The history of the origin of the musical instrument. Organ - musical instrument
The largest, most majestic musical instrument has ancient history The occurrence of many stages of improvement.
The ancestor of the authority is most distant from us in time, it is customary to consider the Babylonian Volyn, common in Asia in XIX-XVIII centuries BC. In this instrument, the air was injected through the tube through the tube, and on the other hand, a housing with models having holes and tongues was located.
The history of the emergence of the body remembers and "Traces ancient Greek Gods": The deity of forests and groves Pan, according to legend, came up with combining reed sticks of different lengths, and since then the Flute Pan has been inseparable with the musical culture of ancient Greece.
However, the musicians understood: on one twin play easily, but on a few - there is not enough breathing. The search for the replacement of human breathing for the game on musical instruments was brought by the first fruits already in the II-III century BC.: Hydraulos came to the musical scene for several centuries.
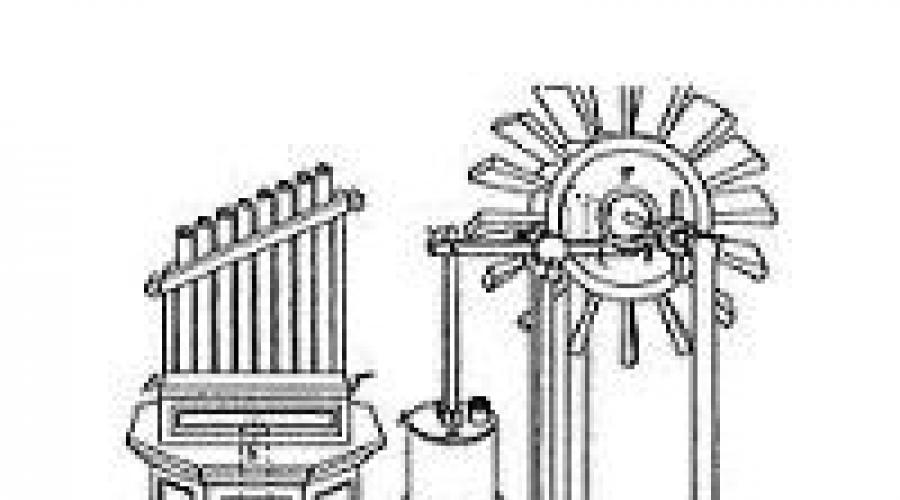
Hydraulos - the first step to the magnitude of the organ
Approximately in the III century BC. Greek inventor, mathematician, "Pneumatics Father" Ktezibiy Alexandrian has created a device consisting of two piston pumps, water tank and tubes to emit sounds. One pump filed the air inside, the second served it to the pipes, and the water tank leveled pressure and ensured a more flat sound tool.
After two centuries, Gereon Alexandrian, Greek mathematician and engineer, improved the hydraulus, adding a miniature windmill into the construction and a metal ball chamber, immersed in water. The improved water body received 3-4 registers, each of which contained 7-18 diatonal tuning pipes.
 The water body was greatly distributed in the countries of the Mediterranean region. Hydraulos sounded on the competitions of gladiators, weddings and feasts, in theaters, circuses and at the racetracks, during religious rites. The body has become a favorite instrument of Emperor Nero, his sound could be heard throughout the Roman Empire.
The water body was greatly distributed in the countries of the Mediterranean region. Hydraulos sounded on the competitions of gladiators, weddings and feasts, in theaters, circuses and at the racetracks, during religious rites. The body has become a favorite instrument of Emperor Nero, his sound could be heard throughout the Roman Empire.
 In the service of Christianity
In the service of Christianity
Despite the common cultural decline, observed in Europe after the fall of the Roman Empire, the body was not forgotten. Already by the middle of the 5th century, improved winds were built in the churches of Italy, Spain and Byzantium. The centers of organ music became the countries of the greatest religious influence, and from there the tool spread across Europe.
The medieval organ was significantly different from the modern "fellow" smaller number of pipes and a large key size (up to 33 cm long and 8-9 cm wide), for which the sound was beaten with a fist. "Portal" was invented, a small portable organ, and "positive" - \u200b\u200ba miniature stationary body.
 The XVII-XVIII century is considered the "golden age of" organ music. Reducing the size of the keys, the acquisition by the body of the beauty and diversity of the sound, crystal grain clarity and the appearance of whole pashades predetermined the magnificence and greatness of the organ. Solemn music Bach, Beethoven, Mozart and many other composers sounded under high vaults of all Catholic Cathedrals in Europe, and almost all the best musicians served as church organists.
The XVII-XVIII century is considered the "golden age of" organ music. Reducing the size of the keys, the acquisition by the body of the beauty and diversity of the sound, crystal grain clarity and the appearance of whole pashades predetermined the magnificence and greatness of the organ. Solemn music Bach, Beethoven, Mozart and many other composers sounded under high vaults of all Catholic Cathedrals in Europe, and almost all the best musicians served as church organists.
With all the inseparable communication with the Catholic Church, a lot of "secular" works, including Russian composers, is written for the organ.
 Organ music in Russia
Organ music in Russia
The development of organ music in Russia went exclusively on the "secular way: Orthodoxy categorically rejected the use of the organ in worship.
The first mention of the authority in Russia is found on the frescoes of the Sofia Cathedral in Kiev: "Stone Chronicle" Kievan Rus, dated by the X-XI centuries, has kept the image of a playing musician and two cats (people by downloading air into fur).
