Dangerous neighbor. Milky way galaxy
Read also
The solar system is immersed in a huge star system - the Galaxy, numbering hundreds of billions of stars of various luminosities and colors (Stars in the section: "The life of stars"). Astronomers are well aware of the properties of different types of stars in the Galaxy. Our neighbors are not just typical stars and other celestial objects, but rather representatives of the most numerous "tribes" of the Galaxy. At present, all or almost all stars have been investigated in the vicinity of the Sun, with the exception of very dwarf stars that emit very little light. Most of them are very faint red dwarfs - their masses are 3-10 times less than that of the Sun. Stars similar to the Sun are very rare, only 6%. Many of our neighbors (72%) are grouped into multiple systems, where the components are linked to each other by gravitational forces. Which of the hundreds of nearby stars can claim the title of the Sun's closest neighbor? Now it is considered a component of the famous triple system Alpha Centauri - the faint red dwarf Proxima. The distance to the proximal is 1.31 pc, and the light travels from it to us for 4.2 years. The statistics of the circumsolar population gives an idea of the evolution of the galactic disk and the Galaxy as a whole. For example, the luminosity distribution of solar-type stars shows that the age of the disk is 10-13 billion years.
In the 17th century, after the invention of the telescope, scientists first realized how many stars there are in outer space. In 1755, the German philosopher and naturalist Immanuel Kant suggested that stars form groups in space, just as planets make up the solar system. He called these groups "star islands". According to Kant, one of such countless islands is the Milky Way - a grandiose cluster of stars visible in the sky as a light hazy streak. In ancient Greek, the word "galacticos" means "milky", therefore the Milky Way and similar star systems are called galaxies.
The size and structure of our Galaxy
Based on the results of his calculations, Herschel made an attempt to determine the size and forms a kind of thick disk: in the plane of the Milky Way it extends to a distance of no more than 850 units, and in the perpendicular direction - 200 units, if we take the distance to Sirius as a unit. According to the modern distance scale, this corresponds to 7300X1700 light years. This estimate as a whole correctly reflects the structure of the Milky Way, although it is highly imprecise. The fact is that, in addition to stars, the Galaxy disk also includes numerous gas and dust clouds that weaken the light of distant stars. The first explorers of the Galaxy were unaware of this absorbing substance and believed that they could see all of its stars.
The true dimensions of the Galaxy were established only in the XX century. It turned out that it is a much flatter formation than previously thought. The galactic disk is over 100,000 light-years in diameter and about 1,000 light-years thick. Due to the fact that the solar system is located practically in the plane of the Galaxy, filled with absorbing matter, many details of the structure of the Milky Way are hidden from the view of the terrestrial observer. However, they can be studied using the example of other galaxies similar to shasha. So, in the 40s. XX century, observing the galaxy M 31, better known as the Andromeda nebula, the German astronomer Walter Baade noticed that the flat lenticular disk of this huge galaxy is immersed in a thinner spherical star cloud - a halo. Since the nebula is very similar to our Galaxy, he suggested that the Milky Way has a similar structure. The stars in the galactic disk were named type I populations, and the halo stars were called type II populations.
As shown by modern studies, the two types of stellar population differ not only in spatial position, but also in the nature of movement, as well as in chemical composition. These features are primarily associated with the different origins of the disc and the spherical component.
Galaxy Structure: Halo
The boundaries of our Galaxy are determined by the size of the halo. The radius of the halo is much larger than the size of the disk and, according to some data, reaches several hundred thousand light years. The center of symmetry of the Milky Way's halo coincides with the center of the galactic disk. The halo consists mainly of very old, dim, low-mass stars. They are found both singly and in the form of globular clusters, which can include over a million stars. The age of the population of the spherical component of the Galaxy exceeds 12 billion years. It is usually mistaken for the age of the galaxy itself. A characteristic feature of halo stars is their extremely small proportion of heavy chemical elements. The stars that form globular clusters contain hundreds of times less metals than the Sun.
