Russian Japanese war wiki. Russian-Japanese War: Results and Consequences
About the Russian - Japanese war in brief
RUSSKO - Yaponskaya Voyna (1904 - 1905 g)
Russian-Japanese War Beginning
Russian-Japanese war reasons
Russian-Japanese war steps
Russian-Japanese War Results
The Russian-Japanese war briefly outlined was the result of a complex relationship between the two countries arising from the expansion of the Russian Empire in the Far East. The country experienced an economic rise and the opportunity to strengthen its influence, first of all, on Korea and China. This, in turn, caused strong dissatisfaction of Japan.
The causes of the war are Russia's attempt to spread their influence in the Far East. The reason for the war was the rent of Russia in China by the Liaodong Peninsula and the occupation of Manchuria, which had species of Japan herself.
The requirements of the Japanese government to leave Manchuria meant the loss of the Far East, which was impossible for Russia. In such a situation, both sides began preparation for war.
Describing the Russian-Japanese war briefly, it should be noted that in the highest circles the authorities had hope that Japan would not decide on hostilities with Russia. Other opinions was Nicholas II.
By the beginning of 1903, Japan was completely ready for war and only waiting for a convenient reason to start her. The Russian authorities acted indecisively, to the end and without realizing their plans for the preparation of a military company in the Far East. This led to a threatening situation - the military forces of Russia largely inferior to Japanese. The number of ground troops and military equipment was almost twice as smaller than Japan. For example, by the number of the Ministry of Economics, the Japanese fleet had three-time superiority over Russian.
However, the Russian government, as if not seeing these facts, continued expansion towards the Far East, and the war with Japan decided to use as an opportunity to distract people from serious social problems.
War began on January 27, 1904. The fleet of Japan suddenly attacked Russian ships from the city of Port Arthur. It was not possible to capture the city itself, but the most combat-ready Russian ships were bred. Japanese troops were able to unhindered to fall in Korea. Railway communication between Russia and Port Arthur was violated, and the siege of the city began. In December, the garrison, moved a few heavy attacks of the Japanese troops, was forced to surrender, to flood the remnants of the Russian fleet so that he did not get Japan. The passage of Port Arthur actually meant the loss of the Russian army.
On land, Russia also losing war. Mukden Battle, the largest at the time, Russian troops could not win and retreated. The Tsushim battle destroyed the Baltic fleet.
But Japan was exhausted by the war to the war so much that he decided to go to peace negotiations. She achieved his goals and spend on their resources and did not want their strength. The Russian government agreed to the conclusion of the world. In Portsmouth, in August 1905, Japan and Russia signed a peace treaty. He cost the Russian side expensive. According to him, Port Arthur, as well as the southern part of the Sakhalin peninsula now belonged to Japan, and Korea finally got under its influence.
In the Russian empire, the loss in the war strengthened dissatisfaction with power.
More war, battles, battles, riots and uprisings in Russia:
- Caucasian War
Russian-Japanese war - This is a war that was conducted between the Russian and Japanese empires for control over Manchuria and Korea. After a break in a few decades, it became the first big war with the use of the latest weapon : long-range artillery, armadiors, destroyers, wire barrels under the current of high voltage; as well as using spotlights and field kitchen.
Causes of war:
- Rent of Russia Liaodong Peninsula and Port Arthur as a naval base.
- Construction of the CERE and Russian economic expansion in Manchuria.
- The struggle for spheres of influence in China and Copee.
- Resolving means of revolutionary movement in Russia ("Little Victorious War")
- The strengthening of Russia's position in the Far East threatened the monopolies of England, the United States and the Military aspirations of Japan.
Character of war: Unfaithful on both sides.
In 1902, England concluded a military union with Japan and together with the United States embarked on the path of her preparation for war with Russia. For a short time, Japan built on the shipyards of England, Italy, the USA armored fleet.
The base of the Russian fleet on the Pacific Ocean - Port Arthur and Vladivostok - defended from each other by 1,100 miles and were poorly equipped. By the beginning of the war, about 100 thousand were deposited from 1 million 50 thousand Russian soldiers in the Far East. The Far Eastern army was removed from the main supply centers, the Siberian railway had low bandwidth (3 trains per day).
COURSE OF EVENTS
January 27, 1904 The attack of Japan into the Russian fleet. The death of cruiser "Varangian" and the Korean canoners in the coast of Korea. Blocked in ChelPo "Varyag" and "Korean" rejected the proposal to pass. Trying to break through in Port Arthur, two Russian ship under the command of the captain of the 1st rank V. F. Rudnev entered into battle with the 14th enemy ships.
