Visual perception of the world. Visual perception and application of gestalt principles in web design
Read also
Insects
The visual apparatus of birds has features that have not survived in human vision. So, in the bird receptors there are microspheres containing lipids and carotenoids. It is believed that these microspheres are colorless, as well as painted in yellow or orange color - Perform the function of specific light filters that form "curve of visibility".
Eye man
Stereoscopic vision
Many species, the lifestyle of which requires a good estimate of the distance to the object, eyes look forward toward, rather than on the sides. So, mountain rams, leopards, monkeys provide better stereoscopic vision, which helps to evaluate the distance before the jump. Man also has good stereoscopic vision (see below, section ).
An alternative mechanism for estimating the distance to the object is implemented in some birds, the eyes of which are located on different sides of the head, and the field of volume is small. So, the chickens perform constant oscillatory movements head, while the image on the retina quickly shifts, inversely proportional to the distance to the object. The brain processes the signal, which allows you to catch fine mining with a high accuracy with a beak.
Each person's eyes seem identical, but still somewhat different, so the leading and slave eye is distinguished. Determining the lead eye is important for hunters, video operators and individuals of other professions. If you look through a hole in an opaque screen (hole in a sheet of paper at a distance of 20-30 cm.) To the removal item, and then, not a shifting head, alternately close the right and left eye, then for the driving eye the image does not shift.
Human view physiology
Color vision
A person's eye contains two types of photosensitive cells (receptors): highly sensitive sticks responsible for twilight (night) vision, and less sensitive columns responsible for color vision.
Uniform irritation of all three items corresponding to the weighted average daylight, also causes a feeling. white color (See Psychology of color perception). The three-storey theory of color view was first expressed in 1756 by M. V. Lomonosov, when he wrote "about the three-matters of the bottom of the Oka." A hundred years later, a German scientist was developed by G. Helmholtz, who does not mention famous work Lomonosov "On the origin of light", although it was published and briefly set out in German.
In parallel, there was an opponent theory of the Color of Evald Gering. She was developed by David Hail (en: David H.Hubel) and Torsten N.Wiesel (en: Torsten N.Wiesel). They received the Nobel Prize of 1981 for their discovery. They suggested that the brain comes into the brain is not at all about red (R), green (G) and blue (b) colors (theory of Young-Helmgolts color,). The brain receives information about the brightness difference - about the difference in the brightness of white (y max) and black (y min), about the difference of green and red colors (G-R), about the difference between blue and yellow colors (B-Yellow), and yellow (Yellow \u003d R + G) is the amount of red and green flowerswhere R, G and B are the brightness of the color components - red, R, green, G, and blue, B.
Despite the seeming contradiction of two theories, modern ideas, orders are both. At the retinal level, the three-hundredth theory is valid, however, the information is processed and the data is entered into the brain already consistent with the opponent theory.
For the color vision of man and monkeys correspond to the three genes encoding photosensitive proteins of the arms. Availability three are different Proteins reacting to different wavelengths is sufficient for color perception. In most mammals, only two such genes are, so they have non-bloody eyesight. In the event that a person has two proteins encoded by different genes, it is too similar, Daltonism develops.
Binocular and stereoscopic vision
| Kind of animal | The ratio of the number of non-integrated cross-fibers |
|---|---|
| Sheep | 1 : 9 |
| Horse | 1 : 8 |
| Dog | 1 : 4.5 |
| Opossum | 1 : 4 |
| The guinea pig | 1 : 3 |
| Cat | 1 : 3 |
| Ferret | 1 : 3 |
| Toque | 1 : 1.5 |
| Human | 1 : 2; 1 : 1.5; 1 : 1* |
- - Data from different authors
Most of the characteristics of human binocular vision is due to the characteristics of neurons and neural connections. Neurophysiology methods show that decoding the depth of an image specified on the retina with a set of disparatomes begin the binocular neurons of the primary visual bark. It was shown that the most important requirement for the implementation of stereoscopic vision is the differences in the images on the retina of two eyes.
Due to the fact that the fields of view of both eyes of a person and higher primates are largely intersecting, the person is capable of better than many mammals, determine appearance And the distance (the accommodation mechanism also helps) to close objects mainly due to the effect of stereoscopicity of vision. The stereoscopic effect is preserved at a distance of approximately 0.1-100 meters. The person has spatially visual abilities and volumetric imagination is closely related to stereoscopy and ipsey bonds.
Properties of Vision
Luminous sensitivity of the human eye
Light sensitivity is estimated by the magnitude of the threshold of the light stimulus.
A man with good eyesight is able to see night light from the candle at a distance of a few kilometers. However, the light sensitivity of the view of many night animals (owls, rodents) is much higher.
The maximum light sensitivity of the eye sticks is achieved after a sufficiently long-lasting dark adaptation. It is determined by the action of a light flux in a body angle of 50 ° at a wavelength of 500 nm (maximum sensitivity of the eye). Under these conditions, the threshold energy of light is the amount of about 10 -9 Erg / s, which is equivalent to the flow of several optical range quanta per second through the pupil.
The sensitivity of the eye depends on the completeness of adaptation, on the intensity of the light source, the wavelengths and the angular sizes of the source, as well as from the time of the irritant. The sensitivity of the eye decreases with age due to the deterioration of the optical properties of the sclera and pupil, as well as the receptor link of perception.
Visual acuity
The ability of various people to see large or smaller items from the same distance at same form The eyeball and the same refractive strength of the dioptric ocular system is determined by the difference in the distance between the cylinders and the retinal flashes and is called urgency. To verify the visual acuity, the table is applied.
Binocularity