Spherical stars are concentrated towards the center of the Galaxy. The central, densest part of the halo within a few thousand light years of the galactic center is called the "bulge" ("thickening"). Stars and star clusters in the halo move around the center of the Galaxy in very elongated orbits. Due to the fact that the rotation of individual stars is almost random, the halo as a whole rotates very slowly.
Galaxy Structure: Disk
Compared to the halo, the disk rotates noticeably faster. Its rotation speed is not the same at different distances from the center. It rapidly increases from zero in the center to 200-240 km / s at a distance of 2 thousand light years from it, then decreases slightly, increases again to approximately the same value, and then remains almost constant. The study of the peculiarities of the disk rotation made it possible to estimate its mass. It turned out that it is 150 billion times the mass of the Sun. The population of the disk is very different from the population of the halo. Young stars and star clusters, whose age does not exceed several billion years, are concentrated near the plane of the disk. They form the so-called flat component. There are many bright and hot stars among them.
Gas in the disk of the Galaxy is also concentrated mainly near its plane. It is located unevenly, forming numerous gas clouds - giant, heterogeneous superclouds several thousand light-years in length to small clouds no larger than a parsec. The main chemical element in our Galaxy is hydrogen. It is about 1/4 helium. Compared to these two elements, the rest are present in very small quantities. On average, the chemical composition of stars and gas in the disk is almost the same as that of the Sun.
Galaxy Structure: Core
One of the most interesting regions of the Galaxy is considered to be its center, or core, located in the direction of the constellation Sagittarius. The visible radiation from the central regions of the Galaxy is completely hidden from us by powerful layers of absorbing matter. Therefore, they began to study it only after the creation of receivers for infrared and radio radiation, which is absorbed to a lesser extent. The central regions of the Galaxy are characterized by a strong concentration of stars: in each cubic parsec near the center there are many thousands of them. The distances between the stars are tens and hundreds of times less than in the vicinity of the Sun. If we lived on a planet near a star located near the core of the Galaxy, then dozens of stars would be visible in the sky, comparable in brightness to the Moon, and many thousands brighter than the brightest stars in our sky.
In addition to a large number of stars in the central region of the Galaxy, a circumnuclear gaseous disk is observed, consisting mainly of molecular hydrogen. Its radius is over 1000 light years. Closer to the center, there are regions of ionized hydrogen and numerous sources of infrared radiation, indicative of star formation taking place there. In the very center of the Galaxy, it is assumed the existence of a massive compact object - a black hole with a mass of about a million solar masses. In the center is also the bright radio source Sagittarius A, the origin of which is associated with the activity of the nucleus.
Divided into social groups, our Milky Way galaxy will belong to the robust "middle class". So, it belongs to the most widespread type of galaxies, but at the same time it is not average in size or mass. There are more galaxies smaller than the Milky Way than larger ones. Our "star island" also has at least 14 satellites - other dwarf galaxies. They are doomed to circle around the Milky Way until they are absorbed by it, or fly away from the intergalactic collision. Well, so far this is the only place where life probably exists - that is, you and me.
But the Milky Way remains the most mysterious galaxy in the Universe: being on the very edge of the "star island", we see only a part of its billions of stars. And the galaxies are completely invisible - it is covered with dense arms of stars, gas and dust. The facts and secrets of the Milky Way will be discussed today.
The Milky Way Galaxy contains the solar system, the Earth and all the stars that are visible to the naked eye. Together with the Galaxy of the Triangle, Andromeda and dwarf galaxies and satellites, it forms the Local Group of Galaxies, which is part of the Virgo Supercluster.
According to an ancient legend, when Zeus decided to make his son Hercules immortal, he put him on the breast of his wife Hera to drink milk. But the wife woke up and, seeing that she was feeding a step-child, pushed him away. A jet of milk splashed and turned into the Milky Way. In the Soviet astronomical school it was called simply "the Milky Way system" or "our Galaxy". Outside of Western culture, there are many names for this galaxy. The word "milky" is replaced by other epithets. The galaxy consists of about 200 billion stars. Most of them are located in the form of a disk. Most of the mass of the Milky Way is contained in a halo of dark matter.