January 27 - December 20, 1904. Military fortress defense Port Arthur. During the siege for the first time, new types of weapons were applied: rainfall warmness, machine guns Maxim, hand grenades, mortars.
Commander of the Pacific Fleet Vice Admiral S. O. Makarov Preparing for active operations on the sea and the protection of Port Arthur. On March 31, he brought his squadron to the external raid to enter into battle with the enemy and lure his ships under the fire of coastal batteries. However, at the very beginning of the battle, his flagship ship "Petropavlovsk" blew up on Mine and sank for 2 minutes. Most of the team died, the whole headquarters S. O. Makarov. After that, the Russian fleet moved to defense, since the Commander-in-Chief of the Far Eastern Forces Admiral E. I. Alekseev refused active actions to the sea.
Terrestrial defense of Port Arthur headed the head of the Quantong Fortified District General A. M. Peresssel. The main struggle in November turned around the mountain high. On December 2, the head of the land defense was killed, its organizer and inspirer General R. I. Kondratenko. StASSEL on December 20, 1904 signed capitulation . The fortress was withstanding 6 assaults and was transferred only as a result of the betrayal of commandant, General A. M. Stesel. For Russia, the fall of Port Arthur meant a loss of access to the non-freezing yellow sea, deterioration of the strategic situation in Manchuria and a significant exacerbation of the domestic political situation in the country.
October 1904 The defeat of the Russian troops on the Shahome River.
February 25, 1905 The defeat of the Russian army under Mukden (Manchuria). The largest land battle in history to the First World War.
May 14-15, 1905 Battle in the Tsushimsk Strait. The defeat of the Japanese fleet of the 2nd Pacific squadron under the command of Vice-Admiral Z. P. Rodless, aimed at the Far East from the Baltic Sea. In July, the Japanese took Sakhalin Island.
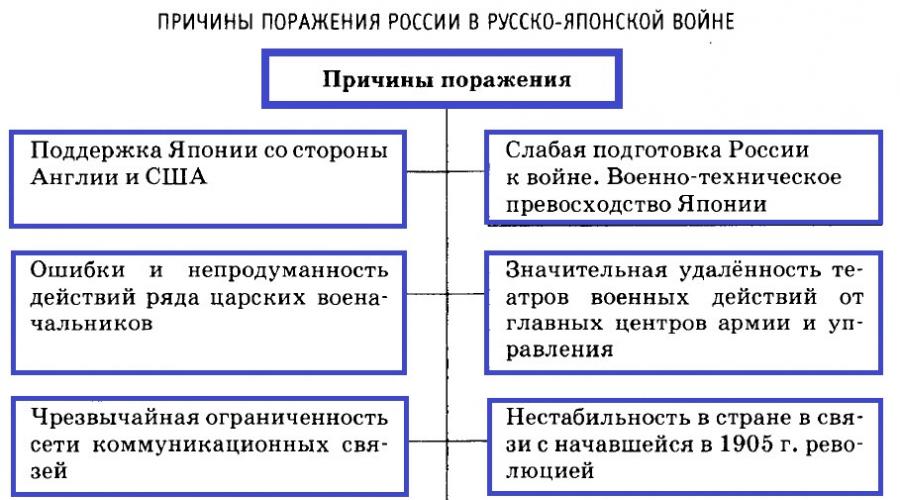
Causes of defeat of Russia
- Japan support from England and the United States.
- Weak Russia's preparation for war. Military-technical superiority of Japan.
- Errors and ill-impact actions of the Command of Russia.
- The absence of the possibility of rapid transfer reserves to the Far East.
Russian-Japanese war. RESULTS
- Korea recognized the sphere of influence of Japan;
- Japan received in possession of South Sakhalin;
- Japan received the right of fisheries along the Russian shores;
- Russia handed over Japan to the lease of the Liaodan Peninsula and Port Arthur.
Russian commander in this war: A.N. Kuropatkin, S.O. Makarov, A.M. Stresser.
The consequences of Russia's defeat in the war:
- the weakening of Russia's position in the Far East;
- public dissatisfaction with autocracy, loser war with Japan;
- destabilization of the political situation in Russia, the growth of the revolutionary struggle;
- active reform of the army, a significant increase in its combat capability.

The Russian-Japanese war briefly.
Causes of the start of war with Japan.
