In the late 1980s. There are numerous national Movementswho have been aimed at the revival of the native language and culture. Often, their activities were accompanied by the strengthening of ethnocentricism and nationalism, ethnic conflicts. In the struggle of the Russian republics for sovereignty and raising the status, ethnic reasons were not always the main. Most often basic driving power The conflict with the federal authorities was the desire of republican elites to greater independence from the center, for which the national map was played.
Real manifestations of separatism were the most powerful in Chechnya, where the conflict lasted for more than 10 years. In the early 1990s Separatism was noticeable and in Tuva, which several decades had their own statehood and only in 1944 was attached to the Soviet Union. A positive example of the achievement of a compromise between the federal and republican authorities was the Republic of Tatarstan, the first concluded agreement on the delimitation of powers, which put an end to the confrontation.
Another reason for the occurrence of conflicts are inter-ethnic contradictions, which caused the deportations of some nations during the war (see the section "Migration of the population") and a repeated redistribution of republics. The most acute became the armed clashes of Ingush and Ossetians for the suburban area belonging to North Ossetia, but the previously part of the Chechen-Ingush Republic. Similar contradictions exist between the peoples of Dagestan, but they are resolved in a peaceful way. The change in the republic boundaries led to the transmission to their composition of the part of the plain lands populated by the Cossacks. The growing agrarian overpopulation of the republics of the North Caucasus strengthened competition for land, which is now leading to the oss of Russians from these areas, increasing contradictions between different ethnic groups.
Conflicts associated with the numerical predominance of one of two ethnic groups and the concentration of power in the hands of its representatives exist in Kabardino-Balkaria and Karachay-Cherkessia. Some other problems are characteristic of Bashkiria, where Bashkirs were only the third in numbers after Russian and Tatars by the people (census 2002 and 2010. recorded in Bashkiria, there are already a slightly greater number of Bashkir than the Tatar).
Most inter-ethnic conflicts have roots in a long time and recent Russian history, exacerbated with ethnodemographic, economic problems, therefore, there are no simple ways to consent. To resolve inter-ethnic problems, the improvement of national policies is needed, strengthening real federalism, creating conditions for the free development of languages \u200b\u200band cultures, strengthening guarantees that exclude the infringement of citizens' rights on ethnic signs, the accounting of the vital interests of small peoples in the implementation of large projects on the main territory of their residence.
167
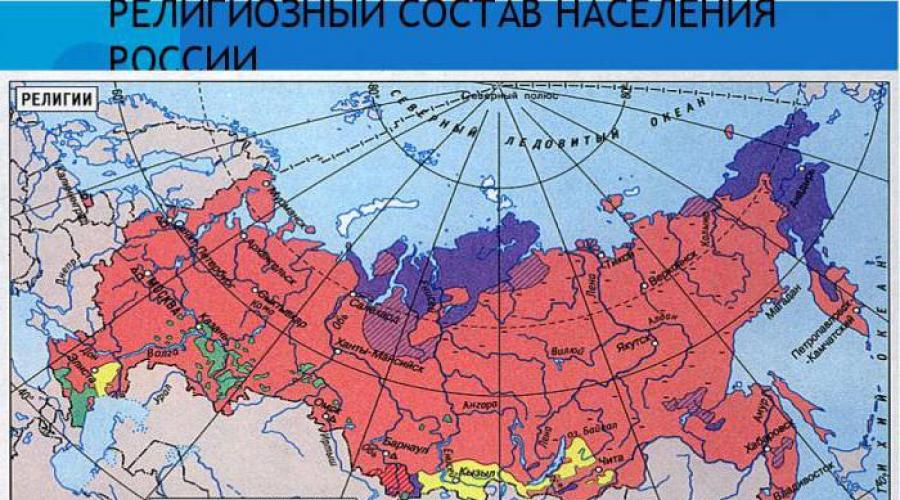
A confessional (religious) composition of the population of Russia is characterized by the absolute predominance of Orthodoxy. Orthodoxy confesses the overwhelming majority of believers among East Slavic peoples - Russians, Ukrainians, Belarusians, the Finno-Ugric peoples of Russia - Mordvov, Udmurts, Mari, Komi, Komi-Permyakov, Karelov, a number of Turkic peoples - Chuvash, Khakas, Yakuts. Among the peoples of the North Caucasus, Orthodoxy profess only Ossetians.
The second largest religion in Russia is Islam. He is confessed by Tatars, Bashkirs and almost all the peoples of the North Caucasus (except for Ossetians).
Buddhism was distributed among the Mongolian-speaking peoples - Buryat, Kalmykov, as well as among Tuvintsev.
Most believers among the representatives of the small peoples of the North, Siberia and the Far East (Nenets, Khanty, Mansi, Shorts, Evenks, Nanice, etc.) are officially considered Orthodox, but in most cases they are confessing both tribal, pagan beliefs (shamanism).
The number of believers of supporters of other denominations in Russia is small. Recently is active missionary activity Representatives of non-traditional confessions for Russia.
Questions and tasks Give the definition of the ethnos. Describe the main approaches to ethnicity. What are you knowing ethnic processes? Give examples of Ethnic
processes. Give the characteristic of the ethnogeographic position of Russia. Specify the main factors for changing the ethnic structure on
russia's village in the post-Soviet period. What ethnic groups of Russia changed due to the mass
ethnic migration after 1991? What ethnides of Russia are most actively affected by the AC process
similarations? Bring the ethno-speaking classification of ethnic groups living
in Russia. List the five most numerous peoples of Russia. Give the characteristics of the ethnic structure of the regions of Russia.
168. What are the main causes of ethnic contradictions? What religions prevail in Russia?
Literature http://demoscope.ru - Demographic weekly "Demoskop" http://www.perepis-2010.ru - Portal "All-Russian census of us
2010. http://www.gks.ru - official website Federal Service state
dURATING STATISTICS. http://www.cisstat.com - interstate statistical
cIS mitty. http://www.iea.ras.ru - website of the Institute of Ethnology and Anthropology
Wounds http://www.ethnology.ru - the site "Ethnography of the peoples of Russia". http://socioline.ru - the site "Sociology in a new way".
