Oxygen deficiency of the body. To your health! Health problems are solved here

Intrauterine fetal hypoxia is a dangerous process that, unfortunately, is very common. The consequences of hypoxia can negatively affect the development of the fetus and its activity. internal organs... The life and health of the unborn child largely depends on timely diagnosis and treatment.
Waiting for a miracle
Pregnancy is a very exciting and joyful time for every woman. But to the joyful anticipation of the birth of a baby, anxiety for his health is added. On the expectant mother there is a heavy burden of responsibility. For nine months, it develops and grows new life... The health of an unborn baby directly depends on the well-being of his mother.
There are many guidelines on how to manage your health during pregnancy. This applies to nutrition, lifestyle, emotional stress and much more. Failure to comply with these simple rules can have adverse effects and damage the health of the fetus.
One of these consequences can be intrauterine hypoxia, which entails disturbances in the development of the fetus and, in some cases, the fading of pregnancy. To avoid this, the expectant mother needs to carefully study the risk factors that lie in wait for her during pregnancy and try to prevent their occurrence.
What is hypoxia
"Hypoxia" is an ancient Greek word that literally translates as "low oxygen". This term denotes oxygen starvation, which is experienced by the body or its individual organs as a result of exposure to certain factors.

With prolonged oxygen starvation, irreversible morphological processes occur in the human body. They change the structure of tissues and organs and disrupt their functional abilities. With oxygen starvation of the fetus, the process of formation of internal organs slows down and is disrupted, the child can be born with a developmental lag. important systems or perish. These are the consequences of intrauterine hypoxia. The heart, kidneys, liver and central nervous system are most strongly affected by hypoxia.
Oxygen deficiency can accompany any disease or arise as an independent process, entailing defects of internal organs. For this reason, hypoxia cannot be classified as a disease, it is a pathological process, the same as inflammation or dystrophy.
Symptoms of fetal hypoxia
It is noted that in the first three months of pregnancy, oxygen deprivation develops quite rarely. Most often, this can happen in the second and third trimester. This is due to the fact that with the growth of the fetus, an increase in its need for oxygen also arises, and under some unfavorable circumstances the body of a pregnant woman cannot cope with this task.
Oxygen deficiency in a baby is difficult to identify without diagnostic tests, especially in early pregnancy. But there are some signs of intrauterine hypoxia, which should be an alarming signal for the expectant mother.
The first thing to look out for is fetal activity. Approximately ten movements per day are considered the norm. In the initial stages of hypoxia, the baby begins to feel discomfort, therefore, is overly active. With a longer oxygen deficiency, the amount of perturbation decreases. In addition, intrauterine hypoxia can be characterized by frequent fetal hiccups.
If the deviation in the number of movements from the norm and frequent hiccups are not associated with physical activity a future mother or being in an uncomfortable position, it is required to consult a specialist as soon as possible, who will identify the cause of this fetal behavior and, if necessary, prescribe treatment.
Causes of occurrence
The causes of intrauterine fetal hypoxia can be different. These include diseases that a pregnant woman suffers, pathologies of the placenta, infection, fetal malformations.
Of the diseases of the mother leading to fetal hypoxia, the following can be distinguished:
- anemia;
- disturbances in the work of the cardiovascular system;
- respiratory diseases;
- diabetes.
In addition, bad habits that the expectant mother suffers from affect the baby's health. Prevention of intrauterine hypoxia includes complete cessation of smoking and alcohol. Any deviation from the generally accepted norms of pregnancy can lead to oxygen starvation of the fetus. Such deviations can be detachment and premature aging of the placenta, prolonged fetal life, or increased uterine tone.

Another factor that leads to oxygen deficiency is the incompatibility of the Rh factor of the mother and the child. Such incompatibility can lead to hemolytic disease of the fetus, which is often accompanied by hypoxia. In addition to the above factors, the influence can have a mechanical effect on the fetus - entanglement with the umbilical cord, squeezing the head during childbirth, and so on.
The causes of intrauterine hypoxia can also become the causes of other, no less serious complications. To avoid an adverse effect on the development of the fetus, the expectant mother needs to be monitored by a qualified specialist throughout the entire period of pregnancy.
Types of fetal hypoxia
Depending on how long oxygen deprivation lasts, intrauterine hypoxia has two forms: acute and chronic. Acute hypoxia is characterized by a sharp decrease in the supplied oxygen. The most common acute form occurs during childbirth or with profuse uterine bleeding. Chronic intrauterine hypoxia forms over a long period of time, gradually disrupting the processes of fetal development.
