Society is a dynamic system. Society as a complex dynamic system
In determining the concept of "society" in the scientific literature, there is a variety of approaches, which emphasizes the abstract nature of this category, and, defining it in each particular case, it is necessary to proceed from the context this concept is used.
1) Natural (influence of geographical and climatic conditions for the development of society).
2) Social (causes and initial moments of social development are due to the Society itself).
The combination of these factors predetermines social development.
There are various ways of development of society:
Evolutionary (gradual accumulation of changes and their natural-conditioned character);
The revolutionary (characterized by relatively rapid changes subjectively directed on the basis of knowledge and actions).

Diversity of paths and forms of social development
Public progress in the XVIII-XIX centuries created. Labor J. Condorse, G. Hegel , K. Marx and other philosophers were understood as a regular movement in one for the whole mankind. On the contrary, in the concept of local civilizations, progress is presented in different civilizations in various ways.
If you mentally observe the course of world history, then in the development of different countries and peoples, notice a lot in common. The primitive society was changed everywhere with a society managed by the state. Centralized monarchies came to replace the feudal fragmentation. In many countries, bourgeois revolutions occurred. The colonial empires collapsed, and dozens of independent states arose in their place. You yourself could continue the listing of similar events and processes that took place in various countries on different continents. In this similarity, the unity of the historical process is manifested, a certain identity of replacing each other orders, the community of fate of various countries and peoples.
At the same time, concrete ways of development of individual countries and peoples are diverse. No peoples, countries, states with the same history. The manifold of specific historical processes is caused by the difference in natural conditions, and the specifics of the economy, and the originality of spiritual culture, and the pattern of lifestyle, and many other factors. Does this mean that each country is predetermined its own development option and is it the only possible? Historical experience suggests that in certain conditions there are various options for solving the urgent problems, it is possible to choose methods, forms, ways to further development, i.e. a historical alternative. Alternative options are often offering certain groups of society, various political forces.
Recall that when preparing Peasant reform conducted in Russia in 1861, various public strengths offered unequal forms of change in the life of the country. Some defended the revolutionary path, others - reformist. But among the latter there were no unity. Several options for reforms were offered.
And in 1917-1918. A new alternative arose before Russia: either the Democratic Republic, one of whose symbols was the nationally elected constituent meeting, or the Republic of the Soviets led by the Bolsheviks.
In each case, the choice was made. Such a choice is made by state leaders owned by the elites, folk masses depending on the relationship between the strength and the influence of each of the stakeholders.
Any country, any people at certain times of history find themselves before the fateful choice, and its history is carried out in the process of implementing this choice.
The multivariates of the paths and forms of social development is notless. It is included in the framework of certain trends in historical development.
So, for example, we have seen that the elimination of the existing serfdom was possible in the form of a revolution, and in the form of reforms carried out by the state. And the granted need for accelerating economic growth in different countries was carried out either by attracting new and new natural resources, i.e. extensively, or by introducing new equipment and technology, improve the qualifications of workers, based on the growth of labor productivity, i.e. intensive way. In different countries or the same country, various options for implementing the same type of change can be used.
Thus, the historical process in which general trends are manifested - the unity of diverse social development, creates the possibility of choice, on which the originality of ways and forms of further movement of this country depends. This indicates the historical responsibility of those who make this choice.
In accordance with the point of view common among the sociologists, society is a complex dynamic system. What does this definition mean? What characterizes society as a dynamic system?
- study of the term "dynamic system";
- the study of practical examples reflecting the legality of the considered definition of society.
Let's study, thus, their more.
What does the term "dynamic system" mean?
Dynamic, or dynamic system is the originally mathematical term. In accordance with the common theory within the framework of this accurate science, it is customary to understand the combination of elements, the position of which in the phase space changes over time.
Translated into the language of sociology, this may mean that society as a dynamic system is a combination of subjects (people, communities, institutions), the status of which (activity) in the social environment changes over time. How legitimate is this statement?
In general, it fully reflects social reality. Each person over time acquires new statuses - during the preparation of education, socialization, due to the achievement of legal personality, personal success in business, etc.
Communities and institutions also change, adapting to the social environment in which they develop. Thus, public power can be characterized by a large or smaller level of political competition, depending on the specific conditions of the country's development.
In terms of which the word "system" is present. First of all, it assumes that the corresponding elements characterized by dynamic features play a steady role. So, a person in society has civil rights and obligations, and the state is responsible for solving the tasks of "on the macro level" - such as the protection of borders, the management of the economy, the development and execution of laws, etc.
There are other essential signs of systemic. In particular, this is self-sufficiency, some sovereignty. Regarding society, it is able to be expressed in the presence of all the institutions necessary for its functioning: rights, government, religion, families, production.
The system is usually characterized by such a property as self-governess. If we talk about society, it can be mechanisms that ensure effective regulation of certain social processes. Their development is carried out at the level of the marked institutions - in fact, these are their main role.
The following system indicator is the interaction of its component elements with others. The person thus carries out communications with society, institutions, individuals. If this does not happen, then the society is simply not formed.
It can be concluded that society as a dynamic system characterizes the following basic properties:
- there is a change in the status of the components of its elements over time;
- there are sovereignty implemented due to the presence of formed key social institutions;
- self-governess is realized, thanks to the activities of social institutions;
- the constant interaction of the elements constituting society is carried out.
Let us now consider how the dynamism of society can be traced in practical examples.
Society Dynamism: Practical examples
Above, we noted that a person is able to change, mastering new knowledge and skills or, for example, achieving success in business. So, we marked one of the practical examples of dynamism in society. In this case, the corresponding property is characterized by a person as a society element. It becomes a dynamic subject. Similarly, we led to an example of a change that characterize the activity of state power. Subjects of political governance are also dynamic.
