Methods for increasing the reliability and efficiency of technological and energy equipment of the production and transport of oil and gas of the Snod of Evgeny Anatolyevich. Increased reliability and efficiency
Improving the reliability and efficiency of the budgeting system in the company Sika Kazakhstan LLP
Enterprises engaged in the production of building mixes and concrete additives play an important role in the country's economy, since they perform the function of production and ensuring the state and industrial organizations with resources for the entire construction required for their normal functioning. If in Kazakhstan in the last 5 years there is a decrease in the construction index by 2-3%, the Almaty region demonstrates the sustainable growth rates of production, dry and liquid mixtures of concrete additives: the index in 2014 in relation to 2013 amounted to 103%. Probably, growth is mainly due to the increase in the price of manufactured and imported goods. In essence, worn out of fixed assets, deficiency of resources and the use of obsolete production technologies allow us to talk about the crisis state of the capacity engaged in the production of dry and liquid mixtures of the Almaty region.
Since the end of 2012, namely, from the moment of the formation of Sika Kazakhstan LLP, the situation began to change for the better, but it is too early to talk about full solutions to all the problems.
There are also specific features in the functioning of these enterprises: the seasonal nature of income in the implementation of certain types of products (priority) in the conditionally constant nature of the cost; The need to take into account the magnitude of the peak load of the equipment; The presence of certain categories of the company with benefits for paying for debt, compensation for which occur with the lag in time.
Naturally, this specificity is inherent in Sika Kazakhstan TOO.
Currently, it should be recognized that the highest management recognizes the need to increase the reliability and effectiveness of the existing budgeting system at Sika Kazakhstan TOO. Thus, the first step in improving this system was made.
Solving the issue, which way to reform the system, it has become closely in the course of activity: it became clear - the further functioning of the budgeting system based on the MS Excel table system is unacceptable due to the essential drawbacks of this approach. It was decided to automate this process.
Automation will require a lot of time and resources, but it is expected that the effect of implementing software products will block all costs.
Automation of the budgeting system will make it clear and formalized to determine the main factors characterizing the results of activity, their details for each level of management and specific tasks for managers of structural units that ensure their implementation.
Budgeting automation will be able to provide better coordination of economic activities, improve the handling and adaptability of enterprises engaged in the production and resale, to changes in the internal and external environment. It is able to reduce the possibility of abuse and mistakes in the planning system, to ensure the relationship of various aspects of economic activities, to form a unified vision of enterprise plans and problems arising in the process of their implementation, to ensure a more responsible approach of specialists to decision making and better motivation of their activities.
To set the budgeting system, the necessary element is the availability of basic internal regulatory organizational and administrative documents and formalized management processes (rules, description of procedures, etc.). The need for regulation is caused by the fact that the formation of information on production as it may repeat the course of the production process itself and is predetermined by the movement of material resources in the process of the technological process and the increase in labor costs as the source materials are processed. The organizational structure of the enterprise actually ensures the coherence of certain types of economic activities of the enterprise to fulfill the main tasks and goals. Therefore, the organizational and production structure of the enterprise, its internal mechanism is a basis when reforming planning and implementing automated budgeting.
It was taken into account by the management of Sika Kazakhstan LLP and are currently being implemented for the development and coordination of the regulations for the automated budgeting system, which will replace the existing one.
The advantages of automation of the budgeting system are as follows:
- 1. The quality of work on the implementation of the strategy is significantly improved, since strategic goals are formalized and communicated to each department.
- 2. The possibility of a more objective assessment of the contribution of each TFO due to the validity of the plans and stimulate their clear execution.
- 3. The automated budgeting system provides a product of evaluating the effectiveness of the developed activities throughout the entire budgeting management cycle.
Thus, the company's management is on the right track, preferring a time response strategy. The measures taken will allow the company to achieve strategic goals and develop business. But it is very important not to "be knocked out" from the planned path, and this in the process of solving such a task as an increase in the reliability and efficiency of the company's budgeting system is very likely.
To prevent miscalculation, the company's management should expand its cooperation with a wider range of firms offering budgeting automation services in order to be able to select the most optimal platform option.
In addition, it would be advisable to attract independent specialists as consultants when choosing a system that takes into account the specifics of Sika Kazakhstan LLP.
In general, the measures taken in the company will allow to implement the intended goals. But when Ignoring the above aspects, the process of the process may shift that it will still not allow to get the full return from the embedded system.
"Methods of increasing the reliability and efficacy of technological and energy equipment in the processes of production and transport of oil and gas ..."
For manuscript rights
Evgenya Snods Anatolyevich
Methods of increasing reliability
And technological efficiency
And energy equipment in processes
Oil and gas production and transport
Specialty: 05.02.13 - "Machines, aggregates and processes"
(oil and gas industry)
05.26.03 - "Fire and Industrial Safety" (Oil and Gas Industry)
Dissertations for the degree of doctor of technical sciences
The work was performed in the Ufa State Oil Technical University.
Scientific consultant Doctor of Technical Sciences, Professor Baikov Igor Ravilievich.
Official opponents: Doctor of Technical Sciences, Associate Professor Novoselov Vladimir Viktorovich;
doctor of Technical Sciences, Associate Professor Yamaliev Vil Uzbekovich;
doctor of Technical Sciences, Professor Gmer Reef Saifulovich.
Leading organization "Center for Energy Saving Technologies of the Republic of Tatarstan" under the Cabinet of Ministers of the Republic of Tatarstan.
The defense will take place on February 20, 2004 at 14-00 at the meeting of the dissertation council D 212.289.05 at the Ufa State Oil Technical University at the address: 450062, the Republic of Bashkortostan, Ufa, ul. Cosmonauts, 1.
The dissertation can be found in the library of the Ufa State Oil Technical University.
Scientific Secretary of the Dissertation Council Ibrahimov I.G.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION OF WORK
Relevance Problems. Ensuring the reliability of the exploitation and production safety of objects of the oil and gas industry in modern society is the most important task. The technological processes of production and transport of hydrocarbon raw materials are potentially dangerous in nature, which is associated with large volumes of fuel organic raw materials produced in fishery and transported to distant distances.Large accidents at the enterprises of the industry lead to environmental catastrophes, to eliminate the consequences of which significant financial costs are needed, and many years are leaving for the restoration of the natural environment.
The level of reliability of technical systems of the oil and gas industry has a direct impact on the production efficiency. Problems of improving the efficiency of the oil and gas industry are closely related to the task of reducing production costs, in particular, the energy resources and repair and recovery activities. In turn, these tasks Determined by the technical condition of the equipment of the industry, and, therefore, their decision is possible by developing measures to improve the reliability of equipment and improving the methods of technical diagnostics.
Currently, objective conditions have appeared to solve the listed problems. First of all, they are due to the wide introduction of microprocessor equipment into oil and gas technologies, which allows to obtain production information in high-quality and quantitative relations, not comparable to available 5-10 years ago. Information Systems (IIS) allow you to obtain, accumulate and save for almost unlimited time arrays of production data to which are not only the current operating parameters of the equipment, but also the electronic databases of dispatch services.
Special attention should be paid to the development of new mathematical methods of data processing and building on their basis of models of technical systems, the use of which has become possible at present. These include synergetic and dynamic chaos methods, fuzzy logic, theoretical and gaming methods, neural networks and cellular machines and many others developed and successfully used in such areas as economics and finance, meteorology, geophysics, forecasting emergency situations, but not found Wide use in industrial sectors.
The overall structure of the task of increasing the reliability and efficiency of the oil and gas industry enterprises can be represented as a simplified scheme (Fig. 1). The basis for setting and solving the problem is the initial data of the IIS, on the basis of which mathematical models are built, describing the characteristics of objects and the process of their development in time. These may be equipment reliability indicators, parameters characterizing the current technical condition of the object, or a separate parameter that determines the effectiveness of a technological process.
Building an adequate model of a technical system, a separate object, units of equipment or its node, aims to obtain a forecast for changing the technical parameters or reliability parameters in time. The forecast, in turn, makes it possible to make reasonable decisions on carrying out maintenance activities, planning repair activities, equipping the repair and technical services to the necessary equipment and recruitment of the equipment reserve fund.
An integral part of the problem of improving the reliability of exploitation and energy efficiency of enterprises is to develop methods of rational energy supply. The energy component in the cost of hydrocarbon raw materials reaches 15%, and the continuity of technological processes in the oil and gas industry is directly related to the efficiency of energy supply.
Improving the efficiency of enterprises is achieved by solving the entire complex of listed tasks.
- & nbsp- & nbsp-
Production efficiency is an important aspect of the problems of the oil and gas complex. Under efficiency it is understood primarily, the level of costs of all possible resources, including energy, to maintain the functioning of the enterprise. Cost of production, as one of the main components of the cost of products, are currently a serious obstacle to the competitiveness of Russian hydrocarbon raw materials in the international market. Therefore, recently requires the development and implementation of energy and resource-saving technologies.
The development of methods for solving listed tasks should be based on the increased level of quality and the amount of source information provided by automated control systems and diagnostics, widely used in the enterprises of the industry.
Purpose The dissertation work is to increase the efficiency and production safety of oil and gas enterprises by developing methods for managing the reliability parameters of equipment and reduce production and energy production costs.
Main goals
research:
1. Development of methods for diagnosing and predicting the reliability parameters of equipment operation based on the construction of models of technological systems of production and transport of hydrocarbon raw materials.
2. Creating diagnostic parameter systems to evaluate the current technical condition and residual equipment resource based on the integrated use of automated data collection devices.
3. Development of the theoretical foundations and practical methods for operational control of the technical condition of oil and gas transport systems using statistical, phenomenological and dynamic models.