Considering the subject with both eyes, we see it only then is single when the eye axes form such an angle of convergence (convergence), in which symmetrical reinforced images on the retina are obtained in certain respective places of sensitive yellow spot (FOVEA centralis). Thanks to this binocular vision, we are not only judged about the relative position and the distance of objects, but also perceive the impressions of the relief and volume.
The main characteristics of the binocular vision are the presence of elementary binocular, deep and stereoscopic vision, the sharpness of stereo and the fusion reserves.
The presence of elementary binocular vision is checked by splitting some image into fragments, some of which is presented to the left, and part is the right eye. The observer has elementary binocular vision, if it is able to make a single source image from fragments.
The presence of deep vision is verified by presenting silhouette, and stereoscopic - accidentally point stereograms, which should cause a specific experience of the depth, differing from the impression of spatiality based on monocular features.
Stereo severity is the value of the reverse threshold of stereoscopic perception. The stereoscopic perception threshold is the minimum detected disparativity (angular displacement) between the parts of the stereogram. It uses the principle that is as follows. Three pairs of figures are presented separately to the left and right eye of the observer. In one pairs, the position of the figures coincides, in two others one of the figures is shifted horizontally to a certain distance. The subject is asked to specify the figures located in ascending order of the relative distance. If the figures are specified in proper sequenceThe test level increases (disparatosis decreases), if not - disparatosis increases.
Fusual reserves - conditions under which there is the possibility of a motor fusion stereogram. Fusion reserves are determined by the maximum disparativity between the parts of the stereogram, under which it is still perceived as a bulk image. For measuring the fusion reserves, the principle is used inversely used in the study of the sharpness of stereoment. For example, the subject is asked to connect (spin) into one image two vertical stripes, one of which is visible to the left, and the other is the right eye. The experimenter begins to slowly breed the bands first at the convergent, and then with divergent disparacy. The image begins to "fall apart" with the values \u200b\u200bof the disparacy characterizing the observer fusion reserve.
Binocular may be violated with squinting and some other eye diseases. With strong fatigue, there may be temporary squint caused by the disconnection of the slave eye.
- See also binocular, stereoscope.
Contrast sensitivity
Contrast sensitivity - the ability of a person to see objects, weakly differing in brightness from the background. The assessment of contrast sensitivity is made according to sinusoidal lattices. Increasing the threshold of contrast sensitivity can be a sign of a number of eye diseases, and therefore its study can be applied in diagnosis.
Adaptation of vision
The above properties of vision are closely related to the ability of the eye to adapt. Adaptation occurs to changes in illumination (dark adaptation), the color characteristics of the lighting (the ability to perceive white items white even with a significant change in the spectrum of the incident light, see also white balance).
Adaptation is also manifested in the ability of vision to partially compensate for the defects of the visual apparatus (optical defects of lens, retinal defects, cattle, etc.)
Defects of Vision
The most massive disadvantage is fuzzy, unclear visibility of close or remote items.
Defects Crustalika
Network defects
Literature
- A. Agel "Anomalies, Refraction and Accommodation Eye" (1881, Translation from german Dr. Dobrovolsky);
- Longmore, "Guide to the study of view for military doctors" (recycled by Lavrentiev, 1894);
- A. IMBERT, "LES ANOMALIES DE LA VISION" (1889).
Have you ever thought about how we see objects? How to catch them from all visual manifolds ambient With the help of sensory stimuli? And how do we interpret what you see?
The processing of visual data is the ability to understand the images that allows people (and even animals) to process and interpret the meaning of the information we receive thanks to our vision.
Visual perception playing important role in everyday lifeHaving help in learning and communicating with other people. At first glance, it seems as if perception occurs easily. In fact, a complex process is hidden for the intended ease. Understanding how we interpret what we see helps us design visual information.
Balanced infographics involves competent use visual representation (for example, diagrams, graphs, icons, images), appropriate selection of colors and fonts, suitable layout and site cards, etc. And you can not forget about data, their sources and topics, which is no less important. But today it will be not about them. We will focus on the visual side of the informational design.
Psychologist Richard Gregory (Richard Gregory, 1970) was convinced that visual perception Depends on the downstream processing.
Downstream processing, or conceptually managed process, is carried out when we form an idea of \u200b\u200ba big picture from small details. We are building an assumption that we see, on the basis of expectations, beliefs, former knowledge and previous experience. In other words, we make a deliberate assumption.
Gregory theory confirms numerous evidence and experiments. One of the most famous examples - Effect of hollow mask:
When the mask turns the face with the face, you see a normal face
Gregory used a rotating mask Charlie Chaplin to explain how we perceive the hollow surface of the mask in the form of convexities based on our ideas about the world. According to our preceding knowledge of the structure of the face, the nose must speak. As a result, we subconsciously reconstruct hollow face and see normal.
How do we perceive visual information according to Gregory theory?
1. Almost 90% of the information arriving through the eyes, does not reach the brain. Thus, the brain uses previous experience or knowledge available for constructing reality.
2. The visual information that we perceive is connected with previously preserved information about the world we obtained by experimental.
3. Based on different examples The theory of downlink information it follows that the recognition of images is based on contextual information.
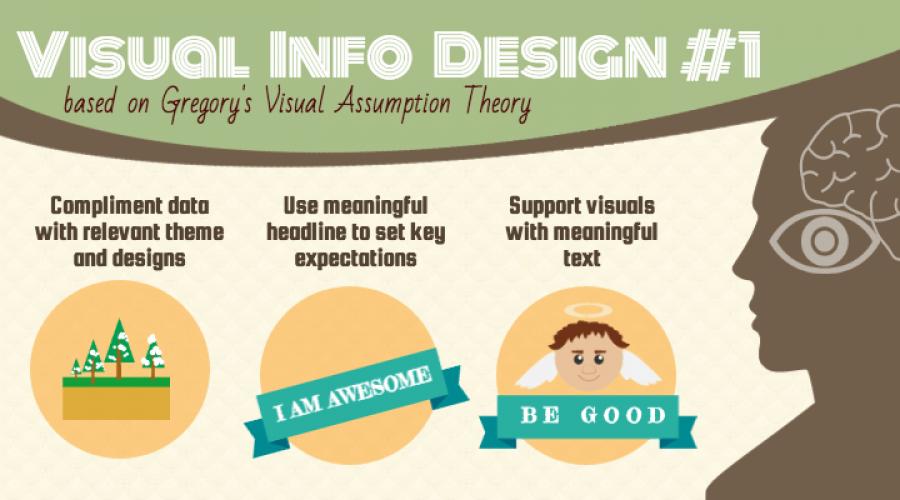
Tip №1 for information design, based on the theory of the visual assumption of Gregory: add data to the appropriate topic and design; Use a significant header to set key expectations; Support a visual number of expressive text.

