Financial position of the enterprise.
To the question " How to determine the financial condition of a person?"Everyone is responsible in different ways. As a rule, first of all, to determine the financial condition, pay attention to the next two months:
1. How many people earn;
2. What property is owned by him.
In fact, these two parameters by themselves absolutely do not characterize the financial condition of a person, and that's why ...
For greater clarity, we compare a person with the enterprise. Evaluation of the financial condition of the enterprise always comes down to determine the profitable enterprise or unprofitable. Take for example, all sorts of large enterprises (plants, combines, etc.) remaining since the USSR. They have plenty of property owned, its cost is millions, their revenues were also calculated by millions. And despite this, the overwhelming majority of such enterprises have long been recognized by bankrupt, and every year the number of such banks is replenished. Why? Yes, everything is very simple: these enterprises spend more than they earn, that is, their costs exceed income.
Thus, the financial condition is characterized by not the size of the income and the presence of property owned, but, in the first place, the ratio of the profitable and expenditure part of the budget!
The same can be attributed to a person, considering it. From the income of a person, from how much he earns, financial condition, of course, depends, but only by 50%. For the remaining 50%, the consumables of the personal budget affects, that is, how many people spend.
In addition, an important role is played by the availability of monetary (reserves, savings, capital) and material (property owned, business, securities, precious metals) of assets on one side and debts, loans, loans and other debts on the other.
The presence of any debts (ranging from bank loans and ending between familiar "to salaries" and debt to pay for utilities) has an extremely negative impact on the level of the financial condition of the person. Including And because the use of borrowed funds in most cases implies additional costs (interest and commission on loans, penalties, fines for the delay of mandatory payments, remuneration and gifts with familiar, lending tools, etc.)
Property owned and other material assets cannot be considered as indicators of a financial condition, if they are purchased at the expense of borrowed funds, and this debt is still fully repaid. This is especially true of the property acquired for personal consumption. In this case, on the contrary, the presence of property purchased on credit reduces the level of man's financial condition. Therefore, considering ways to improve the financial condition, the loan should be thought of last, and only in order to raise the income (and not expenditure!) Part of the personal budget, and best - not to think at all.
A distress financial situation is a position in financial affairs or a general economic condition, in which revenues reduced or an increase in costs, as a result of which incoming income cannot cover consumption. A distress financial situation can ultimately lead to bankruptcy, that is, financial collapse. A distressive economic situation can be caused by various reasons, to concern various groups of people. Depending on this kind of differences, there are various classifications of this situation.
Who can have a distaffinity?
A distress financial situation may arise from various groups of people, consider the basic options for its origin.
- 1. Plot financial situation in individuals It can be called a whole number of circumstances that either depend or do not depend on the individual. When the position of the disaster comes, the individual cannot "reduce the ends with the ends," pay for their expenses. The plight financial situation in individuals allows them to count on support from the state, since the state's tasks include support for poor citizens. Various social benefits that state issues today are possible ways to neutralize the financial crisis at the civil level. State deductions are known to us: these are benefits for unemployment, children's payments and so on.
- 2. Plug financial situation in legal entities caused by economic penalties in the enterprises created by the entrepreneur. The causes of their occurrence may also be different, but in contrast to the similar situation among individuals, entrepreneurs only in certain situations can count on the aid of the state. - This is a certain activity in order to obtain the profit, which is carried out at its own risk. For this reason, the opportunity to get help from the state is minimized. Finance penalties lead to a decrease in the company's solvency. This in turn leads to a decrease in confidence from the banking system. All this is closer to the financial collapse.
- 3. Disabled financial situation of the state. Typically, the cause is high or military actions. Disaster in the state economy leads to high emigration of the population. Naturally, if the outflow of human resources occurs, the state loses stability in almost all spheres of life. The state can only count on the rescue of other states, so the governments of different countries are actively united in alliances: the Union of Independent States (CIS, which includes the countries of the former Soviet Union), the Union of Europe, which is customary to be called the European Union and so on. States in alliances provide each other support, but for joining the alliance, the state must comply with certain criteria that are mostly related to currency policies. Today we can notice that Ukraine, who experiences a dishearsal financial situation, appeals to the support of the European Union and the United States of America.
These are key options for distinguished financial position. Now let's try to consider the reasons that cause such a position, and it does not matter for what level.
Causes of distress financial situation
- 1. Military Actions both within the state and on its borders reduce the economic potentials of the country. This leads to the outflow of the population. Also, military actions rebuild the country's industry indigenously, orient it is not to meet the needs of the majority of the population, but to ensure the increase in defense capability. Wars weaken such important parties to public life as agriculture and industry. To keep the country afloat, the government is making various ways to motivate citizens. For example, in the Soviet Union, the movement of two shells in revolutionary and post-revolutionary years was actively developed. Two hundredthovers acted for overfulfing a 200 percent plan, it made a lot of economic potential. In modern post-industrial society, this technique is unlikely to work effectively, since production requires a high degree of skills and skills, simple conveyor production is not enough.
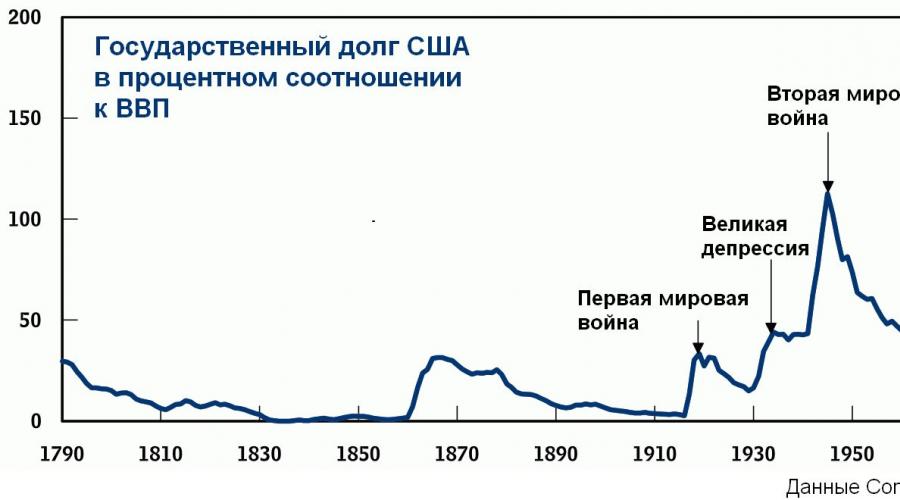
- 2. Government debt growth One state before others. The growth of public debt can lead the country to the economic default, which will cause the overall financial collapse and economic depression. Something strange, the United States of America, which have the status of the world power, is constantly experiencing a threat of default, since they have become the largest debtor in the world. This was largely influenced by the military industry during the Cold War period between the Blocks of the United States and the USSR. Also, high debt today from the Greek government, according to the latest reports from the media, it is possible to conclude about the brewing revolutionary acts within the state. The Government of the debtor will look for different ways to exemplate from debt. Some countries are asking for support from lenders, some (including Greece, who received a refusal to write off the debt) refer to competitors of creditors for help. The debt needs to be paid either by financial or material assets, of course, the government of the debtor states nor the other method is suitable.