4. Improving the efficiency of oil and gas equipment based on the optimal planning of repair and recovery activities.
5. Development of the methods for calculating the cost of maintaining repair and repair services, allowing to minimize damage from accidents equipment.
6. Development of methods for improving the reliability and efficiency of the operation of energy equipment, taking into account variable loads, which are a consequence of changes in the working conditions and the technical condition of energy consumers.
7. Development of the theoretical foundations of planning the territorial placement of facilities and communications of enterprises of the oil and gas industry in order to increase the reliability of energy supply and reduce energy losses, equipment restoration time and capital costs in the construction of communication facilities.
8. Improving the reliability of energy supply systems from fields based on the creation of the principles for the placement of autonomous energy sources.
Methods for solving problems. When solving the tasks, probabilistic statistical methods, elements of the theory of deterministic chaos, methods of game theory, mass maintenance theory, methods for solving transport optimization tasks were used. To confirm the conclusions and the implementation of the methods and algorithms proposed in the dissertation work, industrial information obtained by the Skat-95 information system on a number of Western Siberia oil deposits, the database of computer measuring and control systems of the compressor stations of Bashtransgaz, Vibro and gas-dynamic data Diagnostics of the TSPTL LLC Bashtransgaz, data of dispatching journals of OJSC UralTransnefteprodukt and other production information.
Scientific novelty lies in the following:
1. The need to collect and constantly storing the entire volume of production and diagnostic information is substantiated, and it has been shown that such information is of great value in terms of developing promising diagnostic methods based on mathematical processing of large amounts of source data, such as methods of mathematical statistics, dynamic chaos, Development of simulation models, etc.
2. The need to take into account the temporal dependence of the flow failure flow due to the change in the field characteristics in the process of its development. The three-parameter model of predicting the time of the trouble-free operation of technological equipment of oil and gas production makes it possible to increase the accuracy of forecasts of more than twice.
3. It is shown that various types of equipment failures have a deterministic nature at the location of the location of accidents, and statistically significant links between the types of failures and the technological parameters of the wells are established.
4. A method for analyzing vibration diagnostics data is proposed, which allows the consideration of the destructive impact of stochastic processes in complex technical systems and ensuring recognition of developing defects of oil and gas transport equipment, not available to traditional methods.
5. A complex of methods of optimal planning of the timing of the repair of oil-producing and gas transmission equipment, allowing minimizing enterprise losses and based on retrospective analysis of automated measuring databases on the dynamics of the flow of wells and numerical solutions obtained on the basis of the simulation model is developed. The proposed methods allow us to take into account not only the characteristics of the reliability of the equipment, but also the influence of such factors as the current prices for the raw materials and the negative impact of maintenance activities themselves.
6. Theoretical provisions are presented to determine the strategy for the choice of types and places for the placement of autonomous energy sources in the field of deposits, which make it possible to increase the reliability of the energy supply of oil and gas fields and reduce the cost of thermal and electrical energy consumed.
The defense is taken out The results of scientific developments in the field of technological processes and the improvement of diagnostic methods in order to improve the reliability of the operation of technological equipment and ensuring the energy efficiency and industrial safety of the facilities of the oil and gas industry.
Practical value and the implementation of work. Methods and algorithms for predicting the timing of the failures of the underground equipment of oil production developed in the dissertation work are included in the automated system for controlling the parameters of oil production "Skat-95". This system is operated on a number of oil-producing enterprises of Western Siberia.
The use of proposed techniques allowed to increase the accuracy of forecasts for the failure of ECH pumps in 2-5 times.
The methods of calculating the frequency of sellers were tested at OJSC UralTransnefteprodukt in dissertation. Studies have shown high efficiency and sufficient accuracy of assessments for practical use.
The results of the calculations were used in planning the sewage activities of Salavat-Ufa petroleum products, "Ufa-Kambarka", "Sanegyglazovo-Sverdlovsk".
The methodology for determining the technical condition and energy efficiency of gas turbine aggregates developed in the dissertation work was tested by the Bashtransgaz CPTL Security Service and is used to control the technical condition of the GPA.
Suggestions and recommendations on the principles of choice and territorial placement of autonomous power plants are considered to LLC Urengoyagazprom OAO Gazprom, COP "Kogalymneftegaz", TPP "URAINTEFTEGAZ", Langepasneftegaz TPP, TPP "Plyshikineegaz".
Approbation of work.
Basic provisions The work was reported at the following seminars, scientific and technical councils and conferences:
1. All-Russian Scientific and Technical Conference "Novoselovsky Readings" (Ufa, 1998).
2. The 5th International Scientific Conference "Methods of Cybernetics Chemical and Technological Processes" (Ufa, 1999).
3. The III All-Russian Conference "Regional Problems of Energy Saving and Ways to solve them" (N.-Novgorod, 1999).
4. Interregional scientific and methodological conference "Problems of the oil and gas industry" (Ufa, 2000).
5. Scientific and practical conference "Energy Saving in Chemical Technology - 2000" (Kazan, 2000).
6. All-Russian Scientific Conference "Energy Saving in RB", (Ufa, 2001).
7. The International Conference dedicated to the 50th anniversary of FTT UGNTU (Ufa, 2002).
- & nbsp- & nbsp-
The dissertation work consists of an introduction, five chapters, basic conclusions; Contains 315 pages of typewritten text, 32 tables, 84 drawings, bibliographic list of 240 names.
In the introduction The relevance of the topic of dissertation work is justified.First chapter It is devoted to the analysis of modern methods for modeling technical systems of the oil and gas industry, analyzes methods for monitoring and regulating the reliability of equipment and gas equipment and gas equipment and are considered ways to reduce the cost of consumed energy resources.
The analysis showed that the existing models for predicting the reliability of oil and gas equipment are static and do not take into account the dynamics of changes in the characteristics of the object in time. At the same time, there are a large number of well-developed mathematical methods that allow modeling real physical processes in complex technological systems. Until recently, the implementation of these methods was restrained by the lack of sufficient source information, which was used as a rule, data from dispatch journals. Thanks to the introduction of automation and computer technologies in the oil and gas industry and the accumulated large arrays of operational data, it was possible to create and use algorithms and computer programs implementing modern modeling methods that allow substantially to increase the level of operational reliability of the facilities of the oil and gas industry.
The main methods for the diagnosis of the technical condition of oil and gas energy equipment are considered and it is shown that they do not have the required accuracy. Thus, the analysis of the results of the vibrational diagnosis of gas-pumping units showed that in many cases the development of defects is not recognized using existing methods of processing vibration signals. It was concluded that it was necessary to expand the set of diagnostic signs and improving diagnostic data processing methods, allowing to adequately evaluate the current technical condition of the energy shelf.
- & nbsp- & nbsp-
Fig.4. Comparison of the prognostic capabilities of models of various complexity.
Cause of the accident - clogging of the working bodies of the pump of sand. The interval "A" is the base for the forecast, the interval "B" - the forecast. 1 - polynomial 1st degree; 2 - polynomial 2nd degree; 3 - polynomial 3rd degree; The triangle markers are actual data immediately before full failure outputs of fishing equipment are the events relatively rare, and therefore, the volumes of sampling on emergency repairs and / or equipment replacements during the period of time when the conditions for its operation can be considered unchanged, small. In addition, reliable information on the failures of the technological equipment stored in the databases of modern automated systems covers the time interval of 5 years. Taking into account the average developments on the failure and total number of units of the same type of equipment, such a volume of information does not exceed 10-20 life cycles of the technological equipment of oil fields. Therefore, the task of modeling reliability parameters taking into account the small volume is 0.9 0.85
- & nbsp- & nbsp-
0,75 0,7 0,65 0,6 0,55
- & nbsp- & nbsp-
Fig.5. The average value of the hurst indicator for various types of sample failures on emergency events and the requirement of the highest prediction accuracy.
To solve the task, a comparison of the accuracy of forecasts (by retrospective data) was compared for three methods for constructing an optimal model - the method of smallest squares, methods of minimizing medium risk and methods of fuzzy set theory. It has established that under conditions of small samples, the most reliable forecasts gives a model recommended by methods of the theory of fuzzy sets.
The forecast of the accident at instant failures such methods is impossible. In this case, it is necessary to find some "precursors" of accidents that would respond to the approach of refusal at almost constant working parameters of the well.
Such a precursor can be the fractal characteristics of the temporary series of debates. Studies have shown that chaotic changes in oil-producing wells have a deterministic nature, and the fractal characteristics of the time series of measurements of the flow rate make it possible to detect developing defects that are not available to traditional methods (Fig. 5).
In custody The second chapter is considered the impact on the reliability of the operation of the rod deep pumping plants of the high-frequency component of the load in the column of the rod, caused by resonant phenomena. To evaluate the degree of danger of this type of variable loads, a mathematical model of a tent depth pumping unit (ShGNU) has been developed, describing the dynamic loads in the rod column, and the basic dependences of their destroying effect on the technical characteristics of the equipment and the physical properties of the produced fluid are determined. The relationship between the probability of the breakpoint of the rod and the amplitude of dynamic loads is revealed, recommendations are given to reduce them.
- & nbsp- & nbsp-
Fig.10. Spectrograms of acoustic signal, the news of turbulent flows excited by a ball valve a) - airtight crane; b) - a leakage crane;
gas. The turbulent gas stream when the hole is exposed from the hole or when flowing into the body flow, generates acoustic oscillations, the frequency of which depends on the characteristic dimensions of the damage and parameters of the moving medium (Fig. 10).
Generated oscillations have a wide spectrum, which is associated with physical processes, leading to the generation of acoustic waves, namely, the formation and breakdown of gas vortices. Each elementary whirlwind has certain physical and energy characteristics, but since the parameters of elementary vortices are largely a random variable, the spectrum of acoustic oscillations at different time intervals is different.
