What colors are primary. What are primary colors, secondary colors, tertiary colors? Watch what is "secondary colors" in other dictionaries
Read also
Passion for color
Why do you need a color circle?
The color circle demonstrates the interaction of subtractive colors with each other.
This is the main tool of colorist in working with color.
Color circle - color model colorist, makes it possible to understand how colors interact with each other, and use this knowledge in the work. The better you understand the color circle, the more studying it, the work with the color becomes more and more interesting. Checked!
The study of the color circle is the basis of all further knowledge of hair coloring. Understanding the color circle determines your color perception.
The color circle demonstrates primary and secondary subtractive colors and describes their interaction with each other. This makes it the main tool in working with color. We all studied the color circle at the beginning of a career, but not everyone paid enough attention to this, considering this information a secondary.
Primary and secondary colors
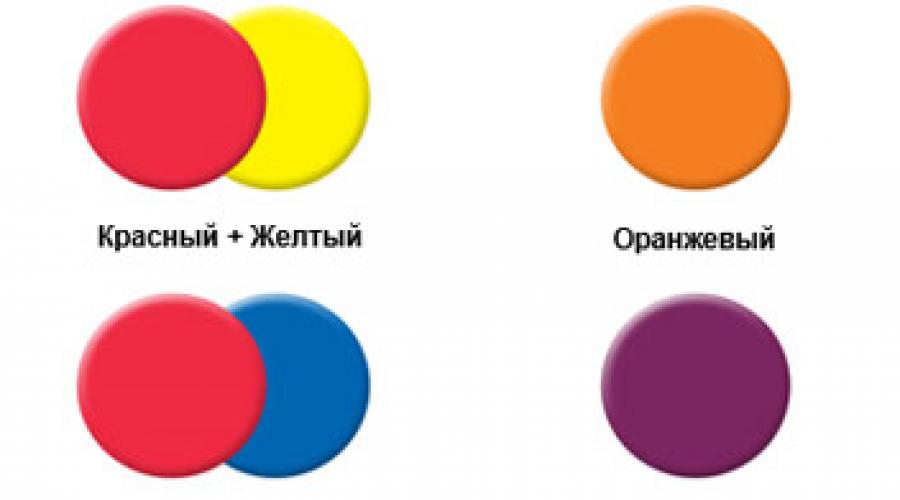
Primary colors are colors that cannot be obtained by mixing others.By mixing these three colors, you can get all the other colors and their shades. At the subtractive model of colors, which are in question, the primary colors are Cyan, Majer and Yellow.
In the description of the color theory, with regard to hair coloring, it is impossible to use a pure cyan and clean mandgen (they are not used in the production of dyes), therefore, they are used the closest blue and red colors.
 Secondary colors are obtained by mixing primary in equal proportions
Secondary colors are obtained by mixing primary in equal proportions
These six colors form the basis of the color circle.

3. Tertiary colors

Mixing one primary and one secondary color in equal proportions gives color, called tertiary: yellow-orange, red-orange, red-purple, blue-purple, blue-green, yellow-green. These colors are also called intermediate.
Color circle
 Primary colors have no same intensity
Primary colors have no same intensity On the color circle you can see that not all primary colors have the same intensity.
The effect of red on the color result of the composition will always be more noticeable than the effect of yellow.
Intermediate colors distinguished by the eye in the yellow-orange spectrum will be less than in blue-green.
Colors having different tones with other characteristics are perceived by us with different sides. The yellow tone itself is the brightest, and blue or blue-purple is the most dark.
 Complementary colors have 2 contradictory effects:
Complementary colors have 2 contradictory effects: - Mutual neutralization
- enhancing brightness of each other
Each color has a complementary color to him. This is a color that occupies the opposite position in the color circle.
Both effects can be used in colors. The ability to use these effects is expanding the possibilities of colorist.
How it works?
1. If you mix 2 complementary colors of equal intensity, then they mutually neutralize each other, the color result should be neutral, gray brown.
This effect is very useful in the daily practice of a hairdresser and is often called the neutralization effect.
2. Nevertheless, if you place these two colors next to each other in the sector staining so that they are not mixed, the effect will be the opposite: the colors will be visually perceived brighter than they are, and you will get the maximum contrast. In this way, one color can be maximally distinguished by placing it "against the background" of another, complementary color to it.
Chromatic and Achromatic colors
 Chromatic colors are clean colors that do not contain white, black and gray.
Chromatic colors are clean colors that do not contain white, black and gray. The color circle demonstrates only chromatic colors.
