Make up geometric figures. Short-term educational practice "Cheerful tangram. "Hare
Natalia Kazakova
Short-term educational practice "Cheerful tangram. "Hare"
Routing
short-term educational practice.
Full title practices« Cheerful tangram» Constructive activities (geometric designer, magic square).
Short name « Cheerful tangram»
Children's age 6-7 years old - 11 people
Relevance to instill interest in accurate sciences scientific research, ancient Chinese game « Tangram» .
The purpose of the program to form initial ideas about the game, its history.
The tasks contribute to the development of the ability to play according to the rules and execute instructions, vividly figurative thinking, imagination, attention, understanding of color, values \u200b\u200band shapes, perception., Combinatorial abilities.
Materials and equipment envelopes with 7 geometric shapes, sample with the image of the hare.
Parts OP Copher Organizational, Basic, Final
Finite results children make sure:
1. Collect out geometric figures Figure hare in sample.
2. Conditions to navigate on a sheet of paper, table.
Specific, measurable criteria and performance indicators. As a result of exercises and tasks for this game, children will learn to analyze simple images, To allocate geometric shapes in them, will learn to visually break the whole object on the part and, on the contrary, make a specified model from the elements.
Prospects for further implementation of the OPC continue to work with the game « Tangram» ,
Collect more complex figures.
Cop: « Cheerful tangram. « Hare» .
Relevance:
The problem is that most parents do not pay enough time to their children, communicate little. You need to teach children to see the wonderful, develop creative and mathematical abilities of children.
I stage:
purpose: Acquaintance with the ancient Chinese game « Tangram» , Her story.
Tasks:
Improve knowledge of geometric figures.
Contributes to the development of the ability to play the rules and execute instructions,
Develop vividly creative thinking, imagination, attention, understanding of color, values \u200b\u200band shapes, perception, combinatorial abilities.
Material: Envelopes with geometric shapes « Tangram» For each child.
Project participants:
* Children - 11 people
* Educator
Project implementation deadlines - 1 day.
Preliminary work: Reading Stories N. Nosova "Adventures minor".
Stage II:
Educator: Guys, a guest came to visit today. And to find out who, guess my riddle:
Mystery:
He does not know anything.
You know him.
I am answered without a rustle
What is his name?
Children: (Dunno).
Educator: Right, it's a messy (The tutor puts a brand stick on flannelugaph).
Dunno brought the envelope on which it is written « Tangram» . What he does not know with him.
The teacher opens the envelope: - It is not a letter, but geometric shapes and a scheme.
It turns out that Znika gave the task of Slank. Need from geometric shapes collect hare. If Dunno cope with this assignment, Zinka promised him that Dunno will manage aircraftWhen they go on a trip. I really want to be most important on the ball, so he came to us for help. He knows that in our group there are very smart children, and will definitely help him and teach to play this game.
Educator: Guys, let's help me.
Children: Let's help.
The tutor pulls the circuit from the envelope on which the figure of the hare is depicted. Offer collect harefrom 7 figures tangram.
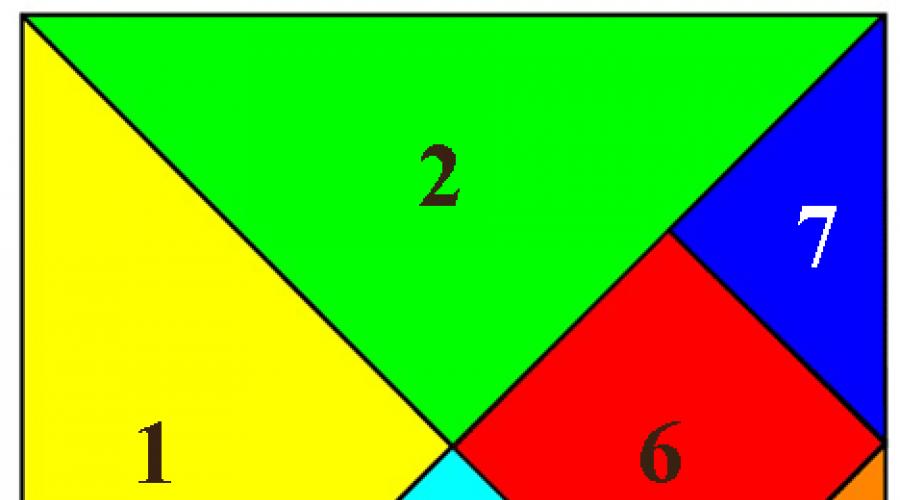
Educator: What geometric shapes it consists of?