In the period 1904, Russia led the active development of land of the Far East, developing trade and industry. The country of the rising sun blocking access to these lands, at that time she occupied China and Korea. But the fact is that under the department of Russia there was one of the territories of China - Manchuria. Here is one of the main reasons for the beginning of the war. In addition to this, Russia, by the decision of the triple union, was given to the Liaodan Peninsula, which belonged to the Japan once. Thus, Russia has disagreements with Japan, and the struggle for domination in the Far East arose.
The course of events of the Russian-Japanese war.
Using the effect of surprise, Japan attacked Russia in the place of Port Arthur. After disembarking the landing troops of Japan at the Kwantunsky Peninsula, Port Atrut remained cut off from the outside world, and respectively helpless. After two months, he was forced to resort to surrender. Further, the Russian army loses the battle of Liaoyan and the battle with Mukden. Until the first world war, these battles were considered the most large-scale in the history of the Russian state.
After the battle of the Tsushim, almost the entire Soviet flotilla was crushed. Events unfolded on the yellow sea. After another battle, Russia loses the Sakhalin peninsula in unequal battle. General Kurophatkin, the leader of the Soviet Army for some reason applied passive struggle tactics. In his opinion, it was necessary to wait until the strengths and reserves of the enemy would be on the outcome. And the king at that time did not give it much importance, since the revolution began on the territory of Russia.
When both sides of hostilities were morally and materially exhausted, they agreed to sign a peace treaty in American Portsmouth in 1905.
Results of the Russian-Japanese war.
Russia lost the southern part of his Sakhalin Peninsula. Manchuria has now become a neutral territory, and from there all troops were bred. Oddly enough, but the contract was conducted on equal conditions, and not as a winner with defeated.
The largest armed conflict of the end of the XIX - early XX century. He was the result of the struggle of the great powers - the Russian Empire, Great Britain, Germany, France and striving for the role of the dominant regional power of Japan for the colonial section of China and Korea.
Causes of war
The reason for the emergence of the Russian-Japanese war should recognize the clash of the interests of Russia, which conducted expansionist policies in the Far East, and Japan, who made attempts to approve their influence in Asia. The Japanese Empire, who made up the modernization of the social system and the Armed Forces during the "Revolution of Maidzi", sought to turn into his colony to the economically retarded Korea and take part in the section of China. As a result of the Japanese War, 1894-1895 The Chinese army and fleet were quickly defeated, Japan occupied Taiwan Island (Formozo) and part of Southern Manchuria. According to the prisoner of the peace treaty in Simonoski, Japan acquired Taiwan Islands, Penghudao (Pescador) and the Liaodan Peninsula.
In response to the aggressive actions of Japan in China, the Russian government, headed by the Emperor Nikolai II, in 1894, a supporter of expansion in this part of Asia, intensified his own Far Eastern Policy. In May 1895, Russia forced Japan to revise the conditions of the Simonoski peace treaty and abandon the acquisition of the Liaoda Peninsula. From this point on, the armed confrontation between the Russian Empire and Japan became inevitable: the latter began to carry out systematic preparation of a new war on the continent, adopted in 1896 a 7-year-old program for the reorganization of the land army. With the participation of Great Britain, a modern navy began to be created. In 1902, the United Kingdom and Japan entered into an allied treaty.
In 1895, the Russian-Chinese bank was established in 1895 economic penetration in Manchuria, and next year the construction of the Sino-Eastern Railway was laid through the Chinese province of Heilongjiang and designed to connect the Chitu with Vladivostok along the shortest path. These events were made to the detriment of the development of the weakly populated and economically developed Russian Camurian Territory. In 1898, Russia was rented by China for 25 years the southern part of the Liaodong Peninsula with Port Arthur, where it was decided to create a naval base and fortress. In 1900, under the pretext of the suppression of the "rebellion of the Etoeuan", the Russian troops occupied all manchuria.
Far Eastern policy of Russia at the beginning of the XX century
From the beginning of the twentieth century. The Far Eastern policy of the Russian Empire began to determine the adventuristic court group headed by State Secretary A.M. Disorders. She sought to spread the influence of Russia in Korea using a logging concession on the Yal River for this, and prevent Japan's economic and political penetration into Manchuria. In the summer of 1903, in the Far East, the vicarity headed by Admiral E.I. Alekseev. The negotiations held in the same year between Russia and Japan on the delimitation of spheres of interest in the region did not give results. On January 24 (February 5), 1904, the Japanese side announced the termination of the negotiations and ruined diplomatic relations with the Russian Empire, taking a course to unleash the war.
