Organ musical instrument brief content. Organ - musical instrument twenty-eight centuries
The largest, most majestic musical instrument has an ancient history of the occurrence of the many stages of improvement.
The ancestor of the body is most distant from us in time, it is customary to consider the Babylonian Volyn, common in Asia in the XIX-XVIII centuries to our era. In this instrument, the air was injected through the tube through the tube, and on the other hand, a housing with models having holes and tongues was located.
The history of the emergence of the body remembers and "traces of the ancient Greek gods": the deity of the forests and groves Pan, according to legend, invented to combine reed sticks of different lengths, and since then the Pan's flute has become inseparable with the musical culture of ancient Greece.
However, the musicians understood: on one twin play easily, but on a few - there is not enough breathing. The search for the replacement of human breathing for the game on musical instruments was brought by the first fruits already in the II-III century BC.: Hydraulos came to the musical scene for several centuries.
Hydraulos - the first step to the magnitude of the organ
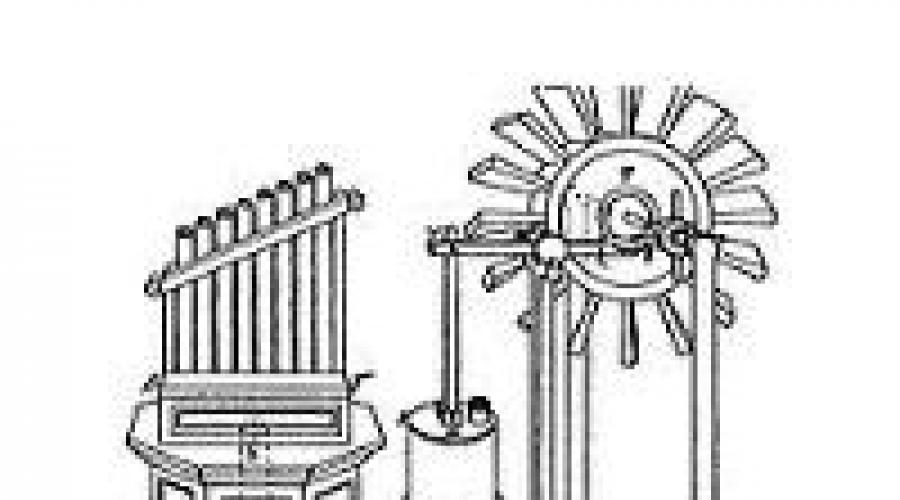
Approximately in the III century BC. Greek inventor, mathematician, "Pneumatics Father" Ktezibiy Alexandrian has created a device consisting of two piston pumps, water tank and tubes to emit sounds. One pump filed the air inside, the second served it to the pipes, and the water tank leveled pressure and ensured a more flat sound tool.
After two centuries, Gereon Alexandrian, Greek mathematician and engineer, improved the hydraulus, adding a miniature windmill into the construction and a metal ball chamber, immersed in water. The improved water body received 3-4 registers, each of which contained 7-18 diatonal tuning pipes.
 The water body was greatly distributed in the countries of the Mediterranean region. Hydraulos sounded on the competitions of gladiators, weddings and feasts, in theaters, circuses and at the racetracks, during religious rites. The body has become a favorite instrument of Emperor Nero, his sound could be heard throughout the Roman Empire.
The water body was greatly distributed in the countries of the Mediterranean region. Hydraulos sounded on the competitions of gladiators, weddings and feasts, in theaters, circuses and at the racetracks, during religious rites. The body has become a favorite instrument of Emperor Nero, his sound could be heard throughout the Roman Empire.
 In the service of Christianity
In the service of Christianity
Despite the common cultural decline, observed in Europe after the fall of the Roman Empire, the body was not forgotten. Already by the middle of the 5th century, improved winds were built in the churches of Italy, Spain and Byzantium. The centers of organ music became the countries of the greatest religious influence, and from there the tool spread across Europe.
The medieval organ was significantly different from the modern "fellow" smaller number of pipes and a large key size (up to 33 cm long and 8-9 cm wide), for which the sound was beaten with a fist. "Portal" was invented, a small portable organ, and "positive" - \u200b\u200ba miniature stationary body.
 The XVII-XVIII century is considered the "golden age of" organ music. Reducing the size of the keys, the acquisition by the body of the beauty and diversity of the sound, crystal grain clarity and the appearance of whole pashades predetermined the magnificence and greatness of the organ. Bach's solemn music, Beethoven, Mozart and many other composers sounded under high vaults of all Catholic Cathedrals of Europe, and almost all the best musicians served as church organists.
The XVII-XVIII century is considered the "golden age of" organ music. Reducing the size of the keys, the acquisition by the body of the beauty and diversity of the sound, crystal grain clarity and the appearance of whole pashades predetermined the magnificence and greatness of the organ. Bach's solemn music, Beethoven, Mozart and many other composers sounded under high vaults of all Catholic Cathedrals of Europe, and almost all the best musicians served as church organists.
With all the inseparable communication with the Catholic Church, a lot of "secular" works, including Russian composers, is written for the organ.
 Organ music in Russia
Organ music in Russia
The development of organ music in Russia went exclusively on the "secular way: Orthodoxy categorically rejected the use of the organ in worship.
The first mention of the body in Russia is found on the frescoes of the Sofia Cathedral in Kiev: "Stone Chronicle" of Kievan Rus, dated by the X-XI centuries, has kept the image of the musician and two catholds playing on the "positive" of the musician and two cats (people by downloading air into the fur).