- 3. Unstability of the global currency Actively affects economic well-being, when the assets that do not change in value are not fixed. As you know, the American dollar has long had gold security for a long time, until it remained, a stable state was observed in the US economy. In 1971, American President Nixon without coordination with the congress deprived the gold collateral dollar. On the one hand, it was the right decision, because the country was threatened with a new Great Depression, on the other, the dollar, devoid of gold support became more inflation. The depreciation of the currency becomes the reason for the weakening of the state. Why began to happen? Because the government got the opportunity to print in unlimited quantity - the dollar is not secured by gold, therefore, it is worth nothing. Inflation goes into hyperinflation, the latter generates a plundest financial situation in the state. Foreign economic factors can also affect the stability of the global currency. For example, the cost of the ruble on the global foreign exchange market depends largely on the political climate and such an indicator as the price of on. Depending on the change in the quotations of other currencies, the ruble quotation will also change.
- 4. Fallet of the population. In the first paragraph, we mentioned that the outflow of the population will also negatively affect the country's economy. It is worth allocating this item separately, because the outflow can be called not only by military actions, but also the economic attractiveness of one state in front of others. We can observe, for example, active migration to Europe or Russia Roma from Romania. In foreign countries there are more stable economic conditions, the possibilities of good earnings and so on. The smaller the people remain in the country, the lower the economic potential will be, since the population is the basis of the economy. The population pays taxes, performs work in private and state-owned enterprises, military detachments are formed from the population and so on. States are trying to create economic programs that would not only hold the indigenous population in the country, but also attracted immigrants from abroad.
- 5. Political instability. This can also include the political incompetence of power. Permanent government shifts will lead to a change in the legislative base, and this will lead to a permanent restructuring of the economy. If communism was regularly changed in Russia and, the country simply could not adapt to changing the conditions for the development of the economy, the crisis would enter the protracted phase, and a distinguished economic situation would simply cause a default.

These are the main causes of a distinguished economic situation. The reasons can be attributed not only to the state, but also by its key components, that is, entrepreneurs and individuals. They will also be recorded negatively, and if economic instability will develop in Nizakh, that is, among individuals, entrepreneurs and the government will also fall into the situation of economic instability.
The consequences of a disgraced financial situation in the state
We have already reviewed several possible consequences of a disastrous financial situation in the state, which will touch this moment a little more detail. The consequences for individuals and legal entities are extremely clear - financial collapse in the absence of proper support measures. The state is increasingly difficult and diverse.
- 1. Mass outflow of the population. Economic instability caused by a financial disaster will lead to a mass outflow of the population. It is rapidly impossible to hold people, it is possible to keep only the male population, making it military service if it does not contradict the state's constitution. In the remaining cases, people will try to leave an economically unstable country and move to more reliable areas.
- 2. Inflation. Financial disaster will definitely weaken the national currency. If the currency is interstate, for example, a dollar or euro, then the fall does not have to be or be high. But national currencies, such as rubles or hryvnia in any case, will fall in price with an economic crisis. After the authorization of the Russian Federation by the countries of the European Union and the United States of America sharply decreased in price about the dollar: before the dollar was worth about 30 rubles, after the authorization he had sharply rose to 50 rubles. A similar situation with the euro. Inflation will negatively affect industry, as well as on interstate trade. If the state focuses the population for self-sufficiency: active development of agriculture and other measures, one can count on some stability and equilibrium in the economy.
- 3. Devolition of the currency reserve and reducing economic capital. With the outflow of the population, the outflow of capital will occur in foreign states, since people will take money with them. The number of labor will decrease, will flow less taxes, which will lead to a decrease in funds in the state treasury. To overcome these consequences, the government of the country will try to reduce the migration of the population abroad. Since the income of the banking system are payments on loans that people make, with the outflow of the population, these revenues will decrease. If the banks begin to lose their income, the state will simply come: the economy will burst, because its costs will exceed income.
Another number of negative consequences of a plight economic situation in the state can be given. There is, however, positive aspects: a distinguished financial situation can be used in good by several ways.
Positive impact of poor financial situation
The first positive aspect of a plight financial situation is to restructure industry and the creation of a new economic course. This happens with the variation of economic cycles, developing innovative solutions for activities. During the crisis period, the competitiveness of various enterprises occurs, with the result that new enterprises get the opportunity to enter. New enterprises make new technical developments that promote the strengthening of the economy. So in periods of economic crises, conveyor production was born, the first machines to facilitate labor workers and so on. Innovation of this kind will allow the economy to rise in their development even higher than in the pre-crisis period.
This is one positive aspect of a financial disaster. Another is to attract investment. All investors are known that during the period of disaster the cost of enterprises falls, because entrepreneurs are ready to get even at least the minimum of money to continue. At this time, it is very convenient to invest money. If the investor has enough financial experience, it will be able to competently invest in cheap and earn then when the business rises in price. American entrepreneur Robert Kiyosaki wrote that he was engaged in an active buying real estate during the years when the US real estate market fell in price. To date, all objects acquired by him increased in price, and he returned the money spent. Many immovable assets remained non-soldered and bring revenues in the form of rent. This is an excellent example of a positive effect of a distinguished financial situation.
If we consider an example with the state, then it can be noted that the government of the distinguished state is ready to attract investors from the part. Example: Soros visit to Ukraine in order to invest capital in the Ukrainian industry. You can do with minimal investments, since the country is experiencing the period of the civil war, and over time, get enough profit. Of course, large financial knowledge and experience are needed, otherwise you can easily burn out and lose everything.
How to overcome a distinguished financial situation?
What steps need to take to return to economic stability, which was in the pre-crisis period?

- one. . Changing this element can change the entire financial life of a person, so you need to pay special attention to it. What is the financial plan of most people? Most plans are simply no, their main goal of life is to buy, that is, to buy homes for personal stay, cars, luxury items, and so on. For all purchased liabilities, it is necessary to pay taxes: real estate, transport tax, luxury, and so on. As a result, expenses exceed income, and this, as we have already written at the beginning of the text, leads to a disastrous financial situation. What needs to be changed? You need to buy assets instead of liabilities. Do not think that to buy assets you must need big money. Of course, it is advantageous to buy such as real estate or something like that, but you can begin with smaller investments. For example, on the Internet today you can buy and sell articles, create your own paid courses and so on. Many seems to be difficult, because people do not try to acquire the necessary knowledge. In fact, everything is easier than it seems, in the Internet there are plenty of trainings and instructions. By increasing the number of assets, you will increase your income, while consumption in the absence of liabilities will remain the same. This will allow you to reiterate yourself at the normal level and even go to the level of financial independence. You can also try to reduce the number of liabilities to speed up this process.
- 2. Emigration to another state. You can emigrate from one country to another, with better financial conditions for life. Of course, it will be associated with a number of difficulties, such as learning a language, addictive to local culture and so on. However, having moved to another country, you can discover more new opportunities financially.
