Food dependence of Russia from imports. Myth about the food dependence of Russia
There is an opinion that Russia has a strong food dependence on abroad. Like 35% of food, we import. As always in gullible people, these numbers cause horror. And on the other hand, why horror, because in 2008 wrote "Why Russia imports 50% of food?" . In just 5 years, imports have become 15% less. And here for another 2 years passed.
The most amazing thing is that food addiction is considered in dollars. Did these patriots of food security, eat bucks?
They write that in 2012 a negative food balance amounted to $ 23.8 billion But since then another 2 years has passed.
In 2013, Russia imported food products worth $ 43 billion and exports of food and agricultural products from Russia amounted to $ 15.6 billion. Balance was $ 27.4 billion.
In 2014, Russia imported foodstuffs worth $ 39.7 billion. In 2014, food and agricultural exports increased by 16.5% - to $ 18.9 billion (more than trade of weapons). Balance was -$ 20.8 billion
But people eat not dollars, but food. And food buy usually by weight. And by weight, a completely different picture comes out.
It turns out that this is already abroad depends on us, in 2013 we imported 23 172 201 tons of food, and exported almost29 528,049 tons of food.
For 2014 I did not find data. But imports declined, and the export of only grain rose by another 5 million tons.
That is, in 2014, we imported 20 million tons of food, and exported 35 million tons of food
We can say that this Russians are already fed the world. After all, they eat not dollars, but food.
And if you consider the strongest drop in food imports in connection with the sanctions from Russia to the last half of 2014 and the first half of 2015. It will most likely it turns out that we export twice as much as we import in tons.
And even if you consider in dollars, it is not clear why the food dependence is made by the import of expensive wine, exotic fruits and sweets) most likely the balance of import and export of food in 2015 will decrease to 5-10 $ billion (the crop of grain again promise for 100 million tons), and in 2016 the negative balance will come at all. But the fact that we already feed the world will remain
Of course, ton of coffee is more expensive than tons of grain or tons of meat,. But if you consider in the tones of food, then Russia already feeds the world 
to calculate the volume per resident of Russia, the population is adopted equal to 143666931 (Rosgosstat, section "Evaluation of the number of permanent population on January 1, 2014)
The volume of production of agriculture of all agricultural producers (agricultural organizations, peasant (farmer) farms, economy) increased by 103.7% in 2014. Gross grain collection in the Russian Federation in 2014 exceeded 12.4% the level of the previous year. Gross potato and vegetable fees increased by 3.0% and 2.3%, respectively, due to the growth of yield.in 2014, the production of livestock and birds at slaughter in live weight reached 12.7 million tons in Russia compared with 12.2 million tons in 2013 (an increase of 4.1% by 2013)
Ministry of Education of Russian Fediocy
Tomsk State Pedagogical University
Faculty of Economics and Prelimination
Allow protection to
Director IEP Professor Sizov V.V.
COURSE WORK
On the topic: Food Imports in Russia
Pribments and consequences
Student Group ES-31 Vinogradova S.V.
Manager:
Candidate of Economic Sciences, Associate Professor Romaichina I.A.
Introduction
. Food in Russia
. Danger of the loss of food independence of the country
Import restrictions
3 .1.Frichina
3.2. Restriction by quantity
Marriage problems in import
An example of economic non-unity
Conclusion.
Literature.
Application.
Introduction
Importing supplies traditionally play a significant role in solving many vital problems of the country's socio-economic development and the provision of both the production sector and the population by the types of products that are not produced or are produced in insufficient volumes. The problems of the country's industrialization in the years of the first five-year plan, the reconstruction of the national economy in the post-war years, the correction of the unfavorable balance of food products in the lack of town years and many other no less important nationwide problems were solved to a large extent using imports.
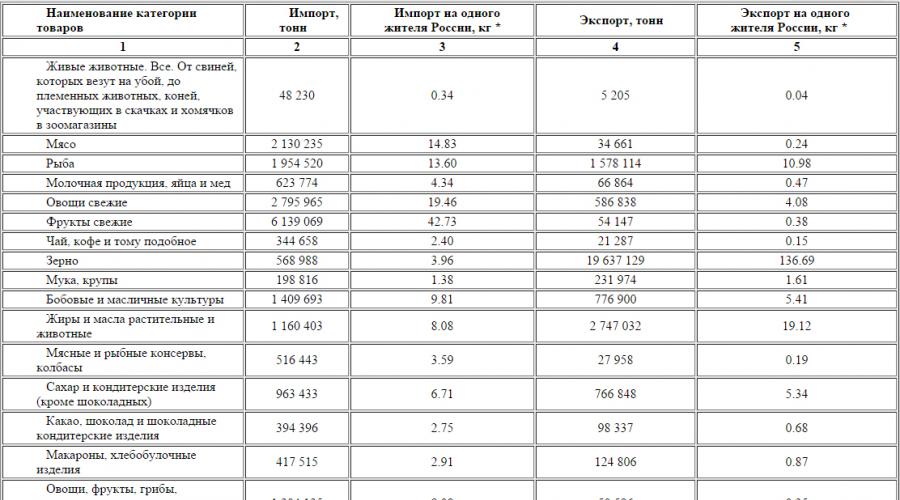
The commodity structure of imported deliveries over the past ten years is fairly stable, despite the significant reduction in the value parameters of the import (table, application).
In the structure of imports, the share of food and agricultural raw materials is essential for their production, which is caused, except for other reasons, a sharp reduction in the national production of agricultural products. Russia currently imports more than 40% of the total domestic food consumption, and in the food balance of Moscow and St. Petersburg, the share of imports is more than 70%. Consider how much this phenomenon is negative.
Food in Russia.
In recent years, the needs of Russia's population in food products is satisfied with domestic producers by about 50%, taking into account the expert assessment of the volume of inorganized import and sale of goods in food markets. The Food Security Border is, according to various estimates, at the level of food imports in the amount of 18 - 35% of the need. A significant exceeding critical point, even at the lowest estimated, in Russia is due primarily to the crisis position of domestic agriculture, production in which is about 60% of the average annual level for 1986 - 90g. Such a drop in production is due to both transformational decline and inefficient ways of conducting in general economic reform and agrarian, in particular. A significant reduction in state support for agriculture, which decreased from a third of the huge state budget to 2.7% of GDP in the Budget for 1998, left the peasantry one on one with a variety of problems. However, despite the overall decline of agriculture, store shelves remain crowded. This happens, firstly, due to the reduction of consumption by the population of food by almost 1.5 times (exceptions are such low-value foods, like breadfinding products and potatoes, which increased somewhat increased, despite the significant increase in prices). Secondly, the most important cause of this situation is an increasingly increasing import of agricultural products, the volumes of which exceeded all permissible norms and is already directly threatened by the country's security.