Moscow sizes of different historical periods showed a living interest in the body and organ music: Ivan III, Boris Godunov, Mikhail and Alexey Romanov "discharged" from Europe of organists and builders of bodies. Under the rule of Mikhail Romanov, not only foreign, and Russian organists, such as Tomila Mikhailov (demons), Boris Ovsons, Meleneti Stepanov and Andrei Andreev became known in Moscow.
Peter I, who dedicated life to the introduction into the Russian society, the achievements of Western civilization, in 1691 instructed the German specialist Arpa Schnitgeru to build a body with 16 registers for Moscow. After six years, in 1697, Schnitger sends another, 8-register tool to Moscow. During the lifetime of Peter in Lutheran and Catholic churches, dozens of bodies were built on the territory of Russia, including gigantic projects for 98 and 114 registers.
Empress Elizabeth and Ekaterina II also contributed to the development of organ music in Russia - under their rule, dozens of tools received St. Petersburg, Tallinn, Riga, Narva, Yelgava and other cities in the north-western region of the Empire.
Many Russian composers used a body in their work, it is enough to remember the "Orleans" Tchaikovsky, "Sadko" Roman-Korsakov, "Prometheus" Scriabin ,. Russian organ music combined the classic Western European music forms and traditional national expressiveness and charm, possessed a strong influence on the listener.
 Modern organ
Modern organ
After passing the historical path in length in two millennia, the organ of the XX-XXI century looks like this: several thousand pipes located on different tiers and made of wood and metal. Wooden pipes of the square section make bass low sounds, and metal pipes from tin alloy and lead have a round cross section and are designed for a thinner, high sound.
The record holders are spelled out by the ocean, in the United States of America. The body located in the Philadelphia Macy's Lord & Taylor shopping center, weighs 287 tons and has six manuals. The tool located in the consent hall of the city of Atlantic City is the largest organ in the world and has more than 33,000 pipes.
The largest and magnificent organs of Russia are located in the Moscow House of Music, as well as in the concert hall. Tchaikovsky.


Development in new directions and styles has significantly increased the number of types and varieties of the modern body, with their differences in principle work and specific features. Today's classification of organs is such:
- spiritual body;
- symphony;
- theatrical body;
- electors;
- hammond organ;
- tiff organ;
- steam organ;
- street body;
- orchestrion;
- organola;
- pyrophone;
- marine body;
- chamber organ;
- church organ;
- home organ;
- organs;
- digital organ;
- rock authority;
- pop organ;
- virtual authority;
- melodium.
In contact with
The organ is a musical instrument, which is called "King of Music." The grandeur of his sound is expressed in the emotional effect on a listener who has no equal. In addition, the world's largest musical instrument is organ, and he has the most perfect management system. Its height and length are equal to the walls of the wall from the foundation to the roof in a large building - a temple or concert hall.
The expressive resource of the body allows you to create the music of the widest volume of content: from thinking about God and Cosmos to the subtle intimate reflections of the human soul.
The organ is a musical instrument with a unique history in its duration. His age is about 28 centuries. Within the framework of one article, it is impossible to trace the great path of this tool in art. We limited ourselves to a short essay of the genesis of the body from ancient times to those centuries, when he acquired the appearance and properties known to this day.
The historical predecessor of the body is the tool of Flute Pan (named, as mentioned in myth). The appearance of the Pan flute is dated to the 7th century BC, but the real age is probably much more.
This is the name of a musical instrument consisting of a vertically delivered a number of cane tubes of different lengths. Side surfaces they adjacent to each other, and the apart are combined with a rusting of a sturdy matter or a wooden plank. The performer blows the air from above through the holes of the tubes, and they sound - each at its height. The real sample game can use two or even three tubes to extract simultaneous sound and get a two-voice interval or, with special skill, three-voice chord.
Flute Pan personifies an eternal desire of a person to inventiveness, especially in art, and the desire to improve the expressive possibilities of music. Before this tool appeared on the historical scene, there were more primitive longitudinal flutes at the disposal of the oldest musicians - the simplest shoes with the finger holes. Their technical capabilities were small. On the longitudinal flute it is impossible to simultaneously extract two or more sounds.
In favor of a more advanced sound, Pan Flute also says the next fact. The way of blowing air into it is non-contact, the air jet is given by lips from a certain distance, which creates a special timber effect of mystical sound. All the predecessors of the organ were brass, i.e. The driving-controlled live strength was used to create these features of these features - a multi-champion and the ghostly fantastic "breathable" timbre - were inherited in the sound palette of the authority. It is they who underlie the unique ability of an organ sound - to introduce a listener into trance.
Five centuries have passed from the appearance of Pan flutes until the invention of the next predecessor. During this time, the connoisseurs of the brass recovery found a method that allows infinitely to increase the limited time of human exhalation.
In a new tool, air supply was carried out with the help of leather fur - like those who used a blacksmith to injected air.
There is also an opportunity to automatically support two-rode and truder. One or two voices - the bottom - without a break pulled the sounds, whose height did not change. These sounds, called "Burdoni" or "Fograms", were removed without the participation of the voice, directly from the fur through the openings open in them and there were something like a background. Later they will receive the name of the "Organ Point".
The first voice, thanks to the already known method of closing holes on a separate "flutfactory" insertion in the beam, was able to play quite a variety of and even virtuoso melodies. In the insertion, the performer blowing the air lips. Unlike Bourdon, the melody was removed in contact method. Therefore, there was no nuclei of mysticism - he was taken over bardon pegs.
