Custom system in India. Indian castes
caste System), the system of social bundle of OB-WA, with a swarm, people are grouped in accordance with the definite. rank. Options K.S. You can find in all ind. Relig. Obrah, not only Hindu, but also at Jainists, in Musulm., Bud. And Christ. communities. The division on the caste comes from the three-tier social division of Ariii, which they invaded in North. India approx. 1500 BC. However, only Hindus have developed theological. and law. The basis of caste division of Hindu law). Three hierarchy K.S., or Varna, represented Brahmins (clergymen and intellectuals), Kshatriev (rulers, warriors and managers) and Vaishev (farmers and merchants). Each Varna shared on several. Cast, or jami, traditionally determined by occupation, but often associated with geography of residence, wedding relationships or singularities. Relig. Confirmation of the Varna-Jati system is contained in the Rigveda, the ancient text of the Vedas, where it is described as Purusha, originally space. man, was divided by the gods on Varna, each of which has distinctive features and special role in about ve. One of the prejudices of K.S. - The concept of cleanliness: the degree of pollution is determined by the genius of jami, their traditions. Power or customs. Performing naib, dirty work refer to untouchable. The latter are outside Varna, although they are part of K.S. Mahatma Gandhi, with the aim of improving the status of untouchables, renamed them to Harjanz (the children of God), but from this name. Subsequently, he refused to favor Dr. - Dalit (oppressive). Uncompaired remain the most oppressed members of the ind. Oba, despite the law, stipulates the right to state for them. work, place in educational institutions and parliament. IN last years Suggestions of such positive discrimination for others. Cast was ch. concern ind. politicians. Critics. Discrimination argue that in the Democr. System Such a policy is no more than a pre-election trick and that urbanization and modernization will gradually destroy the K.S., but its supporters refer to ch. on the resistance of k.s.
I will face, I know many IndoMan travelers who live there for months, but are not interested in caustes because it is not necessary for life.
The caster system today as a century ago is not an exotic, this is part of the complex organization of Indian society, a multifaceted phenomenon that is not already the first century of indologists and ethnographers, dozens of thick books are written about it, so I will publish here only 10 interesting facts About Indian Casters - About the most popular matters and misconceptions.
1. What is Indian Caste?
Indian caste - the phenomenon is so complicated that give exhaustively full definition Just not possible!
Castes can only be described through a number of signs, but exceptions will still be.
Caste in India - Social Stratification System, a separate public group related origin and legal position His members. Castes in India are built according to principles: 1) General (this rule is always complied); 2) one profession is usually hereditary; 3) Caster members enter only among themselves, as a rule; 4) members of the caste as a rule are not eaten with outsiders, with the exception of other Hindu castes a significantly higher social position than their own; 5) Custom members can be determined by the fact that they can take water and food treated and crude.
2. In India 4 castes
Now in India there is not 4, but about 3 thousand castes, they may be called in different parts Countries in different ways, and people with one profession may have different castes in different states. Full list Modern caste on the states, see http: // SocialJustice ...
What unnamed people On tourist and other near-Indian sites are called 4 castes - this is not a caste at all, these are 4 Varna - Coochavarnia on - an ancient social system.
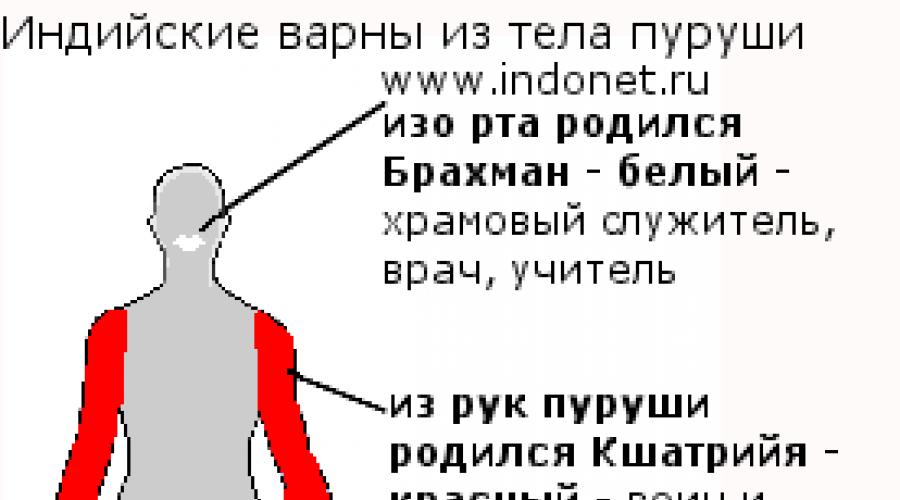
 4 Varna (वर्ना) is an ancient Indian class system. Brahmanov (more correctly Brahmin) historically are the ministers of the cult, doctors, teachers. Varna Kshatriyev (in antiquity she was called Rajan) - these are rulers and warriors. Varna Vaisya is farmers and merchants, and Varna Shudr is workers and landless peasants who work for others.
