Countries leaders in the length of the railway network. History of Russia Railways
Railwaytransport (railway) - terrestrial type of rail vehicles.
The two main components of railway transport are the material (railway road and artificial structures, traction and non-fighting rolling stock, SCB devices, contact network, etc.) and operational (dispatching guide (at levels from station duty to the senior road dispatcher), Development of optimal receptions for managing the transportation process).
Actually phrase "Railway" Indicates the railway infrastructure, i.e. railway track and signaling.
Railway path - Complex design consisting of the upper and lower structure of the path.
Railway tracks are divided into Station and special purpose. The stationery includes: main station, receiving-sending, sorting, exhaust, loading, unloading, running, connecting, etc. The main station pathways are the continuation of the paths adjacent to the distillation station and do not have deviations on the shooting transfers. The receiving and sending paths are designed to receive trains to the station, parking and departure for the distillation. At large stations, the paths intended for the implementation of homogeneous operations are combined into the parks.
Special destination paths include Access pathways (industrial railway transport), safety and catching deadlocks.
The upper structure includes Rails, sleepers, rail bonded, ballast prism. The rail grille consists of two rails laid and attached to transverse beams - sleepers. It is possible to mount on special plates that perform the same function as the sleepers. The sleepers or stoves are usually stacked on crushed stone (less often pebbles, sand, asbestos), dumbfounded in the form of a prism and called ballast prism (ballast pillow). The bridges differ ballast design (special troughs are organized for the placement of ballast) and nonsense - when the sleepers or plates are attached directly on the bridge structures.
To the lower structure belong Earth canvas and artificial structures (bridges, pipes, overpasses, etc.).
Standard Rail Length In Russia, 12.5 or 25 meters, however, at present, the so-called shameless way is used on inter-resistant distilts and routes - welded leaves from rails reaching 800 meters and more than a length. On the roads of Russia in 2004, the R65 (94.3%) and P50 (3.5%) (3.5%) (approximately 65 kg and 50 kg were 65 kg (3.5%) (approximately 65 kg and 50 kg per straight line meter, respectively), were used for particularly shipped lines. Rails brands - P75 (1.2%). Practically do not apply light rail brands (1%) - P43 and P38.
Permissible slope of the railway track It is very insignificant (compared to road slots, for example) and during the design of new lines can not exceed 12 in areas with a diesel load or 15 in areas with an electroworous burden. However, on already existing railways there are slopes to 25 ‰ and even 30, there are multiple thrust (pushing).
To connect the railway tracks, arrow transfers, which, due to its design, create continuity of the rail track and allow moving composition to move from one path to another. Now most of the shooting transfers are controlled centrally, from the post of electrical centralization (EC). Earlier, the arrows manually translated on duty shooting posts as directed by a person guiding maneuver or train work.
Railroad station - This is a separate point having a way development that allows you to perform operations on receiving, departing, exciting and overtaking trains, operations for receiving, issuing goods, luggage and cargo and passenger service, and with developed travel devices - maneuver work on disbanding and forming trains and Technical operations with trains. Each post of management of arrows and signals at the station should be carried out only one employee carrying the sole responsibility for the management of arrows and signals and for the safety of the movement - duty at the station.
Distance between rails, measured between the internal edges of the rail heads, call the width of the gauge. Different countries adopted a different width of the rut, for example, in the USSR (until the end of the 1960s) and Finland (up to the present) - 1524, in the USSR since 1970 - 1520 mm. In foreign Europe (with the exception of Spain and Portugal) - 1435 mm, in China and Iran - 1435 mm, in India and Pakistan - 1676 mm.
Maintaining the railway track in good condition is engaged in the distance distance (IF).
Rolling stock It happens: traction is locomotives, (diesel locomotives, electric locomotives, steam locomotives), electric trains, diesel trains and netting - wagons (passenger, cargo), as well as a special rolling stock.
The train is a formed and adhesive composition of wagons with one or more actant locomotives or motor cars having installed signals.
Russian Railways They have a wide range of rolling stock. Traction - various locomotives: (diesel locomotives, electric carriers) of electric trains, diesel trains, automobiles, drowsins and other self-propelled equipment. Netaging rolling stock are various cars (passenger, cargo), as well as a special rolling stock.
Russian Railways are the heirs of almost all Railways of Russia. Therefore, in the history of these railways, almost all modifications of world rolling stock were passed.
Length of the railway network of different countries
In many countries, the length of the railway network is reduced. So, in the USA in the 1920s there were more than 400,000 km of railways.
|
№ |
Country |
Length railway (km) |
|---|---|---|
|
The whole world |
1 122 650 |
|
|
USA |
194 731 |
|
|
Russia |
87 157 |
|
|
China |
71 600 |
|
|
India |
63 518 |
|
|
Canada |
49 422 |
|
|
Germany |
45 514 |
|
|
Australia |
41 588 |
|
|
Argentina |
34 463 |
|
|
France |
32 682 |
|
|
Brazil |
31 543 |
|
|
Poland |
23 420 |
|
|
Japan |
23 168 |
|
|
Ukraine |
22 473 |
|
|
South Africa |
22 298 |
|
|
Mexico |
19 510 |
|
|
Italy |
19 493 |
|
|
Great Britain |
16 893 |
|
|
Spain |
14 189 |
|
|
Kazakhstan |
13 601 |
|
|
Sweden |
11 481 |
|
|
Romania |
11 385 |
List of systems (and countries using specified systems):
Eurasian - United Kingdom, France, Andorra, Spain, Portugal, Monaco, Switzerland, Luxembourg, Belgium, Netherlands, Germany, Denmark, Liechtenstein, Italy, San Marino, Vatican, Austria, Czech Republic, Poland, Slovakia, Norway, Sweden, Finland, Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania, Belarus, Ukraine, Moldova, Hungary, Romania, Serbia, Slovenia, Croatia, Bosnia and Herzegovina, Albania, Kosovo, Montenegro, Macedonia, Bulgaria, Greece, Turkey, Russia, Georgia, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Kazakhstan, Uzbekistan, Tajikistan, Afghanistan, Turkmenistan, Kyrgyzstan, Mongolia, China, DPRK, South Korea, Vietnam, Iran, Syria, Iraq, Lebanon, Kuwait, Israel, Jordan, Egypt, Libya (Eastern part)
North American - Canada, USA, Mexico, Guatemala, Salvador, Honduras, Nicaragua, Costa Rica.
