The concept and types of innovative strategies. Innovative strategies of the enterprise
Innovative strategies are the vector of development of the enterprise, taking into account directional changes in production.Under directional changes are understood by such innovations in the production, management or assortment of goods, which are determined and controlled by the enterprise themselves. An antipode of aimed change can be considered changes in the background, occurring under pressure from society and competitors.
Innovative strategies for the organization and their functions
In the contemporary market, no production can exist without changes that improve its condition. The higher the level of competition of this product and services, the more active should be an innovative strategy of enterprises producing this product.
In the battle for the buyer, any manufacturer may:
- reduce prices;
- increase product range of the same type;
- increase the variety of all products and services;
- increase the variety of functions of traditionally produced products;
- improve the quality of the goods;
- influence the life cycle of goods.
 In the latter case, measures are being taken to improve the quality of goods, which increases its relevance, but can reduce demand, because the better thing, the longer it serves a person, the less often he buys. You can go on the famous Chinese path of carefully verified hangurial when things are knowingly poor-quality, but very cheap.
In the latter case, measures are being taken to improve the quality of goods, which increases its relevance, but can reduce demand, because the better thing, the longer it serves a person, the less often he buys. You can go on the famous Chinese path of carefully verified hangurial when things are knowingly poor-quality, but very cheap.
The Chinese economic miracle is the implementation of an innovative minimization strategy for the production of goods. This allows you to greatly reduce the price. The low price increases demand. A short life cycle of things this demand increases even more. As a result, a cheap low-quality product, which serves its owner is extremely bad and long, it turns out to be popular and competitive compared with a high-quality product with high consumer properties.
In the fact that the Chinese economic miracle is a consequence of an innovative strategy, no doubt causes, because for its implementation it was necessary to introduce new production cycles, materials and in a new way to organize the entire production process.
 Antipode of the Chinese strategy is the Japanese strategy of technical progress. Innovation allowed Japanese electronics manufacturers, cars and household appliances to seize their market niches due to high quality, diversity of functions and assortment.
Antipode of the Chinese strategy is the Japanese strategy of technical progress. Innovation allowed Japanese electronics manufacturers, cars and household appliances to seize their market niches due to high quality, diversity of functions and assortment.
Thus, the strategy of innovation in the modern world performs functions:
- increasing competitiveness;
- reducing the cost and product price;
- creating a brand as a way to hold a market niche;
- enhance the sustainability of the company's development.
Types of innovative strategies and their features
Innovative strategies have a significant impact on the fate of the enterprise.
In modern market conditions, they are an integral part of the general strategies of most organizations. For this reason, scientists allocate many different types of strategies.

- Offensive innovation strategy. Combines both high risk levels and high efficiency. The choice of this strategy requires high costs for applied and fundamental research. Some large firms spend money both on the maintenance of their own research teams and on financing the areas of work of research organizations, individual scientists and inventors, as well as on the permanent purchase of ready-made technologies. The high risk of this strategy should be compensated by the ability to quickly develop new technologies in production. Management and Marketing. Such a strategy can be implemented mainly by large associations and companies. For small enterprises, an offensive strategy may be available subject to specialization in a small number of innovative projects.
- Protective strategy of innovative development. It has a low level of risk with high technical and technological potential, as well as a firmly held market niche. Organizations that adhere to such a strategy produce high-quality products at stable low costs. Such organizations maintain a sustainable position in marketing and production, but lagging behind in research and innovation work. It creates risks of the loss of a market niche. The development of an innovative defense strategy is aimed at reducing this risk.
- Intermediate strategy. It uses the weaknesses of competing manufacturers and their own strengths in the absence of direct confrontation with competitors. Most often, this strategy is chosen by small enterprises that have their own market specialization. The increase in competitiveness is determined by the fact that the enterprise, using its own studies, identifies gaps in the market niche of its competitors and fills it with a similar product with modification differences. Usually such a strategy is implemented in the market of high-tech goods.
- Absorbing strategy. A distinctive feature of this strategy is to use new technologies and other innovative achievements developed by other scientific or scientific and manufacturing organizations. The choice of an innovative absorbance strategy can be made by manufacturers of any level. It is forced to choose even major firms with their research structures, since it is not able to cover the whole range of developments in various industries.
- Simulation strategy. Almost this version of the absorbing strategy, since the manufacturer in this case uses the development available for it, performed in other organizations with its own modifications. Usually these enterprises have the long-standing traditions of high production culture and are steadily held in their market niche. Such simulators of the innovation process often quickly bypass initial innovators, because they use flexible maneuver policies in a constantly changing market.
- Robbery strategy. The name of this strategy is not associated with illegal or ethically not correct actions. The company becomes a robber when its innovative strategy is sent to the implementation of fundamentally new developments. This new product for the market and society is collapsed by the market of old goods and creates large problems with their manufacturers. A vivid example of such collapsions can be considered the appearance of calculators that have entered the arithmometers and scores, mobile phones who have undermined the monopoly of the phones of wired, computers who have fallen into the market of printed machines.
This strategy most often enjoy small innovative organizations that still specialized in the release of goods from other areas and niches. These are organizations that rushing radically change their production for the sake of survival and capture a new niche. And not their fault is that they are inappropriately changing the world.