4 Varna (वर्ना) is an ancient Indian class system. Brahmanov (more correctly Brahmin) historically are the ministers of the cult, doctors, teachers. Varna Kshatriyev (in antiquity she was called Rajan) - these are rulers and warriors. Varna Vaisya is farmers and merchants, and Varna Shudr is workers and landless peasants who work for others.
Varna is a color (on Sanskrity again), and every Indian Varna - its color: Brahmins - White, Kshatriev - Red, Vaishyev - Yellow, has a black, and earlier, when all representatives of Varna wore a sacred cord - He was just their Varna.
Varna relate to the castes, but very different, there are sometimes direct links, and since we are already delighted in science, I must say that Indian castes are unlike Varn called Jati - जाति.
Read more about Indian Casters in Contemporary India
3. Caste Non-subsided
Non-suited is not a caste. During the time of the ancient India, everyone who did not enter 4 Varna, automatically turned out to be "overboard" the Indian society, these strangers were avoided, they were not allowed to live in the village, so they are called untouchables. In consequence, these non-subsided strangers began to be used on the most dirty, low-paid and shameful work, and have formed their own social and professional groups, that is, the castes are not enough, in modern India, there are several of them, as a rule, it is connected either with dirty work, or with murder living beings or death, so all hunters and fishermen, as well as gravers, and leathermen - untouchables.
4. When did the Indian caste appear?
Regulatoryly, that is, the legislative system of Cast-Jati in India was recorded in the laws of Manu, which relate to 2 centresses to our era.
The Varna system is much ancient, there is no accurate dating. In more detail about the history of the issue, I wrote in the article by the caste of India, from Varn to modern times
5. Castes in India canceled
Castes in modern India are not canceled and not prohibited, as often writes.
On the contrary, all the castes in India are recalculated and listed in annex to the Indian Constitution, which is also called the CAST table. In addition, after a census of the population, changes are made to this table, as a rule, an add-on is not that new castes appear, but that they are fixed in accordance with the data specified about themselves by the census participants.
Only discrimination on the basis of the caste is prohibited, this is written in Article 15 of the Indian Constitution, see at http: //lawmin.nic.in ...
6. Each Indian has a caste
No, it also does not correspond to reality.
Indian society is very heterogeneous by its structure, and except for dividing on the caste there are several others.
There are caste and non-caste, for example, representatives of Indian tribes (Aborigines, Adivasi) with rare exceptions do not have castes. And part of the non-caste indians is quite large, see the results of the census, see http: //censusindia.g ...
In addition, for some misconduct (crimes), humans can be expelled from the caste and thus deprive of his status and position in society.
7. Castes are only in India
No, this is a delusion. Castes are in other countries, for example, in Nepal and Sri Lanka, since these countries have developed in Lona all the same enormous Indian civilization as well as on. But the caste has both in other cultures, for example, in Tibet, and the Tibetan castes with Indian will not correlate at all, since the texture structure of the Tibetan society was formed from India.
About the castes of Nepal, see Ethnic Mosaic Nepal
8. Caste is only in Hindus
No, now it is not so, you need to go deep into history.