In the 1980s, scientists put forward the opinion that the Milky Way is a barred spiral galaxy. The hypothesis was confirmed in 2005 with the Spitzer telescope. It turned out that the galaxy's central bar is larger than previously thought. The diameter of the galactic disk is approximately 100,000 light years. Compared to the halo, it rotates much faster. At different distances from the center, its speed is not the same. Studies of the disk's rotation helped estimate its mass, which is 150 billion more than the mass of the Sun. Young star clusters and stars are gathered in the vicinity of the disk plane, which form a flat component. Scientists speculate that many galaxies have black holes in their cores.

A large number of stars are collected in the central regions of the Milky Way Galaxy. The distance between them is much less than in the vicinity of the Sun. According to scientists, the length of the galactic bar is 27 thousand light years. It passes through the center of the Milky Way at an angle of 44 degrees ± 10 degrees to the line between the center of the galaxy and the Sun. Its component is predominantly red stars. The jumper is surrounded by a ring called the "Ring of 5 kiloparsec". It contains a large amount of molecular hydrogen. It is also an active star-forming region in the Galaxy. If viewed from the Andromeda galaxy, the bar of the Milky Way would be the bright part of it.

Since the Milky Way Galaxy is considered spiral, it has spiral arms that are located in the plane of the disk. A spherical crown is located around the disk. The solar system is located 8.5 thousand parsecs from the center of the galaxy. According to recent observations, we can say that our Galaxy has 2 arms and a couple more arms in the inner part. They transform into a four-arm structure, which is observed in the neutral hydrogen line.

The galactic halo has a spherical shape that extends beyond the Milky Way by 5-10 thousand light years. Its temperature is approximately 5 * 10 5 K. The halo consists of old, low-mass, dim stars. They can be found both in the form of globular clusters, and singly. The bulk of the galaxy is dark matter, which forms the dark matter halo. Its mass is approximately 600-3000 billion solar masses. Star clusters and halo stars move around the galactic center in elongated orbits. The halo rotates very slowly.

History of the discovery of the Milky Way Galaxy
Many celestial bodies are combined into a variety of rotating systems. Thus, the Moon revolves around the Earth, and the satellites of the major planets form their systems. The earth and other planets revolve around the sun. Scientists had a completely logical question: is the Sun part of an even larger system?

For the first time, William Herschel tried to answer this question. He calculated the number of stars in different parts of the sky and found that there is a large circle in the sky - the galactic equator, dividing the sky in two. Here the number of stars turned out to be the largest. The closer this or that part of the sky is to this circle, the more stars there are on it. Ultimately, it was discovered that the Milky Way is located at the equator of the galaxy. Herschel came to the conclusion that all stars form one star system.

Initially, it was believed that everything in the universe is part of our galaxy. But even Kant argued that some nebulae can be separate galaxies, like the Milky Way. It was only when Edwin Hubble measured the distance to some spiral nebulae and showed that they could not be part of the galaxy that Kant's hypothesis was proven.
The future of the galaxy
In the future, collisions of our Galaxy with others, including Andromeda, are possible. But there are no specific predictions yet. It is believed that in 4 billion years the Milky Way will be swallowed up by the Small and Large Magellanic Clouds, and in 5 billion years it will be swallowed up by the Andromeda Nebula.

Milky Way planets
Despite the fact that stars are constantly being born and dying, their number is clearly counted. Scientists believe that at least one planet revolves around each star. This means that there are from 100 to 200 billion planets in the Universe. Scientists who worked on this statement studied red dwarf stars. They are smaller than the Sun and make up 75% of all stars in the Milky Way Galaxy. Particular attention was paid to the star Kepler-32, which "sheltered" 5 planets.

Planets are much more difficult to spot than stars because they do not emit light. We can confidently say about the existence of a planet only when it obscures the light of the star.
There are also planets that are similar to our Earth, but there are not so many of them. There are many types of planets, for example, pulsar planets, gas giants, brown dwarfs ... If a planet is made of rock, it will be a little like Earth.

Recent studies claim that there are between 11 and 40 billion Earth-like planets in the galaxy. Scientists examined 42 stars similar to the Sun and found 603 exoplanets, 10 of which met the search criteria. It has been proven that all planets similar to Earth can maintain the required temperature for the existence of liquid water, which, in turn, will help the emergence of life.

Stars have been discovered near the outer edge of the Milky Way that move in a special way. They drift along the edge. Scientists speculate that this is all that remains of the galaxies that were swallowed up by the Milky Way. Their collision happened many years ago.
Satellites galaxies
As we said, the Milky Way Galaxy is spiral. It is a spiral of imperfect shape. For years, scientists have been unable to find an explanation for the galaxy's bulge. Now everyone has come to the conclusion that this is due to satellite galaxies and dark matter. They are very small and cannot affect the Milky Way. But when dark matter moves through the Magellanic Clouds, waves are created. They also affect gravitational attraction. Under this action, hydrogen escapes from the galactic center. Clouds revolve around the Milky Way.

Although the Milky Way is called unique in many ways, it is not a rarity. If we take into account the fact that there are about 170 billion galaxies in the field of view, it can be argued that there are galaxies similar to ours. In 2012, astronomers found an exact copy of the Milky Way. It even has two moons that correspond to the Magellanic Clouds. By the way, it is assumed that in a couple of billion years they will dissolve. Finding a galaxy like this was an incredible piece of luck. It is called NGC 1073. It is so much like the Milky Way that astronomers are studying it to learn more about our galaxy.