Vivious interest in the body and organ music showed Moscow sizards of different historic periods: Ivan III, Boris Godunov, Mikhail and Alexey Romanov "discharged" from Europe of organists and builders of bodies. Under the rule of Mikhail Romanov, not only foreign, and Russian organists, such as Tomila Mikhailov (demons), Boris Ovsons, Meleneti Stepanov and Andrei Andreev became known in Moscow.
Peter I, who dedicated life to the introduction into the Russian society, the achievements of Western civilization, in 1691 instructed the German specialist Arpa Schnitgeru to build a body with 16 registers for Moscow. After six years, in 1697, Schnitger sends another, 8-register tool to Moscow. During the lifetime of Peter in Lutheran and Catholic churches, dozens of bodies were built on the territory of Russia, including gigantic projects for 98 and 114 registers.
Empress Elizabeth and Ekaterina II also contributed to the development of organ music in Russia - under their rule, dozens of tools received St. Petersburg, Tallinn, Riga, Narva, Yelgava and other cities in the north-western region of the Empire.
Many Russian composers used a body in their work, it is enough to remember the "Orleans" Tchaikovsky, "Sadko" Roman-Korsakov, "Prometheus" Scriabin ,. Russian organ music combined the classic Western European musical forms and traditional national expressiveness and charm, possessed a strong influence on the listener.
 Modern organ
Modern organ
Passage historic Path Two thousand years long, the organ of the XX-XXI century looks like this: several thousand pipes located on different tiers and made of wood and metal. Wooden pipes of the square section make bass low sounds, and metal pipes from tin alloy and lead have a round cross section and are designed for a thinner, high sound.
The record holders are spelled out by the ocean, in the United States of America. The body located in the Philadelphia Macy's Lord & Taylor shopping center, weighs 287 tons and has six manuals. The tool located in the consent hall of the city of Atlantic City is the largest organ in the world and has more than 33,000 pipes.
The largest and magnificent organs of Russia are located in the Moscow House of Music, as well as in the concert hall. Tchaikovsky.


Development in new directions and styles has significantly increased the number of types and varieties of the modern body, with their differences in principle and specific features. Today's classification of organs is such:
- spiritual body;
- symphony;
- theatrical body;
- electors;
- hammond organ;
- tiff organ;
- steam organ;
- street body;
- orchestrion;
- organola;
- pyrophone;
- marine body;
- chamber organ;
- church organ;
- home organ;
- organs;
- digital organ;
- rock authority;
- pop organ;
- virtual authority;
- melodium.
In contact with
Organ - ancient instrument. His remote predecessors were, apparently, like a floly and flute Pan. In ancient times, when there were no complex musical instruments, several cane swords of different magnitudes began to connect together - this is the Flute Pan.
It was believed that his god of forests and groves Pan came up with. On one pipe to play easily: she needs some air. But to play several at once much more difficult - there is not enough breathing. Therefore, in deep antiquity, people were looking for a mechanism replacing human breathing. Such a mechanism was found: the air became fuzzled by furs, the same as those blacksmiths blown fire in Mountains.In the second century BC in Alexandria Ktesebius (Lat.Cesibius, about III - II centuries. BC. E.) invented the hydraulic organ. Note that this Greek nickname literally means "Creator of Life" (Greek. KTESH-BIO), i.e. Simply the Lord God. This Ktybiy allegedly invented the float water clock (not reached us), piston pump and hydraulic drive
- long before the opening of Torrichelli law (1608-1647). (What is thoughtfully in the II century BC er it was possible to ensure the tightness required to create a vacuum in Ktybia? From what material a rocked pump mechanism could be made - because to ensure the sound of the organ requires the initial overpressure of at least 2 atm. ?).
In hydraulosity, air was injected not with furs, but a water press. Therefore, he arrived evenly, and the sound got better - smaller and more beautiful.
Hydraulos was used by the Greeks and Romans on the racetracks, in circus, as well as to accompany the pagan mysteries. The sound of the hydraulio was unusually strong and piercing. In the first centuries of Christianity, the water pump was replaced by air furs, which made it possible to increase the size of the pipes and their number in the organ.
There were century, the tool was improved. The so-called performing console or performing table appeared. On it, several keyboards located one above the other, and at the bottom of the huge keys for the legs - the pedals, which were removed the lowest sounds. Of course, reed shoes were forgotten forgotten - Pan flutes. Metal pipes sprouted in the organ, and their number reached many thousands. It is clear that if the key corresponded to each pipe, it would be impossible to play on the tool with thousands of keys. Therefore, the keyboards made register knobs or buttons. Each key corresponds to several tens, and even hundreds of pipes, emitting the sounds of one height, but of different timbre. They can be turned on and off with register handles, and then, at the request of the composer and artist, the organ sound becomes similar to the flute, then on oboe or other tools; He can imitate even the singing of birds.
Already in the middle of 5th century, organs were built in Spanish churches, but since the tool sounded loudly, it was used only in the days of large holidays.
By the 11th century, the bodies built all Europe. An unusual size was known to the body, built in the 980 year in Wenchester (England). The contained keys were replaced by clumsy large "plates"; The tool diapass is wider, the registers are more diverse. At the same time, a small portable body was entered into widespread use - portal and miniature stationary organ - positive.
The musical encyclopedia says that the keys of the organ up to 14 V. were huge
- 30 -33 cm long and 8-9 cm wide. The game technique was very uncomplicated: on such keys they were beaten fists and elbows (it. Orgel Schlagen). What organized sublime governments could sound in Catholic Cathedrals (it is believed that with the VII century. N.) With this technique of execution ?? Or were these orgies?
17-18 centuries. - Golden Age of Organizations and Organization.