The share of imports in the total food volume according to different estimates is from 30 to 50%. This is not surprising, since it is now per capita in Russia for a year 43 kg of meat and 194 kg of milk. At the same time, a physiologically reasonable consumption rate per person is 81 kg of meat and 392 kg of milk. Food shortage is covered by import, but not completely.
The population of our country is not provided by a normal level of nutrition. According to estimates, daily consumption per person in Russia is an average of 2,200 kcal (2590 kcal - in 1990). We are already behind Africa, where 2300 kcal consumed on average, not to mention the US and the EU, where the caloric content level is 3500-3600 kcal. At the same time, according to the international classification of the World Food Organization (FAO), nutrition at the level of 2150 calories characterizes the conditions of permanent malnutrition. The normal level for humans is 2600 calories.
These disappointing figures are explained by the fact that over the years of reforms, the production of basic food products in Russia has been steadily reduced. Name only some indicators. Compared to 1990, the grain fee dropped 2.5 times, sugar beets - 3 times, the production of meat was reduced by 2 times, milk - 1.6 times, eggs - 1.5 times, 2 times the livestock decreased by 2 times Cattle, birds - 1.5 times, pigs - 2 times, sheep and goats - almost 4 times.
True, last year there were definite positive symptoms. The production of individual food types increased, the proportion of imports has decreased. But it should not be self-prior: this is due to the devaluation of the ruble in 1998, somewhat raised the competitiveness of domestic goods by reducing food imports. On the other hand, the real incomes of the population fell by 15%, the rise in prices was continued, including in domestic products. Therefore, even when the gross production of basic foods (meat, milk, animal oil), the share of Russian-made goods in the domestic market has increased. However, if the real revival of agriculture does not begin, the situation may change and the proportion of imported products will begin to increase again.
However, there are no prerequisites for the real revival of agriculture. It is enough to look at the gross production indicators in recent years. We see the steady drop in its volumes, which today constitute only 50% of the pre-reform level. The volume of capital investments in the APC decreased by 20 times. 22 million hectares of farmland were seized from the turnover, sown areas decreased by almost 14 million hectares. According to the Institute of Economics of the Russian Academy of Sciences and ROSKHN, by 2003, while maintaining a modern trend will be treated with 30% of the Land from the level of 1997. In general, almost 90% of farms of all types of ownership are unprofitable,
One of the main reasons for this state of the APC is the price dispensation between agricultural products and industrial. Prices for industrial products in the years of reforms grew 4-5 times faster than agricultural products. The APC was not able to recoup the cost of production, because of which he became a debtor as a federal budget and private financial structures.
In Russia, it is necessary to move from a tough protectionist policy to targeted support for domestic agricultural producers through subsidizing income and maintaining a common price level under their sharp fluctuations. In ensuring food security, it is necessary to rebuild with external, purely fiscal methods (customs duties), to maintain domestic agricultural production.
Considering the problems of the economic security of Russia in the context of the transition to the market, it is impossible not to note the following phenomena, which are directly related to the damage of economic security to our state:
Sharp deterioration in the demographic situation;
Criminalization of the economy;
Destruction of science and technological potential;
destruction of the financial and credit sphere.
Danger of the loss of food independence of the country
The aggravation of price disproportions between industry and agriculture, the refusal of reasonable paternalism in relation to domestic producers and the almost complete opening of the domestic market for the import of food - all this undermines the database for the country's self-sustament. But this does not mean the course of the country's full isolation from the world market. World practice has developed a number of important and reliable approaches to solving this problem, among them - flexible and efficient protection of domestic manufacturers, regulation of relationships that allow the entire import of food products to be exported also for food, the production of which is more efficient.
Now there is a threat to the loss of food independence of the country, which will be accomplished by the fact that the danger will not be promptly realized and radical measures will not be taken to reflect.
Food in human life, and if we speak on a global scale - humanity, play a special role. Experts believe that there is already a food problem during the lifetime of the current generation in a deep international crisis. 17 percent of the population of the Earth today experiencing hunger and in the next decade this number may increase one and a half times
There are a lot of reasons for this. One of them - the production of food in the world is reduced. That is why in 1992, 1600 world scientists, including. 102 Nobel Prize laureate, published a memorandum, entitled "Scientists warn mankind." It refers to it that irresponsible attitude towards natural resources is able to change the planet so much that it will not be able to preserve the lives of people on the level achieved.
This appeal was distinguished by almost all states. In November 1996, the World Conference on Nutrition was held in Rome, in which 173 countries participated, including Russia. The reports stated that only 840 million people are chronically starved in developing countries. At the same time, 50 percent of food produced in the world consume the most developed countries in which only the fifth of the world's population lives.
In order not to sneak against the truth, it can be described by other very expressive figures, a quarter of the Earth's population lives in 26 developed capitalist countries. But their peoples consume 75 percent of the entire energy produced on the planet, almost 80 percent of fossil fuels, 85 products of grainworking, more than 70 - steel production. The United States with its three-story millions people use such a quantity of raw materials, energy, fuel, food, which could provide the life of three hundred billion people - at the current level of consumption of the population of India.
To solve the problem of nutrition, it was said in the conference materials, it is necessary to increase the production of food for at least 75 percent in the next decade. Scientists, economists, production organizers see at least a partial solution of food problems in the intensification of production, in careful attitude to Earth, in the proper spending of energy resources, fresh water reserves.
By the way, some scientists are advised not to be very involved in genetic engineering, since changes in such a structure of plants can lead to unpredictable consequences for the animal world, and then a person. Scientists say: no need to invade the limits created by God. The priorities of governments and state leaders, they consider the care of land, agricultural production, promoting its development, its priority financing. Here is a brief list of ways to increase food production.
There is a completely natural question: what about us, in Russia, are things with food security? If you determine the essence of the moment, it is as follows: a severe alert struck the power. Today, more than half of the population lives below the poverty line. The position of Russia is not only complicated, but also dangerous. During the reforms, agriculture received a blow, comparable from the results with a nuclear war, and discarded in the tail of civilization. Especially injured the basis of all agriculture - the fertility of soil not receiving fertilizers is lost. Half livestock livestock, birds and almost all sheep, pigs. Investments in the village decreased by about 200 times.