In the modern world, Russia is the largest countryHaving occupying an extensive area - more than seventeen thousand square kilometers. Two continents divide it into parts - European and Asian. Each of them is more in the territory of many not such and small states of the Earth.
By the number of population, however, our country is only in the ninth place. The number of Russians today does not reach a hundred and fifty million people. The problem is that most of the territory of the country lies under deserted steppes and taiga, for example, these are the most distant areas of Siberia.
However, it is compensated by the number of peoples living here. So it was predetermined by the past. Historically, Russia is a multinational state, which has become, absorbing neighboring peoples, attracting strangers by large territories and wealth. According to official data, now in the Russian state there are almost two hundred peoples, sharply differing in numbers: from Russians (more than one hundred ten million people) to Kerek (less than ten representatives).
How many of us?
How many peoples live in Russia? How to find out? The leading sources of useful information about the population of our country are statistical census, regularly held in recent years. At the same time, according to modern methods and according to democratic approaches, the data of the national affiliation of residents of Russia by origin is not noted in the documents, which is why digital census material appeared on the basis of the self-determination of Russians.
Total in recent years, a few more than 80% of the country's citizens declared themselves Russian by nationality, only 19.1% remained on representatives of other peoples. Almost six million census participants could not allocate their nationality or determined it in the form of a fantastic people (elves, for example).
Summing up the final calculations, it should be noted that the cumulative volume of the peoples of the country, which do not consider themselves to Russian population, did not exceed twenty-five million citizens.

This suggests that the ethnic composition of the population of Russia is very complicated and requires constant special attention. On the other hand, there is one major ethnos, an employee of a kind of rod of the entire system.
Ethnic composition
The basis of the national composition of Russia is, of course, Russians. This people are going on historical roots From the eastern Slavs, who lived in Russia from ancient times. A significant part of the Russians exists, of course, in Russia, but there are large strata in a number of former Union republics in the United States. This is the most significant European ethnic group. To date, more than one hundred thirty-three million Russians live in the world.
Russians are the title people of our country, its representatives dominate the significance of the regions of the modern Russian state. Of course, this led to side effects. Distribution of this nation over several centuries in the extensive territory during historical Development He led to the formation of dialects, as well as individual ethnic groups. For example, on the coast of the White Sea, there is a pomper that make up the subethnos of local Karelians and who arrived in the past Russians.
From among more complex ethnic associations, a group of peoples can be noted. The largest group of peoples represent Slavs, mainly from the Eastern subgroup.
In aggregate, representatives of nine large language families lived in language, culture, everyday life live in Russia. With the exception of the Indo-European family, they mainly have an Asian origin.
Such is the approximate ethnic composition of the population of Russia today according to official data. What can be said definitely, so this is what our country is distinguished by a significant variety of nationalities.

The largest peoples of Russia
Nationalities living in Russia are quite clearly divided into numerous and small. The first, in particular, belong:
- Russian residents of the country number (according to the last census) more than one hundred and ten million people.
- Tatars of several groups that have reached 5.4 million people.
- Ukrainians who have two million people. The main part of the Ukrainian people lives in Ukraine, in Russia, representatives of this people appeared in the course of historical development in pre-revolutionary, Soviet, the newest periods.
- Bashkirs, another nomadic people in the past. Their number is 1.6 million people.
- Chuvashi, residents of the Volga region - 1.4 million.
- Chechens, one of the peoples of the Caucasus, - 1.4 million, etc.
There are other nations with a similar number, which played an important role in the past and, possibly, the future of the country.
Small peoples of Russia
How many peoples live in Russia from among small? There are many such ethnic groups in the country, but in the total volume they are weakly represented, since very small. These national groups belong to the peoples of Finno-Ugric, Selfie, Turkic, Sino-Tibetan Group. Especially small are kerges (tiny people - only four people), the people of water (sixty-four people), Enzi (two hundred seventy seven), ultra (almost three hundred people), chulymtsy (just over three and a half hundred), Aleuts (almost half thousand) , nonhydals (a little more than five hundred), Orochi (almost six hundred). For all of them, the problem of survival is an acute and everyday question.
Map of the peoples of Russia
In addition to the strong scatter in the number of the national composition of Russia and the inability of many ethnic groups, in modern times, to maintain their number on their own, there is also a problem of distribution in the country. Russia's population is resettled very inhomogeneously, which is due primarily by economic motivations both in the historical past and in modern times.
The main mass is located in the area between the Baltic St. Petersburg, the Siberian Krasnoyarsk, the Black Sea Novorossiysk and Far Eastern Primorsky Krah, where all the large cities lie. The reasons for this are a good climate and a favorable economic background. To the north of this territory there is a long-term Merzlot, caused by eternal cold, and to the south - huge expanses of lifeless desert.

In the density of the population, Siberia received one of the last places in the modern world. It is constantly less than 30 million inhabitants on its extensive territory. This is only 20% of the country's total population. While in its extensive Square, Siberia reaches three-quarters of the expanses of Russia. The most populated places are the directions of Derbent - Sochi and Ufa - Moscow.
In the Far East, a significant density of the population passes through the length of the entire transdiebirsk road. Increased settlement density standards are allocated in the area of \u200b\u200ba blacksmith coal basin. All these areas attract Russians with their economic and natural wealth.
Self large peoples Countries: Russians, to a lesser extent, Tatars and Ukrainians are mainly located in the south-west of the state. Ukrainians today for the most part are in the territory of the Chukotka Peninsula and in the Khanty-Mansiysk District, in the distant Magadan region.
Other small peoples of the Slavic ethnic group, like the Poles and Bulgarians, do not create large compact groups and scattered throughout the country. A fairly compact group of the Polish population is only in the Omsk region.