Children: 5 triangles, 1 square and 1 diamond.
III stage:
Children collect a hare from geometric shapes.
Dunno is very pleased and thanks you for work. Now he knows. What « Tangram» And how to collect it.
Educator: Well done boys! You helped melanchka, fulfill a difficult task.
Publications on the topic:
Short-term educational practice "Competent Buyer" 1 Slide) Short-term educational practice for children 4-5 years old on the socio-communicative development of children "Competent Buyer". (2.
Short-term educational practice "Vase with flowers" Mosaic "Vase with flowers" Explanatory note. Mosaic is a drawing made up of small pieces or different materials. Mosaic.
Short-term educational practice "Wonderful Pouch" Short-term educational practice "Wonderful Pouch" Group: 2-3 years Purpose: Development creative abilities In children in the visual.
Short-term educational practice for "Easter egg" for children 4-5 years Program Passport Short Name Program: "Easter egg" Full name of the program: "Decoration of an Easter egg for Easter" Dates.
Short-term educational practice "Christmas tree" in the style of origami Short-term educational practice "Christmas tree in Origami technique" age of children: 5-6 years old ( senior group) Purpose: - To acquaint with art.
Short-term educational practice "Mukosolka" (salty dough modeling) Municipal autonomous preschool educational institution « Kindergarten № 296 "Perm Short-term educational practice.
Tangram is a puzzle, which is a square cut into 7 parts in a certain way. For preschoolers, tangram is a great lesson for school preparation. And at the age of 5 - 6 years, children love to play. They are interested in puzzles with pictures.
The goal of the game is to collect the figures of people, animals, birds, numbers, objects from the details of Tangram, ...
Rules of the game Tangram:
- -In the collected figure should include all seven parts.
- - Do not lean on each other.
- - Party must adjoin each other.
Tangram scheme
(print can be in Word, download File clicking on the drawing by the mouse)
Parts of Tangram
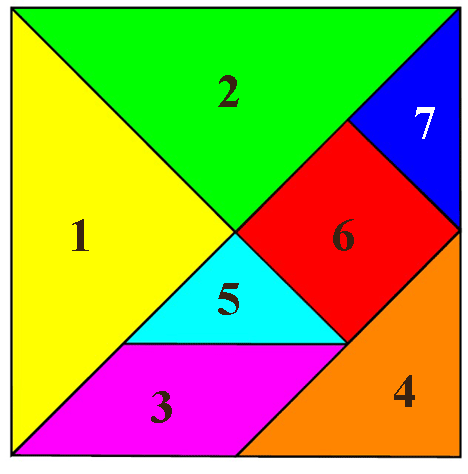
This is the tangram himself, the invented pictures are obtained from its parts. It can be bought, but it's easy to do and taking the installation scheme with your own hands. The drawing can be printed on color paper on the printer or draw yourself using a ruler. Cut parts puzzle pieces made of colored paper. Then, laying out the desired figure to glue on a tight sheet.
An example of a dog scheme - made grades 1 class to the lesson of mathematics and technology.
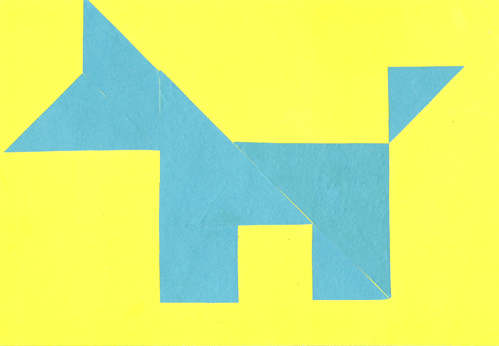
The game for children tangram can be in several levels of difficulty. It is better to start with the simplest - lay out the sample figure.
