The formation of knowledge about geometric figures. An abstract classes "Generalization of knowledge of geometric shapes. Consolidation of knowledge of geometric figures
Read also
Children of the senior group get acquainted with the fact that geometric shapes can be conditionally divided by two groups: flat (circle, square, oval, rectangle, quadrangle) and volumetric (ball, cube, cylinder], learn to examine the form, allocate the characteristic features of these figures, find Similarity and difference, to determine the form of objects, comparing them with geometric shapes as standards.
It is expected that in this exercise, students will be able to integrate what they learned in the process of class development and complete the learning process. It is also proposed that students will find out about their learning process and on the strategies that they themselves used. It is expected that students will apply what they learned through exercises that will serve as an appraisal situation. The associated resource will allow students to observe and integrate common elements of executed geometric figures. It is very important that all students can see the projection without difficulty. If some students stayed behind or distinguished from them, they are invited to approach. The closure contains two points: one, which seeks to strengthen what was worked out during the session, and the other that hopes to show what was studied during the day. Closing can be processed sequentially or parallel. Select the suitable way. Consistently: First, students perform their activities individually, and then work collectively. In parallel: the activity is carried out jointly, while working with the proposed resource and ending with the assessment sheet. Reinforcement is supported by collective support in the first part of the presentation. Students must be motivated to reply and give examples of this case. If it is difficult for them to accomplish this task, give them forest elements to do it yourself. Remember that you should only submit a figure and the correct concept after the implementation of collective detection activities with students. Registration sheets are distributed to assess, each student puts their name on them, and the instructions are read together. Students must respond to this form individually to follow the achievement of the class goal. Record sheet can also be processed with the support of a specific material. It is recommended that the teacher read the offer and that students respond to it, and then move on to the next one. When a student makes an error, the wrong answer should not be washed, but the correct answer should be with a pencil of another color in another line to have an entry about the errors made.
- Therefore, the use of issues is a key activity.
- The closing of the class work is supported by the projection.
The method of forming geometric knowledge in the group of children of the sixth year of life does not change fundamentally. However, the examination becomes more detailed and detailed. Attendance with the practical and direct comparison of well-known geometric figures, overlapping and applying is widely used as a methodological method for measuring the conditional measure. The geometric figures are built on comparison and comparison of their models.
These arts can be elevated best part Souls to contemplation of the best beings: good. Time Plato - the most sublimated work ancient philosophy. Plato and Athens Academy. Plato was one of the philosophers, which had the greatest influence on the "history of thought" and thought more about the ideas about mathematical reality. He was a great inspirer of almost the whole mathematical activity of his time. Being one of the most wise people of his time, Plato was not properly mathematician, but his enthusiasm in mathematics and his conviction in the importance that this science had as a propiance of philosophy, in the upbringing and training of young people, in understanding of space and formation state Worker Made it with an outstanding architect of mathematicians, thanks to its disciples and friends, almost all the huge mathematical production of their time.
To identify the signs of similarities and differences in the figures of their model, first compare in pairs (square and rectangle, circle and oval), then three-four-epigurians of each type are compared, for example, quadrangles.
So, acquaintance with the rectangle, children showing the rectangles, different in size made from different materials (paper, cardboard, plastics
Platonov's doctrine of the greater influence in the "History of Thought" is the theory of ideas that has its origin in geometric formsAnd it is in the mathematical field that it is best possible to illustrate, consequently, the importance of mathematics in nature and the development of Plato's philosophy. In fact, many Meno dialogues, laws, theatette and especially the Republic and Time - suffer from mathematical discourses, and especially in the republic, Plato prescribes that the spirit of the ruling philosopher requires comprehensive learning in four sciences of the Pythagorean Quadrivium as the inevitable preliminary basis of the highest dialectical knowledge of goodness, Beauty and justice, the true goal of philosophical research, so that in each intellectual activity of the academy, mathematics, and especially geometry, reaches the meaning of philosophical and ethical, aesthetic and political value are inevitable.
sy). "Children, look at these figures. This is rectangles." Entries attention to the fact that the form does not depend on sizes. It is demonstrates to take a figure in the left hand, and the right hand to circulate along the contour. Details detect the features of this figure: Parties are equal, the angles are also equal. Check this flexion, overlapping one to another. They consider the number of sides and corners. The point compare the rectangle with the square, find similarities of differences in these figures.