Historically, when the overwhelming part of the population of India professed - all the Hindus belonged to any caste, the exception was only expelled from Cast Paria and Natives, tribal peoples India, who did not confess Hinduism and were not included in the Indian Society. Then other religions began to spread in India -, India was subjected to invasions from other peoples, and representatives of other religions and peoples began to adopt the Hindus of their class system of Varna and a professional caste system. Now the castes are in Jaisinme, Sikhism, Buddhism and Christianity, but they differ from the Hindu Cast.
It is curious that in Northern India, in the modern states of Pradesh and the system of caste Buddhists is not Indian, but Tibetan origin.
It is even more curious that even Europeans are drawn into the Indian caster's system - Christian preachers: those who preached the teachings of Christ to High-Room Brands were in the Christian "Brahmin" Caste, and those who communicated with non-fishermen became Christian untouchable.
9. Indian Cast, with whom you communicate, you need to know and behave accordingly
This is a commodity misconception, constructed by tourist sites is not known for anything, nothing is found.
To determine which caste the Indian applies only in its mind it is impossible, according to his occupation - often too. One friend worked as a waiter, although it took place from a noble Rajputsky kind (that is, he is Kshatriya). I managed to identify behavior as an aristocrat as a familiar behavior, since we were familiar for a long time I asked and he confirmed that this is true, and the guy works not because of the lack of money at all.
My old friend Began his own labor activity At 9 years old as a handyman, removed the trash in the shop ... Do you think it's a sudra? No, he is Brahmin (Brahman) from poor family and 8 child account ... Another 1 familiar Brahmin trades in the shop, he is the only son, you must earn ...
Another my friend is so religious and brighted that it would be possible to think that he was real, perfect Brahmin. But no, he is just a sudra, and he was proud of it and those who know what the Seva would become clear why.
And even if the Indian will tell what he is a caste, although this question is considered not decent - anyway, this will not give anything to the tourist, a person who does not know India, not to understand what and why it works in this an amazing country. So you are not worth puzzled by a caste, because India is sometimes difficult to install even the floor of the interlocutor, and it is probably more important :)
10. Custom discrimination in our time
India is a democratic country and in addition to the ban of custom discrimination introduced benefits for representatives of lower castes and tribes, for example, there are quotas for admission to higher educational establishments, to occupy posts in state and municipal authorities.
Discrimination of people from the lower castes, dalitov and tribal people in India are quite serious, Casteism is still the basis of the life of hundreds of millions of Indians outside of major cities, it is there that still remains a custom structure and all prohibitions from it, for example, in some temples of India Indians are not allowed, it is there that almost all caste crimes occur, for example, a very typical crime

Instead of pre-school.
If the CAST system in India interests you seriously can recommend that the section of articles on this site and publications in Hindunet to read large European indologists of the 20th century:
1. Academic 4-Tomny Labor R.V. Russell "and Caste Central Provincial India"
2. Monograph Louis Dumon "Homo Hierarchicus. Experience description of the system of caste"
In addition, in recent years, a number of books on this topic issued in India, unfortunately they did not hold them in their hands.
If you are not ready to read scientific literature - Read the novel of the very popular modern Indian writer Arundhati Roy "God of Small Thoms", it can be found in RuNet.
Sometimes it seems that we are so accustomed to the XXI century with its equality, civil society, as well as development modern technologiesthat the existence of strict social layers in society is perceived with surprise.
But in India, people live, belong to some particular caste, (which determines the volume of rights and obligations), from the times that existed before our era.
Varna
Initially indian people divided into four classes, which were called "Varna"; And this division appeared due to the decomposition of the primitive-communal layer and the development of property inequality.
Belonging to each of the estates was determined exclusively by birth. Even in Indian laws, Manu can find a mention of the following Indian varnars that still exist to this day:
- . Brahmins have always been the highest layer in the custom system of the Honorary Castle; Now these people are mainly spiritual dignitaries, officials, teachers;
- Kshatriya - Warriors. The main task Kshatriev was the guard of the country. Now, in addition to the service in the troops, representatives of this caste can occupy various administrative positions;
- Vaisya - farmers. Engaged in cattle breeding and trade. Basically, these are finance, banking, since Vyachya preferred not to participate in the processing of the Earth directly;
- Speuds - infrigious members of society that do not have all the full rights; The peasant layer, which was originally subordinate to other higher castes.