Scheme - Rocket
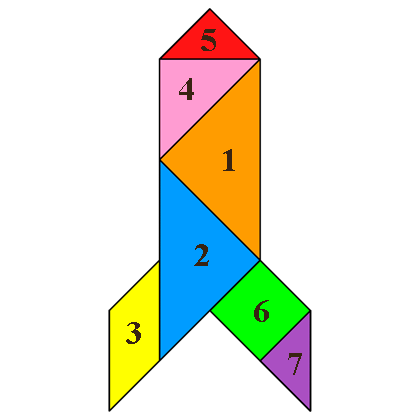
So you can fold from the Tangram house.
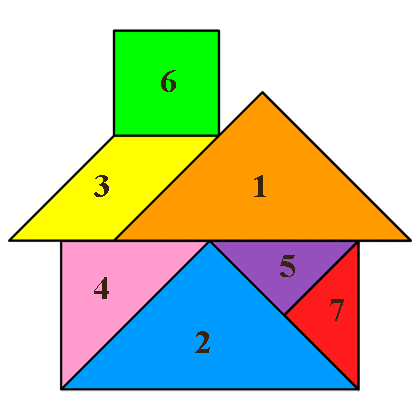
At the second stage, you can offer children to lay out figures on a solid drawing.
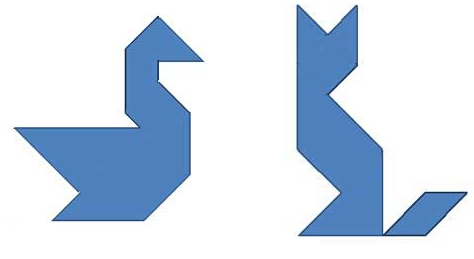
And the third level, the most complicated: come up with your shapes similar to people, animals, birds. We offer pictures invented by children.
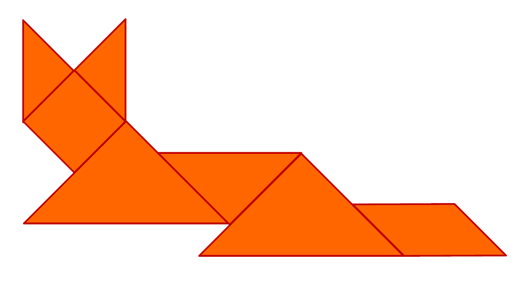
Tangram scheme - Fox
Hare and camel
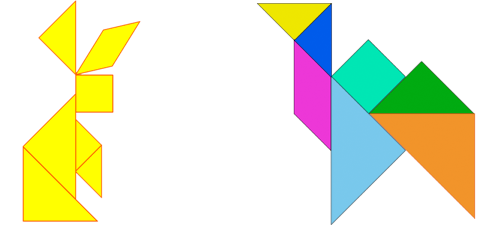
Scheme - man

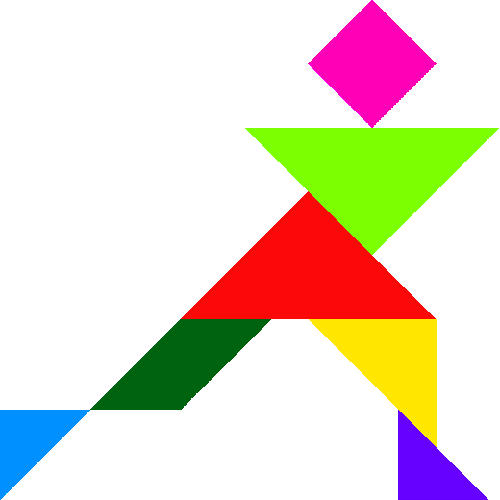
Figures - Fish

Print to the tangram scheme.
(Fox, cat, hare, camel, horse, dog)
Print the Tangle Schemes
(When you click on the image, the file is downloaded document Word. In DOCX format, which can be printed using a WORD)
There are various legends about the appearance of Tangram. Here is one of them ...
