Unpaired ringing sounds. Deaf and ring consonants
Some of the sound and deaf consonants forms a pair.
In the formation of consonants [p], [l], [m], [n], [j],
Deaf [x], [x "], [C], [h"], [sh "] do not have paired holes of ringing consonants.
Notes.
1. The sound [j] in school practice is denoted by [th "].
2. The sound [sh "] is indicated on the letter of the letter or some combinations of consonants. Horizontal trait at the top denotes that the sound is long.
Paired ringing consonants at the end of the word and before the deaf consonants, that is, in a weak position, they sound like a pair of deaf consonants. This phenomenon is called stunning.
Paired deaf consonants in front of paired bellows, i.e. in a weak position, sounds like a pair of voiced consonants. This phenomenon is called spinning.
Strong positions by deaf-belling for consonant sounds are provisions before vowels, in front of the sonar and in.
The consonants are divided into solid and soft. When pronuncified by solid and soft sounds, the different position of the language. Part of the consonant sounds forms a pair of hardness-softness.
When writing, the softness of the consonants is indicated:
1) With a soft sign: Dove, Dictionary:
2) With the help of letters E, E, Yu, I, and: remote, Lipa.
Before soft consonants, the softness of the consonants is not always referred: a bow - ba [n "T"] IR.
More on the topic Write and deaf, solid and soft consonants:
- § 3. Spelling of the consonants (checked and unverified, ringing, deaf and unprofitable consonants; double consonants; combinations of consonants)
Oral speech possession is very important for the social life and development of the individual. Much attention in the study of a native (or foreign) language is paid to the spoken speech - the right pronunciation of the phone. There are many words that differ only in individual sounds. Therefore, special attention is paid to the functioning of speech organs and sound formation.
Production of sounds
Sound formation occurs as a result of human mental and speech activity. The voice apparatus consists of a diaphragm, larynx, the nastestrian, pharynx, voice ligaments, the cavity of the nose and mouth, tongue, nose (soft and solid), alveol, teeth, tongue, lips.
Language with the bottom lip is actively involved in sound operating. Teeth, packed, the upper lip remain passive.
The production of sounds (background) includes:
- respiration - Breath,
- lancture - use of larynx and voice folds to create a phone game,
- articulation - work for sound operating.
Noisy (deaf) Russian language
Letters in Russian Rivne 33, and sounds much more - 42. Public phones consisting of a pure voice - 6. The remaining 36 sounds are consonants.
In the creation of 16 consonants, only the noise is involved, which is formed as a result of overcoming the exhaled airflow, some obstacles, which are interacting speech bodies.
[k,], [p,], [s,], [t,], [f,], [x,], [h,], [sh,], [k], [p], [with ], [T], [F], [x], [C], [sh] - deaf consonant sounds.
To learn how to determine which consonant sounds are deaf, it is necessary to know their main features: what way and in what place they are formed, how vocal folds in their production are involved, there is a palatalization during pronunciation.
The formation of noisy consonants
In the process of producing deaf consonants, the interaction of various organs of the speech apparatus occurs. They can be closed with each other or form a gap.
Deaf consonant sounds are born when exhaled overcomes these obstacles. Depending on the type of obstacles, the deaf phonemes are divided into:
- flicer explosive [K, P, T, K, P, T];
- fit sloping (affrust) [C, h,];
- sloves (fricative) [C, F, X, Sh, C, F, X, W].
Depending on the places where barriers are formed, among the deaf phonemes distinguish:
- lights [P];
- long-dental [F, F];
- advanced tooth [C, C, T, T, C];
- front-band-in-lubricant-tooth [h, sh, sh];
- rear-speaking posterior [k, x, k, x].
Palamatory and Veselization
Noisy phonemes are classified according to the degree of tension of the middle of the language. When the front and average language of the tongue rise during sound operating system, a palatalized consonant (soft) deaf sound is born. Rearized (solid) phones are produced by raising the root of the tongue to the back area of \u200b\u200bthe soft noise.
6 soft and 6 solid noisy deaf backgrounds make up pairs, the rest of the steam do not have.
Paired deaf consonants - [K, - K], [P], [C, - C], [T, - T], [F, - F], [X, - X]; [C, h, sh, sh,] - Deaf unpaired consonant sounds.
Articulation
The combination of all works of individual organs of the speech apparatus involved in pronouncing the background is called articulation.
So that it is clear that you need to be able to clearly vote sounds, words, suggestions. To do this, you need to train your speech apparatus, process the pronunciation of the phone.
Understanding how deaf consonants are formed, as they correctly pronounce, a child or an adult will greater than the speech greeting.
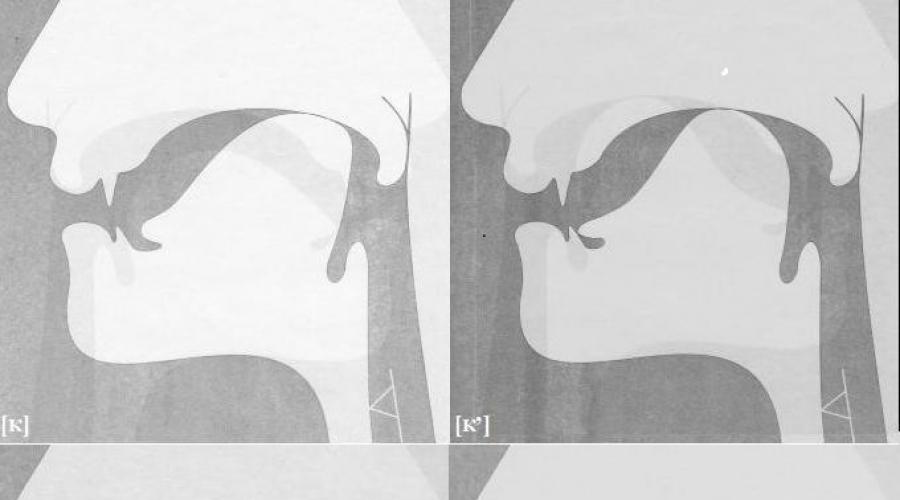
Sounds [K - K, X - X,]
Lower the end of the tongue, slightly move away from the cutters of the lower jaw. Roth open. The back of the tongue is to raise it so that it becomes in touch with the border zone of the raised soft and solid nose. Through a sharp exhalation, the air overcomes the barrier - [to].
Cook the end of the tongue to the lower front teeth. The middle and rear of the language brought closer with the mid-rear area of \u200b\u200bthe solid nose. Exhale - [k,].
In the production of phones [x - x,] the speech organs are arranged similarly. Only between them remains not a bow, but a gap.

Sounds [P - P,]
Splesh lips, leaving the language loose freely, the tip of it slightly move away from the lower cutters. Exhalation. The air jet breaks through the lips - [P].
Lips are also located. The end of the tongue to press to the slope of the lower jaw. To solid nebu, raise the middle of the language. A sharp impetus is overcome by a lifting barrier - [p,].

Sounds [C - C,]
Lips stretch, teeth almost sick. The end of the tongue to touch the front teeth of the lower jaw. Intrind the language by lifting the middle back to the nebu. His side edges are pressed against the upper chewing teeth. The air flow passes through the groove resulting in the middle of the language. Overcomes the gap between the alveolar arc and the front back of the language - [s].
The phoneme [C,] is pronounced similarly. Only the middle rises higher, and the front is launched (the groove disappears).
Sounds [T - T,]
Operate lips. The end of the tongue is rested into the cutters of the upper jaw, forming a bow. The stream of exhaled air with force breaks through the barrier - [t].
Lip position is the same. The tongue of the tongue is nourished to the lower cutters. The front of the language touch the upper alveolar arc, creating a bow. Under the pressure of the air jet overcomes the barrier - [t,].

Sounds [F - F,]
The bottom lip is slightly drawn and press it the upper cutters. The back of the tongue is lifted to the back area of \u200b\u200bsoft nob. In exhalation, the air passes through a flat slit formed by lip and teeth - [f].
Lips and teeth in the same position. The tip of the tongue is moved to the bottom cutters. The middle part of the tongue is raised to the nebu. The air flow penetrates through the lip-toothbrush - [F,].