- 3. Molding a new profession. Perhaps looking in new professional activity, you can earn more than earned before. At the moment, you can easily get comfortable with freelance - remote work on the Internet, which will bring you extra income and very good. If you have free time, why not try something new to not only get out of the distress financial situation, but also prevent it in the future? Of course, a simple increase in working hours is not the most productive way out of the crisis, try to turn your income not to active, but in passive, then to achieve financial prosperity will be much easier.
We reviewed the basic issues related to the disastrous financial situation: the reasons for its causing, consequences of the situation, positive and negative aspects of the financial disaster, the way to overcome it. In general, a financial disaster happens in the economy periodically, because the cyclicity associated with the obsolescence of some technologies and the birth of other, economic reorganization is characterized by economic activity. You just need to be able to properly approach the emerging situation, be able to analyze it, find not only disadvantages, but also the pros. Any distress financial situation can be overcome and again to go on economic growth, but this requires financial engineering and cold-blooded economic thinking that are not inherent to all people.
Stay aware of all important events United Traders - subscribe to our
4. Critical financial position.
This situation means that the enterprise cannot pay on time with its creditors. In a market economy, in chronic repetition of the situation, the enterprise must be announced bankrupt.
To assess financial stability, a methodology for calculating a three-component indicator of the type of financial situation is used.
For the characteristics of stock formation sources and costs, indicators are used that reflect various types of sources.
1) The presence of own working capital (SOS), defined as the difference between own capital and the cost of non-current assets.
2) the presence of own and long-term borrowed (DP) sources of stock formation and costs (SOS + DP).
3) the presence of own, long-term and short-term (CP) sources of stock formation and costs (SOS + DP + KP).
Three indicators of the presence of sources of stock formation and costs (ZIZ) correspond to three indicators of stocks and costs of sources of formation:
1. Excess (+) or drawback (-) of own working capital (F s):
± F C \u003d SOS - ZIZ (2.17)
2. Excess (+) or disadvantage of own and long-term borrowed sources of stock formation and costs (F (F T):
± F T \u003d (SOS + DP) - ZIZ (2.18)
3. Excess (+) or disadvantage of the total value of the main sources for forming stocks and costs (Fo):
± F o \u003d (SOS + DP + KP) - ZIZ (2.19)
Using these indicators, you can define a three-component indicator of the type of financial situation.
Allocate four types of financial situations:
1. The absolute independence of the financial state corresponds to the following conditions: F s ≥ 0; F t ≥ 0; F o · 0; That is, a three-component indicator of the type of situation:
S \u003d (1,1,1) (2.20)
2. Normal financial state independence, which guarantees solvency:
F S.< 0; Ф т ≥ 0; Ф о ≥ 0, то есть S = {0,1,1} (2.21)
3. An unstable financial condition associated with a violation of solvency, but at which the possibility of restoring equilibrium is still maintained by replenishing sources of own funds (reduction of receivables, accelerating stock turnover):
F S.< 0; Ф т < 0; Ф о > 0; That is, S \u003d (0.0.1) (2.22)
4. Crisis financial condition in which the enterprise depends entirely on borrowed sources of financing. Own capital and long-term and short-term loans and loans are not enough to finance material working capital, that is, replenishment of stocks comes at the expense of funds resulting from repayment of payables, S \u003d (0.0.0).
To determine the type of financial stability, we analyze the dynamics of sources of means necessary to form stocks in the table.
Table 2.11 - Indicators of the type of financial stability
| Indicators | At the beginning of the period | At the end of the period | Change |
|
| Thousand rub. | % | |||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 1. Sources of own funds | 3534015 | 4599513 | 1065498 | 30 |
| 2. Overseas assets | 6095813 | 8706995 | 2611182 | 43 |
| 3. The presence of own working capital (GR.1- GR.2) | 2561798 | 4107482 | 1545684 | 60 |
| 4. Long-term loans and loans | 1000000 | 377097 | -622803 | -62,2 |
| 5. The presence of own and long-term borrowed funds for stock formation (gr. 3 + gr. 4) | 3561798 | 4484579 | 922781 | 26 |
| 6. Short-term loans and loans | 135683 | 1119982 | 984299 | 725 |
| 7. The total value of the main sources of funds on the coating of stocks and costs (gr. 5 + gr. 6) | 3697481 | 5604561 | 1907080 | 51,5 |
| 8. Stocks and costs | 740525 | 1290014 | 549489 | 74,2 |
| 9. Excess (+), disadvantage (-) of own working capital on reserves and costs (gr. 3 - gr. 8) | (2561798-740525) | (4107482-1290014) | 996195 | 55 |
| 10. Excess (+), disadvantage (-) of own working capital and long-term borrowed funds to cover stocks and costs (gr. 5 - gr. 8) | (3561798-740525) | (4484579-1290014) | 373292 | 13,2 |
| 11. Excess (+), disadvantage of (-) total sources of funds for stocks and costs (gr. 7 - gr. 8) | (3697481-740525) | (5604561-1290014) | 1357591 | 46 |
| 12.Trechcomponant indicator of the type of financial stability | (1,1,1) | (1,1,1) | ||
According to the data of the table, and at the beginning and at the end of the analyzed period, the company does not have a lack of its own and attracted sources of funds for the formation of reserves and therefore refers to the first type - an absolutely financial independent enterprise.
The solvency characterizes the possibility of an enterprise to repay payment obligations in a timely manification. Thus, the enterprise is solvent, subject to the availability of free monetary resources sufficient to repay existing commitments.
The company can be solvent in the absence of the required amount of free cash, if it is capable of realizing its current assets for settlements with creditors.
In the practice of financial analysis distinguishes current and long-term solvency. Under long-term solvency is meant the ability of the company to pay for its long-term obligations. The ability of the enterprise to pay in its short-term liabilities characterizes the current solvency.
An accounting balance is used to assess the solvency of the enterprise.
The absolute liquidity ratio (to al) is determined by the ratio of the most liquid assets - cash (DS) and short-term financial investments (KFV) to the sum of short-term debt obligations under the formula:
To al \u003d (ds + kfv) / ko (2.23)
The ratio of absolute (urgent) liquidity shows which part of the current debt can be repaid in the near future. A number of authors recommend a normal limit for this indicator in the range of 0.2 - 0.5.
The rapid, or critical, liquidity ratio (KL) is determined by the ratio of the amount of the most liquid funds and rapidlyizable assets - short-term receivables (DZ) and other current current current assets (TD) - to the sum of short-term debt obligations under the formula:
KL \u003d (DS + KFV + DZ + TA) / BEA (2.24)
This figure characterizes that part of the current liabilities, which can be repaid not only at the expense of cash, but also due to the expected receipts for shipped products, performed works or services rendered.
The critical liquidity ratio reflects the projected payment capabilities of the enterprise, subject to timely settlements with debtors. The recommended value of this indicator is 0.8 - 1.
The current liquidity coefficient (to TL), or the total coating coefficient is equal to the ratio of the value of all current current assets (TA) to the magnitude of short-term debt obligations:
To TL \u003d TA / CDO (2.25)
The current liquidity coefficient characterizes the expected solvency of the enterprise for a period equal to the average duration of one turnover of all working capital. It shows the payment capabilities of the enterprise provided not only timely settlements with the debtors and the sale of finished products, but also in the case of the sale of other elements of material working capital.