The organs of this time were characterized by beauty and a variety of sound; Exceptional timbre clarity, transparency made them excellent instruments for execution polyphonic music.
In all Catholic cathedrals and large churches organs were built. Their solemn and powerful sound, as it is impossible to suit the architecture of cathedrals with leaving up lines, high vaults. The best musicians The world served as church organists. Many magnificent music was written for this tool with different composers, including Bach. Most often wrote for the "baroque body", which was more common than the bodies of the preceding or subsequent periods. Of course, not all the music created for the organ was a cult associated with the church.
They composed for him and the so-called "secular" works. In Russia, the body was only a secular instrument, since in the Orthodox Church, unlike Catholic, he was never put.
Starting from the 18th century, composers include an organ in the oratorio. And in the 19th century he appeared in the opera. As a rule, it was caused by the stage situation - if the action occurred in the temple or near it. Tchaikovsky, for example, took advantage of the organ in the Oremean Deva opera in the scene of the solemn coronation of Karl VII. We hear the organ and in one of the scenes opera Guno "Faust"
(scene in the cathedral). But Roman-korsakov in Opera "Sadko" instructed the authority to accompaniate the song of the heart-mogly-hero, who interrupts the dance
Sea king. Verdi in Opera "Othello" with the help of the organ mimics the noise of the sea storm. Sometimes the body is included in the score symphony works. With his participation, the third symphony of Saint-Sansa, the poem of Ecstasy and Prometheus Scriabin in the Symphony "Manfred" Tchaikovsky also sounds the authority, although the composer did not provide for this. He wrote a party of the Fisharmonium, which the organ there often replaces.
Romanticism of the 19th century, with his desire for expressive orchestral sound, had a dubious influence on organization and organ music; The masters tried to create tools that are an "orchestra for one performer", as a result, the case was brightened to the weak imitation of the orchestra.
However, in the 19th and 20th centuries. A lot of new timbres appeared in the authority, and significant improvements in the instrument design were made.
The trend towards creating increasingly large organs has reached the climax in a huge, numbering 33112 pipes, an organ in Atlantic City (pcs. New
Jersey). This tool has two departments, and on one of them - 7 keyboards. Despite this, in the 20th century. Organists and human buildings realized the need to return to simpler and convenient types of otter.
The remains of the oldest organ-containing tool with hydraulic drive were found in 1931 during the excavations of Aquincum (near Budapest) and dated 228 g. e. It is believed that this city, which had a system of forced water supply, was destroyed in 409. However, in terms of the development of hydraulic equipment, it is the middle of the XV century.
The structure of the modern organ.
Organ - keyboard musical instrument the largest and most difficult existing tools. Play on it, like on the piano, pressing the keys. But unlike the piano, the body is not a string, and the ovens and relative, it turns out to be non-key tools and a small flute.
A huge modern body consists of from three or more organs, and the performer can manage both by all. Each of the organs belonging to such a "large organ" has its own registers (pipe sets) and their keyboard (manual). Pipes built into the ranks are located in the interior of the organ; Part of the pipes can be visible, but in principle, all pipes are hidden by the facade (avenue), consisting partially made of decorative pipes. The organist is sitting behind the so-called spacing (department), in front of it - the keyboard (manuals) of the organ, located in the terraces one above the other, and under the feet - a pedal keyboard. Each of the organs belonging to
"Big Organ", has its own purpose and name; Among the most common - "main" (HAUPWERK), "Upper", or "Woolvers"
(It. Oberwerk), "Rosepositive" (Rykpositiv), as well as a set of pedal registers. The "main" body is the largest and containing main instrument registers. "Roseposive" is similar to the "main", but less and sounds softer, and also contains some special soloing registers. "Upper" authority adds new solo-resistant timbres to the ensemble; Pipes are associated with a pedal, emitting low sounds to enhance bass parties.
The pipes of some of their named organs, especially the "upper" and "backpap", are placed inside the semi-closed shutters, which can close or open with the help of the so-called channel, resulting in the effects of Crescendo and Diminuendo, inaccessible on the organ without this mechanism. In modern organs, air is injected into the pipes using an electric motor; Through wooden air bodies, the air from the fur enters the winddares - a system of wooden boxes with holes in the upper lid. In these holes, organ pipes are strengthened with their "legs". From the winddow, the air under pressure enters this or that pipe.
Since each pipe is able to reproduce the sound height and one tone, a set of at least 61 pipes is needed for a standard manual of five octaves. In general, in the authority can be from a few hundred to many thousands of pipes. A group of pipes producing the sounds of one tone is called a register. When the organist includes a register on a spa (using a button or lever located on the side of manuals or above them), access to all pipes of this register. Thus, the performer can choose any register you need or any combination of registers.
There are various types of pipes that create a variety of sound effects.
Pipes are made of tin, lead, copper and different alloys
(mainly lead and tin), in some cases a tree is used.
The length of the pipes can be from 9.8 m to 2.54 cm and less; The diameter varies depending on the height and timbre of sound. The pipes of the organ are divided into two groups of the method of sound recovery (labial and boring) and four groups on the challenge. In the laborative pipes, the sound is formed as a result of the blowing of the air jet about the lower and upper lip of "Rotika" (labium) - cut at the bottom of the pipe; In the tongue pipes, the source is driving a metal tongue under pressure under pressure. The main family of registers (timbres) are principles, flutes, gamps and boring.