State administration focused in the hands of the first two Varna. To move from one Varna to another categorically forbidden; There were also restrictions on mixed marriages. You can learn more about this from the article "".
Caste
Gradually, a custom system is formed in India. Varna is beginning to share on the caste, and each caste is characterized by a certain profession. Thus, the caste division reflected the public division of labor. Until now, in India, Vera is very strong in the fact that, observing all the rules of the caste and not disturbing the prohibitions, a person in next life Go to a higher Casta (and those who violate the requirements, waiting for a decrease in the social staircase).
Castes in modern India
Caste, as social organization In society, there is everywhere throughout India, but in each region it can be their own. Moreover, each caste contains a lot of podcast (jati), which makes them  the number is really countless.
the number is really countless.
All this even led to the fact that in the censions of the population ceased to consider belonging to the caste, because every year their number more and more increases.
For example, there are tailor castes (Darzi), waterpaths (JKHINVAR), garbered (Bhang) and even caste Brahmanov, living thanks to the alms (Bhattra).
Sure, custom system In modern India, it has not been long for the meaning that she was attached to ancient times. Now the tendency towards reducing the influence of caste, social layers on the lives of residents of the country.
If almost everything was determined social origin, now, for example, and promotion in service is possible thanks individual characteristics, skills and skills of a person, and not only because of birth.
Unprofitable
- this is a special name of some castes that occupy the most low position In modern India (and, this is as much as 16% of the country's total population).
Non-affected are not included in the four Indian Varna, but are as it were beyond this system, and even outside the society as a whole. They are engaged in the most dirty work - cleaning of toilets, dead animals, etc.
It is believed that representatives of this caste group are able to insult other Varna, especially Brahmins. For a long time, even temples remained closed for untouchables.
Ascending to the ancient Indian Varna and sanctification, the caste ancient system was the basis of the social structure of India. Belonging to one or another caste was associated with the birth of a person and determined his status for his entire life. At times, life made amendments to a rigid scheme: the rulers of states and the principalities acquired the status of Kshatriya from the Wedrel. The same status was acquired by those ingenians who, like Rajput, remained primarily by the warrior and thereby served the functions of ancient kshatriys. In general, the varnarious-caste status of Kshatriys, more than other political conditioned and therefore, very dynamic factors, was quite flexible in this sense. It was much more tough was the hereditary status of Brahmins: it was very difficult to lose, even when Brahman stopped being a priest and was engaged in other, much more worldly causes, but even more difficult, it was almost impossible to gain, rebound. As for Vaishiyev and Sudra, the difference between them in the status hierarchy from antiquity everything decreased and was almost now small, but the edge changed somewhat: the castes of merchants and artisans began to belong to the Visiam, and the farmers were mostly. The proportion of extrakast rogue, untouchables (Haridjan, how they began to be called later), who performed the most severe and dirty work.
The varnaro-caste system as a whole due to its rigid hierarchyness was the backbone of the social structure of India; Unique in shape, it not only turned out to be an effective alternative to the weak political administration (and maybe, on the contrary: its uniqueness caused to life and led to the weakness of the state administration - for which a strong administrative system is needed, if there is no lower link, if the bottoms live according to the laws Self-regulating caste principles and community standards?), but also successfully compensated for this weakness, although this kind of compensation, as was already discussed, did not contribute to the political stability of states in India. However, the society as a whole from this instability did not suffer - this traditional India was also profitable from Islamic states, and from the Far Eastern, where the state crisis was consistently reflected on the well-being of society.
The fact is that the varnaro-caste system for any political perturbations very successfully retained the unshakable status quo in the lower floors of society. Of course, the society was not indifferent, go war or not; From them, Indian bases, like everywhere, suffered a lot. And it is not about the fact that society bolitted when States led each other armed struggle for power. Meaning something other: this struggle did not led to the crisis in social structure And did not coincide with something like that. And the uphety political struggle for power did not noticeably affected the main mass of Indians. And here playing her important role Not only a varnaro-caste system, but also the traditional Indian community, built on the basis of the same system.