This tool acquired great popularity, especially in folk creativity, as well as among the wandering musicians, and became known as Volyn. Thanks to its invention, the future organ sound acquired a practically unlimited length. While the performer pumps air furs, the sound is not interrupted.
Thus, three of the four future sound properties of the "King of Tools" were manifested: polyphony, mystical uniqueness of the timbre and absolute length.
Starting from the 2nd century BC. Constructions appear that are increasingly approaching the image of the organ. To discharge the air, the Greek inventor of Ktesebiy creates a hydraulic drive, this allows you to increase the power of the sound and provide an emerging colossing tool with rather long sounding pipes. On the hearing the hydraulic organ becomes loud and sharp. With such properties of sound, it is widely used in mass views (hipcodromic jumps, circus shows, mysteries) in Greeks and Romans. With the appearance of early Christianity, the idea of \u200b\u200bair injection mechanis was returned again: the sound from this mechanism was more alive and "humane."
In fact, at this stage, it is possible to consider the main features of organ sound: a multi-voice texture, powerfully attracting the attention of the timbre, unprecedented length and special power suitable for attracting a large mass of people.
The next 7 centuries were for the body defining in the sense that it was interested in its capabilities, and then firmly "assigned" them and developed the Christian church. The authority was destined to become a mass sermon tool, which he remains up to the present day. To this end, its transformation moved along two channels.
First. The physical dimensions and acoustic abilities of the tool reached incredible values. In accordance with the growth and development of the temple architecture, the aspect of architectural and musical progressed. The organ began to embed into the wall of the temple, and his thunder sound was subordinate and shook the imagination of the parishioners.
The number of organ pipes that have now been made from wood and metal reached several thousand. The timbres of the body have gained the widest emotional range - from the similarity of the Glass of God to the quiet revelations of religious individuality.
The possibilities of sounding previously acquired on the historic path were needed in church use. The polyphony of the body allowed the complicating music to reflect the multifaceted interlacing of spiritual practice. The length and injection of the tone exhibited the aspect of live breathing, bringing the nature of the organ sound to the experiences of human life.
From this stage, the body is a musical instrument of a huge convincing force.
The second direction in the development of the instrument went on the way to strengthen its virtuoso opportunities.
To control the thousandth arsenal of pipes, a fundamentally new mechanism was needed, giving the performer to cope with this inconspicuous wealth. The story itself suggested the right solution: the idea of \u200b\u200bthe keyboard coordination of the whole array of sound was perfectly adapted to the device "King of Music". From now on, the body is a key-brave tool.
The giant management focused on a special console, which combined the enormous capabilities of keyboard techniques and brilliant inventions of organ masters. The organist now was located in a stepwise order - one above the other - from two to seven keyboards. At the bottom, at the very floor under his feet there was a large pedal keyboard to extract low tones. They played legs on it. Thus, the technique of the organist demanded great mastery. The landing place of the artist was a long bench, supplied from above over a pedal keyboard.
The joining of the pipes managed the register mechanism. There were special buttons or handles near the keyboards, each of which led tens, hundreds and even thousands of pipes at the same time. In order for the organist not to be distracted by switching registers, he had an assistant - usually a student who had to deal with the basics of the organ.
The body begins a victorious procession in world artistic culture. By the 17th century, he reached a heyday and unprecedented heights in music. After immortalizing the organ art in the work of Johann Sebastian Baha, the greatness of this tool remains unsurpassed to the present day. Today the body is a musical instrument of the newest story.
Organ (Lat. Organum from Dr. Greek. ὄργανον - "Tool, gun") - keyboard musical instrument, the largest view of musical instruments.
Device and sound
Its height and length are equal to the walls of the wall from the foundation to the roof in a large building - a temple or concert hall.
The device, the principles of sound formation and other characteristics of this or that organ directly depend on its type and view.
In acoustic organs (wind, steam, luminous, wind, hydraulic, mechanical, etc.), the sound is formed due to the vibration of air in special organ pipes - metal, wooden, bamboo, cane, etc., which can be with the tongues, either without tongs. In this case, the air may be injected in the pipe pipe in various ways - in particular, with the help of special fur.
Over the course of several centuries, exceptionally wind organs were used for the performance of almost all church music, as well as musical works written in other genres. However, it is known about the church and secular use and an organoder, not the wind, and the string keyboard tool with organic properties.
The electrical organ was initially created for electronic imitation of the sound of winds, but then the electrical orders for their functional purpose began to divide into several types:
- Church electrical orders whose capabilities are as adapted to the execution of spiritual music in the iconic temples.
- Electricalganas for the concert performance of popular music, including jazz and rock.
- Electricians for amateur homemovication.
- Programmable Electrical Heads for Professional Studio Work
Consider the structure of the oven body. It consists of the following parts:
Remote controller
Under the elution of the organ imply controls, which include all numerous keys, register shift levers and pedals.
Playing devices include manuals and pedals.
To timbre - switches of registers. In addition to them, the remote control consists of: dynamic switches - channels, a wide variety of foot switches and kopul inclusion keys that carry one manual registers to another.
Most of the organs are supplied with copulins to switch registers to the main manual. Also, with special levers, the organist can switch different combinations from the bank of register combinations.
In addition, a bench is installed in front of the remote control, on which a musician sits, and the organ switch is located nearby.
Manual
Keyboard, in other words. But only in the body there are keys to play legs - pedals, therefore it is correct to say exactly what manual.
Usually in the body from two to four manuals, but sometimes there are copies with one manual, and even such monsters that have as many seven manuals. The name of the manual depends on the location of the pipes with which it controls. In addition, each manual is assigned its own set of registers.