Plato mathematicizes all reality, but not only physical reality, but also the spiritual sphere is moral, aesthetic, political, etc. - in an ambitious project that wants to cover the global nature of nature and man - the structure of mathematics manages not only "Nature human soul", But also" the nature of the soul of the world. " For Plato, mathematics is endowed with the nature of the Divine necessity, which synthesizes in Maxim "God always makes geometry" - the phrase attributed to Platon Plutarch. With a platonic geometry becomes the heuristic tool of all its work, which reflects the guesses and feelings of the whole greek culture.
The square to the rectangle is four angle and four sides, all the corners are equal to each other. However, the rectangle differs from the square in that the square has everything side, and the rectangle is equal only to the opposite, that is,. pairwise.
Particular attention in this group should be given to the image of geometric figures - laying out of the county points, from the paper strips. This work is carried out with both demonstration (near the table of the educator) and handouts.
Over the next ten years, with inexpressible literary art, Plato wrote the first dialogues in which he conveyed the teaching of Socrates. Having learned about the restrictions of the philosophy of their teacher, he begins to look for more strong elements on which a more positive philosophy is based and finds them in mathematics in general and in Pythagorism in particular. As a geometer, Architas was a pioneer in assessing the study of three-dimensional geometry, inheritance inherited by Plato. Although, perhaps, his influence on Plato and his salvation from his life was the biggest contribution to mathematics from his life, a petition for him in front of Tiran Dionysus.
At one of the classes, the teacher lays out a rectangle to Flanc-Lemraffe. "What is this figure? How many sides of the rectangle? How many corners are there?" Children show the parties, the corners of the rectangle. When you ask what kind of figures you can get from Rectangle (create smaller rectangles, squares, triangles)? "An additional paper strips are used with it. This is considered to consider the parties and obtained.
In his stay in Italy, Plato is shipped to Pythagorean theses - immortality and soul resettlement; structuring, description and interpretation of the Universe in terms of mathematical objects; close mutual relations between mathematics and philosophy; Mystical enthusiasm of passion for mathematical knowledge as a way philosophical lifeFormulated in the community, etc. Upon returning to Athens, Plato writes other dialogues in which, in the mouth of Socrates, it reveals not only a reduction, but also the Pythagorean doctrine, which develops in relation to the original Platonic topics.
Based on the identification of essential signs of geometric shapes, summarized the concept quadrangle.Comparing the square and rectangle among themselves, children establish that all these figures have four sides and four angle that the number of sides and angles is a common feature that is based on the definition of the concept quadrangle.
The Academy is founded by Plato in 387. Nevertheless, the Academy developed great intellectual freedom, opposing the esoteric dogmatism of the Pythagoreans. With his foundation, Plato creates the most important Center mathematical and philosophical irradiation of antiquity. From the works of Plato, we can conclude that the goal of the Academy as the Institute could be a solid intellectual formation of a group of people, a kind of enlightened technocrats, - an anachronism - very well prepared to be able to replace the Athenian political class, in the Academy, intellectual activity was developed on colloquiums, Discussions and conversations led by the moderator, as well as on master's lessons, in which Plato himself and his assistants of Professor Mathematics taught the doctrine.
In the senior preschool age, it is formed to be able to be able to use the mined knowledge into the situation that is not familiar before the situation, use these knowledge in independent activities. Signs about geometric figures are widely used, clarified, fixed in visual sections, designed.
Such classes allow children to acquire skills in dividing the complex pattern to composite elements, as well as create drawings complex form Of one or two types of geometric shapes of different sizes.
The famous phrase of admission to the Academy is not among those who are ignorant in geometry - this is an emblematic epigraph of Platonic and spirit, in which the program that Platon spent in the Academy ratified by numerous excerpts of the republic. The Academy became an important forum for discussions and controversy in philosophical, scientific and mathematical problems, where their own discoveries and research of the academy itself were collected, speculating the Ionic Physical Philosophy, the doctrines of Pythagora and Parmenide and even the atomistic concepts of Levkippa and Democritus.