Tatara
The number of Tatars living in Russia, as noted above, surpassed the level of three percent of the common Russian population. About a third of them compactly lives in the region of the Russian Federation called the Republic of Tatarstan. Group settlements exist in the regions of the Volga region, in the extreme north and so on.
A significant part of the Tatars - supporters of Islam Sunni sense. Separate groups Tatars possess language differences, culture and life. The common language is within the framework of the Turkic group of languages \u200b\u200bof the Altai language family, he has three dialects: Mishar (Western), more common Kazan (medium), a little distant Siberian-Tatar (East). In Tatarstan, this language is manifested as official.
Ukrainians
One of the numerous East Slavic peoples - Ukrainians. More than forty million Ukrainians live on their historical homeland. In addition, significant diasporas exist not only in Russia, but also in Europe and America.
Ukrainians living in Russia, including labor migrants, make up about five million people. Significant number is in the cities. Especially large groups of this ethnos are placed in the capital, in the oil and gas-bearing areas of Siberia, the Far North, and so on.
Belorus
In modern Russia, Belarusians, taking into account their total number in the world, co-becoming a large number. According to the Pea-Pi-si Russian on-section 2010, Belarusians living in Russia, a little more than half a million people. Know-Chi-Tel, the share of Be-Lo-owls is the capitals, as well as in a number of re-hy--new, for example, in Karelia, Kaliningrad region.

In pre-revolutionary years, a large number of Belarusians moved to Siberia and the Far East, the national administrative units were later there. By the end of the eighties, Belarusians were in the territory of the RSFSR more than one million people. Nowadays, their number has decreased twice, but it is obvious that the Belarusian interlayer in Russia will be preserved.
Armenians
Armenians living in Russia, quite a lot, however, according to various sources, their number diverges. Thus, according to the 2010 census materials, there were few more than one million people in Russia, that is, less than one percent of the cumulative population. According to the assumptions of Armenian public organizations, the number of Armenian layers in the country at the beginning of the twentieth century exceeded two and a half million people. And Russian President V. V. Putin, speaking about the number of Armenians in Russia, voiced the figure of three million people.
In any case, Armenians play a major role in the public and cultural life of Russia. Thus, Armenians work in the Russian government (Chilingarians, Bagdasarov, etc.), in show business (I. Allegrova, V. Dobrynin, etc.), in other fields of activity. In sixty-three regions of Russia there are regional organizations of the Russian Union of Armenians.
Germans
The Germans living in Russia are representatives of the ethnos who survived the controversial and even a tragic story. Massly transplancing in the eighteenth-nineteenth centuries at the invitation of the Russian government, they mostly settled in the Volga region, Western and South provinces Russian Empire. Life on good lands was driving, but in the twentieth century historical events Painfully hit the Germans. First, the first world, then the Great Patriotic War led to mass repressions. In the fiftieth eighties of the last century, the history of this ethnos was made. Not in vain in the nineties began the mass migration of the Germans, the number of which, according to some information, barely exceeds the number in Halmillion.
True, in recent years there is an episodic response from Europe to Russia, but until it reached a large scale.

Jews
How many Jews live in Russia at the present time, to say not easy due to their active migration both in Israel and back to the Russian state. In the historical past in our country, Jews were a lot - in soviet era Several million. But with the collapse of the USSR and significant migration to the historical homeland, the number of them decreased. Now, according to public Jewish organizations, in Russia there is about one million Jews, half of them are residents of the capital.
Yakuta
This is Turkic Press numerous people, Indigenous, adapted to the local conditions of the population of the region.
How many Yakuts in Russia? According to the All-Russian census of the domestic population of 2010, there were several less than half a million people mainly in Yakutia and nearby regions. Yakuta is the most numerous (about half of the population) the people and the most significant of the indigenous peoples of Russian Siberia.

In the traditional economy and material culture of this nation, many close, similar moments with cattlemen of South Asia. On the territory of Middle Lena, an option for the economy of Yakutov, uniting nomadic cattle breeding and the most important extensive types of fisheries (mining meat and fish), suitable to the local one formed. In the north of the region there is also a distinctive form of hardened reindeer!
Causes of settlement
The history of the ethnic composition of the population of Russia in the course of its development is extremely ambiguous. The accelerated settlement of the Russian state Ukrainians occurred in the era of the Middle Ages. In the sixteenth-seventeenth centuries on instructions government agencies Settlers from southern lands were sent to the East to master new territories. After some time, they began to send representatives of social layers from different regions.
Representatives of the intelligentsia voluntarily moved to St. Petersburg in the era, when this city had the status of the capital of the state. Nowadays, the Ukrainians make up in Russia the largest ethnic group after, of course, Russians.
There are representatives of small nations on another pole. In much danger there are kerges that have the smallest number. According to the last census, there are only four representatives left, although even fifty years ago, Kerekov had only a hundred people. Leading languages \u200b\u200bfor these people are the Chukotka and the generally accepted Russian, the native Kereksky is found only in the form of an ordinary passive language. Kerki in terms of culture, ordinary daily activities are very close to the Chukchi people, because of which they were in constant assimilation with him.
Problems and Future
The ethnic composition of the population of Russia in the future will undoubtedly develop. IN modern conditions It is well noticeable revival of ethnographic traditions, culture of peoples. However, the development of ethnic groups is experiencing a number of problems:
- bad fertility and gradual reduction of most peoples;
- globalization, and at the same time the influence of the culture and life of large peoples (Russian and Anglo-Saxon);
- general problems of the economy, which boil the economic base of peoples and so on.
Much in such a situation depends on the national governments themselves, including Russian, and from the global opinion.
But I want to believe that the small peoples of Russia will continue to develop and increase in subsequent centuries.
The Russian Federation belongs to the number of multinational states of the world.
In the list of nationalities, more than 160 ethnic groups are allocated.