Public institutions can also change. Among the most indicative areas for which very intensive dynamism is peculiar is the right. The laws are constantly adjusted, complemented, canceled, returned. It would seem that the conservative institute as a family should not change much - but it also happens. The polygamy that existed in the East may experience a significant impact of Western monogamous traditions and becomes an exception to the rules in those countries where it is traditionally perceived as part of the cultural code.
Sovereignty of society, as we noted above, is formed as key social institutions formation. In addition, as soon as they appeared - dynamism begins to acquire systematic.

A person gets the opportunity to change, acting regardless of people belonging to other societies. The state can adjust the mechanisms of organization of political governance, without consulting, conventionally speaking, with metropolis and other entities capable of providing a potential impact on the adoption by the authorities of certain decisions. The legal system of the country may begin to regulate those or other public relations, based on their local specifics, and not under the influence of foreign trends.
One thing is to have sovereignty. Another thing is to use it effectively. State, legal, public institutions should function correctly - only so sovereignty will be real, not formal. And only on this condition, the society as a dynamic system will acquire a fully systemic nature.
Criteria for the quality of the relevant elements of society can be the most different.
So, as regards the Institute of Law, it must be characterized: the relevance (laws should not be lagging behind the current social processes), the general competition (equality of citizens to legislative provisions), transparency (people need to be understood how certain norms are taken, and if possible - participate in the process of lawmaking).
The institution of the family must function in the interests of at least the majority of people who are society, and ideally all citizens. At the same time, if it is assumed to incommens to certain landmarks - for example, monogamions and polygamy, then other social institutions (right, the state) should contribute to peaceful joint residence of people who consider themselves adherents of the relevant principles.
And this traces the mutual influence of elements forming society. Many of the subjects cannot play their role in society without interaction with others. Key public institutions are always related. State and law - elements constantly carrying out communications.
Man also acts as a social entity. If only because he communicates with other people. Even if it seems to him that he does not, - some derivatives from personal communications will be used. For example, living on a uninhabited island and reading a book, a person, perhaps, and not suspecting this, "communicates" with its author, taking his thoughts and ideas - literally either through artistic images.
Man is a reasonable creature. He chooses housing, food and where to attach strength. However, it is pointless to have freedom of choice, if no one will appreciate your choice.
We need society. Nature has endowed us unchanged trait - thirst for communication. Thanks to this feature, we think not only about yourself. Within the family or a whole planet, a person makes decisions for the sake of general progress. Thanks to the thirst for communication, we pushing the world forward.
It cost our ancestors to descend from the palm trees, they encountered the increasing hostility of nature. Little primacy could not defeat Mammoth. Natural skins are not enough to warm up in winter. Sleep outdoors dangerous in triple.
Nazable consciousness understood - you can only survive. The forefathers have created a primitive language to understand each other. They were going to the community. Communities were divided into castes. The hunt went strong and fearless. The offspring was grieved soft and understanding. Shackles built smart and practical. Already then the person was engaged in what was predisposed.
But nature gave only rude raw materials. From some stones it is impossible to build a city. Stones are hard to kill the animal. The rapids studied to process materials to work more efficiently and live longer.
In widespread definition society- tightened a part of nature, using the will and consciousness for survival.
In the group, we can not spray for superficial knowledge. Each of us has their inconsistencies. Professional plumber and for a million salary will not be happy to grow bonsai - brains are sharpened technically. The union allows us to do your favorite thing, and the rest is entrusted with others.
Now we understand a narrow definition societies - a conscious meeting of personalities for work for the common goal.

Society as a dynamic system
We are cogs in the social mechanism. Objectives determines not someone alone. They come as common needs. Society due to the strength of individual members solves an endless flow of problems. Decision search forces society to become better and generates new complex problems. Humanity is building himself, which characterizes society as a dynamic system capable of self-development.
Society has a complex dynamic structure. Like any system, it consists of subsystems. Subsystems in the group are divided by the spheres of influence. Sociologists celebrate four subsystems of society:
- Spiritual - responsible for the culture.
- Political - regulates relations with laws.
- Social - Caste separation: nation, class, social layer.
- Economical - Production and distribution of goods.
Subsystems are systems in relation to individual members. They work only when all the elements are in place. Both subsystems and individual parts are inextricably linked. Without production and regulation, spiritual life loses its meaning. Without a person, another life is not sweet.
The social system is continuously moving. It is driven by the subsystem. Subsystems are moving due to elements. Elements are divided into:
- Material - Plants, dwellings, resources.
- Ideal - Values, ideals, beliefs, traditions.
Material values \u200b\u200bare more characterized by subsystems, while ideal - human trait. Man is the only indivisible element in the social system. Human has the will, aspirations and beliefs.

The system works due to communication - social relationship. Social relations are the main binder of the link between people and subsystems.
People play roles. In the family we play an exemplary father. At work, unquestioned subordination is waiting for us. In the circle of friends we are the soul of the company. We do not choose role. They dictate our society.
Every person has one person, and immediately several. Each person in its own way behaves in different situations. You can't scold the boss just like a child, right?
Animal has a fixed social role: if the leader "said" that you will sleep below and is the last, it will be all my life. And even in another flock, the person will never be able to take the role of a leader.
Man is universal. Every day we put there are dozens of masks. Thanks to this, we easily adapt to different situations. You are the main thing that you understand. You will never demand submission from a competent leader. Magnificent survival mechanism!

Scientists share social relations:
- between individuals;
- inside the group;
- between groups;
- local (indoors);
- ethnic (within the framework of race or nation);
- within the organization;
- institutional (within the borders of the Social Institute);
- inside the country;
- international.