If we enter the concept of an "instant" spectrum, understanding the spectrum spectrum for a sufficiently small time interval T \u003d 1 / F0, (4) where F0 is the lowest component of the spectrum components of interest to us, it can be said that the narrowband "instant" spectrum makes stochastic Displacement in some frequency range, the average frequency of the FCP of which is associated with the number of stream
- & nbsp- & nbsp-
Consequently, the study of spectral and statistical patterns of acoustic characteristics makes it possible to obtain information on the geometric sizes of the emitting object and the rate (flow rate) of the gas environment. Knowing the average speed of the noise strip in the acoustic spectrum, from the ratio (5), it is possible to estimate the characteristic size of the damage D on the tap seal and the value of the q gas leakage. For the spectrum presented in Fig.10 (FCR \u003d 1750 Hz), we have
- & nbsp- & nbsp-
what is about one percent of the gas pumped gas by the GTK-10 unit and commensurate with the error of the flow meter. The advantage of the proposed diagnostic method is the ability to carry out measurements without stopping the crane operation.
In the third section of the chapter, the possibility of constructing a diagnostic phenomenological model, which makes it possible to calculate the efficiency of GTU without attracting additional measurements.
The urgent task of controlling the technical condition of the equipment are studies aimed at developing methods for calculating the parameters of the equipment for which additional measurements are required not provided by standard devices. These include, in particular, methods for calculating the efficiency of pumping and compressor aggregates. Each of the nodes of the mechanical system can be characterized by some result parameter, which is the criterion of the technical condition of this node. For example, for a GPa as a whole, as an estimate of the technical condition, you can take the value of the total efficiency of the unit or the residual resource of the work.
Denote by the I-th recorded by standard devices, the parameter of the unit of the unit through Xi, then the technical state of the YJ jth node can be defined as a function of parameters, i.e. Yj \u003d fj (x), where x \u003d (xi).
Each of the recorded parameters XI changes over time, and the recording is made at an equal interval of time with the interval T, i.e. TK \u003d NT, where N is the dimension number in the series. Therefore, the registered time series of parameter values \u200b\u200bcan be represented as xi \u003d xi (tk). The calculated indicator of the technical state Yj will also be a temporary range of YJ (Tk), which makes it possible to study the trend of the technical condition and prediction of defects of oil and gas equipment.
Efficient efficiency of GTU depends on the mode of operation of the GPU and is a known function of many regime parameters: \u003d F (x), where x \u003d (xi) is a complex of parameters measured (including abnormal means) for calculations. Over time, when changes in the mode of operation of the GPA, parameters are changed, i.e. xi \u003d xi (Tj), and efficiency j \u003d f (tj).
On the other hand, it is possible to submit a complex function F simpler (for example, a linear) function of the parameters XK (measured by standard devices) with unknown constant coefficients:
N * j \u003d f * (t j) \u003d a0 + ak xk (t j), (6) k \u003d 1
- & nbsp- & nbsp-
the temporal rows of parameters XK (TJ) and efficiency (TJ) and setting the level of confidence of correlation.
The AK coefficients are calculated from the function of minimizing the functional F (X) -F * (x) min. (7) Similarly, the task of determining other diagnostic indicators - the coefficients of the technical condition for power, efficiency or fuel gas.
Fig.11 shows a comparison of the efficiency calculated according to the standard method (requiring additional measurements) with calculations on the proposed model. The error of the calculated values \u200b\u200bof K is 2% and is systematic, while the curves are equidistant. Therefore, it can be considered that the regression equations obtained using the proposed procedures are sufficiently accurate, and with their help it is possible to conduct estimates of the coefficients of the GPA technical condition.
The advantages of the proposed method are the use of only standard measurements, the efficiency of calculation and the possibility of incorporating the developed algorithm into the functions of the IIS of the compressor station to display the current technical condition of each of the aggregates.
The fourth chapter is devoted to the issues of rational maintenance of hydrocarbon production and transport facilities.
In the first section of the chapter, possible schemes for organizing servicing oil and gas production facilities, allowing minimizing production costs and reduce damage from equipment downtime.
Analysis shows that more than half of the defects of the equipment are developing in time. The characteristic times of the complete development of the defect, for example, in oil production, is the time interval up to 90 days.
Repair work immediately after the detection of a developing defect is inappropriate, since the equipment has not yet fully developed a resource, and its replacement for a new requires significant costs. On the other hand, the operation of equipment with a developing defect leads to a decrease in profits due to a decrease in oil production. In addition, unprofitable and simple well during restoration work. Thus, it is necessary to solve a multicriterial optimization problem - to determine the moment of the start of repair work, in which the damage of the enterprise from reducing oil production will be minimal. Consider the solution of the task of optimizing the timing of the repair work under the assumption that the function describing the decrease in the flow rate Q (T) of the well has already been determined and parametrized.
We will take for the beginning of the timing of time t \u003d 0 the moment of the beginning of the decline in the flow rate.
The profit of the enterprise obtained during the operation of the well during this period is determined by the income from the sale of the product
- & nbsp- & nbsp-
B C. (11) Slave + slave + slave + C Rem + C El p slave \u003d 0 CQ0 Equation (11) represents an algebraic equation of a third degree relative to the desired solution, which can be calculated by cardano formulas.
Calculations given taking into account the operation of pumping equipment to failure, showed that, subject to the execution of these recommendations, the specific income of the oil-producing enterprise increases by 5-7%.
A similar task occurs when planning repair work on gas transmission equipment. The paper proposed a simulation model that allows the basis of statistical data on the failures of the elements of gas transmission equipment to calculate the optimal interremary period of operation of gas-pumping aggregates. The developed model can be applied to planning calendar timing of the planned and capital repairs of a GPA of any type.
The model adopted for calculations has the following structure.
Suppose that the GPA consists of n elements, for each of which you can determine the integral function of the distribution of the time for the failure of FI (T), 1in. The emergency failure of the unit is considered to have occurred at the failure of at least one element. After the emergency failure, a repair is made, which completely or partially restores the resource of the refused element of the GPA. There is also the possibility of implementing planned warning repairs of one or more elements, as well as those from the capital repairs in which the HPA resource is completely restored.
To carry out the calculations, it is necessary to know the form and parameters of the FI (T distribution laws), which can be obtained from the analysis of statistical data on emergency failures of the GPA. It is known that the initial section of the exploitation, which corresponds from the moment of launching the GPA after major repairs is the most dangerous in the sense of unexpected failures, which is typical for most technical devices. Failures on the initial section of operation are associated with the development of hidden defects after poor-quality repairs, their intensity over time decreases fairly rapidly (time period). After the end of the period of development of failures, mainly occur as a result of the physical wear of the elements of the GPA, and the function of the distribution of failures in this case corresponds to the normal law.
To determine 0.08.
- & nbsp- & nbsp-
where n is the drive power, kW;
Q - Nominal productivity, M3 / day.
The graph of the dependence z \u003d z (q), calculated according to the above formula based on the characteristics of the pumps and the liquid built for the height of the fluid in the range of 600-1000 m is shown in Fig.16. From the graph, it follows that the efficiency of the pump-power unit depends on its performance and varies from ~ 0.35 at Q \u003d 30-50 m3 / day to ~ 0.70 at Q 100 m3 / day.
According to the structure of the structure of the pumping park and flow rate of wells, we calculate the specific costs in the field in the field (for the real structure of the park
ETSN):
- & nbsp- & nbsp-
esn Park.
Evaluation of real cost Fig.16. The calculation of the specific costs of the passport was given according to the data of the treated ECH.
the rhenium of the total flow rate of wells, equipped with ECH, and the total power consumed by pumping equipment. Operated at the studied deposit of IIS "Skat-95" allows you to conduct similar estimates. So, at the time of measurements, the total daily flow rate of the fluid oil hydroprishesis was 35031 m3 / day, while the actual total power of drive engines was 9622 kW. Calculation by relation (26) in this case gives z \u003d 6.6 kWh / m3. Thus, the actual specific energy costs almost twice the lower limit for this field.
An analysis carried out in order to determine the reasons for the difference in actual and theoretically possible for the conditions of this field of specific energy consumption, revealed the following main reasons:
Significant thermal losses in the power cable due to a small cross section of conductive livers;
Non-compliance with the size of the supply voltage on the transformer substation with nominal or skew phases;
Losses in transformers;
Unsatisfactory technical condition of the pump, engine or pump-compressor pipes.
One of the methods for the reduction of irrational losses of electrical energy is to ensure the rational load of transformer substations. This task is solved in the dissertation work by developing an algorithm for calculating loads, which allows optimizing the distribution of the load of transformer substations of oil and gas fields, taking into account possible changes in the actual power of energy consumers.
The irrational loading of technological equipment leads to a reduction in the resource of its work and at the same time increases the specific energy consumption for the extraction of hydrocarbon raw materials. This fully applies to the bush transformer substations (CTP), the installation of which was carried out in most cases at the initial stages of the development of oil and gas fields.
Previously operating in the nominal regime of the KTP due to the fall in oil production turned out to be in most cases either shortwatened or overloaded. Statistical analysis of the database of iis "Skat-95" showed that the general rule is currently underloading KTP by 40-60%. Moreover, the distribution of the load between the KTP (if there is more than one KTP on the wells bush) in the real case can be completely random.
It is also necessary to note that the load of the KTP does not remain constant over time. For example, the failure of one of the pumps leads to a reduction in the load. Taking into account the waiting time of repair (10-30 days) and repair itself (3-5 days), the emerging non-rational distribution of loads leads to a significant overflow of electricity.
To increase the reliability of the operation of bush transformer substations and reduce the irrational electricity losses, it is necessary to solve the task of the distribution of loads between the KTP, taking into account the actual performance of the pumping equipment and the temporary nature of the change in the connected loads caused by the emergency disabling of pumps.