Community form of the organization of farmers is universal. The specifics of India was not the fact of the existence of the community there, albeit even strong, and then the place which community is due to the existence of the varnaro-caste system in the social and economic structure of society. IN a certain sense It can be said that the structure of the Indian community and its internal relations were an unbreakable microcosm of the Indian society, which, in turn, as Macrocosm copied this structure. What did this cell be reduced to?
The traditional Indian community in its medieval modification was, especially in the south, complicated social education. Geographically, it usually included several neighboring villages, sometimes a whole district, organizationally combined into something in one. In each of the villages there were their heads, often the community council (pouch), and representatives of each village, the elders and members of Parachet, were included in the community council of the whole major community. In the north of the country, where communities were smaller, they could consist of one large village and adjacent to it several neighboring small villages and have one older and one community council. He headed by the Council, elected often from the number of farmers in one, dominant in the pancaste, the community was a self-regulating mechanism or, more precisely, a social organism, practically almost no contact with the outside world. Inner life The communities, strictly regulated by the norms of the community routine and caste, was obeyed by the same principle of Jadzmani, studied by experts relatively recently, on the example of a fairly late Indian community, but clearly leaving roots in the depths of centuries. Its essence was reduced to a strictly compulsory reciprocal exchange, to strictly and well-adjusted for centuries in relation to the relationship with the products and services necessary to everyone in the community-based framework - in mandatory accordance with the norms of the varnaro-caste hierarchy.
Dominated in the community full of its members, community farmers who owned communities put on them and had the hereditary right to them. Powers could have been different. Each family, big or small, led the farm individually on its plot, which could sometimes even alternate, albeit under the control of the community. Not all landowners in the community themselves treated their sections. The most prosperous families, most often Brahmansky, used the work of small-earth neighbors, giving them to rent their land. It was also used by the work of incomplete members of the community, mercenarm - mercenaries (carmakars), etc. It was too good to say that the poor and incolment-free, tenants and even more so the battles most often belonged to the lower caustes. Moreover, the entire caste system of compulsory reciprocal interchange (Jadzmani) comes down first of all to consecrate and legitimize the social and property inequality in the community, as in society as a whole. Representatives of the higher caste had, according to the established standards, the undeniable right to enjoy literally for the guys of the services of immigrants from the lower castes and the more unacpended, to which it should also be treated with contempt. And that is characteristic: such a right to nobody has never been exposed to the shadow of doubt. So it is necessary, this is the norm of life, the law of life. This is your destiny, such is your karma - the caste tops of the community, and caste and extra beds lived with such consciousness.
In practice, the principle of Jadzmani meant that every member of the community - be it an agriculture, a bareman, rich brahman, an artisan, a despised cattle kidder or a garrist, a laundry, etc. - in a word, each in its place and in strict accordance with its caste It was not only clear to know his place, rights and obligations, but also strictly fulfill all the fact that others have the right to expect from him. Actually, this was exactly what the community is self-regulating and viable, almost independent of contacts with foreign world. At the same time, the principle of Jadgemani did not mean at all that everyone who enjoyed by the work, products and services of others, for this equivalently pays - the more precisely with those who gave him or did it. Most often, the case was just the opposite: everyone performed her duties, serving everyone else, giving others what he had to give, and at the same time necessary for his life (in accordance with the conditioned custom quality of his life) products and services. Outside the Jadzmani system in the community there were only private transactions of the type of rental or hiring a barrack. Everything else was tightly tied by this traditional system of interconnection in strict accordance with caste duties and the position of each of those who lived in the community.
Led all complex system Internal relations Community Council, who also disassembled complaints, spoke the court, carried out sentences, that is, was simultaneously the governing body of the Corporation (community), and the authority in the field. A significant role in the council was played by the headman, the prestige of which was high, and the income is usually too. For the outside world, and in particular, for the administrative and political and fiscal system of the state, it was the headman who was the representative of the community, and the agent of the government in the field responsible for the payment of taxes and order.