Principles are the foundation of all organ sound; Flute registers sound calmer, softer and to some extent resemble the timbre orchestral flutes; gambins (string) piercing and sharper than flutes; The timbre of the tongue is metallic, imitating the timbres of orchestral wind instruments. Some organs, especially theatrical, also have percussion timbres, such as imitating plates and drum.
Finally, many registers are built so that their pipes do not provide the main sound, and its transposition to octave above or lower, and in the case of so-called mixtures and aliquots - even not one sound, as well as overtones to the main tone (aliquots reproduce one overtone, medicine - up to seven overtons).
Authority in Russia.
The organ, the development of which has been associated with the history of the Western Church since the history of the Western Church, and in Russia, where the Orthodox Church prohibited the use of musical instruments during worship.
Kievan Rus (10-12VV). The first organs in Russia as in Western Europe came from Byzantium. It coincided with the adoption of Christianity in Russia in Russia in 988 and the Board of Prince Vladimir Saint (approx. 978-1015), with an era of especially close political, religious and cultural contacts between Russian princes and Byzantine rulers. The body in Kiev Rus was sustainable part of Courtnaya I. folk culture. The earliest certificate of the body in our country is located in the Kiev Sofia Cathedral, which is due to its long-term construction in 11-12 centuries. became the "stone chronicles" of Kievan Rus.This, the fresco was preserved, which depicts a playful musician and two Calcanta
(Organ Fur Kachers), pumping air into the furs. After death
Kiev state during the Mongol-Tatar rule (1243-1480) the cultural and political center of Russia becomes becoming the Moscow.
Moscow Great Principality and Kingdom (15-17 centuries). In this era between
Moscow I. Western Europe There were increasingly close relationships. So, B1475-1479. Italian architect Aristotle Fioravati erected in
The Moscow Kremlin Assumption Cathedral, and the brother of Sofia Paleologist, the nieces of the last Byzantine emperor Konstantin XI and from 1472 years of the king's wife
Ivan III, brought to Moscow from Italy by the organist John Salvator.
The royal courtyard of that time showed a lively interest in organ art.
This allowed in 1578 to settle in Moscow to the Dutch Organist and the Organizer Gottlip Eylgofu (Russians called him Danilo Necchin). 1586 Dated a written message of the English Messenger Jerome Gorsey for the purchase for the queen Irina Fedorovna, Boris Godunova's sisters, a few keychairov and organ built in England.
Organs and among the widespread simple people.
Stranded rushes in the portatives. According to the most diverse reasons that condemned orthodox Church.
During the reign of Tsar Mikhail Romanova (1613-1645) and further, up to
1650, except for Russian organists Tomila Mikhailov (Besov), Boris Obsonova,
MENEENTIC STEPANOVA AND ANDREY ANDREYEVA also worked foreigners in the fun chamber: the Poles of Jerzy (Yuri) Proskurovsky and Fyodor Zavalsky, organ buildings Brothers - the Dutch of Yagan (probably - Iohan) and Melchurt Lun.
With Tsar, Alexei Mikhailovich from 1654 to 1685 served at the court of Simon
Gutovsky, Musician "Master on All Hands" of Polish origin, coming from
Smolensk. His multifaceted activities of Gutovsky made a significant contribution to the development of musical culture. In Moscow, built several organs, in 1662p on the command of reigning, he and four of his submasters went to
Persia to convey one of his tools as a gift to Persian Shah.
One of the most significant events in cultural life Moscow was the foundation in 1672 of the court theater, which was also equipped with an organ
Gutovsky.
The era of Peter the Great (1682-1725) and its receivers. Peter I was vividly interested Western culture. In 1691, the nineteen-year-old young men, he instructed the famous Hamburg organ builder Arp Schnitgeru (1648-1719) to build an organ with sixteen registers for Moscow, decorated on top of the figures from a walnut tree. In 1697, Schnitger sent another one in Moscow, this time an eightner-stroke instrument for a certain Mrnhorn. Peter
I, who was striving to adopt all Western European achievements, among other things, instructed the Gerlitovik's organist to Christian Ludwig Boksberg, who demonstrated the king of the new organ of Eugen Kasparini in the Church of St. Peter and Paul in Gerlice (Germany), installed there in 1690-1703, designed for the Metropolitan Cathedral in Moscow an even more grand organ. The projects of the two disposites of this "giant organ" by 92 and 114 registers were prepared by Boxberg OK. 1715. During the reign of the king - the reformer, the authorities were built throughout the country, primarily in Lutheran and Catholic churches.
In St. Petersburg important role were playing catholic Church sv. Catherine and Protestant Church of SVV. Peter and Paul. For the latter B1737, the body built Johangerrich Joachim (1696-1752) from Mitau (now Yelgava in Latvia).
1764 In this church, concerts of symphonic and oratorical music were held weekly. So, in 1764, the royal court was conquered by the game of the Danish organist Johann Gothelm Painthau (1741 or 1742-1813). In the end
1770s Empress Ekaterina II instructed the English master of Samuel
Green (1740-1796) Construction of an organ in St. Petersburg is presumably for Prince Potemkin.
Famous Organity Builder Heinrich Adreas Contius (1708-1792) from Galle
(Germany), mainly working in the Baltic cities, and also built two organs, one - in St. Petersburg (1791), the other in Narva.
The most famous human builder of Russia is the end of the 18th e. Was Franz Kirchik
(1741-1802). Abbot Georg Izief Fogler who gave in April and May 1788 in St.
Perburgburg two concerts, after visiting the Circiic organ, was under such a strong impression of his tools that he invited in 1790 his assistant Master Rakvitz first in Warsaw, and then in Rotterdam.