Almost two and a half thousand years ago, China's elderly emperor was born long-awaited son and heir. Years passed. The boy grew up healthy and intelligent not in the years. One disturbed old emperor: his son, future lord a huge countryI did not want to learn. The boy delivered a greater pleasure all day to toys toys.
The emperor called for three wise men, one of whom was known as a mathematician, the other became famous as an artist, and the third was a famous philosopher, and commanded them to come up with a game, to having fun, his son would have become the beginning of mathematics, learned to look at the world The artist's close eyes would be patient as a true philosopher, and would understand that often complex things consist of simple things.
Three wise men invented "Shi-Chao-Tyu" - a square, cut into seven parts.
From the parts of the Tangram you can get a lot of figures. You can offer a child to do, for example, a transport boiler, a plane, figurines - fencers, cock, pelican, wood, candle.
Games for the compilation of geometric figures from parts
The program is given much attention Exercises for the preparation of geometric figures from parts, drawing up patterns, ornaments. These exercises are developing sensory abilities, We train visual-shaped and verbal-logical thinking. Recreation games are very popular among preschool children.
They are taken with passion for those tasks that seem fantastic, magic - games with transformations, because of the ugly pieces they manage to fold the familiar figure. In addition, the variety of approaches to solving the problem, multivariate and exclusion of violations of the conditions of gaming action additionally contribute creative processWhat is one of the main advantages.
Games for recreation of objects geometric shape From parts, those games and exercises are preceded by the skill to highlight geometric shapes in the figure, drawing, in the surrounding setting. You can associate these games with the formation of quantitative representations, with accounting activities, suggesting children to count the total number of figures (how many circles? How many triangles? What figures are more (less)?). At first, it is advisable to offer those drawings that are composed of the geometric shapes of one form (Christmas tree, snowman, nevosha), then a few forms (car, house). In this case, no geometric shape is superimposed on the other, it does not require a particularly deep image analysis. Then you can offer drawings and drawings more complex, where one figure can consist of several figures, including others. Children are given the following tasks: 1. Corresponding as in the picture of triangles:
To enhance interest in such games, you can offer the game "Magic glasses". To play you need to make special glasses with "windows" of different shapes. Owing such "magic glasses" can be seen objects of the shape that corresponds to the form of glass.
The selection of figures in the environment is associated with the definition of the shape of the objects by comparing them with geometric shapes as sensory references.
The solution to this task contributes to such games as "for which it looks like", "pick up in form", "help the artist". In the game "Help the artist", children turn geometric shapes with a color pencil into some objects, animals, etc.
In the younger group, children offered the game "Composition Figure", in which they made of separate geometric shapes made up a robot, a lamb, a truck, a bird, a Christmas tree, chicken, a clock, a house.
By making familiar silhouettes, the children simultaneously practiced in the score, comparing the geometric figures in magnitude.
After children learn to freely solve the above tasks, one can move to a more complex, aimed at drawing up geometric figures from individual parts. Games of this type include such famous gameslike "tangram", "Columbovo Egg", "Pythagore Puzzle", "Pentamino", "Magic Circle", "Vietnamese Game", "Sverava Square" bp Nikitina et al.
The games of this group are aimed at developing skills to work according to the sample: analyze the sample, highlighting its component parts (that is, geometric shapes), to synthesize parts into a holistic image, identical pattern; They contribute to the development of spatial imagination, logical and intuitive thinking.
In my work in the class I used such games as "Speak Square", "Tangram". With these games introduced children, starting with middle group.
The game "Tangram", which is also called " geometric designer"Created by Chinese scientist Ta -ng, who lived several thousand years ago, and named after him.
From a certain set of geometric shapes (two large triangles, two are small, one - medium, square and quadrangle) are made up not only various geometric shapes, but also figurative flat figuresand from two sets you can make a story.
Creating figures, it is necessary to take into account the following rules: the composition of each silhouette should include all parts of the game, it is possible to connect them only on the sides, not allowing the overlay of one part to another.