A kind of option for the community-caste system was the organization of Indian cities. In the cities of the caste played, perhaps, more big roleThan in the community village - at least in the fact that the communities here were usually one-window here, that is, the entire co-writing coincided, whether it was the workshop of representatives of any craft or the guild of merchants. All artisans and merchants, all the labor population of the city strictly shaped on the caste (caste of weaves, gunsmiths, dyeers, vegetable oil traders, fruit, etc.), and representatives of related or related castes, I have often connected to larger specialized specialized Sregna Corporation, also headed by advice and managers responsible for the authorities. Indian craft - weaving, jewelry, etc. - famous for the whole world. Trade relations joined Indian cities with many countries. And in all these links, the role of caste and corporations of urban artisans and merchants who solved all the issues and regulating their members, from the rationing and quality of products to litigation and donations in favor of the temples.
We already live in the 21st century and think that many secrets of science and technology are already revealed, many social issues are allowed, etc. Despite all these achievements, there are still places where todayday social Society They are divided into different layers - castes. What is the CAST system? Caste (from Portuguese Casta - Rod, Generation and Origin) or Varna (Translation from Sanskrit - Color), The term applied primarily to the main division of the Hindu Society on the Indian Subcontinent. According to Hindu belief, there are four main Varna (caste) - Brahmans (officials), Kshatriya (warriors), Vaishi (merchants) and shudras (peasants, workers, servants). From the most early works Sanskrit literature It is known that the peoples who spoke on the Aryan adverbs during the initial settlement of India (approximately from 1500 to 1200 BC) have already been divided into four main estates, later called by Varna. Modern caste They are divided into a lot of podcast - jati. Hindus believe in reincarnation and believe that one who keeps the rules of his caste in of the future life Racing by birth in a higher Casta, the same who violates these rules will lose social status. Brahmans Brahmans are the highest layer of this system. Brahmins serve spiritual mentors, work with accountants and accountants, officials, teachers, master the lands. They are not supposed to go for a plow or carry out certain types of work related to manual labor; Women from their environments can be serving in the house, and landowners to handle outwards, but not to plow. Members of every Brahmansky caste concludes marriage only in their circle, although it is possible to marry the bride from the family belonging to a similar podcast from the neighboring area. In the choice of food, Brahman observes many prohibitions. He is not entitled to use food, cooked outside his caste, but from the hands of Brahmans can eat members of all other castes. Some brahmin podcasts can use meat. Kshatriyi Kshatrii stand immediately behind the brahmanas in a ritual attitude and their task, mainly to fight, guard their homeland. Today, the classes of Kshatriy are the work of managers in the estates and service in various administrative positions and in the troops. Most of the kshatriy use meat and, although allowing a marriage with a girl from lower podcasts, but a woman in no way can marry a man's podcasts below her own. Vaishi Vaishi - layers that are engaged in trading. Waisy more strictly follow the rules relating to food, and even more carefully try to avoid ritual desecration. Traditional occupation Vaishiyev served trade and banking, they seek to stay away from physical labor, but sometimes included in the management of landowners and village entrepreneurs, directly not participating in the processing of the Earth. Studs "clean" shudras - peasant caste. They, due to their number and possession of a significant part of local land, play an important role in solving social and political issues of certain areas. Studras eat meat, marriage of widows and divorced women are allowed. Lower shudras are numerous podcasts whose profession is purely specialized. This is a caste of gonchars, blacksmiths, carpenters, carpets, weales, maslodes, vinokurov, masonry, mercenaries, musicians, leather goods, butchers, garbers and many others. Non-affected unsuccessful - those engaged in the most dirty works, in many respects they are outside the Hindu Society. They are engaged in the cleaning of dead animals from streets and fields, toilets, stretching of leather, etc. It is forbidden to visit the houses of "clean" castes and take water from their wells, they are even forbidden to attack the shadows of other castes. Most Hindu temples until recently were closed for untouchables, there were even a ban approach people from higher castes closer than the set number of steps. The character of caste barriers is such that it is considered as if they continue to desecrate the members of the "clean" caste, even if they have long left their caste lessons and are engaged in ritually neutral activities, for example farming. Although in other social conditions and situations, for example, being in an industrial city or in a train, the untouchable may have physical contact with members of higher castes and not to desecrate them in their native village Non-rehabilitation of it from him, no matter how he does. Throughout Indian history, the custom structure demonstrated amazing stability before change. Nor Buddhism nor Muslim invasion ended with the formation of the Mughal Empire nor the establishment of British domination did not lay the fundamental foundations of the company's customic organization.