Indochinese - Cambodia, Thailand, Malaysia, Singapore, Laos.
Indian - Pakistan, Iran (Sistan and Belukhistan), India, Nepal, Bangladesh.
South American-North - Ecuador, Colombia, Venezuela.
South American-South - Peru, Bolivia, Brazil, Argentina, Uruguay, Paraguay, Chile.
South African - South Africa, Namibia, Botswana, Zambia, Zimbabwe, Mozambique, Angola, Tanzania, Malawi, Zaire (southern part), Swaziland.
North African - Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya (Western part).
East African - Kenya, Uganda, Somalia (southern part), Zaire (Northern).
Nubian - Sudan, Ethiopia, Eritrea, Somalia (North).
West African-South - Gabon, Congo.
West African-Central - Cameroon, Nigeria, Benin, Niger.
West African-Western - Mauritania, Senegal, Gambia, Guinea, Sierra Leone, Liberia, Côte d'Ivoire, Mali, Ghana, Togo.
Celtic - Ireland, United Kingdom.
Antilles - Haiti, Dominican Republic.
Arabian - Saudi Arabia, UAE, Oman.
Short story.
The emergence of a steam machine and a variety of locomotive.In the 60s - 80s of the XVIII century, first in England, and then in other countries the industrial rise began. Instead of manual labor, machine production appeared, instead of craft workshops and manufactories - large industrial enterprises.
In 1763, the Russian engineer I. I. Polzunov presented a project of a steam engine for supplying air to melting furnaces. Steam Machine Polzunova had a power of 40 horsepower.
The real revolution in the industry produced a steam machine created by James Watt engineer in 1784. The universality of the WATT steam machine allowed to apply it at any production and in transport.
The steam engine gave a powerful impetus to the development of transport. In 1769, the French artillery officer Joseph Kyuno invented the first steam wagon for the movement of heavy guns. She turned out to be a cumbersome and during the tests on the streets of Paris struck the wall at home. This wagon found its place in the Paris Museum of Arts and Crafts.
In 1802, English designer Richard Trevik made a steam car. The crew was moving with a crash and chad, scaring pedestrians. Its speed reached 10 km / h. To get such a speed of movement, Treventik made huge driving wheels that were a good help on bad roads.
The appearance of the railway.In 1755, a narrow-skinned path with wooden rails was already built for the transportation of rocks on the Altai mines, along which the wooden trollees moved. Along the way the cable loop was stretched. To bring it in motion, horses rotated pulleys were used. On each trolley there were two clamps, which could be alternately to traile in one or the other side of the hinge of the leading cable. Due to this, it was possible to stop the trolleys or change the direction of their movement with the continuous movement of the leading cable.
In 1788, the first railway in Russia appears in Petrozavodsk (it is the first railway in the world of factory destination). The railway was built on the Alexandrovsky plant for the needs of the enterprise. (Now the sections of the first Russian railway are kept in Petrozavodsk near the building of the OTZ Museum and in the Governor Garden; In addition, wheels from the trolley are stored in the Governor's garden).
The appearance of the locomotive.For a long time, railway tracks were constructed only on the mines, but then passenger roads with equestrian traction were distributed. The first such railway was arranged in 1801 in England between Undesworth and Croydon.
The first steam locomotive was built in 1804 by Richard Treventik, In his youth familiar with James Watt, the inventor of the steam car. However, iron in those years was too expensive, and cast-iron rails could not withstand heavy machine.
In subsequent years, many engineers tried to create steam locomotives, but the most fortunate of them was Georg Stephenson, which in 1812-1829. Not only suggested several successful construction constructions, but also managed to convince the shaftholders to build the first railway from Darlington to Stockton, able to withstand the steam locomotive. Later, Stephenson's locomotive "Rocket" won a specially arranged competition and became the main locomotive of the first Public Road of Manchester Liverpool.
Electrification railways
Railway electrification - A set of events performed on the railway site to be able to use the electro-separation composition: electric locomotives, electrical components or electric trains.
For traction of trains on electrified areas of railways, electric locomotives are used. Electroscopes or electric trains are used as a suburban transport.
Electrification systems You can classify:
with contact suspension
with contact rail
d.C.
alternating current:
current frequency
number of phases
by type of conductors:
by tension
by the clan:
Usually use permanent or single-phase alternating current.
The use of three-phase current requires the suspension of at least two contact wires, so this system has not taken root.
When using direct current, the voltage in the network is made quite low to turn on the electric motors directly. When using AC, it is possible to choose a much higher voltage, because on the electric locomotive voltage can be easily reduced using a transformer.
DC system.