For example, during one of the classes, children distributors with a set of models of geometric shapes. The tutor shows the applique of the "robot" composed of squares and rectangles of different sizes and proportions. Although everyone consistently consider the sample. Install from which parts (figures) each part is made (Fig. 24). Then work is performed according to the sample. Teachers can show two or three pictures and offers to choose one of them, carefully examined it, fold the same.
Plato himself, being an undisputed leader, noted an outstanding academic tone and character in modern sense, encouraging graduate students and debate among dedicated. The decisive authority of Platon over the Academy could not happen through his writings made throughout his life, and his oral lessons, conversations and reflections not only because of the liveliness and timeliness of debates, but because of his own plato, Poshpon attached much more importance to pronounced Word than writing, as he himself emphasizes in the Dialogue of Fedra.
Many of the reflection of Plato, which we know according to the testimony of his great student of Aristotle, are an important addition To understanding Platonov's doctrine. Platonic theory of ideas and mathematical objects. Attempt to substantiate mathematical knowledge was to become one of Platonov's motivations for the development of ideas theory, but at the same time its mathematical origin is an important aspect The importance of mathematics in nature and development Platonic philosophy Platonov's theory of ideas or forms proceeds from a very consistent rapprochement and synthesis of Pan-Pythagorean worldview, from a radical difference between reasonable and understandable Parmenides, as well as for considerations of Socrates to define and concept, true antecedent of ideas and a platoon .
In children of this age, it is important to form legal skills to show the elements of geometric fi gur. In the recalculation of the corners of the kids indicate only the top of the corner. You do not explain what is the faith of the corner, but simply so far as the point of crossing two sides Show, conducting a palm pallet along the entire segment, from one vertex angle to other. Harbor as part of a flat-rice<24 сти дети показывают одно-
It is in the mathematical field that the theory of Platon's ideas is best illustrated. For example, the circle is defined in geometry as a flat figure consisting of points equidistant from the specified one. But no one really saw this figure and cannot see her. The circular shape of geometers does not relate to sensitive objects. What we often see are the figures - a plate, a wheel, complete objects of the lunar material, which we also call circles, and which are in shape close to the perfect circle.
Therefore, the form of a circle is not in the physical world, but in the kingdom of ideas, as a clear, unchanged and timeless object, which can only be perceived by reason. The theory of ideas has its origin in geometric forms, but is not limited to them. Moreover, Plato's goal is to achieve in its idealism of the whole region of morality. And if the objectivity of the geometry makes the existence of a perfect form of a breathtaking circle separated from a circular reasonable object, which is approaching or resembles the ideal form and the need to protect the objectivity of moral forces to postivate the existence of ideal and perfect forms of good and justice, separated from earthly people and institutions, which Should approach them.
temporarily with two fingers and index.
In bulk figures (such as cylinder, cube), they allocate and call the sides and bases. For this, this can be shown by several fingers or the whole palm. The sixth year of life often independently organize didactic games that allow them to consolidate the knowledge about geometric figures. So, they organize games "garages", "Who will find?", "Order", "What box?" and etc.
Exercises for self-test
oval
quantity Task
The children of the sixth year of life introduce a new figure - ... and give the concept of ... .... The main ..., standing in front of the educator of this group, is that
Consolidation of knowledge of geometric figures
Abstract lesson mathematics
If you analyze the content of textbooks of mathematics for primary classes, you can see that the geometric material is assigned to them from one to four percent of the study time. Therefore, teachers independently select a geometric material for lessons, as they understand the need for its use for the development of visual-shaped thinking of younger students.
2nd class
Subject."Fastening knowledge about geometric figures."
Goals. Consolidate knowledge of geometric figures; the ability to solve examples in the column for the addition and subtraction of two-digit numbers; develop observation, cognitive abilities, thinking, spatial imagination, skills recognition of geometric shapes; the ability to use mathematical terms; bring up the right scientific worldview; Expand the idea of \u200b\u200bthe environment.