All those inhabiting the Russian Federation peoples belong to nine language families: Indo-European, Carvela, Ural-Yukagirskaya, Altai, Eskimo-Aleutskaya, North Caucasian, Yenisei, Sino-Tibetan, Chukotka-Kamchatka.
In addition, one people (Nivhi) occupies an isolated position in language relations.
The overwhelming majority of ethnic groups of Russia, in the aggregate of 122.9 million people. (84.7% of the population of the country) belongs to Indo-European peoples.
The Indo-European family is divided into several groups, of which in Russia the following are the following: Slavic, Baltic, German, Romanesque, Greek, Armenian, Iranian and Indoary.
The largest of these groups is Slavic (119.7 million people-82.5% of total). First of all, the main people of the country include the Russians, the Russians, according to the 2002 census, 115.9 million people, accounting for 79.8% of the total population of Russia. Slavs are Ukrainians, Belarusians, Poles, Bulgarians, and representatives of some other peoples in Russia. Russians sharply prevail in the overwhelming majority of the subjects of the Russian Federation. Of all the constituent entities of the Russian Federation below, the share of Russians in the Republic of Dagestan, and after the well-known military events, she probably became even lower and in Chechen Republic.
Such a big and widespread people, as Russian, despite significant monolithium, naturally, includes sub-ethnic groups of different hierarchical levels. First of all, the northern and southern Velicors are distinguished, substantially differing in a dialect, individual elements of material and spiritual culture. However, the general features in the culture of different groups of the Russian people are much larger than differences. The unity of the Russians is emphasized by the fact that along with the Northern and South Velicors there is a transitional Middle Russian group, in the culture and language of which are combined both the northern and southern elements.
The region of resettlement of northern Velicors extends from the Finnish bay to the Urals and the more eastern regions, covering the Arkhangelsk, Murmansk, Vologda, Leningrad, Novgorod, Yaroslavl, Kostroma, Ivanovo region, Northeast of the Tver region, the Northern and Central Parts of the Nizhny Novgorod region, Kirov region., Perm region, Sverdlovsk, Orenburg, Ulyanovsk region, Eastern part of the Saratov region, Astrakhan region, as well as the Republic, the Republic of Komi, the Udmurt Republic, the Republic of Mari El, the Chuvash Republic - Chuvashia, the Republic of Tatarstan (Tatarstan), the Republic of Bashkortostan (along with the indigenous population of these republics).
A number of northern gigs are allocated ethnographic groups Lower hierarchical level. This is, first of all, a pomper, as well as close to them on the origin and culture of mesenz, emptyers and ust-cilles. Several separate groups of northern gigs are also cargopes, Zaenozhana, Ilmen Posover, Poshechona, Kerzhaki.
The range of the Central Russian group is located mainly in the interfluve of the Volga and Oka rivers. The composition of this group is distinguished by Tudomlyans, living in the Tver region along the Tud River (the influx of the Volga River) and representing the origin of the Russorest Belarusians, and the Russian Meshchera, resettled in the north of the Ryazan region and in a number of other areas and possibly genetically connected with marked in The chronicle of the Finno-speaking meshlora.
A transitional group that lives in the Pskov and Smolensk regions and neighboring regions of the Tver and Kaluga regions and has a number of linguistic and cultural traits rapping it with Belarusians is occupied. This is especially true of the population of the Smolensk region, colloquial which is closer to the tongue than to Russian (although the group is undoubtedly Russian).
Southern Velicors are resettled in the southern strip of Russia, from the River River Basin in the West to the Rips of the Hoper River and the Mesmen in the East, from the average course of the Oka River in the north to the main Caucasian ridge on South.
From the ethnographic groups of southern Velicors in the territory of the European part of Russia, Fields are inhabited, which are considered to be the descendants of the ancient population of Russia, never left with other South-Russian groups to the north of the nomad attack; In addition to them, Sayans and Tsukans are distinguished as several separate groups.
The Russian population of Siberia and the Far East developed as a result of a resettlement from various regions of Russia, and the share of these regions in different historical periods It was unequal. The Siberian Old-timer population is predominantly northern Greets of the XVI-XVIII centuries., "Novoseli", or, as they are called Russian, "Russian", are mainly from the southern provisions of Russia (the second half of the XIX century).
Among the old-timing population there are several very specific groups, many of whom on economic classes, culture and language are strongly alleged from the main part of the Russian population. This is the so-called Obski old-timers, sir trunks and flavors, the culminated peasants, who have learned the language, Russian-Ustyintsy or Indigirkers, Kramchans or Nizhnekolomtsy, who partially switched to the Yakut language of the Hikorda or Midklavians, Markovtsy.
Russian resettlement

Cossacks occupy a completely special position among subecadet groups of the Russian population. Possessing a number of common cultural and domestic traits, nevertheless, they are one. Don Cossacks are settled in the Rostov and Volgograd regions, Kuban - in the Krasnodar Territory (there are a very significant component in their composition), Tereski - in the Stavropol Territory, as well as in the Kabardino-Balkarian Republic, in the Republic of North Ossetia-Alania, in the Chechen Republic and The Republic of Dagestan, Astrakhansky - in the Astrakhan region, Orenburg - in the Orenburg, Chelyabinsk and Kurgan regions, Trans-Baikal (have a significant impurity) - in the Chita region and the Republic of Buryatia, Amur - in the Amur region and the Jewish Autonomous Region, Ussuri - in Primorsky and the region. The Ural Cossacks living in Russia are concentrated in a number of southwestern regions of the Orenburg region, Siberian Cossacks in some areas of the Omsk region.
Ukrainians (2.9 million people-2% of the population of Russia) form the highest share in the population of some northern subjects of the Russian Federation: in the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous Okrug, in the Chukotka Autonomous District, the Magadan region and the Khanty-Mansiysk Autonomous District - Ugra. Specific gravity Belarusians (as a whole in the country there are 815 thousand people, which is 0.6% of the population) relatively high in the Kaliningrad region and the Republic of Karelia. (73 thousand people) are resets through the territory of Russia dispersed, forming significant groups in the cities of St. Petersburg and Moscow; In the Omsk region there is a small area of \u200b\u200ba rural enclave, where the Polish population prevails. Bulgarians, Czechs, are also resets very scattered.