Galactic year
The Earth year is the time during which the planet makes a complete revolution around the Sun. In the same way, the solar system revolves around a black hole, which is located in the center of the galaxy. Its full turnover is 250 million years. When describing the solar system, it is rarely mentioned that it moves in outer space, like everything else in the world. Its speed is 792,000 km per hour relative to the center of the Milky Way Galaxy. If we compare, then we, moving with a similar speed, could go around the whole world in 3 minutes. A galactic year is the time it takes for the Sun to orbit the Milky Way. At last count, the sun has lived for 18 galactic years.
The Milky Way Galaxy is very majestic, beautiful. This huge world is our Motherland, our solar system. All the stars and other objects visible to the naked eye in the night sky are our galaxy. Although there are some objects that are located in the Andromeda Nebula - a neighbor of our Milky Way.
Description of the Milky Way
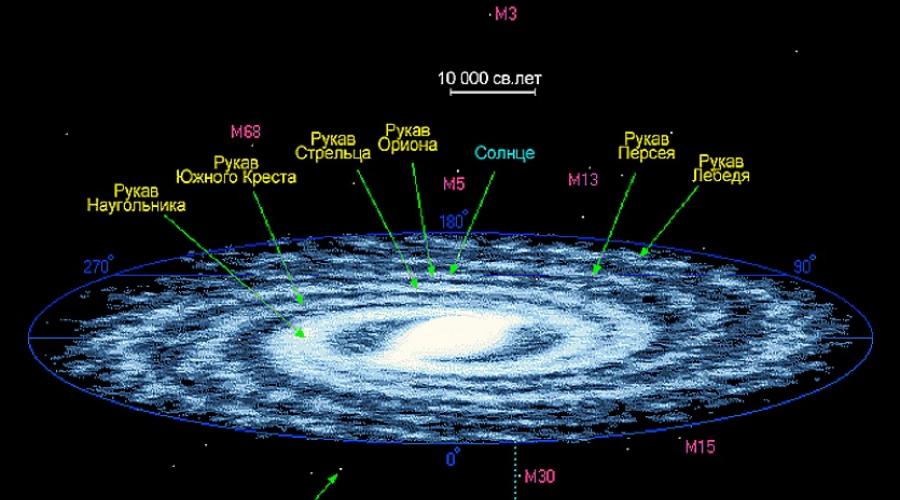
The Milky Way Galaxy is huge, 100 thousand light years in size, and, as you know, one light year is equal to 9460730472580 km. Our solar system is located from the center of the galaxy at a distance of 27,000 light years, in one of the arms, which is called the arm of Orion.
Our solar system revolves around the center of the Milky Way galaxy. This happens in the same way as the Earth revolves around the Sun. The solar system completes a full revolution in 200 million years.
Deformation
The Milky Way Galaxy looks like a disc with a bulge in the center. He's not in perfect shape. On the one hand, there is a bend to the north of the center of the galaxy, and on the other, it goes down, then turns to the right. Outwardly, such a deformation is somewhat reminiscent of a wave. The disc itself is deformed. This is due to the presence of the Small and Large Magellanic Clouds nearby. They rotate around the Milky Way very quickly - this was confirmed by the Hubble telescope. These two dwarf galaxies are often referred to as satellites of the Milky Way. The clouds create a gravitationally bound system that is very heavy and quite massive due to the heavy elements in the mass. It is assumed that they are pulling a rope between galaxies, creating vibrations. The result is a deformation of the Milky Way galaxy. The structure of our galaxy is special, it has a halo.
Scientists believe that in billions of years, the Milky Way will be swallowed up by the Magellanic Clouds, and after a while it will be swallowed up by Andromeda.

Halo
Wondering which galaxy is the Milky Way, scientists began to study it. They managed to find out that 90% of its mass consists of dark matter, which creates a mysterious halo. Everything that can be seen with the naked eye from Earth, namely that luminous matter, is approximately 10% of the galaxy.
Numerous studies have confirmed that the Milky Way has a halo. Scientists have drawn up various models that take into account the invisible part without it. After the experiments, the opinion was put forward that if there were no halo, then the speed of movement of the planets and other elements of the Milky Way would be less than now. Because of this feature, it was assumed that most of the components are composed of invisible mass or dark matter.
Number of stars
One of the most unique is the Milky Way galaxy. The structure of our galaxy is unusual, it contains more than 400 billion stars. About a fourth of them are large stars. Note: other galaxies have fewer stars. There are about ten billion stars in the Cloud, some others consist of a billion, and in the Milky Way there are more than 400 billion of various stars, and only a small part of it is visible from the Earth, about 3000. It is impossible to say exactly how many stars are in the Milky Way, because how the galaxy is constantly losing objects due to their transformation into supernovae.