War availability
By the beginning of hostilities, Japan mainly completed the modernization program of the Armed Forces. After mobilization, the Japanese army consisted of 13 infantry divisions and 13 reserve brigades (323 battalions, 99 squadrons, over 375 thousand people and 1140 field weapons). The Japanese connected fleet consisted of 6 new and 1 old squadron armadapors, 8 armored cruisers (two of them acquired from Argentina were commissioned after the start of the war), 12 lung cruisers, 27 squadron and 19 small destroyers. Japan's war plan provided for the struggle for the domination of the sea, landing of troops in Korea and South Manchuria, the seizure of Port Arthur and the defeat of the main forces of the Russian army in the Liaoyan region. The general leadership of the Japanese troops carried out the head of the General Staff, subsequently, the Commander-in-Chief of the Ground Forces, Marshal I. Oyama. The connected fleet commanded Admiral H. Togo.
At the beginning of the twentieth century The Russian Empire had the largest land army in the world, but in the Far East, as part of the Camuro Military District and the troops of the Quantong Region, it was extremely insignificant forces scattered in a huge territory. They consisted of the I and II Siberian Army Corps, 8 Eastern Siberian Rifle Brigades, with the beginning of the war deployed in division, 68 infantry battalions, 35 squadrons and hundreds of cavalry, just about 98 thousand people, 148 field guns. To war with Japan, Russia was not ready. The small throughput of the Siberian and East-Chinese Railways (as of February 1904 - 5 and 4 pairs of military trains, respectively) did not allow to rely on the rapid strengthening of troops in Manchuria with reinforcements from European Russia. The Russian Navy in the Far East had 7 squadron battleships, 4 armored cruisers, 7 lung cruisers, 2 mine cruisers, 37 squadrock destroyers. The main forces were the Pacific Squadron and was based on Port Arthur, 4 cruisers and 10 destroyers were in Vladivostok.
Plan of military action
The Russian plan of war was prepared in the temporary headquarters of the governor of his imperial Majesty in the Far East of Admiral E.I. Alekseeva in September-October 1903 on the basis of plans developed independently of the headquarters of the Military District and at the headquarters of the Kwannun region, and approved by Nikolem II 14 (27) January 1904. He intended to focus the main forces of Russian troops on the Mukden line -Loyan-Heichen and Port Arthur defense. With the beginning of mobilization to the aid of the Armed Forces in the Far East from European Russia, it was assumed to send major reinforcements - X and XVII Army Corps and four reserve infantry divisions. Before the reinforcement approach, the Russian troops had to adhere to a defensive image of actions and only after creating numerical superiority could go to the offensive. From the fleet it was necessary to fight for the domination of the sea and prevent landing of Japanese landings. The Commanding of the Armed Forces in the Far East with the beginning of the war was assigned to the governor of Admiral E.I. Alekseeva. He was obeyed by the commander of the Manchurian army, who became a military minister General from Infanteria A.N. Kuropatkin (appointed 8 (21) of February 1904), and the commander of the Pacific Escader Vice-Admiral S.O. Makarov, who replaced February 24 (March 8) of the Initiative Vice Admiral O.V. Stark.
The beginning of the war. Military actions on the sea
Military actions opened on January 27 (February 9) 1904 by the sudden attack of the Japanese destroyers to the Russian Pacific Squadron, which was not properly completing the Earth's external raid. As a result of the attack, two squadron battleships and one cruiser came out. On the same day, the Japanese detachment of counter-admiral S. Uriu (6 cruisers and 8 of the Ministry of Foreign Ministry) attacked in the Korean port of Chelpo as stationers of the Russian cruiser "Varyag" and the Korean canonerer boat. The "Varyag" received severe damage was flooded by the crew, and the Korean blown up. January 28 (February 10) Japan declared the war of Russia.
After the attack of the Japanese destroyers, a weakened Pacific squadron was limited to defensive actions. Arriving in Port Arthur Vice Admiral S.O. Makarov began to prepare a squadron for active actions, but on March 31 (April 13) died at the squadron "Petropavlovsk" who broke into mines. Accepted the command of the Marine Forces Council Admiral V.K. Withette refused to fight for the domination of the sea, focusing on the defense of Port Arthur and support for the ground forces. During the hostilities under Port Arthur, the Japanese suffered significant losses: 2 (15) May on mines died as Squadors Khacksee and "Yasima".