The degree of progression of oxygen deprivation
There are three degrees of development of fetal hypoxia. At first, the fetus, having not received the required amount of oxygen, tries to compensate for its lack. The first degree is to compensate for the lack of oxygen. In the baby's body, changes begin to occur aimed at increasing the volume of incoming oxygen. The level of a hormone that increases the tone of blood vessels, cortisol, is increasing. Elevated level cortisol stimulates an increase in the volume of blood that circulates through the vessels and an increase in heart rate. The composition of the blood changes: the level of hemoglobin and erythrocytes increases. In addition, there is an increased activity of the baby. He begins to move more intensively and make breathing movements, despite the closed glottis.
At the second stage of partial compensation, the body's protective functions are determined by priority organs that are supplied with oxygen in the first place. These organs are the heart and the brain, respectively, other organs (kidneys, lungs, gastrointestinal tract) receive oxygen-poor blood, which leads to disruptions in their development and work. Lack of oxygen also leads to the breakdown of glucose. This contributes to a decrease in the supply of energy in the cells of the body and metabolic disorders.
Chronic intrauterine fetal hypoxia also has a third stage of progression - decompensation. Outwardly, the stage manifests itself as a decrease in fetal activity and a decrease in heart rate. The work of protective mechanisms aimed at providing organs with oxygen fails. Cortisol is produced in insufficient quantities, respectively, blood flow slows down, and the volume of circulating blood decreases. The blood is saturated with carbon dioxide, blood clotting is impaired, which leads to the formation of blood clots and bleeding.
Diagnostic measures
Methods of instrumental diagnostics help to determine the presence and degree of oxygen starvation. The first such method is cardiotocography (CTG). This diagnostic method is completely safe. The cardiotocography apparatus continuously records the fetal heart rate and uterine contractions. A tachogram is displayed using an ultrasonic graph. This is a graph that reflects the number of contractions of the heart muscle in a given period of time. measures fluctuations in pressure and uterine tone, displaying a hysterogram - a graph of the muscle activity of the uterus. CTG counts the number of movements and allows you to track the dependence of the heart rate on the activity of the fetus.

Starting from the twentieth week of pregnancy, an ultrasound examination with Doppler ultrasound is possible. This method is aimed at examining blood flow from the mother to the placenta and from the placenta to the fetus and allows detecting disorders of the uteroplacental circulation. Through this method diagnostics can also determine the quality of amniotic fluid.
In addition to the above methods, a specialist listens to the fetal heart to assess its work using an obstetric stethoscope. However, this method is inaccurate, therefore, if a heart anomaly is suspected, the doctor directs the pregnant woman to undergo CTG and ultrasound.
Treatment
Treatment of intrauterine hypoxy requires monitoring of the pregnant woman in the hospital. The woman is provided with complete rest and a therapeutic method of treatment is prescribed, which is aimed not only at enriching the blood with oxygen, but also at identifying true reason the occurrence of hypoxia. As a rule, abnormalities in the course of pregnancy, such as intrauterine fetal hypoxia, are the consequences or symptoms of a disease.
The doctor prescribes drugs for the pregnant woman that reduce the viscosity of the blood, improve blood flow from the mother to the placenta and normalize the metabolism between the mother and the fetus. The appointment of other drugs and procedures depends on the cause of hypoxia, if it is identified, and is aimed at eliminating this cause.
With positive dynamics, the patient is discharged and given recommendations for the prevention of hypoxia. These include walks on fresh air, decrease physical activity, refusal bad habits and compliance certain rules in nutrition. If the treatment was unsuccessful, and oxygen deficiency persists, prompt extraction of the fetus is required. If the gestation period exceeds twenty-eight weeks, the doctor prescribes an operation - a cesarean section.
Prevention
There are a number simple recommendations, the observance of which will help reduce the risk of oxygen deficiency in the baby. Before planning a pregnancy, a woman needs to deal with the treatment of chronic diseases, get rid of bad habits. When pregnancy occurs, it is important to register with a medical institution for early term... Throughout the entire period of pregnancy, it is necessary to regularly visit a doctor, take tests and do an ultrasound scan. This will ensure control over the health of the pregnant woman and the baby, and, therefore, help to avoid the development of possible pathological conditions of the fetus.

An important aspect in the prevention of intrauterine hypoxia is maintaining a healthy lifestyle. It is necessary to spend a lot of time outdoors, sleep eight hours a day, balance the diet.
During pregnancy, you need to replenish the supply of vitamins and nutrients, the level of which decreases due to the additional load on the body. Levels of calcium, magnesium and other minerals should be maintained. It is especially important to control the iron content in the blood, since its low level leads to anemia - one of the main causes of hypoxia. Vitamin preparations should be taken as prescribed by your doctor.