Types of strategic innovative behavior of organizations
The formation of an innovative strategy of the enterprise depends, of course, from the will of his leadership and the team. However, not all so simple. Any decision-making entity is always in the vice of objective reality and limiting factors. Within this framework, he is trying to take the most optimal solution. Actions to make decisions under pressure from objective reality, it is customary to be called the behavior of organizations, and any behavior is always implemented according to certain rules. These rules, as it turned out, is so universal for different systems, which is the basis for the classification of types of strategic competitive innovative behavior of organizations, a biological approach to the classification of competitive behavior, developed by the Russian scientist LG, was found. Ramensky for environmental systems. All systems are self-organized by similar programs, in this regard there is no significant difference between the strategic behavior of the Christmas trees, birch, larch, TNC, the network of grocery stores and a small brick stock company. According to this universal approach, strategic behavior can be divided into four types.

- Cellular. In all complex systems, the viruses are leaders who have a monopoly position. Their behavioral strategy is not aimed at the conquest of new niches, but on confident retention of previously engaged. This is a strategy characteristic of large companies, TNCs carrying out mass production. In the choice of innovation strategy, they are most often limited to such species as a protective or intermediate strategy.
- Patient. Patients are narrowly adapted parts of the system. The economy includes enterprises that occupy narrow niches and often specializing in the release of new or modernized products with unique characteristics. It can choose a robbery strategy and change the world of consumption and production.
- Exceler. Experiencers are the types of organisms and organizations that survive at the expense of a constant flow from some conditions to others. Such manufacturers often enter the market with an innovative product, exciting with its help part of the market, not occupied by other organizations.
- Total. This is a special state of extensors that adapt to the conditions of the local market, swaying into small niches, not occupied by virus and patient. Their winning strategy is an innovative imitation. It is she who allows you to quickly maneuver between large manufacturers, mastering new services and products.
Factors affecting the choice of innovative strategies in the enterprise
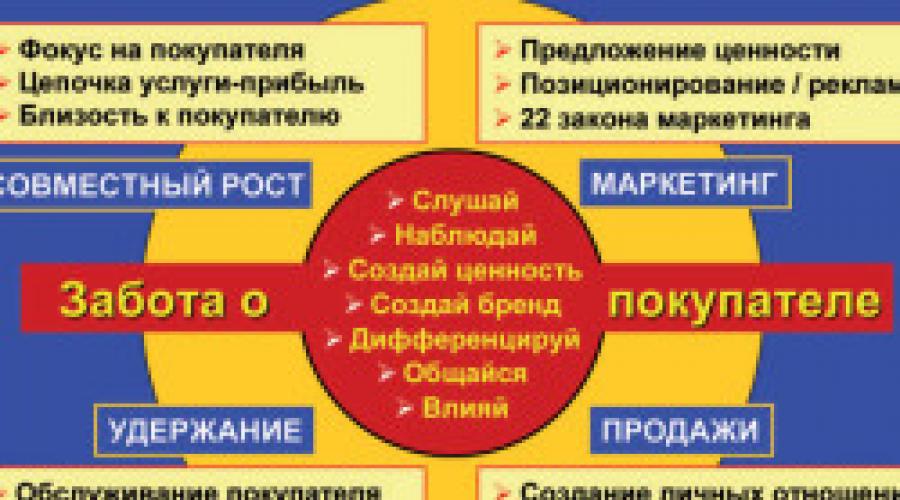
An innovative strategy of an enterprise is a set of measures and actions aimed at developing an enterprise, an increase in income, stabilizing the position in the market. The difference from other strategies is that the innovative strategy is the direction of searching for a new way both for production and to manage the organization. Decisions on the choice of such a strategy are made on the basis of accounting of the following factors:
- Investment opportunities of the enterprise.
- The provisions of this organization in the market.
- Market states regarding new or modified products.
- Peculiarities of marketing actions and opportunities for the formation of demand for new products.
Any innovative strategies contain a certain risk that can be acceptable for one enterprise, and for another unacceptable. Decision is always searching for a compromise between acceptable and permissible.
Federal Education Agency
State Educational Institution
Higher professional education
"St. Petersburg State University
Economy and Finance "
Department of Economics Enterprise and Production Management
Test
in the course "Innovation Management"
On the topic: "Innovative strategy of the company"
student 5 Course Group 556
specialty Management Management
Gerasimova M. V.
cANCING BOOK №098736.
Introduction 3.
Concept Innovation Strategy 5
Types of innovative strategies 8
Choosing and developing an innovative strategy 10
Innovative strategy of the Corporation "General Electric" 20
List of literature used 23
Introduction
Modern economy can be called a "innovative economy" with confident. The development and implementation of new types of products, technologies and services becomes one of the key factors of competitiveness and the main strategy of enterprises. In order to fully understand what kind of "innovative strategy" is, I begin my testing with more general definitions.
Innovative Management 1 - A interconnected complex of actions aimed at achieving or maintaining the necessary level of viability and competitiveness of the enterprise using innovative processes management mechanisms.
Innovation and innovative process are innovation.