In the cultural life of Moscow, the famous trace left thirty-year activity german composer, Organist and Pianist Johanna Wilhelm
Gesslera (1747- 1822). The game on the organ, Gessler, studied at the student I. S. Baha
Johanna Christian Kittel and therefore in his work adhered to the tradition of the Leipzig Cantor of the Church of St. Foma .. In 1792, Hesser was appointed Imperial Court Vaper Makester in St. Petersburg. In 1794, moved to
Moscow, hesitated the glory of the best piano teacher, and thanks to numerous concerts dedicated to the organ creativity I. S. Baha, had a huge impact on Russian musicians and music lovers.
19 - Start 20 century. At 19 in. In an environment of Russian aristocracy, an interest in musitizing on the body in the journalism was spread. Prince Vladimir
Odoevsky (1804-1869), one of the most remarkants of the Russian society, friend M. I. Glinka and the author of the first in Russia of original writings for the body, in the late 1840s invited Master George Melzel (1807-
1866) for the construction of a body that has entered the history of Russian music as
"Sebastian" (named Johanna Sebastian Baha). During the home body, in the development of which the prince of Odoyevsky took the participation. This Russian aristocrat saw one of the main goals of his life in the awakening of interest in the Russian musical public to the body and to the exclusive personality of I. S. Baha. Accordingly, the programs of its home concerts were primarily devoted to the work of the Leipzig Cantor. Precisely from
Odoevsky proceeded and the call to the Russian public to collect funds for the restoration of the Bakhakh authority in the Novof Church (now the Bahukhskaya Church) in Arnstadt (Germany).
Often, M. I. Glinka improvised on the organ of Odensky. From the memories of his contemporaries, we know that Glinka was endowed with an outstanding improvisoric talent. Highly appreciated the organ improvisation of Glinka F.
Sheet. During his tour in Moscow on May 4, 1843, the sheet acted as an organ concert in the Protestant Church of the SVV. Peter and Pavel.
Did not lose its intensity in the 19th century. and organization of human builders. TO
1856 There were 2280 church organs in Russia. In the construction of bodies established by B19, German firms took part.
In the period from 1827 to 1854 in St. Petersburg, Karl Wirth was worked as a piano and organ master (1800-1882), which built several organs, among which one was intended for the Church of St. Catherine. In 1875, this tool was sold to Finland. To Moscow, Kronstadt and Petersburg supplied its bodies of the British firm "Brindley and Foster" from Sheffield, the German company Ernst Reverver from Hausnaindorf (Hartz) in 1897 built one of his bodies Moscow, Austrian human-building workshop brothers
Riger erected several organs in churches of Russian provincial cities
(in Nizhny Novgorod - B1896, in Tula - in 1901, in Samara - in 1905, in Penza - in 1906). One of the most famous organs of Eberhard Friedrich Valker with
1840 was in the Protestant Cathedral of the SVV. Peter and Paul in St. Petersburg. He was erected by a sample of the large organ in the church of St. Paul in Frankfurt am Main.
A huge rise in Russian organ culture began with the foundation of organ classes in the St. Petersburg (1862) and Moscow (1885) conservatories. As the first teacher of the body in St. Petersburg, a graduate of the Leipzig Conservatory, a native of the city of Lubeck Gerich Shtil (1829-
1886). His teaching activities In St. Petersburg lasted from 1862
1869. B. last years Life He was an organist of the church Olya in Tallina, Calnery and his successor in the St. Petersburg Conservatory lasted from 1862 to 1869. In the last years of his life, he was an organist of the Church of Olya in Tallina Callery and his successor in the St. Petersburg Conservatory Louis Gomilius (1845-1908), in his pedagogical Practice was focused primarily on a German organ school. The occupations of the body of the St. Petersburg Conservatory in the early years were held in the Cathedral of the SVV. Peter and Paul, and among the first students-organists were P. I. Tchaikovsky. Actually, in the conservatory itself, the body appeared only in 1897.
In 1901, the Moscow Conservatory also receives a magnificent concert organ. During the year, this body was an exhibition exhibit in
Russian pavilion of the World Exhibition in Paris (1900). In addition to this tool, there were two more organs of the Laelegast, which1885 found their place in the male hall of the conservatory, a larger of them donated to the merchant and patron
Vasily Khludov (1843-1915). This body was used in the Conservatory until 1959. Professor and students regularly participated in concerts in Moscow and
St. Petersburg, and graduates of both conservatories also concerted in other cities of the country. In Moscow also performed and foreign performers: Charles
Marie Vido (1896 and 1901), Charles Tournewner (1911), Marco Enrico Bossi (1907 and
1912).
Organs and for theaters, for example, for the imperial and for
Mariinsky theaters In St. Petersburg, and later for the Imperial Theater in Moscow.
The successor Louis Gomilius in St. Petersburg Conservatory was invited by Jacques
Ganshin (1886-1955). The native of Moscow, and in the subsequent citizen of Switzerland and the student of Max Reer and Charles-Marie Viors, he from 1909 to 1920 headed the organ class. Interestingly, organ music belonging to Peru professional composers of Russia, starting with DM. Brathy (1751-
1825), combined Western European musical forms with traditional Russian Melosomes. This contributed to the manifestation of special expressiveness and charm, thanks to which Russian essays for the organ stand out by identity against the world of the global repertoire, it became the key to that strong impression that they produce on the listener.
Getting Started about the structure of the instrument's instrument, you should begin with the most obvious.
Under the elution of the organ imply controls, which include all numerous keys, register shift levers and pedals.
So, K. game devicesbelieve manuals and pedals.