Moldovans (172 thousand people of the country's population), Romanians, Spaniards and Cubans (6 thousand people, 2 thousand people, and 1.6 thousand people, reside, reside from the peoples of the Romance Group in Russia dispersed in the country.
The Greek group includes some Greeks (98 thousand people), mainly focused in the Krasnodar and Stavropol Territories.
The Armenian group is also represented by one ethnic group - Armenians (1.1 million people - 0.8% of the population of Russia). Armenians are widely resets throughout the country, but most of all live in the south of the European part of Russia. A significant group of Armenians live in Moscow.
The Baltic Group is prepared by a relatively small number and Latvians (respectively, 45 thousand people and 29 thousand people), separated in a number of areas of the country. With a sufficiently dispersed resettlement, they form small compact arrays in the Krasnoyarsk Territory. A significant number of Latvians, in addition, lives in the Omsk region, Lithuanians in the Kaliningrad region. And Lithuanians also live in the cities of Moscow and St. Petersburg. There are representatives of the Latgaltsev ethnic group (in most Catholics), which were previously considered a separate people.
The German group includes primarily the Germans (597 thousand people - 0.4% of the population of Russia). They are resettled in the country quite dispersed, but the main area of \u200b\u200btheir residence is the south of West and Central Siberia. Russian Germans are inhomogeneous: among them, in the tongue and some characteristics of culture, the descendants of immigrants from South and North are highlighted, and among the latter, a special ethno-graphic group is formed by Mennonites.
Conventionally, Jews (230 thousand people were 0.2% of the population of Russia) may be counted to the German group. The overwhelming majority of Russian Jews refers to those who have spent no time for Yiddish, but among them there is also a small number of sephards integrated into the composition of Ashkenazov. Among the Jews in cities, mainly in large, the most numerous groups are concentrated in Moscow, Samara, Chelyabinsk, Rostov-on-Don, Saratov,.
The Iranian group includes the first of all Ossetians (515 thousand people, 0.4% of the population of Russia) and mountain Jews (3 thousand people). Basically focused in the Republic of North Ossetia-Alanya; They are in neighboring areas with her. Mountain Jews live, mainly in the Republic of Dagestan and the Kabardino-Balkarian Republic. Iranian-speaking is dispersed in Russia.
The Indoary Group is presented in Russia primarily (183 thousand people - 0.1% of the population of Russia). Gypsies are resettled in the country wide and exist in almost all subjects of the Russian Federation. However, partially retaining the traditions of nomadic life they are more likely to southern, "warm" districts. The most significant groups of Gypsies form in the Krasnodar and Stavropol Territories, as well as in the Rostov region.
The cargo family includes Georgians (198 thousand people - 0.1% of the country's population). They nowhere in the country do not constitute significant groups. Above only the share of Georgians in the population of a number of regions of the North Caucasus (Republic of North Ossetia-Alania, Krasnodar Territory, Stavropol Territory), as well as in Moscow; But in these places there are few them. Among Georgians in Russia have megrellas (and a small number of savs) and Jews (1.2 thousand people).
The Ural-Yukagir family in Russia is quite widely represented, although it is very inferior to an Indo-European family in its number. It belongs to 2.8 million people. - 1.9% of the population of Russia. The Urals-Yukagir family is divided into three groups: Finnish-Ugors (it belongs to the majority of the peoples of this family), self-dyan and Yukagir.
Karelia is owned to the Finno-Ugric group (125 thousand people - 0.1%), Izhhorians (0.4 thousand people), Finns (in the overwhelming majority of Ingermanlade - 47 thousand people.), Estonians (46 thousand. pers.), (probably 0.2 thousand people), Veps (12 thousand people), Saama, or blades (2 thousand people), Mordva (935 thousand people - 0.6%) , (595 thousand people - 0.4%), Udmurts (713 thousand people - 0.5%), fermenmen (10 thousand people), Komi (358 thousand people - 0.2%) , Komi-Permyaky (141 thousand people - 0.1%), (22 thousand people), (8 thousand people) and Hungarians (6 thousand people).
Charles are concentrated primarily in the Republic of Karelia, however, they constitute a minority of the population. The second important place of residence of Karel is the Tver region, where Karelia occupy a fairly compact area. Karelias also live in the Murmansk and Leningrad regions and the city of St. Petersburg. The close people of Izhhorians are mainly concentrated in the Leningrad region. Finns live, mainly in the Republic of Karelia, the Leningrad region and the city of St. Petersburg. Remiss the country dispersed. The most significant groups of them are available in the Krasnoyarsk Territory and the city of St. Petersburg. Quickly assimilated by the surrounding Russian population, malnian ethnos. The water, (the overwhelming majority of which do not know the native language and speaks only in Russian) lives in several villages of the Leningrad region. Veps are concentrated, mainly in the Republic of Karelia, Leningrad and Vologda regions. Saama are presented in Russia a small group, the overwhelming majority of which are concentrated in the Murmansk region. The largest people of the Ural-Yukagi family in Russia is Mordva. It occupies the eighth place among the peoples of the Russian Federation. The people are very dispersed, and in the Republic of Mordovia lives about a third of the entire face. Significant groups of Mordov are available in Penza, Ulyanovsk, Samara, Orenburg and Nizhny Novgorod regions. In the Volga region, several northeries Morder, Mari men, whose settlement is also dispersed. In the Republic of Mari El lives only half of all Mariers of Russia. The share of Mariers in the population of the Republic of Bashkortostan, the Kirov region, the Sverdlovsk region and the Republic of Tatarstan (Tatarstan) is essential. Urals living in the Urals are mainly concentrated in the Udmurt Republic, although they constitute about a third of the population. From other subjects of the Russian Federation in which the Udmurts live, the Kirov region, the Perm region, the Republic of Tatarstan (Tatarstan), the Republic of Bashkortostan and the Sverdlovsk region should be noted. In the northern part of the Udmurt Republic lives the small people internmantic, assimilated in the language (but not in ethnic!) The environment. Komi, living in the north of the European part of Russia, or Komi-Zyryan in the overwhelming majority are concentrated in their Komi Republic. Outside of the republic, the most significant components of the Comience group are available in the Nenets Autonomous District and in the Khanty-Mansi Autonomous District - Ugra. Close to Komi-Zyryanam Komi-Permyaki, which are also mainly concentrated in the Perm Territory. Khanty living in Western Siberia, mainly concentrated in the Khanty-Mansi Autonomous District - Ugra and the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous District. Severed south-west Mansi in the overwhelming majority live in the Khanty-Mansi Autonomous District - Ugra.