Gases and dust
About 15% of the galaxy's constituent is dust and gases. Could it be because of them that our galaxy is called the Milky Way? Despite its enormous size, we can see about 6,000 light years ahead, while the galaxy is 120,000 light years across. Maybe it is larger, but even the most powerful telescopes do not see further than this. This is due to the accumulation of gas and dust.
The thickness of the dust blocks visible light, but infrared light does pass through it, and scientists can create maps of the starry sky.
What came before
According to scientists, our galaxy has not always been like this. The Milky Way emerged from the merger of several other galaxies. This giant conquered other planets, areas, which had a strong impact on size and shape. Even now, the planets are being captured by the Milky Way galaxy. An example of this is the objects of Canis Major, a dwarf galaxy located near our Milky Way. Dog stars are periodically added to our universe, and from ours they move to other galaxies, for example, there is an exchange of objects with the Sagittarius galaxy.

Milky Way View
No scientist or astronomer can say exactly what our Milky Way looks like from above. This is because Earth is located in the Milky Way galaxy 26,000 light-years from the center. Due to this location, it is not possible to take pictures of the entire Milky Way. Therefore, any image of a galaxy is either images of other visible galaxies, or someone's fantasy. And we can only guess how it really looks. There is even a possibility that we now know as much about it as the ancient people who considered the Earth to be flat.
Centre
The center of the Milky Way galaxy is called Sagittarius A * - a great source of radio waves, suggesting that there is a huge black hole in the heart. It is believed to be just over 22 million kilometers in size, and this is the hole itself.
All substances that try to get into the hole form a huge disk, almost 5 million times larger than our Sun. But even this pulling force does not prevent new stars from forming at the edge of the black hole.
Age
According to estimates of the composition of the Milky Way galaxy, it was possible to establish an estimated age of about 14 billion years. The oldest star is just over 13 billion years old. The age of a galaxy is calculated by determining the age of the oldest star and the phases preceding its formation. Based on the available data, scientists have suggested that our universe is about 13.6-13.8 billion years old.
First, the bulge of the Milky Way was formed, then its middle part, in the place of which a black hole subsequently formed. Three billion years later, a disk with arms appeared. It gradually changed, and only about ten billion years ago it began to look the way it is now.

We are part of something more
All the stars in the Milky Way galaxy are part of a larger galactic structure. We are part of the Virgo Supercluster. The closest galaxies to the Milky Way, such as the Magellanic Cloud, Andromeda and other fifty galaxies, are one cluster, the Virgo Supercluster. A supercluster is a group of galaxies that covers a huge area. And this is only a small part of the stellar neighborhood.
The Virgo Supercluster contains more than a hundred cluster groups spread over 110 million light years in diameter. The Virgo cluster itself is a small part of the Laniakea supercluster, and it, in turn, is part of the Pisces-Cetus complex.
Rotation
Our Earth moves around the Sun, making a complete revolution in 1 year. Our Sun revolves in the Milky Way around the center of the galaxy. Our galaxy is moving in relation to a special radiation. The relic radiation is a convenient reference point that allows you to determine the speed of various matters in the Universe. Studies have shown that our galaxy rotates at a speed of 600 kilometers per second.
Appearance of the name
The galaxy got its name from its special appearance, reminiscent of spilled milk in the night sky. The name was given to it in ancient Rome. Then it was called "expensive milk". Until now, it is called the Milky Way, associating the name with the appearance of a white stripe in the night sky, with spilled milk.
References have been found about the galaxy since the era of Aristotle, who said that the Milky Way is the place where the celestial spheres are in contact with the earthly ones. Until the telescope was created, no one added anything to this opinion. And only from the seventeenth century people began to look at the world differently.
Our neighbours
For some reason, many people think that the closest galaxy to the Milky Way is Andromeda. But this opinion is not entirely correct. The closest "neighbor" to us is the Canis Major galaxy, located inside the Milky Way. It is located at a distance of 25,000 light years from us, and 42,000 light years from the center. In fact, the Big Dog is closer to us than to the black hole in the center of the galaxy.
Before the discovery of Canis Major at a distance of 70 thousand light years, Sagittarius was considered the closest neighbor, and after that - the Large Magellanic Cloud. Unusual stars with a huge density of class M were discovered in Pse.
According to the theory, the Milky Way absorbed Canis Major along with all its stars, planets and other objects.