Military operations on land
In February - March 1904, the 1st Japanese army of General T. Kurokov landed in Korea (about 35 thousand bayonets and saber, 128 guns), which by mid-April came to the border with China on the Yal River. By the beginning of March, the Russian Manchurian army finished its deployment. It consisted of two avant-gardes - southern (18 infantry battalions, 6 squadrons and 54 guns, an Incou-Gayzhou-Senyuyuche region) and East (8 battalions, 38 guns, the Yaul River) and a total reserve (28.5 infantry battalion, 10 hundred, 60 guns, Liaoyan Mukden area). In North Korea, there was an equestrian squad under the command of General-Major P.I. Mishchenko (22 hundred) with the task of reconnaissance for the Yalu River. February 28 (March 12) on the basis of the eastern avant-garde, enhanced by the 6th East Siberian Rifle Division, was formed an oriental detachment led by Lieutenant General M.I. Zasilem. In front of him there was a challenge to make the enemy transition through Yala, but in no case do not join the Japanese in a decisive collision.
On April 18 (May 1) in battle at the Taurenna, the 1st Japanese army defeated the Eastern detachment, dropped him from Yalu and, advanced to Fynhuanchean, went to the flank of the Russian Manchurian army. Thanks to the success of the Taurena, the enemy mastered the strategic initiative and April 22 (May 5) was able to start at the Liaodo Peninsula in the Bitszvo landing of the 2nd Army of General Ya. OKU (about 35 thousand bayonets and a saber, 216 guns). The southern branch of the Sino-Eastern Railway, leading from Liaoyan in Port Arthur, turned out to be a convergent enemy. Following the 2nd army, the 3rd Army of General M. The legs, intended for the siege of Port Arthur had to land. From the north, its deployment was provided by the 2nd Army. In the Dagushan district, preparation for landing for the 4th Army of General M. Nodzu was carried out. She had a task together with the 1st and 2nd armies to act against the main forces of the Manchu Army and ensure the success of the 3rd army in the struggle for Port Arthur.
On 12 (25) May 1904, the OKU army came out to the positions of the Russian 5th East Siberian Rifle Shelf on the Isthmus in the Jinzhou area, covered the long approach to Port Artur. The next day, the Japanese at the cost of huge losses managed to discard Russian troops from the positions occupied, after which the path to the fortress was opened. 14 (27) May the enemy without a fight took the port of far, which became the basis for the further actions of the Japanese armies and the fleet against Port Arthur. In the distant immediately began landing of parts of the 3rd army. In the port of Takushan began to plan the 4th Army. The two divisions of the 2nd Army, who completed the task, were directed to the north against the main forces of the Manchurian army.
May 23 (June 5) under the impression of the results of an unsuccessful Jinzhowsky battle E.I. Alekseev ordered A.N. Kuropatkin Send to the revenue of Port Arthur detachment by force of at least four divisions. Commander of the Manchurian army, who considered the transition to the offensive premature, sent against the OKU's army (48 battalions, 216 guns) Only one strengthened I Siberian Army Corps of Lieutenant General G.K. Shakelberg background (32 battalion, 98 guns). June 1-2 (14-15) 1904. In the battle of Wafanglo, the troops von Stotelberg suffered a defeat and were forced to move to the north. After the failures of Jinzhou and Wafango Port Arthur turned out to be cut off.
By 17 (30) May, the Japanese broke the resistance of the Russian troops who occupied intermediate positions on distant approaches to Port Artur, and approached the walls of the fortress, starting her siege. Before starting the war, the fortress was completed only by 50%. As of mid-July 1904, the land front of the fortress consisted of 5 forts, 3 fortifications and 5 separate batteries. In the intervals between long-term fortifications, the defenders of the fortress equipped rifle trenches. On the seaside front there were 22 long-term batteries. The garrison of the fortress consisted of 42 thousand people at 646 tools (of which 514 are on the land front) and 62 machine guns (of which 47 are on the land front). The general leadership of Defense Port Arthur carried out the head of the Quantong Fortified District, Lieutenant General A.M. Stresser. The land defense of the fortress was headed by the head of the 7th East Siberian Rifle Division, Major General R.I. Kondratenko. In the 3rd Japanese army, 80 thousand people were listed, 474 guns, 72 machine guns.
In connection with the beginning of the siege of Port Arthur, the Russian command decided to save the Pacific Squadron and lead it to Vladivostok, but in battle in the yellow sea on July 28 (August 10) the Russian fleet failed and was forced to return back. In this battle, the commander of the squadron counter-admiral V.K. Vithette. 6-11 (19-24) August The Japanese held an assault port Arthur, shot down with large losses for attackers. An important role in the beginning of the defense of the fortress was played by the Vladivostok Craisers, acting on the enemy's maritime communications and destroyed 15 steamats, including 4 military transport.