We communicate not only with whom we want, but also if necessary. For example, we do not want to communicate with your colleague, but he sits with us in one office. And we must work. therefore relationships are:
- informal - with friends and friends, whom we ourselves have chosen;
- formalized - With whom we are obliged to contact by necessity.
You can communicate with like-minded people and with enemies. There are:
- cooperative - cooperation relations;
- competitive - confrontation.

RESULTS
Society - complex dynamic system. People only once launched her, and now she defines each stage of our life.
- flexibility - regulates all spheres of life, even if they have not appeared yet;
- mobility - continuously changes as needed;
- complicated filed mechanism from subsystems and elements;
- independence - society itself creates conditions for existence;
- interconnection all elements;
- adequate reaction On changes.
Thanks to the dynamic social mechanism, a person is the most lively creature on the planet. For only a person changes the world around him.
Video
From the video you will learn that there is a society, his concept and the relationship of man and society.
Didn't get the answer to your question? Offer authors the topic.
SOCIETY
Society and Nature
Culture and civilization
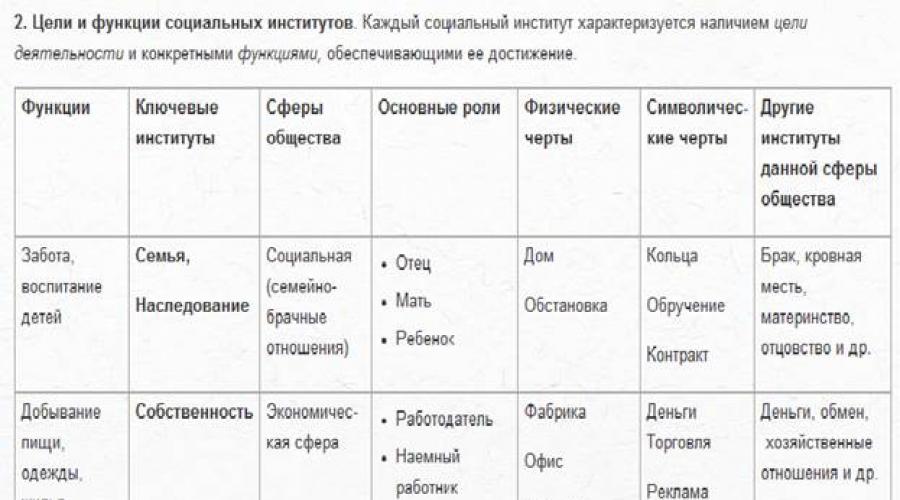
The most important institutions of society
society - this is a certain group of people
You can determine society And as big,
society and Nature.
Society and Nature
culture
1. "Exactly
question about O. legal protection of nature .
Legal protection of nature
.
.
Public relations
An important role in the functioning of society is played public relations. This concept is denoted by diverse ties arising between social groups, classes, nations, as well as within them in the process of economic, social, political, cultural life and activity.
Material public relations There are in the field of production, during practical activities. Material relations are divided into industrial, environmental and attitudes.
Spiritual relations As a result of the interaction of people in the process of creating and distributing spiritual and cultural values. They are divided into moral, political, legal, artistic, philosophical and religious public relations.
Special view of social relations are interpersonal (ie Relations between individual individuals).
Evolution and revolution
There are two main ways of change - evolution and revolution. Evolutioncomes from the Latin word "deployment" -
these are slow, constant changes in the preceding state. The revolution(from Latin turn, change) is a change in all or most of the parties to social life affecting the foundations of the existing social system.
At first glance, the revolution differs from evolution only by the tempo of changes. However, in philosophy there is a point of view of the relationship of these two phenomena: the increase in quantitative changes in development (evolution) in the end leads to a qualitative change (revolution).
In this regard, the concept of the evolutionary path in public development is close reform. Reform - This is a transformation, reorganization, a change in any part of social life, which does not destroy the foundations of the existing social structure.
Reforms in Marxism were opposed to the political revolution, as an active political action of the masses, leading to the transition of the management of the company in the hands of a new class. At the same time, revolutions were always more radical and progressive by transformation in Marxism, and reforms were considered as half, painful for the masses, transformations that mostly were allegedly due to the potential threat of revolution. Revolutions are inevitable and natural in society, where timely reforms are not held.
However, political revolutions usually lead to great social shocks and victims. Some scientists generally denied revolutions in the possibility of creative activities. So, one of the historians of the XIX century compared the Great French Revolution with a hammer, which only broke the old clay forms, opening the world an already cast bell of a new social system. Those, in his opinion, the new public system was born in the course of evolutionary transformations, and the revolution only bold obstacles for him,
On the other hand, the story knows the reforms that led to indigenous transformations in society. F. Engels, for example, called the "revolution from above" the reform of Bismarck in Germany. The "revolution from above" can also be considered the reforms of the late 80s - early 90s. XX century, which led to a change in the existing structure in our country.
Modern Russian scientists recognized the equivalent to reforms and revolutions. At the same time, the criticism of revolutions, as an extremely inefficient, bloody, replete, with numerous costs and leading to the dictatorship of the journey. Moreover, great reforms (that is, revolutions from above) are recognized as the same social anomalies as the great revolutions. Both of these methods of solving public contradictions are opposed to normal, healthy practice "permanent reform in self-regulating society."
And reforms and revolutions are treated already launched disease (the first - therapeutic methods, the second - surgery. Therefore, constant innovation - as a single one-time improvement associated with an increase in the adaptability of society to changing conditions. In this sense, innovation is similar to the prevention of the occurrence of the disease (i.e. social contradiction). Innovation in this respect belong to the evolutionary path of development.
This point of view comes from opportunities for the alternativeness of social development. Neither the revolutionary nor the evolutionary path of development can be adopted as the only lawsuit.