In the middle group, I introduced children with the game: pointed out the number of game elements, their shape, size. After familiarization with the game switched to practical activities - the preparation of two or three figures available - new:
- Of the two large triangles, make consistently: square, triangle, quadrangle.
- Of the two small triangles, make the same figures, having them differently in space.
- Of the large and medium triangles make a quadrilateral.
- Make a new figure from a square and two small triangles (first the square, then the quadrilateral).
The tasks can be changed by offering children to make new figures according to the sample, interpretation, intent. All of them are aimed at developing spatial representations, elements of geometric imagination, on the production of practical skills in the compilation of new figures by attaching one of them to another.
These exercises are preparatory for the second stage of mastering the game - the preparation of figures silhouettes divided into parts of the samples. This stage is the most important for assimilation in the future complex ways drawing up figures.
Exercises for the preparation of figures of the silhouettes began with the viewing along with the sample children. Analysis of the location of the figures should be started from the main part (the wall of the house, the body of a person, an animal), after that the structure of the rest is marked. Children not only practiced in the location of the figure, which must be compiled, but also joined the visual and mental analysis of the sample. Here it is necessary to teach children not only to analyze the sample, but also verbally express the method of connecting parts and their spatial location.
Analysis should be prepared by silhouettes and comparing them with a sample. By the end of the middle group, almost all children loosely laid out silhouettes of chanterelles, bunny, house, goose, ostrich, kangaroo, looking at the dismembered sample. These games caused increased interest in children.
In senone preschool age I switched to the main stage - learning children to compose figures according to the samples of a contour or silhouette - unrelated. Recreation of figures on the contour samples requires a visual separation of the shape of a particular figure for components, that is, the geometric shapes from which it is composed. Each analyzes the sample independently and expresses the assumption that must be checked in practice. You can suggest a child to tell how it will make a figure. Children should argue, prove, refute.
In the future, children make up images on their own design. The creation of a silhouette based on imagination represents a problem task for a child; At the same time, it is necessary to find the only right path of the decision, which threaded incorrect. This is preceded by the emergence of the assumption, ideas, plan. The solution of this kind of tasks contributes to the development of imagination, creative abilities, action planning skills, predicting the result.
Children preparatory group In order to develop creative abilities, you can offer more complex tasks: Make up two or three sets of game shape-silhouette for sample or on your own intention.
The game "Tangram" I used both in classes in mathematics and in the free time.
Children also enjoyed playing games like "Columbovo Egg", Pythagora puzzles, Archimedes, and others, to which they have free access to the "corner of entertaining mathematics".
Interesting games for children who contribute to the development of design skills are such games as the four-color "Squadrat of Vosobovich", the developing game "Transparent digit", "Mouch Pattern" B.P. Nikitin, various geometric mosaics and constructors.
In my work in the class I used such games as "comprehend the square", "Composition Circle" proposed by bp Nikitin. I started this work already with junior Group, with the easiest and sidelines, when the child is given a sample and an envelope with a square. The child picks up pieces of one color and folds the square. Then the number of squares different color Increases. Squares that are given to children of the middle group can be numbered. Thus, in this game several tasks are solved at once: the development of color perception, fixing the knowledge of numbers and visual analysis of the shape, size, proportions of parts. The child sorts, looking for their ratio and method of drawing up figures.
At the older age, it is already possible to propose a circle and squares from parts. This task implies the addition of geometric figures from parts that may have a complex configuration when dividing. The child is given two or three different sets, parts of which are mixed. Giving children a task, you can use various options based on the level of child's development.
For development logical thinking Children in the senior preschool age I used exercises based on the analysis of the dependence between pairs of figures or a group of figures, "How has the figure change?"
This dependence is expressed in the transformation of the figures depicted in the drawings, cards: a change in color, color, shape, location, etc.
The child is given samples that show models for changing objects. By analogy with them, the child independently finds the necessary figure or an object, mentally analyzing the sample.
Types of transformation that can be used:
1) color change;
- change of size;
- changing the number of parts or figures;
- contour transformation by outbreaking a part or a whole figure;
- transformation by adding:
- changing the location of the figures by sliding parts or figures;
- change in location by overlaying, compounding figures;
- changing the location of the figures by reversal.