At this time, the Russian Manchurian Army (149 thousand people, 673 guns), increased troops of the X and XVII of Army Corps, in early August 1904 took defensive positions on distant approaches to Liaoyan. In Liaoyan battle on August 13-21 (August 26 - September 3), the Russian command could not use a numerical superiority over the 1st, 2nd and 4th Japanese armies (109 thousand people, 484 guns) and, despite that all the attacks of the enemy were repulsed with the big losses for him, ordered the troops to the north.
Fate Port Arthur
6-9 (19-22) September, the enemy took another attempt to master the Port Artur, which again failed. In mid-September, in order to help the besieged fortress A.N. Kuropatkin has decided to go to the offensive. From September 22 (October 5), on September 4 (17), 1904, the Manchu Army (213 thousand people, 758 guns and 32 machine guns) conducted against Japanese armies (according to Russian intelligence - over 150 thousand people, 648 guns) operation On the Shahoe River, which has completed to no avail. In October, instead of one Manchurian army, the 1st, 2nd and 3rd Manchurian army were deployed. A.N. became the new commander in the Far East. Kuropatkin, replaced by E.I. Alekseeva.
The fruitless attempts of Russian troops defeat the Japanese in South Manchuria and break through to Port Artur decided the fate of the fortress. October 17-20 (October 30 - November 2) and November 13-23 (November 26 - December 6), the third and fourth storms of Port Arthur, newly reflected by the defenders took place. During the last storm, the enemy mastered the dominant terrain of the mountain high, thanks to which he was able to adjust the fire of siege artillery, represented incl. 11-inch warmts, whose shells targeted ships of the Pacific squadron, stood on the domestic raid, and defensive structures of Port Arthur. 2 (15) December, during the shell, the head of the land defense General Major R.I. Kondratenko. With the fall of forts No. II and III, the position of the fortress was critical. December 20, 1904 (January 2, 1905) Lieutenant General A.M. Stesssel gave an order about the surrender of the fortress. By the time of the surrender of Port Arthur in its garrison, 32 thousand people were listed (of which 6 thousand wounded and patients), 610 good guns and 9 machine guns.
Despite the fall of Port Arthur, the Russian command continued attempts to defeat the enemy. In the battle of Sandip 12-15 (25-28) January 1905 A.N. Kuropatkin conducted a re-occurrence of the 2nd Manchurian army between the Honghe and Shahoe Rivers, which again ended in failure.
Battle under Mukden
On February 6 (19) - February 25 (March 10), 1905, the largest battle of the Russian-Japanese war was held, a predetermined outcome of the struggle on land - Mukden. In his progress, the Japanese (1st, 2nd, 3rds, 4th and 5th Army, 270 thousand people, 1062 guns, 200 machine guns) An attempt to bypass both flank of Russian troops (1st , 2nd and 3rd Manchurian armies, 300 thousand people, 1386 guns, 56 machine guns). Despite the fact that the idea of \u200b\u200bthe Japanese command was torn, the Russian side suffered severe defeat. The Manchurian army moved to Supingan positions (160 km north of Mukden), where they remained before the conclusion of the world. After Mukden Battle A.N. Kuropatkin was shifted from the post of commander-in-chief and replaced by a general from infanteria N.P. Linevich. By the end of the war, the number of Russian troops in the Far East reached 942 thousand people, and Japanese, according to Russian intelligence, - 750 thousand. In July 1905, the Japanese taught the Sakhalin Island.
Tsushimsky Boy
The last major event of the Russian-Japanese war was the Tsushim sea battle 14-15 (27-28) of May 1905, in which the Japanese fleet completely destroyed the United Russian 2nd and 3rd Pacific squadrons under the command of Vice Admiral Z.P. Rodial, sent from the Baltic Sea to the aid of the Port Arthur Squadron.
Portsmouth peace treaty
In the summer of 1905, negotiations between the Russian Empire and Japan began in North American Portsmouth, with the mediation of the US President T. Roosevelt. Both sides were interested in the soon conclusion of the world: despite military successes, Japan fully exhausted financial, material and human resources and could no longer lead a further struggle, and the revolution began 1905-1907 in Russia. On August 23 (September 5), 1905, a portsmouth peace treaty was signed, completing the Russian-Japanese war. According to his conditions, Russia recognized Korea to the Sphere of Japanese influence, referred Japan rental rights of Russia to the Quantongous region with Port Arthur and the southern branch of the Sino-Eastern Railway, as well as the southern part of Sakhalin.