Innovation 2 (Eng. Innovation) is an introduced innovation that provides high-quality growth in the effectiveness of processes or products, in demand by the market. It is the end result of the intellectual activity of a person, its fantasy, creative process, discoveries, inventions and rationalization. An example of innovation is to remove products to the market (goods and services) with new consumer properties or a qualitative increase in the efficiency of production systems.
In accordance with international standards innovation it is defined as the final result of innovation activities, which has embodied in the form of a new or improved product introduced in the market, a new or improved technological process used in practical activity, or in a new approach to social services.
Innovative process 3 - This is the process of consistent transformation of ideas to the goods, the passing stages of fundamental and applied research, design development, marketing, production and sales.
Innovative activity of the company 4 - It is the preparation and implementation of updating products (services) and production (fixed assets), including the creation of new products and technologies. Innovative activity is the main means of developing an enterprise, improving the efficiency of production, quality of product quality and competitiveness.
In accordance with the legislation of the Russian Federation, innovative activities include:
research, applied and experimental work necessary to create innovations;
work related to the creation of experienced and serial samples of new products and technologies;
work related to the preparation of production and conducting industrial tests;
work related to certification and standardization of innovative products;
work related to marketing research and organization markets for marketing innovative products;
all types of mediation and other types of work, interconnected into a single process in order to create and disseminate innovation
One of the main tasks of innovative management is to develop a strategy of innovation themselves and measures aimed at their incarnation. R & D, the development and production of new types of products becomes the priority direction of the company's strategy, as it determines all other areas of development.
Concept of innovative strategy
In its general sense strategy It can be defined as a set of actions taken by the enterprise to achieve the corporate goals.
Innovative strategy 5 - these are targeted activities to determine the most important ways, selecting priorities for promising development of the enterprise and the development of the set of measures required to achieve them.
The innovative strategy of the enterprise should increase and / or maintain the competitive status of products manufactured by the enterprise.
It should be noted that the essence of the current stage of development as a national economy as a whole and individual enterprises reflects such a category as "innovative development."
At the same time, the innovative development of the enterprise is not only the main innovative process, but also the development of a system of factors and conditions necessary for its implementation, that is, innovative potential.
Therefore, it can be said that an innovative strategy of an enterprise should reflect the content and main directions of the process of innovative development of the enterprise.
An analysis of modern innovative issues makes it possible to allocate the following main types of innovation:
Innovation of products 6 (services) is the process of updating the sales potential of an enterprise that ensures the survival of the enterprise, expanding its share in the market, the maintenance of customers, strengthening the independent position of the enterprise, etc. Innovation of technological processes, or technological innovation - is the process of updating the production potential of the enterprise that is sent On the growth of labor productivity and resource savings, which, in turn, makes it possible to increase profits, improve safety, conduct environmental activities, introduce new information technologies, etc.
Organizational innovation 7 It is the process of improving the organization of production and management at the enterprise.
Social innovation 8 - this is the process of improving the social sphere of an enterprise, which mobilizes staff to implement the company's strategy; expands the capacity of the enterprise in the labor market; Strengthens the credibility of the company's social obligations to employees and society as a whole.
When formulating an innovative strategy, a number of external and internal factors should be taken into account, among which are forecasts of the economic environment, an analysis of the potential of the enterprise, the correspondence of innovation of the general strategy of the enterprise, etc. The innovative strategy binds together the general strategy of the enterprise, an analysis of the economic environment, scientific and technical, personnel, resource potential of the enterprise and specific innovative projects. The main elements of the innovative enterprise strategy include 9:
improvement of already manufactured products and used technologies;
creating and mastering new products and processes;
improving the quality level of the technical and technological, research and development base of the enterprise;
improving the efficiency of the use of personnel and information potential of the enterprise;
improving the organization and management of innovation activities;
rationalization of the resource base;
ensuring environmental and technological safety;
achievement in the domestic and foreign market of competitive advantages of the innovative product in comparison with similar purpose products.
Analysis of the innovation situation that established at the enterprise should be the initial moment of the process of forming an innovative strategy of the enterprise. It should begin with a brief description of the main goals and objectives facing the enterprise in this field of activity. At the same time, special attention should be paid to analyzing and evaluating the market position of the enterprise. At the same time, it is advisable to give a description: the innovative potential of each produced goods or groups of goods; used at the present stage of innovative strategy and tactics; allocate and evaluate the specific factors of the outer and internal environment; Analyze and assess the positions and actions of competitors.
The identification of innovative opportunities and shortcomings in the innovative development of the enterprise is advisable to implement in order to assess the innovative opportunities that arise from him, as well as expected dangers. This phase should contribute to the implementation of the processes of prediction of changes in the economic situation in the enterprise in the implementation of innovative planning. It should be noted that great opportunities provide computer technologies. Moreover, it is necessary to use precisely specific, innovative advantages of these technologies.
In general, an innovative strategy of an enterprise (strategy of innovation) can be described as a certain logical construction, on the basis of which an enterprise solves the main tasks facing it in the innovation field of activity. It should be borne in mind that both for each individual innovation and each produced goods (services) there are strictly individual strategies and tactics. At the same time, a comprehensive vision of innovative activities of the enterprise includes both specific strategies and various aspects of the production and implementation of innovation. In addition, it is necessary to provide a real estimate of costs and results from innovation in the enterprise.
Types of innovative strategies
You can select the following types of innovative strategies 10 .