The material and technical base underwent special destruction. The annual production of tractors decreased almost to 10 thousand (on average by 22 times), plows up to one thousand. Cultivators are produced less than 31 times, seeders - 39 times, combine harvesters ~ 66 times, forage - 44 times. The production of many other types of equipment is generally suspended. Even the number of enterprises producing agricultural equipment has decreased. But the presence of equipment is of paramount importance in improving labor productivity, reducing the cost of production and in general, in increasing food production.
Our European and American "Friends" sometimes in the form of humanitarian assistance send us low-grade, often seeded products.
This is this example: in November last year, the Grain State Inspectorate under the Government of the Russian Federation banned the use of about two and a half thousand tons of food received from the United States within humanitarian assistance. Of the proven two thousand tons of flour, only 390 tons were suitable for use. In the rest - an increased maintenance of metallomagnetic impurities. In addition, more than a thousand tons of beans were rejected. Upon conclusion of the veterinary service, it cannot be used even for the feed of pigs.
From abroad, up to 40 percent of food. This is statistical data, and actually happens more. That is, this is an indicator that we are already on the verge of fuel security.
And now, running forward, let's imagine and ask the question: if for any circumstances America and Europe will stop tomorrow, or rather, the sale of Russia grains, meat and makeup products, fruits, vegetables? What then? After all, we do not have any reserves. Yesterday the powerful superpower as a result of "reforms" will turn into a half-rolled analogue of a poor African state?
In the last decade, bread and potatoes predominate in the nutrition structure of our compatriots. Let's look at official numbers. So, in 1999, compared with the 1990s, on average per person, meat consumption decreased by 44 percent, dairy products - at 47, eggs - on 24, fish - by 51, sugar - by 28 percent. These figures are not only impressive, but they will make thinking. In the next UN report, "On the Development of Human Resources in 1999" Russia has defined 71st. It is at Somalia, Lebanon. Such shifts in nutrition, of course, affected the demographic setting in our country.
But back to the machine-tractor fleet of Russia again. For his condition causes serious anxiety. It is well known that the service life is calculated 8-10 years, and depending on the operating conditions and in short. "Reformers" significantly reduced the admission of equipment on the village. For every 1000 hectares of Pashny in our country, there are eight tractors, in the USA - 27, in Poland - 92, in Europe - 114, in Japan - 564 units. At the same area of \u200b\u200bsowing grain, we have five combines. Load for one combine - 200 hectares. But it is on average, but it is sometimes twice as high. At the same time, in the United States for a thousand hectares of crops of grain, there are 18 combines, in Europe - 17, in Japan - 524. Figures, as they say, beat novel.
Frost period we have 120-130 days. Given the period of vegetation of different cultures, Herborobam accounted for tremendous efforts to fit in these times. For the period of cleaning, we have to maximize rain, the terms are stretched, which is lost to a quarter of the harvest. From here and for other reasons, the security of the people of the grain is: with the norm, one ton of grain per person in Russia has collected 375 kilograms in Russia last year, that is, 27 percent of the need. In the States, meanwhile, they are collected by one and a half tons per resident.
Last year, the grain area we had 46 million hectares, that is, less than in the first post-war year and less than ever for the entire period, since 1913. Then the Russians sowed 63 million hectares. During the years of "reform" of agricultural production, sowing decreased by such an area, which is equivalent to the sowing squares of Great Britain, Italy, Germany, Denmark, is taken together, that is, 30 million hectares. If from those areas to receive not four or five tons of grain, both in Europe or America, and only at least one tonne, then we would not have purchased in Canada and the states those 15 million tons of grain, for which we almost annually spend two billion dollars.
It should be added to this that our fields are extremely amazed by weeds, diseases and pests of agricultural plants, which launched amelioration. The government every spring and summer exhausts fuel from oil magnates to conduct sowing and harmful, as a result of mismanagement, the average yield rolled up to 11 centers of grain from hectare.
It is agriculture that the industry, with the help of which the country's economy may, in the shortest possible time, achieve a jerk forward. But it so happened that in recent years they supported not domestic peasants, but farmers of the West and America. What does this mean? A lot of things. Specialists in agricultural issues believe that with such a situation, our fellow citizens can very much without bread and other foods. And buy tractors or combines to the rural producer in principle not by pocket. And it is not so important that the technique produced in our country, according to knowledgeable people, in some cases of poor quality. Much more importantly, according to official statistics over the past eight years, prices for agricultural products increased only 1500 times, and 15 thousand times for the technique. There are no such crazy money in farms.
The collection of grains this year is 10 million tons more than in 1999. But for more significant growth there are still no funds. And again it is impossible not to resist comparisons. According to the ECC technical and economic information information, in the United States, the total transfers to agriculture is 94 billion dollars a year, in Japan - 89, in European countries - 134 billion. Even in a small area and the population of Finland - almost four billion. In vast Russia, it stands out ten times less than in Finland, and 230 times less than in the United States.
There is only one way of fighting indigestible - urgently launch the conveyors of tractor and combine plants. According to the calculations of specialists, the technique will pay for itself at the expense of savings in the first year at the production of grain and animal husbandry products. The APC needs the state regulation of the system of short-term and long-term loans, in the fastest formation of state agriculturalbank.
It is very important to further develop lease in the acquisition of technology. The Ministry of Finance complains that many amounts are not returned to the budget. Maybe at the start stage it is, but they return, in fact, an invaluable gift for people - food. In our natural conditions there should be an effective insurance system. The main land tax according to the cadastral assessment of the Earth should be the main.
Import and exports of agricultural products are obliged to take into account primarily the interests of the agrarian market of the CIS countries. It should include wholesale universal markets - trading houses, fairs, auctions. For some projects, it is possible to attract foreign investors. The interests of the APC strongly need to improve the quality of domestic technology. There is a need to restore the connections and supply of equipment from the CIS countries.
Legal mechanism must be created. All this would be faster to the desired goal, if you reinforce legal acts. We immediately need such of them as "on state support for agricultural producers", "On the development of the infrastructure of the food market", "On the production of environmentally friendly products", "On the provision of food for military and other special consumption", "about quarantine in crop production", " Protection of plants from agricultural pests and painful "and other, extremely necessary legal acts regulating activities. Self-producers.
Now laws are needed "On the Peasant, Farming Economy", "On Personal Subsidity", "On the creation and actions of joint-stock companies", "on agricultural administrations in the APC", "On improving management in APK". The country, in fact, still has no land cadastre, land management, lease rules. There is no law on the best use of state and municipal lands, monitoring and pledge and other documents. Close to consideration the law "On the material and technical support of the apk". Oposition: problems and development trends. ...