When mixing 2 primary colors, another chromatic color is obtained. Chromatic colors are colors that do not contain white, black and gray impurities.
Achromatic colors
 White and black - primary achromatic colors; All shades of gray, resulting in mixing white and black, are secondary achromatic colors.
White and black - primary achromatic colors; All shades of gray, resulting in mixing white and black, are secondary achromatic colors. White and black are achromatic flowers. These colors are not included in the color circle.
In its characteristics, they have the status of primary colors.
All grades of gray, resulting in mixing white and black, are secondary achromatic colors. Using the achromatic colors, we add depth chromatic colors.
How is the depth of tone?
By mixing all three primary colors or two primary with black, the desired depth is achieved. We can get any shade, mixing chromatic and ahromatic colors: red and yellow with black or gray.
 By mixing three primary colors or two primary with black, the desired depth of tone is achieved. In the theory, the end result of mixing three primary colors in the maximum concentration will be black. In practice (that in hair staining, that in the printing house) the result of such mixing will be very dark gray-brown, since the applicable pigments are not pure primary colors.
By mixing three primary colors or two primary with black, the desired depth of tone is achieved. In the theory, the end result of mixing three primary colors in the maximum concentration will be black. In practice (that in hair staining, that in the printing house) the result of such mixing will be very dark gray-brown, since the applicable pigments are not pure primary colors.
When the color depth is inevitably reduced the brightness of relatively pure primary color. Therefore, colors having a depth can be called dim.
All artificial hair colors, as well as natural, are colors of dim.
The more we add depth, the darker it turns out the result and the less brightness will have a shade.
Natural hair color is also a combination of chromatic and ahromatic colors (feomelanin and eumeline).
In the color circle, neutral chromatic colors are located in the center.
When staining hair, you need to understand the effect of the depth of the tone on the color. The character of any color will change when changing its depth.
Tip: Reproduction of the YTENT table helps to train color perception.
 This table allows you to estimate the change in the shade when it changes its depth and compare different colors of one depth of the tone. You can reproduce the table using sliced \u200b\u200bcards or using strands from the palette.
This table allows you to estimate the change in the shade when it changes its depth and compare different colors of one depth of the tone. You can reproduce the table using sliced \u200b\u200bcards or using strands from the palette.
For example: the shade that we used to call chocolate is essentially dark orange.
A rich chocolate tone is a combination of color and depth. If there is no sufficient depth, the color will be close to orange.
If you apply a shade "medium brown chocolate" on a light database, for example, 7-0, the absence of the necessary depth will result in a brighter, more orange shade.
Green, blue and purple conditionally belong to a group of cold (matte) shades. Red, orange and yellow - to a group of warm (fashionable) shades.
Gray / Blue-Purple \u003d Sandre
Gray / Blue \u003d ash
Olive / blue \u003d matte
Yellow \u003d Golden
Orange \u003d copper
Red \u003d red
Purple \u003d purple
The color circle has changed to correspond to modern terminology and practice and more accurately reflect the rules for working with color. The names of some colors differ from the original titles to meet the results obtained. For example, staining ash shades gives a muffled ash result, not a bright blue color.

Knowing the exact positions of shades in the flower circle helps when drawing up a coloring formula.
Having learned to work with this tool, you can make formulas of staining, accurately predicting the final color result. But do not forget that as a result of the painting, not only the formula you are drawn by you, but also the background of clarification, to calculate which you need to understand what will happen with natural pigments in the process of staining.
Astronomer, writer, chemist, physicist, philosopher - Isaac Newton. And he once put the experience with priscious, through which ordinary sunlight passed. What was the surprise of the naturalist when he saw white light - a real rainbow. And then in the course of further experiments, other scientists have already understood that in fact there are only three main colors.
Every hunter wants to know ...
Each is red
Hunter - Orange
Wishes - yellow
Know - Green
Where - Blue
Sits - blue
Pheasant - purple
In this well-known mnemonic, all the main colors of the spectrum are encrypted. Observation people have already noticed that there is no black and white. But such states in the spectrum are usually not considered, so they did not fall into the saying.
However, from all this manifold, scientists have allocated three main colors - blue, red and yellow. And all other colors, tones, halftone and shades are obtained from mixing these three paints. As it is well known, for example, artists familiar with the palette and owner art to seek the desired shade on canvas.
Man and colors
The human eye is able to perceive colors, since the retina has three types of special colums operating independently. They contain various pigments that respond to certain colors, red, green and so on.
