In P. Odoevsky interesting moments of life. Most importantly brief biography
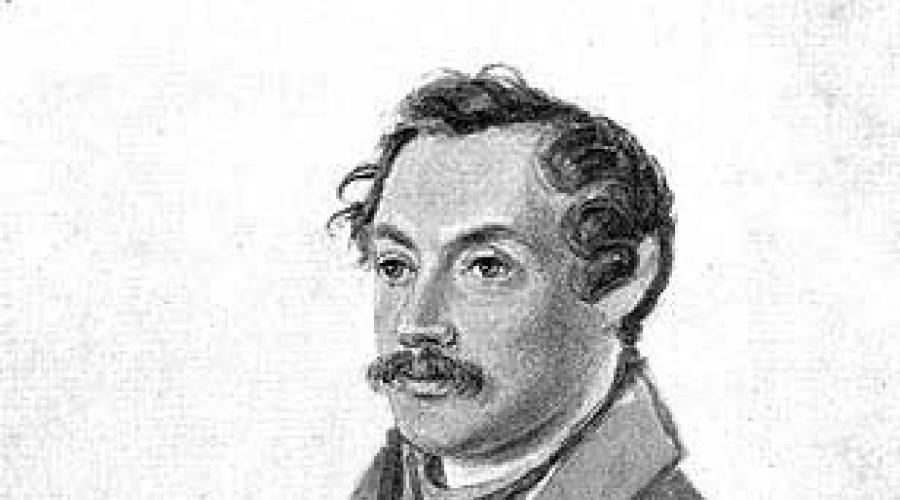
Talented musicologist, writer and one of the pillars of Russian romanticism - all this is equally applicable to Vladimir Odoyevsky. The hereditary prince, he received a great education and made an invaluable contribution to the development of the culture of his era. His literary works Until now, extremely highly valued by the most different literary critics.
- The father of Odoyevsky was the prince and head of the department of state bank in Moscow, and the mother is a fortress peasant.
- Having lost her parents in early childhoodHe became the last representative of the ancient princely kind, one of the older branches of Rurikovich. Vladimir himself, however, almost did not give it meanings.
- Odoevsky brought up his distant relative, General Zagrevsky. The boy lived in the Small Kozlovsky Lane, almost all the buildings in which belonged to his father.
- After the end of the guesthouse future writer He worked in the Ministry of Internal Affairs, where he answered for censorship questions.
- When Odoyevsky was 20 years old, he and his friends founded the "Lyomomudium circle", whose members read German philosophers, discussed read books and read their own essays on sublime topics.
- Odoyevsky published literary almanac, where Pushkin, Baratinsky and Griboedov were printed ().
- During work in the Imperial Office, he became the compiler of a new censorship charter, which entered into force in the late 1820s.
- In the mid-19th century, Odoyevsky appointed the head of the museum, where the collection of books, coins and documents of the Goskantzler Rumyantsev accommodated. After moving along with the exposition to Moscow, he simultaneously led the local departments of the Senate.
- For the passion for the occultism and mysticism, he was awarded the title of "Russian Faust".
- This writer was one of the genericants of the genre of the philosophical story in Russia.
- Odoyevsky was not only an official and writer, but also a music lover. He is considered the first in Russia by the author of critical articles about music and composers, and was also the author scientific LaborsFor which you can find out everything about the development of Russian music for 4 decades.
- A small body was installed in the mansion of Odoevsky, which he called "Sebastion" in honor of Bach. The volume of the instrument of the original design depended on the position of special switches.
- In Moscow, a unique keystone, created by theoretical calculations of the writer, is stored. Outwardly, it resembles a piano that doubles the number of black keys. Odoyevsky believed that such a tool was more suitable for execution folk music.
- The cousin of Odoevsky Alexander was the writer and the Decembrist.
- In the middle of the 19th century, he participated in the foundation of the RGO.
- The writer offered to put signs of the question and exclamations on both sides of the proposal. This borrowing from Spanish, in his opinion, would facilitate the task of readers.
- Odoyevsky sometimes subscribed to a strange set of capital letters - K.V.O. and b. These are the first and last letters of his title and name.