In the main manual, the loudest registers are usually located. It is also called Hauptwerk. It can be located as closest to the performer and in the second row.
Oberwerk - a little more hidden. His pipes are located under the pipes of the main manual.
Rückpositiv is a completely unique keyboard. It controls those pipes that are located separately from all others. So, for example, if the organist sits to the tool face, they will be placed behind.
Hinterwerk - This manual controls pipes that are located in the rear of the organ.
Brustwerk. But the pipes of this manual are located either directly over the remote control itself or on both sides.
SOLOWERK. As one can judge from the very name, the pipes of this manual are equipped with a large number of solo registers.
In addition, other manuals can occur, but those are listed above are used most often.
In the seventeenth century, the organs appeared a kind of volume control - a box through which pipes with shutters were held. Manual, who ruled by these pipes, was called Schwellwerk and placed at a higher level.
Pedals.
Initially, the organs did not have a pedal keyboard. She appeared at about the sixteenth century. There is a version that it came up with a Brabant organist named Louis Wang Valbec.
Now there are a variety of pedal keyboard depending on the structure of the organ. There are both five and thirty-two pedals, there are organs and without a pedal keyboard. They are called portatives.
Typically, the pedals are controlled by the most basciferous pipes for which a separate notional mill is written, under double score, which is written for manuals. Their range is two, or even three octaves below the other notes, so a large organ may have a range of nine and a half octave.
Registers
Registers are a number of pipes of the same tone, which are, in fact, a separate tool. For switching registers, handles are provided, or switches (for electrical control organs), which are located on the remote control or above the manual, or beside the sides.
The essence of register control is: if all the registers are turned off, then the organ when you press the key will not be.
The name of the register correlates with the name of its largest pipe, and each handle relates to its register.
There are both labial and tongue registers. The first refers to pipe control without tongues, these are open flute registers, there are also registers of closed flutes, principles, the registers of the prideshoes, which, in fact, form the color of the sound (medicine and aliquots). In them, each note has several weaker overtone pride.
But the tongue registers, as can be seen from their very name, control pipes with tongues. They can be combined in sound with labial pipes.
The selection of the register is provided in the note mill, it is written above the place where one or another register should be applied. But the case is complicated by the fact that at different times and even simply in different countries, the registers of the organs differed sharply from each other. Therefore, the register of the organ party is rare when it is specified in detail. Usually it is accurately indicated only by manual, the size of the pipes and the presence or absence of tongues. All other sound nuances are given to the artist.
Pipe
As expected, the sound sound is in strict dependence on their size. Moreover, the only pipes that sound exactly how it is written in a new mill - these are eight-foot pipes. Smaller pipes sound are respectively higher, and large - lower than what is written in a new mill.
The largest pipes that are far from all, but only in the largest organs of the world, have a size of 64-foot. They sound three octaves lower than what is recorded in a notch mill. Therefore, when, when playing in this register, an organist involves pedals, already infrasucuke is published.
To set up small labial (that is, those that without tongue), use SHMYORN. This is a rod, at one end of which there is a cone, and on the other - a cup by which the pipes of the organ expand or narrow or narrow, than achieving changes in the height of the sound.
But to change the height of the sound of large pipes, additional metal flaps are usually cut out, which are bent like the tongues and thus change the sound of the organ.
In addition, some pipes can be purely decorative. In this case, they are called "blind". They do not sound, but have an exclusively aesthetic value.
The tract of the oven organ
Tract has a piano. There is a mechanism for transferring finger strike force from the key of the key directly to the string. The body tract plays the same role and is the main control mechanism.
In addition, the authority has tract that controls the pipe valves (it is also called game tracts), it also has register tract that allows you to turn on and disable entire registers.
The medicine is a group of registers that are currently involved. Game tract involves not those pipes that are involved using register tract, if you can say so, of course.
It is with register tract that the authority is working when whole registers are included or turned off. Something it resembles modern synthesizers. These can be both fixed combinations of registers and free, that is, those selected by the musician in an arbitrary order.
The organ is a musical instrument with a unique history in its duration. His age is about 28 centuries.
The historical predecessor of the body is the tool of Fleute Pan (named Greek God, as mentioned in myth). The appearance of the Pan flute is dated to the 7th century BC, but the real age is probably much more.
This is the name of a musical instrument consisting of a vertically delivered a number of cane tubes of different lengths. Side surfaces they adjacent to each other, and the apart are combined with a rusting of a sturdy matter or a wooden plank. The performer blows the air from above through the holes of the tubes, and they sound - each at its height. The real sample game can use two or even three tubes to extract simultaneous sound and get a two-voice interval or, with special skill, three-voice chord.
Flute Pan personifies an eternal desire of a person to inventiveness, especially in art, and the desire to improve the expressive possibilities of music. Before this tool appeared on the historical scene, there were more primitive longitudinal flutes at the disposal of the oldest musicians - the simplest shoes with the finger holes. Their technical capabilities were small. On the longitudinal flute it is impossible to simultaneously extract two or more sounds.
In favor of a more advanced sound, Pan Flute also says the next fact. The way of blowing air into it is non-contact, the air jet is given by lips from a certain distance, which creates a special timber effect of mystical sound. All the predecessors of the organ were brass, i.e. Used the driving controlled strength to create artistic images. Subsequently, these features are a polyphony and the ghostly fantastic "breathable" timbre - were inherited in the sound palette of the authority. It is they who underlie the unique ability of an organ sound - to introduce a listener into trance.