Consequences
The consequences of intrauterine hypoxia depend on its type. Chronic hypoxia, which began early in pregnancy, when the formation of the vital systems of the fetus is just beginning, can lead to the formation of congenital defects. Hypoxia, transferred in late pregnancy, can cause a delay in fetal development, and also leads to ischemia and necrosis of individual organs. A newborn baby often has a lack of height and weight, as well as a difficult adaptation period (restructuring of the body in a new environment). In the future, oxygen starvation experienced in the womb can cause diseases such as epilepsy and cerebral palsy.
Acute intrauterine hypoxia of the child leads to ischemia and tissue necrosis. If acute hypoxia occurs during childbirth, several consequences are possible, depending on the cause of oxygen starvation:
- The baby's airways are not completely cleared of amniotic fluid. In this case, the development of pneumonia is possible, in the worst case, the death of a child from suffocation.
- Loss of large blood volume. A newborn develops hemorrhagic shock, which disrupts the mechanisms of work of all systems. Under such circumstances, there is a threat to the life of not only the baby, but also the mother.
After the birth of a baby who has undergone hypoxia in the womb, he needs constant monitoring qualified specialists... The consequences of oxygen starvation may appear not in the first days of life, but much later. Therefore, it is very important to monitor changes and abnormalities in the development of the baby in order to identify and prevent the development of adverse effects of hypoxia.
We are glad to present you the first in the Russian-speaking Internet social network supporters of a healthy lifestyle and a full-fledged platform for the exchange of experience and knowledge in everything related to the words "health" and "medicine".
Our task is to create an atmosphere of positive, kindness and health on the site, which will cheer you up, heal and prevent, because information and thoughts are transformed into material events! ;-)
We strive to create a highly moral portal in which it will be pleasant to be the most to different people... This is facilitated by the fact that we control the actions of all users. At the same time, we want the site to be fairly objective, open and democratic. Here everyone has the right to express their personal opinion, to their own assessment and comment on any information. In addition, anyone can have an article, news or any other material in most sections of the site.
The project "To health!" positioned as a portal about health, not medicine. In our opinion, medicine is the science of how to recover from a particular disease, and health is the result of a lifestyle in which you will not get sick. The more health you have, the less likely you are to get sick. Our body is conceived in such a way that with the right lifestyle we shouldn't get sick at all. Therefore, let's improve our health instead of studying diseases. There are many sites about medicine, but in our opinion, they are intended more for medical professionals than for ordinary people... We strive to talk with you about health. We do not want to write a lot about diseases and methods of their treatment - enough has already been written about this. Instead, we'll focus your attention on how to avoid getting sick.
We are interested in a healthy lifestyle and want to live happily ever after. We believe you, too, are not indifferent to the topic of healthy longevity. Therefore, if you wish to have an environment healthy people and those who strive for this, this site will help you solve this problem. Our plans include the creation of an active community of people leading a healthy lifestyle, and in this regard, we are pleased to offer you the following opportunities:
- create your own page with personal photos, blog, forum, calendar and other sections
Do what you like, and we will try to provide you with everything you need to do this. We strive to make this site the most comfortable for you. There is still a lot of new and interesting ahead.
Register yourself and invite your colleagues, friends and close people to the site for constant contact with them and exchange of experience. Be always in touch, discussing all the news and interesting in the field of health.
Stay with us!
For a normal existence, our body desperately needs food, water and oxygen. We all know how long a person can live without food, water and air.
We are well aware of the feeling of hunger, thirst, and not everyone knows about oxygen starvation, although the lack of oxygen supply to tissues is extremely dangerous and can even lead to death. Consider the causes of hypoxia (lack of oxygen), characterized by a reduced amount of oxygen in human tissues.
Causes of hypoxia
Certain disorders and diseases lead to oxygen deficiency, poor oxygen supply to human tissues. Hypoxia is histotoxic, hypoxic and hypoxemic. In case of poisoning with toxic substances that can inhibit tissue respiration, as well as some metabolic diseases that disrupt tissue respiration, histotoxic oxygen starvation occurs. Hypoxic oxygen deficiency appears as a result of respiratory disorders (diseases of the respiratory system, oxygen deficiency in the atmosphere). Diseases of the heart and blood vessels, bleeding and blood diseases lead to impaired oxygen transport - hypoxemic lack of oxygen.