Culture and civilization have been identified for a long time. but Culture and civilization
already in the XIX century, the scientific meaning of these concepts differed. And at the beginning of XX
centuries German philosopher O. Spengler in its work "Sunset Europe"
and at all opposed them. Civilization appeared in him the highest stage of culture, on which its final decline occurs. Culture is a civilization that has not reached its maturity and not ensuring its growth.
Differences between the concepts of "culture" and "civilization" emphasized other thinkers. So, N. K. Roerich reduced the difference in culture and civilization to oppose the heart of the mind. He connected the culture with the self-organization of the Spirit, the world of spirituality, and civilization - with civil, public dispensing of our lives. Indeed, the word "culture" goes back to the Latin Word, meaning cultivation, cultivation, processing. However, the word upbringing, reverence, as well as the cult (as worshiping and reading something) rises to the same root (Cult-). The word "civilization" comes from Latin Civilis - civil, state, but the word "citizen, resident of the city" dates back to the same root.
Culture is a core, soul, and civilization - shell, body. P. K. Grechko believes that civilization records the level and result of the progressive development of society, and culture expresses the mechanism and the process of mastering this level - result. Civilization places the land, our lives, makes it comfortable, comfortable, pleasant. The culture is "responsible" for constant dissatisfaction achieved, the search for something unattainable, worthy of above all souls, and not the body. Culture is the process of humanization of public relations, human life, while civilization is gradual, but steady technologization.
Without culture, civilization cannot exist, because the system of cultural property is that a sign that distinguishes one civilization from another. However, culture is the concept of a multifaceted, it includes the culture of production, tangible relations and political culture and spiritual values. Depending on which sign, we allocate as the main criterion, the division of civilizations into individual types is changed.
Types of civilization
Depending on the concept and criteria, various researchers offer their own variants of the civilization typology.
Types of civilizations
However, division in civilization was widely established in publicist literature western (innovative, rationalistic) and oriental (traditional) type. Sometimes more so-called intermediate civilizations are added to them. What features are they characterized? Consider this using the example of the next table.
The main features of the traditional society and Western society
| Traditional Society | Western Society |
| "Continuity" of the historical process, lack of explicit boundaries between individual epochs, sharp shifts and jolts | The story moves unevenly, "jumps", gaps between epochs are obvious, transitions from one to another often take the form of revolutions |
| Incomparable concept of linear progress | Public progress is quite obvious, especially in the field of material production |
| The relationship of society to nature is based on the principle of merger with her, and not domination of her | Society seeks to maximize the use of natural wealth for their needs |
| The basis of the economic system - community-state-state forms of ownership with the weak development of the Institute of Private Property | Fundamental Economics - Private property. Ownership is considered as natural and inherent |
| The level of social mobility is low, partitions between the castes, the classes are few permeable | Social mobility of the population is high, the social status of a person can change significantly throughout life |
| The state subordinates society, controls many parties to people's lives. Community (state, ethnos, social group) have a priority to a separate person | The civil society has developed, in many respects autonomous from the state. Personality rights are prioritized and enshrined constitutionally. Personality and society relations are built on the basis of mutual responsibility. |
| The main regulator of public life - tradition, custom | Special value has readiness to change, innovations |
Modern civilization
Currently, there are civilization of different types on Earth. In remote corners of the planet, the development of a number of peoples still preserved the features of primitive society, where life is entirely subordinated by the natural cycle (Central Africa, Amazonia, Oceania, etc.). A part of the peoples in their lifestyle has retained the features of the eastern (traditional) civilizations. The influence of post-industrial society for these countries is reflected in the growing of crisis phenomena, instability of life.
Active propaganda by the media of the values \u200b\u200bof post-industrial society, the construction of them in the rank of universal values \u200b\u200bcauses a certain negative reaction from traditional civilizations, seeking not only to preserve their values, but also to revive the values \u200b\u200bof the past past.
Thus, the Arab-Islamic civilization include Iran, Afghanistan, Pakistan, the United Arab Emirates, Saudi Arabia, etc. Between individual Islamic countries and even within these countries, the struggle is exacerbated between supporters of rapprochement with Western civilization and Islamic fundamentalists. If the first allow the expansion of secular education, the rationalization of life, the widespread introduction of modern achievements of science and technology, then the second believe that the basis (foundation) of all areas of life is the religious values \u200b\u200bof Islam and occupy an aggressive position in relation to any innovations and borrowings from Western civilization.
India, Mongolia, Nepal, Thailand, etc. can be attributed to Indo-Buddhist civilization, and others. The traditions of Hinduism, Buddhism prevail, is characterized by religious tolerance. In these countries, on the one hand, economic and political structures inherent in the industrial society have developed, on the other - a significant part of the population lives by the values \u200b\u200bof the traditional society.
To the Far Eastern Confucian civilization include China, Korea, Japan, etc. The cultural traditions of Taoism, Confucianism and Sintoism dominate here. Despite the preserved traditions, these countries in recent years are convergered and developed Western countries (especially in the economic sphere).
What type of civilizational development can include Russia? There are several points of view in science on this:
Russia is the European country and the Russian civilization is close to Western Type, although it has its own characteristics;
Russia is an original and self-sufficient civilization that occupies its special place in the world. This is not an Eastern and not Western, but Eurasian civilization, for which super-ethnicity, intercultural exchange, the proper nature of spiritual values;
Russia is internally dividing, "pendulum" civilization for which the constant confrontation of Western and Eastern features is characteristic. In its history, cycles of convergence are clearly noted with Western, then with Eastern civilizations;
To determine which point of view is more objective, turn to the characteristic of Western civilization. Researchers believe that there are several local civilizations inside her (Western European, North American, Latin American, etc.). Modern Western civilization is a post-industrial civilization. Its features are determined by the consequences of the scientific and technical revolution (HTR), which happened in the 60-70s. XX century.