Five centuries have passed from the appearance of Pan flutes until the invention of the next predecessor. During this time, the connoisseurs of the brass recovery found a method that allows infinitely to increase the limited time of human exhalation.
In a new tool, air supply was carried out with the help of leather fur - like those who used a blacksmith to injected air.
There is also an opportunity to automatically support two-rode and truder. One or two voices - the bottom - without a break pulled the sounds, whose height did not change. These sounds, called "Burdoni" or "Fograms", were removed without the participation of the voice, directly from the fur through the openings open in them and there were something like a background. Later they will receive the name of the "Organ Point".
The first voice, thanks to the already known method of closing holes on a separate "flutfactory" insertion in the beam, was able to play quite a variety of and even virtuoso melodies. In the insertion, the performer blowing the air lips. Unlike Bourdon, the melody was removed in contact method. Therefore, there was no nuclei of mysticism - he was taken over bardon pegs.
This tool acquired great popularity, especially in folk creativity, as well as among the wandering musicians, and became known as Volyn. Thanks to its invention, the future organ sound acquired a practically unlimited length. While the performer pumps air furs, the sound is not interrupted.
Thus, three of the four future sound properties of the "King of Tools" were manifested: polyphony, mystical uniqueness of the timbre and absolute length.
Starting from the 2nd century BC. Constructions appear that are increasingly approaching the image of the organ. To injected air, the Greek inventor of Ktesebiy creates a hydraulic drive (water pump). This allows you to increase the sound power and supply an emerging colossus tool with rather long sounding pipes. On the hearing the hydraulic organ becomes loud and sharp. With such properties of sound, it is widely used in mass views (hipcodromic jumps, circus shows, mysteries) in Greeks and Romans. With the appearance of early Christianity, the idea of \u200b\u200bair injection mechanis was returned again: the sound from this mechanism was more alive and "humane."
In fact, at this stage, it is possible to consider the main features of organ sound: a multi-voice texture, powerfully attracting the attention of the timbre, unprecedented length and special power suitable for attracting a large mass of people.
The next 7 centuries were for the body defining in the sense that it was interested in its capabilities, and then firmly "assigned" them and developed the Christian church. The authority was destined to become a mass sermon tool, which he remains up to the present day. To this end, its transformation moved along two channels.
First. The physical dimensions and acoustic abilities of the tool reached incredible values. In accordance with the growth and development of the temple architecture, the aspect of architectural and musical progressed. The organ began to embed into the wall of the temple, and his thunder sound was subordinate and shook the imagination of the parishioners.
The number of organ pipes that have now been made from wood and metal reached several thousand. The timbres of the body have gained the widest emotional range - from the similarity of the Glass of God to the quiet revelations of religious individuality.
The possibilities of sounding previously acquired on the historic path were needed in church use. The polyphony of the body allowed the complicating music to reflect the multifaceted interlacing of spiritual practice. The length and injection of the tone exhibited the aspect of live breathing, bringing the nature of the organ sound to the experiences of human life.
From this stage, the body is a musical instrument of a huge convincing force.
The second direction in the development of the instrument went on the way to strengthen its virtuoso opportunities.
To control the thousandth arsenal of pipes, a fundamentally new mechanism was needed, giving the performer to cope with this inconspicuous wealth. The story itself suggested the right solution: keyboard tools appeared. The idea of \u200b\u200bthe keyboard coordination of the whole array of sound perfectly adapted to the device "King of Music". From now on, the body is a key-brave tool.
The giant management focused on a special console, which combined the enormous capabilities of keyboard techniques and brilliant inventions of organ masters. The organist now was located in a stepwise order - one above the other - from two to seven keyboards. At the bottom, at the very floor under his feet there was a large pedal keyboard to extract low tones. They played legs on it. Thus, the technique of the organist demanded great mastery. The landing place of the artist was a long bench, supplied from above over a pedal keyboard.
The joining of the pipes managed the register mechanism. There were special buttons or handles near the keyboards, each of which led tens, hundreds and even thousands of pipes at the same time. In order for the organist not to be distracted by switching registers, he had an assistant - usually a student who had to deal with the basics of the organ.
The body begins a victorious procession in world artistic culture. By the 17th century, he reached a heyday and unprecedented heights in music. After immortalizing the organ art in the work of Johann Sebastian Baha, the greatness of this tool remains unsurpassed to the present day. Today the body is a musical instrument of the newest story.
The expressive resource of the body allows you to create the music of the widest volume of content: from thinking about God and Cosmos to the subtle intimate reflections of the human soul.
Which sounds with the help of pipes (metal, wooden, without tongues and with tongues) of various timbres, in which air is injected using fur.
Game on the organ It is done using several keyboards for hand (manuals) and a pedal keyboard.
On sound wealth and abundance of musical means, the body ranks first among all the tools and is sometimes called the "king of instruments." Due to its expressiveness, he has long become the property of the church.
Man performing musical works on the organ called organist.
The Soviet reactive systems of the BM-13 bm-13 soldiers of the Third Reich called the "Stalin authority" due to the sound issued by the plumage of rockets.
History of the Organ
The embryo of the body can be seen, as well as in. It is believed that the organ (hydraulos; also Hydraulikon, Hydraulis - "Water Organ") invented Greek Ktezibiy, who lived in the Alexandria of Egyptian in 296-228. BC e. The image of a similar tool is available on one coin or a token of the times of Nero.
Large sizes appeared in the IV century, more or less advanced organs - in the VII and VIII centuries. Pope Vitalyan (666) introduced an organ in the Catholic Church. In the VIII century, Byzantium was famous for its bodies.
The art of building organs developed in Italy, from where in the 9th century they were discharged to France. Later, this art developed in Germany. The largest and widespread spread of the body begins to receive in the XIV century. In the XIV century, a pedal appeared in the authority, that is, the keyboard for the legs.
Medieval organs, in comparison with later, were coarse work; Manual keyboard, for example, consisted of keys wide from 5 to 7 cm, the distance between the keys reached one and minute and a half, see hit the keys not with fingers, as now, and fists.
In the XV century, the keys were reduced and the number of tubes was increased.
Authority
Improved organs reached a huge number of pipes and tubes; For example, an organ in Paris in the church of St. Sulpice has 7 thousand pipes and tubes. In the body there are pipes and tubes of the following values: in 1 foot notes, three octaves above the written, 2 feet - notes sounded two octaves above the written, 4 feet - notes sounds octowed above written, 8 feet - notes sound like writing, in 16 feet - notes sounds octowel below the written, 32 feet - notes sounds two octaves below the written. Closing the pipe from above leads to a decrease in the sounds of the sounds to the octave. Not all organs have pipes of large sizes.
Keyboards in the organ happens from 1 to 7 (usually 2-4); They are called manuals. Although each keyboard organ has a volume of 4-5 octave, thanks to pipes that sound for two octaves below or three octaves above the written notes, the volume of the large organ has 9.5 octave. Each set of pipes of the same voice is like a separate tool and is called register.
Each of the retractable or movable buttons or registers (located above the keyboard or on the sides of the tool) activates the corresponding row of tubes. Each button or register has its own name and appropriate inscription, with the length of the largest pipe of this register. The name of the register and the magnitude of the pipes The composer may designate in the notes above the place where this register should be applied. (The choice of registers for the execution of the musical work is called register.) Registers in organs are from 2 to 300 (most often occurs from 8 to 60).
All registers disintegrate into two categories:
- Registers with pipes without tongues (labial registers). This category includes open flute registers, closed flute registers (Bourdons) registers (medicine) registers in which each note has several (weaker) harmonic pride.
- Registers that have pipes with tongues (Language registers). The connection of the registers of both categories along with the mixture is called Perein Jeu.
Keyboards or manuals are located in the organs terrace, one above the other. In addition to them, there is another pedal keyboard (from 5 to 32 keys), mainly for low sounds. Party for hands is written on two notonic - in the keys and as for. The batch of pedals is written more often separately on one note mill. On the keyboard pedals, called just "pedal", play both legs, using an alternately with a heel and toe (until the XIX century - only to the sock). The organ without pedal is called a positive, a small portable body - portal.
Manuals in organs have names that depend on the location of pipes in the organ.
- The main manual (having the loudest registers) - in the German tradition called Hauptwerk. (FR. Grand Orgue, Grand Clavier) and is located closest to the performer or on the second row;
- The second most important and volume of the manual in the German tradition is called Oberwerk. (loud option) or Positiv (light version) (fr. Rositif), if the pipes of this manual are located above the pipes of Hauptwerk, or Ruckpositiv, if the pipes of this manual are located separately from the rest of the organs of the organ and installed behind the organist's back; The Oberwerk and Positiv keys on the game panel are located above the Hauptwerk keys, and the RUCKPOSITIV key levels below the Hauptwerk keys, thereby reproducing the architectural structure of the tool.
- Manual, whose pipes are located inside a peculiar box having a vertical shutter in the frontal part of the blinds in the German tradition called Schwellwerk. (FR. Recit (Expressif). Schwellwerk can be located both at the top of the organ (more common option), and at the same level with Hauptwerk. Schwellwerka keys are located on a player at a higher level than Hauptwerk, Oberwerk, Positiv, Ruckpositiv.
- Existing varieties of manuals: Hinterwerk. (pipes are located in the rear of the organ), Brustwerk. (pipes are located right above the place of the organist), SOLOWERK. (solo registers, very loud pipes located in a separate group), Choir. etc.
The following devices are facilitated for playing and means to enhance or loosening the tempering:
Kopula - The mechanism by which two keyboards are binding, with what registers extended to them act simultaneously. Kopulu gives the opportunity to enjoy the launched registers on one manual.
4 steps above the pedal keyboard (Padale de Combinaison, Tritte), of which each acts on a certain definite combination of registers.
Jalousie - A device consisting of a door closing and opening the entire room with pipes of different registers, as a result of which gaining or weakening sound. Doors are driven by footrest (channel).
Since the registers in different organs of different countries and epochs are not the same, then in the organ party they are usually not denoted in detail: they write over the one or another place of the organ party only manual, designation of pipes with or without pipes and the size of the pipes. The remaining details are provided by the Contractor.
The body is often connected to the orchestra and singing in oratoriors, cantata, psalms, as well as in the opera.
There are also electrical (electronic) organs, for example, Hammond..
Composers writing organ music
Johann Sebastian Bach
Johann Adam Resenken
Johann Pakhelbel
Dietrich Buxtehude
Dzhirolammo Frescobaldi
Johann Jacob Frombersger
Georg Friedrich Handel
Siegfried Karg-Elert
Henry Porssell
Max Reger
Vintagen Lubeck
Johann Ludwig Krebs.
Matias Vekman
Dominico Cipoli
Cesar Frank
Video: organ on video + sound
Thanks to this video, you can familiarize yourself with the tool, watch the real game on it, listen to his sound, feel the specifics of the technique:
Tools for sale: where to buy / order?
In Encyclopedia, there is still no information about where you can buy or order this tool. You can change it!
When an inconspicuous door, painted in a beige color, opened, glansed only a few wooden steps from the darkness. Immediately outside the door, a powerful wooden box, similar to ventilation, is coming out. "Careful, this is the organ pipe, 32 feet, a bass flue register," my walking warned. - Wait, I'll turn on the light. " I wait patiently, anticipating one of the most interesting excursions in my life. In front of me entrance to the organ. This is the only musical instrument inside which can be logged.

Funny tool - lifting harmonic with unusual tools for this tool. But almost exactly the same design can be found in any large organ (like what is shown in the picture on the right) - this is exactly what "tongue" organ pipes are arranged

The sound of three thousand pipes. The general scheme in the diagram is presented a simplified scheme of the organ with mechanical tract. Photos showing individual knots and instrument devices are made within the body of the Big Hall of the Moscow State Conservatory. The scheme does not show the store fur that supports constant pressure in Windows, and barx levers (they are in pictures). Also no pedal (foot keyboard)
Organ for more than a hundred years. He stands in the Great Hall of the Moscow Conservatory, the most famous hall, from the walls of which portraits of Baha, Tchaikovsky, Mozart, Beethoven ... However, everything that is open to the viewer's eye is turned to the hall of the organist and a little frosted wooden " Avenue "with vertical metal pipes. Observing the facade of the body, the person's uninitiated will not understand how and why this unique tool plays. To reveal its secrets, you have to approach the question on the other hand. Literally.
To become my guide, Natalia Vladimirovna Malina - Guardian of the body, teacher, musician and organ master agreed to become kindly agreed. "In the authority you can move only face ahead," she explains strictly. To mysticism and superstitions, this requirement has no low relationship: simply, moving back or sideways, an inexperienced person may occur for one of the organ pipes or to hurt it. And the pipes of these thousands.
The main principle of the body, distinguishing it from most wind instruments: one pipe is one note. An ancient ancestor of the organ can be considered a fuel pan. This tool, which existed from time immemorial in different parts of the world, is somewhat connected together hollow cohesions of different lengths. If you look at the corner at the mouth of the shortest - thin high sound will be heard. Longer cohesies sound below.
Unlike the ordinary flute, the height of the sound of a separate tube cannot be changed, so Pan's flute can play smoothly as notes as the sorsalines in it. To force a tool to make very low sounds, you need to turn on the tube of large length and large diameter. You can make a lot of flute pan with tubes from different materials and different diameters, and then they will blow the same notes with different timbres. But it will not be possible to play on all these tools at the same time - they should not be held in their hands, and there is not enough breathing on the gigantic "Costainka". But if you put all our flutes vertically, to supply each individual tube with an air intake valve, come up with a mechanism that would give us the opportunity to control all the valves from the keyboard and, finally, create a design for the injection of air with its subsequent distribution, we have just It turns out the authority.
On an old ship
Pipes in organs make two materials: wood and metal. Wooden pipes used to extract bass sounds have a square cross section. Metal pipes are usually smaller, they are cylindrical or conical in shape and manufactured, as a rule, from alloy tin and lead. If tin is more - the pipe is a ringing, if more lead, recoverable sound is deaf, "cotton".
Alloy tin and lead is very soft - this is why organ pipes are easily deformed. If you put a large metal pipe on the side, after a while, it will take an oval cross section under their own weight, which will inevitably affect its ability to remove sound. Moving inside the body of the Big Hall of the Moscow Conservatory, I try to concern only wooden parts. If you come on a pipe or embarrassing to grab it for it, new troubles will appear at the organ master: the pipe will have to "treat" - straighten, or even pan.
The body within which I am, is far from the biggest in the world and even in Russia. In terms of size and number of pipes, it is inferior to the organs of the Moscow House of Music, the Cathedral in Kaliningrad and the concert hall. Tchaikovsky. The main recordsmen are outside the ocean: for example, a tool established in the Atlantic City Congresses Hall (USA) has more than 33,000 pipes. In the body of the large hall of the pipe conservatory, ten times less, the "total" 3136, but this considerable amount cannot be compact on the same plane. The organ inside is a few tiers on which the pipes are installed in rows. To access the organ master to the pipes on each tier, a narrow passage is made in the form of a platform. The tiers are interconnected by stairs in which ordinary crossbars perform the role of the steps. Inside the body is closely, and the movement between tiers requires a known dexterity.
"My experience says," says Natalia Vladimirovna Malina, - that the authority master is best to be thin addition and have a small weight. A person with other dimensions here is difficult to work, not harming the tool. Recently, the electrician - a cargo man - changed the light bulb over the organ, stumbled and broke a couple of milking milking powder. There were no victims and injuries, but dropped apartments damaged 30 organ pipes. "
Mentally pretending that a couple of organ masters of ideal proportions would be easily placed in my body, I look at the clutching stairs, leading to the upper tiers. "Do not worry," Natalia Vladimirovna soothes me, "go only forward and repeat the movements for me. The design is strong, she will withstand you. "
Whistling and tongues
We rose to the upper tier of the organ, from where the conservatory inaccessible to the simple visitor opens views of the large hall from the top point. On the stage below, where the rehearsal of the string ensemble was finished, little men with violins and alto. Natalia Vladimirovna shows me near the pipe of Spanish registers. Unlike other pipes, they are not vertically arranged, but horizontally. By forming a kind of visor over the organ, they are trough directly into the hall. The creator of the Bolshoi Hall of Aristide Kawai-Kohl came from the Franco-Spanish genus of organ masters. Hence the Pyrenean traditions in the instrument at the Big Nikitskaya Street in Moscow.
By the way, about Spanish registers and registers in general. "Register" is one of the key concepts in the construction of the body. These are a number of organic pipes of a certain diameter forming a chromatic source, respectively, the keys of their keyboard or part of it.
Depending on the menzures included in their composition of the pipes (Menzura - the ratio of the most important for the nature and quality of the sound of the pipe parameters) registers give sound with different timbre color. Focusing comparisons with Flute Pan, I almost missed one subtlety: The fact is that not all the pipes of the organ (like the stranded flutes) are aerophones. Aeroophone is a fuch tool in which the sound is formed as a result of air column oscillations. This includes flute, pipe, tube, horn. But the saxophone, oboe, the harmonica is consisting in the group of idiophones, that is, "self-refined." It hesitates not air, but a stream of air the tongue. Air pressure and the force of elasticity, counteracting, force the tongue to tremble and spread the sound waves, which are enhanced by the tool with a resonator.
In the body, most pipes are Aerofons. They are called labial, or whistle. The idiophone pipes constitute a special group of registers and carry the name of the tongues.
How many hands do the organist?
But how can the musician manages all these thousands of pipes - wooden and metal, whistle and tongue, open and closed - dozens or hundreds of registers ... sound at the right time? To understand this, let's go down at the time from the upper tier of the organ and come to the department, or the organist's console. The uninitiated at the sight of this device covers the thrill both before the dashboard of the modern airliner. Several hand keyboards - manuals (there can be five and even seven!), One foot plus is still some mysterious pedals. There are still many exhaust levers with inscriptions on the handles. Why all this?
Of course, the organist has only two hands and playing at the same time on all manuals (in the body of the Big Hall of their three, which is also a lot) he will not be able to. Several manual keyboards are needed in order to mechanically and functionally divide the registers groups, just as in the computer one physical hard drive is divided into several virtual. For example, the first manual of the Bolshoi Authority manages the pipes of the group (German term - Werk) registers called Grand Orgue. It includes 14 registers. The second manual is also responsible for 14 registers. The third keyboard - recit expressif - 12 registers. Finally, the 32-key foot keyboard, or "pedal", works with ten bass registers.
Arguing from the point of view of profan, even 14 registers per keyboard - it is somehow a bit too much. After all, by pressing one key, the organist is able to make it sound at once 14 pipes in different registers (and more really because of the MIXTURA registers). And if you need to fulfill the note in just one register or in several selected? For this purpose, the exhaust levers located on the right and left of the manuals are actually used. Extinguish the lever with the register name written on the handle, the musician opens a kind of damper that opens access to the pipes of a specific register.
So, in order to play the desired note in the desired register, you need to choose the manual to the manual or pedal keyboard, pull the lever that corresponds to this register and click on the desired key.
Powerful doubt
The final part of our excursion is devoted to air. The very air, which causes the body to sound. Together with Natalia Vladimirovna, we descend on the floor below and find ourselves in a spacious technical room where there is nothing from the solemn attitude of the large hall. Concrete floor, white walls, driving up supporting structures from an old bar, ducts and electric motor. In the first decade of the existence of the body here in the sweat of the face worked, catchers-Calcans. Four healthy men got up in a row, grabbed with both hands for a stick, which grows into the steel ring on the rack, and alternately, then one, then the other foot was pressed on the levers, inflating fur. The change was calculated for two hours. If a concert or rehearsal lasted longer, the tired swingrs replaced the fresh reinforcement.
Old bellows, four, have been preserved until now. As Natalia Vladimirovna tells, a legend walks at the conservatory that once the work of the frauders tried to replace the horse force. For this, a special mechanism was supposedly created. However, along with the air, the smell of horse manure rose to the large hall, and the founder of the Russian Organ School A.F. Giedie, taking the first chord, displeased to the nose and sentenced: "Stinks!"
Truthful this legend or not, but in 1913, muscular power finally replaced the electric motor. With the help of pulley, he spun the shaft, which in turn through the crank-connecting mechanism led to the movement of the beam. Subsequently, they refused this scheme, and today the air pums the electric fan.
In the body, the injected air falls into the so-called store beef, each of which is associated with one of the 12 windows. Windlada is a view of a wooden box of a compressed air tank, which, in fact, the rows of pipes are installed. On one Windlad, several registers are usually placed. Large pipes that are not enough space on Windows are installed aside, and with Windows, they bind them the aircraft in the form of a metal tube.
Winders of the body of the Big Hall (the design "Coplade") are divided into two main parts. At the bottom, constant pressure is maintained using store mechanics. Top is divided with airproof partitions on the so-called tone channels. All pipes of different registers operated in the tone channel, controlled by one manual or pedal key. Each tone channel is connected to the bottom of the windder by a hole, a closed spring-loaded valve. When you press the key through the tract, the movement is transmitted to the valve, it opens, and the compressed air falls upward into the tone channel. All pipes that have access to this channel, in theory, should start to sound, but ... this, as a rule, does not occur. The fact is that through the entire top of the Windows undergo the so-called plumes - dampers with holes located perpendicular to the tone channels and have two positions. In one of them, the plumes completely overlap all the pipes of this register in all tone channels. In the other - the register is open, and its pipes begin to sound, as soon as the air key is pressed into the appropriate tone channel. Clap management, as it is easy to guess, is carried out by levers on the remote control through the register tract. Simply put, the keys are allowed to sound all the pipes in their tone channels, and the loops define the favorites.
We thank the leadership of the Moscow State Conservatory and Natalia Vladimirovna Malina for help in the preparation of this article