1. Offensive strategy. It is characterized by a large risk and rapid payback in case of the success of innovation in the market. Requires high personnel qualifications, the ability to see new market prospects and the ability to quickly embody them into products. It requires a research orientation in combination with the application of new technologies. As a rule, large firms are resorted to an offensive strategy - market leaders in competitive industries, where the leaders' positions can be undermined as a result of the introduction of more advanced products in scientific and technical terms.
2. Defensive strategy based on the rapid introduction of imitation reactive innovations in response to the actions of competitors. It implies a low, compared with the offensive strategy, risk. This strategy is suitable for large companies with a sustainable market position and paying more attention to production and marketing issues than R & D, however, with significant scientific and technical potential for a rapid response to the actions of competitors. In innovation, these enterprises are focused on the development and adaptation of existing advanced technologies.
3. Licensing (absorbing strategy). It is based on the acquisition of the best scientific and technical results obtained by other enterprises during R & D. Even large companies leaders cannot be limited to the results of their own research and development. On the other hand, the sale of a license for their own innovations can be a significant element of the offensive strategy of the enterprise. The same is true for small enterprises, which, due to the limited of their own financial resources, cannot fully independently implement major innovative projects.
4. Intermediate strategy related to the search for market niches. It is built on conscious efforts aimed at avoiding direct competition, based on the analysis of the weaknesses of competitors, taking into account their own advantages. This strategy is often successfully applied by enterprises of small innovative business.
5. Creating a new market. Associated with radical innovations. In this case, you can achieve a high rate of profit without substantial risk. However, such innovations and the possibilities that are covered in connection with their implementation are rather rare. As a rule, they occur in the early stages of the industry or market.
6. "Robbery" strategy It allows you to apply new advanced technologies strong in technological and production relation, but unstable enterprises in the market to supply a new product when this innovation reduces the total market volume. In this case, market leaders are not inclined to implement an innovation, since it can create a threat to their positions. For enterprises resorting to the "robbery" strategy, it is important to keep in mind that they will be able to achieve sustainable success in the case when they will use the offensive strategy after entering the market.
7. Attracting specialists. This strategy allows you to acquire knowledge, experience, skills, and in some cases - know-how with minimal cost. Many enterprises themselves are not engaged in vanishing specialists from ethics considerations and prefer to contact the help of recruiting agencies.
Innovative Coursework \u003e\u003e Management
... strategy firms; Consider the relationship of investment and innovative processes. Consider the role and sources of investment in innovative strategy firms. 1. The relationship of investment and innovative ...
The choice of strategy is the key to the success of innovation. The firm may be in the crisis, if it does not be able to anticipate the changing circumstances and respond to them on time.
The choice of strategy is the most important component Cycle innovative management.
Strategy - This is a detailed comprehensive integrated plan for achieving goals.
Innovative strategy - One of the means to achieve the objectives of the organization (corporation, firms), differing from other means of its novelty, primarily for this organization and, possibly, for the industry, market, consumers.
Innovative strategies can be:
· Innovative organization activities aimed at obtaining new products, technologies and services;
· Application of new methods in R & D, production, marketing and management;
· Transition to new organizational structures;
· Application of new types of resources and new approaches to the use of traditional resources
There are many classifications of innovative strategies
Allocate the following types of innovative strategies:
According to the manager's "behavior", on the basis of the C. Friman classification, the following modifications of the innovative strategy of the enterprise are distinguished.
Offensive- Ambition in this case is to be the first in the market. Characteristic to firms based on their activities on the principles of competing. It has a big risk and high possible payback. It requires managers of a certain classification in the implementation of scientific and technical innovations, the ability to issue new market prospects and changes to quickly realize them in products. In most cases, research is needed in combination with the application of new technologies. Such firms seek to be the first on the market, which requires its management of high organized and qualifications, the search for effective innovation, active R & D, marketing management system. This is a merger strategy, acquisition strategy. It is characteristic of small innovative firms.
Defensive -it is aimed at keeping the competitive position of the company on the existing markets. The main function of such a strategy is to activate the "cost - result" ratio in the innovation process. Such a strategy requires intensive R & D enterprises to conduct research and developments without claims to occupy leading positions, their goal is to keep up with others in the field of technical and technological development and increase the technical level of production. This is a very expensive strategy. It is mainly used in separate (state) research institutions.
Intermediate- comes down to reasonable competition. Success is achieved at the expense of independent effectively innovative policy in order to keep up with the leading company, while at the same time it is necessary to avoid risk in the high-level consumer market with careful selection of products. Such a strategy can be called passive, as it means a change of goods, which does not require major changes in the means and technologies of production, does not need significant additional costs of mental labor, does not lead to indigenous changes in technical and technological characteristics.
Protective- involves high risk and suitable for firms capable of making profits in competition. To do this, it is necessary to conquer a significant market share and maintain the rate of profit by means of low production costs. As foreign experience shows, the success of the firms that have strong positions in production and marketing. At the same time, it is necessary to maintain sufficient scientific and technical potential to quickly respond to innovations implemented by a competitor.
Traditional -it is aimed at keeping the available positions in the market, the company seeks only to improve the quality of existing products. It concentrates the attention of the enterprise to the actions of competitors and responds to a lesser extent to the needs and behavior of consumers. Therefore, for sure in the long run, it will first be laid in technical and technological, and then economically.
Opportist -the company is engaged in the search for such a product that does not require too much costs of research and development, but with which it will be able to single in the market for a certain time. The search and use of such sectors suggest deep knowledge of the market situation, a high level of technical and technological development and adaptive abilities. In this case, the degree of risk of rapid loss of the monopoly position is high.
Imitation - Used by firms that have strong market and technological positions. It is used by firms that are not pioneers in publishing a market for certain innovations that copy the basic properties of the product manufactured to the market in innovative firms. At the same time, the main consumer properties (but not necessarily technical features) of innovations issued to the market with small innovative firms or leadership firms. The innovative strategy comes from the principle of "time - money". The new technology is purchased from others, for example, by purchasing licenses. The license is much cheaper, acquired faster and acts more reliable than its own developments, inventions. This is a successful strategy, but to adapt the original and creating a monopoly situation of the mental labor product (invention), high special qualifications and tireless maintenance of the achieved level are necessary. This type of strategy is also called adaptation.
Dependent -it is observed mainly in small enterprises, which are large to impose a new product or production method. Characteristic for franchising firms.
Absorbing- refers to cases where the acquired license is implemented in fundamentally new products with high profit and new market.
Innovative enterprise strategies (L. Kudinov), can be divided into two main groups:
1) strategies for NIO CRP - related to the company's research and development. They determine the nature of the borrowing ideas, investment of R & D, their relationship with existing types of products and processes;
2) strategies and adaptation of innovations - refer to the production update system, the output of products to markets, the use of technological advantages
Briefcase of innovative strategies It is formed under the influence of various factors of innovative development. Their level is determined for each enterprise separately. For the purpose of growth in production, various strategies are applied at high and low level of factors of innovative development.
Types of behavior of firms on the market: strategies for exchers, fusion, patients, commutants
The implementation of the innovative strategy of the company largely depends on its organizational form and competitive behavior. To analyze the position of the company, it is necessary to clearly submit to how its scientifically gathering, technological, personnel and organizational resources correspond to market needs and what should be taken to achieve such compliance with minimal costs.
A.Yu.Yudanov, depending on these indicators, the company is divided into four types: cellites, Communities, Patients, Experiencers. H. Friesievinkel associated the behavior of firms with competitive behavior in the animal world. The table shows the comparative characteristics of firms corresponding to the type of strategic competitive behavior.
It is important to realize that the strategy determines the direction of the company's movement to the implementation of the goals. It does not contain a specific algorithm for action and responses to problematic issues. For example, an innovative development program will help to cope with the difficulties of the already current strategy.
General information about innovation strategy
Modern strategic innovations are a totality of rules, actions, intermediate goals and methods for increasing financial capital and work efficiency.
This strategy opens a new look at the supervisors to the existing problem, helps to solve it with new, more efficient ways. It is accompanied by both the specifics of the field of activity and the work of the organization itself.
Features of the innovative strategic behavior of the enterprise are as follows:
- Changes in all managerial and production levels.
- Enhancing the risk level of the company.
- Risk risks associated with investment investments.
The best solution of the head who has chosen the innovation program will be a skillful combination of stability and gradual introduction of innovations.
Classification of strategic innovation
Experts identify certain types of innovative strategies.
Defensive
This type of strategy is used by companies that have an unchanged market share with decent production technology, competent personnel.
An organization that has chosen a defensive program, puts on the first plan to preserve and strengthen existing positions.
Imitation
The essence lies in the "imitation" of competitors products. The prerequisite is to introduce innovations into old products (new components, designer design, manufacturing technology), which should attract new consumers.
This program is in demand among enterprises that have strengthened in the market and have the opportunity to save a budget. Acting according to a specific algorithm, the company will be able to drag customers and bypass a competitor.
Offensive
Encompasses a detailed analysis of the sectoral market on the profitability of the production of high-tech products. It is popular among large organizations that are able to conduct tough competition and with a staff of high-income employees.
You can choose this program and small companies, but you need to make a lot of effort to achieve positive results.
Intermediate
Choosing this strategy, the company must analyze the market and, as a result, find the strengths and weaknesses of competitors. The next task of the enterprise is to skillfully use the "gaps" found and fill them with their own products (service).
Robbery
The program is highly efficient at the initial stage of development of the enterprise. It implies the release of a large number of standard product with a certain novelty to its development. The main task is to extend the operational period of products.
To do this, the product of the opponent can be used, but a serious technical base is needed to improve.
Absorbing
The absorbing system is often used in the complex with others. By producing its own products, the strategy involves the use of both its scientific developments and other people (with a discouragement of all rights). To buy out other people's ideas is easy if they are not suitable for the company's requirements that were created. Sometimes it brings the result.
Selection methods
There are several methods for selecting strategic innovation:
- Analysis of vocabulary and terms. The possibility of transition of terminological units from one field of activity to another is analyzed, which allows you to argue about the possibility of developing a new entrepreneurial branch and draw up its strategy.
- Determining the parameters of publishing activity. Publications about the enterprise are studied as a holistic organism, based on what conclusions are made and relevant recommendations are given.
- Method of proportions. The documents on the dynamic movement of indicators of global technostulas are underway on the basis of development recommendations.
- Structural morphological analysis. Tracking innovations, fixing them and creating business principles on this basis.
- Patent analogue method. The world experience is taken into account; The concept patented during the reporting period is considered and trends are determined, in accordance with which the development path is elected.
Development of strategic innovation
When developing a strategy, it is necessary to take into account the stages of the life cycle of products: the origin of the idea, the birth of the product, its approval on the competitive market, stabilization, simplification, the fall in demand, the outcome, complete cancellation of the release and search for a new idea.
With strategic planning it is important to clearly determine the outcome of the production of one product and the origin of the other. For this, the entrepreneur must be aware of new trends in the market and invest in their capital investment.
The development of an innovative program can be engaged in both special employees (there is even the position of the director of innovation) and the head of the company himself. In the latter case, two options for the development of events are possible:
- The strategy is developed "from above", and its provisions are communicated to the divisions.
- The divisions themselves form a package of proposals for management, on the basis of which a strategy is formed.
Each of the versions involves risks and temporary factors.
The successful work of the organization depends on the competence of personnel composition, management style of the head and many other factors. Sophisticated this mechanism will make a properly selected strategy for the development of the enterprise. Knowing the types of strategies and ways of their applications described in this article, the founder easier to make a choice in favor of a particular program.
The strategy is a comprehensive comprehensive plan of action to achieve the objectives of the organization. The main task of the strategy is to translate the organization from its present state into the desired future.
The feature of innovative strategies is to choose the directions and determination of the proposed changes. At the same time, their scale and the desired rates depend on the possibilities of the enterprise to realize (innovative potential) and the state of the external environment (innovation climate).
Innovative strategies Enterprises (organizations) are developing to achieve the following purposes:
- ensuring the competitive position of the enterprise (organization);
- reactions to the influence of the external environment;
- opportunities using predominantly product-innovation
take another previously occupied market niche;
- opportunities to go from competition by creating a new market niche;
- Opportunities to increase production production (works or services).
The basis for developing an innovative strategy is the goal of the company, the theory of the life cycle of the product, the market position of the company and its scientific and technical policy.
Depending on the objectives of the company allocate four types of strategies (or four types of companies): COLORTS, Patients, commutants, Experchents.
Table 8.1.
Characteristics of competitive strategies _
|
Competitive strategy |
Innovative |
condition |
Competitive advantages |
Quality product |
|
|
Vivent |
New, mastered |
High Performance, Low Prices |
|||
|
Patientaya |
Mastered |
Maximum adaptation to a specific market |
|||
|
Genty |
Mastered |
Flexible reaction to the market needs |
|||
|
Exceler |
Using innovation |
Cellular (powerful) strategycharacteristic for firms operating in the field of large standard production. Fundamental source of forces - mass production of good products (medium) quality at low prices. Due to this, the firm provides a large supply of competitiveness. The motto of firms: "cheap, but decent" (but not "expensive and bad"). Depending on the dynamics of development, several types of virulents are distinguished.
Lions are large firms, leaders in a number of areas of innovation activity, for them the aggressive nature of competition and large costs for R & D are typical.
Elephants are particularly large firms, leaders in one-two directions of innovation activity that have a large network of foreign branches and a niche nature of competition.
"Hippopots" is a large amount of excessive diversification, they are characterized by the increase in the technological lag, small expenses for R & D and the passive nature of competition.
Patent (niche) strategy("Surgery Lisa") is typical for firms in the path of narrow specialization for a limited circle
tweets. They address their expensive and high-quality goods to those who do not suit ordinary products. Their motto is "expensive, but well." They seek to avoid direct competition with leading corporations. For domestic firms, this strategy can be accepted as entrepreneurial philosophy. She calls for not fighting directly with leading corporations, but to seek unavailable areas of activity. This approach seriously increases the chances of weak in rivalry with strong. These firms are profitable. At the same time, there is a possibility of making an incorrect decision leading to the crisis. In such firms, it is advisable to the position of a permanent innovative manager, designed to secure their activities. The main goal of the innovation manager is to reduce the risk in the life of the company.
Puttan (connecting) strategy("Gray Mouse") prevails with ordinary business in local (local) scales.
The power of the local non-specialized enterprise is in its best fitness to the satisfaction of small volumes (and often short-term) needs of a particular client. This is the way to improve consumer value not at the expense of ultra-high quality (like a patient), but at the expense of individualization of the service. "You pay extra for the fact that we solve your problems" - the slogan commutants. Celllets and patients can not always satisfy individual needs, then switches are performed on the stage, ready to use any opportunity for business. Increased flexibility of commutants allows them to hold their position in the competitive struggle.
An innovative manager of such a company should well understand in the specifics of the buyer of goods, the situation in the market, accurately, promptly and reliably anticipate possible crises. Passionate strategy is characteristic of many private Russian firms.
Exceler (Pioneer) Strategy("The first swallow") is associated with the creation of new or radical transformation of old market segments, it is "pioneers in finding and implementing revolutionary solutions preferably the first move." Among them are pioneers in the release of personal computers, biotechnologies, robots, etc. They work in the "surroundings" stage of the maximum cycle of inventive activity from the very beginning of production.
The power of extensors is due to the introduction of fundamental innovations, they benefit from the initial presence in the market. In 85 cases, they suffer from 100, but due to 15 cases, a huge technical, financial and moral success is obtained. They are engines of scientific and technological progress. Explorer motto: "Better and cheaper, if possible."
In front of the company-expirept (pioneer) there is a problem of production, when an attractive novelty has already been created for the market. For this, the extensors conclude an alliance with a large firm. The extension cannot independently replicate the proven innovations. Deletion with replication threatens the appearance of copies or analogues. The union with a powerful company (even subject to absorption and subordination) allows you to achieve favorable conditions and even preserving the known autonomy. The choice of such a partner depends on the specifics of the consumer.
Depending on the market position of the company Allocate the following types of innovative strategies.
- 1. Offensiveproviding technological leadership by independently developing and implementing a high degree of radicalism innovations.
- 2. Defensiveaimed at keeping the competitive position of the company on the existing markets. The main function of such a strategy is to intensify the ratio of "cost-results" in the innovation process. Such a strategy requires intensive R & D.
- 3. Imitationfocused on dynamic reproduction of technological leadership achievements and the effective development of free market segments.
Consider these innovative strategies in more detail. Offensive strategy The development of the enterprise involves the development and implementation of the innovation of a high degree of radicality based on large inventions or even discoveries. It covers the full life cycle of innovations, as a result, the longest and resource-intensive. Intellers to use this strategy to significantly coincide with the motivation of the development of radical innovation.
An offensive strategy is the role of pioneer. The company based on this strategy offers products, services, technologies that are fundamentally new ones in the global or national market. The purpose of the offensive strategy is to gain a leading position in the market. The development and implementation of large-scale innovation earlier than competitors becomes a necessary and important condition for the implementation of this strategy.
For its implementation requires the following conditions:
- Effective innovative activity;
- The management of the company, prone to new ideas;
- good market knowledge;
- effective marketing;
- Employees of a creative warehouse;
- The possibility of risk distribution.
A prerequisite for the offensive strategy is technological jerk and a quick response to market changes due to flexible organizational structure and available unique resources.
The main competitive advantage of innovators is that due to the created and accumulated specific knowledge and skills, they are able to make an innovation better than their competitors. Technological breakthroughs are provided by the presence of specialized research laboratories and engineering and technical divisions; The presence of high technological potential exceeding the need of current production.
The offensive strategy is characterized by high R & D costs, as a rule, provides a high rate of profit, but has an increased risk, which can be a consequence of technical failures, poor choosing the moment of product implementation.
Several innovative offensive strategies are allocated.
- 1. Creating a new market - A rather rare strategy when, based on a new idea, a unique product is produced that has no analogues. Such a product at one time has become television gaming consoles. It is implemented by an enterprise with a sufficiently strong division of R & D engaged in diverse studies, including interdisciplinary. The conducted studies are aimed at fulfilling promising fundamental developments that contribute to the occupation of a monopoly marketplace. The restriction is acting antitrust law, prohibiting more than 35-55% of the market. Contrary to ideas, only a truly new product brings the highest return, and the imitation of these goods is more risky than the independent development of new products: anyone who imites others will certainly face competition. True, only the development of unoccupied market segments is given.
- 2. Purchase of Companies - A strategy involving the acquisition of a company with significant intangible assets (development and technology, methods and business models, engineering and technical workers, market image, etc.). As a result, a new enterprise is being formed and a significant expansion of its market is ensured.
- 3. "Robbery" strategy. Its essence is that on the basis of the new technology, the company produces to the market from
a good product that has significantly improved characteristics, which reduces the total market size. An example is the drugs of prolonged action and others.
- 4. Continuous Improvement Strategy (Kaisen) It is to improve production technologies and quality due to highly educated and professionally trained personnel, which is given a key value. This is a strategy of leading Japanese firms that every day, even hourly, carry out minor improvements in all concerning production.
- 5. Strategy of comparative advantages Based on the production of a product that combines the properties of several goods, without deteriorating the characteristics of the base product (for example, the production of mobile phones with built-in video cameras). The application of this strategy is caused by the employment of traditional markets and the need to search for an unoccupied niche. It requires active R & D, high level of technology.
Defensive or stabilization innovative strategy Used by firms that do not claim to the championship of bringing innovation to the market, but seeking to keep their positions. As a rule, the innovations of recognized leaders are borrowed with some changes to the products, i.e. Products are created.
At the same time, the company refuses the possibility of a high level of initial income in exchange for the safety of late market, which is ensured by knowing the results of the sale of the product. In addition, the costs of developing innovation, marketing and advertising are reduced. Therefore, the costs of R & D and the commercialization of innovation in this case are lower than that of the leader. This is a low innovative risk strategy. Several options for innovative strategies aimed at preserving and strengthening positions in the market and in the industry are allocated.
- 1. Opportunist strategy - The company is engaged in the search for such a product that does not require too much costs of research and development, but with which it will be able to single in the market for a certain time. The search and use of their niches implies a deep knowledge of the market situation, a high level of technical and technological development and adaptation abilities of the company. As a rule, these products have patent protection (patents for useful models, industrial samples).
- 2. Dependent strategy suggests that the company is focused on the development of goods and technology of large leading
companies. Its purpose is self-preservation based on the implementation of contractual work for these companies. It is widely used in the production of parts for plants for the assembly of finished products (for example, automotive plants in Japan).
- 3. Protective strategy It is based on the fact that research and development are conducted without claims to the work of leading positions and their goal is to keep up with others in the field of technical and technological development and, if possible, increase the technical level of production.
- 4. Selective (selective) strategy It involves the concentration of resources at certain, most effective directions, which creates conditions for the transition to an offensive strategy.
Simulation strategy It assumes copying in real investment of technologies and (or) products previously used or manufactured by technological leaders, in a constant or modified form.
In this case, the technology or product is purchased from other enterprises, for example by purchasing a license. Often for firms a license is much cheaper, it is most likely becoming more reliable than holding its own R & D. This is a successful strategy, but to adapt the invention as an original and creating a monopoly product situation, a high technological level of production, professionalism of engineering and technical workers, workers who can quickly master the "alien" development are needed to the conditions of concrete production.
Using simulation strategy It can be based on the unfilled dynamically growing market, which the firm is a technological leader for some reason cannot completely occupy.
There may be the following reasons for the inability of the technological leader to master the market independently:
- non-compliance of innovation by existing product lines;
- The high value of the transaction costs for imitation is over the cost of patenting;
- lack of finance for mastering and promoting innovations;
- Obstacles to the comprehensive capitalization of innovation from
When using a simulation strategy, an innovative risk disappears, a technological risk is reduced to a minimum, commercial and financial risks are reduced.
This caused the latitude of disseminating a simulation strategy in world practice.
The effective use of this particular strategy was one of the main conditions for the emergence of the so-called "Japanese Economic Miracle" in 1960-1970. For Japanese firms, at that time, an active adaptation of other people's achievements was characterized, leadership at the stage of development and expansion in narrow segments of fast-growing markets by price competition provided by savings. The technological level of the Japanese industry formed during these decades was the basis of the fact that in the 1980s. Japan has become not only a global technological leader, but also an innovative leader in many high-tech industries, in particular, occupying the first place in the world by the number of patents in the automotive industry.
For the development of the Russian economy, the use of all three strategies and offensive, and defensive, and imitation. This is also stated in the Concept 2020 that Russia is faced with the task at the same time advanced and catching development.
An offensive strategy (advanced) is possible for those industries and enterprises where there is a serious scientific bore.
Modern Russian science in many fundamental areas of knowledge did not lose its global level and is able to answer innovative challenges, primarily in the field of physics, mathematics, chemistry, physiology, medicine, as well as on the applied developments of laser and cryogenic equipment, new materials, aerospace technology , A number of samples of military equipment and technologies, communications and telecommunications, computer science, software for computer, etc.
In our country, there are still powerful scientific and innovative bindings on nuclear, cosmic, aircraft technologies, in the production of weapons, chemical, energy, transport engineering, as well as separate technologies in oil and gas production, processing and in the chemical industry.
In Russia, global positions in 17 priority scientific and technological developments are maintained, and about 20 critical technologies developed in our country correspond to the world level, which in the aggregate is about one third of world research in the field of high technologies. For example, the competitive technologies created by Russian scientists at the borders of the new millennium can include aerospace, nuclear-energy and laser technologies, the development of a fundamentally new medium of information - three-dimensional optical electrical memory continues. The successful implementation of this promising project can turn the most modern information technicians.
nologis in the technology of yesterday. In addition, breakthroughs in new directions for the study of information and communication systems in such areas are carried out: Mechanotronics, the creation of an element base for computers of 5-6 generations; holography; Small communication specialized satellites; long-wave communication channels; Global environmental monitoring systems, etc.
For example, a computer processor "E2K", developed by a group of Russian companies "Elbrus", using a binary compilation method, for technical solutions and basic characteristics surpasses the western powerful processor "MERCED",which company "Intel" Only plans to release.
However, in many industries, enterprises where there are no serious innovative nearers, it is advisable to use catching development based on a simulation strategy. Borrowing experience and development of developed countries will contribute to overcoming the lagging for domestic enterprises of the relevant industries, an increase in the competitiveness of their products and an increase in production efficiency.
Such a way to successfully overcoming the backlog in its development was used by the country of the "Economic Miracle", such as Japan and South Korea.
As for the defensive strategy, it will be used by those enterprises that already have a fairly modern level of development, they only need to be tracked and respond to the emergence of new innovative developments.
According to the results of a survey of 1,000 large and medium industrial enterprises in Russia, the choice of development strategy is characterized by the following data (in% of responding):
- become one of the leaders in the production of new unique products - 32.2;
- Conscient the market for traditional mass demand products - 45.5;
- Release products on the analogues of leading firms - 16.9.
As can be seen from the given data, almost one-third of the surveyed industrial enterprises chose an offensive strategy of its development based on the development and implementation of unique products, 45.5% of the surveyed enterprises chose a defensive strategy of their development, almost 17% of enterprises intend to use a simulation strategy for development.
- Ivassenko L.G., Nikonova Ya.P., Sizova D.O. Decree. op. P. 189.
- Novitsky N.A. Decree. op. Pp. 171.
- Expert. 2010. No. 36. P. 38.