In fact, each kolkin reacts to all light waves (except ultraviolet and infrared), but "its color" is felt by the pigment better. Further the received signals are transmitted to the brain and it already analyzes the information received and gives us an understanding of one or another shade.
Interestingly, the basic colors cannot be called the property of the color, rather, they are due to the ability of the human eye to distinguish them. In addition, it is influenced by various technical systems that are playing color.
From the point of view of psychophysiology, scientists believe that in fact "clean" colors are four - red, green, yellow and blue. Among them are yellow and blue form one axis in color contrast, and red and green - the other. However, there are people who cannot distinguish between the main colors or some separate shades. They are called dalundons. Contrary to popular belief, they do not see the world as a black and white photo, but simply cannot perceive concrete colors well.
In kindergarten you probably taught that there are primary colors - red, yellow and blue, and everyone else is created from them. Bruce still remembers how his first teacher, Mrs. Anderson, said that the same amount of red, yellow and blue forms gray. Bruce tried to portray the gray cat, but he turned out some kind of dirty, multicolor messenger, and then he decided that it would be much better to take advantage of a simple pencil, and Mrs. Anderson either a full range of Mrs. And Merson is in drawing. Now, tracing the origins of your inclination to question authorities, he returns again to the day.
The lesson Mrs. Anderson turned out to be insolvent, but the grain of truth in it was still the idea that all the variety of colors was achieved by a combination of three primary components. Different people work with color in different ways, but at the same time there is always a concept about three components that form a color in their arguments. An art editor, speaking about color correction, prefers to operate the terms "color tone", "brightness" and "saturation". The one who works on the computer is possible to describe the color in RGB values. Scientists argue about color, relying on the theory - here and Cie Lab, and HSB, and LCH. And prepress specialists talk about the percentages of CMYK points.
And although the creators of Photoshop tried to take into account and meet the needs of all these thinking people in different ways (and coped with their task well), many users closed only on a single color vision. It is quite natural and understandable - we are all inclined to adhere to the method of thinking, which seems most convenient for us. However, this may make it difficult to communicate with Photoshop and overlook the work. If you understand that all the ways of presenting a color based on your own are the same - a combination of three components, you will learn to understand the proposed method of working with them and choose the most appropriate option for each specific task.
"Wait-ka," you say. "But in CMYK not three color components, and four." It can be seen, you also tend to question authorities when noting that the ends meet with the ends. Well, since we took on the role of authorities, we will do the same way, as you usually receive authorities when they ask difficult questions: we will ask you to trust us. Leave your doubts for a while. We promise to return to this topic later.
In this lecture, we consider the fundamental moments of color relationships and color representation methods in Photoshop. Sometimes we will have to turn to theory, but we strongly recommend it carefully to read everything, as it will be needed in the future, when discussing the tone and color correction.
For many types of work with color on a computer, the concept of primary colors is fundamental. We are talking about three colors, which in combination form all the others. By setting different proportions of primary colors, you can form other colors, and adjusting their ratio - to perform color correction images. Primary colors have two fundamental features (until we take into account, from which colors they themselves).
- They do not decompose on the color components.
- Fully in different proportions, primary reproduce the entire range of colors.
By the way, there are secondary colors that are formed by a combination of two primary and the exception of the third. But they do not imagine much interest to us.
Additive and subtractive colors
Before captivating the behavior of spherical objects - apples, billiard balls and planets, Sir Isaac Newton experimented with light and prisms. He found that the white light is divided into red, green and blue components - a phenomenon is quite ordinary, known for many centuries. But the discovement was that by combining the red, green and blue components, he managed to recreate the white light. Red, green and blue colors are called additive primary colors (from the English. Add - add). Their addition gives brighter colors, up to white, while black means the complete absence of light (see Fig. 4.1). So the color is formed on the TV screen and on a computer monitor.
Fig. 4.1.
But on the printed page, the colors behave differently. Unlike the TV screen, the page does not radiate light, but reflects it. When playing color images on print, we first have a case not with light, but with pigments (paints, toner, wax), which are absorbing alone, and others reflect.
The primary films are blue, yellow and purple. They are called subtractive primary colors (from the English. Subtract - deduct). When applying paint on white paper, absorption (subtraction) of light occurs, and the reflected color becomes darker. (Perhaps it will be clearer like this: to obtain white color, additive colors need to be folded with each other, and subtractive - subtract). Blue pigment absorbs red light, purple absorbs green, and yellow - blue. When the blue, purple and yellow maximum intensity is addition, black is theoretically formed (see Fig. 4.1).