RESULTS
The Russian-Japanese war was worthwhile to participating in large human and material losses. Russia lost about 52 thousand people, Japan, more than 80 thousand people who died from RAS and illness. Military operations cost the Russian Empire at 6.554 billion rubles, Japan - 1.7 billion yen. The defeat in the Far East undermined the international authority of Russia and led to the termination of Russian expansion in Asia. The English-Russian Agreement of 1907, which established the delimitation of the areas of interest in Persia (Iran), Afghanistan and Tibet, actually meant the defeat of the Eastern Policy of the Government of Nicholas II. Japan as a result of the war established himself as a leading regional power in the Far East, strengthened in North China and attaching Korea in 1910.
The Russian-Japanese war had a great influence on the development of martial arts. It demonstrated the increased importance of artillery, rifle and machine-gun fire. During the fighting, the dominant role has gained a struggle for fire dominance. Actions with closed masses and a bayonet hit lost their former importance, the main martial construction was the rifle chain. During the Russian-Japanese war, new positional forms of struggle arose. Compared to the XIX wars. The duration and scale of battles have grown, which began to decay into separate army operations. She got the spread of artillery shooting from closed positions. Siege artillery began to be applied not only to deal under the fasteners, but also in the field battle. To the sea to the Russian-Japanese war, the torpedoes were widely used, marine mines were also actively used. For the defense of Vladivostok, the Russian command first attracted submarines. The experience of the war was actively used by the military-political leadership of the Russian Empire during military reforms 1905-1912.
The fleet of Japan unexpectedly, before the official announcement of the war, attacked the ships at the external Ride of Port Arthur.
As a result of this attack, the most powerful ships of the Russian squadron were disabled.
Russia to protect its geopolitical interests and borders in the Far East, in the growing rivalry with England, France and Germany in their predatory division of China, needed to acquire a non-freezing port in the Pacific Ocean.
In March 1898, a convention with China for rent for 25 years of the Quantong Peninsula with surrounding stations and Port Artur was concluded. Here, on the flagpole of the Golden Mountain, the Russian flag was raised under the Salute squadron. The construction of the naval base and the fortress began.
Strengthening Russia's military presence in Manchuria and Korea met the energetic resistance of other countries, especially Japan, where the propaganda campaign against Russia began. Japan pushed European countries to this, especially after the conclusion of the Anglo-Japanese Union in 1902. The contract guaranteed the "special interests" of England in China, and Japan - in Korea and Manchuria.
Germany participated in the training of the Japanese army. But the main support was made from the USA, which stated that they will support Japan in case of its conflict with Russia. To this, the US government spoil influential financiers headed by Yakov Schiff, the head of Jewish financial Mira in the United States, seeking to bind Russia into a protracted unpopular war and initiate a revolutionary confusion on this basis.
It must be admitted that with such an alignment of the forces of the war with Japan could only be protracted and very difficult for Russia. Although Japan was weaker than Russia in economic and military relations, she received unlimited loans from Schiff and his partners, sieving in a short time to mobilize their resources and modernize the army.
For a decade from 1894 to 1904. The Japanese army rose almost 2.5 times. At the beginning of the war, she numbered 375 thousand people and 1140 guns. The Japanese fleet consisted of 3 escords and 168 warships, many of which in their tactical and technical data (booking, speed, speed-fire and firing range of the main caliber guns) exceeded the ships of the Russian fleet.
Russia has had a personnel army in 1.1 million people and 3.5 million people in stock, but in the Far East in January 1904 there were only about 98 thousand people and 148 field weapons. In addition, in the border guard - 24 thousand people and 26 guns. These forces turned out to be scattered in a huge territory - from Chita to Vladivostok and from Blagoveshchensk to Port Arthur.
Manchurian theater actions was associated with the center of Russia only by Malopropusk Railway. It pretended to quickly strengthen and supply armed forces in the East. Military Minister General-Adjutant A.N. Kuropatkin did not see the impending danger from Japan and did not take proper measures in advance.
The Russian government has tried to negotiate with Japan, but she was not satisfied with small concessions on Korean affairs and clearly went to military conflict with the support of the United States, having decided to fulfill his claims to the whole Korea and Manchuria.