TO tembrov - Register switches. In addition to them, the remote control consists of: dynamic switches - channels, a wide variety of foot switches and kopul inclusion keys that carry one manual registers to another.
Most of the organs are supplied with copulins to switch registers to the main manual. Also, with special levers, the organist can switch different combinations from the bank of register combinations.
In addition, a bench is installed in front of the remote control, on which a musician sits, and the organ switch is located nearby.
Example of copula organBut first things first:
- Kopul. The mechanism that can transfer one manual registers to another manual, or a pedal keyboard. This is relevant when it is necessary to transfer registers of the sound of weaker manuals to stronger, or withdraw the sound registers on the main manual. Copulas are included with special foot levers with retainers or using special buttons.
- Channel. This device, with which you can adjust the volume of each individual manual. At the same time, the shutters are regulated in the box through which the pipes pass by this manual.
- Bank memory of register combinations. This device is available only in electrical organs, that is, in organs with electrical tract. Here would make the assumption that the body with electric tract is something related to the doppoplated synthesizers, but the ovensoral body itself is too ambiguous tool so that it can be easily allowed to allow such an oversight.
- Ready register combinations. Unlike the memory bank for register combinations, which remotely resemble the presets of modern digital sound processing processors, ready-made register combinations relate to organs with pneumatic register tract. But the essence is the same: they make it possible to use ready-made settings.
- Trete. But this device includes manuals and all registers. Here is such a switch.
Manual
Keyboard, in other words. But only in the body there are keys to play legs - pedals, therefore it is correct to say exactly what manual.
Usually in the body from two to four manuals, but sometimes there are copies with one manual, and even such monsters that have as many seven manuals. The name of the manual depends on the location of the pipes with which it controls. In addition, each manual is assigned its own own set Registers.
IN the main thingthe manual is usually located the loudest registers. It is also called Hauptwerk. It can be located as closest to the performer and in the second row.
- Oberwerk - a little more hidden. His pipes are located under the pipes of the main manual.
- Rückpositiv is a completely unique keyboard. It controls those pipes that are located separately from all others. So, for example, if the organist sits to the tool face, they will be placed behind.
- Hinterwerk - This manual controls pipes that are located in the rear of the organ.
- Brustwerk. But the pipes of this manual are located either directly over the remote control itself or on both sides.
- SOLOWERK. How can you judge from the very name, the pipes of this manual are equipped with large quantity solo registers.
In addition, other manuals can occur, but those are listed above are used most often.
In the seventeenth century, the organs appeared a kind of volume control - a box through which pipes with shutters were held. Manual, who ruled by these pipes, was called Schwellwerk and placed at a higher level.
Pedals.
Initially, the organs did not have a pedal keyboard. She appeared at about the sixteenth century. There is a version that it came up with a Brabant organist named Louis Wang Valbec.
Now there are a variety of pedal keyboard depending on the structure of the organ. There are both five and thirty-two pedals, there are organs and without a pedal keyboard. They are called portatives.
Typically, the pedals are controlled by the most basciferous pipes for which a separate notional mill is written, under double score, which is written for manuals. Their range is two, or even three octaves below the other notes, so a large organ may have a range of nine and a half octave.
Registers
Registers are a number of pipes of the same tone, which are, in fact, a separate tool. For switching registers, handles are provided, or switches (for electrical control organs), which are located on the remote control or above the manual, or beside the sides.
The essence of register control is: if all the registers are turned off, then the organ when you press the key will not be.
The name of the register correlates with the name of its largest pipe, and each handle relates to its register.
There is something labial, so I. language Registers. The first refers to pipe control without tongues, these are open flute registers, there are also registers of closed flutes, principles, the registers of the prideshoes, which, in fact, form the color of the sound (medicine and aliquots). In them, each note has several weaker overtone pride.
But the tongue registers, as can be seen from their very name, control pipes with tongues. They can be combined in sound with labial pipes.
The choice of register is provided in muscle StanHe is written above the place where one or another register should be applied. But the case is complicated by the fact that different times And even just in different countries The registers of the organs were sharply different from each other. Therefore, the register of the organ party is rare when it is specified in detail. Usually it is accurately indicated only by manual, the size of the pipes and the presence or absence of tongues. All other sound nuances are given to the artist.
Pipe
As expected, the sound sound is in strict dependence on their size. Moreover, the only pipes that sound exactly how it is written in a new mill - these are eight-foot pipes. Smaller pipes sound are respectively higher, and large - lower than what is written in a new mill.
The largest pipes that are far from all, but only in the largest organs of the world, have a size of 64-foot. They sound three octaves lower than what is recorded in a notch mill. Therefore, when, when playing in this register, an organist involves pedals, already infrasucuke is published.
To set up small labial (that is, those that without tongue), use SHMYORN. This is a rod, at one end of which there is a cone, and on the other - a cup by which the pipes of the organ expand or narrow or narrow, than achieving changes in the height of the sound.
But to change the height of the sound of large pipes, additional metal flaps are usually cut out, which are bent like the tongues and thus change the sound of the organ.
In addition, some pipes can be purely decorative. In this case, they are called "blind". They do not sound, but have an exclusively aesthetic value.

Tract has a piano. There is a mechanism for transferring finger strike force from the key of the key directly to the string. The organ plays the same role and is the main mechanism for managing the body.
In addition, the authority has tract that controls the pipe valves (it is also called game tracts), it also has register tract that allows you to turn on and disable entire registers.
The tool king is so often called the organ, the appearance of which causes the feeling of delight, and the sound fascinates and inspires. A large, heavy string-key tool with a widestime sound register, rightfully considered something like "legends in the flesh." Who invented the authority and how is this heavyweight unique?