- In his unfinished novel-utopia, the writer actually predicted the invention of the network.
- He also produced several magazines for peasants in which simple language It was told about the latest achievements of sciences, medicine and literature.
- Odoevsky together with friends celebrated New Year February 19, as he considered the day of the cancellation of the serfdom by the beginning of a new era.
ODOevsky, Vladimir Fedorovich (1803-1869), Prince, Russian writer, journalist, publisher, musicologist. Born on July 30 (August 11) 1803 (for other information, 1804) in Moscow. The last descendant of an old princely kind. His father served as director of the Moscow Branch of the State Bank, the mother was a fortress peasant. In 1822, Odoevsky graduated with honors from the Moscow University Noble Pension, where P. Negazky and P. Schadaev, Nikita Muravyev and Nikolay Turgenev were also trained. IN student years He was influenced by the Professor of the Moscow University, Schellingians I.I. Dodavov and M.G. Pavlov. From 1826, Odoyevsky served in the censored committee of the Ministry of the Interior, was the compiler of the new censored charter of 1828. Upon the transition of the Committee, the Ministry of Folk Enlightenment continued to serve as a librarian. From 1846 - Assistant Director of the Imperial Public Library and Head of the Rumyantsev Museum, then was located in St. Petersburg. From 1861 - senator.
The first performance of the Odoyevsky in the press was transfers from the German, published in the "Bulletin of Europe" in 1821. In 1822-1823 letters to Luzhnitsky Starta are published, one of which, the days of Dzhada, attracted by the attention of A.S. Griboyedov, who I met Odoevsky and remained his close friend until the end of my life. IN youth years Odoevsky was friendly with his seniors cousin, poet and future Decembrist A.I. Odoevsky, as his student's diary (1820-1821) testify: "Alexander was a epoch in my life." The brother unsuccessfully tried to launch him from the "deep deseparation of incomprehensible sillying", but the cousin showed hardness and independence in judgments. In the early 1820s, Odoyevsky visited the meetings of the "Free Society of Lovers of Russian Literature," where F. Glinc dominated, and was part of the translator and Poet of S.E.rach, a member of the Union of Benency. It became close to V.Kuhehelbecker and D.Veevitinov, together with which (and with the future prominent Slavophil I. Kireevsky) in 1823 he created a circle "Society of Lyubomatry", becoming his chairman. As one of the "Lubomuds" recalled, the German philosophy dominated "Society": more than two decades remained its most active and thoughtful explanatory clarifier.
In 1824-1825, Odoyevsky with Kühelbecker publish Almans "Mnemozin" (published 4 KN), where they are printed, except for the publishers themselves, A.S. Pushkin, Griboedov, E.A. Bratynsky, N.Muzykov. The participant of the publication N.Poleva wrote later: "There were unknown to the views on philosophy and literature ... Many laughed at the" mnemosinoy ", others wondered." It is "thinking" and taught Odoyevsky; Even his spontaneous Etude Piece of Lights Yelladi V. G. Belinsky called "thoughtful story."
To those who opened after the events of December 1825, the plans of conspirators, with many of which Odoyevsky was friends or closely familiar, he treated sad understanding and unconditional condemnation. However, the Nikolaev reprisals with the Decembrists condemned much more sharp, although it was ready to rapidly divide the fate of the convict friends. The Investigation Commission did not find it "guilty enough" for this, and he was granted to himself.
In the late 1820s - early 1830s, Odoyevsky jarnyly performed official duties, Pedantically replenished his immense knowledge, produced the worldview and created his main experience in the field artistic literature - Philosophical romance Russian nights, completed by 1843 and published in 1844 as part of three volumes of the compositions of Prince V.F. Odoevsky. The novel, in essence, is a sentence of German philosophy on the face of Russian thought, expressed in the externally whimsical and extremely consistent alternation of dialogues and parables: European thought is declared unable to resolve the most important questions russian life and worldwide being.