Leasing B. Russia. Problems and solutions
Coursework \u003e\u003e EconomyWar ammunition, equipment, food and strategic raw materials, ... accounted for import equipment from ... entails various legal effects. Concluding a financial contract ... and the tax aspects of leasing in Russia and problemsassociated with changes in tax ...
Problem Business security threats
Essay \u003e\u003e Life SafetyFurnishing in various regions Russia. Non-free competition and ... entrepreneurs, though effects His effects are very ... exports of oil and metals, import food and others. Real owners ... will not solve all problems enterprises. The only thing, ...
Mortgage bank lending in russia problems and development prospects
Degree work \u003e\u003e bankingTransition economies. Existing in Russia problem non-payment, the prevailing atmosphere ... Practice leads to the following negative consequences: 1) information contained ... Critical import (medicines, foodsome deficit ...
In 2017, Russia for the first time since the beginning of sanctions wars increased imports of agricultural products.
In total last year, 21.5 million tons of food and raw materials were imported to Russia (except for textile) in the amount of $ 28.8 billion. This is more similar indicators of 2016 by 6% and 15%, respectively. The increase in the import of the APC products is confirmed by the data of the Ministry of Agriculture: according to its information, in January-November 2017, Russia imported agricultural products by $ 25.7 billion, which is almost 16% more than the same period of the previous year.
Two factors are very strong on the import of food (not only agricultural products): the income of the population and the dollar rate. The reason is that not all Russian products are competitive in price and quality, so as the income or strengthening of the ruble increases, the population begins to buy imported goods.
For the characterization of income growth, a variety of indicators can be applied. For example, instead of income index - indicators of sales of food products. On the fig. one It is shown how the index of physical sales of food products changed (in comparable prices). For clarity, the figure shows the purchase ratio at each of the months of 2013-2017. If the economic situation is favorable, then the volume of purchases is growing.
According to the schedule it is clear that only from July 2017, food retail sales began to slowly grow - for the first time since August 2014 in December 2017, they bought more than in December 2016, but less than in December 2015, 2014 G. and 2013
Fig. 1. Indices of the physical volume of retail sales of food products,% to the corresponding month 2012
If we talk about imports, it also fell from August 2014. In 2013, it amounted to $ 43.3 million, and for 2016 - only 25 billion (drop by 42%). Imports sporadically increased in some months (starting from 2015) when the ruble was strengthened. However, the general trend towards growth began to be observed only since 2017, when the ruble rate was sufficiently stable in the range of 1.98-1.78 from the course in 2013 ( fig. 2.). In December, imports are traditionally growing, even if the ruble is weakening, but in 2017 the growth of imports was against the background of strengthening the ruble.
Fig. 2. Dynamics of the ruble course (left scales) and import (scale rights) to the corresponding month of 2013
The dependence of imports from the course of the national currency was also observed in the 1998 crisis. A sharp drop in the ruble exchange rate in August 1998 was reflected in imports. If in August 1998, the dollar cost about 6.5 rubles, then in October of the same year, 15.5 rubles already. This affected the imports of food and agricultural: it fell from $ 13.3 to $ 7.3 million, or 45% ( fig. 3.).
Fig. 3. Dynamics of food imports before and after the devaluation of the ruble in 1998 and 2014.
Import began to grow only two years after 1998, exceeding the pre-crisis level in 2004, and by 2007 exceeded the level of 1997 already twice. The repetition of the situation we are observed and now.
Obviously, after the devaluation, Russian agricultural producers received advantages. However, if the period of special possibilities was not implemented in order to modernize, improve labor productivity and make Russian products competitive, then imports will increase. In addition, it will grow on those products that will never be produced in Russia due to climatic conditions. It is not by chance that in 2017 it has grown up the import of fruits, nuts. This product group takes about 15% in the import structure.
Russian exports also grows. Compared to 2016, the export of food and agricultural raw materials increased by 21.5% - to $ 20.3 billion. An important result of this year is that import growth rate is significantly inferior to the growth rates of food exports: 15% against 21, five%.
Natalia Shagayda - Doctor of phone, head. Laboratory of Agricultural Policy IPE
After 2014, the imports of products decreased due to the oscillations of the ruble and falling income of the population. If these factors stop acting, then the main issue of the competitiveness of Russian products will again be
Introduction In August 2014, the embargo on the importation of products from the EU, USA, Canada, Australia and some other countries now is now considered by many as a tool that allowed to promote noticeably along the way of import substitution. Even the tradition of appeals appeal to extend the embargo to the president from agricultural producers and officials from agriculture. To improve the quality of the state-made decisions, it is useful to analyze the situation.
Imports of food and agricultural disease after the introduction of the embargo decreased significantly. Compared to 2013 - by 42%: from $ 43.3 billion to $ 25 billion in 2016. If you calculate the share of the imported food component (at a price at the border) in the cost of food consumed by the population, then it was 7% in 2016. By the way, from 1999 to 2013, this figure ranged in the range of 11-14%, so that it was possible to say that the Embargo could be said that Russia's dependence on imports is very exaggerated.
Import reduction could not be explained only by the embargo. Our calculations have shown that the stable effect on imports to a greater extent is to fluctuate the ruble exchange rate and real monetary incomes of the population, and not the fact of the introduction of the embargo.
Consequences for manufacturers and trade
The introduction of the embargo turned out to be a favorable signal for agricultural producers (the state thinks about them) and alarming - for retailers (you need to build connections with local manufacturers, as new limitations may be suddenly introduced). As a rule, retailers preferred imported products: they come uninterrupted, homogeneous parties and in a sustainable assortment, which is often difficult to achieve from Russian manufacturers.
For example, the suppliers of chilled meat clearly won, since it will not bring it from afar: you can bring a pork from Brazil to Russia, but it will be frozen pork. In 2013, the cooled pork without bones in Russia was supplied by 12 countries. In 2016, only Belarus, which was the largest beneficiary of the introduction of the embargo.
The same applies to cheap cheaps from traditional suppliers: from Finland, Germany, Lithuania, Poland, Ukraine. In 2014, from the ten largest suppliers of cheese, seven were represented by the EU plus Ukraine, also under the ban. In 2016, only two remained from this tent. Belarus increased the export of cheese to Russia, while the growth of milk production in the Belarus itself did not happen - imported Polish milk and part of the Belarusian, which was released due to the fall of milk consumption in Belarus, went on the production of cheese. The fall in imports of cheeses and cheese products 1.7 times, from 440 thousand tons in 2013 to 222 thousand tons in 2016, occurred with the growth of its own production of cheese in Russia by 165 thousand tons. And the milk production itself Grew, and the deficit led to price increases.