On January 24, 1904, in St. Petersburg, the Ambassador of Japan was transferred to the Minister of Foreign Affairs of Russia two notes. In an ultimative form, the Japanese government announced the termination of negotiations, about the rupture of diplomatic relations with the Imperial Russian Government.
On the same day, even before receiving the answer to these notes, the Japanese began aggressive actions, capturing Russian civilian vessels in the whole region. On the night of January 26, the Japanese destroyers suddenly attacked the Russian squadron, which was standing at the external Ride of Port Arthur, damaging three Russian ship. Peel one Japanese destroyer.
On the morning of January 27, the squadron and the fortress entered into battle with the main detachment of Japanese ships, which had 16 pennants. The Japanese admiral of Togo, seeing the tactical disadvantage of his position, changed the course and went south at high speed.
Port Arthur defenders lost 14 killed and 71 wounded, the Japanese, according to their data, had 3 killed, wounded - 69 sailors and officers. At the same time, 6 Japanese cruisers and 8 destroyers attacked the Korean port of Chelpo to the Korean cruiser and the Korean canonerer boat. The heroic unequal battle of these two ships is well known: the sacrificial feat of the Russian sailors shook the entire Russian people.

Port Arthur was also rejected by the Russian army and was not ready for long defense. In service, he had only 116 guns, of which on the sea 108 and on the land - only 8, instead of 542 by the project. The land garrison of the fortress consisted of 12 100 soldiers and officers (without sailors of the fleet crew).
The war found and the Pacific squadron is not sufficiently prepared for military actions on the sea. Only 7 armored vehicles were based in Port Arthur, 1 armored cruisers, 5 light cruisers, gunboats and the police officers. Mobilization plan and strategic deployment were not fulfilled.
Admiral S.O. Makarov repeatedly went out into the sea, drove fighting with Japanese ships, threw the admiral attempt to block the Russian fleet in the harbor. Makarov was preparing a squadron to a decisive battle in the open sea. Unfortunately, he failed to fulfill a lot: he died at the headquarters at the Petropavlovsk battleship, which broke up on Mine. The artist V.V. Vereshdygin died on the ship. Few.
Makarov commanded the fleet only 36 days, but left a significant trail in the affairs, as well as in the hearts of subordinates. After his death, the active actions of the Russian fleet almost ceased. Taking advantage of this, the Japanese began landing the army on the Liaodan Peninsula.
The Russian fleet due to the passivity of the leadership turned out to be unable to prevent the enemy to carry the landing on the Yellow Sea and plant it ashore. Thus, the fate of the fortress, and hence the fleet, was solved on the land front. Here the Japanese focused big strengths and constantly replenished them.
The defense of Port Arthur fortress - the heroic page in the Russian-Japanese war. From the military chronicle of the protection of marine fortresses, the Port Arthur epic is comparable only with the defense of Sevastopol. Here, in the conditions of the land and sea blockade, patriotism, the courage of Russian soldiers, sailors and officers, and their loyalty to military duty were manifested with a special force.
Almost eleven months continued bloody confrontation. During this time, the brave garrison of the fortress successfully beat off 4 fierce assault of the enemy, which had (with the last of them) fivefold superiority. Only the act of surrender, signed on December 20, 1904 by the head of the garrison gene. Sveta (contrary to the will of most of the Military Council), stopped further resistance.
Expensive paid the enemy for Port Arthur. The decline in the Japanese troops, storming the fortress, exceeded 110 thousand people or the sixth of all the losses of Japan in the war of 1904-1905.
At the same time, the war revealed as a funded by international Jewry (all of the same Schiff, which recognizes even the English "Jewish Encyclopedia") of the fifth column of revolutionaries - the most vivid example of its actions: the provocation of "bloody Sunday" and the irresponsible liberal intelligentsia, joying Russian defeats The troops, and, unfortunately, also the sideways and the confusion of Russian officials.
The latter the most depressing manner was reflected in the history of the phenomenon of the Mother of the Mother of Port Arthur and in non-fulfillment by military officials of her wishes for the spiritual protection of Port Arthur of her miraculous icon.

According to the Potsmouth Peace Treaty, the Rental Rental of Port Arthur was inflicted by Russia of Japan. However, when in 1923, the contract for the lease was expired, Japan refused to return Port Arthur China, turning it into his colony.
In August 1945, the Soviet Army took Port Arthur. By agreement with the Chinese government, the USSR received the right to lease Port Arthur since 1945 for a period of 30 years. But after the death of Stalin, his successor Khrushchev brought the troops from Port Arthur in 1955 and donated this naval database of "fraternal communist China".
- Tags: