What is a local act? Local regulations of the organization. Charter and system of local acts of the educational organization
Read also
Topic 1 Charter of the educational organization
The main characteristics of the organization of the educational process, including:
Language (languages) on which training and education are underway;
Rules for receiving students, pupils;
Duration of training at every stage of training;
The procedure and foundation of the deductions of students, pupils;
§ 1.3. The procedure for adoption, approval and registration of the Charter of the educational organization
According to the Law of the Russian Federation "On Education" (paragraph 2 of Art. 13), the charter of the civil educational organization in a part, not resolved by the legislation of the Russian Federation, is developed and adopted by the educational organization and is approved by its founder.
The procedure for approving the charter of the Federal State Educational Institution is established by the authorized Government of the Russian Federation by the federal executive body, a state educational institution under the jurisdiction of the subject of the Russian Federation, the authority of the executive authority of the subject of the Russian Federation, the municipal educational institution - the local government body. Thus, in each municipal district and the urban district, a regulatory legal act must be adopted, which determines the procedure for approving the Charter. The absence of such a regulatory legal act is violation of legislation in the field of education from the relevant authorized local government body. It should be noted that the charter of the Law of the Russian Federation "On Education" on the approval of the Charter, the founder does not mean that the Charter is approved by one body that performs the functions of the founder. Thus, in order of approval of the Charter, a sufficiently multi-stage assertion procedure may be described, which involves participating in the approval of several government bodies or bodies of local governments that perform the functions of the founder within various procedures for visiting, approval, etc.
Subparagraph 12 of paragraph 2 of Art. 32 of the Law of the Russian Federation "On Education" clarifies that the competence of an educational organization includes the development and adoption of the charter by the team of the educational organization for approval. " Under the team, in our opinion, it is necessary to understand not only employees of the educational organization, but also other participants in the educational process: students, parents (legal representatives). The charter can be adopted at the general meeting of the participants of the educational process or at their conference.
The situation is somewhat more complicated with the statement of the Charter when creating an educational organization. The charter is a prerequisite for state registration of the creation of an educational organization as a legal entity, in connection with this, it must be approved before the formation of the educational organization team. Separate typical positions contain a norm regulating this situation. Thus, in accordance with paragraph 34 of the Model Provision on the educational institution of primary vocational education approved by the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation of 01.01.01. No. № 000, it is assigned that the Charter is approved for the founder for a period of no more than 1 year. It seems that in the newly created educational organizations of other types and species (for example, schools) before the formation of the collective, the Charter may be approved by the founder for a period no more than a year. It is advisable that such a norm is present in the act of local self-government body, which establishes the procedure for approving the statutes, and then in the Charter itself.
Any changes and additions to the charter of the educational organization are accepted in the same manner as the Charter itself.
The charter, adopted and approved by the founder (changes to the Charter) subject to state registration. The procedure for state registration of changes to the constituent documents of legal entities is settled by the Federal Law "On State Registration of Legal Entities and Individual Entrepreneurs" of August 8, 2001 (with subsequent changes and additions). Regarding the registration of changes to the constituent documents of state and municipal educational institutions, there are registration forms and registration procedures provided for for commercial organizations, and the registration itself is carried out in the territorial bodies of the Federal Tax Service (tax inspectorates) (clauses 4.1., 4.2., 5 tbsp. 1 Federal Law "On Non-Profit Organizations"). Statutes of non-state (private) educational organizations are registered in a special manner provided for non-profit organizations in the bodies of the Ministry of Justice of the Russian Federation (Art. 23 of the Federal Law "On Non-Profit Organizations")
Control questions about the topic 1
1. List the signs of the Charter as the main local act of the educational institution
2. List special requirements for the content of the charter of the educational institution
3. Describe the algorithm to make changes to the charter of the educational institution
Topic 2 Concept, signs and types of local acts
§ 2.1. The concept of local act
The system of local acts of the educational organization is the subject of oversight of compliance with the legislation of the Russian Federation in the field of education, which is one of the main functions of government bodies, carrying out control and supervision in education. When conducting measures to oversee the observance of the legislation of the Russian Federation in the field of education, the supervision persons check, first of all, the content of the regulatory framework of the educational organization developed and adopted at the local level and then direct activities of the organization, i.e. as data Local acts are implemented in practice.