In case of difficulty, you can use cards-keys: the child must carefully consider the card and determine the nature of the change, choose the desired card-answer card. The nature of the changes is depicted on the card-key symbolically.
All these exercises are aimed at the development of understanding and the ability to transform the situation.
Download:
Preview:
Games for the compilation of geometric figures from parts
The program pays great attention to the exercises for the preparation of geometric figures from parts, drawing up patterns, ornaments. These exercises develop sensory abilities, train visual-shaped and verbally logical thinking. Recreation games are very popular among preschool children.
They are taken with passion for those tasks that seem fantastic, magic - games with transformations, because of the ugly pieces they manage to fold the familiar figure. In addition, the diversity of approaches to solving the problem, multivariate and elimination of violations of the conditions of gaming action additionally contribute to the creative process, which is one of the main advantages.
2. How many squares, rectangles, quadrangles in the picture?
Games on recreating the objects of geometric shapes from parts are preceded by those games and exercises that are directed to the ability to highlight geometric shapes in the figure, drawing, in the surrounding atmosphere. You can associate these games with the formation of quantitative representations, with accounting activities, suggesting children to count the total number of figures (how many circles? How many triangles? What figures are more (less)?). At first, it is advisable to offer those drawings that are composed of the geometric shapes of one form (Christmas tree, snowman, nevosha), then a few forms (car, house). In this case, no geometric shape is superimposed on the other, it does not require a particularly deep image analysis. Then you can offer drawings and drawings more complex, where one figure can consist of several figures, including others. Children are given the following tasks: 1. Corresponding as in the picture of triangles:
To enhance interest in such games, you can offer the game "Magic glasses". For the game you need to make special glasses with "glass" of different shapes. Owing such "magic glasses" can be seen objects of the shape that corresponds to the form of glass.
The selection of figures in the environment is associated with the definition of the shape of the objects by comparing them with geometric shapes as sensory references.
The solution to this task contributes to such games as "for which it looks like", "pick up in form", "help the artist". In the game "Help the artist", children turn geometric shapes with a color pencil into some objects, animals, etc.
In the younger group, children offered the game "Composition Figure", in which they made of separate geometric shapes made up a robot, a lamb, a truck, a bird, a Christmas tree, chicken, a clock, a house.
By making familiar silhouettes, the children simultaneously practiced in the score, comparing the geometric figures in magnitude.
After children learn to freely solve the above tasks, one can move to a more complex, aimed at drawing up geometric figures from individual parts. Games of this type include such famous games like "Tangram", Columbovo Egg, "Pythagora Puzzle", "Pentamino", "Magic Circle", "Vietnamese Game", "Svadrat" bp Nikitina et al.
The games of this group are aimed at developing skills to work according to the sample: analyze the sample, highlighting its component parts (that is, geometric shapes), to synthesize parts into a holistic image, identical pattern; They contribute to the development of spatial imagination, logical and intuitive thinking.
In my work in the class I used such games as "Speak Square", "Tangram". With these games introduced children, starting from the middle group.
The game "Tangram", which is also called the "geometric designer", was created by the Chinese scientist Ta -ng, who lived several thousand years ago, and was named after him.
From a certain set of geometric shapes (two large triangles, two-small, one - medium, square and quadrilateral) are made up not only various geometric shapes, but also shaped flat figures, and from two sets you can make a story.
Creating figures, it is necessary to take into account the following rules: the composition of each silhouette should include all parts of the game, it is possible to connect them only on the sides, not allowing the overlay of one part to another.
In the middle group, I introduced children with the game: pointed out the number of game elements, their shape, size. After familiarization with the game switched to practical activities - the preparation of two or three figures available - new:
- Of the two large triangles, make consistently: square, triangle, quadrangle.
- Of the two small triangles, make the same figures, having them differently in space.
- Of the large and medium triangles make a quadrilateral.
- Make a new figure from a square and two small triangles (first the square, then the quadrilateral).