2. Experiment of Sanokia and Sulman on color ratios
According to numerous psychological research, the combination of homogeneous colors is more harmonious and pleasant. While contrasting colors are usually associated with chaos and aggression.
In 2011, Thomas Sanoki (Noah Sulman) and Noah Sulman (Noah Sulman) conducted an experiment in order to study how the combination of colors affects short-term memory - our ability to memorize what we just saw.
Four different experiences were carried out using harmonious and disharmonious color palettes. In each test, the participants of the experiment showed two palettes: first one, then the second, which was necessary to compare with the first one. The palettes were demonstrated at a certain time interval and several times in randomly compiled combinations. The subjects needed to determine whether the palettes were identical or different. Also, the participants of the experiment should have evaluated the harmony of the palette - a pleasant / unpleasant combination of colors.
Below are 4 examples palettes that were demonstrated by the participants of the experiment:

How do colors affect our visual perception according to the theory of Sanoki and Sulman?
- People remember the palettes in which colors are combined with each other.
- People better remember the palettes containing a combination of only three or less colors than those in which four or more colors.
- Contrast of the next colors affects how well the person remembers the color scheme. In other words, this means that the color difference between the context and the background can increase our ability to concentrate on the context.
- We can remember pretty a large number of color combinations At the same time.
Thus, the results of the experiment indicate that people are better able to assimilate and memorize more information, perceiving images with a contrasting, but harmonious color gamut, preferably with a combination of three or less colors.
Tip # 2 for information design, based on the results of the experiment of Sanoki and Sulman: Use as little as possible different flowers in comprehensive content; Increase the contrast between visual information and the background; Choose themes with a harmonious combination of shades; Use disharmonious combinations of colors with mind.

Binocular rivalry occurs when we see two different images In one place. One of them dominates, and the second is suppressed. Dominance alternates after certain intervals. So, instead of seeing the combination of two pictures at the same time, we perceive them in turn, like two competing for the dominance of the image.
In 1998, Frank Tong (Frank Tong), Ken Nakayama, Jay Thomas Vogan (J. Thomas Vaughan) and Nancy Kanwisher (Nancy Kanwisher) during the experiment concluded that if we look at two different images simultaneously The effect of binocular rivalry occurs.
Four trained person participated in the experiment. As incentives through glasses with red and green filters, they showed images of the face and at home. In the process of perception, irregular alternation of signals from two eyes took place. Stimulus-specific reactions of the subjects were monitored using functional magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).

How do we perceive visual information according to the Tong Experiment?
- According to MRI, all subjects have observed an active binocular rivalry when they showed heterogeneous pictures.
- In our visual system, the effect of binocular rivalry occurs during the processing process of visual information. In other words, for a short period of time, when the eyes look at two heterogeneous images located close to each other, we are not able to determine what we actually see.
David Carmel (Michael Arcaro), Sabine Kastner (Sabine Kastner) and Uri Hasson (Uri Hasson) conducted a separate experiment and found out that binocular rivalry can be manipulated using such parameters of the stimulus as color, brightness, contrast , shape, size, spatial frequency or speed.
The contrast manipulation in the example below leads to the fact that the left eye perceives the dominant image, while the right one - the depressed:

How does contrast affect our visual perception according to the experiment?
- Manipulating the contrast leads to the fact that the strong stimulus turns out to be dominant large quantity time.
- We will see the merge of the dominant image and parts of the depressed until the effect of binocular rivalry.
Council №3 for information design, based on the effect of binocular rivalry: n e overload content; Use thematic icons; Select key points.

4. Influence of typography and aesthetics on the reading process
Did you know that the typography can influence the mood of a person and his ability to make decisions?
Typography is the development and use of fonts as a means of visual communication. Nowadays, typography from the field of typography passed into a digital sphere. Summarizing all sorts of definitions of the term, it can be said that the purpose of typography is to improve the visual perception of the text.
In his experiment, Kevin Larsen (Kevin Larson, Microsoft) and Rosalind Picard (Rosalind Picard, Mit) found out how typography affects the reader's mood and its ability to solve problems.
They spent two studies, in each of which 20 people took part. Participants were divided into two equal groups and gave 20 minutes to read on the tablet The New Yorker magazine. One group got text with a bad typography, the other - with good (examples are shown below):

In the course of the experiment, participants were interrupted and asked how much, in their opinion, the time had passed since the beginning of the experiment. According to the data psychological research (Weybrew, 1984): People who find their lesson are pleasant and stay in positive mood, believe that they spent much less time reading.
After reading the texts of the participants in the experiment, they asked to solve the task with the candle. They needed to attach a candle to the wall so that the wax does not drop, using the stationery buttons.
How do we perceive a good typography and its influence?
- Both groups of participants incorrectly estimated the time spent on reading. This means that reading was for them a fascinating occupation.
- Participants who were offered text with good typography, significantly underestimated the reading time compared to the participants who got text with a bad typography. This means that the first text seemed to them more interesting.
- None of the participants who read the text with a bad typography could not solve the task with the candle. While less than half of the second group coped with the task. Thus, a good typography influenced the ability to solve problems.
Tip №4 for information design, based on the experiment of Larsen and Picard, detecting the influence of typography: Use readable fonts; Separate text from images; Do not overlap pictures or icons on text; Leave enough free space between paragraphs.