The local act of the educational organization is the official legal document based on the legislation, adopted in the established procedure by the competent authority of the educational organization and regulating relations within the framework of this educational organization.
§ 2.2. Signs of local act
Consider in detail the signs that all local acts of the educational organization must meet.
1. The local act of the educational organization is the official legal document published in writing and containing the necessary details:
(a) the name reflecting the form of the act and its brief content (for example, the rules of behavior of students);
(b) the date of publication;
(c) sequence (registration) number
(d) Signature of an authorized official
(e) In the necessary cases of approval visas and the printing of a general education organization (for example, a local act defining the annual calendar learning schedule should have a visa agreement with the local government body, subparagraph 8 of paragraph 2 of Art. 32 of the Law of the Russian Federation "On Education").
It should be noted that currently there is no compulsory requirements for the design of local acts. Requirements GOST R 6.30-2003 "Unified documentation systems. Unified system of organizational and administrative documentation. Requirements for paperwork "are recommended.
2. The local act of the educational organization is based on legislation in the broad sense of the word, that is, not only on federal laws and laws of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation, but also on sub-law regulations. First of all, any local act must comply with the Law of the Russian Federation "On Education", as well as a Model Regulations on the educational organization of the appropriate type and view. In addition, it is necessary to remember that the legal support of the activities of the educational organization is of a multi-level character. The activities of the educational organization are regulated by federal regulatory acts and regulatory acts of the authorities of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation. In addition, some issues of the activities of municipal educational institutions can be resolved locally, in accordance with the competence of local governments.
Inspection checks conducted in various regions of Russia have shown that the formation of the legal field of the activities of educational institutions began to be implemented everywhere with great or less successful.
Despite differences in the pace and character of changes in the educational situation in various regions of the country, general problems arise in the heads of educational institutions. First of all, this is due to the established RF "On Education" by self-determination in the form of educational institutions and the need to form a legal field of their activities. Democratization of education determines the state-public management of the management, thanks to which they are united and interacting, coordinate their actions of state and public associations, management structures, organizations.
At interregional seminars, meetings conducted by the Office of General Education and Inspection in 1999-2001, it has already been noted that in accordance with the Law of the Russian Federation "On Education" in the editorial office of the Federal Law of 13.01.96 N 12-ФЗ educational institution was granted the right to independently Determine the regulatory legal framework for its activities. This is the competence of an educational institution. For education authorities - recommendations and control.
The Ministry of Education of Russia, analyzing the results of the inspections, notes that in the development of the legal field of the activities of educational institutions, the following problems were designated:
4. Compliance with the developed regulatory legal framework governing the activities of the educational institution, the current legislation of the Russian Federation in the field of education.
If the first first of the listed problems are organizational in nature, the two latter indicate that at the present stage, the quality of the formed legal field is becoming increasingly valid.
It is relatively simple to the specialists of the education authorities to check the decision of the first, organizational, problems. An exemplary list of local acts has already been discussed at an inspection meeting in Pskov, published in the collection of information materials following this meeting and in the methodological recommendations "Local acts of the educational institution" of the State Inspectorate in the Ministry of Education of Russia. Therefore, when checking the charters, which are a fundamental document for the formation of the legal field of the activities of educational institutions, it is necessary to highlight the list of local acts for this institution and compare its completeness with the list, which is given in the annex to the Charter.
The "Charter of the educational institution" of the Law of the Russian Federation "On Education" shows that in the charter of the educational institution, it is mandatory: "The structure, procedure for the formation of the management bodies of the educational institution, their competence and procedure for organizing activities." Therefore, it is necessary to determine:
This refers to the Council of the Educational Institution, the Pedagogical Council, the Parental Committee, the General Assembly of the Labor Collection, Methodological Associations in the specialties, Senigod Soviets, the Councils of graduates and other authorities of the educational institution (the Law of the Russian Federation "on Education").
The classic organizational method of distribution and consolidation of tasks, functions (duties), rights and responsibility, the establishment of relationships is to regulate. Regulation is carried out using provisions, job descriptions and other regulations.
The "Functions (duties)" section contains a list of functions, which ensures the solution of the tasks assigned to the authority of self-government with a certain specificization of work for each function.
The "Management Organization" section contains a description of the organizational structure of the self-government body, instructions on the place of managers within the authority itself (for example, in the presence of groups, commissions, etc.), determines the frequency, time and type of organizational events (planners, meetings, etc. .).