The conventional normative value of the coefficient varies from 1.5 to 2.
In the global practice of market relations, the ratio of 1: 2 is considered optimal, that is, to ensure the minimum guarantee, investments for each short-term debt rules account for two rubles of working capital. The coefficients characterizing the solvency and liquidity of the enterprise are shown in Table 2.12.
Table 2.12 - analysis of liquidity indicators
| Indicators | At the beginning | Deviation |
||
| 1 | Initial data for calculation: | |||
| 2 | Cash, thousand rubles. | 139959 | 129114 | -10845 |
| 3 | Short-term financial investments, rub. | 84 | 1422 | 1338 |
| 4 | Total most liquid assets, rub. | 140043 | 130536 | -9507 |
| 5 | Fast implementation assets (short-term receivables), rub. | 715250 | 885424 | 170174 |
| 6 | 6thit of the most liquid and fast R7alizable assets, rub. | 855293 | 1015960 | 160667 |
| 7 | Mincened assets (stocks, VAT), rub. | 740525 | 1290014 | 549489 |
| 8 | Total liquid assets, rub. | 1595818 | 2305974 | 710156 |
| 9 | Short-term debt obligations, rub. | 1895031 | 4065627 | 2170596 |
| 10 | Relative coefficients: | |||
| 11 | The ratio of absolute liquidity (to al) | 140043/1895031= 0,07 | 130536/4065627= 0,03 | -0,04 |
| 12 | Critical liquidity ratio (KL) | 855293/1895031= 0,45 | 1015960/4065627= 0,25 | -0,17 |
| 13 | Current liquidity ratio (to TL) | 1595818/1895031= 0,84 | 2305974/4065627= 0,6 | -0,24 |
Table data indicate that the enterprise is insolvent. The liquidity ratios for the reporting period have slightly decreased significantly lower than the recommended values.
The absolute liquidity ratio decreased from 0.07 by 0.04 points and shows that by the end of the year 3% of short-term liabilities can be repaid through the use of funds and securities of the enterprise. If you compare the value of the indicator with the recommended level (0.2 - 0.3), it can be noted that the company has a cash deficiency for covering current obligations. This circumstance can cause distrust of this enterprise from providers of material and technical resources.
The critical liquidity ratio shows that the short-term debt obligations at the beginning of the period were covered with cash, securities and means in the calculations. By the end of the reporting period, the value of the coefficient decreased by 0.17 points and shows that current obligations can be repaid by the most liquid assets and rapid realization asses by only 25%. Moreover, the repayment of short-term debt obligations (the current solvency of the enterprise) largely depends on the quality of receivables and the financial state of the debtor. In general, this ratio can be called forecast, since the company cannot know exactly when and in what quantity the debtors pay off their obligations, that is, the liquidity of the enterprise depends on their solvency. In our example, the level of fast liquidity coefficient is lower than the recommended value (0.8 - 1) and indicates that the amount of liquid assets of the enterprise does not comply with the requirements of the current solvency.
The current liquidity ratio (or coefficient of the coating) for the reporting period decreased by 0.24, reaching 0.6 by the end of the year. The company only 60% covers short-term debt obligations by liquid assets.
For clarity of the outlined conclusions, it is possible to use graphs, the construction of which is based on comparison of the absolute amounts of liquid assets with short-term debt obligations.
The necessary element of financial analysis is the study of the results of financial and economic activities of the enterprise, which are characterized by the amount of profit or loss.
Profit is the standard of successful work of the enterprise. The magnitude of profits depends on the production, equipped, sales and commercial activities of the enterprise. Due to profit, debt obligations of the enterprise in front of creditors and investors are repaid.
Analysis of financial results includes an assessment of the following profit indicators: Gross, profits from sales, profits before tax, profits from ordinary activities, net profit of the enterprise.
The final financial result (net profit or loss) is composed of the financial result from conventional activities, as well as other income and expenses.
The results of the analysis are used to make economic decisions aimed at efficient use of resources, the choice of the best investment option, the substantiation of the prospects for the development of the enterprise, etc.
Table 2.13 - Analysis of the dynamics of financial performance of the enterprise
| Indicators | Previous period thousand rub. | Reporting period | Change (+, -) | |
| Thousand rub. | % | |||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
| 1. Profit (loss) from the sale of products | 917850 | 1187835 | 269985 | 29,4 |
| 2. Interest to getting | 1054 | 2608 | 1554 | 147 |
| 3. percentages to pay | 67189 | 187870 | 120681 | 180 |
| 4. Operating income | 27359 | 1183693 | 1156334 | 4226 |
| 5. Operating expenses | 291913 | 390876 | 98963 | 34 |
| 6. Revenues from participation in other organizations | 604 | 10700 | 10096 | 1671 |
| 7.Tenerization income | 102218 | 96479 | -5739 | -6 |
| 8.Vnerization | 373870 | 285745 | -88125 | -23,5 |
| 9. Profit (loss) to taxation | 316113 | 1616824 | 1300711 | 411 |
| 10. Profit Tax and Other Similar | 133398 | 471496 | 338098 | 253 |
| 11. Profit (loss) from common activity | 182715 | 1145328 | 962613 | 526 |
| 12. Emergency revenues | 106 | 546 | 440 | 415 |
| 13. Emergency expenses | 36 | 1685 | 1649 | 4580 |
| 14. Net profit (Retained earnings (loss) of the reporting period) | 182785 | 1144189 | 961404 | 525 |
According to the table, it can be seen that the amount of profit before tax increased in the reporting year four times. This led to an appropriate increase in profits remaining at the disposal of the enterprise. In the dynamics of financial results, the following positive changes can be noted.
Net profit grows faster than profits from sales and profit before tax.
The increase in the total profit is due to an increase in profits from sales of products for 26,9985 rubles, or by 29.4%, as well as a reduction in non-delaimal costs by 88125 rubles, or 23.5%. At the same time, the dynamics of financial results includes negative changes. In the reporting year, compared with the previous period there was a reduction in other non-dealer income on 5739 rubles, or 6%.
Consider the influence of factors on the relative change in the amount of taxable profits. If the change in the indicator contributes to increasing profits, the factor is positive, and vice versa.
1. The impact of increasing the amount of profit from sales by the amount of taxable profit: 269958/316113 * 100 \u003d + 85.3%.
2. The effect of increasing other operating income on the amount of taxable profit: 1156334/316113 · 100 \u003d + 365%.
3. The impact of a decrease in non-revenue income on the value of taxable profits: -5739 / 316113 · 100 \u003d - 1.8%.
4. The effect of increasing other operating expenses on the amount of taxable profit: 98963/316113 · 100 \u003d - 31.3%.
5. The impact of the reduction of non-validation costs for the value of taxable profits: -88125 / 316113 · 100 \u003d + 28%.
6. Summary of factors: 85.3 + 365 - 1.8 - 31,3 + 28 \u003d 445.2
The results of factor analysis have shown that an increase in the profit of other operating income (365%) and the amount of sales (85.3%) had the greatest impact on the increase in taxable profit. A negative impact on the magnitude of the profit is caused by an increase in other operating expenses. Consequently, reducing costs and increasing income are reserves of enterprise profits.