5. Perception of the essence of the scene by Castelano and Hendersen
Have you ever wondered what actually mean the expression "one picture says more than a thousand words"? Or why do we perceive the image better than the text?
This does not mean that the image tells us all the necessary information. Just a person has the ability to grab the basic elements of the scene from one glance. When we fix a look at the subject or objects, we form general view And we recognize the meaning of the scene.
What is the perception of the essence of the scene? According to the researcher from Nissan Research & Development Ronald A. RenSink (Ronald A. Rensink):
"The perception of the essence of the scene (Scene Gist), or the perception of the scene is a visual perception of the environment as an observer at any time. It includes not only the perception of individual objects, but also parameters such as their interpretation, as well as the idea of \u200b\u200bwhat other types of objects are found. "
Imagine that you see some objects that are two signs with symbols, and a scheme, symbolizing a fork and indicating two different ways. Most likely, the next scene originated in front of you - you are in the middle of the jungle / forest / highway and ahead of two ways that lead in two different destinations. Based on this scene, we know that you need to make a decision and choose one way.
In 2008, Monica S. Castellano (Monica S. Castelhano) from the University of Massachusetts in Amherst and John M. Henderson (John M. Henderson) from Edinburgh University during the experiment studied the effect of color to the ability to perceive the essence of the scene.
The experiment included three different tests. Students showed several hundred photographs (natural or man-made objects) in various conditions for each test. Each image was shown in a certain sequence and time. Participants were asked to answer "yes" or "no" when they will see the details corresponding to the scene.
Normal and blurred photos were presented with color and monochrome, respectively.

To determine the role of colors in the perception of the essence of the scene for the following examples of photos, anomalous colors were used:


How do we perceive visual information on the basis of conclusions of Castelano and Hendersen?
- The subjects grabbed the essence of the scene and the target object in seconds. This means that people can quickly understand the value of the normal scene.
- The subjects fastened the correspondence of color pictures than black and white. Thus, the color helps us better understand the picture.
- In general, colors determine the structure of objects. The better the color corresponds to how we usually perceive the world, the easier it is to understand the meaning of the image.
Council №5 for information design based on research of the Scene Scene Castelane and Hendersen: Use suitable icons or pictures to submit data; Position the content in the correct sequence; Use usual colors for important objects.

conclusions
Understanding how people perceive visual information helps to improve infographics. Summarizing the conclusions of the experiments considered, we bring to your attention key advice on the design of visual information:
1. Layout and design
- Theme and design must comply with the information.
- Do not overload the infographics of your page.
- Use thematic icons.
- Position the content in the proper sequence.
- Use headlines to set key expectations.
2. Video series
- Visual effects must accompany the text.
- Show important numbers on charts and diagrams.
- Use the correct pictures and icons to submit your data.
- Reduce the number of colors for comprehensive content.
- Do contrast above between important visual information and background.
- Use harmonious themes of theme.
- Use disharmonious colors with the mind.
- Use ordinary colors for important objects.
4. Typography
- Choose readable fonts.
- Leave enough empty space between title and text or picture.
- Do not overlap pictures or icons on text.
- Install sufficient gaps between characters.
Now that you know all the subtleties of creating beautiful and convincing infographics, the matter is yours!
The visual analyzer is perhaps the strongest of all existing ones. Using vision, a person knows the surrounding reality, perceives the primary information about the world. What he sees causes his positive or negative emotions, helps to understand the life around the way around.
People with violation of vision suffer not only from the fact that they cannot see something, they have a state of deprivation from the impossibility of filing their emotional sphere new impressions. It is often possible to observe how visually impaired personalities begin to permanently listen to sounding word, trying to somehow compensate for your drawback.
Features of visual perception
As with any other analyzer, the vision has its own physiological features, allowing it to fully perceive the objects and phenomena of the surrounding world.
Flower perception
A healthy human eye is able to perceive all existing colors. Such a phenomenon is possible due to the perfect structure of the visual analyzer. Scientist Helmholtz formulated the concept of photosensitivity and determined, from which the perception of green, red, purple and other colors depends. He also said about the excitement, which are governed by visual neurons in the cerebral cortex and create a feeling of any kind of color.
Perception of space

Under the urgency of view it is usually understood by the ability to distinguish individual objects. The clearer this feature, the brighter the possibility of a person to see well. Visual acuity is checked using specially designed tables in which letters are located in such a way as to make the most clearly and fully display a real picture. The human eye is able to argue quite a large space around him, catch the smallest units that are near and away. Moreover, with a very close distance, some things are often overwhelmed, and at a distance are more distinct.
Perception of distance

Distances may be a sufficient obstacle to consider objects only in a person who has progresses or already has myopia. Otherwise, having healthy vision, people do not have to complain that some objects located in the distance, they are not perceived clearly. In essence, the visual analyzer can be equally well to see both near and away.
Dark perception