Who invented an unusual tool?
The history of the legendary tool, learn how to play on which not everyone is capable professional musician, Hours hundreds of centuries.
The name "Organum" is mentioned in the ancient Scriptures of the Great Aristotle and Plato. But to answer exactly who invented this miracle is not possible. According to one of the versions of his sonor, the Babylonian violence, which formates the sound due to the direction of the air jets towards the edges of the tube. On the other, the Flute Pan or Chinese Shan, functioning in the same principle. Playing on the connected swords was not very convenient, because the performer sometimes did not have enough air in the lungs. The idea of \u200b\u200bswing the air during the game of furs was a real salvation.
A close brother of the organ, its water analogue, was invented by the Greek craftsman as KTESIBIE in the 200th to AD. It is called hydraulos. Later, the hydraulic design was replaced by furs, which made it possible to significantly improve the sound quality.
Musical instruments are more familiar to us sizes and external view began to appear in the IV century. During this period, due to the efforts of Pope Vitalian, the organs began to engage in the role of accompaniment of Catholic worship services. Starting from the first half of the V century, the string-key tool became an unchanged ceremonial attribute not only by the Byzantine, but also the entire Western European imperial power.
The legendary "keyboard player" received widespread in Europe in Europe, received by the middle of the 14th century. The tool of that time was far from perfect: it had a smaller number of pipes and wider keys. For example, in the manual keyboard, with the width of the keys itself, the order of 50-70 mm between them was 15-20 mm. To extract sounds, the Contractor accounted for a huge and heavy keys not "run" with fingers, and literally knocking with elbows or fists.
Organity has acquired the greatest scope in the XVI-XVII centuries. In nice famous epoch Baroque Masters learned how to create tools that their powerful sound could safely compete with the whole symphony orchestra. The sound capabilities of the tools allowed to mimic the ringing of bells, rocks of the stonepad and even the sliding singing of birds.

Apotheosis of organ structures is considered to be 1908, when a model comprising 6 manuals was presented at the World Exhibition. The world's largest operating body weighs just over 287 tons. Now he decorates shopping center Macy's Lord & Taylor in Philadelphia.
The fact that the connoisseur of organ music is observed from the hall - the facade of the instrument. It is hidden a spacious room, sometimes turns on several floors, tired by mechanical elements and thousands of tubes. To understand the principle of action of this miracle, it is worth considering at least his brief description.
The body is one of the most high-profile musical instruments. Such an effect is achieved at the expense of registers comprising several rows organ pipe. These registers on the color of the sound and a number of other unifying features are divided into several groups: medicines, aliquots, gamps, flutes, principals. Register pipes sound in accordance with the notebook. They can include both individually and at the same time. For this, the handle keyboard arranged on the side panels.
The control panel of the performer working for the tool is manuals, a pedal keyboard and the registers themselves. The number of manuals depending on the modification of the "keyboard player" can vary from 1 to 7. They are located terrace: one directly over the other.
The pedal keyboard may include from 5 to 32 keys, by means of which registers forming low sounds are run. Depending on the application of the musical instrument, the performer presses to the pedal keys to the toe or heel.

The presence of several keyboards, as well as all sorts of togglers and levers, quite complicates the game process. Therefore, often his assistant sits at the instrument together with the performer. For the convenience of reading the notes and achieve the synchronization of the execution, the feet for the legs is traditionally located on a separate note box directly under the party for hands.
In modern models, the function of injection of air into fur is performed by electric motors. In the Middle Ages, this work was performed by specially trained cats, whose services had to be paid separately.
Despite the widespread organs of the organs today, it is almost unrealistic to meet two identical models, since they are all going on individual projects. Settings may vary from 1.5 m to 15 m. The width of large models reaches 10 m, and the depth is 4 m. The weight of such structures is measured in tons.
Recordsmen of different nominations
The most ancient representative of the legendary instrument, the timing of "life" of which is dating 1370-1400 years, can be found in the Stockholm Museum. He was brought from the church coming of the Swedish Island Gotland.
The leader in the nomination "The most loud organ" decorates the hall of the harmony in Atlantic City. The record holder includes 7 manuals and a rather extensive timbre set, formed by 445 and registers. The sound of this giant will not be able to enjoy, because his sound can provoke a breakpoint breakpoint from the listeners. Weighs this musical instrument over 250 tons.

The tool decorating the Church of St. Anne, which is located in the capital of Poland, is notable for including the longest pipes in the world. Their height reaches about 18 meters, and the sound published is capable of stunning literally. The frequency range of the tool is located within the limits covering even the ultrasound area.

XYLOPHONE
Ding Ding, tone tone,
Xylo-xylo-xylo-background.
Xylophone on the cabinet climbed,
He flamingo was frightened.
- You, Flamingo, Wait!
The beak is not very stucha
Better Hand take.
And you hear a gentle ringing.
Just a miracle - xylophone.
"Xilophone" translated from Greek means a singing tree. The first xylophone appeared, perhaps when primitive hit a stick on the dry tree and heard unusual sound. Currently, similar simplest xylophones are found in Africa, Asia and South America. In Europe, it was delivered by the wandering musicians.
Xylophone consists of large number Wooden shelches emitting when hitting the sounds of different heights. Bruks are made of maple, alder, nuts, sometimes from the rosewood. They have them on a wicker burning from straw, rogers or rubber. The design is usually installed on the table, sometimes resonators are fixed under the parschers - hollow metal cylinders. The sound of xylophone is crushed, dryish and clicking. It is extracted with the help of "goat legs" - wooden sticks with thickening at the ends, similar to spoons.