We formalize the formulation of the problem as follows. There are N KTP serving M wells. All KTPs work with underload (on the left branch of the CPD curve). It is necessary to redistribute the load of consumers between the CTP in such a way that the total electricity loss is the smallest.
The comparative analysis of the characteristics of the efficiency of transformers showed that the most reliably in the class of elementary functions The left branch of the efficiency curve is described by the function of the form \u003d A (1 exp (n)), (28) where - the transformer efficiency;
a, - empirical coefficients;
N - power consumption.
Consider the function Y, which characterizes the operation of the KTP group:
n n \u003d i \u003d Ai (1 EXP (I N i)). (29) i \u003d 1 i \u003d 1 In the physical sense, the maximization of the functionality corresponds to a minimum of heat losses in the magnetic circuit and the windings of a group of transformers.
Obviously, the left part of the equation (29) will achieve the maximum value when N
- & nbsp- & nbsp-
The dependence (31) allows you to calculate the optimal load of each transformer in the group, if a common consumable power of the bush equipment is known.
Comparison of the numerical value of the total efficiency of a group of transformers obtained as a result of optimizing the load distribution, with the case of an existing load distribution showed that electricity losses on the KTP serving well bush decrease by at least 2%. Given that the number of transformers in NGDU can reach several thousand, electricity savings will be very significant. The proposed algorithm makes it possible to increase the durability of the transformer substation and power equipment by approaching the degree of their loading to the nominal.
In the conclusion of chapters, issues of rational energy supply of oil and gas enterprises are considered.
To increase the energy security of the operation of oil and gas-producing enterprises, an increase in the reliability of energy supply and reduce losses in transformation and transformation, as well as to reduce the cost of electrical and thermal energy, currently in the oil and gas industry are increasingly used autonomous energy sources. At the same time, the task of choosing type, power and location of autonomous power units, taking into account their reliability, work resource, cost and minimum energy loss when transmitting it to consumers.
An analysis of the performance characteristics of industrial mini-power stations of domestic and foreign production was carried out. It was shown that according to the criteria "Durability - the cost of electricity - reliability" the priority for oil and gas production enterprises are partitioned gas pipeline mini-power plants with a capacity of 1 ... 5 MW, working on passing gas.
Currently, there was a rather extensive market for autonomous energy sources, and the task of reconstruction is reduced to the choice of optimal type and power of power plants and their territorial placement, both from the point of view of reliable energy supply of industries and in terms of decreasing specific energy consumption for oil and gas production.
The task of choosing the optimal system of energy supply of oil and gas fields should be solved with regard to the territorial placement and capacity of both consumers and sources of electrical energy. Therefore, the formulation of the optimization task should be carried out individually for each field.
The initial information for the calculations is a large-scale map of the field, which causes all power consuming objects (wells of wells, water pumps, etc.) with an indication of their installed power.
Analysis shows that electricity consumption within the field has a pronounced uneven character. The surface of the power consumption has a number of local extremums, the location of which corresponds to the areas of maximum and minimum power consumption.
The task of placing objects for this case is formalized as follows.
In the field of deposits, it is necessary to place N autonomous sources of electricity with a known total power of N0 kW so that the load of the electrical receivers correspond to their nominal indicators, and the total thermal losses in the power lines were minimal.
Let M be existing objects (wells of wells, pumping stations and other consumers) are placed at different points P1, ..., PM plane, and new objects (autonomous power sources) - at points x1 ... xn. The distance between the location points of the J-th and the i-th existing objects will be denoted as d (xj, pi). Denote the annual specific energy loss in the cable between the j-M new and the I-M existing object via Wij \u003d F1 (Ni). Then the general annual energy loss will be determined as M f (x) \u003d Wij D (x j, pi), (32) i \u003d 1
- & nbsp- & nbsp-
where E i \u003d (x a i) + (y b i) +.
(h) (H) 2 (H) 2 The calculation of the optimal arrangement of autonomous power units, carried out according to the data of iterative formulas, makes it possible to determine the arrangement of an arbitrary number of sources (Fig. 17).
The proposed algorithm allows not only to increase the reliability of energy supply of oil and gas fields, but also reduce in 2 ... 5 times the loss of electricity in power lines.
General conclusions
1. A mathematical model of predicting the time of operations for the failure of technological equipment is developed, taking into account both the operating conditions and its design and qualitative indicators. The quantitative criteria for the effects of the operating conditions of this equipment on its working resource are established. It is shown that the accuracy of the developed models is not less than twice the accuracy of the forecast of models using the stationary flow of failures.
2. A technique has been developed for recognizing the abnormal zones of the development of oil and gas fields predisposed to increased emergency equipment. It has been established that various types of equipment failures have a deterministic nature at the location of the location of accidents. Statistically significant connections are established between the types of failures and the technological characteristics of the operation of wells.
3. The methods of diagnosing the technical condition of gas turbine machines based on the provisions of the theory of dynamic chaos are proposed. Based on the nature studies of stochastic processes in complex mechanical systems, a methodology for analyzing the spectral data of vibrationagnicity was developed, which makes it possible to record the destructive impact of stochastic processes in complex technical systems and ensuring recognition of developing defects in oil and gas equipment that are not available to traditional methods.
4. A complex of methods for predicting the timing of the occurrence of failures in the work of oil and gas equipment with developing defects of various kinds has been developed. Approbation of the technique showed that its use allows you to increase the prediction accuracy of at least 10 ... 30% compared with the traditional methods of forecast.
5. The methods of optimal planning of the timing of the repair of oil producing and gas transmission equipment, allowing minimizing the losses of the enterprise. The proposed methods are based on a retrospective analysis of the Database of IIS about the dynamics of the fall of the flow of wells and numerical solutions obtained on the basis of the simulation model of the bounce of gas-pumping equipment. It has been established that such long-term planning allows you to reduce accidents, reduce equipment downtime and increase the profit of the enterprise by 5 ... 7%.
6. A method for increasing the reliability and efficiency of the energy equipment under conditions is proposed when the attached load changes as a result of the failures of power consuming installations. It has been established that the use of the proposed technique allows to reduce electricity losses on bush transformer substations by no less than 2%.
7. A strategy for choosing types and places for the placement of autonomous energy sources based on the use of autonomous gas turbine and gas supply energy modules, which makes it possible to increase the reliability of the energy supply of oil and gas fields and reduce the cost of thermal and electrical energy consumed. It is shown that for this purpose, the use of gas supply plants of a single power of 1-2 MW operating on passing gas is the most efficient. The algorithms for the placement of such energy installations on the territory of oil fields, allowing to reduce the losses in the power lines 2-5 times.
1. Baikov I.R., Sneakers E.A. Principles for the creation and use of the database for critical modes of the COP. // Novoselovsky reading: Tez.D.
Vseros. scientific school. Conf.-Ufa, 1998, p.8.
2. Baikov I.R., Smerozodov E.A., Sneakers O.V. The use of rank criteria for vibrationagnicity GPa. // Novoselovsky reading: Tez. For. Vseros.
scientific school. Conf.-Ufa, 1998, C.9.
3. Baikov I.R., Sneise E.A., Smerozodova O.V. Diagnosing the technical condition of gas-pumping equipment by methods of the theory of image recognition. // Novoselovsky readings: Tez. Vseros. scientific school.
conf.-Ufa, 1998, C.7.
4. Baikov I.R., Sneise E.A., Smerozodova O.V. The choice of optimal frequency of vibration surplus of gas-pumping units of compressor stations. // Novoselovsky reading: Tez. Vseros. scientific school. Conf.-Ufa, 1998, C.6.
5. Sneakers E.A., Sneakers O.V. Determination of looseness of locking equipment of trunk gas pipelines. / Energy saving: Tez. Vseros. scientific school. Conf.-Ufa, Ugatu, 1998, p.18.
6. Baikov I.R., Smerozodov E.A., Sneakers O.V. The generation of ultra-low frequencies in the operation of gas-pumping units and their influence on vibration spectra // Izv. Universities. Oil and gas.- 1999.- №4.- S.62-67.
7. Sneakers E.A., Sneakers O.V., Musin D.Sh. Development of a contractual strategy of refinery enterprises with power systems // Regional problems of energy saving and ways to solve them: Tez. Dokl.
8. Baikov I.R., Sneise E.A., Akhmadullin K.R Optimization of the periodicity of purification of petroleum product pipelines // Transport and storage of petroleum products. - 1999.-№8.- S.8.
9. Baikov I.R., Sneise E.A., Sneakers O.V. Optimization of the placement of energy facilities by criterion of minimum energy loss. // Izv.
Universities. Energy problems. - 1999.- №3-4.- p.27.
10. Sneakers E.A., Kitaev S.V. Study of the dynamics of dependencies between the operating parameters of gas-pumping units. // Methods of cybernetics of chemical and technological processes: Tez. Dokl. 5th international. Scientific conf.
-Full: UGNTU, 1999.- T.2.-KN. 2.-C.167.
11. Sneakers E.A., Sneakers O.V., Shakhov M.Yu. Low-frequency oscillations of bearing assemblies of gas pumping units. // Methods of cybernetics of chemical and technological processes: Tez. Dokl. 5th international. Scientific
conf. -Full: UGNTU, 1999.- T.2.-KN. 2.-C.161.
12. Baikov I.R., Sneakers E.A., Smerozodova O.V. Simulation modeling of bounce of gas pumping devices. // Methods of cybernetics of chemical processing processes: Tez. Dokl. 5th international. Scientific conf. -Full:
UGNTU, 1999.- T.2.-KN. 2.-p.139.