The human eye has a unique ability to see in complete darkness. If the individual is suddenly placed in the dark space, he will first see anything at first, it will not be able to distinguish between objects. But after a couple of minutes, the visual analyzer adapts to new conditions and gradually becomes possible to distinguish the outlines of individual items, and then even navigate in space. The protective mechanism, which is included in the structure of the eye, allows a person, being in extreme conditions, maintain the ability to orientation on the ground.
Violation of visual perception
The visually impaired people cannot perceive the world with that sharpness, which is accessible to a healthy person. Any violation of vision necessarily affects the ability of the eye to accommodation and actually perceiving objects and phenomena. It was experimentally proven that in part of the partially silent people the speed of perception of objects is significantly reduced. That is, those who see weakly, first need to approach the subject for a certain distance, consider it, and then form its individual attitude to him. A healthy person can make the same actions almost instantly, easily, without thinking about what is happening next minute.
The violation of the visual analyzer is characterized by a number of features and features that must be denoted separately.
- Reducing the ability to see in the dark. People who have a vision in one degree or another, often complain that in the pitch darkness, even after two to five minutes, the eyes are difficult to adapt, and they literally lose the landmark in space. If a person is sharply moved from a light medium to the dark, it will be quite difficult for him to understand which way to move. In this situation, perhaps only staying in a familiar setting and an idea of \u200b\u200bthe location of items.
- A feeling of discomfort. A person who sees badly is constantly experiencing an internal inferiority. He has to strain considerably in order to get necessary information. Despite all his efforts, nevertheless, it never has information in full, as part of it necessarily turns out to be lost. Often, such a person is forced to refer to other people asking for assistance (for example, read the small text, which is at some distance), which in itself can sometimes be accompanied by awkwardness and embarrassment.
- Psychological deprivation. This state comes because a person during life, one way or another, gets used to comfortable conditionsthat surround it. The ability to see is perceived by them not as a huge physical phenomenon, but rather, as a given, without which it is impossible to do. Therefore, when the vision suddenly begins to decline in an incomprehensible reason, the personality is in the situation of confusion. There is an oppressed state of the soul when it seems that the paints of the world are melting in their eyes and will never be better done. If at the same time a person is forced to postpone his classes (for example, work at a computer), then there is an additional feeling of limitedness and often hopelessness until real help and support will be provided.
Correction of visual perception
Any violation of the visual analyzer needs mandatory correction. Unfortunately, currently when most of People prefers to spend their leisure not in communicating with loved ones and nature, but at a computer and TV, vision will deteriorate much faster than in previous years. Young people imperceptibly spends more and more time before the monitor, thereby gradually "comes" eyes and does not even fix these changes. Below are given useful recommendationsSuppose to keep vision for a long time and improve it in case there are small disorders.
Preventive inspection. A doctor - an ophthalmologist need to visit at least one - two times a year. During this period, it is quite possible to identify visible changes in visual acuity and take appropriate steps. If on the next inspection it turns out that the vision has noticeably deteriorated, then it should be consulted as possible to improve it. Often at the initial stage you need to drink certain vitamins, and vision will gradually begin to come back. The doctor - an ophthalmologist will give the necessary recommendations, if necessary, he will write corrective glasses.

Make breaks in your computer. Activities requiring a high concentration of attention and concentration of view, sometimes leads to one or another issues with vision. If your work requires a permanent seating for the monitor, there is a reason to think and worry about your health. You can not sit for a few hours in a computer behind the computer and do not tear off. It is noticed that in this position we blink much less often, which leads to the drying of the cornea of \u200b\u200bthe eye. It will not hurt to buy drops for the eyes, purchase special glasses to work on the monitor if the voltage occurs daily.

Wear glasses if they are shown. Many neglect this simple rule and continue to overvolt their eyes. Instead of carrying glasses, people for some reason prefer to pushed, feel certain inconveniences. Someone is frankly shy to wear glasses, others are inconvenient, others just forget. Of course, when the vision is not much reduced, it is quite possible to do without this accessory. But if there is a place of myopia in hard form, then no longer do without them.

Exercises for eyes. Everyone knows that eye exercises have high efficiency. But people for some reason are little use by this means, although it is impossible to measure from it. And you only need to work out the habit of regularly perform these simple actions.

Confront yourself reasonable breaks. People whose profession is associated with a computer should understand that without daily care of their eyes, they can gradually spoil eyesight. That is why it is so necessary to make small breaks every hour for ten - fifteen minutes. At this time, you can drink a glass of tea or coffee, go out into the street to breathe fresh air or just walk around the room.