Equipment. Tutorial "Mathematics" for the 2nd class, Part 2, 2002, Avt. M.I. Moro; Map Scheme "Flight to Cosmos"; Methodological manual "Book"; line; Colored shallow; ropes; punch cards; sets of geometric shapes; record player; recording music "take off", "landing"; Melody of the song "What is taught at school"; colour pencils.
DURING THE CLASSES
I. Organizational moment
II. Message Topics lesson
Teacher.Today at the lesson of mathematics, we will consolidate your knowledge of geometric figures and the ability to solve examples in the column for the addition and subtraction of double-digit numbers. But the lesson is unusual. We will fly to space. During the flight, be friendly, go on comrade, do not forget that we are a single team.
III. Preparatory conversation
The board opens a flight map.
W.We start preparing for flight. What was the name of the first cosmonaut of our country?
Children. Yuri Alekseyevich Gagarin.
W.What was the name of the spacecraft on which Yuri Alekseevich Gagarin rose into space?
D."East".
W.What modern space ships do you know?
D."Shatla", "Columbia", "Union".
IV. Verbal counting
In the parties for students, sets with geometric shapes.
W.Open the design bureau. We work in pairs. From a set of geometric shapes, we build a space missile.
Children perform a task.
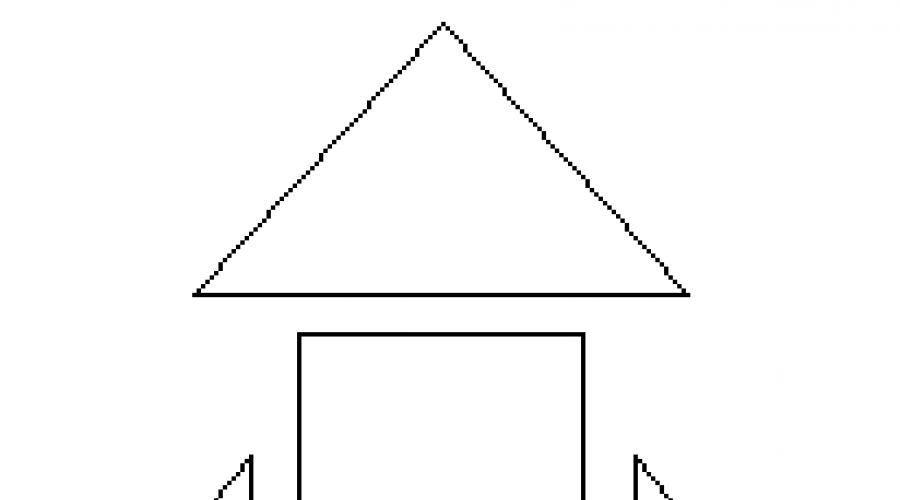
- What geometric figures is our missile?
D.From triangles and square.
W.How many triangles?
D.Three.
W.Why did you decide that these are triangles?
D.Figures have three corners, three vertices, three sides.
W.Look at the central part of the rocket. What is the figure?
D.Rectangle.
W.What do you know about a rectangle?
D.It has four sides, four vertices, four straight corners.
W.What else do you know about this figure?
D.The opposite directions of the rectangle are equal.
W.Measure the length of the side of the rectangle. What are they equal?
D.10 cm and 5 cm.
W.Find the perimeter of the rectangle. Let's remember what is called a perimeter.
D.Perimeter is the sum of the lengths of all sides.
W.What is the perimeter?
D.30 cm.
W.How did you find the perimeter?
Children answer.
- Well done! So that our rocket soared, you need to know the encrypted word. To do this, perform calculations and use the alphabetic key. Consider verbally, and write the answers to the notebook.
On the magnetic board, the first sheet of the methodical manual "Book".
Children perform a task.
- Record the answers on the second line in ascending order, and under them - letters.
W.What word did it work?
D.Takeoff.
W.We start counting together, all together.
D.5, 4, 3, 2, 1 - Start!
Music "take-off" sounds, a line on the moon is held on the scheme.