At the same time, the novel Russian nights contains an exceptionally high assessment of Schelling's creativity: "In beginning of xi A century Shelling was the same than Christopher Columbus in XV, he opened a person an unknown part of his world ... His soul. " Already in the 1820s, experiencing the passion for the philosophy of art Schelling, Odoyevsky wrote a number of articles on the problems of aesthetics. But the passion for shelling in the spiritual biography of Odoyevsky is far from the only one. In the 1830s, he was under the strong influence of the ideas of the new European mystics Saint-Marten, Arndt, Portridge, Baader, and others. In the future, Odoyevsky studied the Patristic, showing, in particular, a special interest in the tradition of Isychasm. The result of many years of reflection on the fate of the culture and sense of history, the Russian nights became the last and future of the West and Russia.
"One-sidedness is the poison of the current societies and the reason for all complaints, sink and bewilderment," said Oroevsky in Russian nights. This universal one-sidedness, he believed, there is a consequence of rationalistic schematics that could not be able to offer any complete and holistic understanding of nature, history and man. According to Odoevsky, only the knowledge of the symbolic can bring to the comprehension of "mysterious elements, forming and communicating spiritual and real life." For this, he writes, "the naturalist perceives the works of the real world, these symbols of real life, the historian - the living characters made in the chronicles of the peoples, the poet - the living symbols of their soul." Thoughts of Odoyevsky on the symbolic nature of knowledge are close common Tradition european romanticism, in particular, the theory of Schelling symbol (in his philosophy of art) and the teachings of F.Shleglev and F. Shleermahra about a special role in the knowledge of hermeneutics - art of understanding and interpretation. A person, according to Odoevsky, literally lives in the world of characters, and this applies not only to cultural and historical, but also to natural life: "In nature, there is a metaphor of one another."
Esvisivated and man himself. In a person, the romantic thinker argued, "three elements are merged - a believer, learning and aesthetic." These starts can and should form harmonic unity not only in human soulbut in public Life. There was no such wholeness to be discovered by Odoyevsky in modern civilization. Considering that the United States personifies a completely possible future of mankind, Odoyevsky wrote about the fact that on this "advanced" turning occurs already " full immersion In real benefits and complete oblivion of other, so-called useless impulse of the soul. At the same time, he was never an opponent of scientific and technical progress. On the slope of the years, Odoyevsky wrote: "What is called the fate of the world depends on this moment from the lever, which is invented by some hungry overhaul on some attic in Europe or in America and who solve the issue of aerostat management." An indisputable fact was that "with each discovery of science, one of the suffering of human legs is done less." However, in general, despite the constant growth of civilizational goods and the power of technical progress, Western civilization, on the conviction of Odoevsky, due to the "one-sided immersion in the material nature" can provide a person only the illusion of the completeness of life. For flight from being in the "world of dreams" of modern civilization, a person sooner or later has to pay. Inevitably the awakening occurs, which brings with him "unbearable longing".
Defending their social and philosophical views, Odoyevsky often entered the controversy both with Wessengers and Slavophiles. In a letter to the leader of Slavophilov A.S. Homyakov (1845), he wrote: "My strange fate, I am western progressive for you, for St. Petersburg - an expanded Strukhni-mystic; It makes me happy, because it serves as a sign that I am on the narrow path that one leads to the truth. "
Russian nights were preceded by many creative achievements: In 1833, motley fairy tales with a red sense were published, collected by Irinem Modestovich Gomozheyo (Odoyevsky used this verbal mask until the end of the days), which made an extreme impression on N.V. Gogol and anticipate the imagery and the tonality of his Nose, Nevsky Prospekt and portrait. In 1834, the town in Tabakcoque is published separately, one of the best in all global literature literary fairy talesHolding a comparison with Andersenovskiy and became an indispensable reading of Russian children. There are several romantic leadsStarting from the last quartet of Beethoven, published in 1831 in Almanacia "Northern Flowers". Gogol wrote about them: "Imagination and mind - a bunch! This is a number psychological phenomena, incomprehensible in man! " We are talking, in addition to the Quartet, about Opere Del Cavaliere Giambatista Piranese and Sebastian Bach - especially about the last one. Subsequently, they were supplemented, according to the expression of the poets to K. Pavlovoy, "Russian Gofmaniana": the story of Segeliel, Cosmorama, Sylphide, Salamander. True, inviting Odoyevsky to the nearest cooperation in the journal "Contemporary", Pushkin wrote: "Of course, Princess Zizi has more truth and enormity than Sylphide. But every giveness is your good. " Princess Mimi (1834) and Princess Zizi (1835) - the secular stories of Ooevsky, continuing the line "Metaphysical Satira" in Ellady. Taking on the lifetime of Pushkin's efforts by publishing the second book of "Contemporary", Odoyevsky after his death alolibly released the seventh. "Contemporary" lasted before Belinsky's intervention only thanks to Odoevsky. Meanwhile, Odoyevsky continues to be scheduled in the motley fairy tales and the town in Tabakcoque: the fairy tales published in 1838 and the story for children grandfather Irinea become a husty children reading. Success encourages Odoevsky, and he develops him, taking in 1843 the publication " folk journal", I.e. Periodic Collection " Rural reading»: In 1843-1848 published 4 books, reprinted (up to 1864) 11 times. According to Belinsky's testimony, Odoyevsky spawned "whole literature of books for prosecution." In the articles of the Odoyevsky edition under the mask of uncle (and later "grandfather") IRINEY spoke about of most difficult issues Simple people's Languagewho admired V. Dal. From the accomplishments of the One-year 1830s, it is necessary to celebrate his play with a good salary (1838) - scenes from the official life, obviously anticipating A.N.ostrovsky. In 1850-1860, Odoyevsky is engaged in the history and theory of "original Velikoshos music": subsequently his work is published on the question of the ancient Russian chanting (1861) and Russian and so-called general music (1867). He is considered and claim the commemor of the official "nation"; Meanwhile, he writes: "Nature is one of the hereditary diseases that the people die, if it does not bring his blood spiritual and physical convergence with other peoples." The Sanovnik and Knyaz-Rurikovich who had said in all, was busy at the time of the historical study on the reign of Alexander II about Russia in the second half of the XIX century. Organic (in the Spirit of Schelling) Promotion russian culture To the European and was all his life occupied by Odoyevsky. Two years before his death, he answered the PRTTUREENS PRESENTATION PRESIDATION PRELOX! The modest and firm program of activity of Russian enlightenment under the name is not pretty! Odoyevsky died in Moscow on February 27 (March 11) 1869.
Vladimir Fedorovich Odoyevsky- Russian writer, philosopher, teacher, musicologist and music theorist.
He was the last representative of one of the oldest branches of Rurikovich.
Born in Moscow, August 13, 1803
Education received at the Moscow University Noble Guesthouse.
In the early 1820s, Odoyevsky publishes his first literary works In the journal "Journal of Europe".
In the same years, Oroevsky, together with Kühelbecker, publishes the Almans "Mnemozin" and writes the novel "Jeronim Bruno and Pietro Aretino", which remained not completed.
In 1826, he moved to St. Petersburg.
For the St. Petersburg period in the work of Odoyevsky, a passion for mystical teachings, medieval natural magic and alchemy is characterized. He continues to study literary creativity. He writes romantic and didactic stories, fairy tales, journalistic articles, cooperates with the Pushkin "Contemporary", "Bulletin of Europe" by several encyclopedias.
By the same time refers to the best general recognition, from his works - a collection philosophical essay and stories under common title "Russian nights."
In 1861, Oroevsky returns to Moscow. At the same time, he was appointed senator of Moscow departments of the Senate, where it consisted of death.
Odoevsky belongs to the building in the device of children's shelters; According to his thoughts, a hospital for coming hospital is founded in St. Petersburg; He was the founder of the Elisavtian Children's Hospital in St. Petersburg and the second chairman of the crusal community sisters of mercy.
Odoyevsky died on March 11, 1869, without leaving after himself neither children nor a state.
Buried at the Don Cemetery in Moscow.
In the unfinished utopian novel "4338th year", written in 1837, Vladimir Odoevsky, as it were, predicted the emergence of the Internet and blogs:
"Magnetic telegraphs are arranged between familiar houses, through which those who live on a distant distance communicate with each other."
Odoevsky was born in 1803 in Moscow in the family of a major official. Odoevsky belonged to the old princely family (the father led his pedigree from the legendary Varyag Rurik). Their genus found himself at the time of birth Vladimir Fedorovich. ABOUTtecz died when the boy was not and five years old. Mother came out again married, the child grew in the family of relatives of the father, appointed by his guardians; Relations with them were complex. In early childhood, friendship began with a cousin - the future Decembrist Alexander Odoevsky.
In 1816, Vladimir Odoyevsky enters Moscow University Noble Pension, which gave a deep and comprehensive education. The young man with special interest studied philosophy, in particular, carried away by the works of Schelling. He visits literary circles, meetings of the Society of Russian Literature Fans. PRINTING OOEEVSKY BEGINNING IN THE YEARS OF HERMY: The first works ("Talk about how dangerous to be vain", "DAYS DAYS") come out in the journal "Journal of Europe".
In 1822, graduating from the Golden Medal, the young man plunged into science, in literary and philosophical classes. He studies anatomy, physics, chemistry, technique, becomes the frequenter of the Signaida Salon Volkonskaya. In 1823. year together with university friends:Venivitinov, Koshelevy, Homyakovcreates a society "Lyubomatry" (so they transferred to the Russian Greek word "philosophy"). The purpose of its participants was to study the ancient and German philosophers, the creation of the original domestic philosophy, from which new Russian literature should have occurred. "Lyomududry" preached the need for literature not only feelings, but also thoughts, and for science - not only logic, but also imagery. Philosophy was represented by them the omnipotent key to the great regions of being.
Unlike the Decembrists, members of society saw their central task in the educational institution, in gradual cultural transformations. Odoevsky and Kühelbecker begin to emanate "Mnemozina" almanacs, in which Pushkin, Griboedov, Baratynsky, Vyazemsky are printed. The publication is, as well as the Society of Lomatria, ceases to exist after the Decembrists' uprising. Fearing persecution, Odoyevsky burns the protocols of assembly.
In 1826, Odoyevsky marries and moves to St. Petersburg. He enters the service of the Censored Committee of the Ministry of the Interior. It is one of the authors of the liberal censorship charter, the first copyright laws.
All the next decades, his name is widely known, it is located in the very center of the literary and cultural life Russia, cooperates with " Literary newspaper", With almanac" Northern Flowers ". Pushkin invites him to participate in the publication of the "Contemporary" magazine conceived by him (it lasted for some time and after the death of Pushkin). In the literary salon, the Odoevsky gather outstanding writers (Pushkin, Wings, Griboedov, Gogol, Lermontov, Koltsov, Turgenev, Dostoevsky, Ostrovsky, Goncharov), Musicians (Glinka, Dargomyzhsky, Balakirev, Rubinstein), publishers, scientists, travelers.  He acts as a philosopher, prose, literary and musical critic. In 1833, "motley fairy tales" were published, which caused Gogol delight. In 1834, a separate "town in Tabakcoque" was published separately, one of the best in the whole world literature of literary fairy tales, withstring a comparison with Andersenovsky and became the indispensable reading of Russian children. The text tales and stories for children grandfather Irinea (1838).
He acts as a philosopher, prose, literary and musical critic. In 1833, "motley fairy tales" were published, which caused Gogol delight. In 1834, a separate "town in Tabakcoque" was published separately, one of the best in the whole world literature of literary fairy tales, withstring a comparison with Andersenovsky and became the indispensable reading of Russian children. The text tales and stories for children grandfather Irinea (1838).
Vladimir Fedorovich Odoyevsky. Watercolor nickname Bestumeva (Petrovsky Plant, 1833)
There were several romantic agents with "musical" plots - "Last Quartet Beethoven", Opere del Cavaliere Giambatista Piranese, Sebastian Bach; "Russian Gofmaniana" is the story of "SEGELIEL", "Cosmorama" "Sylphide", "Salamandra". The success of his secular stories - "Princess Mimi" (1834) and "Princess Zizi" (1835). The chief experience of Odoyevsky in the field of artistic literature was the philosophical novel "Russian nights", published in 1844.
As a state official and public figure Odoyevsky actively engaged in enlightening the people. He was one of the publishers of the rural reading collections, where popular articles were placed on the most different problems - from medical and hygienic to religious and moral. It also became one of the founders of the society to visit the poor and for several decades played a prominent role in the development of Russian charity.

From 1846 to 1861, Odoevsky was an assistant director of the Imperial Public Library and the head of the Rumyantsev museum, the keeper of his values, subsequently laid for the Russian state Library. In the 40-60s, the writer serves as a court, becomes a chamber, then the courtyard's gofmaster, then a valid Stat advisor, and in 1861 - by a senator.
In 1862, in connection with the transfer of the Rumyantsev Museum to Moscow, Odoevsky returns to native city. There he continues to service and participates in cultural and public life: promotes the founding of the conservatory, Russian music society, participates in the meetings of the society of fans of Russian literature and the Moscow artistic mug, reads popular lectures, collects the writers, musicians, scientists around themselves.

Vladimir Fedorovich Odoyevsky. Lithography P. Borel
In the 60s, Odoevsky leaves the literature and gives practical activities. He welcomes the abolition of serfdom, studies Russian antiquities in the storage facilities of the Monasteries near Moscow, writes articles on pedagogy, listens to the case in the Senate.
For three years before death, he responds to imbued with mournful depressions, the article of Turgenev "Pretty!" article "displeased!", which is imbued with the ideas of educational and faith in moral development mankind.
Vladimir Fedorovich Odoyevsky died on February 27, 1869. Buried at the Don Cemetery in Moscow.
booksReader.org\u003e Author ... vladimir-fedorovich
Music Theory and Music Practice
According to the memories of contemporaries, the interest in music in Odoevsky woke up in early youth. Even in his small apartment in the newspaper alley there was a small cabinet piano. Especially attracted him music theory. The inapplicability of a uniform tempered chromatic gamma used in classical musicTo reproduce the musical lads used in the people's musical practice, it became obvious to him when he recorded folk jerseys from the voice. This discovery made at the end of the 1840s, largely determined the direction of its further research and proved to him the effectiveness of the methods of experimental science of the new time.
Odoyevsky has passed from folk music to the study of the ancient church wards. He realized that and here the tradition does not fit into the framework set by the uniform temperativity, and began to study the possibilities of enharmonic musical instruments. The results of these studies were reflected in the series of articles ("Russian and so-called general music", "about the original Great Russian song", we are talking to the opening of the Moscow Conservatory "On the study of Russian music not only as art, but also as sciences", " Musical gram or the basis of music for non-musicants "," Music from the point of view of acoustics ").
Odoyevskypartlyi embodied my ideas in the "enharmonic keystone" created by him.This tool was ordered from Master Kampa, who lived in Moscow and contained a piano factory in the newspaper alley, which pulled down at the end of the century to his daughter in marriage Smolyaninov. The archive preserved a receipt from February 11, 1864 on paying 300 rubles with silver for the manufacture of the instrument. Although Odoyevsky called him "keycover", it was a standard hammer piano, with the only difference that each of his black keys was shared in half, in addition he had one black key there, where they were usually not - between SI and before and between and fa. Thus, instead of the usual 12 halftone in one octave on the Odoevsky instrument there are 17 "microtons", which corresponds to the representations of the excellence about possible logical temperatures. This tool is kept in the museum musical culture them. Glinka in Moscow.
Vladimir Odoyevsky took place from ancient and noble kind. On the one hand, he was in kinship and with Russian kings, and with the lion himself, and on the other, his mother is a fortress peasant. Of particular Titulas Odoyevsky never attached. Vladimir has always participated in public circles, engaged in music and literature.
The life of Odoevsky is conditionally divided into three periods.
First. Moscow.
Sirota Vladimir brought up his uncle. Later, he is given to training in the guesthouse. Great value Delivered Vladimir influence of his brother.
The first public circle where Odoyevsky participated, closed the "wine" of the Decembrists. At that time, Vladimir began writing a novel, but did not complete this work. But it edits a lot, including magazines. At that time, Odoyevsky became interested in mystics, occult.
St. Petersburg.
Having traveled to B. north capital, Odoyevsky married. Together with his wife, they opened a popular literary salon, where much attention was paid to both music, and even cooking. The passion for the occultism develops into interest in alchemy and magic. However, Odoevsky is friends and with priests helps them.