The "relationship with other divisions" section is developed on the basis of incoming and outgoing documentation with the definition of basic relationships. This section may establish the relationship of this self-government body with public units (organizations) - all sorts of public councils and commissions, trade union, etc.
The "Responsibility" section provides for the establishment of the responsibility of the authority of self-government and its head for the tasks and the implementation of functions. This section is characterized by the greatest difficulty of development, as it is necessary to indicate the application of sanctions for failure to comply with or poorly performing tasks, functions, as well as to determine the conditions under which one or that responsibility comes. But, as a rule, in this section there is such an entry: "the authority of the self-government is responsible for performing the tasks and functions assigned to it."
The basis for the compilation of job descriptions of employees of educational institutions should be the charter and provision on the type and view of the educational institution, the qualifications and qualification requirements for positions, the standards of labor costs for work.
Official instructions, as a rule, is developing the head of the management body with the help of the workers themselves for which they are published. At the same time, the entire amount of the work of work inherent in this body is taken into account. In controversial cases, the so-called is held. Photos of the working day. Official instructions are recommended to revise and update, as necessary, due to the change in the function of the management authorities.
What are locally-regulatory acts?
Local-regulatory acts -these are documents that establish certain regulations for multiple applications, mandatory for all employees of the organization, that is, possessing regulatory.
Signs of regulatory acts:
- written design (no oral regulations);
- adoption in the prescribed manner;
- action on an uncertain circle of persons;
- multiple use;
- creation for regulatory regulation.
It is worth noting that LNA can not be confused with regulatory actssince the concept "legal" It applies only to those documents that are accepted by the authorities. Regulatory acts are located in a certain hierarchy, where the main document is the Constitution of the Russian Federation, the Federal NPU followed (laws and codes), and then regional. Documents of the lowest stage cannot contradict the legal acts of the highest level, and all acts must comply with the Constitution of the Russian Federation.
In the educational organization, local regulatory acts also constitute a hierarchy. The local act of higher legal force in the organization should recognize its charter, followed by orders, provisions and orders. Documents of the educational organization cannot contradict its statute, regional and federal legislation.
What types of L N are divided into?
Local-regulatory acts according to the degree of importance are divided into mandatory and optional. The composition of the mandatory LNA is determined by law, the optional LNA is not provided for by law. Their facility takes at its discretion. For example, job descriptions, the provision on the organization of children's rest, the provision on the training of employees and so on.
For educational organizations, mandatory LNA establishes Article 30 of the Federal Law N 273-FZ. It says that educational organizations are developing LNA on the organization and implementation of educational activities, including:
- rules of reception;
- classes;
- current control and intermediate certification (procedure, form and frequency);
- translation, deduction or recovery of students (procedure and base);
- the procedure for registration of the occurrence, suspension and termination of relations between OO and students or their parents (legal representatives).
Please note that this article does not specify a specific type of LNA - order, order or position. Only themes of these documents are given.
The obligatory also includes documents regulating labor relations: internal regulations, the provision on certification, instructions and rules governing the safety and protection of labor in the institution, the Regulation on remuneration and others.
These documents should be in any organization and are developed in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation:
- lNA standards should not worsen the position of employees compared with labor legislation, collective agreement, agreements;
- documents are brought to the attention of employees under the signature;
- local-regulatory acts are mandatory. For non-fulfillment of their provisions, an employee can attract disciplinary responsibility, and an employer to administrative.
According to the method of adopting LNA are divided into:
- accepted by the head alone (staffing schedule, job descriptions, orders, orders);
- accepted, taking into account the views of the representative body of workers (the provision on the training, retraining and advanced training of employees). In such cases, the procedure provided for in Article 372 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation is observed.
The opinion of the representative body of workers is taken into account when adopting:
- documents establishing rules of labor (Article 162 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- replacement schedules (Article 103 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- labor payment provisions (article 135 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- internal regulations (Article 190 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation);
- local acts establishing forms of preparation and additional professional education of workers (Article 196 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
By the nature of the action, LNA is distinguished:
- general - apply to all employees of the organization (the rules of the internal regulations, the regulation on labor payment);
- special - distributed to a certain category of workers (a provision on a particular unit, a regulation on the direction of business trips).