13. Baikov I.R., Sneise E.A., Smerozodova O.V. Rating criteria in Vibrodiagnosis of the GPA // Materials of Novoselovsky Readings: Sat. Scientific Tr. Vseros.
scientific school. Conf.- Ufa: UGNTU, 1999.- p.130.
14. Baikov I.R., Sneakers E.A., Sneakers O.V. Select the frequency of vibration surveys of technological equipment of the gas main transport system. // Materials of Novoselovsky Reading: Sat. Scientific Tr. Vseros.
scientific school. Conf.- Ufa: UGNTU, 1999.- p.134.
15. Baikov I.R., Sneise E.A., Smerozodova O.V. Making decisions on the repair of equipment of compressor stations using the methods of game theory. // Materials of Novoselovsky Reading: Sat. Scientific Tr. Vseros. scientific school. Conf.Uf: UGNTU, 1999.- p.138.
16. Sneakers E.A., Sneakers O.V. Some empirical dependencies on refusing gas pumping units of compressor stations. // Materials of Novoselovsky Readings: Sat. Scientific Tr. Vseros. scientific school. Con.- Ufa:
UGNTU, 1999.- p.142.
17. Baikov I.R., Sneakers E.A. Diagnostics of the technical condition of mechanisms based on statistical analysis of vibration signals // Izv. Universities. Energy problems. -1999.-№11-12.- C.24-29.
18. Baikov I.R., Sneakers E.A., Sneakers O.V. The use of methods of the theory of self-organization in the diagnosis of the technical condition of the mechanisms. // Izv.
Universities. Energy problems. - 2000.- №1-2.- S.96-100.
19. Baikov I.R., Poppers E, A, Smerozodov O.V. Modeling the failures of gas-pumping aggregates by Monte Carlo // Gas Industry. M..20-22.
20. Kurochkin A.K., Sneakers E.A., Zakiyev A.A. Determination of some empirical dependences of the energy parameters of rotary hydroacoustic emitters. // Energy Saving in Chemical Technology - 2000:
Materials are Vseros. scientific study. conf. - Kazan: KSTU, 2000, p.119-120.
21. Kurochkin A.K. EA samples, power distribution in high-speed rotary hydroacoustic emitters // Energy saving in chemical technology - 2000: Materials of Vseros. scientific study.
conf. - Kazan: KSTU, 2000, p.69-73.
22. Kurochkin A.K., Smerozodov E.A., Alekseev S.Z. The study of the expenditure characteristics of high-speed hydroacoustic emitters. // Energy Saving in Chemical Technology - 2000: Materials Oversk. scientific study. conf. - Kazan: KSTU, 2000, p.121-122.
23. Kurochkin A.K., Sneakers E.A., Zakiyev A.A. The study of the spectral composition of acoustic oscillations of high-speed hydroacoustic emitters. // Energy Saving in Chemical Technology - 2000: Materials of scientific time. conf. - Kazan: KSTU, 2000, p.117-118.
24. Kurochkin A.K., Sneakers E.A. Experimental studies of the dependence of the cavitation noise of the high-speed hydroacoustic emitter from the frequency of rotation of the rotor and static pressure. // Energy Saving in Chemical Technology - 2000: Materials Oversk. scientific study. conf.
- Kazan: KSTU, 2000, p.123-124.
25. Smorodov E., Deev V. Aplication of Serial Statistics for Diagnostics of the Oil and Gas Equipment // Journal of Fushun Petroleum Institute.- №4.-2000.- R.52-57.
26. Baikov I.R., Sneakers E.A., Smerozodova O.V. The use of rank criteria for vibrodiagnosis of gas-pumping units // Gas industry. Special edition.-2000.- p.42-44.
27. Snodov E.A., Kitaev S.V. Methods for calculating the coefficients of the technical condition of the GPA // Gas industry.-2000.-№5.-C.29-31.
28. Baikov I.R., Smerance E.A., Kitaev S.V. Studying the influence of sewage sections of flowing parts of axial compressors on the reliability of gas turbine installations // Izv. Universities. Energy problems. - 2000. - No. 5-6.S.77-82.
29. Baikov I.R., Sneise E.A., Sneakers O.V. and others. Refinement of forecasts of emergency failures of technological equipment by methods of the theory of fuzzy sets // Izv. Universities. Energy problems. - №7-8.- 2000.- p.17-22.
30. Sneakers E.A., Deev V.G. Strategy for relations between suppliers and consumers of electricity // Izv. Universities. Problems Energy. C.36-43.
31. Baikov I.R., Smerance E.A., Deev V.G. Mathematical modeling of failures of pumping and power equipment oil-producing industries // Mountain Bulletin.- 2000.-№3.- S.51-54.
32. Sneakers E.A., Deev. Evaluation of the quality of the Foundation for oil-producing wells // Problems of the oil and gas industry: Interregion materials. Scientific program.
conf.-Ufa.- 2000.- C.93-95.
33. Sneakers E.A., Deev V.G. Control of the equilibious rocking machine based on the processing of synchronous dynamograms and tocograms // Problems of the oil and gas industry: materials of the Multi-regional scientific and methodological conference. -Uf, 2000.- C.95-97.
34. E.A. Sneakers, Deev V.G., Ismakov R.A. The methods of express assessment of the quality of the foundation of oil-producing wells. // Izv. Universities. Oil and gas. -2001.- №1.S.40-44.
35. Baikov I.R., Smerance E.A., Shakirov B.M. Principles of reconstruction of the energy supply system of settlements // Izv. Universities. Energy problems. - 2001.- №9-10.- S.77-81.
36. Sneakers E.A., Ismakov R.A., Deev V.G. Optimization of the timing of the repair activities of underground equipment // Petroleum economy 2001.-№2.- S.60-63.
37. Baikov I.R, Goljanov A.I., Sneise E.A. and others. Clarification of the methodology for determining the technical condition of the flow part of gas pumping units // Izv. Universities. Energy problems. - 2001. - №3-4.- p.3-6.
38. Sneakers E.A., Deev V.G. Operational control of the balance of the Machine Rocking Machine of the SHGN on the basis of dynamometry // Petroleum economy. S.57-58.
39. Baikov I.R., Sneakers E.A., Kostareva S.N. Assessment of the technical condition of GKU using vibration // Gas industry. - 2001.- №4.- C.39-41.
40. Baikov I.R., Sneakers E.A., Soloviev V.Ya. Optimization of loads of bush transformer substations of the oil-producing enterprise // Izv. Universities. Energy problems. - 2002. - №11-12. P.32-36.
41. Baikov I.R., Smerozodov E.A., Shakirov B.M. Evaluation of the efficiency of using a mini power plant // Izv. Universities. Energy problems. - 2002.c.115-120.
42. Baikov I.R., Sneakers E.A., Deev V.G. Analysis of temporary series as a method for predicting and diagnostics in oil production // Petroleum economy. S.71-74.
43. Baikov I.R., Sneakers E.A., Soloviev V.Ya. Dynamic loads in the rods of deep pumps and their effect on the safety of operation // Izv.
Content 1. Program "Maintenance ..." Galimullin Minivaris Lutfullinovich Development of technical means of improving the working capacity of well plunger pumps Specialty 05.02.13 - "Machines, aggregates and countries, a search mechanisms for the effective interaction of the state and private b ..." State University . Adm. G.I. Nevelsky "V. V. Tarasov, S. B. Malyshko, S. A. Gorchakova Materials Science Teaching Guide Recommended ..."
"Installing ultrasonic preservative cleaning of small-sized tools Uzumi-05 (Registration certificate No. FSW 2007/01155 dated November 20, 2007) Operation manual 9451-006-26857421-2007 RE Saratov Contents Contents. Introduction .. 3 2. Purpose .. 3 3. Basic technically ... "
"Budget Educational Institution of Higher Professional Education" St. Petersburg State Forestry University named after S. M. Kirov "Department of Road, Industrial Affairs ..."
"Section 1 Paleontology, Stratigraphy and Regional Geology Space Methods of Geological Studies, Forecast and Search for Fields A.A. Kisses1, Associate Professor, Yu.S. Ananyev1, Associate Professor, VG ... "
10.04.2018
Source: ProNeft magazine
Management of Reliability and Integrity of Equipment Is An Important Tool for Enhancing Business Efficiency
UDC 338.45: 622.276
V.R. Amirov
PJSC Gazprom Neft
Keywords: Reliability, integrity, equipment, risk, costs, efficiency, budget, planning, production security, operating system management system (sode)
V.R. Amirov.
Gazprom Neft PJSC, RF, Saint-Petersburg
The ARTICLE IS DEVOTED TO IMPROVEMENT OF OPERATIONAL EFFICIENCY OF OEIL AND GAS FEELDS AND EXAMINES OF THE OPERATIONAL MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (OMS). This Direction Is The Management of Reliability and Integrity of Equipment - Implemented by The Deming Cycle. A Prerequisite of Effective Management of Reliability and Integrity Is A Correct Assessment of the Current Condition of The Asset Through the Risk Assessment and Registration Costs and Damages. The Risk-Based Approach Allows for Comparable Levels of Direct Costs for Management of Reliability and In- Tegrity, to Improve The Total Economic Result (Direct Costs + Damage) While Reducing the Number of Failures. In Conclu- Sion, The Assessment of the Current State of Management of Reliability and Integrity in Upstream Division of GPN
Keywords: RELIABILITY, INTEGRITY, EQUIPMENT, RISK, COST, Efficiency, Budget, Planning, Production Safety, Operational Management System (OMS)
Doi
: 10.24887/2587-7399-2018-1-10-15
Introduction
The task of the "Etalon" program (operating system management system (sode)) PJSC Gazprom Neft is to ensure the maximum operating efficiency of the company through the reliability and safety of production activities and involve all employees in the process of continuous improvement. Managing the reliability and integrity of equipment (UNCO) is a set of activities that ensures uninterrupted operation of oilfield equipment throughout the entire period of operation. The importance of this direction of production activities is reflected in its allocation in a separate element of the sud.
Direct costs and cumulative economic results
In conditions of objective deterioration of the conditions of operation in the oil and gas industry (depletion of deposits, an increase in the waterproofing of wells, etc.), it is advisable to evaluate the "fresh look" the cost structure for maintaining the current activities of assets. A significant proportion (up to 20) occupy the costs of UNCO. They are distributed across various asset budget items and can be divided into the following areas (direct costs):
1.1. maintenance of equipment;
1.2. Overhaul (or replacement) of equipment (partially carried out due to capital investments);
1.3. Diagnostics of the state of equipment (including the expertise of industrial safety of equipment with an expired service life, measures for corrosion monitoring, etc.);
1.4. Equipment protection (including the choice of materials, applying protective coatings, inhibition of corrosion, etc.).
In addition, in the process of operating activities, additional costs of UNCO, which also affect the cost of oil production are arisen:
2.1. the cost of eliminating equipment failures and the elimination of the consequences of these failures;
2.2. Penalties and payments related to the integrity disorders and equipment failures.
The third cost group, or rather, the losses that affect the financial result of the activity of the asset during the reporting period include:
3.1. Product loss associated with integrity disabilities and equipment failures. These three groups of asset costs are differently related to the risks of the integrity of the equipment. Costs 1.1., 1.2., 1.4. Reduce these risks (both the probability and consequences), cost 2.1., 2.2., 3.1. arise due to the realized risks. Costs 1.3. Evaluate the risk data assessment and do not affect the amount of risk. EFFECT EFFICIENCY is estimated at the aggregate economic result, which represents the amount of all the above costs. Management of the cumulative economic result is the basis of UNCO and includes: planning, execution, control of implementation and evaluation of efficiency and actualization of the ONSO approach.
Risk and damage
The value of risk assessment and damage - values \u200b\u200bthat characterize the predictive and actual result of the activities associated with UNCO.
The risk of integrity violation is the predicted amount of damage from failures and disorders of the integrity of the equipment for the planned period. The quality of this risk assessment is determined by the comparison of this assessment with the amount of damage incurred during this period, taking into account prevented damage. Since currently the amount of damage from failures and disorders of the integrity of the equipment is taken into account by incompleteness, the quality of the assessment of the relevant risk is not easy due to the lack of a comparison base.
Under these conditions, justifying the activities related to UNCO, it can only be the confidence that costs (1.1., 1.2., 1.3., 1.4.) Significantly less damage that they must prevent. For new growing assets, such an assumption is usually true, but as the marginality decreased
business, the question of the validity of these costs is raised.
In general, the activities associated with UNCO has economic meaning if
where zi - costs in the directions 1.1., 1.2., 1.3., 1.4. during the reporting period; U - damage from failures and disruption of equipment integrity during the reporting period (2.1., 2.2., 3.1.); UPR - prevented damage during the reporting period.
In order to economically substantiate the costs of UNCO, costs are required to account 1.1., 1.2., 1.3., 1.4. During the reporting period, damage to failures and disruption of equipment integrity (costs 2.1., 2.2., 3.1.), as well as prevented damage during this period.
These tasks are solved as part of the organization of relevant reporting: on direct costs for UNCO, on damage to equipment failures and disorders of the integrity of equipment, the effectiveness of direct costs of UNCO.
Risk-oriented approach to the reliability and integrity of equipment
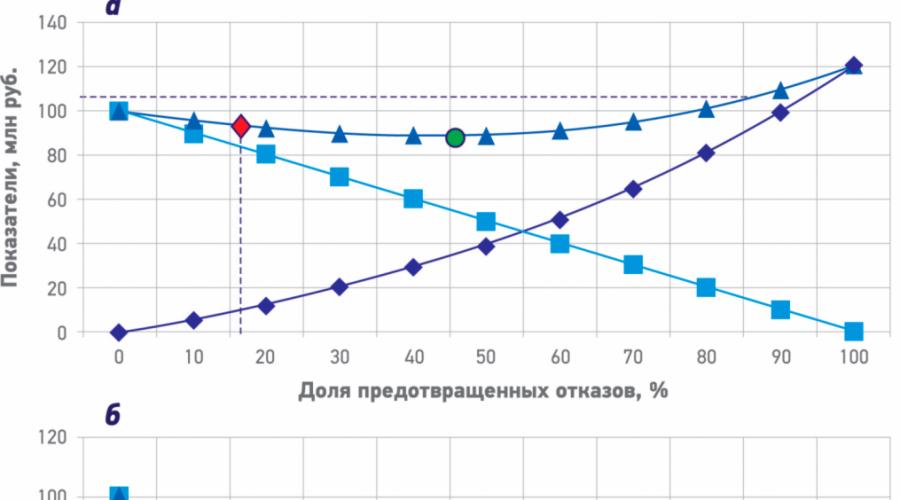
Currently, the oil and gas industry uses mostly two approaches to UNCO. 1. Repair and replacing equipment are carried out in a minimum volume on the fact of refusal. Diagnostics of equipment is carried out in accordance with the requirements of the legislation (technical inspection on the standards of safety rules, an examination of industrial safety for equipment with an expired service life, etc.). The cumulative economic result of this approach is presented in the figure, and in the form of a red rhombus and far from the optimal one by the number of prevented failures (green circle). This approach is characteristic of mature assets at the late stage of development of deposits with significant operating costs.
2. Repair and replacement of equipment are carried out in accordance with regulatory terms, manufacturer's recommendations, taking into account the results of technical examination. Diagnostics of equipment is carried out in accordance with the requirements of the legislation (technical inspection on the standards of safety rules, an examination of industrial safety for equipment with an expired service life, etc.).

Cumulative economic result of the implementation of approaches 1 and 2 (a) and risk-oriented approach (b)
This approach is characteristic of developing assets with growing mining. The cumulative economic result of this approach is shown in the figure, and the yellow rhombus is also not optimal. In addition, the amount of direct costs for UNCO in this case is more damage to the implementation of the above condition, it is necessary to assess the amount of prevented damage, which, as already noted, is quite difficult.
An alternative is an approach based on the risk assessment of failures and integrity of equipment (RBI - Risk Based Inspection, RCM - RELIABILITY CENTRED MAINTENANCE), which is called risk-oriented. The result of the implementation of this approach is shown in the figure, b. It should be noted that with this approach, the curve form characterizing damage from failures differs from the shown in the figure as well. This is due to the fact that in a risk-oriented approach, the costs are primarily sent to prevent failures with the most negative consequences (damage to people, the environment, the company's reputation, significant production losses), i.e. unacceptable risks. On the segment of the curve corresponding to 70 - 100 prevented failures, there are no insignificant consequences. Comparison of curves in the figure, A, B shows that a rislar fired approach allows at comparable levels of direct costs of UNCO to improve the cumulative economic result while reducing the number of failures. The optimal cumulative economic result is shown in the figure, a green circle. This approach is particularly effective in companies with different assets (new, developing, mature).
To use the risk-oriented approach to UNCO, two tasks must be solved.
1. Perform a qualitative assessment of the risks of the integrity of various types of equipment at the planned period, including the development and implementation of the calculation model:
- probabilities of equipment failure depending on key (internal and external)
the factors of the influence to which the service life, the results of technical examination, the state of the protection of the equipment, the material of manufacture, the conditions and history of its operation, etc.;
- the consequences of equipment failure, depending on its performance, operating parameters, costs, installation sites (in relation to other equipment, locations of personnel, settlements, water protection zones, etc.), a time interval of response to critical deviations of operating parameters, maintainability of equipment , state of external protection and response systems, etc.
2. To form automated reporting for a certain period
- on the direct costs of UNCO by type of equipment (1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 1.4);
- On the realized risks of failures and integrity of equipment (2.1, 2.2, 3.1).
The submitted approach is applied to short, medium-term planning activities related to UNCO.
Current state and prospects UNCO Block of Intelligence and Production of PJSC Gazprom Neft
To solve the first task in the Directorate for Extraction (DD) block of exploration and production (BRD), PJSC Gazprom Neft has developed and implements a program of reliability and integrity of oilfield equipment (NGOs), including:
- assessment of the risk of violation of NGO integrity through filling and analysis of estimated sheets by types of NGOs;
- Development based on this assessment of the cost planning methodology for UC NPO;
- the formation of units on UNCO in subsidiaries;
- Assessment of the effectiveness of the implementation of the NGO maintenance and repair program.
In the Gas and Energy Directorate (DGIE), a pilot project "Creating a Unified System for Planning and Control Planning and Planning Energy Equipment", the main tasks of which are to reduce the number of repairs and costs on them by determining the type and scope on the basis of assessment Technical state of power equipment (RBI) and balance between the required level of reliability and maintenance costs (RCM). In addition, in the near future, DGIE plans to start the implementation of the pilot project "Testing predictive analytics systems on the main equipment of power plants and gas transport facilities", the task of which is to improve the reliability of work, reducing the time of unscheduled equipment downtime by preventing and eliminating malfunctions at an early stage (RBI) .
The second task in terms of damage assessment is assumed to be solved by the introduction of a methodological document of the MD-16.10-05 "Methodology of financial assessment of damage from accidents in the field of production security" by allocating incident information systems from existing information systems in CT-55 from existing information systems. Classified as disorders of the integrity of the equipment (all failures, impulses of pipelines, etc.).
The organization of reporting on direct ONSO costs should be carried out on the basis of:
- the introduction of the fundamental standard of PJSC Gazprom Neft on UNCO, the development of which the Sud Development Center completes in 2018;
- Analysis of the existing automated management reporting system.
conclusions
1. The cumulative economic result is a key indicator of the effectiveness of activities related to UNCO.
2. Implementation and analysis of cost reporting and damage from failures and disruption of equipment integrity make it possible to prioritize the costs of UNCO.
3. Risk-oriented approach ensures the most efficient distribution of direct costs for UNCO.
4. The current state of UNCO to the RDA in part of both procedures and providing regulatory documentation allows you to implement the fundamental standard for UNCO without significant changes in the current documents.
1.4.1. Introduction Amusement valves of piston compressors
Valve- Independent assembly unit as part of the compressor stage. It serves to periodically connect the working chamber to the cavities of suction and discharge.
Fig. 5.9. Valve concept.
1 - saddle, 2 - limiter, 3 - springs, 4 - locking body.
Despite the diversity of valve designs, they can be reduced to a single concept shown in Fig. 5.9. In the general case, the valve consists of a seat 1, limiter 2, a locking organ 4, and one or more springs 3, and also contains the elements of the seat fastening with the limiter. In some structures, an elastic element is used as a shut-off organ, simultaneously performing and spring functions. In the assembled form, the locking body of the valve is pressed to the saddle and separates cavity with various pressure relative to each other.
In accordance with Fig. 5.9 The gas flow through the valve is possible only when moving the locking body by 0< h ≤ h кл в случае r 1 > r 2. The condition for the beginning of the movement of the shut-off body is the excess of the gas force acting on the shut-off body, over the elastic power of the springs ![]() .
.
Elastic Spring Power is determined by the relation
![]()
It follows from this expression that at a certain number of springs acting on the valve plate, their stiffness and preliminary tension in the assembled valve value ![]() .
.
The force is determined by gas pressures operating on both sides to the frontal surface of the shut-off body, i.e.
where is the coefficient that takes into account the shape of the pressure of the pressure on the surfaces of the shut-off authority, as a rule, is experimentally. Let's take: ![]() - gas pressure in the cylinder of the compressor stage variables at the corner of the shaft rotation at discharge pressure
- gas pressure in the cylinder of the compressor stage variables at the corner of the shaft rotation at discharge pressure ![]() . When performing the condition of the valves of the compressor steps automatically open. According to this sign, they are called consistent, i.e. Automatically open at a certain pressure difference in the cavities separated by the valve. With a decrease in the active pressure drop, the valve is automatically closed under the action of springs.
. When performing the condition of the valves of the compressor steps automatically open. According to this sign, they are called consistent, i.e. Automatically open at a certain pressure difference in the cavities separated by the valve. With a decrease in the active pressure drop, the valve is automatically closed under the action of springs.
According to a constructive performance, the flow part of the valve is a combination of one or more channels of the changes close to the patterns in the direction of gas flow to the nozzle. In this case, the sections of the channels at the inlet (from the side of the saddle) and the outlet (from the side of the limiter) are constant, while the cross section in the valve slot is minimal, depends on the movement of the locking body and changes during operation in the range, where - the maximum size of the geometric sequence of the slot For a fully open valve. The volume of gas contained in the valve channels is the main proportion of the dead volume of the compressor stage and from this point of view is minimized.
In essence, the valve flowing physical processes can be viewed as local resistance with a geometric cross section and an equivalent cross section. ![]() , where - gas flow rate via valve, depending on the shape of the valve channels.
, where - gas flow rate via valve, depending on the shape of the valve channels.
The feature of the valve operation is the occurrence of shock stresses in the valve elements when the locking organ with the saddle and the limiter, the value of which depends primarily on the height of the movement of the locking organ and the rotation frequency of the compressor n.
On the pushing of gas through the valve requires additional cost of the operation proportional to the current pressure drop
 ,
,
where -liness of the gas at the inlet to the valve channels;
m is the mass flow rate through the valve.
From the above expression it follows that to reduce the value, the equivalent cross-section of the valve gap should be selected as possible. However, this leads to an increase in the dead space in valve channels and, as a rule, is accompanied by an increase in the height of moving shut-off values, which worsens the performance and reliability of the compressor stage.
Given the above, a number of requirements are presented to the design of the valves. We highlight among them the main:
1. High level of performance of valves, provided by the maximum possible increase in the cross section of the slit at the given surfaces of the compressor stage, on which the valves are placed. At the same time, additional energy costs are usually limited in valves for stationary compressors and 12 ÷ 15% for mobile and special high pressure compressors from indicator power.
2. The guaranteed level of reliability, the indicator of which is usually the estimated valve operation until the first failure. In modern structures of piston compressors, this value lies in the range from 2 to 10 thousand hours, where the upper limit corresponds to large stationary compressors, and the lower - high-speed low-power compressors.
These requirements come into contradiction with each other. In particular, the desire to increase efficiency usually leads to a decrease in the reliability of the valve. Therefore, when designing valves, as a rule, they are going along the way of finding a compromise solution.
In addition to the above, a number of additional requirements are presented to the valves, among which we note the following:
Dynamic tightness, i.e. The timeliness of their closure;
Static tightness of valves in a closed state;
Minimal dead space in valve channels;
Ease of installation, dismantling and maintenance, especially in cases of work on contaminated gases and in the absence of cylinder lubrication;
Minimal mass-duct parameters, cost and delivery time;
Guaranteed after-sales service by the manufacturer.
Characterizing the design of the valves, usually consider 2 major sections of the channels for the passage of the gas: the section in the saddle and in the slot of the fully open valve. In general, the value is determined by the equation
F Sh \u003d P ∙ H CL,
where n is a sealing perimeter of the closed valve;
- The maximum movement of the valve plate.
The values \u200b\u200bof n and for the main types of valves are shown in Table. 5.3.
Table 5.3.
Parameters section of the slit of self-use valves.
Note: L (L), B (B) - dimensions of the shut-off;
- average diameter of the annular plate;
- the diameter of the opening at the inlet to the valve;
Z is the number of rolling elements of the valve.
The main task in the preliminary justification of the design of the selected type valve for the compressor under consideration is the determination of the desired cross section of the slot of the valve-dependent valves, the active area of \u200b\u200bthe piston, its average speed with n, the gas temperature at the inlet in the valve T., Gas constant R and adiabudes K. The connection of the specified parameters for the fully open valve is described by criteria dependence
 ,
,
where M is the criterion of gas flow rate in the valve. Its magnitude for modern valve designs lies in the range ![]() ;
;
- Flow coefficient of the valve.
The value for a specific type of valve is usually determined by experimentally, considering it depending on the current height of the movement of the valve plates. For fully open valves, you can recommend the values \u200b\u200bgiven in Table. 5.4.
Table 5.4.
Consumption coefficient of basic valve designs
In the reference literature, the valve is characterized by an equivalent cross section. ![]() . Its value according to the above criteria dependence will be equal to
. Its value according to the above criteria dependence will be equal to

At the found value of F, a standard valve is selected or a new one with specific geometric parameters is developed.
A similar method of selecting valves does not guarantee the required level of performance and reliability indicators. Therefore, at the final stage, it is advisable to perform the calculated analysis of the operation of the selected valves in the real stage of the compressor. This uses test calculation programs, providing for mathematical modeling of a complex of workflows and dynamics of movement of locking organs, which allow for the design of the design to justify the optimal combination of the geometric parameters of the valve elements in relation to the compressor with a given geometry steps, known by the modest parameters and properties of the working substance.
An indicator of the reliability of the developed valves, which formed as a result of many years of experience of a number of generations of researchers, manufacturers and consumers of compressor equipment is the implementation of the condition: estimated (at the design stage) or experimentally defined landing rate of valve plates per seat W with ≤ 1.5 m / s .
Finally, the valuation efficiency and reliability assessment is made on the basis of extended thermal tests of compressors providing for the determination of performance, power consumption, discharge temperatures over steps and developing to the 1st failure.
In the following materials, the author puts and solves the task of developing, researching and creating self-acting valves, the effectiveness and reliability of which are justified at the design stage when using the modernized commened program.
1.4.2. Basics of optimizing piston compressor valves
Selection of characteristic valve parameters in terms of equivalent secting in the gap fully open valves Ч does not guarantee the optimal combination of the design parameters of the valves (thickness Δ pl and mass m. Ploves movable valve plates, their maximum movement h. CL, stiffness FROM PR, numbers Z. pr and pre-tight springs h. 0 acting on separate valve plates), and therefore, does not allow to predict the actual level of static ν and dynamic ν not the tightness of the valves with the overall dimensions or landing diameters selected during the preliminary thermodynamic calculation d. one . The consequence of this approach is the discrepancy between the calculated and actual performance, the power on the shaft of the machine and the indicators of the reliability and efficiency of the work and the aggregate as a whole.
Given these factors, it is appropriate to fulfill comprehensive testing calculation as numerical experiment In the course of which a comparative analysis of the options for the compressor stage equipped with valves of various structural execution is carried out. According to the results of a numerical experiment, it is recommended " optimalVariant »Valves, under which the required performance performance is ensured, a modern level of efficiency and reliability of valves when working on nominal and other modes.
This aspect of the work is presented in detail in section 7.
1.4.3. On the feasibility of using fungal type valves
as part of the steps of opposite compressors
Under the "fungal" valves in the literature, individual valves are understood in the form of a circular plate, the surface of which from the saddle side is made by a profile that provides minimal gas-dynamic resistance during gas through the valve channels. The movable valve body externally resembles a fungus with a "hat" of a spherical shape facing the valve seat. Structurally fungal valves are practically different from valves with spherical plates (see Fig. 5.10-A and 5.10-b). By virtue of a number of features of the valves of this type, they are used, as a rule, in small-scale vehicle-action machines and on high-pressure steps with small diameters of cylinders. Existing methods for calculating spherical valves are fully applicable and when analyzing the operation of compressor steps with compressed fungal valves.