Global problems
The global problems of humanity are called problems regarding all people living on Earth, which depends not only by further social progress, but also the fate of all mankind.
Global problems appeared in the conditions of the scientific and technological revolution in the second half of the twentieth century, they are interrelated, cover all parties to the lives of people and concern all countries without exception.
We list the main problems and show their relationship with each other.
The threat of the thermonuclear catastrophe is closely interconnected with the threat of nuclear war, as well as technogenic catastrophes. In turn, these problems are interrelated with the threat of a third World War. All this is due to the depletion of traditional sources of raw materials and search for alternative types of energy. The nonresistance of this problem leads to an ecological catastrophe (the depletion of natural resources, pollution of the environment, food problem, a lack of drinking water, etc.). There is an acute problem of climate change on the planet, which can lead to disastrous consequences. The environmental crisis in turn is associated with a demographic problem. The demographic problem is characterized by a deep contradiction: in developing countries there is an intensive growth in the population, and in developed countries there is a demographic recession, which generates tremendous difficulties for economic and social development.
At the same time, the problem of "North-South" is exacerbated, i.e. The contradictions between the developed countries and the developing countries "of the Third World" are growing. The problems of health care and the prevention of the spread of AIDS, drug addiction are also becoming increasingly important. The problem of the revival of cultural and moral values \u200b\u200bis important.
After the events in New York on September 11, 2001, the problem of combating international terrorism sharply aggravated. The following innocent victims of terrorists can be residents of any country in the world.
In general, global problems of humanity can be schematically represented in the form of a transshipment of contradictions, where diverse threads are drawn from each problem to all other issues. What is the same the strategy for the survival of humanity in the context of global problems? The solution of global problems is possible only by the joint efforts of all countries coordinating their actions at the international level. Selfolation and development features will not allow individual countries to remain aside from the economic crisis, nuclear war, the threat of terrorism or the AIDS epidemic. To solve global problems, overcoming the danger that threatens all humanity, it is necessary to further strengthen the relationship between the diverse modern world, the change in the interaction with the environment, the refusal of the cult of consumption, the development of new values.
In the preparation of this chapter, materials from the following textbooks were used:
- Grechko PK Introduction to social studies. - M.: Pomatures, 2000.
- Kravchenko A. I. Society. - M.: "Russian Word - RS" - 2001.
- Kurbatov V.I. Social science. - Rostov-on-Don: "Phoenix", 1999.
- Man and Society: Tutorial on social studies for students of 10-11 cl. / Ed. L.N. Bogolyubova, A.Yu. Lazebechnaya. M., 2001.
- Lazebnikova A.Yu. Modern school social studies. Questions of theory and techniques. - M.: School - Press, 2000.
- Klimenko A.V., Romanine V.V. Social Score Exam: Response Abstracts. - M.: 2000.
- Social science. 100 exam answers. / Ed. B.Yu. Serbinovsky. Rostov-on-Don.: "Mar.t", 2000.
SOCIETY
Society as a dynamic system
Society and Nature
Culture and civilization
Relationship of the economic, social, political and spiritual spheres of society
The most important institutions of society
Diversity of paths and forms of social development
Problem of public progress
The integrity of the modern world, its contradiction
Global problems of humanity
The concept of "society" is meaningful. In its initial meaning, this is a certain community, union, cooperation, association of individual people.
From a sociological point of view society - this is a certain group of peopleCombined by common interests (purpose) for joint activities (for example, the society of animal protection or, on the contrary, the society of hunters and fishermen).
The historical approach to understanding society is associated with the allocation. specific stage in the historical development of any people or all mankind (for example: primitive society, medieval society, etc.).
The ethnographic meaning of the concept of "society" focuses on ethnic features and cultural traditions of a certain population of people (for example: Bushmen society, the society of American Indians, etc.).
You can determine society And as big, sustainable group of people occupying a certain territory having a common culture, feeling a sense of unity and considering themselves as a very independent education (for example, Russian Society, European Society, etc.).
What is united by the above interpretations of society?
- the Company consists of individuals who have will and consciousness;
- it is impossible to call the society just a certain number of people. People combines joint activities, common interests and goals;
- any society is a way to organize human life;
- the connected link of society, its frame, are connections that are established between people in the process of their interaction (public relations).
Society as a complex dynamic system
In general, the system is called a set of interrelated elements. For example, bricks should not be called a system, but the house built on them is a system where every brick occupies its place, is interrelated with other elements, has its own functional importance and serves as a common goal - the existence of a solid, warm, beautiful building. But the building is an example of a static system. After all, the house cannot be improved by itself, develop (it can only collapse if the functional relations between the elements are bricks).
An example of a dynamic self-developing system can be called a living organism. Already in the embryo of any living organism, the main signs are laid, which under the influence of the environment determine the essential aspects of changes in the body throughout life.
So society is a complex dynamic system that can exist, only constantly changing, but at the same time maintained the main features and qualitative definition.
There is a wide, philosophical point of view on society.
Society is the form of an organization of individuals that arose in opposition to the environment (Nature) lives and develops in its own objective laws. In this sense, society is a set of forms of association of people, "team collective", all of humanity in its past, present and future.
Based on this wide interpretation, consider the relationship society and Nature.
Society and Nature
And society and nature are part of the real world. Nature is the basis on which society originated and develops. If naturally understand the whole reality, the world as a whole, the society acts as part of it. But often the word "nature" denote the natural habitat of people. With such an understanding of nature, the Company can be viewed as part of the real world, but society and nature did not lose their relationship. This relationship always existed, but changed over the centuries.