Collision of galaxies
Recently, more and more information has been encountered that the nearest galaxy to the Milky Way, the Andromeda Nebula, will swallow our universe. These two giants formed at about the same time - about 13.6 billion years ago. It is believed that these giants are capable of uniting galaxies, and due to the expansion of the Universe, they must move away from each other. But, contrary to all the rules, these objects are moving towards each other. The speed of movement is 200 kilometers per second. It is estimated that in 2-3 billion years Andromeda will collide with the Milky Way.
Astronomer J. Dubinsky created the collision model presented in this video:

The collision will not lead to a global catastrophe. And after a few billion years, a new system will form, with the usual galactic forms.
Lost galaxies
Scientists have carried out a large-scale study of the starry sky, covering about an eighth of it. As a result of the analysis of the star systems of the Milky Way galaxy, it was possible to find out that there are previously unknown streams of stars on the outskirts of our universe. This is all that remains of small galaxies that were once destroyed by gravity.
The telescope installed in Chile took a huge number of pictures that allowed scientists to assess the sky. The images estimate that our galaxy is surrounded by a dark matter halo, rarefied gas and scanty stars, remnants of dwarf galaxies that were once swallowed up by the Milky Way. With a sufficient amount of data, scientists have managed to collect the "skeleton" of the dead galaxies. It's like in paleontology - it's hard to tell from a few bones what the creature looked like, but with enough data, you can assemble a skeleton and guess what the lizard was. So it is here: the information content of the images made it possible to recreate eleven galaxies that were swallowed up by the Milky Way.
Scientists are confident that as they observe and evaluate the information received, they will be able to find several more new decayed galaxies that were "eaten" by the Milky Way.
We're under fire
According to scientists, the hyperspeed stars in our galaxy did not originate in it, but in the Large Magellanic Cloud. Theorists cannot explain many points regarding the existence of such stars. For example, it is impossible to say exactly why a large number of hyperspeed stars are concentrated in Sextant and Leo. After revising the theory, scientists came to the conclusion that such a speed can only develop due to the impact on them of a black hole located in the center of the Milky Way.
Recently, more and more stars are being discovered that do not move from the center of our galaxy. After analyzing the trajectory of superfast stars, scientists managed to find out that we are under attack from the Large Magellanic Cloud.
Death of the planet
By observing the planets in our galaxy, scientists were able to see how the planet died. She was consumed by an aging star. During the expansion and transformation into a red giant, the star engulfed its planet. And another planet in the same system changed its orbit. Seeing this and assessing the state of our Sun, scientists have come to the conclusion that the same will happen with our star. In about five million years, it will turn into a red giant.

How the galaxy works
Our Milky Way has several arms that rotate in a spiral. The center of the entire disk is a giant black hole.
In the night sky, we can see the galactic arms. They look like white stripes, reminiscent of a milky road that is strewn with stars. These are the branches of the Milky Way. They are best seen in clear weather during the warm season, when there is the greatest amount of cosmic dust and gases.
The following arms are distinguished in our galaxy:
- A branch of a square.
- Orion. Our solar system is located in this arm. This sleeve is our "room" in the "house".
- Carina-Sagittarius Sleeve.
- Branch of Perseus.
- Shield Branch of the Southern Cross.
Also in the composition there is a core, a gas ring, dark matter. It supplies about 90% of the entire galaxy, and the remaining ten are visible objects.
Our solar system, Earth and other planets are a single whole of a huge gravitational system that can be seen every night on a clear sky. In our "house" a variety of processes are constantly taking place: stars are born, disintegrate, other galaxies are bombarding us, dust and gases appear, stars change and go out, others flare up, lead a round dance around ... And all this is happening somewhere, far away in a universe about which we know so little. Who knows, maybe the time will come when people will be able to get to other arms and planets of our galaxy in a matter of minutes, travel to other universes.
In our century, illuminated by hundreds of electric lights, the inhabitants of the city do not have the opportunity to see the Milky Way. This phenomenon, which occurs in our sky only at a certain period of the year, is observed only far from large settlements. In our latitudes, it is especially beautiful in August. In the last month of summer, the Milky Way rises above the Earth in the form of a giant celestial arch. This weak, blurry streak of light looks denser and brighter in the direction of Scorpio and Sagittarius, and paler and more diffused - near Perseus.
Stellar mystery
The Milky Way is an unusual phenomenon, the secret of which has not been revealed to people for a whole string of centuries. In the legends and myths of many peoples, it was called differently. An amazing glow was the mysterious Star Bridge leading to the heavenly tabernacles, the Road of the Gods and the magical Heavenly River carrying divine milk. Moreover, all peoples believed that the Milky Way is something sacred. The shining was worshiped. Even temples were built in his honor.
Few people know that our New Year tree is an echo of the cults of people who lived in earlier times. Indeed, in ancient times it was believed that the Milky Way is the axis of the Universe or the World Tree, on the branches of which the stars ripen. That is why the Christmas tree was decorated at the beginning of the annual cycle. The earthly tree was an imitation of the eternally fruitful heavenly tree. Such a ritual gave hope for the favor of the gods and a good harvest. So great was the significance of the Milky Way for our ancestors.
Scientific speculation
What is the Milky Way? The history of the discovery of this phenomenon goes back almost 2000 years. Plato also called this strip of light a seam connecting the heavenly hemispheres. In contrast, Anaxagoras and Demoxide argued that the Milky Way (which color we will consider) is a kind of illumination of the stars. She is the adornment of the night sky. Aristotle explained that the Milky Way is the glow in the air of our planet of luminous near-moon vapors.
There were many other assumptions as well. So, the Roman Mark Manilius said that the Milky Way is a constellation of small celestial bodies. It was he who was closest to the truth, but he could not confirm his assumptions in those days when the sky was observed only with the naked eye. All ancient explorers believed that the Milky Way was part of the solar system.
Galileo's discovery
The Milky Way revealed its secret only in 1610. It was then that the first telescope was invented, which Galileo Galilei used. The famous scientist saw through the device that the Milky Way is a real conglomeration of stars, which, when viewed with the naked eye, merged into a continuous faintly shimmering strip. Galileo even succeeded in explaining the heterogeneity of the structure of this strip.