Classes for the development of visual perception
Below are the exercises that allow you to adjust the downstream vision and contribute to its preservation on long years. The development of visual perception begins with the adoption of a conscious decision. If you meet these recommendations every day, the result will notice in a week. Wait tension and burning in the eyes.
- Palming. This exercise is sometimes called "the warmth of your palms." Its essence is as follows: you need to close your eyes, put your palms on them and sit in this position for a few minutes. It is especially effective when you are very tired and the text on the monitor screen is already not perceived. For five to seven minutes, the eyes will rest and it will be easier for you. Prerequisite: Eyes need to close the palms in such a way that the daylight does not penetrate into them. In this case, the darkness will affect as a therapeutic factor, having a beneficial effect.
- Draw "Snake." At the time of strong fatigue, you can try to draw the movement of the eye of the snake, which crawls right to left, and then from left to right. Such training is perfect for those who have any activity require constant concentration and tension. The exercise allows you to relax the eye muscles and return the former visual sharpness.
- Eyes "in a circle." Mentally draw a circle and drive through the eyes in a circle: up - right - down - left. Repeat several times. The essence of this wonderful exercise is to ensure that this action can be accurate. During the exercise, the eyes relax and rest.
- "In different directions". Try chaotically make simple movements through your eyes: up, down, right, left, look at the distant corner of the room and on the tip of your own nose. The essence is to perform these actions not in a clear sequence, but a blizzard. This is achieved by visual acuity and attention to trifles.
Thus, the visual perception of a person is a complex and highly organized process requiring a competent responsible approach. The work of the visual analyzer is very important for the whole organism and, fortunately, it is amenable to correction.
"Creativity begins with vision. Vision -
this is already a creative act requiring voltage "
Henri Matisse
The theory of aesthetic perception is based on the fact that the perception of its basis is a cognitive process determined by the forms and type of visual perception.
Special accent will be made on the fact that aesthetic perception is not a passive, contemplative act, and creative, active process.
Every act of visual perception, according to Arnheim (the author of the most interesting book "Art and visual perception"), is an active study of the object, its visual assessment, the selection of existing features, comparing them with the movements of memory, their analysis and organization of all this holistic image.
In 20 years, now the last twentieth century has appeared a new direction in psychology, it is called Gestalt. The term Gestalt is not amenable to a clear translation into Russian, it has a number of values: a holistic, image, structure, shape. And it can be used without translation, meaning a holistic combination of elements of mental life, which is unavoidable to the amount of parts components. In their works, GestaltPsychologists have paid much attention Problems of perception. They performed primarily against the associative theory of perception that dominated the psychological theories of the X1x century. They sought to prove that perception is of a holistic nature and is based on the creation of holistic structures - Gestaltov. Instead of abstract questions about how we see three dimensions, what the sensory elements are, as possible, their association, gestaltpsihologists put forward real and specific problems: how we see things as they are in reality, as the figure is perceived separately from the background, what is Surface that is a form why it is possible without changing anything in the subject, "change" its weight, sizes and other parameters.
Let us try to figure out how we see and, thereby, to help yourself learn how to manage visual perception.
So - any perception is also thinking, any reasoning is at the same time intuition, any observation is also creativity. And every person sees and hears only what he understands and rejects what he does not understand.
It is often believed that the eye is similar to the camera. However, there are absolutely not suitable signs of perception. The eye supplies the brain with information encoded in nervous activity - a circuit of electrical pulses, which, in turn, with the help of its code and a certain structure of brain activity reproduces items. It is like letters when reading, characters are not pictures. No inner picture arises! For the brain, this structural excitement is the subject.
Very interesting, the tendency of our brain is grouping objects and simple figures and continue (drawing) unfinished lines. Several lines are what you need for the eye, the rest will finish the brain in the measure of my development and understanding. (Caricatures, vision in the flame or in the clouds - faces and figures, fortune telling on the coffee grounds, etc.)
It is possible to say with full confidence that knowledge of the object received from past experience is included in the process of visual perception, and this experience is not limited to vision, here and touching and taste, color, olfactory, auditory, and possibly even temperature, pain and other sensual Characteristics of this subject.
Perception goes beyond the sensations directly to us sensations. Perception and thinking do not exist independently of each other. Phrase: "I see what I understand" - indicates a connection that really exists.
Describing items and things, we constantly point out their correlation with the environment. No item is perceived isolated. The perception of something means attributing this "something" of a certain place in the system: the location in space, the degree of brightness, color, size, size, distances, etc. By changing the hairstyle, we suddenly notice that the face was slightly rounded. Selecting the style of the dress, we dream to "pull out" legs and neck and "reduce" the waist amount. It can be said with complete confidence that we see more than getting on the retina eye. And it is not an action of intelligence!
It seems incredible, but any line drawn on paper or applied on the surface of the subject (in our case on clothes or on the face), similar to the stone abandoned in the quiet water of the pond. All this is resting, mobilization of space, action, movement. And vision perceives this movement, this action.
Perceptual power comes into operation. Are these strengths are real? In the perceived objects, there are naturally no (of course, you did not grow up, putting clothes into a vertical strip and did not expand from horizontal), but they can be considered psychological twins or equivalent of physiological forces acting in the visual region of the brain. There are no foundations with illusions to call these forces, they are illusory not more than the colors inherent in subjects themselves, although the colors from a physiological point of view is just a reaction nervous system On the light with a certain wavelength (but a little later).
Equilibrium mental and physical.
Discussing the issue of the influence of the location of the object to his perception, we inevitably face the equilibrium factor. From the point of view of physics, equilibrium is the state of the body in which the forces acting on it compensate each other. This definition applies to perceptual forces. Like any physical body, each having border visual model has a point of support or center of gravity. What is the balance in creating an image? Unbalanced composition, whether it is a drawing, placement of furniture, selection of clothing or colors and makeup lines and hairstyles, looks random, temporary. When there is no calm and clarity, we have the impression of destruction or non-accuracy. For example, clown clothing - a red and blue, dividing the body in half - and the figure seems ridiculous, although both halves of the torso and their physical weight are equal. It is possible to say with full confidence that the absence of equilibrium leads to the impossibility of perception of a whole.