To assess the effectiveness of the use of resources consumed in the production process, profitability indicators are applied.
Profitability indicators characterize the relative yield or profitability of various activities of the enterprise. They are more fully than profit, reflect the final results of the management, since their value shows the ratio of the effect with cash or used resources. Indicators are measured in relative values \u200b\u200b(percentages, coefficients).
1. The cost-effectiveness (R s) is characterized by the ratio of profits from the sale of products (PR) to the full cost of sales (with P),%:
R z \u003d (n / s n) · 100%, (2.26)
The coefficient shows the level of profit per 1 ruble of the funds spent. It is calculated in general on the enterprise, individual divisions and types of products.
2. The profitability of sales (R n) is measured by the ratio of profits to the sales volume. Sales is expressed by the revenue indicator from the sale of products for a minus value added tax, excise taxes and similar mandatory payments.
Depending on the profit indicator, sales profitability distinguish:
a) as the ratio of profits from the sale (PR) to the revenue from the sale (R PR),%:
R PR \u003d (n p / in p) · 100%, (2.27)
b) as the attitude of taxable profits (PN) to sales revenue (R n),%:
R n \u003d (n / in pv) · 100% (2.28)
c) as a ratio of net profit (P h) to revenue from the sale (R h),%:
R h \u003d (p h / in p) · 100% (2.29)
Profitability of sales characterizes the effectiveness of entrepreneurial activities: shows how much profits received from the ruble sales. It is calculated in the whole enterprise, individual types of products.
3. Capital profitability coefficients are calculated by the ratio of profits to the average annual capital and its component parts. When calculating the coefficients, taxable profit is used (PN), net profit (P h).
Depending on the type of capital, profitability indicators distinguish. a) the profitability of the entire property (R i) - as the attitude of the taxable profit of the enterprise to the average annual value of the property of the enterprise,%:
R and \u003d (n /<И>) · 100%, (2.30)
<И> - The average annual value of the property of the enterprise, determined according to the balance of the balance as a medium-tariff value at the beginning and end of the analyzed period, RUB:
<И> \u003d (BB H + WB K) · 0.5, (2.31)
WB H, WB to - Balance currency (total value of property), respectively, at the beginning and end of the reporting period, which is equal to the sum of the results of the section I and II of the balance of the balance
WB \u003d I r AB + II r AB (2.32)
The coefficient shows how many cash mines received by the enterprise from the unit of value of property (assets), regardless of sources of attraction of funds.
b) the profitability of equity (R IC) is calculated by the ratio of net profit to the average annual value of its own (joint-stock) capital,%:
R SK \u003d (p h /<СК>) · 100%, (2.33)
<СК> - The average annual cost of equity, defined as the average efficient result of its own sources of means of the enterprise (summary of the III section of the balance sheet) to the beginning (CK N) and the end (SK K) of the analyzed period, RUB:
SC \u003d (SK N + SK K) · 0.5 (2.34)
The coefficient plays an important role in assessing the level of stock of shareholder companies on the stock exchange.
The profitability of the property differs from the profitability of appropriate capital, since in the first case all sources of financing are evaluated, including external, and in the second - only own.
If the borrowed funds bring more profit than the payment of interest on this borrowed capital, then the difference can be used to increase the return of equity. However, in the event that the profitability of assets is less than percentages paid for borrowed funds, the influence of funds raised on the activities of the enterprise should be assessed negatively.
Analysis of profitability indicators is based on the accounting reporting data (Form No. 1, 2) using an analytical table 2.14.
Table 2.14 - Dynamics of profitability coefficients
| Indicators | Previous period | Reporting period | The change |
| Initial data, thousand rubles. | |||
| 1. Sold (net) from sale product | 6846740 | 8938445 | 2091705 |
| 2. Complete cost realized products | 5928890 | 7750610 | 1821720 |
| 3. Profit from the sale of products | 917850 | 1187835 | 269985 |
| 4. Profit before tax | 316113 | 1616824 | 1300711 |
| 5. Net profit | 182785 | 1144189 | 961404 |
| Profitability coefficients | |||
| 6. Cost profitability,% | 917850/5928890*100 =15,4 | 1187835/7750610*100 = 15,3 | -0,1 |
| 7. Sales sales on taxable profits,% | 316113/6846740*100 = 4,6 | 1616824/8938445*100 = 18 | 13,4 |
| 8. Profitability of sales according to profits from the sale,% | 917850/6846740*100 = 13 | 1187835/8938445*100 = 13 | 0 |
| 9. Profitability of sales on net profit,% | 182785/6846740*100 = 2,6 | 1144189/8938445*100 = 13 | 10,4 |
| 10. Profitability of property,% | 316113/6095813*100 = 5 | 1616824/8706995*100 = 19 | 14 |
| 11. Protectivity of own capital,% | 182785/3534015*100 = 5 | 1144189/4599513*100= 25 | 20 |
Table data allow you to draw the following conclusions.
In general, the enterprise has an improvement in the use of property. From each ruble of funds embedded in assets, the company received a profit in the reporting year than in the previous period. If earlier, each ruble embedded in the property brought almost 5 kopecks. Profit, now - 19 kopecks.
The profitability of equity capital increased during the reporting period by 20 percentage points. Also increased profitability of net profit. The cause of positive shifts in the level of profitability was the leading growth rates received from the results of financial and economic activities (profits before tax) and net profit, compared with the growth rate of property and sales. An increase in sales profitability can mean an increase in demand for products, improving its competitiveness.
At the same time there was a decrease in the level of profitability of the costs calculated by profits from the sale. The profitability ratio of sales calculated on taxable profits, above the level of profitability of sales, calculated on profits from the sale.
In domestic business practice, a system of criteria is used to determine the unsatisfactory balance structure and the possibility of recovery or loss of solvency of the enterprise.
Indicators for assessing the structure of the balance are:
Current liquidity ratio;
Property ratio of own means.
1. The current liquidity ratio characterizes the overall security of the enterprise by working capital to conduct economic activities and the timely repayment of the urgent obligations of the enterprise. For calculating the coefficient of current liquidity (K 1), the formula is used:
Pa - the outcome of the section II of the balance of the balance;
VP - the result of the section V liabilities of the balance;
630, 640, 650 - the corresponding lines of the balance sheet.
Regulatory value to 1 ≥ 2.
2. The coefficient of provision of own funds characterizes the presence of own working capital from the enterprise necessary for its financial stability.
The coefficient of the provision of own means (K 2) is defined as the ratio of the difference between the volumes of sources of own funds (the summary of the III section of the balance sheet) and the actual value of non-current assets (the result of the Balance Asset section) to the actual value of the cost of working capital (total II of the section Balance Asset) by Formula:
![]()
IIII - the outcome of the III balance of the balance sheet;
Ia - the outcome of the section I of the balance of the balance;
IIA - the result of section II of the balance of the balance.
Regulatory value K 2 ≥ 0.1.
The basis for recognizing the structure of the balance of the enterprise is unsatisfactory is the implementation of one of the following conditions:
The coefficient of current liquidity at the end of the reporting period is less than 2;
The coefficient of the provision of its own means at the end of the reporting period is less than 0.1.
3. With the unsatisfactory balance structure to verify the real possibilities of the enterprise to restore its solvency calculates the coefficient of recovery of solvency for a period of 6 months, determined by the formula:
![]()
To 1F - the actual value (at the end of the reporting period) of the current liquidity coefficient (K 1);
K 1N - the value of the current liquidity coefficient at the beginning of the reporting period;
To 1norm - the regulatory value of the current liquidity coefficient;
To 1norm \u003d 2;
6 - a period of recovery of solvency in months;
T - reporting period in months.
Regulatory value K 3 ≥ 1.
The solvency recovery coefficient is calculated if at least one of the coefficients K 1, K 2 takes the value less than the normative.
The coefficient of recovery of solvency that makes value greater than 1 indicates the presence of a real opportunity from the enterprise in the near future to restore its solvency.
The coefficient of recovery of solvency that makes a value of less than 1 indicates that the company in the near future (within 6 months) does not have a real opportunity to restore solvency.
K 1N \u003d 1666306/1895031 - (10943 + 83084 + 71617) \u003d 0.96
K 1F \u003d 2389253/4065627 - (12047 +78816 +400804) \u003d 0.66
K 2N \u003d 3534015 - 6095813/1666306 \u003d - 1.5
K 2F \u003d 4599513 - 8706995/2389253 \u003d - 1.7
The coefficients K 1 and K 2 at the time of the estimate are lower than the recommended level, in connection with which the coefficient of recovery of solvency K 3 is calculated.
K 3 \u003d 0.66 + 6/12 * (0.66 - 0.96) / 2 \u003d - 0.405
6 - a period of recovery of solvency (in months), adopted for the calculation;
12 - reporting period (in months) according to annual accounting reporting.
The results of calculations are made in the analytical table.
These calculations allow you to draw the following conclusions:
1. The coefficient of current liquidity at the end of the reporting period is less than 2, which shows the lack of working capital to cover the short-term debt of the enterprise.
2. The coefficient of the provision of its own means at the time of the assessment of the balance structure is less than 0.1, that is, the company is experiencing financial instability due to the lack of own funds for replenishing current assets.
3. The company has an unsatisfactory balance structure, since the current liquidity ratio and the coefficient of their own funds below the regulatory values.
4. Recovery coefficient less than 1, therefore, the company does not have the ability to restore solvency within six months from the date of evaluation.
3.1 Conceptual approach to assessing the financial condition of the enterprise
The most important tasks of financial management at the level of the industrial enterprise include: assessment of a really current level of solvency, assessment of the asset management level, an assessment of the degree of dependence on external sources of financing, as well as the calculation of indicators characterizing the change in the level of business activity, economic and financial profitability.
The listed tasks are closely interrelated. Therefore, only their systemic solution, only their cumulative results can give an objective picture of the financial condition of the enterprise. The qualitative diagnosis of the company's financial parameters allows the use of the data obtained both to correct the existing development strategy and for the design of a new one.
There are different approaches to financial analysis, this problem can be considered from the inside of the enterprise, and from the outside.
Internal analysis is needed by the enterprise itself for more efficient planning and management of its activities.
When forming both current and long-term plans, the actual financial position of the enterprise is first rated, and then the effect of the proposed behavioral strategies in the future is determined. As a rule, the tasks aimed at adjusting the financial policy of the enterprise are put by its administration. The result of the analysis for the domestic user is a set of management decisions - a combination of various measures aimed at optimizing the production and sale of enterprise products, taking into account the impact of changes in the macro and microeconomic environment.
Each enterprise, being a subject of market relations, interacts with other economic agents. These include suppliers, consumers, lenders, investors, etc. The company's research by third-party organizations concerns mainly the implementation of specific plans for this enterprise: acquisitions, lending, concluding and implementing contracts. In this case, the results of financial analysis are intended for external users. Organizations that provide loans are primarily interested in the analysis of the liquidity of the enterprise. Since only short-term loans are really obtained, it is best to fulfill the ability of the enterprise to fulfill these obligations can be appreciated precisely by analyzing liquidity. The company's shares holders want to know about the level of liquidity, mainly about its ability to serve debts, that is, to pay interest and repay the bulk amount. It is possible to estimate this ability by analyzing the capital structure of the enterprise, the main sources and use of funds, the profitability of the enterprise for a long period and the forecast estimate of profitability in the future. In relation to external management, the main indicator is the rate of income on investment in various assets and the effectiveness of the management of these assets.
Differences in the formulation of analysis tasks are associated with differences in choosing indicators that determine managerial solutions of internal and external information users. Of course, indicators can be distinguished, equally important both for external and internal analysts (for example, liquidity, the value of the cash flow, etc.). However, for each of these groups there is a special set of indicators that are determining when making a decision regarding the enterprise under consideration. Thus, the analysis of the financial condition of the enterprise is preceded by a certainty that this work will be carried out from whose point of view.
The main problematic issues arising and taken into account during the financial analysis of the enterprise are to identify the trends and patterns of the development of the enterprise to the period under study; identifying "narrow" places of production and the degree of their impact on the financial condition; identifying reserves that can be used to improve the financial condition.
Financial analysis involves the study of the financial statements contained in such sources of information as "Balance of the enterprise", "Profit and Loss Statement", "Report on Capital Movement", "Information on the cost of production and sales of products (works, services)", " Information about the presence and movement of fixed assets (funds) and other non-financial assets ", a number of others, internal and external for a particular enterprise.
The listed financial statements performs a number of important functions. First, it gives an idea of \u200b\u200bthe means and obligations of the enterprise at a particular point, usually at the end of the year or quarter. This form is known as a balance. Secondly, the profit and loss statement contains information about revenue, cost, taxes, enterprise profits for a certain time. But if the balance is an instant photo of the financial condition of the enterprise, the report on profit and loss draws a picture of the profitability of the enterprise throughout the period. From these documents, some derivatives can be obtained, for example, on retained earnings or on sources of formation and use of funds. To answer questions about how many funds need an enterprise in the future and what will be caused by this need, such analytical instruments will be applied, as drawing up a report on the sources and the use of funds, data on cash flow.
Calculation of production capacity and planning the production and economic activity of OJSC Shu Obukhovskaya

The calculation of the bandwidth of the mine is presented as a planogram (Fig. 1) It can be concluded that as a result of the calculation of the production capacity of the enterprise, the "narrow" places for production capacity were not detected. Fig. 1 Mine throughput 3. Planning production at Mine 3.1 Production plan at a coal mine in physical terms A coal mining plan for ...
Answer a question how correctly the enterprise managed financial resources during the period preceding this date. After analyzing the main technical and economic indicators, it can be concluded that the financial situation of LLC Obukhovsky Shupbzavod causes the leadership to make urgent measures to improve it. The methodology for analyzing the financial condition of the enterprise includes ...





In the gravity of the block of external conditions, the required block and the internal filter unit in the motif structure. The figure also shows the presence of features in the structure of the motivation of the professional activities of mines. For underground workers, the predominance of external motives is characteristic. Spearman correlation coefficient [- 0.77]; Pearson correlation coefficient [- 0,78]), that is, the connection ...
The company is an independent business entity created for business activities, which is carried out in order to extract profits and meet social needs.
Under the financial condition of the enterprise means the ability of an enterprise to finance its activities. It is characterized by the security of financial resources necessary for the normal functioning of the enterprise, the appropriateness of their placement and efficiency of use, financial relations with other legal entities and individuals, solvency and financial stability.
The financial condition of the enterprise can be sustainable, unstable and crisis. The company's ability to make payments in a timely manner, to finance their activities on an extended basis indicates its good financial condition. The financial condition of the enterprise depends on the results of its production, commercial and financial activities. If production and financial plans are successfully implemented, this positively affects the financial condition of the enterprise, and, on the contrary, as a result of the failure to fulfill the production plan and sales plan, the revenue decreases and the amount of profit is reduced, therefore, the financial condition of the enterprise and its solvency deteriorates. .
A sustainable financial position in turn has a positive impact on the performance of production plans and ensuring the needs of the necessary resources. Therefore, financial activities as an integral part of economic activities are aimed at ensuring the systematic receipt and spending of money resources, the fulfillment of the calculated discipline, the achievement of rational proportions of its own and borrowed capital and its most efficient use. The main goal of financial activities is the decision, where, when and how to use financial resources to effectively develop production and obtain maximum profit.
To survive in a market economy and prevent the bankruptcy of the enterprise, it is necessary to know well how to manage finances, which should be the structure of capital in composition and sources of education, which proportion should occupy its own and borrowed funds. Such concepts of the market economy are also known as business activity, liquidity, solvency, enterprise creditworthiness, profitability threshold, financial stability (security zone), risk degree, financial lever effect, and others, as well as methods of their analysis.
Therefore, financial analysis is a significant element of financial management and audit, almost all users of financial reporting of enterprises use financial analysis methods for making decisions to optimize their interests.
Owners analyze financial reports to increase capital profitability, ensuring the stability of increasing the company. Lenders and investors analyze financial reports to minimize their risks on loans and deposits. It can be firmly said that the quality of the decisions made entirely depends on the quality of the analytical substantiation of the solution.
The purpose of the analysis consists not only to establish and evaluate the financial condition of the enterprise, but also to constantly carry out work aimed at improving its improvement. An analysis of the financial condition of the enterprise shows which areas it is necessary to conduct this work, makes it possible to identify the most important aspects and the weakest position in the financial condition of the enterprise. In accordance with this, the results of the analysis give an answer to the question of what is the most important ways to improve the financial condition of the enterprise in a specific period of its activities. But the main purpose of the analysis is to identify and eliminate the disadvantages in financial activities and find reserves for improving the financial condition of the enterprise and its solvency. To assess the sustainability of the financial condition of the enterprise, a whole system of indicators characterizing changes are used:
the capital structures of the enterprise for its placement to the sources of education;
efficiency and intensity of its use;
solvency and creditworthiness of the enterprise;
the reserve of its financial stability.
Indicators should be such that all those who are associated with economic relations could answer the question of how reliably the company is as a partner A, therefore, decide on the economic profitability of continuing relationships with him. An analysis of the financial condition of the enterprise is based mainly on relative indicators, since the absolute balance sheet indicators in the conditions of inflation is almost impossible to lead to a comparable appearance. Relative indicators can be compared with:
generally accepted "standards" to assess the degree of risk and forecasting the possibility of bankruptcy;
similar data from other enterprises, which allows to identify the strengths and weaknesses of the enterprise and its ability;
similar data for previous years to explore the improvement trend or deterioration of the financial condition of the enterprise.
Basic analysis tasks:
timely identification and elimination of deficiencies in financial activities, and search for reserves for improving the financial condition of the enterprise, its solvency;
forecasting possible financial results, economic profitability, based on the actual conditions for economic activities and the availability of own and borrowed resources, the development of financial state models in various ways of using resources;
development of specific activities aimed at more efficient use of financial resources and strengthening the financial condition of the enterprise.
Analysis of the financial condition of the company is engaged in not only the heads and the relevant services of the enterprise, but also its founders, investors in order to study the efficiency of resource use, banks to assess the conditions for lending and determine the degree of risk, suppliers for timely receipt of payments, tax inspectors to fulfill the receipt plan for funds in Budget, etc.
The main purpose of the financial analysis is to obtain a small number of key (most informative) parameters that give an objective and accurate picture of the financial condition of the enterprise, its profits and losses, changes in the structure of assets and liabilities, in settlements with debtors and creditors. At the same time, analyst and manager (manager) may be interested in both the current financial condition of the enterprise and its projection on the nearest or more distant perspective, i.e. Expected financial status parameters.
But not only the temporary boundaries determine the alternativeness of the objectives of financial analysis. They also depend on the goals of the subjects of financial analysis, i.e. specific financial information users.
The analysis goals are achieved as a result of solving a certain interconnected set of analytical tasks. Analytical task is the specificization of analysis objectives, taking into account organizational, information, technical and methodological capabilities of analysis. The main factor, ultimately, is the size and quality of the source information. It should be borne in mind that the periodic accounting or financial statements of the enterprise is just "raw information", prepared during the implementation of accounting procedures at the enterprise.
To make decisions on production management, sales, finance, investment and innovations, management needs permanent business awareness of relevant issues, which is the result of the selection, analysis, assessment and concentration of initial raw information, it is necessary to analytical reading the source data on the basis of analysis and management purposes. .
The main principle of analytical reading of financial reports is a deductive method, i.e. From the common to the private, but it should be applied multiple times. During such an analysis, as it were, the historical and logical sequence of economic facts and events, the focus and the power of influence on their results.
The introduction of a new accounting account plan, bringing the forms of accounting to greater compliance with the requirements of international standards causes the need to use a new financial analysis methodology that meets the conditions of the market economy. This technique is needed for the reasonable choice of a business partner, determining the degree of financial sustainability of the enterprise, assessing business activity and the effectiveness of entrepreneurial activity.
The main (and in some cases the only) source of information on the financial activity of the enterprise is the accounting statements that became public. The reporting of the enterprise in a market economy is based on the generalization of data of financial accounting and is an information link connecting the enterprise with society and business partner users of information on the activities of the enterprise.
In certain cases, only accounting reporting is not enough to implement the objectives of financial analysis. Separate user groups, such as management and auditors, have the ability to attract additional sources (production and financial accounting data). Nevertheless, most often annual and quarterly reporting are the only source of external financial analysis.
The financial analysis methodology consists of three interrelated blocks:
- 1) analysis of the financial results of the enterprise;
- 2) analysis of financial condition;
- 3) analysis of the effectiveness of financial and economic activities.
The main source of information for analyzing the financial condition is the balance sheet of the enterprise (form N1 annual and quarterly reporting). Its value is so great that the analysis of the financial condition is often called balance analysis. The data source for analyzing financial results is a report on financial results and their use (form N 2 annual and quarterly reporting). The source of additional information for each of the blocks of financial analysis serves to the balance sheet (form N 5 of annual reporting).