Once in primitive times, small societies of hunters and collectors completely depended on the cataclysms of nature. Trying to defend from these cataclysms, people created cultureAs a totality of all the material and spiritual values \u200b\u200bof society, having artificial (ie, not natural) Origin. Below we will not talk about the diversity of the concept of "culture". Now we emphasize that culture is what is created by society, but the oppositely natural environment, nature. So, the manufacture of first tools of labor, the skills of fire production are the first cultural achievements of humanity. The appearance of agriculture and cattle breeding is also the fruits of culture (the word culture itself comes from the lat. "Soil processing", "cultivation").
1. "Exactly due to the dangers that nature threatens us, we also united and created culturedesigned by the way to make our social life possible. - wrote Z. Freud. - In the end, the main task of culture, a genuine justification - protection of us from nature. "
2. As the cultural achievements develop, the society is no longer so depended on nature. Wherein society did not adapt to nature, but actively changed the environment, transforming it in its own interests.. This change in nature led to impressive results. Recall thousands of types of alcoholic plants, new types of animals, drained swamps and blooming deserts. However, society, transforming nature by exposing it to cultural impact, often guided by momentary benefits. Thus, the first environmental problems began to occur in antiquity: many species of plants and animals completely disappeared, most of the forests in Western Europe were cut back in the Middle Ages. In the twentieth century, the negative impact of society in nature became particularly tangible. Now we are talking about an ecological catastrophe, which can lead to the destruction and nature and society. therefore question about O. legal protection of nature .
Under the protection of the environmental environment, it is understood as the preservation of such its quality, in which, firstly, the preservation, protection and restoration of the healthy state and the integrity of the Earth's ecosystem, and secondly, the preservation of the biological diversity of the planet.
Environmental law is engaged in legal protection of nature. Ecology (from the "ECOS" - House, location; and "Logos" knowledge) is a science of human and society interaction with a natural habitat.
The environmental legislation of the Russian Federation includes a number of provisions of the Constitution, 5 of the Federal Law on Environmental Protection, 11 Non-Purchase Legislative Acts, as well as decrees of the President of the Russian Federation, the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation, etc.
Legal protection of nature
So in the Constitution of the Russian Federation in Art. 42 refers to the right of every person on a favorable wedliness on reliable information about its condition. Article 58 indicates the duties of each to preserve nature and the environment, carefully refer to the natural wealth of Russia.
The legal protection of nature is devoted to federal laws on the protection of the environmental environment (1991), "On Environmental Expertise" (1995), "On the Protection of Atmospheric Air" (1999), etc. Attempts to conclude an international treaty on nature protection are being made. December 12, 1997 was signed in the city of Kyoto International Protocol on the regulation of industrial waste emissions to the atmosphere (Kyoto Protocol).
Thus, the relationship of nature, society and cultures can be designated as follows:
society and Nature in relationships form the material world. However, society was aligned with nature, creating a culture as a second artificial nature, a new habitat. However, even protecting himself from nature a kind of border of cultural traditions, society is not able to break relations with nature.
V. I. Vernadsky wrote that with the emergence and development of society biosphere (earth sheath, covered by life) goes to the nosphor (region of the planet, covered by reasonable human activity).
Nature and now has an active impact on society. So, A. L. Chizhevsky established the relationship between the cycles of the activity of the Sun and the social shocks in society (war, uprising, revolution, social transformations, etc.). L. N. Humilyov wrote about the impact of nature to society in his work "Ethnogenesis and the Biosphere of the Earth".
The relationship of society and nature We see in a variety of manifestations. So, improving the agrotechnical techniques of the cultivation of the soil leads to an increase in yield, but an increase in air pollution by industrial waste can lead to the death of plants.
Society is a complex dynamic system.
C1.. Name any three characteristics of society as a dynamic system.
C2. What social and economic formations allocate Marxists?
Sz. Name three historical types of society. What features are they highlighted?
C4.. There is a statement: "Everything for humans. It is necessary to produce as much products as possible for it, and for this you have to "invade" in nature, violating the natural laws of its development. Either a person, his well-being, or nature and its well-being. There is no third".
Your attitude to this judgment? Justify your answer, relying on the knowledge of the social science rate, the facts of public life and personal experience.
C5.. Give three examples of the relationship of global problems of humanity.
C6.
Gaining all new and new forces, civilization often detected explicit
the tendency to impose ideas with missionary activities or direct
violence coming from religious, in particular Christian, traditions ... so
civilization has steadily extended to the planet, using all for this
possible paths and means - migration, colonization, conquest, trade,
industrial development, financial control and cultural influence. Few-
intow all countries and peoples began to live according to its laws or created them
mounted sample ...
The development of civilization, however, was accompanied by the flourishing of rainbow hopes and illusions that could not be implemented ... The basis of its philosophy and its actions was always lying elitarism. And the Earth, no matter how generous is, is still unable to place a continuously growing population and satisfy all new and new needs, desires and whims. That is why there is now a new, deeper split - between super-crucial and underdeveloped countries. But even this riot of the world proletariat, who seeks to join the wealth of their more prosperous fellows, proceeds in the framework of all the same dominant civilization ... It is unlikely that it will be able to withstand and this new test, especially now, when her own organism is torn by numerous ailments. The HTR also becomes more suspension, and it is harder and more difficult to pacify it. Having endured us with an unprecedented dotol strength and instilling the taste for such a level of life, which we did not even have thought about, the HTR does not give us so much wisdom to keep our capabilities and requests under control. And our generation is time, finally, to understand that only us now ... the fate is not individual countries and regions, but in total humanity as a whole.
A. Pechesti
1) What global problems of modern society stands out the author? Specify two or three problems.