V. Fastening the material passed
W.We made a landing on the moon. But the first people went down to the surface of the moon back in 1969. These were American astronauts Neil Armstrong and Edwin Oldrin. Here we have to do a mathematical task - to solve examples from the task number 1 on with. 33. We work according to options.
Option 1 - examples under the number 2.
Option 2 - examples under digit 3.
Getting to work.
Children perform a task in notebooks.
At the board - two student.
Option 1
Option 2.
Examples are checked.
- How do examples write in the column for addition and subtracting two-digit numbers?
D.Units are written under units, dozens write under dozens.
W.How do double-digit numbers?
D.Units with units, tens of dozens.
W.How do double-digit numbers deduct?
D.Units are subtracted from units, dozens are deducted from dozens.
W.Okay. Close the tutorial. You can go to another planet.
Vi. Fizkultminutka
The teacher includes audio cassette. To the music of the song "What is taught at school" children perform exercise.

VII. Fastening the material passed (continued)
W.We flew to the planet Mars.
A line is on the map scheme.
- Would you like to learn anything about this planet?
Mars - Planet of the Solar System, the fourth of the sun.
At the discretion of the teacher, you can choose a material for a small message about Mars.
This is what task you are offered on Mars: Find your geometric shapes familiar to you. Remember how they are called.
The magnetic board opens the second sheet of the methodical manual "Book".
Children answer.
- And now let's make some constructions.
On the chalkboard, the construction performs the teacher, children work in notebooks by performing all the task stages.
- Draw a straight line. Can we portray the whole straight?
D.Not.
W.Why?
D.It is extended in both directions endlessly.
W.What are we black?
D.Part of straight.
W.Mark the point on it BUT. How to get a segment?
D.We must put another point.
W.Denote her letter FROM. Name a segment.
D.Section AC.
W.What is a segment?
D.Part of a straight line limited to two dots.
W.Mark red pencil cut AC. What are the unwitted parts direct?
D.Rays.
W.Right. Show them . What is a beam?
D.Part of a straight line that has the beginning, but no end.
The teacher gives the rope for children.
W.Now let's try to get these figures practically - on the rope. Your fingers are points.
Show cut. Show the beam.
Children perform a task.
- Well done! Let's fly further. Our path lies on the planet Jupiter. While the rocket goes on the autopilot, you have another interesting task. On the table you have perfocarts. It is necessary to independently find the perimeter of the shape given in it.
Children proposed four options for cards. They perform a task, recording a solution in notebooks.
- We arrived on the planet Jupiter ( line is conducted on the map scheme). This is the largest planet of the solar system. Look at the card scheme. What geometric figure depicts our route?
D.Loaven.
W.How many links in it?
D.Three.
W.Build yourself alone broken from three links with lengths of 7 cm, 3 cm, 2 cm. We work with colored pencils.
Find the length of the broken, draw the segment of the same length.
Children perform a task.
- We completed a lot of interesting mathematical tasks by traveling by the planets of the solar system. It's time to go back to the ground, where we love and wait. To return, you need to guess to everyone together to guess the crossword.
VIII. Total lesson
On the magnetic board - the third sheet of the methodical manual "Book".
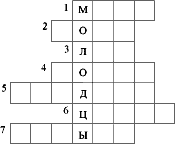
1. Measure of length, consisting of 10 dm.
2. Geometric shape with equal parties, but indirect corners.
3. Part of the direct, which has the beginning, but there is no end.
4. The smallest geometric figure.
5. Rectangle with equal sides.
6. Sign (symbol) to designate the number.
7. The following number 3.
Answers: 1 meter. 2. Rhombus. 3. Ray. 4. Point. 5. Square. 6. Figure. 7. Four.
W.What word happened in the isolated cells?
D. Well done.
On the map scheme the line is carried out to the ground.
Sounds music "Landing".
W.From the flight returned
And landed to Earth.
What will you tell me at home? Start your answer from any of these proposals.
On the magnetic board - the fourth sheet of the methodical manual "Book".
Lisviar to the answers of children.
- Thank you for work! The lesson is over.