WEIGHT. When creating a visual composition, you can not forget about the apparent weight. Weight depends on the location of the part or object. The element located in the center of the composition or close to it weighs less than others. The item in the upper part seems harder than below, and the right side has a greater weight than with the left. The weight depends on both the size, naturally, that the larger item will look harder. Now, as for the "weight" of color, then red (warm) is heavier than blue (cold), and bright and bright colors are heavier dark. For example, to interpret black and white it is necessary to make a black space area to make a little more white. The weight also affects the form of the subject and the direction of perceived objects. The correct geometric form always looks harder than the wrong. For example, when compared with the same weight and color of the ball, the square and triangle, it seems the ball.
DIRECTION.The direction, as well as the weight, affects the equilibrium, i.e. To create overall impression from the subject. It is very important to understand and remember that in the elongated forms, the spatial orientation of which deviates from the horizontal or vertical to a small angle, this direction becomes dominant. The simplest and most affordable example of this rule is a slightly displaced seam on once fashion stockings with a seam!
Right and left side.A difficult problem arises in connection with the asymmetry of the right and left. Any item located on the right looks heavier left. Experts consider everything that is located on the left has a greater value for the observer than what is located in the center or right. Remember where the speaker's tribune is where the main action is on the scene: in the middle, and more often on the left. This phenomenon is associated with the dominance of the left hemisphere of the cerebral cortex, which contains the highest brain centers - speech, reading and writing.
Outline.In essence, vision is a means of practical orientation in space. The visual process means "grasp", the rapid awareness of several characteristic features of the object. (Poor printed photo turned the face into several gray spots, but we find out) we can say that human look - This is to some extent, the penetration into the essence of the subject. And the outlination is just one of the essential characteristics of the subject, captured and conscious of the human eye. The outline is the border of the mass. But here is an interesting example, we do not see the hidden side of the ball, but we firmly know that the ball is round. What is familiar to us, acts as knowledge, which is added to direct observation.
Gestaltpsihologists believe that any stimulating model is perceived the easiest, i.e. The subject we see consists of a small number of characteristic structural features. And the farther from us is the subject, the more simple form form we see. With a closer look at, we begin to see the details.
SIMILARITY. When creating any composition, it is necessary to remember the principle of similarity: the more parts of any perceived model similar to each other, the stronger they will be combined into an integer. Elements associated with shape, colors, size, etc., strive to be located in the same plane. The similarity creates a strong visual effect, forming and forming visual models. And what simply modelThus, the stronger they rush, often breaking the composition or creating a new one.
Further development of the principle of similarity of parts is expressed in patterns, which deals with an internal similarity of a visually perceived object: when there is a choice between several possibilities for continuing curves (and the human body, I want to remind, consists of only of them), then preference is given to the one that most Consistently retains the internal structure. And yet, always intervals between curvilinear segments mentally filled with us and completed to a complete circle. It is also proven that the likeness of the figures or color spots is not expressed in strict repetition of the previous one, but in a gradual change in the form. And the eye of the viewer, forced to follow this perceptive movement, sees a new form!
Following this Arnheim made an article by "Art Symbols - Freudian and Other". In her, he returns to criticism of aesthetics of psychoanalysis. According to Arnheim, the excursions of psychoanalysts in the art area are absolutely trying.
"Every year we get any other interpretation of an Edip or Hamlet's image. These analyzes are or easily swallowed, or ignored, and most often cause laughter from readers and do not give a reason for any constructive discussion. " Interpretations of works of art that Freudian gives, arbitrary and random. By bringing art to the symbolic expression of sexual motives, Freudists, according to Arnheim, are detaining art. "Even if he writes, when the interpretation is not purely arbitrary, but it is based on something, we, nevertheless, stay halfway into the holy of holy arts when we hear statements that the work of art is only an expression of sexual Desires, longing to return to the maternal womb or fear of castration. The benefit from this kind of messages is extremely insignificant, and have to be surprised why art was considered necessary in every culture known to us and why it penetrates so deeply into our lives and nature. "
The controversy with representatives of Freudian aesthetics is also contained in the book "Art and Visual Perception". Arnheim opposes a number of representatives of the theory of psychoanalysis. It makes little enough, for example, the writer of the Freudistsky sense of the city of Grojdek, who in his work "man, as a symbol" trying to interpret some pictures of Rembrandt in a sexual sense and present the sculptural group Laocoon as a symbolic image of the genital organs. "The most common objection against such interpretation," writes Arnheim, is indicated on its one-sidedness, which is expressed in recognizing sex the most important and main point of human life, which is spontaneous everything comes down. Psychologists have already indicated that this provision is not proven. At best, this theory is true only in relation to individual individuals with a disturbed psyche or even for certain periods of culture, during which "superfluid sexuality overstifts all sorts of limits". "
No less acute Arnheim is against the famous English art historian and theorist of the Art of Herbert Reed. The subject of criticism of Arnheim is the book of Reed "Education of Art", where Reed in the spirit of Freuddism seeks to interpret children's creativity As an expression of congenital and subconscious characters.
Following the Jung, Reed believes, for example, that the use of children in their work of such universal forms, as a circle, is an expression of archetypes or sexual complexes lying somewhere in the depths of the unconscious. Arnheim refutes such an opinion, proving his subjectivity and groundlessness. "Spectacularly perceived symbols," he writes, "cannot be adequately studied without circulation to perceptual and visual factors. A supporter of psychoanalysis, who believes that the child begins his artistic activities from the image of the circles due to his memories of the mother breast, which was the first significant object of his life experience, neglects elementary motor and visual conditions that cause preference to a circle or circumference. Such real characters as a sunbarrow or cross reflect the main types of human experience with the help of basic visual forms. "
Thus, Arnheim throughout his book opposes Freudian aesthetics with its search for clinical symptoms and sex symbols, a hoax of artistic creativity. True, it is impossible to lose sight of the fact that the criticism of Freudism is conducted by Arnheim not from the perspective of consistent materialistic philosophy. But, taking into account this circumstance, it has great importance.