The tasks can be changed by offering children to make new figures according to the sample, interpretation, intent. All of them are aimed at developing spatial representations, elements of geometric imagination, on the production of practical skills in the compilation of new figures by attaching one of them to another.
These exercises are preparatory for the second stage of mastering the game - the preparation of figures silhouettes divided into parts of the samples. This stage is the most important for assimilation in the future more complex ways to compose figures.
Exercises for the preparation of figures of the silhouettes began with the viewing along with the sample children. Analysis of the location of the figures should be started from the main part (the wall of the house, the body of a person, an animal), after that the structure of the rest is marked. Children not only practiced in the location of the figure, which must be compiled, but also joined the visual and mental analysis of the sample. Here it is necessary to teach children not only to analyze the sample, but also verbally express the method of connecting parts and their spatial location.
Analysis should be prepared by silhouettes and comparing them with a sample. By the end of the middle group, almost all children loosely laid out silhouettes of chanterelles, bunny, house, goose, ostrich, kangaroo, looking at the dismembered sample. These games caused increased interest in children.
In the older preschool age, I switched to the main stage - learning children to compose figures according to the samples of a contour or silhouette character - unrelated. Recreation of figures on the contour samples requires a visual separation of the shape of a particular figure for components, that is, the geometric shapes from which it is composed. Each analyzes the sample independently and expresses the assumption that must be checked in practice. You can suggest a child to tell how it will make a figure. Children should argue, prove, refute.
In the future, children make up images on their own design. The creation of a silhouette based on imagination represents a problem task for a child; At the same time, it is necessary to find the only right path of the decision, which threaded incorrect. This is preceded by the emergence of the assumption, ideas, plan. The solution of this kind of tasks contributes to the development of imagination, creative abilities, action planning skills, predicting the result.
For children of the preparatory group, with the goal of developing creative abilities, more complex tasks can be offered: draw up a two or three sets of the game figure-silhouette or on its own design.
The game "Tangram" I used both in classes in mathematics and in the free time.
Children also enjoyed playing games like "Columbovo Egg", Pythagora puzzles, Archimedes, and others, to which they have free access to the "corner of entertaining mathematics".
Interesting games for children who contribute to the development of design skills are such games as the four-color "Squadrat of Vosobovich", the developing game "Transparent digit", "Mouch Pattern" B.P. Nikitin, various geometric mosaics and constructors.
In my work in the class I used such games as "comprehend the square", "Composition Circle" proposed by bp Nikitin. I started this work with the younger group, with the easiest and sake tasks, when the child is given a sample and an envelope with a square. The child picks up pieces of one color and folds the square. Then the number of squares of different color increases. Squares that are given to children of the middle group can be numbered. Thus, in this game several tasks are solved at once: the development of color perception, fixing the knowledge of numbers and visual analysis of the shape, size, proportions of parts. The child sorts, looking for their ratio and method of drawing up figures.
At the older age, it is already possible to propose a circle and squares from parts. This task implies the addition of geometric figures from parts that may have a complex configuration when dividing. The child is given two or three different sets, parts of which are mixed. Giving children a task, you can use various options based on the level of child's development.
To develop the logical thinking of children in the older preschool age, I used exercises based on the analysis of the dependence between pairs of figures or a group of figures, "How did the figure change?".
This dependence is expressed in the transformation of the figures depicted in the drawings, cards: a change in color, color, shape, location, etc.
The child is given samples that show models for changing objects. By analogy with them, the child independently finds the necessary figure or an object, mentally analyzing the sample.
Types of transformation that can be used:
1) color change;
- change of size;
- changing the number of parts or figures;
- contour transformation by outbreaking a part or a whole figure;
- transformation by adding:
- changing the location of the figures by sliding parts or figures;
- change in location by overlaying, compounding figures;
- changing the location of the figures by reversal.
In case of difficulty, you can use cards-keys: the child must carefully consider the card and determine the nature of the change, choose the desired card-answer card. The nature of the changes is depicted on the card-key symbolically.
All these exercises are aimed at the development of understanding and the ability to transform the situation.