Questions:
1. Goals, objectives and methods for analyzing financial condition
2. Analysis of property and sources of its financing
3. Analysis of liquidity and solvency
4. Analysis of financial stability
5. Analysis of the financial results of the enterprise
6. Analysis of cash flows
7. Analysis of business activity of the enterprise
8. Evaluation of the probability of bankruptcy
1. Goals, objectives and methods for analyzing financial condition
Financial situation is the most important characteristic of the business activity and reliability of the enterprise. The results of economic analysis give an answer to the question, what are the most important ways to improve the financial condition of the enterprise in a specific period of its activities. The purpose of the analysis consists not only to establish and evaluate the state of the enterprise, but also to constantly carry out work aimed at its improvement.
The main tasks of the company's financial analysis are:
The share of own funds in turnover assets is more than 10%,
Lack of uncovered losses, overdue debts, etc.
Structure and Dynamics Indicators Balance is important for understanding the overall picture of the financial condition. Comparing structural changes in the asset and liability, it can be concluded that through which sources was the influx of new funds and in which assets these funds are invested. The deterioration of the financial situation can be judged by the adverse relationship between the magnitude of current assets and short-term obligations. The difference between them will show the presence of (+) or the disadvantage of (-) of its own working capital.
When analyzing assets, it should be found out due to what types of assets has changed the total value of the property. In this case, it is preferable to increase the specific weight of current assets as the most liquid part of the property and their fastest growth compared with non-current assets.
A more detailed estimate of the composition, structure and dynamics of working capital will make reasonable conclusions about the mobility of current assets, possibly unreasonable distraction of funds to receivables or illiquid reserves of inventory-material values.
Comparing the pace of changes in balance and sales revenue, it is possible to conclude about accelerating or slowing the turnover of current assets. Reducing the share of mobile means, slowing down turnover of current assets indicate a deterioration in the financial condition.
Analysis of the structure and dynamics Liabilities allows you to establish possible causes of financial stability (instability) of the organization. At the same time, it is evaluated to changes in the sources of financial resources. The passion for the share of equity due to any of the sources contributes to an increase in the financial sustainability of the Organization, and the presence of retained earnings is considered as a source of replenishment of working capital and a reserve of reducing payables, as a stock of financial strength.
It is necessary to estimate in detail the dynamics and structure of borrowed funds, especially short-term, attracting data on their composition contained in the attachment to the balance sheet. At the same time pay attention to the sharp increase in the most dangerous for the financial state of types of debt (before budget and extrabudgetary funds, overdue debts).
It is advisable to compare not only absolute amounts, but also the growth rates of receivables and payables, as they must balance each other.
The deterioration in the financial situation of the organization can be judged by the change in receivables and payables:
Sharp growth and increasing the share of receivables in the composition of current assets means deterioration of the state of calculations, the weakening of control over the timeliness of calculations, reduce the liquidity of the balance;
Consistent differences in the dynamics and amounts of receivables and accounts payable can mean violation in payment discipline, disproportions between receivables and payables.
Analysis of the dynamics of the balance currencyThe structures of assets and liabilities make it possible to draw conclusions about the financial position of the organization. Reducing the balance of the exchange currency during the reporting period may indicate a reduction in the turnover of funds, reducing property potential under the influence of various factors (insolvency of the organization or its partners, the implementation of part of assets, etc.). In stable conditions, an increase in the balance of the balance is assessed positively, and the decrease is negative.
3. Analysis of liquidity and solvency
The financial condition of the organizations can be estimated on the basis of integrated balance sheet items, which are combined into four groups:
1) liquidity and solvency indicators;
2) financial stability indicators;
3) indicators of business activity;
4) profitability indicators.
The first group includes liquidity and solvency indicators.
Solvency of the company They call his willingness to pay off debts in the case of the simultaneous requirements for payments from all creditors. To determine the readiness to repay its debt, indicators of the solvency of the organization and liquidity of the balance are used.
This indicator measures the financial risk, that is, the probability of bankruptcy. In general, the organization is considered solvent if its general assets exceed its external obligations. Therefore, the more general assets exceed external obligations, the higher the degree of solvency. We give the indicators of liquidity and solvency:
| Indicators | Method of calculation | Comment |
| 1. The coefficient of solvency | Current assets Long- + short-term liabilities | Shows the ability to cover their debts due to current assets, without resorting to the sale of property. More than 1. |
| 2. The coefficient of general liquidity | Current assets Short-term liabilities | Shows to what extent obligations are covered by current assets. Characterizes the ability to calculate with debts. From 2 to 3. |
| 3. Fast liquidity ratio | Fast-liquid current assets Short-term liabilities | Determines the ability of the organization to fulfill obligations from fast-liquid assets. From 0.7 to 1. |
| 4. The absolute liquidity ratio | Den. Funds + brief urgent fin. investments Short-term liabilities | Characterizes the ability of the organization to settle with debt immediately. What he is higher, the more reliably the organization. 0.2 to 0.3. |
| 5. Property coefficient own means | Equity - Fixed assets Current assets | Shows how many own working capital accounts for 1 ruble of current assets. The value of more than 0.1. |
| 6. The ratio of payables and receivables | Payables debt Receivables debt | Shows how many times payables exceeds receivables. The figure is higher, the greater the dependence on creditors. |
These indicators are of interest Not only for the management of the enterprise, but also for external analysis subjects: the absolute liquidity ratio - for suppliers of raw materials and materials, the rapid liquidity ratio - for banks, the coefficient of general liquidity for investors.
Analysis of the liquidity of the balance is a comparison of funds on the asset grouped by the degree of decreasing liquidity, with short-term liability obligations, which are grouped by the degree of urgency of their repayment.
The first group (A 1) includes absolutely liquid assets, such as cash and short-term financial investments.
The second group (A 2) includes rapidly implemented assets: TO-Vary shipped, receivables, taxes on acquisitions. Their liquidity depends on the timeliness of the shipment of products, forms of calculations, from demand for products, solvency of buyers, etc.
The third group (A 3) is slowly realized assets (production reserves, incomplete production, ready-made product). It will take a much longest period to turn them into cash.
The fourth group (A 4) is difficult toalizable assets (fixed assets, intangible assets, long-term fi-nanced investments, unfinished construction, long-term receivables).
Accordingly, the obligations are broken into four groups:
P 1 - the most urgent obligations (payables and loans of the bank, whose return periods come, overdue payments);
P 2 - short-term loans of the bank and loans;
P 3 - long-term loans of the bank and loans;
P 4 - own capital, which is at the disposal of the enterprise.
Balance is considered absolutely liquid if:
A x\u003e p 1; A 2\u003e p 2; A 3\u003e p 3; A 4.<П 4 .
The study of the ratios of groups of assets and liabilities over a number of periods will allow to establish trends in the structure of balance and its liquidity.
4. Analysis of financial stability
The financial condition of the organization must be assessed not only in the short term, which show indicators of solvency, but also in the long term through the calculation of financial stability indicators. Let us give financial stability indicators:
| Indicators | Method of calculation |