2) What does the author mean, claiming: "When you putting us with an unprecedented dotol strength and instilling the taste for this level of life that we didn't even think about, the HTR does not give us so much wisdom to keep our capabilities and requests under control? Make two assumptions.
3) Illustrate on the examples (at least three) approval of the author: "The development of civilization ... was accompanied by a flourishing of rainbow hopes and illusions that could not be implemented."
4) Is it possible, in your opinion, in the foreseeable future to overcome the contrast between rich and poor countries. Justify the answer.
C7. Choose one of the proposed statements and state your thoughts about the raised problem in the form of a brief essay.
1. "I am a citizen of the world."
(Diogen Sinopsky)
2. "I am too proud of my country to be a nationalist."
(J. Volify)
3. "Civilization is not a greater or less refinement. But in consciousness, general for the whole people. And this consciousness is never sophisticated. On the contrary, it is quite healthy. Representing the civilization of the creation of the elite means to identify it with a culture, including this is completely different things. " (BUT. Camus)
C8.. Read the text and perform tasks to it.
"Human society is the highest level of the development of living systems, the main elements of which are people, the forms of their joint activities, especially work, works of labor, various forms of ownership and the age-old struggle for it, politics and the state, a set of various institutions, the sophisticated Sphere of Spirit. Society can be determined both as a self-organizing behavior system and the relationship between people's arcs with a friend and with nature ...
The concept of society covers not only living people now, but all past and future generations, i.e. All mankind in his history and the future. The combination of people in the holistic system occurs and is reproduced regardless of the will of its members ...
The life of society is not exhausted by the life of the components of his people. The Company creates material and spiritual values \u200b\u200bthat cannot be created by individual people ... Society is a single social organism, the internal organization of which represents a combination of certain, characteristic of a given system of diverse bonds, which ultimately lies human labor. The structure of human society is formed: production and developing production, economic, social relations based on it, including class, national, family relations; Political relations and, finally, the spiritual sphere of life of society - Science, philosophy, art, morality, religion, etc.
People constantly carry out the process of social production of their lives: the production of material benefits, the production of people of public beings, the production of a corresponding type of relationship between people, the most form of communication and the production of ideas. In society, economic, economic, state, family relations, as well as a number of ideological phenomena phenomena are intertwined, intentionally intelligently intertwined ...
It is the society that is the main condition of more or less normal being and development of people ... "
1) Find in the text and write down two suggestions in which the author lists the main elements of society.
2) scientists call society by a dynamic system. Find three other words in the text that the author characterizes society as a system.
4) Relying on the content of the text and knowledge of the social science rate, bring three evidence that the society "will ultimately lies human labor."
C9.. Read the text and perform tasks to it.
It seems to me that today, when humanity came to an ecological catastrophe, when all the terrible consequences of utopian claims for total management of social processes are extremely clear, the fate of the humanistic ideal is connected with the refusal to the idea of \u200b\u200bmastering, suppressing and domination. A new understanding of the nature of nature and humanity is not the ideal of anthropocentrism, but developed by a number of modern thinkers, in particular, the idea of \u200b\u200bcoevolution, the joint evolution of nature and humanity, which can be interpreted as the attitude of the equal partners, if you want, interlocutors In a non-programmed dialogue ...
It may and should be understood in a wider plan. Freedom as an integral characteristic of a humanistic ideal is conceived not as mastering and control, but as the establishment of equal partnerships with what is outside of a person: with natural processes, with another person, with the values \u200b\u200bof other culture, with social processes, even with non-inflexible and " Opaque "processes of my own psyche.
In this case, freedom is understood not as an expression of a projective-constructive attraction to the world, not as the creation of such a substantive world, which is controlled and managed, but as such when I take another, and the other accepts me. (It is important to emphasize that the adoption does not mean simple content that there is, but involves interaction and interconnection.) At the same time, we are talking about a free adoption based on understanding as a result of communication. In this case, we are dealing with a special kind of activity. This is not an activity to create an item in which a person is trying to capture and express itself, that is, a subject that belongs to the subject. This mutual activity, the interaction of fluent partners who participates in the process of equal partners, each of which is considered to be different and as a result of which they are changed.
(V.A. Kittorsky)
1) What two realities of modern society require, according to the author, a new understanding of the humanistic ideal? What does he see the essence of this new understanding?
2) Give any two phrases in which the author's understanding of freedom is reflected.
3) Explain why the humanistic ideal at the present stage ceased to correspond to anthropocentrism (the idea of \u200b\u200bmastering and domination). Give three explanations based on social science and facts of public life.
4) The author writes about the need to "establish equal-partnership relations with what is outside of a person." Relying on the content of the text and knowledge of the social science rate, suggest that these relationships can consist with any three of the partners called by the author. (First, name the partner, with which partnerships are established, and then express the assumption.)
Answers
Part 1 Level A
| Quest Number | answer |
Part 2 level in
| Quest Number | answer |
| Natural | |
| regression | |
| A B C D | |
| In; a; g; b | |
| In; g; w | |
| In; a; b; g | |
| spiritual | |
| 2,3,4 | |
| spiritual | |
| 1,3,4,5,6 | |
| 1,2,4,6 | |
| manual | |
| 1,2,4,6 | |
| 3,5,6 | |
| VVBG | |
| Public | |
| BVA | |
| 3,4,2,1,5 | |
| Spheres, spheres | |
| Public Progress | |
| B; a; g; in | |
| 1st, b, d, s, k, l, o, p, t, c, yu, i; 2-in, e, and, m, n, s, y, f; 3rd, g, r, f, x, h, sh, uh, u | |
| G; in; b; d; a | |
| 1)2,3,7,8,9,12; 2)4,6,8,11; 3)1,5,10 | |
| 1,3,4.7,9 | |
| 5,10,12,13,14 | |
| 3,4,5,7,8,9 |
Part 3. Level with
C1.The correct answer may contain the following characteristics:
Integrity;
Consists of interrelated elements;
Elements vary over time;
The nature of the relationship between systems is changing;
The system is changing in general.