- Make 2. equal triangles out of 5 sticks
- Create 2 equal squares of 7 sticks
- Create 3 equal triangles of 7 sticks
- Create 4 equal triangles of 9 sticks
- Create 3 equal squares of 10 sticks
- From 5 sticks to make a square and 2 equal triangles
- From 9 sticks to make a square and 4 triangles
- From 9 sticks to make 2 squares and 4 equal triangles (from 7 sticks are 2 squares and divided into triangles
Drawing up geometric figures
Purpose: Exercise in the preparation of geometric shapes on the plane of the table, analysis and examination by their visual tangible way.
Material: Accounting sticks (15-20 pieces), 2 thick threads (length 25-30cm)
Tasks:
- Make a square and triangle little size
- Make a small and large squares
- Create a rectangle, the upper and lower sides of which will be equal to 3 wands, and the left and right - 2.
- Make up the thread sequentially shapes: a circle and oval, triangles. Rectangles and quadries.
Chain of examples
Purpose: Exercise in the ability to produce arithmetic action
Game traffic: Adult throws the ball a child and calls a simple arithmetic, for example 3 + 2. The baby catches the ball, gives the answer and throws the ball back, etc.
Help Cheburashka find and send a mistake.
The child is invited to consider how geometric shapes are located, in which groups and what feature are combined, to notice the error, correct and explain. The answer is addressed to Cheburashka (or any other toy). An error may be that a triangle can be in the square of the squares, and in the group of figures of blue color - Red.
Only one property
Purpose: Secure the knowledge of the properties of geometric shapes, develop the ability to quickly choose the desired figure, characterize it.
Game traffic: In two playing on a complete set of geometric shapes. One shapes any shape on the table. The second player must put a figure on the table, different from it with only one sign. So, if the 1st laid a yellow triangle, then the second puts, for example, a yellow square or a blue big triangle. The game is built by Domino type.
Find and name
Purpose: Secure the ability to quickly find a geometric shape of a certain size and color.
Game traffic: On the table in front of the child fold out in the disorder of 10-12 geometric shapes of different colors and size. The presenter requests to show various geometric shapes, for example: big circle, small blue square, etc.
Name a number
Playing becomes against each other. An adult with a ball in his hands throws the ball and calls any number, for example 7. The child must catch the ball and call the adjacent numbers - 6 and 8 (first less)
Mass Svadrat.
Purpose: Development of color, assimilation of the ratio of the whole and part; Formation of logical thinking and ability to break complex task A few simple.
For the game you need to prepare 30 × 80mm square squares. Shades of colors should differ significantly from each other. Then cut the squares. Cut the square, you need to write its number on each part (on the back side).
Tasks for the game:
- Decompose pieces of squares in color
- By numbers
- Fold from pieces a whole square
- Come up with new squares.
Ecological Games
"What would happen if the forest disappeared ..."
The educator proposes to remove insects from the forest:
- What would happen to the rest of the inhabitants? And if the birds disappeared? And if there were berries? And if there were no fungi? And if there were hare from the forest?
It turns out, it is not by chance that the forest gathered his inhabitants together. All forest plants and animals are connected with each other. They will not be able to do without each other.
"What plant did not become?"
Four or five plants are exhibited on the table. Children remember them. The educator offers children to close their eyes and removes one of the plants. Children open their eyes and remember which plant stood still. The game is carried out 4-5 times. You can increase the number of plants on the table every time.
"Where does it grow up?"
Purpose: Learning to use the knowledge of plants, compare the fruits of the tree with its leaves.
Game traffic: Two branches are laid on the flannelhemph: on one - the fruits and leaves of one plant (apple tree), on the other - the fruits and leaves of different plants. (for example, the leaves of the gooseberry, and the fruits of the pear) the educator asks the question: "What fruits mature, and which no?" Children correct the errors made in drawing up the drawing.
"Guess what in hand?"
Children stand, lined up in a circle, hands hold behind her back. The tutor lay out in the hands of children of fruits. Then shows one of the fruits. Then shows one of the fruits. Children who have identified the same fruit at the signal run up to the educator. Look at what lies in the hand, it is impossible, the item needs to be recognized on the touch.