For the absolute majority of Russian manufacturers, not so much embargo was useful as devaluation, since prices for their products have become more attractive compared to all imported products in the domestic market. Exporters also won: the price in dollars could shrink, and in rubles to increase.
By the end of 2016, it was possible to talk about increasing the number of products for which import substitution occurred, such as pork, vegetables, birds, milk powder, butter and sugar. There was no import substitution for fruits, which is natural, as half of imported - citrus and bananas, in cheese and beef.
Consequences for consumers
The fact that after the introduction of the embargoes will rise in price, it was possible to predict before the ban. Thus, prices of deliveries from those countries that came under the embargo were, as a rule, lower than from countries that eventually remained in the list of importers. There is an exception here, and this is again Belarus, products from which were out of competition in price ratio before and after the embargo. However, she could not replace all suppliers.
The overwhelming part of consumers of the decline of imports did not notice: they looked only on what could buy is the part of domestic products, which after devaluation has become cheaper imported. Another part has reduced consumption: Purchases at regular prices fell until June 2017. Only then they began to grow and in September 2017 reached the level of September 2015, but remained below indicators 2014, 2013 and even 2012. Part of the population continued to buy imported products, spending significantly more on them than before the embargo and devaluation: imports in ruble expression in 2016 was 1.2 times higher than the import of 2013, not to mention the import of 2014 and 2015.
In a short period of time after the embargo, a lot of factors agreed, which makes it difficult to assess the impact of the embargo on the growth of internal food prices. For example, additional opportunities have appeared among countries that did not fall under the embargo, but supplied comparable products at a higher price. It predetermined the rise in prices.
Other changes occurred: since 2015, the supply of cheap vegetables to Russia from Iran began after removing part of sanctions from it. The ban on tomatoes from Turkey liberated the market for more expensive winter Russian tomatoes, etc. However, with the entire set of multidirectional factors, food prices began to grow faster than prices for all products (industrial and food).
It is worth recalling that Russia in August 2012 became a member of the WTO. This caused the concerns of domestic agricultural producers about competition with foreign. And indeed, the prices for products that could not be done cheaply, began to decline. From this point on, Russia resorted to the protection of its market with non-tariff methods. The graph shows that relative to January 2011, the rise in prices both in the whole products and services and in food products until mid-2013 practically coincided. But in the middle of 2013, food prices began to grow faster, and after the introduction of the embargo, the gap has even increased.
Scenarios for the future
For the first nine months of 2017, the imports of food and agricultural products grew up in dollar terms by 17% and decreased in ruble less than 1% with respect to 2016, that is, strengthening the ruble exchange rate immediately increased the demand for imported products. According to the experience of the 1998 crisis, a sharp decline in imports by 45% (in 2000 relative to 1997) was replaced by the growth in two years. And now the reduction of 42% (from 2013 to 2016) is replaced by careful growth. As the past crisis shows, the levels of imports of the pre-crisis 1997 were easily blocked: if in 1997 it was covered with products and agricultural seaside for $ 13.2 billion, then in 2013 - already at $ 43.2 billion.
The risk of rolling back, to expanding imports, is if during a sharp weakening of the ruble and falling income of the population will not be able to make Russian products competitive. Importing non-losslessness for consumers is possible only when domestic products will not be more expensive. Otherwise, imports will return, or the country will again introduce non-tariff restrictions that hard to justify.
There is a lot about competitiveness and often repeat that in Western countries it is the result of huge state support for agricultural producers. However, the point is not only that in Europe, the USA and Canada, the state strongly supports farmers. There are many countries where budget support for agriculture is less than in Russia, and products are cheaper. In addition, the state support of large companies in the United States, Canada and the EU is limited, such volumes of direct subsidies that are obtained in Russia individual largest agricultural producers are completely impossible.
If you close your country from cheaper products, limiting competition, it is bad for the consumer and ultimately for the manufacturer. For him, it is bad because the developmental horizon is limited to internal demand: you can't bring non-competitive products to export. OECD estimates, in 2014-2016, buyers of agricultural products in Russia overpayed 10% for Russian goods compared to the price in the global market.
 Attention!
Attention!
In contact with
Odnoklassniki.
In our country, much attention is paid to the supply of foreign goods, that is, the import of products to Russia. The interests and requests of consumers increased, and now they can be satisfied increasingly to be satisfied with the imported goods, which, thanks to a well-organized transportation, hurried to the Russian market. Is it profitable to entrepreneurs honestly developing their business in the context of numerous sanctions? In our article we will try to highlight this topic as much as possible.
What changes have undergone imports of products to Russia after the imposition of sanctions
At the domestic market there are absolutely all products and their components: from grain to dairy meat. On the tables of Russians have already become familiar dairy products from Finland, fruits and vegetables from Poland, fish from Norway, snacks from Hungary, alcohol from France and the United Kingdom and other "overseas goodies." Before the imposition of sanctions, imports of products in Russia included: beef (40%), pork (25%), milk (30%), in addition, industrial equipment for the manufacture of food products was predominantly imported (80% of all used in production). In other words, to establish the domestic production of the same cheeses, candies and canned foods, first needed to purchase foreign devices. Statistical data prior to the introduction of sanctions suggest that almost half (40%) of food products offered by the Russians are made outside the country. And if something has been manufactured in our workshops, imported components or equipment were used. But these times passed, since they introduced sanctions.
The main suppliers of fish to Russia are Norway and Iceland. Despite the fact that the share of this product was small, only 20% of the total volume, the situation on the shelves has changed significantly. Little in the Russian markets of domestic meat, because we prefer the dairy breeds of cows. The share of imported diverse dairy products reaches 60%. Kazakhstan is the main supplier of grain, imports is 1.5%. But vegetables and fruits of imported production on the market more than enough (2/3 fruits and 40% of vegetables are imported). In full, Russia could provide its consumers only eggs, vegetable oil and sugar of domestic production.
Today, imports of products in Russia ceased due to the introduction of sanctions from the EU member states (England, Germany, Greece, etc.), USA and Canada, Australia and Norway. But we have new suppliers of the necessary products:
Belarus,
Azerbaijan,
Kazakhstan,
As well as countries that do not support the adoption of sanctions measures:
-
New Zealand,
Paraguay,
Brazil,
Argentina,
It is worth noting that the change of suppliers does not mean lower prices (according to some positions, on the contrary, their increase is observed). Experts explain this growth in logistics expenses due to the distance between us and suppliers (agree: where Poland, and where New Zealand).