Significantly less than another group of the Ural-Yukagir family - Samiya. It includes only four people: Nenets, Enzi, Nganasans, Selkup. (41 days. People), mainly focused in the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous District, in the Nenets Autonomous District and in the north of the Krasnoyarsk Territory (formerly Taimyr (Dolgano-Nenets) Autonomous District). In these regions, they constitute a small proportion of the population. Enza is one of the most small. According to the 2002 census, there were few more than 300 people. Nganasans, mostly focused on the north of the Krasnoyarsk Territory. Sellockups (4 thousand people), mainly, are resettled in two fairly distant places: Northern (Tazovskie) Sellocks live in the Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous District, South (Tym, Naryn) - in the north of the Tomsk region.
The group unites two people: Yukagirov (about 2 thousand people) and Chuvantans (more than 1 thousand people). Most Yukagirov are resettled in the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia). A relatively small group lives in the Chukotka Autonomous District. In it, the majority of Chuvantans are concentrated. All have lost their own, close to Yukagirsky, language and speak now either in Russian (sedentary Chudans living in the village of Markovovo), or in Chukotsky (nomadic chudvants living in the upper reaches of the Anadyr River).
The Altai family is the second largest in Russia after Indo-European, although almost ten times it is inferior to it. It owns 12.7 million all residents of Russia (8.7% of the total population). It includes five groups, of which four are quite widely represented four: Turkic, Mongolian, Tunguso-Manchurian and Korean.
The largest of these groups is the Turkic, to which the following peoples include the following peoples: Chuvashi (1.6 million people - 1.1% of the population of Russia), Tatars including Siberian (5.3 million people - 3.6%) Moving to Russia Crimean Tatars,
(6 thousand people), quicken (about 300 thousand people - 0.2%), Nagaibaki (10 thousand people), Bashkirs
(1.7 million people - 1.2%), Kazakhs (654 thousand people - 0.5%), (6 thousand people), Nogai (91 thousand people), Kumyki (423 thousand) pers. - 0.2%), Karachay (192 thousand people - 0.1%), (78 thousand people), Azerbaijanis (622 thousand people - 0.4%), Turkmen (33 thousand. pers.), (123 thousand people), or Altai-Kizhi (about 45 thousand people), Telengitis (approximately 5 thousand people), (1.7 thousand people), tubalars (1.6 thousand people.), Kumandintsy (3 thousand people), jackets (0.9 thousand people), Chulymetsy (0.7 thousand people), Shorts (14 thousand people), Khakasy (76 thousand . people.), Tuvintsy (243 thousand people - about 0.2%), Tofalars (0.8 thousand people), Soyota (3 thousand people), Yakuta (444 thousand people - 0, 3%), dolgans (7 thousand people).
The fifth people of the country are half focused in the Chuvash Republic - Chuvashia, where he constitutes the majority of the population. Significant groups of the Chuvash live in the Ulyanovsk region, in the Republic of Tatarstan (Tatarstan), the Samara region, in the Republic of Bashkortostan, in Tyumen, Orenburg and some other areas of the country.
Tatars (the second in numbers after the Russian people of Russia) are quite widely resets in the country. In addition to its republic and nearby subjects - regions of their compact residence, a lot of Tatars live in West Siberian regions (Tyumen, Omsk, Novosibirsk, Tomsk and Kemerovo). The high proportion of Tatars in the Tyumen region is related to the fact that Siberian Tatars live here, which are indigenous inhabitants of these places and recognized by some scientists for a separate ethnos. Siberian Tatars differ from Kazan and other European Tatars with their dialect and anthropological type (they are more mongoloid). Siberian Tatars are very dispersely reset and disintegrate into a series of ethnographic groups: Tyumen-Turin, Tobolsk, Zabolotny (Yaskolbinsk), Tevrisian (), Barabinges, Tomsk, chat rooms, Kalmyks.
Separate people consider themselves silent. Two thirds are concentrated in the Republic of Tatarstan (Tatarstan) (mainly in the commercial and eastern parts), one-third - in other subjects of the Russian Federation: in the Republic of Bashkortostan, Altai and Krasnoyarsk Territories, in the Republic of Mari El and the Udmurt Republic. Nagaibaki, living in two regions of the Chelyabinsk region, are close to the quacks.
The fourth in the number of the people of the Russian Federation, settle down, like many nations and the pre-Urals, very dispersed. In the republic itself, Bashkortostan lives over two thirds of all Bashkir of Russia, but they make up a minority of the population.
Outside of the Republic of Bashkortostan, the largest groups of representatives of Bashkir are available in the Orenburg, Sverdlovsk, Kurgan, Chelyabinsk regions, in the Perm Territory and the Khanty-Mansiysk Autonomous District - Ugra.
Kazakhs are focused primarily in bordering the regions: Astrakhan, Orenburg, Omsk, Saratov, Volgograd regions and in the Altai Territory.
Preferably focused in the Karachay-Cherkess Republic, the Republic of Dagestan and the Stavropol Territory. In the overwhelming majority concentrated in the Republic of Dagestan. Mainly, they live in the Karachay-Cherkess Republic, however, they make a relatively small part of the population there.