In this section of the work, the author analyzes the feasibility of using fungal valves in the steps of modern high-speed (N ≥ 750 rpm) of opposite compressors with dual-action pistons, which predetermines the lateral location of the individual valves with the plant diameter D 1 on the side walls of the cylinder.
Since the fungal valves are structurally identical to spherical, their estimated analysis can be performed on the basis of the commedom application program. The program has proven itself in the practice of the calculated and design divisions of Compressor OJSC S. Petherburg at the stage of development and justification of the optimal variants of low-cost compressors of low, medium and high pressure on U-shaped bases.

Fig. 5.11. Set of fungal valve
with non-metallic shut-off
with a flat-diameter of 125 mm (z cl \u003d 20)
The main advantage of plastic type valves (fungal and spherical) with non-metallic locking bodies their increased tightness in the closed state is considered.
Chief flaw- Low utilization factor of the frontal surface of the valve plate with a landing diameter D 1, within which the N-E number of spherical or fungal valves is installed (see Fig. 5.11).
As an object of the study, the I stage of the gas compressor is selected 4GM2.5-6.67 / 4-50C with dual-action pistons. The working cavities of the stage (A and B) can be equipped with a variety of individual valves with a landing diameter of Ø125 mm with the placement of them on the side surface of the cylinder. During the numerical experiment, the effectiveness of the operation of the stage was estimated when it was estimated by direct-flow (peak), ribbon (LU), strip (PC) and fungal valves while maintaining modest parameters.
At the preliminary stage of the study, the optimal magnitude of the lifting organ of the fungal valve of the valve was determined. The results of the study are given in Table. 5.6. Their analysis made it possible to justify the optimal version of the GRK125-20 valve -14 -2.0 with the diameter of the hole in the saddle d c \u003d 14 mm and the height of the lift of the shut-off organ H CL.OPT \u003d 2 mm.
The results of the 2nd stage of the study shown in Table. 5.7 and in Fig. 5.12 In the form of the current and integral parameters of the compressor stage, the following conclusions are allowed to draw the following conclusions:
1. Pitchflower fungal valves mounted in a stove with a landing diameter Ø125, when arranged on the side surface of the cylinder losing Valves of other types of main indicators, including:
Reducing performance - by 4.3%;
An increase in the total relative losses in the valves χ Sun + NG 2 times;
Reducing isothermal indicator efficiency η iz.Ind - by 8.0%;
Increase the temperature of the injected gas - at 14 K.
Table 5.6.
Integral parameters Stage i Compressor 4GM2.5-6.67 / 4-50s When completeing the valves of fungal type with a variable height of the lifting H CL
| Parameters | Dimension | Number and type of valves installed: | ||||
| Z KL \u003d 1 Sun + 1 ng, type - Fungal | ||||||
| Valve designation I Art. | - | GRK125- 20-14-1.5 | GRK125- 20-14-1.8. | GRK125- 20-14-2.0. | GRK125- 20-14-2.2. | GRK125- 20-14-2.5 |
| H CL | MM. | 1.5 | 1.8 | 2.0 | 2.2 | 2.5 |
| r ng / R Sun | MPa | 1.2 / 0.4 | ||||
| N \u003d r ng / r Sun | - | 3.0 | ||||
| but | 0.34 | |||||
| T. Sun | TO | |||||
| T. Art | 345.2 | 334.9 | 343.1 | 342.9 | 342.7 | |
| T. NG | 433.5 | 430.3 | 428.3 | 427.8 | 427.4 | |
| M 1.A. | kg / ch | 513.44 | 517.26 | 519.94 | 518.58 | 523.88 |
| V N.U.1A. | Nm 3 / min | 7.1011 | 7.154 | 7.1911 | 7.1723 | 7.2455 |
| N Ind.1a | kw | 20.470 | 20.150 | 19.961 | 19.826 | 19.974 |
| N NOM.1A. | 16.736 | 16.781 | 16.841 | 16.796 | 16.938 | |
| Δn Σ. | 3.634 | 3.369 | 3.120 | 3.030 | 3.036 | |
| χ Sun. | - | 0.118 | 0.108 | 0.103 | 0.103 | 0.100 |
| χ NG | 0.105 | 0.093 | 0.082 | 0.077 | 0.079 | |
| Ld | KJ / kg | 143.5 | 140.2 | 138.2 | 137.6 | 137.3 |
| H Sun. | 528.87 | |||||
| h ng. S. | 637.43 | |||||
| H ng | 670.56 | 667.33 | 665.24 | 664.66 | 664.33 | |
| η iz | - | 0.643 | 0.658 | 0.667 | 0.670 | 0.672 |
| λ | 0.5304 | 0.5344 | 0.5372 | 0.5358 | 0.5412 | |
| λ D. | 0.9521 | 0.9632 | 0.9664 | 0.9609 | 0.9709 | |
| λ T. | 0.9619 | 0.9631 | 0.9642 | 0.9658 | 0.9639 | |
| λ O. | 0.5669 | 0.5733 | 0.5746 | 0.5719 | 0.5769 | |
| Δλ Sun. | - 0.0225 | - 0.0123 | - 0.0104 | - 0.0139 | - 0.0131 | |
| Δλ ng | 0.0026 | 0.0021 | 0.0007 | 0.0005 | 0.0041 | |
| ρ 3. | kg / m 3 | 9.919 | 9.962 | 9.988 | 9.984 | 10.005 |
| ρ 1. | 4.362 | 4.418 | 4.437 | 4.419 | 4.458 | |
| ρ 3 / ρ 1 | - | 2.274 | 2.255 | 2.251 | 2.259 | 2.244 |
| W S.VS. | M / S. | 1.14 | 0.91 | 0.96 | 1.21 | 2.26 |
| W S.N. | 1.94 | 1.93 | 1.39 | 1.42 | 2.42 |
Cipher option - GM25-6.7-4-12. Working cavity - BUT.
Air, D c. I \u003d 200 mm, s n \u003d 110 mm, l Ш \u003d 220 mm, n \u003d 980 rpm, with n \u003d 3.593 m / s
Table 5.7.
Parameters Stage i credit compressor 4gm2.5-6.67 / 4-50c
when equipped with valves of various types
Z CL \u003d 1 + 1, Δ SL \u003d 1 μm, ρ Sun.real \u003d 4.7635 kg / m 3
| Parameters | Dimension | Execution option Stage i | |||
| BUT | B. | IN | G. | ||
| Valve type | - | PIK125- 1.0BM-1.5 | LA125-9- 96-8-0.6-1.8 | PC125-9- 96-8-0.6-1.8 | GRK125- 20-14-2 |
| T. NG | TO | 412.9 | 414.6 | 413.7 | 428.3 + 14 to |
| M 1.A. | kg / ch | 532.3 | 545.4 | 542.2 | 519.9 |
| V N.U.1A. | Nm 3 / min | 7.362 | 7.544 | 7.499 | 7.191 - 4.3% |
| V Sun.1a | m 3 / min | 1.862 | 1.908 | 1.897 | 1.819 |
| N Ind.1a | kw | 18.221 | 18.809 | 18.568 | 19.961 |
| ΣΔn CL | 1.036 | 1.502 | 1.392 | 2.957 2 times | |
| χ Sun. | - | 0.034 | 0.048 | 0.044 | 0.103 |
| χ NG | 0.026 | 0.039 | 0.037 | 0.082 | |
| η iz | 0.749 | 0.743 | 0.748 | 0.667 -8% |


Fig. 5.12. Current parameters I compressor stage
4GM2.5-6.67 / 4-50C for n \u003d 980 rpm
GRK125-20-12-2 ------ PK125-9-96-8-0.6-1.8
2. High frequency and amplitude of oscillations of valve springs in periods of suction and discharge (see Fig. 5.12) contribute to premature failure.
Summarizing the resulting data should be indicated that the use of a set of fungal valves in the valve plate plate as part of the steps of large opposite compressors with dual-action pistons at high random frequencies is not advisable. Exception can be some cases of use of fungal valves when equipped with steps low-speed compressors compressing "heavy" - "light" gases (for example, air - hydrogen and hydrogen-containing mixtures) during the period of commissioning tests.
Bibliography
1. Prilutsky I. K., Prilutsky A.I. Calculation and design
piston compressors and detaDers in normalized bases:
Textbook for university students. - SPBGAHPT, 1995. - 194 p.
2. Piston compressors: Tutorial for university students.
B.S. Fotin, I.B. Pirumov, I.K. Prilutsky, P.I. Planner.
- L.: Mechanical Engineering, 1987. - 372 p.
3. Frankel M. I. Piston compressors.
- L.: Mechanical Engineering, 1969. - 744 p.
- M.: Mechanical Engineering, 1979. - 616 p.
4. Catalog of electric motors. BRANCH LLC "ELKOM". - Moscow, Russia
Voroshilov - Ryzhkov:
1. Colding compressors without cooling cylinders -
thermal task (experiment and chain) +
feather finish (Experiment with the participation of the representative of the KKZ and Galyaev ??)
2. Unification of valves I and II compressor steps 4GM2.5-6.67 / 11-64
3. Rational Technical Solutions Masha, damping, unification - Z CL 3: 1 (PAI)
4. Rectangular valves of transport compressors - an alternative to individual valves of round shape forced by middle velocity of the piston and the rotational speed of the shaft (Ukz-Demakov and KKZ)
5. Development of 4U4 base forced by middle speed .............
6. The achieved technical level of compressors.
Prospects for its further increase
7. Integrated settlement and theoretical analysis (2BM2.5-14 / 9) ......... ..