Other characteristics can be given.
C2. Correct answer:
Primitive
Slave owner
Feudal
Capitalist (bourgeois)
Socialist (communist)
SZ. Traditional (pre-industrial), industrial, post-industrial.
Signs:
Pre-industrial Society: Basis - Agriculture;
Industrial Society: Basis - large industry;
Post-industrial (technotronic, technological) Society: base - information.
C4. The correct answer may contain the following positions:
Society and Nature are interrelated;
Nature is a natural habitat of society;
The purpose of production is to satisfy the fundamental needs of a person in food, clothing;
Centuries man enjoyed the riches of nature, polluting the atmosphere, cutting out the forest, mining minerals, infecting water, destroying the soil;
As a result, the threat of a global environmental catastrophe arose - irreversible changes in natural living conditions on Earth, threatening degradation and even human death;
The current Criminal Code of the Russian Federation provides for serious responsibility for such environmental crimes, as a violation of environmental protection rules in the work, water pollution, illegal hunting, etc.
Other positions can be given.
C5.. Any three examples of the relationship of global problems of modernity can be presented, for example:
The threat to the environmental crisis is reflected in the economy: developed countries seek to translate "harmful" production to the third world countries, which exacerbates the "North-South" problem;
The threat of international terrorism is intertwined with the problem of the threat of a nuclear war in connection with the desire of terrorists to access the weapons production technologies of mass lesions;
The demographic problem in the modern world acts primarily as the problem of the rapid demographic growth of the countries of the Third World, which increases the gap in economic terms with the developed countries.
C6.. The content of the right answers to the tasks to the text.
1) problems:
- limited resources;
Non-uniformity of development (the "North-South" problem);
Demographic;
The effects of HTR.
2) Assumptions can be made:
The presence of scientific knowledge and technical means for global transformations has a threat to life itself on Earth;
Formation of consumer society makes speed and comfort priority values.
Other assumptions can be made, not distorting the meaning of judgment.
3) may be indicated, for example:
Communist utopias;
Faith in the omnipotence of scientific and technological progress;
Faith in ideals of freedom and justice in understanding enlightenment figures.
Other examples can be given, not distorting the meaning of judgment.
4) If a negative answer is given, arguments are given:
The demographic situation in poor countries exacerbates their lag from rich countries;
as a result, weak participation in the global division of labor;
as a result, one-sided development of the economy and dependence on rich countries. Other arguments can be shown.
C8.. Text.
1) The correct answer must contain the following items:
1) realitiesmodern Society:
- "Humanity closely approached the environmental catastrophe";
- "All the terrible consequences of utopian claims for total management of social processes are extremely clear;
2) essence of a new understanding Humanistic ideal:
"The idea of \u200b\u200bcoevolution, the joint evolution of nature and humanity, which can be interpreted as the attitude of equal partners, if you please, interlocutors in a non-prominged dialogue."
These elements can be given in other, similar to the content of the wording.
2) The response can contain the following phrases:
1) "Freedom as an integral characteristics of a humanistic ideal thinks ... as the establishment of equal partnerships with what is outside of a person: with natural processes, with another person, with the values \u200b\u200bof other culture, with social processes, even with non-inflexible and" opaque "processes my own psyche ";
2) "Freedom is understood ... as such a relation when I take another, and the other accepts me";
3) "Free adoption, based on understanding as a result of communication."
3) The following explanations can be given:
1) The installation of man's domination over nature led to irreversible changes in the external environment.
2) irreversible changes in the external environment negatively affect human health, society functioning.
3) the number of resources that may be used to develop in a numerical respect for their development are significantly reduced.
4) The installation of dominance has spread to the attitude of a person to her like, public interest.
Other explanations can be given.
4) The correct answer may contain the following assumptions:
1) "Relationships with natural processes": the use of human-saving and resource-saving technologies, restriction of consumption;
2) "Relations with another person": recognition of the unconditional value of the personality of another person, respect for his freedom;
3) "Relationships with other culture values": tolerant attitude to the values \u200b\u200bof other culture and carriers of these values;
4) "Relationships with social processes": a refusal to install personal and group egoism, consumerism, striving for the social world;
5) "Relations with non-inflexible and" opaque "processes of my own psyche": attentive attitude to its own psychological state, gentle by adjustment in the necessary cases, maximum use in the activities of own mental capabilities and states.
Other assumptions may be made.
C9..Text.
1) The correct answer must contain the following positions:
1) "People, the forms of their joint activities, first of all labor, products of labor, various forms of ownership and a century-old struggle for her, politics and the state, a set of various institutions, the sophisticated Sphere of Spirit";
2) "Production and developing production, economic, social relations based on it, including class, national, family relations; Political relations and, finally, the spiritual sphere of society - science, philosophy, art, morality, religion, etc. ".
2) The correct answer may contain the following characteristics:
1) Live system;
2) a holistic system;
3) Self-organizing system.
3) The correct answer may contain the following arguments:
1) only in relations with other people a person can reveal and develop its qualities (socially significant), distinguish from animals;
2) society performs numerous functions that provide physical survival and relatively comfortable existence of a person;
3) Social and spiritual needs of a person are satisfied only in society.
Other having reason arguments are possible.
4) The correct answer may contain, for example, the following explanations:
in the process of labor
1) According to the theory of evolution, the ancestors of a person acquired and developed their human qualities;
2) many social and prestigious human needs are being implemented;
3) satisfied the material needs of society;
4) a certain social organization is formed;
5) The spiritual institutions are formed.