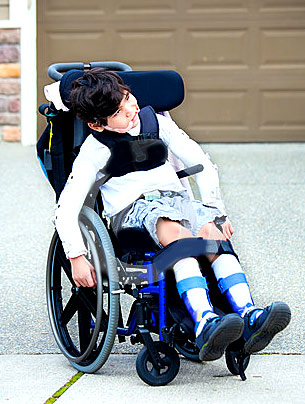 During pregnancy or childbirth, with a lack of oxygen to the fetal brain due to hemorrhages or vascular disorders, the child will be born with such a complex disease as cerebral palsy - cerebral palsy.
During pregnancy or childbirth, with a lack of oxygen to the fetal brain due to hemorrhages or vascular disorders, the child will be born with such a complex disease as cerebral palsy - cerebral palsy.
Development of oxygen deficiency
In the presence of an oxygen deficiency in the human body, a number of balancing compensatory reactions occur that contribute to an increase in oxygen utilization. Biochemical processes are activated that ensure tissue respiration, the amount of hemoglobin in the blood increases, as well as the rate of its flow. In addition, shortness of breath appears (breathing intensifies), both the minute blood volume and the number of red blood cells increase, and tachycardia appears. Further, with the development of oxygen deficiency, the activity of the entire nervous system- first, apathy, lethargy, drowsiness appear, then heaviness arises in the head, sensitivity is disturbed, movement disorders, and also the orientation is lost. Then comes a severe form of oxygen deficiency, which is characterized by involuntary urination, defecation, loss of consciousness, pulse damage, as well as periodic breathing and a decrease in blood pressure. After that, breathing stops and death occurs.
Typically, hypoxia means severe oxygen deprivation. Graded hypoxia (oxygen deficiency) demonstrates a lesser degree of oxygen deficiency. Both terms refer to a form of chronic decrease in the amount of oxygen supplied to the brain and other body tissues.
From this article you will learn what oxygen deficiency is and what it can lead to.
Oxygen deficiency of the body
What can oxygen deficiency lead to?
As a rule, metabolic processes in the body are about 93% aerobic (oxygen reacts with glucose, resulting in the release of energy). In a person with chronic rapid, and therefore shallow breathing, insufficient ventilation of the lungs causes a decrease in the level of oxygen in the body. Together with this, the metabolic process changes, and a sharp increase in the proportion of anaerobic metabolism can occur. In the process of anaerobic metabolism, the body burns other types of fuel instead of glucose. And this leads to increased production of lactic acid by the body, especially in the brain.
The increased content of lactic acid is poorly tolerated by the body, and it seeks to find an opportunity to restore acid-base balance. One way to do this is to increase the rate of respiration, due to which, as a result of the removal of carbon dioxide from the blood, its acid-forming potential decreases. It is now believed that in most cases of unexplained hyperventilation is associated with the accumulation of lactic acid in the body.
If you have a chronic form of hyperventilation and a predisposition to panic attacks, then the exacerbation of the disease is just a matter of time. These attacks are necessary for the body to cleanse the tissues and blood. As soon as the level of lactic acid in the brain reaches a certain value, any situation can provoke an exacerbation. People prone to panic attacks react much more sharply than others to changes in the brain in lactic acid levels.
Aerophobia
Fear of air travel, or aerophobia, is a perplexing phenomenon. Fear of what? Usually it is not a fear of airplanes, not even a fear of heights. People suffering from aerophobia do not even have much fear of the likelihood of dying in a plane crash.
In the passenger seat of an airplane, aerophobia is more like claustrophobia. The most that you can fear is that the door will close, then you will have an irresistible urge to leave the plane, but you will not be able to do it. But why do you fear being unable to leave the airliner? Maybe something in the cabin makes you subconsciously feel uncomfortable?
What causes panic attacks on an airplane?
Based on the belief that panic attacks are associated with breathing, scientists first began to find out what can affect breathing in the cabin. Perhaps the oxygen deficiency of the body is associated with the flight altitude?
No one has ever thought that the reason for the occurrence of panic attacks and fear in flight may be a reaction to a decrease in pressure in the cabin of the aircraft.
In the cabin of the aircraft, pressure is provided corresponding to an altitude of 1500-2000 m above sea level, while the actual flight altitude of a passenger jet plane can be 8000-13000 m. But at an altitude of 1500-2000 m in conditions of low atmospheric pressure, the level of oxygen in the blood decreases, which causes a feeling of discomfort for most people who are not used to such an altitude.
Usually, such a decrease in the level of oxygen in the brain has little effect on it.
While the cause of panic attacks and agoraphobia continues to be debated, debate raises doubts as to whether these attacks are related to breathing. Practice has shown that training correct breathing often helps to overcome these ailments and oxygen deficiency, in particular.