It was caused by the presence of not only star clusters in the celestial phenomenon. There are also dark clouds. The combination of these two elements creates an amazing image of a nighttime phenomenon.
William Herschel's discovery
The study of the Milky Way continued in the 18th century. During this period, its most active researcher was William Herschel. The famous composer and musician made telescopes and studied the science of stars. The most important discovery of Herschel was the Great Plan of the Universe. This scientist observed the planets through a telescope and counted them in different parts of the sky. Studies have led to the conclusion that the Milky Way is a kind of stellar island in which our Sun is located. Herschel even drew a schematic blueprint for his discovery. In the figure, the star system was depicted as a millstone and had an elongated irregular shape. At the same time, the sun was inside this ring that surrounded our world. This is how all scientists imagined our Galaxy up to the beginning of the last century.
It was only in the 1920s that the work of Jacobus Kaptein saw the light of day, in which the Milky Way was described in most detail. At the same time, the author gave a scheme of the star island, which is as similar as possible to the one that is known to us at the present time. Today we know that the Milky Way is a Galaxy, which includes the solar system, the Earth and those individual stars that are visible to humans with the naked eye.
Structure of galaxies
With the development of science, astronomical telescopes became more powerful and more powerful. Moreover, the structure of the observed galaxies was becoming clearer. It turned out that they are not alike. Among them were the wrong ones. Their structure had no symmetry.

Elliptical and spiral galaxies have also been observed. To which of these types does the Milky Way belong? This is our Galaxy, and, being inside, it is very difficult to determine its structure. However, scientists have found an answer to this question as well. We now know what the Milky Way is. Its definition was given by researchers who found that it is a disk with an inner core.
general characteristics
The Milky Way is a spiral galaxy. At the same time, it has a bridge in the form of a huge interconnected gravitational force.
The Milky Way is believed to have existed for over thirteen billion years. This is the period during which about 400 billion constellations and stars, over a thousand huge gas nebulae, clusters and clouds, were formed in this Galaxy.
The shape of the Milky Way is clearly visible on the map of the Universe. When examining it, it becomes clear that this cluster of stars is a disk with a diameter of 100 thousand light years (one such light year is ten trillion kilometers). Thickness - 15 thousand, and depth - about 8 thousand light years.
How much does the Milky Way weigh? This (determining its mass is a very difficult task) is not possible to calculate. It is difficult to determine the mass of dark matter, which does not interact with electromagnetic radiation. This is why astronomers cannot definitively answer this question. But there are rough estimates, according to which, the weight of the Galaxy is in the range from 500 to 3000 billion solar masses.

The Milky Way is like all celestial bodies. It makes revolutions around its axis, moving in the Universe. Astronomers point to the uneven, even chaotic movement of our Galaxy. This is due to the fact that each of its constituent star systems and nebulae has its own, different from others, speed, as well as different shapes and types of orbits.
What are the links of the Milky Way? These are the core and the bridges, the disk and spiral arms, and the crown. Let's consider them in more detail.
Core
This part of the Milky Way is located in the core is a source of non-thermal radiation with a temperature of about ten million degrees. At the center of this part of the Milky Way is a compaction called the "bulge." This is a whole string of old stars moving in an elongated orbit. For most of these celestial bodies, the life cycle is already coming to an end.
In the central part of the core of the Milky Way is located This section of outer space, the weight of which is equal to the mass of three million suns, has a powerful gravity. Another black hole revolves around it, only of a smaller size. Such a system creates so strong that nearby constellations and stars move along very unusual trajectories.
The center of the Milky Way has other features as well. So, it is characterized by a large cluster of stars. Moreover, the distance between them is hundreds of times less than that observed on the periphery of the formation.
It is also interesting that, observing the nuclei of other galaxies, astronomers note their bright glow. But why is it not visible in the Milky Way? Some researchers have even suggested that there is no nucleus in our Galaxy. However, it has been determined that dark interlayers exist in spiral nebulae, which are interstellar accumulations of dust and gas. They are also in the Milky Way. These huge dark clouds do not allow the terrestrial observer to see the radiance of the core. If such a formation did not interfere with earthlings, then we could observe the core in the form of a shining ellipsoid, the size of which would exceed the diameter of a hundred moons.
Modern telescopes, which are capable of working in special ranges of the electromagnetic spectrum of radiation, helped people to answer this question. Using this modern technique, which was able to bypass the dust shield, scientists were able to see the core of the Milky Way.
Jumper
This element of the Milky Way crosses its central region and is 27 thousand light years across. The bridge consists of 22 million red stars with an impressive age. Around this formation is a gas ring, which contains a large percentage of molecular oxygen. All this suggests that the bar of the Milky Way is the area in which the largest number of stars are formed.
Disk
This shape has the Milky Way itself, which is in constant rotational motion. It is interesting that the rate of this process depends on the distance of a particular area from the nucleus. So, in the very center, it is zero. At a distance of two thousand light-years from the core, the rotation speed is 250 kilometers per hour.
The outer side of the Milky Way is surrounded by a layer of atomic hydrogen. Its thickness is 1.5 thousand light years.

On the outskirts of the Galaxy, astronomers have discovered the presence of dense accumulations of gas with a temperature of 10 thousand degrees. These formations are several thousand light-years thick.
Five spiral arms
These are yet another constituent part of the Milky Way, located directly behind the gas ring. The spiral arms cross the constellations Cygnus and Perseus, Orion and Sagittarius, and Centaurus. These formations are unevenly filled with molecular gas. Such a composition introduces errors in the rules of rotation of the Galaxy.
The spiral arms exit directly from the core of the stellar island. We observe them with the naked eye, calling the light strip the Milky Way.
The spiral branches are projected onto each other, which makes it difficult to understand their structure. Scientists suggest that such arms were formed due to the presence in the Milky Way of giant waves of rarefaction and compression of interstellar gas, which move from the core to the galactic disk.
Crown
The Milky Way has a spherical halo. This is his crown. This formation consists of individual stars and constellation clusters. Moreover, the dimensions of the spherical halo are such that it goes beyond the boundaries of the Galaxy by 50 light years.
As a rule, the corona of the Milky Way contains low-mass and old stars, as well as dwarf galaxies and hot gas clusters. All these components produce motion in elongated orbits around the nucleus, making random rotation.
There is a hypothesis according to which the formation of the corona was a consequence of the absorption of small galaxies by the Milky Way. According to astronomers, the halo is about twelve billion years old.
The arrangement of the stars
In the cloudless night sky, the Milky Way is visible from anywhere on our planet. However, only a part of the Galaxy is visible to the human eye, which is a system of stars located inside the Orion arm.

What is the Milky Way? The definition of all its parts in space becomes most understandable if we consider the star map. In this case, it becomes clear that the Sun illuminating the Earth is located practically on the disk. This is almost the edge of the Galaxy, where the distance from the core is 26-28 thousand light years. Moving at a speed of 240 kilometers per hour, the Luminary spends 200 million years for one revolution around the core, so that during its entire existence it traveled around the disk, circling the core, only thirty times.
Our planet is in the so-called corotation circle. This is a place where the rotation speeds of the arms and stars are identical. This circle is characterized by an increased level of radiation. That is why life, as scientists believe, could arise only on a planet near which there are a small number of stars.
Our Earth was such a planet. It is located on the periphery of the Galaxy, in its quietest place. That is why there have been no global cataclysms on our planet for several billion years, which often occur in the Universe.
Forecast for the future
Scientists suggest that in the future, collisions between the Milky Way and other galaxies are very likely, the largest of which is the Andromeda galaxy. But at the same time, it is not possible to speak specifically about anything. This requires knowledge about the magnitude of the transverse velocities of extragalactic objects, which are not yet available to modern researchers.

In September 2014, one of the models of the development of events was published in the media. According to her, four billion years will pass, and the Milky Way will absorb the Magellanic Clouds (Large and Small), and in another billion years it will itself become part of the Andromeda Nebula.