Import of dairy products to Russia
The introduction of sanctions was reflected on the shelves content, for example, it is impossible to find cheese with mold today. However, at the expense of new suppliers, a variety of other dairy products managed to maintain at the same level. Now "Milk" imports of products to Russia are carried out by Belarus (256,758.4 tons of $ 1,817.2 million), Kazakhstan (20,981.2 tons of $ 598.7 million), Argentina (16 481.1 T 78.3 million dollars.), Uruguay (8 373.2 tons of $ 41.2 million).
A comparative analysis of the import of dairy products in January 2016 and January 2017 showed that this year the volumes did not become less, on the contrary, increments increased by 16.7% (milk was taken into account, delivered officially, border trade, not amenable to control Accepted into account).
Most of all increased imports of dry low fat milk from Belarus, Turkey and Argentina, powdered milk powder from 1.5% to 27% supplied by Argentina, Uruguay, Costa Rica and New Zealand, butter from Argentina and New Zealand, Cottage cheese from Kazakhstan Both Belarus, as well as Belarusian cheese products.
As a result, in January 2017, imports of products to Russia amounted to 0.6 million tons (by $ 201.5 million) of milk and dairy products (in terms of milk). The data are official and provided by the FCS of Russia (they do not take into account products entering the territory of the country by entering into individuals by individuals or cross-border trade, because these volumes are not taken into account by customs authorities). Due to the increase in the cost of dairy products in the global market (2nd half of 2016), the cost of "dairy import" to Russia increased by 65.1%.
During 2016, a list of powdered milk supplier countries was significantly replenished, among exporters can be noted Switzerland, Turkey, Moldova, Azerbaijan, Paraguay and Costa Rica. The FCS data suggests that over 11 months of last year, countries that are not members of the EAEU imported more than 32,000 tons in Russia, which is 8 times more compared with 2015.
The Republic of Belarus remains the main partner of Russia in the field of trade, which has a huge impact on the dairy market. The share of the republic accounts for 82% of butter, 87% of cheese, 85% of dry milk and serum, 99% of whole milk from the entire volume of imported products (only official data is presented). Some participants of the "dairy" market have already advanced proposals for the establishment of restrictions on the import of products to Russia, but this issue turned out to be very ambiguous. For example, when in 2016, Rosselkhoznadzor due to violations of technical and veterinary indicators prohibited several Belarusian enterprises to import their dairy products to Russia, the market of dry milk and butter "drank". Due to the excitement by the end of the year, prices in the SCM and oil jumped by 30-40%.

In May 2017, information on the establishment of hard control on the products of nine dairy and combine of the Republic of Belarus appeared on the Rosselkhoznadzor website, since it was their products that did not pass.
The list includes:
OJSC "Slutsky Chemale Plant" with its branches (Kopyl and Lyuban).
OJSC "Baranovichi Milk Plant".
JSC "Kobrinsky Masloryazavod".
OJSC "Pruzhansky Milk Combine".
JSC "Babushkina Kryanka".
OJSC "dairy company Novogrudsky gifts."
OJSC "Molodenensky Material Plant".
Coupups "Mozyr dairy products".
OJSC "Lepelsky Dairy-Canning Plant".
In addition to the above manufacturers, due to the violations detected, the import of products to Russia for PUP "Milk Pole" is limited.
Import meat products to Russia
Until sanctions, 50% of meat came to Russia from the USA, EU, Australia and Canada. To date, this market is divided between Belarus, Brazil, Argentina, Uruguay and Paraguay. Such imports of products in Russia may adversely affect the price, because, unlike the "dairy" supplies, the cost of supplying meat from these countries is higher than those that were proposed before the ban. Today we have the following data:
Uruguay imported 10,442.8 tons by 40.2 million dollars.
Argentina - 28 996.3 tons of 75.7 million dollars.
Paraguay - 53 424.9 tons of $ 215.3 million.
Belarus - 74 796.28 tons of $ 238.16 million.
Brazil - 191 136.9 tons of 741.8 million dollars.
Analytics of the ICAR (Institute of Conjuncture of the Agrarian Market) assessed the situation as follows: Russian meat production increased by 4.4% compared with the 2015 indicators and amounted to 9.9 million tons of slaughter weight. It was possible to increase meat production, mainly due to pig breeding. The share of agricultural producers pork was "2.27 million tons (80% of total volumes), which exceeds the 2015 indicators" by 13%. Poultry farming "promises" to increase supply by 3%, i.e. "By 4.7 million tons, and the supply of beef will not significantly change and will continue at the level of 2015 (1.65 million tons). So, we can note a relatively stable increase (2-3%) supplies of meat from agricultural land.
Importing food to Russia in 2016 to the market of meat and sub-products, according to ICAR, amounted to about 1 million tons. (Which will not exceed 10% of the total meat-selling). The largest percentage of imported meat falls on beef (50%), a little less (30%) comes pork and products from it (spiche and offal), the remaining 20% \u200b\u200bis the proportion of poultry meat supplies. Brazil, Paraguay, Argentina and Belarus are most active in meat-resistant. The total proportion of these countries is 92% of the total meat imported to Russia.
During the first half of 2016, the volume of production of domestic pork has increased dramatically, the indicators of the growth of this market almost 2 times exceeded the growth of poultry meat. In this case, the sanctions went to us for advantage, because the termination of deliveries from the USA and EU countries delivered us from the need to deal with such negative factors as the rise in price of feed and the epidemic of the African plague.
Food security doctrine sets the task: dependence on food imports to minimize. This document was adopted in 2010, precisely when the dependence of the livestock market from imports was the most acute (1/3 of the meat product market was represented by an imported goods), although domestic poultry farming developed a rather rapid rate.
Since 2014, new ways of development of the industry have appeared. The impetus to this was the embargo against the United States, Canada, Australia, Norway and EU member states, when importing products to Russia from these states was discontinued. In 2015, the manufacturers of these countries whose share was up to 45% of the total, completely left our food market. At the same time, the reduction in supplies from South America, who did not fall under the embargo began. Not all CIS countries were able to increase meat supplies, Kazakhstan, Belarus and Ukraine coped with this task. As a result, imports of meat and meat-containing products decreased: in 2014, 1.82 million tons were imported into Russia, and in 2015 about 997 thousand tons.