What is guided by an educational institution when developing LNA?
Almost all requirements for LNA are formulated in the law "On Education in the Russian Federation". How to use it? The principle is quite simple - if the institution has a situation described in the norm of the Law on Education, it also arises and the need to create an appropriate locally regulatory act.
For example, Article 16 of the Law "On Education in the Russian Federation" provides for the possibility of obtaining education remotely. If the educational institution is going to use this opportunity, the corresponding internal document is accepted, if not going, then there is no need for locally-regulatory regulation.
The need to take local acts is also due to those regulatory and legal acts that do not regulate or educational or labor relations. For example, the Federal Law of December 25, 2008 No. 273-FZ "On Countering Corruption" obliges all organizations to take measures to prevent corruption.
In a letter dated April 1, 2013, the Ministry of Education and Science recommends that the adoption of those LNAs that regulate:
- rules of reception;
- classes;
- training according to the individual curriculum;
- forms, frequency and order of current control of academic performance and interim certification of students;
- the procedure and grounds for translating, deducting and restoring students, the procedure for issuing, suspension and termination of relations between the educational organization and training and (or) parents (legal representatives) of minor students;
- scholarship size and fees for using residential premises in a hostel for students;
- the procedure and forms of conducting final certification and others.
In total, the letter contains a list of 28 local regulations, the adoption of which is included in the competence of educational organizations and their founders (paragraph 19.34).
The Ministry of Education and Science offers the leaders of educational organizations when working with documents, use the methodical recommendations set forth in the Ministry of the Ministry of December 20, 2000 N 03-51 / 64. This letter contains the requirements for the preparation of specific types of organizational and regulatory documents, the rules of systematization and storage of documents, the procedure for working with them.
How are LNA accepted in an educational organization?
The procedure for the development, adoption and approval of local regulatory acts is determined by the educational organization itself. This procedure is usually fixed in the establishment charter.
It is important that the language of documents is understandable to people with different levels of education, since local regulatory acts of the educational organization are interesting not only to employees of this institution, but also to parents or learning themselves. Ideally, the text of the documents need to write as if you write for a sixteen-year-old teenager: just with a minimum of special terms.
The procedure for developing local regulatory acts:
- Determination of issues for which the adoption of LNA is needed. Document projects are developed by the decision of the Administration, the Pedagogical Council, the General Meeting of Employees and the Parent Committee.
Any employee of the institution has the right to develop a question about the development and adoption of a locally regulatory act.
- Definition of stages and timing of document development. As a rule, they are set even at the discussion stage.
- Creating a Working Group on LNA. The administration entrusts this work to a division, a third party or develops the project independently.
It is important to competently distribute the tasks between employees: who will draw up a document who will check for compliance with the law, and who will issue it correctly. The LNA Development Working Group may include not only representatives of the administration and pedagogical workers, but also members of the Public Council, parents of students and students themselves (for example, representatives of the student council).
- Preparation of a locally regulatory act: The Working Group prepares a draft document, justifies the need for this act and provides for the consequences of its adoption.
- The project is made to discuss. The developed document is discussed at a meeting of the body, where it is approved or sent to refinement. LNA approval is issued by the Protocol. There may be other forms of submission to the discussion: the placement of the project on the information booth, the site of the educational institution and so on.
- Further step - the introduction of LNA into action. For this, the head publishes the corresponding order. From the date of its publication, locally regulatory comes into force.
Please note that in some cases local acts should be taken with the opinion of the representative body of workers (Article 8 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). Such a body can be a trade union committee.
The accounting procedure is described in Article 372 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The trade unity expresses its opinion on the LNA project in writing and transfers to the head of the organization to five working days from the date of receipt of the document.
If the trade union does not agree with the adoption of LNA, then the head for three days is holding additional consultations with the Committee. If it was not possible to come to the general decision, then the disagreements arising from the protocol. After that, the head has the right to take a local regulatory act, which the trade union committee can appeal in court or in the state inspection of labor.
Elena Zachёsova in the June webinar "Three strategies for educational organizations in the conditions of continuous reform of the education system" recommended unifying all documents in order to simplify the development process, that is, create templates. Do so that all the provisions begin in a single way - for example, "the present position describes that something and that" or "This provision is created with the aim of regulating such and such a thing." Creating templates will greatly simplify your life, over time it will be saved for you.
It will still be good if you choose a separate person who will deduct all these LNA, to check them with the charter, federal and regional legislation, check for errors and typos. For example, you in some state refer to the law "On Education in the Russian Federation", but the number of the law specifically indicated - instead of N 273-FZ wrote N 263-FZ. It would seem that a minor typo in LNA makes a document invalid.
The adoption of local-regulatory acts is not something outside of understanding, but if you underestimate the seriousness of working with documents, this will lead to miscalculations in the organization's activities will complicate it. Local regulations are developed and accepted in the educational organization collectively, the team. This is the task of the leader - to form a team of like-minded people and organize her work.
How to improve your organization's work, you will learn on the online marathon
Any enterprise, a company or firm, among their documentation, current local regulations that may be disciplinary rules, job descriptions or different provisions. Local act may relate:
- to the category of commonly established (mandatory) acts for any enterprise,
- to the category of acts voluntarily created by the employer.
Whatever the locally regulatory acts of the Organization, it is important that they exist within the law, that is, did not have contradictions with law. There is another characteristic feature of such a brand document. The local act is mandatory for execution for both the employer and for its subordinates.
In this article, consider all sorts of features of this type of documents.
Local act is ...
It should be started with the fact that the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (the fifth article TKRF) regulates relations between the employer and the employee through labor protection, possible agreements and acts with labor law norms. Local acts of the organization with the rules of labor law given in them also regulate working relationships.
Such a document is commonly installed for all employers. It corresponds to other documentation that contains similar criteria. This indicates the eighth article (first part) of the Labor Code. However, some definite meaning for the concept of "local act" is not enshrined:
- someone believes that these are local acts of the organization, which contain multiple repetition of existing rules of employee behavior, and establishes their employer (this is an incomplete definition);
- the following value will be more correct and complete: "A document containing the norms of labor law, which is adopted by the employer within its competence in accordance with the laws and other regulatory legal acts, collective agreement, agreements."
Features of the document (locally regulatory act)
- Possible changes in it are determined by the employer.
- The standards contained in the document do not contradict the law or labor contract.
- It is approved in the form of instructions or position by the head by the employer (enshrined in writing). In some cases, when interacting with the organization's union.
- With this document, a staff member must introduce this document, confirming this action by his personal signature.
- It has legal force from the day when it will be accepted, or another date prescribed on paper.
- Terminates its action when its term expires or in case of cancellation by the employer / court.
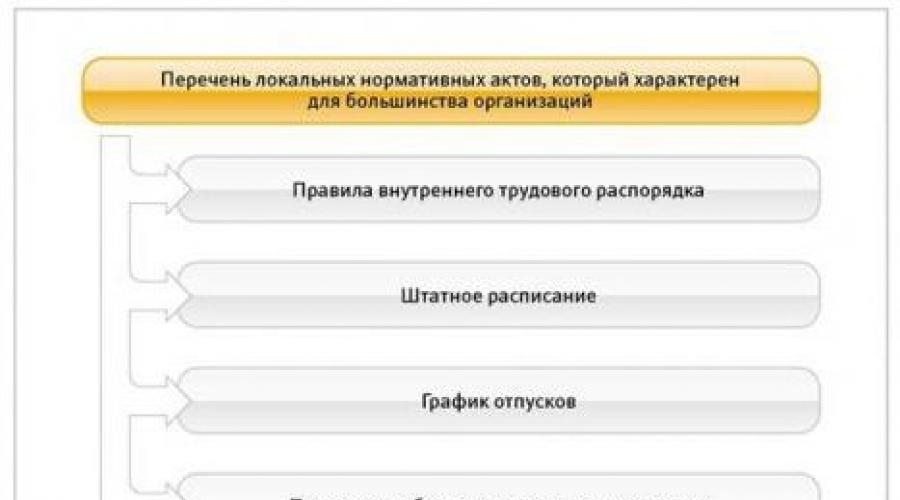
What documents refer to local regulatory acts of the organization?
Below in the photo shows a list of documents that are local regulatory acts characteristic of the majority of organizations.

How are local acts of institution take?
Each local regulatory act of the organization passes certain stages. At first it is developed, then it is coordinated, then it is approved, after which it is legal and enforced.
Such a sequence of creating such documents may also be established by a characteristic local act (for example, according to the organization of the Regulation on the procedure for adopting local regulatory acts - a sample of an act is shown in the photo).

Stage of the development of locally regulatory acts of the organization
The document is being developed directly specially engaged in this activity (to appoint leadership) by the working group of persons (or by the person executor) on the basis of the existing order. This can be done as a simple personnel officer or chief accountant, and the union of the heads of units.

Stage of approval of local acts
After development, a local act is necessarily in the process of coordination with other structural units or departments. At the same time, general comments, comments, consent / disagreement workers reflect on a separate special form.
Stage approval of local acts of institution (organization)
After the coordination process, the document is sent for approval to the authorities.
Before you make your decision, the head must send a project with justifying the trade union organization. This representative body by employees has a maximum of five days for consideration and nomination in the reverse order of its written opinion on this local act.
If the trade union agrees with the local act, this document is entered into its action.

If the trade union provided consent, or provided, but taking into account some wishes, the leader is obliged no later than three days (after receiving an answer) to organize additional consultations with the representative body to achieve mutual understanding and decision.
Local school acts
It is worth a separately discharged for documentation in general education institutions that can independently create their own local regulatory bases from the acts because the law "On education" of the Russian Federation states that the Charter of the General Education should have a certain list of local acts. But when creating additional documents, which add additions to the existing statute (for example, it can be new local acts), it is necessary to register them in the IFTS. Otherwise, inconsistencies in the regulatory framework of the organization will arise.
Local acts of general education institutions are legitimate and official legal documents. They are accepted in proper sequence to regulate relations within school, reflected in the organization's charter.
Local school acts must reflect the following principles:
- They are created for a certain educational institution and act, respectively, within the walls of one organization.
- They are official written legal instruments containing all the mandatory details.
- In the process of creating and introducing a local act, all subjects of the education process are involved.
Types of local acts of the educational institution
School documents, as well as local acts of the DOU (pre-school educational institution) may be regulatory. Such documentation contains a list of certain rules and norms that must be complyed with all participants in the education process. It is characterized by a long-term application. Such acts detail and complement the legal norm regarding each individual school.
Individual local acts are also distinguished. As a rule, they are once and used to secure a certain solution from a legal point of view.
What documents relate to local school acts?
Local acts of education are decisions, decisions, orders, instructions, rules, provisions and contracts. They reflect and regulate different sides of the school. Notice, the same type of documentation has local acts of DOU. Consider every document.
- Resolutions: These local acts can be individual legal documents and regulatory. They reflect the decision of the school manager.
- Solutions: The general meeting of employees takes local such documents very often worry the nature of the recommendations.
- Orders: Such a document is published by the Director of the educational institution to resolve the main tasks. For example, below, in the photo, a sample of the act is given - an order for the approval of the rules of the internal regulation of the school.
The bodies that manage the school, such documents, as decisions and orders, approve the provisions, rules, instructions.

How should locally-regulatory acts
Labor legislation did not create certain requirements regarding the design of such documents. But there is GOST R6.30-2003, which includes information about the necessary requirements that need to be observed when creating and designing a local act. According to him, any document (with the exception of the letter) is drawn up on a special form and contains the following information:
- the full and abbreviated name of the organization (then the name, which is indicated in the constituent documents);
- indication by capital letters of the name after the name of the organization;
- approval date and serial number of the act during registration;
- specifying the place of creation and design of the document;
- the presence of signature (s) coordination;
- note at the end of the application information document;
- compliance with the structure of the document, which includes all the necessary provisions (general, main part and final);
- sections (with number and title), items and subparagraphs are necessarily a meaningful part of the document;
- mandatory in the middle of the top field of the sheet (starting from the second page) is carried out.
- It is necessary to preserve the grinding of the organization's management in the upper right corner. The statement can be represented by either a simple signature of the chief or a separate order created. Everything is assigned to print.
Familiarization with the act of employees of the organization
After approval of the locally regulatory act, it passes the registration stage in a special journal and receives an individual number and indication of the dates from which it enters into legal force.
With this act, management is obliged to acquaint those employees whose activities are affected in this document, according to Article 22 (part 2) of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The familiarization process is reflected in special introductory sheets in the form of a separate application to a locally regulatory act, and is also reflected in the reference journal.
How local acts are stored
All original acts should be stored in one place (office, reception or personnel department). Copying documents occurs when the document is distributed among departments and structural divisions.

Such local documents have an unlimited shelf life in accordance with the list of model management archival documents that are formed during the work of state bodies, local governments and organizations.
Local acts of the educational institution.
The concept of "local act of a general education institution"
The local act of the general education institution is the official legal document based on the legislation, adopted in the prescribed manner by the competent authority of the school management to regulate intraschool relations.
Local act has the following distinguishing features.
1. The locality of the act means that the ACT is valid only within this organization. Local school acts cannot regulate the relationships out of the educational institution.
2. Local act is always based on legislation in the broad sense of the word, i.e. Not only on federal laws and laws of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation, but also on sub-law regulations.
Legal support of the activities of the general education institution is multi-level. The following levels of legal support are distinguished:
1) federal level. Legal support at the given level is the adoption of federal laws based on the Constitution of the Russian Federation, the decrees of the President of Russia, the decisions of the Government of Russia and the regulatory legal acts of the industry executive bodies, primarily the Ministry of Education of Russia.
2) the level of the subject of the Russian Federation. At this level, laws and other regulatory legal acts of state authorities of the constituent entity of the Russian Federation, ensuring the activities of educational institutions.
3) Municipal level. Regulatory legal acts of local governments in the field of education are of the greatest importance for municipal educational institutions.
4) Local regulations of the educational institution. These include orders, instructions, provisions taken within their competence by the bodies of the educational institution and mandatory participants in the educational process or wider by employees, students and their legitimate representatives of a specific institution of education.
The listed regulatory legal acts are in hierarchical coen. This means that the laws of the Russian Federation cannot contradict the Constitution of the Russian Federation, the decrees of the President of the Russian Federation - the Constitution and Federal Laws, the Decree of the Government of the Russian Federation - the Constitution and the Laws of the Russian Federation, the Charter of the educational institution - the Constitution, the laws and regulations of the Government of the Russian Federation, etc. Therefore, changes in legal regulation of education issues, for example, at the federal level entails a chain reaction of changes at all other levels. True, with one important condition: if changes in legal regulation were conducted by federal government bodies within their competence.
3. The local act of the school is the official right act, i.e. A written document containing the necessary details: the name reflecting the form of the act and its summary, the date of publication, the sequence (registration) number, the signature of an authorized official, in the necessary cases of approval visas and the press of a general education institution.
4. To be eligible, the local act of the school should be not only an official legal act corresponding to the legislation, but also the act adopted by the competent authority of the general education institution. The delimitation of the powers between the school principal and the school authorities is determined by the Charter of the general education institution, which is sometimes called the School Constitution *.
Types of local acts of the educational institution
Local legal acts of the school can be regulatory and individual.
Local regulatory act is a legal document containing generally binding rules for all or some school employees and (or) students (their legal representatives), designed for repeated use. For example, the school charter, the rules of the internal labor regulation, the official instruction of the employee. The function of the local regulatory act is detailing, concretization, addition, and sometimes the replenishment of the general, legislative (in the broad sense) of the legal norm in relation to the conditions of this school, taking into account the available features, the specifics of the educational process in this general education institution, other conditions for the existence of the school team.
Individual (abnormative, managerial, law enforcement) Local acts are used to legalize a specific management solution and are not designed for repeated use. For example, an order for employment, about vacation, about dismissal.
Local school acts are published in the form of decisions, orders, decisions, regulations, instructions and rules.
Decision - Local regulatory or individual legal act, containing the solution of the collegial management body of a general education institution. For example, the Decree of the School Council on approval of the school component of the State Educational Standard of General Education, the Resolution of the School Council on leased for the School of Property, the Resolution of the School Council on the exclusion of a student from school.
Order - Local regulatory or individual (administrative) legal act published by the school principal to solve the main and operational tasks facing the general education institution. For example, an order for admission to work, an order to approve the rules of the internal labor regulation of the school.
Decision - Local legal act adopted by the general meeting of employees (students, their legal representatives) for the realization of the right to participate in the management of a general education institution. For example, the decision of the General Meeting on the election of representatives of employees to the Commission on School Labor Disputes; Decision of the parental meeting (meetings of students II and III steps) on the election of their representatives to the school council. Local school acts adopted in the form of solutions, as a rule, are not regulatory.
The decisions and orders of the school management bodies are approved and the local regulations adopted in the form of provisions, instructions and rules are approved.
Position - Local regulatory legal act establishing the legal status of the school management body, structural division of the school or the basic rules (order, procedure) of the implementation of a general education institution of any of its own emphasis. As an example, it is possible to bring the Regulations on the library of the school, the Regulation on the payment of labor and the bonuses of workers, the Regulation on the interim certification and the translation of the students.
Instruction (from lat. Instructio is an instruction) - a local regulatory legal act establishing an order and method of implementation, performing something. Instructions determine the legal status (right, responsibilities, responsibility) of the employee for his position (job description, Slang - "functional"), safe techniques of work (safety instructions for individual traumatic jobs and training books), rules for conducting office work (instructions for office work ). The instructions are characterized by imperative (imperative, non-selective regulatory prescriptions.
rules - Local regulatory legal act, regulating organizational, disciplinary, economic and other special parties to the activities of the school and its employees, students and their legal representatives. A typical example of this type of local acts can serve as the rules of the internal labor regulations of the school, the rules for the school, the rules for the behavior of students, the rules on the promotions and recovery of students.
Rules, instructions, provisions may regulate the most sides of the school's life. In addition to these local regulations, there are specific local acts governing socio-labor relations (for example, a collective employment contract).
Classification of local acts in the direction of school activities
Local acts, both regulatory and individual, are the means of legal support of the school. At the same time, the importance of local regulations is particularly large, since the rule-making activity of the school is related to the provision of an educational institution provided for by the legislation (autonomy).
The rule-making activity of the school is carried out within its competence, defined by Art. 32.2 of the Law of the Russian Federation "On Education".
In accordance with the competence of the general education institution, the following directions of local legal support of its main activity can be distinguished:
legal support of the establishment of agencies as general education (creation, licensing, certification and state accreditation of an educational institution, the formation of the structure of the institution and management bodies);
legal support of the educational process (process of learning and education) and its methodical support;
legal support of financial and economic activity;
legal support of logistics;
legal support of the safe conditions of study and labor in a general education institution;
legal support of labor relations (work with personnel);
Legal support of office work (documentary support) of all parties to the activities of the general education institution.
According to the enlarged areas of school's activities, legal support of the general education institution requires, as a rule, the adoption of the following local acts:
1) acts that determine the legal status of a general education institution, acts on school self-government:
Charter of the general education institution;
Regulations on the Council of the General Education;
Regulations on the Board of Trustees;
Regulations on the Pedagogical Council.
2) acts that determine the status of structural units of the general education institution and the specifics of the rights and obligations of participants in the educational process:
Provisions on structural divisions;
The rules of the internal labor regulation;
Staff schedule;
Job descriptions of employees;
Regulations on the procedure and conditions for providing long-term leave for continuous pedagogical work;
Regulations on the admission to the general educational institution;
Internal regulations for students;
Regulations on interim certification and translation of students in the following class;
Regulations on learning conditions for individual curriculum.
3) acts whose action is aimed at ensuring healthy and safe working conditions and studies:
Instructions on fire safety measures;
Safety instructions for individual traumatic jobs and training books (laboratories, workshops).
4) Acts related to the organization and teaching and methodological support of the educational process:
Regulations on the component of the general educational institution of the State Educational Standard of General Education;
A list of textbooks from the approved federal list of textbooks recommended (admitted) to use in the educational process;
Educational programs and curricula;
Working courses and disciplines;
Calendar training graphs;
Work schedules.
5) Acts related to pay for labor and financial and economic activities of a general education institution:
Regulation on wages and bonuses of workers;
Regulations on the procedure for providing additional educational services;
Regulations on business activities.
6) Acts providing proper workshop of the general education institution:
School business nomenclature;
Instructions for office work.
This list is not exhaustive. Moreover, many of the listed acts are not mandatory.
These acts differ not only in content, but also by the procedure for their adoption. Thus, the school charter is developed and adopted by a general education institution, but is approved by its founder. The rules of the internal labor regulation and a number of other local regulatory legal acts are made taking into account the opinion of the elected trade union body, representing the interests of the school employees. Annual calendar training graphs are developed and approved by agreement with local governments. Many regulatory legal local acts require registration as amendments to the school's charter. More information about the procedure for adoption (approval) of specific local regulations will be described in the practical part of the course.