Balkarians mostly (90%) live in the Kabardino-Balkarian Republic.
To the Ozzskaya, or South-Western, the subgroup of the Turkic Group includes the people living in Russia, the Meskhetian Turks (25 thousand people), Omman Turks (21.5 thousand people) of Gagauz (10 thousand people) and Turkmen . Azerbaijanis are presented in almost all subjects of the Russian Federation, however form a noticeable share of the population only in the Republic of Dagestan. Living in Russia, only in one place - the Stavropol Territory - form a noticeable "clutch" of the population. There are so-called Stavropol Turkmen, or Truchmen. Another Central Asian people - Uzbeks, unlike Turkmen, do not form a compact territorial array and ringed extremely disperse.
Altai (Altai-Kizhi) belong to the South Siberian subgroup of the Turkic Group-Py. Altai, mostly concentrated in the Altai Republic. The Altetsians were first joined by five Turkic-speaking peoples: Telengitis, televisers, tubalars, Kumandintans and Clans. This subgroup also includes chulymtsy, shorts, hakas, tuvintsy and toflars.
Telengitis live in the southeastern part of the Altai Republic, televisers - mainly in the Kemerovo region, tubalars - in the northeast of the Altai Republic, Kumandints - in the south-east of the Altai Territory and the Last North of the Republic of Altai, the jackets are also in the extreme north of this republic. Chulymetsy live in the Chulev River Basin in the Tomsk region and in the south-west of the Krasnoyarsk Territory. Shorets are resettled in the south of the Kemerovo region (Mountain Shoria), as well as in Khakassia. The overwhelming majority (80%) are concentrated in the Republic of Khakassia, almost all Tuvinians (96%) - in the Republic of Tyva. Among the tuvintsev, the sub-ethnic group is allocated (36 thousand people), resettled in the north-east of the Republic of Tyva. Close to Torganis-Torinians, the small Turkic-speaking people of Tofalalar, mainly concentrated in the Irkutsk region. In the neighboring area of \u200b\u200bthe Okinsky district of the Republic of Buryatia, the people of Soyota people are living in the recent census. This people said once in a language, very close to Larsky's tofa, but now almost completely switched to Buryat language.
One of the most northern Peoples - Yakuta - almost entirely focused on the territory of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia), where Yakuts make up a third of the population, heavily inferior in the number of Russians. The yakutams in the language are very close to the Dolgans living, mainly in the north of the Krasnoyarsk Territory, as well as in the adjacent areas of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia).
Another, belonging to the Altai family - the Mongolian group - is represented in Russia, mainly two rather significant peoples: Buryats (445 thousand people - 0.3% of the population of the country) and (174 thousand people - 0.1% Country population). Buryats are mainly focused on three constituent entities of the Russian Federation: the Republic of Buryatia, the Ust-Orda Buryat Autonomous Okrug and the Aginsky Buryat Autonomous District. Between Eastern, Transbaikal, Buryats and Western, Irkutsk, there are some distinguishes in language and culture. The vast majority of Kalmykov live in the Republic of Kalmykia. The group includes a small group of Halha-Mongols living in Russia (2 thousand people).
To the third group of the Altai family - Tunguso-Manchurskaya - include Evenks (35 thousand people), non-rigany (0.8 thousand people), Euren (19 thousand people), Nanice (12 thousand people), ultra (3 thousand people), (ultrasound) (0.1 thousand people), Orochi (0.8 thousand people), Udagei (1.7 thousand people) and, conditionally, Thaza (0, 3 thousand people). It is very dispersed. About half of the total number of them live in the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia), they also have in the Khabahi Territory, in the north of the Krasnoyarsk Territory, in the Republic of Buryatia, Irkutsk and Amur regions and some other places. The nonregidals are concentrated in their majority in the Valley of the Amgun River in the Khabarovsk Territory. Evenov lives the most in the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia), they are also in the Magadan region, the Khabarovsk Territory, the Chukchi Autonomous District. Nanice in the overwhelming majority focused on the Amur River and his tributaries in the Khabarovsk Territory. In the Khabarovsk Territory, mostly settlers are reset; Orcohols, mainly live in the Sakhalin region, Orochi - in the Khabarovsk Territory, Udagei - in the Primorsky and Khabarovsk Territories. Conditionally, Tazy are attributable to the Tungus-Manchu group - the people of Nanay-Ureegia origin, which turned into Chinese and borrowed many elements chinese culture. Now Thaza is concentrated in the village of Mikhailovka Primorsky Krai. Many pelvis became the main language.
The Korean Group includes only one people - Koreans (148 thousand people - 0.1% of the population of the country), which are dispersed in Russia, but there are also a significant group in the Sakhalin region, they are also in the Primorsky and Khabarovsk Territories and the Rostov region.
Very small Eskimo-Aleutian family (it includes 2.4 thousand people, that is, only 0.002% of the population of Russia) unites two people: Eskimos and Aleuts. (1.8 thousand people) live, mainly on the east coast of the peninsula and on the island, Aleuts (0.6 thousand people) - in Kamchatka Territory, mainly in Kamandor's islands.
The North Caucasian family (to which 4.6 million people belongs, that is, 3.2% of the population of Russia) as reflected in its name, unites peoples, in their overwhelming majority seasured in the North Caucasus. The family is divided into two groups: Abkhaz-Adygh and Nakho-Dagestan.
The Abkhaz-Adyg Group includes four nearby Adyghe people, as well as abazin. Adygh nations (, Dargintsev, Kubachinsev, Kaitagtsev, Tabasaran, Langiz, Agules, Rutults, Tzakhurov.

Yenisei family (1.9 thousand people - 0.001% of the population of Russia) is very small: in Russia, its representatives are Kets (1.8 thousand people) and the souctions close to them (0.1 thousand people), from which to some extent remembers native language Only 2-3 people. Some scientists consider the southes by independent people, others believe that this is a subethnos of Ketov. Both kets, and the southes are resettled on the average and lower flow of the Yenisei River and its tributaries, mainly in the Krasnoyarsk Territory.