Such a tendency was possible only due to the fact that the imports replaced due to the ban on the importation of products, the effect of the embargo. It is appropriate to note here that the devaluation of the ruble also had its own positive importance for the liberation of the Russian market from the invasion of imported goods: foreign products began to rise much, so the demand for it began to decline. This, in turn, freed the road to domestic producers. Today, the increase in the release of meat can be observed not only in the poultry farming, but also in other "meat" industries.
Of course, meat production in Russia rose to a new stage of development, but it is also not enough to fully cover consumer demand, including the needs of enterprises producing meat-containing products. For example, in 2015, the consumption of beef decreased (by 6%) due to the reduction of imports of this type of product, which led to a decrease in the volume of sausage products (by 1.5%).
It is worth paying attention to: large agricultural enterprises with their raw materials are in the most profitable position. Manufacturers "Ladge" are forced to get out of the situation using cheaper raw materials and reducing prices for products. However, Russian agrarians solve this problem in two ways: on the one hand, they increase their own production, and on the other, they reduce the amount of consumption. Whatever it was, the import of products to Russia has become much smaller.
Of course, Russian livestock farms faced with many problems, but the industry's rise is obvious. After the devaluation of the ruble and the inevitable rise in price of imported meat, consumers turned, finally, attention to the products of domestic production.
Import of fruits and vegetables to Russia
Earlier, apples were imported to Russia from Poland, but now they disappeared from our counters. Turkish, Argentine, Moroccan, Egyptian and Ecuadorian fruits appeared on the change of Polish. To date, Ecuador (657 620 tons of $ 497.5 million) became the largest supplier of apples. It follows: Turkey (222 166 tons of $ 258.3 million), Egypt (200 233 tons per 188.6 million dollars.), Morocco (180,088 tons by $ 176.5 million) and Argentina (114 021 tons of $ 116.5 million).
The same picture and with vegetables. The main suppliers of vegetables were the EU countries (40% of the market volume). Importing products to Russia from the USA, Canada and the EU cannot be called particularly advantageous for our consumer, since the average price of a ton of vegetables is 40% higher than when delivered from Azerbaijan, Egypt, Turkey, China and Israel. Today, the market is as follows: Turkey imports us 416,058 tons of $ 464.9 million, Egypt - 359,753 tons per 200.7 million dollars, China - 356,826 tons by 290 million dollars, Israel - 243 499 tons of 203.1 million dollars, Argentina - 101 123 tons of 83 million dollars.
The information coming from the FCS (federal customs service) indicates that during the 11 months of 2016, imports of products in Russia decreased sharply (almost 50%). Experts argue that it happened because of the active conclusion on the market of vegetables and fruits of the domestic producer and reduce demand for promonant products that are difficult to call cheap.
According to the FCS, the import of food products to Russia in 2016 decreased in all positions of the assortment series of vegetables. To compare since 2015, the picture is as follows: the cabbage was received only 90,000 tons (50.9%), potatoes - 281,000 tons (51.3%), tomatoes - 419,000 tons (69.3%), cucumbers - 97 400 tons (89.3%), Luke and garlic - 185,000 tons (59%).
More than 50% reduced sugar supply and 84% meat. A slightly increased amount of oil supplied: palm (100.8%) and creamy (101.2%), and sunflower oil volumes were the most significant (164.1%). In addition, more acid-dairy products (105.1%), dry milk and cream (125.8%), citrus and bananas came to the Russian market.
Experts, analyzing the current situation, agreed that such a situation in the market was due to the policy of "substitution of imported goods". The Ministry of Agriculture noted: despite the fact that the import of food to Russia in 2016 was much reduced, some of the market areas were fully secured by the necessary products by the forces of domestic agricultural production.
This is also told in the network of stores "Dixie". During 2016, the proportion of domestic fruits and vegetables entering the trading network has become much higher. For example, the share of Russian cucumbers reached 89% of the total volume, tomatoes - 73%, the proportion of other fresh vegetables reached a 65% mark.
Sergei Korolev (President of the Russian Union of Manufacturers) said that today the volume of incoming and domestic tomatoes are in the ratio of 50x50, although only a couple of years ago, imports of this product amounted to about 80%. As for the cucumbers, earlier we provided the market by only 35%, and today, Russian farmers supply 80% of this product.
At the end of 2015, an embargo was introduced to the import of products to Russia from Turkey, and from 2016, Egypt became the largest fruit supplier. For example, in the first half of 2016, 27% of the total oranges and tangerines arrived from this country. In addition, today Egypt imports the greatest amount of potatoes (48.4%) and Luke (36.6%).
At the expiration of the first half of 2016, the Federal Customs Service noted that Egypt was imported by $ 497.3 million. Fruit and vegetables. In the period from January to June 2015, imports of products to Russia from this country were more (by 583 million dollars).
The introduction of the sanction "took advantage of the Russian manufacturers of vegetables. For example, the volume of internal supply of tomatoes increased by 35%, and in 2015 a kind of record of this vegetable was established (more than 290,000 tons). The proportional ratio of Russian and imported products has undergone serious changes. Compare: In 2012, domestic supplies of tomatoes were only 12% of the total, and in 2016 this indicator reached 40%. In case of extension of restrictions in several years on our vegetable market, exclusively Russian products will be presented. As for cucumbers, their market share is 80%, which is the best indicator.
So, the import of food to Russia in 2016 decreased by almost 60% (vegetables grown in greenhouse conditions). Vegetables grown in open soil are in 90% of cases. Domestic product.
With fruit painting a little different, the share of imported goods is also large on the Russian market. The reason is that the development of a "fruit" production requires a larger amount of time (at least 10-12 years).
In addition, many fruits grow only in certain climatic conditions, and the Russian climate is suitable, probably only for apples. But in this case, 70% of the goods offered are imported apples. During 2016, there was a tendency to reduce supply: the share of imports decreased by 40%.
Import products from Kazakhstan to Russia
The data provided by the FCS, suggests that after the imposition of sanctions, Kazakhstan began to actively import products to Russia. One of the most popular goods became a tomato, its deliveries increased 19 times. For example, during 2013, tomatoes were not supplied, for 8 months of 2014, we received 88 tons, and during the same time 2016 - 1,659 tons. In total, Russia acquired 3,318 tons of tomatoes in Kazakhstan.
Almost 10 times the delivery of cucumbers (from 192 tons to 2,041 tons) and 5 times - cabbage (from 504 tons to 2,618 tons) were increased. The total volume of supplies from Kazakhstan was: cucumbers - 3,414 tons and cabbage - 4,954 tons.