Freudist aesthetics completely excluded the function of knowledge from the art area. In contrast to this Arnheim argues that art is a process of knowledge. According to him, the main danger that threatens art is lies in the loss of art. "We deny the gift of understanding things that our feelings are given to us. As a result, the theoretical understanding of the perception process separated from the perception itself and our thought moves into abstraction. Our eyes turned into a simple measurement tool and identification - hence the lack of ideas that can be expressed in the images, as well as the inability to understand the meaning of what we see. "
The theory of aesthetic perception, which Arnheim develops, is based on the fact that the perception is based on its cognitive process, determined by the forms and type of visual perception. This, perhaps, is the main value of the aesthetic concept of Arnheim.
Considering the perception of art as a cognitive process, Arnheim indicates the specific features of this knowledge. First of all, it focuses on the fact that aesthetic perception is not a passive, contemplative act, and creative, active process. It is not limited only to the reproduction of the object, but also has productive functions that consist in creating visual models. Each act of visual perception, according to Arnheim, is an active study of the facility, its visual assessment, the selection of significant features, comparing them with their memory tracks, their analysis and organization into a holistic visual image.
The visual perception in the interneheim interpretation is an active, dynamic process. Vision cannot be measured in static, quantitative units - centimeters, wavelengths, etc., since it includes as an essential, substantial element, the dynamic ratio of forces. "Each visual model is dynamic ... Any line drawn on a sheet of paper, any simple shape, molded from a piece of clay, is similar to a stone, thrown into the pond. All this is a breakdown of rest, the mobilization of space. Vision is perception of action. "
This active I. creative character Visual perception has, according to Arnheim, a certain similarity with the process of intellectual knowledge. If the intellectual knowledge is dealing with logical categories, the art perception, not being an intellectual process, nevertheless, relies on certain structural principles that Arnheim calls "visual concepts". It allocates two types of such concepts - "perceptual", with the help of which perception occurs, and "visual", through which the artist embodies his thought into the art material. Thus, perception lies in the formation of "perceptual concepts", as well as artistic creativity represents "the formation of adequate visual concepts". Arnheim attaches great importance to these concepts in the process of art perception and creativity. He even says that if Rafael would be born without hands, he would still remain the artist.
According to Arnheim, the visual perception in its structure is a sensual analogue of intellectual knowledge. "Currently, it can be argued," writes Arnheim, - that at both levels - perceptual and intellectual - the same mechanisms operate. Consequently, such terms as "concept", "judgment", "logic", "abstraction", "concluding", "calculation", etc., should be inevitably applied in the analysis and description of sensory knowledge. "
This thought of Arnheim, despite the fact that it constitutes one of the main provisions of his theory of visual perception, it seems to be known to the discussion. In the book "Art and Visual Perception", it plays the role of hypothesis rather than experimentally proven truth. Nevertheless, the assertion of Arnheim on the productive, creative nature of visual perception deserves the most close attention. To a certain extent, it gets recognition in Soviet psychology. Thus, in the article "Productive perception" V. P. Zinchenko, clarifying, in particular, on Arnheim, writes: "Various functional systems are involved in the method of image, and the contribution of the visual system is particularly significant. This contribution is not limited to reproduction of reality. The visual system performs very important productive functions. And such concepts as "visual thinking", "scenic consideration", are not at all metaphor. "
Assessing the book of Arnheim, it is necessary to say a few words about its structure. It consists of ten chapters: "equilibrium", "outline", "form", "development", "space", "light", "color", "movement", "tension", "expressiveness" (in this edition, representing the abbreviated translation of the book of Arnheim, there is no head "Voltage"). In this listing there is its own sequence, its own logic. All heads of book reflect certain points in the development of visual perception, in motion of knowledge from simple, elementary forms to the most complex and significant. The last chapter, "expressiveness," is, according to Arnheim, the "crown" of perceptual categories. It is completing the book and at the same time completion of the process of visual perception. Thus, the structure of the book reveals the structure of the process of aesthetic perception, as represents its Arnheim, the most significant moments in the formation of a holistic artistic image.
The book of Arnheim is written on the basis of the principles and methodology of Gestalt Psychology. This orientation on GestaltPsychology is especially tangible in the "Introduction" and the first three chapters: "Equilibrium", "Outline", "Form". In "Introduction", Arnheim specially emphasizes that the methodology of its research is based on the experimental and theoretical base of Gestalt Psychology. In this regard, he refers to the works of Gestalt Psychologists K.koffki, M.vertheimer, V.Köler, and in the field of psychology of art and pedagogy on the research of the Swiss teacher Gustav Britz and the American psychologist Henry Shefer-Zimmer.
Gestalt Psychology refers to one of the influential directions in modern psychology in the West. Its foundations were laid back in the 20s in the works of German psychologists who put forward the theory of the so-called gestalt. The term "gestalt" is not amenable to a single-valued translation into Russian. It has a whole number of values, such as "holistic image", "Structure", "Form". IN scientific literature This concept is most often used without translation, meaning a holistic combination of elements of mental life, unavoidable to the amount of components of its parts. In their works, GestaltPsychologists paid great attention to the problems of perception. First of all, they performed against the associative theory of perception that dominated the psychological theories of the XIX century. In contrast to this theory, they sought to prove that perception is of a holistic nature and is based on the creation of holistic structures, gestal.
It should be noted that in its desire to disclose the holistic structural nature of the perception of gestaltpsihologists often came to purely idealistic conclusions, to recognizing that the facts of visual perception are explained not only by the properties of the objects of perception, but also a congenital, immanent structure of the phenomenal field, the effect of electric fields of the brain.
"Psychologists-Geshetaltists," notes R. L. Gregory, - believed that inside the brain there were pictures. They represented perception as a modification of electric brain fields, and these fields copy the form of perceived objects. This doctrine, known as isomorphism, has had a detrimental effect on the theory of perception. Since then, there is a tendency to attribute properties with hypothetical brain fields, supposedly "explaining" such phenomena as distortion spectator, and other phenomena. "
Similar evaluation philosophical meaning Gestalt Psychology gives V. P. Zinchenko. "Being at the position of psychophysical parallelism, GestaltPsychology considered the processes of forming a perceptual image as a simple reflection. The physiological processes of structure formation, allegedly occurring inside the nervous system. The position of Gestalt Psychologists that perceptual gestalles are not a reflection of the outside world, but the structures of the internal produced by the brain, represents only a new version of the old idealistic concept of physical idealism. "