Speaking of primary colors, Mrs. Anderson was completely right, only she called not those colors. Painted drawing with red, yellow and blue pencils, you will not be able to get gray, no matter how hard you try.
Imperfect world
A little earlier we asked you to trust us about CMYK, but just said that the combination of blue, purple and yellow theoretically gives black. In fact, however, it turns out brown. Why? As our friend and colleague Bob Sheffl says, "God created RGB, and man is CMYK." And we will add: "Who do you trust more?"
Imperfection of transformation. If we were dealing only with CMYK, everything would be much easier. But a significant proportion of problems is related to the fact that scanners see color in RGB, and we have to transform RGB values \u200b\u200bin CMYK to play prints. Meanwhile, the path of the conversion is not at all the glad (see section "How color parameters interact",
Chapter 2. Color theory
2.1 Classification of colors
Warm colors - These are colors located in a chromatic circle, starting with yellow and finishing red-purple. However, given the phenomenon of the influence of the same color to another, for example, a red-purple may seem warmer if it is located next to the cold green color, and colder, if there is a warm color, for example, orange.
Cold colors - These are colors from blue - purple to yellow - green. However, yellow - green may seem colder next to red and warmer next to blue.
Light or pale colors - These are colors containing this or that amount of white.
Dark colors - These are colors containing black or optional colors.
Bright or saturated colors - These are colors, in principle, nor white, nor gray, nor black nor additional colors. But this concept is relative, since, for example, the bright colors of the blue gamma do not end in a clean blue, in saturated colors include blue containing white or black colors. On the contrary, orange, containing black, belong to dim tones, as it becomes brownish.
Dull colors - These are colors containing a number of gray or additional colors.
2.2 The concepts of primary, secondary and tertiary colors
Primary colors(Figure 1) The primary natural colors of light and the primary colors of pigments are separated (used in painting and printing). These are colors that are not created by mixing. If you mix primary red, blue and green rays, then the white light will turn out. If you mix primary mandgen, cyan and yellow - the colors of pigments - then we will get black.
Figure 1 - Natural Colors
Secondary colors(Figure 2) are obtained by mixing two primary colors. The secondary colors of light include: Majer, Yellow and Cyan (greenish - blue). Secondary red, green and purple pigment colors.

Figure 2 - Secondary colors
Tertiary colors: They are formed by mixing primary and secondary colors. These include - orange, Punchy, light - green, bright blue, emerald - green, dark purple.
Additional colors (Figure 3):located on the opposite sides of the chromatic circle. For example, for red is an additional green (obtained by mixing two primary colors - yellow and cyan (greenish - blue). And for blue, the orange is orange (obtained by mixing yellow and mandgenis).

Figure 3 - chromatic circle of mansell
2.3 MANSELLA SYSTEM
Manowella system describes color, based on three indicators: tonality, lightlock and saturation (Figure 4).
Tonality - This is, for example, yellow or blue.
Svetlota Shows at what level of gray gradations (vertical axis) is color.
Saturation: It shows, at what distance from the vertical axis in the horizontal plane is tone.
Thus, in the mansell system, the colors are located in three dimensions and have tree type. The trunk (vertical axis) represents a scale with gray gradations (from black from the bottom to white above). Tones are on a chromatic circle, which, as it were, "is notated" to the vertical axis. Horizontally axis show the saturation of the tones.

Figure 4 - Mansell System
Chapter 3. Psychological Exposure Color
3.1 Color preferences
The effects of flowers are well known and recognized by the majority of people. It was often investigated in serious scientific experiments. But this impact is not fully studied.
Speaking about the psychological influence of color, it is important to take into account the fact that different points of view exist in various societies. Even independent results of studies of the effect of color are sometimes carrying an outprint of belonging to a certain cultural group of people whose opinion was formed over the centuries.
Why is it impossible to adhere to objective parties when studying this issue? Partly because it is quite difficult to separate the psychology of the color from its symbolism.
The symbolic value of the colors was evolved in certain peoples over the centuries. Take, for example, black and white colors. In the West, black color is perceived as serious, dramatic, sometimes sad. When using black in decorating, warnings of its depressing effect often sound. Traditionally, black is the color of mourning. The white color, on the contrary, is associated with purity, peaceful, optimism. Therefore, a wedding dress in Western countries is traditionally white. Nobody will like to wear white clothes on a mourning ceremony, and the bride attend the wedding in a black dress. Nevertheless, in some countries of the East, it is white, and not black, is a color of mourning.