In addition, the eastern neighbors began to supply turnips, beets and carrots (instead of 638 T it was 2,055 tons). In total, more than 4,077 tons of vegetable crops were imported during the Embargo period.
After the imposition of sanctions, imports of products to Russia from Kazakhstan increased almost all positions. So, 1.5 times the supply of eggplants, spinach, celery, mushrooms and zucchini increased (719 tons were 719 tons, it was 1076 tons). The total supply is 5 110 tons, and this is 27 times more than in 2013.
Oddly enough, but less began to import potatoes, bows and garlic (almost 1.5 times). This year, for the eight months, we received 1,690 tons for eight months, although in 2014 the volumes reached 5,040 tons (onions and garlic), and potato volumes decreased to 579 tons (instead of 931 tons received earlier).
For all the time of sanctions, Russia acquired 12,724 tons of Luke and Garlic and 3,956 tons of potatoes from Kazakhstan.

It is best to deal with the supply of berries and fruits. Imports of cherries and cherries, peaches and apricot grew seven times compared to previous supplies. In the period from January to August 2016, 14,782 tons of Kazakhstani fruits and berries arrived at the Russian markets (for comparison: in 2014, only 2,067 tons were imported for the same period.
There was a significant increase in the supply of quince, apples and pears. Over the eight months of 2014, income amounted to 96 tons of these fruits, and in 2016 (during the same period) received 289 tons. The most successful for Kazakhstan was 2015, when the volumes exceeded 780 tons.
In addition to the above products, Kazakhstan began imports of products to Russia, raging the berry market for Malina, blackberry and silky, although until 2015 these berries came to us from other countries. Imported from January 2016, and by August, over 784 tons of berries passed through the counters of the country.
What is important to know, exercising importing food to Russia
As a rule, imports of products in Russia is carried out in winter, and vegetables and fruits are carried away during this period. Because it comes to a product that has a very limited expiration date, he must undergo customs clearance procedure as soon as possible. Today, Russia receives vegetables and fruits from many sources, including Uzbekistan, Georgia, Azerbaijan, Turkmenistan and other CIS countries, countries of the Customs Union, Turkey, Iran, China, India and others.
Imported vegetables and fruits must be accompanied by a phytosanitary certificate of the sender country. Only if it is presence, it is possible to obtain a similar certificate in Russia.
The data on the manufacturer must be contained in the information base of the Rosselkhoznadzor. Importing products to Russia is accompanied by the payment of the established customs duty and taxes. The system of seasonal duties on import is valid for a number of goods.
"Duty-free import" is possible for products from CIS countries and Serbia. For this, it is necessary for the CIS countries the presence of a certificate of form Article 1, for Serbia - Article 2 (only the VAT payment is made in the amount of 10 or 18% of the cost of cargo).
For the successful passage of customs clearance, it is necessary to present a declaration on the compliance with the technical regulations of the Customs Union, which is issued by the authority to accredit in the Russian Federation. The term of document 1 year, cost "6-7 thousand rubles.
Based on the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (Art. 143) and the TC TC (Article 79, 80), the declarant or carrier must pay VAT. If the declaration is carried out by a broker (customs representative), then, in accordance with the TC TC (Article 15), the responsibility for the payment of the tax is assigned to it.
Importing products to Russia is accompanied by an obligatory payment of VAT, which is paid in the recipient country, in other words, it makes the importer. The importation, in accordance with the Tax Code of the Russian Federation (Article 174 of paragraph 1) and with the TC TC (Article 84), is accompanied by the CAT for the customs authority. But if the products comes from the countries with which Russia is in contractual relationships on the abolition of customs control, the VAT is paid to the tax authorities. This is valid, for example, in relation to the countries participating in the Customs Union.
Importing products to Russia is accompanied by a different tax rate (10 or 18%). It all depends on the type of imported goods (the Tax Code of the Russian Federation Art. 164 of paragraph 5). Knowledge of its tax rate is necessary to correctly calculate VAT, for which it will be necessary to make the following actions:
Identify the code of the imported goods, focusing on the TN EAES, approved by the decision of the Eurasian Council No. 54 of 16. 07. 2012
The resulting code to correlate with the goods, which, in accordance with the list, is subject to VAT in the amount of 10%. The list is approved by the Government of the Russian Federation.
If you found the code related to the import of your product, then you pay 10% VAT (for example, live fish). If not - 18%.
VAT for imports is similar to the "internal" VAT, i.e. It is considered as deduction. However, there are certain nuances:
The imported goods are intended solely for consumption within the country, it is temporarily imported, processed in the territory located outside the authority of the customs. The condition must be confirmed by the Declaration accompanied by the goods (as a rule, it is fed in electronic form, but if necessary, it can be printed).
Products are used in operations taxable VAT (NK of the Russian Federation Art. 171 p. 2).
The goods are registered with any account (NK of the Russian Federation Art. 172 p. 1).
The fact of payment of VAT is confirmed by primary documents (Tax Code of the Russian Federation Art. 172 p. 1). However, there is one condition: VAT must pay the taxpayer personally or with the help of an intermediary, but it is possible to use only his funds (letters of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 03-07-08 / 68143 dated December 29, 2014 and No. 03-07-08 / 123 dated 25.04.2011). If the tax payment made a person carrying out the import of products to Russia, then the buyer has no right to deduct VAT (letters of the Ministry of Finance of the Russian Federation No. 03-07-08 / 188 dated June 14, 2011 and No. 03-07-08 / 193 from 30.06. 2010).
The implementation of imports of products to Russia requires a large amount of information about the market, which the company often does not have. Therefore, it is worth contacting professionals. For example, informational and analytical company "VVS" It is one of those stood at the origins of the processing and adaptation of market statistics collected by federal departments. Main Client Categories Companies: Exporters, Importers, Manufacturers, Commodity Markets and Business Services B2B.
Quality in our business is, first of all, accuracy and fullness of information. When you make a solution based on data, which, to put it mildly, are incorrect, how much will your losses cost? Taking important strategic decisions, it is necessary to rely only on reliable statistical information. But how to be sure that this information is reliable? This can be checked! And we will provide you with this opportunity.
 Attention!
Attention!
VVS is not engaged in customs clearance of goods and does not advise on these issues.
This article is exclusively informational in nature!
We provide marketing services According to the analysis of imported and export flows of goods, research of commodity markets, etc.
You can familiarize yourself with the full list of our services.
In contact with
Odnoklassniki.
© Vladv ServiceService LLC 2009-2019. All rights reserved.