DC electric motors are powered directly from the contact network. Regulation is carried out by connecting resistors, engine rearrangement and excitation weakening. In recent decades, impulse regulation began to spread, allowing to avoid energy losses in resistors.
Auxiliary electric motors (compressor drive, fans, etc.) are usually also powered directly from the contact network, so they are obtained very large and hard. In some cases, they use rotating or static transducers (for example, on ER2T electric trains, ED4M, ET2M uses a motor generator that converts a constant current 3000 V to three-phase 220 V 50 Hz).
Easy electrical equipment, low share and high efficiency led to the wide distribution of this system in the early period of electrification.
The disadvantage of the system is the low voltage of the contact network, which forces the use of a larger summary cross section of the wires and reduce the distance between the traction substations, since according to the law of Ohm, for the transmission of the same power at a smaller voltage, a larger current is required.
On railways mainly used voltage 3000 V and 1500 V. In the early 70s in the USSR in the Transcaucasian railway, practical studies have been carried out with the possibility of electrification on a constant current of 6000 V. trams, trolleybuses, the metropolitan is used voltage 600, 750, 1200 IN.
System of alternating current of the low frequency.
In a number of European countries (Germany, Switzerland, etc.) use a system of single-phase alternating current of 15 kV 16⅔ Hz. The reduced frequency allows using asynchronous AC motors. The engines are powered by the secondary winding of the transformer without any converters. Auxiliary electric motors (for compressor, fans, etc.) are also usually asynchronous, powered by separate transformer winding.
The disadvantage of the system is the need to convert the current frequency at substations or the construction of individual power plants for railways.
System of AC industrial frequency.
The most economical would be the use of an industrial frequency current, but its introduction met many difficulties. At first, I tried to use collector AC motors, motor generators (single-phase synchronous motor plus a direct current generator, from which DC traction electric motors operated), rotating frequency converters (giving current for traction asynchronous electric motors). Collective electric motors worked poorly on an industrial frequency current, and rotating transducers were too heavy.
An industrial frequency single-phase current system (25 kV 50 Hz) began to be widely applied only after creating in France in the 1950s of electric locomotives with static mercury rectifiers (Ignitron; later they were replaced with silicon rectifiers); This system then spread in many other countries (including in the USSR).
When straightening a single-phase current, it is not a direct current, but a pulsating current, therefore special pulsating current motors are used, and in the diagram there are smoothing reactors (choke), reduced current ripples, and resistors of permanent excitation, included in parallel winding of motor excitation and passing the variable which only causes unnecessary heating winding.
The drive of auxiliary machines is used either the pulsating currents are used from a separate transformer winding through the rectifier, or industrial asynchronous electric motors that feed on the phase separator (such a scheme is distributed in French and American electric locomotives, and they were transferred to Soviet), or capacitors ( applied, in particular, on Russian electric locomotives VL65, EP1, 2ES5K).
The disadvantages of the system are significant electromagnetic interference for communication lines, as well as uneven loads of the phases of the external power system. To increase the uniformity of the phase load in the contact network, sections with different phases alternate; Between them are arranged neutral inserts - short, a length of several hundred meters, the plots of the contact network, which the rolling stock passes with the engines turned off, inertia. They are made so that the pantograph does not jumped under high linear (interfacial) voltage of the gap between sections at the time of transition from the wire to the wire. When you stop on a neutral insert, it is possible to supply voltage from the front in the direction of the contact network section.
Railways of the world.
Australia
Railways are represented by five state railways and a number of private railways. King width 1600, 1435, 1067 mm.
Austria
Austrian federal railways (Österreichische Bundesbahnen) - Palute 1435 mm, 1000 mm, 760 mm, length 5624 km, 3186 km electrified, diesel locomotive traction and electric locomotives.
Azərbaycan Dövlət Uşaq Dəmir Yolu
Vitebsk branch of the Belarusian Railway.
Georgia
Georgian Railway. The operating length of the main lines is 1323.9 km. 1422 bridges, 32 tunnels, 22 passenger stations and 114 loading stations are operated.
Uzpocole Railway Borjomi - Bakuriani. RF with a rut width of 900 mm and a length of 37 km. In 1966, electrified at 1500 V voltage (permanent current).
Israel
Israeli railways. The railway network has a length of approximately 750 km, it has 45 passenger stations. In addition to the existing and under construction sites of the railway network, there are extended abandoned and unused sites. Standard Paluing 1435 mm is used. The active lines run through the densely populated coastal, northern, central and some southern regions of the country. On lines are used both single-storey and two-storey wagons, driven by diesel locomotives. Polskie Koleje Państwowe). The length of railways in the country is 26,644 km, including 24287 km with a ripple of 1435 mm, and 2357 km with Koles 1520, 100, 785, 750 and 600 mm. Of the total length of roads, 1138 km has electrified. Advantageously, electrification was carried out on a constant current of 3 square meters.
Russia
Russian Railways. Russian Railways OJSC owns 99% of railway highways in Russia with a total length of 85,500 km (the exception is a number of railways managed by private companies, such as Norilsk Railways, etc.), stations and stations, depot and dispatch systems. The company also owns about 20 thousand locomotives (about 90% of the entire locomotive park), more than 600 thousand cargo and passenger cars. Passenger locomotives make up about 12%. Part of passenger traffic over the network of Russian Railways, in particular, in the direction of Moscow - St. Petersburg, is carried out by private trains.
The United States of America has the world's longest railway network, followed by China and India. We present to your attention the longest railway exercises in the world based on their overall working length.
And so, let's go!
United States: 250 thousand km
The US railway network, which is more than 250,000 km long, is the largest in the world. Cargo lines make up about 80% of the entire railway network of the country, and the total passenger length is about 35,000 km.
The cargo railway network of the United States consists of 538 railways (7 Railways I Class I, 21 Regional Railways and 510 Local Railways), which are managed by private organizations. Union Pacific Railroad and BNSF Railway are among the largest freight railway networks in the world. The AMTRAK National Passenger Railway Network includes more than 30 railway railways connecting 500 destinations in 46 American states.
Currently, the United States has a plan for creating a national system of high-speed railways with a length of 27 thousand km. The construction of a high-speed railway link in California, the first high-speed railway project in the country, has already begun in 2014. Another three high-speed projects are also being developed, including a high-speed railway line on the Midwest, connecting Chicago with Indianapolis or St. Louis, the high-speed Railway of Texas and the North-Eastern Speed \u200b\u200bCorridor (Northeast High-Speed \u200b\u200bCorridor).
China: 100 thousand km
China's railway network with a length of more than 100 thousand km ranks second in the world. In 2013, an extensive network managed by the State Chinese Railway Corporation has numbered 2.08 billion passengers (second largest after Indian Railways) and 3.22 billion tons of cargo (the second largest after the US railway network).
Railway in China is the main type of transport. The country's railway network includes more than 90 thousand km of ordinary railway routes and about 10 thousand km of high-speed lines. By 2050, the total railway network of the country should exceed 270 thousand km.
The rapid expansion of the high-speed railway network in China in recent years makes it largest in the world. The High Speed \u200b\u200bLine of Beijing-Guangzhou (2,298 km) is the world's longest high-speed railway. According to forecasts, by 2020, the total length of the high-speed railway Chinese network will reach 50 thousand km.
Russia: 85,500 km
The whole Russian Railway network managed by the state monopolist "Russian Railways" (Russian Railways) has more than 85,500 km. In 2013, Russian Railways transported 1.08 billion passengers and 1.2 billion tons of cargoes - the third largest volume of goods after the United States and China.
The Russian railway network includes 12 main lines, many of which provide direct relationship with European and Asian national railway systems, such as Finland, France, Germany, Poland, China, Mongolia and North Korea. The Trans-Siberian Highway (line Moscow-Vladivostok) with a length of 9.289 km is the longest and one of the most lively railway lines in the world.
In 2009, Russian Railways commissioned a high-speed express between St. Petersburg and Moscow ("Sapsan"), who did not differ in particular success due to the fact that his movement proceeds by common with the usual compositions of the paths. After that, between the two cities, the construction of a highlighted high-speed corridor with offered investments in the amount of $ 35 billion was planned.
India: 65 thousand km
The Indian nationwide railway network, the fourth largest in the world, belongs and managed by the Indian Railways and includes the maintenance route with a length of more than 65 thousand km. In 2013, the Indian railway network transported about 8 billion passengers (1st place in the world) and 1.01 million tons of cargo (4 in terms of the world).
The Indian railway network is divided into 17 zones and serves more than 19 thousand trains per day, including 12 thousand passenger and 7 thousand cargo. By 2017, the National Railway Operator planned to add 4 thousand km of new lines, and also significantly convert existing ones. It also plans to build an exclusive cargo network with a length of 3.338 km with the introduction of Eastern and Western specialized cargo corridors (DFC) - two of the six planned specialized carridor cargo.
As an experimental project, a high-speed line of 534 km long on Mumbai-Ahmedabad route with alleged investments in the amount of 9.65 billion American dollars is being built.
Canada: 48 thousand km
Railway line Canada - the fifth in the world largest. Canadian National Railway (CN) and Canadian Pacific Railways (CPR) are two large transport railway networks operating in the country, and Via Rail controls 12,500 km of intercity passenger rail. Algoma Central Railway and Ontario Northland Railway are one of the few small railway operators who provide passenger services in some rural areas of the country.
Three Canadian cities - Montreal, Toronto and Vancouver - have extensive suburban communication systems. In addition, the Rocky Mountainer and Royal Canadian Pacific offer luxurious railway tours, during which you can admire the beauty of the picturesque mountainous areas of the country.
However, in Canada there is no single high-speed line in its railway network. Until recently, many suggestions on the construction of high-speed lines, such as Toronto Montreal, Calgary Edmonton and Montreal-Boston, but none of them went beyond preliminary research from January 2014.
Germany: 41 thousand km
The State Deutsche Bahn company has a railway network of 41,000 km in its disposal, which accounts for about 80% of the total amount of freight transport and 99% of passenger over long distances.
In addition to Deutsche Bahn, more than 150 private railway companies providing regional passenger and freight services operate on the network. S-Bahn serves the main suburban and urban areas, and Hamburg Cologne Express (HKX) is a major passenger long-distance operator after Deutsche Bahn.
From mid-2013 in the German railway network, there have been more than 1,300 km of high-speed and more than 400 km of new high-speed lines under construction. In 1991, Deutsche Bahn for the first time discovered the INTERCITY EXPRESS (ICE) high-speed service. Now, the high-speed network, which allows for expressing speeds up to 320 km / h, connects major German cities and neighboring countries, such as France, Switzerland, Belgium, Netherlands and Austria.
Australia: 40 thousand km
Australian railway network is the seventh largest in the world. Most of the railway network infrastructure belongs and supported by the Australian government or federal or at the state level. However, most trains are managed by private companies.
Aurizon (formerly QR National), Genesee and Wyoming Australia, and Pacific National are among the main cargo operators of the country. Great Southern Railway, NSW Trainlink and Queensland Rail are leading cargo operators for long distances. Metro Trains Melbourne, Sydney Trains, V / Line and Adelaide Metro are engaged in suburban passenger transportation to the main areas of Australia. In addition, a number of private mountain railways operate in the country.
At the moment, the Australian railway network has no high-speed line. So far, there are plans for its construction - it must connect Brisbane, Sydney, Canberra and Melbourne. The estimated cost of construction is 114 billion dollars, but the first phase of a 1748-kilometer high-speed network will not be implemented until 2035.
Argentina: 36 thousand km
The current railway network of Argentina is the length of more than 36,000 km takes the eighth place in the world. At the end of World War II, Argentina had about 47 thousand km of railway tracks, which were mainly used by British and French railway companies. But the decline in profits and the growth in the construction of the highway in the following decades led to a reduction in the network up to 36 thousand km, which is at this mark to this day. In 1948, railway companies operating on the network were nationalized and the State Railway Corporation Ferrocarriles Argentinos was formed.
The Argentine Railway was privatized between 1992 and 1995 with the provision of concessions to various private companies to work in six divisions of the railway network previously owned by the state. Cities like Buenos Aires, resistance and Mendoza offer extensive suburban passenger services, as well as passenger services for long-range distance within the country.
Frequently discussed Argentine high-speed railway so far only in dreams. In 2006, the development of a 310-kilometer high-speed line between Buenos Aires and Rosario was announced. However, the project was not implemented. The second high-speed line of 400 km between Rosario and Cordobo was also proposed.
France: 29 thousand km
The French railway network is the second largest in Europe and the ninth largest in the world. The French railway network is predominantly focused on passenger traffic. More than 50% of the country's railway lines are electrified. Société Nationale des Chemins de Fer Français (SNCF) is the main railway operator of the country.
High-speed passenger transportation over long distances in the country is known as TRAIN à Grande Vitesse (TGV), and standard passenger services for long-range distance - branded Intercités. Passenger traffic services for short and medium distances are known as Transport Express Régional (Ter). The network offers links with related countries, such as Belgium, Italy and the United Kingdom.
France was one of the first participants who developed technologies for high-speed railways - SNCF commissioned a high-speed TGV railway in 1981. Current high-speed network of the country exceeds 1550 km. The Tours-Bordeaux high-speed railway project, which was supposed to be completed in 2017, will add another 302 km.
Brazil: 28 thousand km
The first railway line in Brazil began to function in 1984. In 1957, the railway network was nationalized and created Rede Ferroviária Federal Sociedade Anônima (RFFSA). The country's railway network was divided into various services, which since 2007 is served by a number of private and state operators.
The 28,000-kilometer network is mainly focused on freight and iron ore. Passenger traffic services in the country are mainly concentrated in urban and suburban areas. Eight Brazilian cities have a subway system, the largest of them - the subway São Paulo.
In 2012, the Brazilian government announced construction by 2042 10 thousand km of new cargo and high-speed passenger lines. Also in the country is planned to build a high-speed railway communication between São Paulo and Rio de Janeiro with a length of 511 km.
The Trans-Siberian Highway or the Great Siberian Way, which connects the capital of Russia in Moscow with Vladivostok, until recently wore the honorable title in the world in the world of the railway. But when the "new silk path" was launched, he pushed the Transsib to the second place, since it became noticeably longer than the previous record holder. The longest railway routes include unique tracks that have a length of many thousands of kilometers, during the journey through which a person can learn a lot about our planet.
1. Madrid-IU, or "New Schill Way" (13,052 km)
Nowadays, for delivery of goods from the Middle Kingdom to Europe, it is not necessary to make dangerous multi-month roadways on horseback and camels. However, to avoid this, gigantic investments are required. The Chinese historically dreamed of making the direction to the West favorable, rapid and reliable, and at some point they attracted to cooperation and Russian specialists.
The length of the railway line with the loud name "New Silk Road" amounted to 13,052 kilometers. It is so much the railway canvase that it took to connect the capital of Spain with a small Chinese town of Ei. After the construction is completed, this railway has become a record holder in the world throughout. The Chinese government did not praise and spent about 40 billion dollars to improve the infrastructure of the railway and increase the tonnage of goods transported on it.
At the end of 2014, the railway composition from the Chinese city of Yu, located on the coast of the Pacific Ocean, was solemnly moved on the road, and after 21 days he finished in distant Madrid. It was the beginning of work the most extended railway line. Unfortunately, the quality of the path does not allow to let the comfortable passenger expressings on it, the weather and other natural factors have a strong influence on the movement of trains, but despite this, the beginning of the functioning of this highway allowed the global economy to get one step higher.
Most people seek to get a place in an airplane near the porthole to enjoy the views at the bottom, including types of takeoff and ...
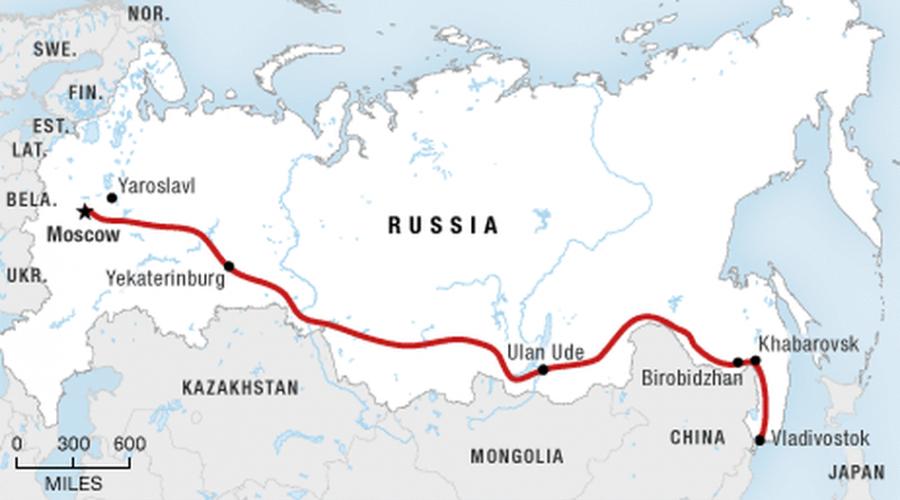
2. Moscow-Vladivostok, or Trans-Siberian Railway Highway (9,289 km)

This road is held exclusively in Russian territory, it is the first globally tied Europe and Asia. The start of the Transsib laying was 1891. The heir to the throne Nikolai Romanov returned from the Multifeciac Sea Cruise from Japan (the future last emperor Nicholas II) laid the first stone of the Ussuri railway in the vicinity of Vladivostok. Long in Russia, the railway as if Beads rose 87 cities, 5 federal districts and 8 time zones. 81% of the length of this path falls on the Asian part, and the rest is on the European one.
Soviet builders of Bama could envy the speed of building this railway line - the path from Kotlas and Miass to Port Arthur and Vladivostok appeared in just 13.5 years (1891-1904). Basically, the "cast-iron" was held in unauthorized lands, sites of permafrost. Through major rivers were transferred many bridges. The construction of Transsib was completed on October 1 (according to the old style) of 1904. But after the official completion, construction lasted for many years. For example, only in 1938 the second rut was completed. This legendary railway, having a length of 9289 kilometers, was launched in the midst of the First World War - in 1916.
To get from the capital to Vladivostok, a traveler will need to spend on a train of 167 hours, which will make 120 stops during this time. Traveling on a transussiba is akin to a long-term tourist warning - passengers will be seen during the path of many well-known settlements, natural sights of incredible beauty and intactness. In addition, wining kilometers, the train gradually crosses 8 time zones.
3. Moscow-Beijing (8,984 km)
.jpg)
Russia and China are long-standing partners who have common interests not only in politics and economics, but also in culture. It is not surprising that the capitals of these huge countries connected the direct railway line, which stretches at 8984 kilometers. Traveling from one capital to another lasts about 145 hours. A significant part of the train route is overcome by the already mentioned Transsib, but in Chita, the wagons are as follows in China towards the Chinese border. This is followed by a 6-hour stop in Zabaikalsk, where border control and change of wheel steam is carried out, since the rut width in two countries is different.
4. Far Eastern Railway (6,826 km)
.jpg)
The length of this route is 6826 kilometers. Railway management is located in Khabarovsk. Throughout the path, the train follows 416 stations, as well as 3 points of intersection of the state border. Traveler sitting in the train will not get bored, because they can admire the nature of the reserves and the view of the zones of many years of marbles.
5. Gorky Railway (5,296 km)
.jpg)
In 1936, Gorky railway was formed with a length of 5296 kilometers. This highway is still upgraded all the time, for example, in 2010 it began to run "Sapsan" - high-speed electric train, produced by the German company Siemens, which began to deliver passengers in a shorter time. For example, with it, to get from Moscow to Nizhny Novgorod became possible in 3.5 hours. Every year, over 52 million passengers pass in the Gorky Railway. For Russia, this direction has long been an important economic and political factor, historical cities are located on its way, on the way you can look at large forest arrays and picturesque landscapes.
Each culture is inherent in their lifestyle, traditions and delicacies, in particular. The fact that for some people seems ordinary, others are perceived ...
6. Lhasa Guangzhou (4,980 km)
.jpg)
Inside China, there is another long railway on which 4980 kilometer pillars are located. It is connected by the port city of Guangzhou and Continental Lhas, located in Tibetan Highlands. Train T264 overcomes this grand path for 54.5 hours. Conductors tell the passengers about the attractions on the windows on three languages. The train around the clock there is a restaurant, where you can enjoy Tibetan and Chinese cuisine.
China in recent decades has reached the leading position in the world to organize modern railways. The Chinese apply the latest building technologies, modern high-speed trains are allowed on the rails that can rush much faster than ordinary cars.
7. Inino-Shanghai (4,742 km)
.jpg)
In 2014, a movement was opened on a new railway route connecting Shanghai and Annin 4742 kilometers long. Passenger trains are moving on it, while they consistently cross 7 Chinese provinces in which 32 stops are made. The time on the way is 56 hours, for which the passengers cross most of China and have the opportunity to admire its beauty, which are really quite a lot.
8. Urumchi-Guangzhou (4,684 km)
.jpg)
This railway connects the northwestern lands of China with its southeast regions, its length amounted to 4684 kilometers, and to overcome them, it will take 49.5 hours. There are three trains here, in which businessmen, politicians and just travelers are most often sitting, who seek to get to Guangzhou.
9. Toronto Vancouver (4,466 km)

In Canada, Via Rail trains on a route 4466 kilometers long run between Vancouver and Toronto. In the way, they make 66 stops. But passengers sitting in comfortable cars are not bored, because the snowy peaks of the rocky mountains are rushed outside the windows, a Canadian taiga and a variety of natural sights. Frequently, the passengers can not only admire landscapes, but also see deer, elk or bears.
The German statistical company JACDEC has compiled its authoritative rating of the safest airlines in the world for 2018. Compilers of this list ...
10. Chicago - Los Angeles (4 390 km)
.jpg)
The transcontinental American highway connects Los Angeles and Chicago, which are on the opposite sides of the North American mainland. This route serves the state company "AMZA". The path length is 4390 kilometers, which trains overcome an average of 65 hours. During the trip, they cross 7 states and make 40 stops on the way. For the convenience of travelers, trains trains have a special design - windows here are not only in their sides, but also on the roof.
The first railways in Russia were built in the middle of the XIX century. In 1837, 12 years after the start of movement in the world in the world of the public road of general use Stockton - Darlington in England, opened "Experimental" Railway Saint Petersburg - Tsarskoye Selo, and in 1851 - the first major railway highway Moscow - St. Petersburg. Already by the end of the XIX century. Rail transport exceeded the freight turnover traditional for Russia, a manpiece and river, and by 1913 surpassed the river turnover in B times.
The main framework of the Russian railway network was formed in the second half of the XIX - early XX century. Railways were built primarily to ensure the transport and economic relations of the Center with the main raw materials and food bases of the country, as well as by the marine ports, which determined their radial configuration.
Railway transport is a leading in the transport system of Russia. Its leading importance is due to two factors: the technical and economic advantages over most of the other types of transport and the coincidence of the direction and capacity of the main transport and promotional interdistrict and interstate (within the CIS borders) of Russia's relations with the configuration, bandwidth and transportability of railway highways (in contrast to the river and Sea transport). This is also due to the geographical characteristics of our country. The length of the railways in Russia (87 thousand km) is less than in the US and Canada, but the work performed by them is more than in other countries of the world.
The main task of railways of Russia is to ensure reliable transportation of the European part of the country with its eastern districts. It should be noted that the most important transport lines are overloaded. The average speed of movement on the railways is about 30 km / h and is constantly decreasing. The most thick and branched network of railways is located in the European part of the Russian Federation.
It is known that the railways of the Russian Federation, which has 11-12% of the total length of the railways of the world, perform more than 30% of the cargo turnover of railways. Railways remain the most economical type of transport (in contrast to air and road transport), yielding in terms of the cost of transportation only by pipeline and sea transport. The advantage of rail transport is independence from natural conditions (the construction of railways is almost on any territory, the ability to rhythmically carry out transportation at all times of the year, in contrast to river transport).
One of the basic industries of the Russian economy is railway transport. The efficiency of this industry affects the growth rates in almost all sectors of the Russian economy. The railway system ensures the unity of Russia, the intensity of economic relations in the country is one of the factors that determine the volumes and directions of our foreign trade. More than 80 percent of cargo turnover (excluding pipeline transport) are on the railways.
The density of citizens in the territory of the Russian Federation and the mobility of labor resources depends on the quality of the railway communication. Railways take over 40 percent of all passenger traffic.
Russia ranks first in the world in the length of electrified railways - more than 44 thousand kilometers (the total length of railway tracks is more than 85 thousand kilometers). The second and third places in this indicator are occupied by China and Germany, which have more than 24 thousand and 21 thousand kilometers of electrified roads, respectively. It is assumed that by 2010, up to 84% of all shipping work will be performed on electrified areas of Russian railways.
The most extended (and at the same time the oldest) among Russian railways is October (commissioned in 1851; reaches length 10334 kilometers; passes through the territories of Moscow and St. Petersburg, Moscow, Leningrad, Novgorod, Pskov, Vologda, Murmanskaya, Tverskaya and Yaroslavl regions and the Republic of Karelia; The maximum speed achieved on the Moscow-St. Petersburg line is 260 kilometers per hour). The October Road is inferior to the Moscow (8984 kilometers) and Sverdlovskaya (7091.3 kilometers). The least extended among Russian railways is Kaliningrad (963 kilometers) and Sakhalin (804.9 kilometers).
The number of goods transported on Russian railways in 2006 amounted to 1 billion 311 million 312 thousand tons (3% more than in 2005, and 0.7% more plan), freight turnover - 1 trillion. 948 billion ton kilometers (growth - 4.8%). Transportation volumes of most of the main types of cargoes, compared with previously planned, were exceeded: oil and petroleum products - by 4.6% (all 228 million 310 thousand tons were transported), coal - by 3.3% (287 million 548 thousand tons), coke - by 0.9% (11 million 347 thousand tons), ore of iron and manganese - by 6.8% (108 million 350 thousand tons), the scrap of ferrous metals - by 2, 2% (26 million 639 thousand tons), cement - by 11.6% (38 million 236 thousand tons), forestry products - by 0.1% (64 million 154 thousand tons). In the first quarter of 2007 The freight turnover of railway transport amounted to 502.5 billion ton kilometers.
The main advantages of railway transport:
High sustainable ability;
Efficiency of mass cargo transport over long distances;
Relatively high speeds;
Reliability and safety;
Low shipping cost;
Lower environmental impact than other types of transport.
The share of railway transport in the total transportation of each country is consistent with economic and geographical, demographic and other factors:
Placement of natural resources and productive forces;
Population population;
The size of the territory;
The presence of non-freezing waterways.
In the Russian Federation with its extensive territory and natural peculiarities, the remoteness of the raw material base from the processing enterprises, railway transport is the basis of the transport system, performing more than 80% of the cargo turnover of all types of transport (without pipeline) and over 40% of the total transportation of common transport transport in far and suburban reports.
Russian railways - the largest, well-developed, dynamically functioning system. Railway network and has a length of more than 85 thousand km.
Railway tracks are suitable for the seabed in Vladivostok
The railway network of the Russian Federation is quite extensive. It consists of several sections of highways, which owns which OJSC "Russian Railways". At the same time, all regional roads are formally branches of Russian Railways, while the company itself speaks by a monopolist in Russia:

The road runs through the territory of the Irkutsk and Chita regions and the republics of Buryatia and Sakha-Yakutia. The length of the highway is 3848 km.
The road passes through two parallel latitudes: Moscow - Nizhny Novgorod - Kirov and Moscow - Kazan - Yekaterinburg, which are related to rockadas. The road connects the central, northwest and northern regions of Russia with the Volga region, the Urals and Siberia. The Gorky Road borders with railways: Moscow (Artwork and Cherustov), \u200b\u200bSverdlovsk (Art. Chepts, Druzhinino), North (Art. Novki, Susolovka, Candle), Kuibyshevskaya (Art. Red Node, Cilyna). The total deployed road length is 12066 km. The length of the main railway tracks is 7987 km.


Railways passes through the territory of five constituent entities of the Russian Federation - the Primorsky and Khabarovsk Territory, the Amur and Jewish Autonomous Region, the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia). The Magadan, Sakhalin, Kamchatka region and Chukotka are also located in its service area - over 40% of Russia. Operational length - 5986 km.
The Trans-Baikal Railway runs in the south-east of Russia, through the territory of the Trans-Baikal Territory and the Amur Region, is located next to the border of the PRC and has the only direct land borderline railway transition through the station Zabaikalsk. Operational length - 3370 km.



The West Siberian Railway passes through the territory of Omsk, Novosibirsk, Kemerovo, Tomsk regions, the Altai Territory and partly of the Republic of Kazakhstan. The launched length of the main route of the highway is 8986 km, operational - 5602 kilometers.
The road works in special geopolitical conditions. Through Kaliningrad runs the shortest path from the center of Russia to the countries of Western Europe. The road does not have common borders with Russian railways. The expanded highway is 1100 km, the length of the main ways is over 900 kilometers.
The highway passes through four major regions - the Kemerovo region, Khakasia, the Irkutsk region and the Krasnoyarsk Territory, connecting the Trans-Siberian and South Eibirsk highway. Figuratively speaking is a bridge between the European part of Russia, its Far East and Asia. The operating length of the Krasnoyarsk Road is 3160 km. Total length - 4544 kilometers.


Railway extended from the Moscow region to the Urals Preignations, connecting the center and West of the Russian Federation with major socio-economic regions of the Urals, Siberia, Kazakhstan and Central Asia. The road is two almost parallel lines running from the west to the east: brownie - Inza - Ulyanovsk and Ryazhsk - Samara, who are connected to the chisma stations by forming a two-way line ending at the revolt of the Ural Mountains. Two other roads of Rozaevka - Penza - Rtishchevo and Ulyanovsk - Syzran - Saratov walk from north to south.
In the current borders, Moscow railway station was organized in 1959 as a result of a full and partial association of six roads: Moscow-Ryazan, Moscow-Kursk-Donbass, Moscow-district, Moscow-Kiev, Kalininskaya and North. The detailed length is 13,000 km, the operating length is 8800 km.
The October highway passes through the territory of eleven constituent entities of the Russian Federation - Leningrad, Pskov, Novgorod, Vologda, Murmanskaya, Tver, Moscow, Yaroslavl regions, cities Moscow and St. Petersburg and the Republic of Karelia. Operational length - 10143 km.


Volga (Ryazan-Ural) Railway is located in the south-east of the European part of Russia in the area of \u200b\u200bthe Lower Volga and Medium Done's average and covers the territories of Saratov, Volgograd and Astrakhan regions, as well as several stations located within the Rostov, Samara regions and Kazakhstan. The length of the road is 4191 km.
The highway connects the European and Asian parts of Russia, from the West to the East stretches on a one and a half thousand kilometers and in the northern direction intersects the polar circle. It passes through the Nizhny Tagil, Perm, Ekaterinburg, Surgut, Tyumen. The Khanty-Mansiysk and Yamalo-Nenets Autonomous District also serves. Operational length - 7154 km. Deployed Length - 13,853 km.

The highway originates in the center of Russia and extends far to the north of the country. Most of the northern highway is exploited in the harsh conditions of the Far North and Polaria. Expanded length - 8,500 kilometers.


In the road service zone there are 11 constituent entities of the Russian Federation of the Southern Federal District, it directly borders Ukraine, Georgia and Azerbaijan. The operating length of the highway is 6358 km.

The South-Eastern Railway occupies a central position on the railway network and connects the eastern districts and the Urals with the center, as well as the areas of the North, the North-West and the Center with the North Caucasus, Ukraine and the Caucasus states. The southeastern road is bordered by Moscow, Kuibyshev, North Caucasian, South Railway of Ukraine. Operational length - 4189 km.
The South Ural Railway is located in two parts of the world - at the junction of Europe and Asia. It includes Chelyabinsk, Kurgan, Orenburg and Cartalin branch. Multiple railway lines are held through the territory of Kazakhstan. The southeastern road is bordered by Moscow, Kuibyshev, North Caucasian, South Railway of Ukraine. Operational length - 4189 km. Expanded length over 8000 km.