Sometimes instead of wooden brooms use metal. This is a metalphone or vibraphone. He has all the plates on the same level, while on xylophone, the bars corresponding to the black piano keys are slightly raised. Vibrafon is a complex design. It is located on a special three-frame table-stand, moving on four wheels. Appeared in the United States at the beginning of the XX century. Thanks to its characteristic timbre and large virtual possibilities, the vibraphone is widely used in music. But if the keyboard mechanism like the piano is like a metalwall, then the chest tool will be. Masters made his master Auguste Muster in 1886. Playing on the challenger is more convenient than chopsticks on the metal fond. And the sound is the same gentle and ringing. During his visit to Paris, P. I. Tchaikovsky heard and was so fascinated by her magic sound, which introduced the batch of this tool into his writings: the Ballad of the "Voivode" and the "Nutcracker" ballet.
For the first time in the orchestra, Xylophone used Ferdinand Kauer in mid XIX. in. In the work "Seven Variations". One of the most famous writingsIn which the xylophone is involved, the Saint-San San San San Syxa's Symphony Poem. The Russian composer of Roman-Korsakov in the "Tales of Tsar Saltan" instructed Xilophone a song "Lie in the garden, in the garden" for the image of a protein, ricking gold nuts.
ORGAN
The organ is the largest musical instrument, unique human creation. There are no two identical organs in the world.
The gigantic organ has many different timbres. This is achieved through the use of hundreds of metal pipes of different sizes, through which the air is purged, and the pipes begin to buzz, or "sing". Moreover, the organ allows the sound of the sound for a long time with constant volume.
Pipes are horizontally and vertically, some are suspended on the hooks. In modern organs, their number comes up to 30 thousand! The largest pipes have a height of more than 10 m, and the smallest - 1 cm.
The control system is called the Department. This is a complex mechanism to manage the organist. The organ is somewhat (from 2 to 7) manual keyboards (manuals) consisting of keys like on piano. Previously, the organ was not played with fingers, but hit fists. There is still a foot keyboard or just a pedal having up to 32 keys.  Usually, the artist helps one or two assistant. They switch registers whose combination generates a new timbre, not similar to the original. The organ can replace the whole orchestra, because its range exceeds the range of all orchestra tools.
Usually, the artist helps one or two assistant. They switch registers whose combination generates a new timbre, not similar to the original. The organ can replace the whole orchestra, because its range exceeds the range of all orchestra tools.
The body is known with deep antiquity. The Creator of the Authority is considered the Greek mechanic Ktyibi, who lived in Alexandria in 296-228. BC e. He invented the water body - hydraulos.
Now most often the body is used in worship services. Some churches and cathedrals are arranged concerts or organ services. In addition, there are organs installed in concert halls. The largest body in the world is in the American city of Philadelphia, in the McCaise department store. Its weight is 287 tons.
Many composers wrote music for the organ, but revealed its capabilities as a virtuoso executor and created unsurpassed work in the depths of the genius-composer Johann Sebastian Bach.
In Russia, Mikhail Ivanovich Glink paid considerable attention to organ art.
It is almost impossible to master the game on the organ. It requires a big music experience. Education on the organ begins in colleges, in the presence of playing skills on the piano. But it is possible to master the game on this tool, to continue learning in the conservatory.
Mystery
The tool is for a long time
Decorated the cathedral.
Decorates and plays
The entire orchestra replaces
(Organ)
VIOLIN
It is believed that the first string-bow tool invented Indian (according to another version - Ceylon) King Ravana, who lived about five thousand years ago. Probably, therefore, the long ancestor of the violin was called Ravanastron. It consisted of an empty cylinder made of a tute tree, one side of which was covered with the skin of a widely extended water beak. The strings were made from gazelle guts, and a bow, curved arc, from bamboo tree. Ravanastron has been preserved and so far in the wandering Buddhist monks.
On a professional scene, the violin appeared at the end of the XV century, and her "inventor" was an Italian from Bologna Gaspar Duipoprugar. The most ancient violin made by him in 1510 for the King Franz I is kept in the Nethergie Meeting in Aachen (Holland). Of course, the violin is owned by the sound of the Master of the Italians Amati, Stradivari and Guardari. Violins Majini's violin are also highly appreciated. Their violins made from well-dried and lacquer-covered maple plates and fir, sank more beautiful beautiful voices. On tools made by these masters, the best violinists of the world are played. Stradivarius still designed an unsurpassed violin, having a richest timbre and exceptional "long-range" - the ability to fill huge halls with the sound. She had inside the body of foes and irregularities, thanks to which the sound was enriched at the expense of the appearance of a large number of high overtones.
Violin is the highest tool tool on the timbre. It consists of two main parts - the housing and the grid, between which four steel strings are stretched. The main advantage of the violin is the singer of the timbre. It can perform both lyrical melodies and dazzling fast passengers. Violin is the most common soling tool in the orchestra. It was greatly expanded by the violin capabilities Italian virtuoso and composer Niccolo Paganini. Subsequently, many other violinists appeared, but no one could surpass it. Wonderful works for the violin created Vivaldi, Bach, Mozart, Beethoven, Brahms, Tchaikovsky, etc.
Outstanding Russian violinist is the festers, or, as he was called, "King David".
There is a tool, outwardly very similar to the violin, but a little bigger size. This is alto.
Mystery
In the forest carved, smoothly otseda,
Sings-poured, what is called?
(Violin)