Sino-Tibetan family (36 thousand people - 0.02% of the population of Russia) is presented in Russia, mainly by the Chinese (according to the 2002 census, 35 thousand people, although in reality they seem much more) . The Chinese are in the Khabarovsk and Krasnoyarsk Territories, the Irkutsk region. In general, for the Chinese in Russia, a dispersed settlement is characterized.
A small number of Chukchotskaya-Kamchatka family (31 thousand people - 0.02% of the population of Russia) includes chukchi, koryakov and alutors, kerkeks, confidence and, conditionally,. The most significant of the listed peoples - Chukchi (16 thousand people) is predominantly zelen in the Chukotka Autonomous District, where it constitutes a relatively small part of the population. They live in the north of Kamchatka Territory (former Koryak Autonomous District). They are divided into two groups: chasing - deer and Ankalyn - coastal. Together with the Alutors, there were 9 thousand people according to the 2002 census. Among the Koryakov are allocated by the Ukrainian (coastal) and suspended (deer). Alutors live in the area of \u200b\u200bCape Olyutorsky and in other areas in the north of Kamchatka Territory. Kersheki is one of the most small peoples of the Russian Federation, there are only 22 people, of which only 3 people speaking in Kereksky. Another people of the Chukotka-Kamchatka family are Itelmen (3 thousand people) - lives in the north of Kamchatka Territory and in the Magadan region. Conditionally to the Chukotka-Kamchatka family can be attributed to Kamchadalov (2 thousand people) - the people of mixed Itelmen-Russian origin, which speaks Russian, but retaining some elements of ITERMENSKAYA culture. Most Kamchadalov live in Kamchatka Territory. In previous census, they were included in the Russians.
Insulated in the language of the people of Nivhi (5 thousand people), mainly raz-selenium within two constituent entities of the Russian Federation - in the Khabarovsk Territory and in the Sakhalin region.
In Russia, there are still representatives of two language families, but they are distributed dispersed, they do not form compact arrays anywhere. These are those belonging to the Semitic family (25 thousand people - 0.02% of the population of the country) Assyrians (14 thousand people) and Arabs (11 thousand people) and related to the Avro-Insian family (26 thousand people - 0 , 02% of the population of the country) Vietnamese.
I would be grateful if you share this article in social networks:
Racial and ethnic composition of the population
Human Race - A historically established group of people who have similar inherited external (bodily) signs.
The composition and structure of human races, (%).
Ethnic groups (peoples) - The established sustainable community of people united by language, territory, household, culture, national self-consciousness and opposing themselves to all other similar teams.
In total, there are 3-4 thousand peoples in the world, or ethnic groups, some of which have developed in the nation, while others are peoples and tribes. Naturally, with such quantities they need their classification. For the geography of the population, the classification of peoples, firstly, in numbers and, secondly, in the language.
The classification of peoples in numbers testifies primarily about extremely large differences between them: from the Chinese, which are already more than 1.3 billion, before the tribe of the values \u200b\u200bin Sri Lanka or Botokuds in Brazil, which are less than 1 thousand people. The bulk of the population of the Earth is large and especially the largest peoples, whereas many hundreds of small peoples have only a few percent of the world's population. But your contribution to world culture Large and small nations contribute and bring.
The classification of peoples in the language is based on the principle of their kinship.
All languages \u200b\u200bare combined into linguistic families who are divided into linguistic groups. The most common one is an Indo-European family.
In the languages \u200b\u200bof this family, 150 peoples are spoken by a total number of more than 2.5 billion people belonging to 11 language groups and living in all parts of the world. In foreign Europe and America in the languages \u200b\u200bof this family, 95% of the total population says.
Over 1 billion. A person speaks in the languages \u200b\u200bof the Sino-Tibetan family, mainly Chinese, more than 250 million - in languages afrazian family, mostly Arabic. The number of most other families is significantly less.
In cases where national (ethnic) borders coincide with political, form one-demonic states; Most of all in Europe, in Latin America, in Australia and Oceania, in the Middle East. There are also binary states - Belgium, Canada. Along with these there are many countries that are multiethnic states; In some of them there are dozens and even hundreds of peoples. In many cases, they have a federal or confederative administrative-territorial device.
Tasks and tests on the "racial and ethnic composition of the population"
- Population and its composition - Earth population grade 7
Lessons: 3 tasks: 8 tests: 1
- Population and countries of North America - North America Grade 7
- Population and countries of South America - South America 7th grade
Lessons: 4 tasks: 10 tests: 1
- Brazil - South America Grade 7
Lessons: 4 tasks: 9 tests: 1
- Placing the population - Earth population grade 7
Lessons: 3 tasks: 9 tests: 1
Leading ideas: The population is the basis of the material life of society, the active element of our planet. People of all races, nations and nationalities are equally capable of participating in material production and in spiritual life.
Basic concepts: Demographics, growth rates and population growth rates, population reproduction, fertility (fertility rate), mortality (mortality rate), natural increase (natural growth rate), traditional, transitional, modern type of reproduction, demographic explosion, demographic crisis, demographic politics, migration (emigration, immigration), demographic situation, sexual agent, sexual Pyramid, EAN, Labor Resources, Employment Structure; resettlement and placement of the population; Urbanization, agglomeration, megalopolis, race, ethnos, discrimination, apartheid, world and national religions.
Skills: be able to count and apply reproduction indicators, security labor resources (EAN), urbanization, etc. for individual countries and groups of countries, as well as analyze and draw conclusions (compare, summarize, determine the tendencies and consequences of these trends), read, compare and analyze the age-age pyramids of various countries and groups of countries; Using the atlas cards and other sources characterize changes in the main indicators throughout the world, to give the characterization of the population of the country (region) according to plan using atlas cards.