He writes journalistic articles, publishes a collection of essay. Also creates a romance-utopia about 4338 (the same name), where it is predicted by the emergence of Internet networks.
Last. Moscow.
Disappointed in mysticism, Odoyevsky believed in enlightenment. Having taught the Senatorial position and the post of Director of the Museum (Rumyantsevsky), ratified for the abolition of serfdom and softening censorship. On the other hand, called for banning the import of "harmful" books to Russia.
IN last years Odoevsky helped a lot poorly. I did not even leave the inheritance to my wife (they did not have children).
Vladimir Fedorovich was remembered by contemporaries as a versatile person. His interests sometimes contradicted themselves. And in this contradictions developed.
Biography of Odoevsky for children 3, 4th grade
V.F. Odoevsky was born in August 1803 in Moscow, in the family of Prince Odoevsky and was the last representative of Rurikovsky. Vladimir Fedorovich is considered one of the famous wristwriters, philosopher and publicist. In general, Oroevsky was a great man, during his life he not only wrote books, but also engaged in patronage, was the inventor of musical instruments, he worked with the poor, helped build orphanages, hospitals.
Vladimir Odoevsky received his own education at the Moscow Institutional Noble Guesthouse. Already while studying, he took up close literature. The first of his works were transfers with german language Letters of famous philosophers.
At the end educational institution Odoevsky began working at the Moscow archive of the Foreign Affairs College, at the same time he began to attend a meeting of the Nomomatrian national community, "where he met such famous peoplelike Griboedov, Kireevsky, Kühelbecker.
In 1824-1825, together with friends, Mnemozin's Almanacs, which included not only the works of Odoyevsky, but also Pushkin, Griboedov, entered. At the same year, Odoevsky began writing the novel "Jerome Bruno and Pietro Aretina", but unfortunately this novel was not over.
In 1826, Vladimir Fedorovich Odoyevsky moved to St. Petersburg and arranged to the service as an assistant director of the St. Petersburg Imperial Office, and later becomes director of the Rumyantsev library. In times of life in St. Petersburg, Oryoevsky became interested in alchemy and cooking, which affected his work. At this time, fairy tales for children come out from under his feather utopic Roman "4338 God", where the appearance of such modern technologies Like the Internet, mobile phones.
In 1840, Vladimir Fedorovich radically changes his views on European philosophy and begins to promote knowledge of Russian literature into the masses. At the same time, he is closer to the laws of the Russian Church, becomes a close friend of the priest and researcher church music D.V. Razumovsky.
In 1861, Odoyevsky returned to Moscow and continued his work on the rooting of Russian customs in the Higher Society, he was against french in communication and import of foreign philosophical books to Russia.
By the end of his life, Vladimir Fedorovich Odoyevsky engaged in self-improvement. His interests covered various sides of life.
Biography of Oden 3 class, 4th grade for children
Biography by dates and interesting Facts. The most important thing.
Other biographies:
- Zinaida Hippius
In 1869, on November 20, the daughter of Zinaida was born in the family of the Russo German and nobleman Nikolai Gippius. The birthday of the future Madonna of Decadence became the small town of Bellev, located in the Tula province.
- Elena Vasilyevna Glinsky
Great Princess Moscow Elena Vasilyevna Glinsky was born in Moscow in 1508 in the family of King Vasily II, also known to nicknamed "Dark". She grew up smart and intelligent girl, taught foreign languages, fond of painting and art.
- Edward Hagerup Grig
Edward Hagerup Grig - the greatest composer, glorifying his beloved Motherland-Norway to the whole world. Norwegian folklore with milk mother, he sought his unique image in his music.
- Princess Olga
Great Princess Olga, ranging from the saints, rules Kievan ruus In the period from 945-960., In the status of recents, with the Minor Suma Svyatoslav. According to the "Tale of Bygone Years" Olga
- Rasul Gamzatov
Poet R. Gamzatov appeared on September 8, 1923 in the Dagestan village of the Tsada. After school studied at the pedagogical school, then went to work as a teacher.