But on the other hand, various societies are attributed to the same color similar properties. So, for example, the opinion of Fengshui specialists about the properties of colors in many aspects coincide with the opinion of Western scientists. This suggests that each color is inherent in certain qualities that lie deep in its nature. It was these properties that were identified by a person and were transmitted from culture to culture, starting from the moment of the great discovery of Venetian Marco Polo.
By what color we prefer in a particular point in time, how do you want to surround yourself in the interior, all this can tell a lot about us.
Color preferences depend on many reasons. Among them can be called age, gender, cultural level, education, features of temperament and character, etc. So, for example, clean bright colors are preferred by people with a healthy psyche, among them are children, young people, as well as open direct nature.
Mixed, complex colors cause ambiguous emotions. These colors are preferred most often by people with a thin nervous organization, sometimes with a fairly tired nervous system.
Psychology of blue (blue) color
First of all, it is soothing color. It contributes to physical and mental relaxation, creates an atmosphere of security and confidence. Blue color is considered color creativity, it is recommended for learning audiences or cabinets. Turquoise hue contributes to communication.
Blue preference means: the desire for peace, harmony with others and with himself, loyalty, a tendency to aesthetic experiences and deep reflections. Phlegmatic temperament.
Deviation of blue: escape from discharge and peace, weakness, long-term depression, lack of friendly relations in the team, unsatisfied ambition, desire for superiority. Often blue color reject smokers.
The definition of basic colors depends on how we are going to reproduce the color. The colors visible during the splitting of sunlight with the help of the prism are sometimes called spectral colors. This is red, orange, yellow, green, blue, blue and purple.
 b.
b.
 in
in
Figure 1.9 - Three types of colors:
but- primary colors; b. - secondary colors; in - Tertiary colors
The color circle is obtained based on the combination of the main - primary, additional - secondary and tertiary colors. The primary colors are red, yellow and blue. In order to get secondary colors, we mix one color with another. Yellow and red give us orange, red and blue - purple, and blue and yellow - green. And what is tertiary colors? Just takes primary color and adjacent secondary is added to it. This means that there are six tertiary colors (two colors from each primary color). (Figure 1.9)
When two or more colors fit "to each other", they call them compliments or complementary with each other with flowers. We formulate a more accurate definition: if two colors, being mixed together, give neutral gray (paint / pigment) or white (light) color, they are called complementary or complimentary colors.
1.7 Title Flowers and Pigments
The names of the colors are classified into three types: Actually Color terms; names of coloring pigment transferred to color; Adjective from nominal names of objects with an attractive memorable color.
Actually, color terms - blue, green, yellow - in the modern language there are no other values. Names of pigment -Chamine, Ossociation, Rhodamine are narrowly and apply only in professions dealing with paints. The names of the painting of objects - lilac, lemon, raspberry - are characteristic of spoken speech, literature, art history. They are very shaped, since the color specified in them is stored in our memory and can be represented, but such designations do not possess the accuracy necessary in scientific definition, and are not used in science.
Any "physical" color name can be deployed in a large number of shades or varieties. How many colors can be seen? The human eye is able to distinguish about 200 color tones. In this manifold, 8 main colors can be distinguished: purple, red, orange, yellow, green, blue, blue, purple.
Purple colors differ from red in what contain purple or blue shade, which is not in the red. The whole group is called paint name, which in antiquity did from sea snail. All colors of the purple group are very interesting. Ruby - noble dark red color with blue. Rhodamine is close to ruby, but has a more noticeable purple shade. Fuxine - comes from the name of the plant, has a very bright light red color with some inner blue.

Figure 1.10 - Chromatic colors

Figure 1.11 - Purple colors
The Red Panel covers all red and wears various names: crimson, crimson, punch, scarlet, coral, pink, terracotta, etc.
Orange, yellow and green groups have many derived shades denoted by pigment (yellow lead, yellow zinc, chromium oxide), natural painting (orange, lemon, herbal greens), or without special names.
In the Blue Group it is necessary to mark cyan blue or turquoise color. In the purple group, lilac (light purple) is allocated.
Most color concepts used in practice occur from comparison with any objects, phenomena, works of nature or art. When studying color associations, it is necessary to take exactly such a differential look at the color. At the same time it turns out that the perception of color is much more stable and more definite than it is considered. The strongest emotions cause the colors of the human body and its separated (although this is not always realized). So, no one remains indifferent to pink - it is either loved, or hate. The finest shades of pink are able to cause a variety of emotions. Also strongly and definitely operates red and other people inherent in color.