Sound [C]
The sound is made in two stages:
- Stretch a little tense lips. The end of the tongue is attached to the front bottom teeth. Raise the front part of the tongue, closer with the hard naba (immediately behind the alveolar arc).
- The air flow enters the oral cavity. The tongue is a little bend - the middle part is lifted, the rear omit, the side edges press to chewing teeth. The bow turns into the gap and the air comes out - [C].
Sound [h,]
The formation of the phoneme consists of two phases:
- Slightly round and push the lips. The end and front part of the tongue to cuddle to solid nebu and the alveolar arc, creating a barrier.
- Push the air: on the site of the bow between the language and the neba, the gap will turn out. At the same time, it is necessary to lift the middle of the language - [h,].

Sound [Sh]
Slightly rounded lips push out. The end of the tongue is raised before the formation of a narrow passage with a nose and alveolar arc (1st gap). Having lowered the middle of the tongue, raise his back (2nd gap). The edges press to chewing teeth by forming a bowl. Smoothly exhale - [sh].
Sound [Sh,]
Lips slide and round down. The end of the language is to lift to the alveolar arc, without pressed, so that there is a lumen. Lower the tongue to solid nebu (except for the front), the edges are nourished to the indigenous teeth of the upper jaw. Exhale slowly. The central part of the tongue goes down, creating a chute through which air flow passes. Language strains - [sh,].

In the speech stream, the deaf consonants are adjacent to other phones if there is a vowel, then the lips take the position to articulate the latter.
Comparison of noisy deaf and ringing background
There are phonemes ringing, in the formation of which voice and noise participate simultaneously (the latter prevails). Some calls have pair sounds from the deaf.
Paired deaf consonants and bellows: [k - g], [k, - g,], [p - b], [p, - b,], [t - d], [t, - d,], [ C - s], [C, - Z,], [F - V], [F, - B,], [sh - F].
Write and deaf unpaired consonant sounds:
- [th, l, m, n, r, l, m, n, p] - ringing (sonorny);
- [x, h, sh, x, c] - noisy deaf.
Noisy background with letters
The ability to competently write is no less important than to talk. Mastering a written speech is associated with even greater difficulties, as some sounds on paper can be recorded by different letters or letters.
The deaf consonants when writing are transmitted similar letters if they are in strong positions.
According to the deaf-belling: before vowels, [in - in,], other noisy (applicable to pair deaf!).
On hardness-softness: before vowel, [b, m, g, k, p, x, b, m, g, k, p, x,] - for sounds [s, s, t, t,], at the end the words.
In other cases, to determine the right letter (or combinations of letters), it is necessary to apply certain rules of the Russian language for a deaf consonant phone game. And sometimes it is necessary to simply memorize the correct writing of words (vocabulary).
Exercise 17, p. 10
17. Help the cat and dog gather into one group of letters that denote ringing sounds, and to another - letters that denote the deaf consonants. Connect the letters of each group.
Deaf → h → x → sh → with → t → c → → → → n → f
 Ringing → Y → L → N → R → → m → d → b → → g → in
Ringing → Y → L → N → R → → m → d → b → → g → in
- Say the sounds that can be marked with highlighted letters
c. - [h '] m. - [M], [m '], J. - [y '] t. - [T], [t ']
Exercise 18, p. 10
18. Read. Enter the missed word in the proposal.
Such a frost street -
I, like icicle, all n Romerz.
L. Yakovlev
- Stress in the highlighted word letters, which are denoted by the deaf steam sound sounds.
Exercise 19, p. eleven
19. Read. Insert the missed words-names of consonant sounds.
1. The deaf consonant sound consists of noise.
2. The ringing consonant sound consists of noise and voices.
Exercise 20, p. eleven
20. Enter into the "house" missed letters denoting pair by deaf-belling consonant sounds.
- Choose and write down words that end with these letters.
Exercise 21, p. eleven
21. Find in the spelling dictionary of the word textbook with pair by deaf-belling consonant sound at the end of the word. Write down a few words.
Alphalia t, suddenly, city, plant, pencil, class, hammer, frost, people, lunch, handkerchief, drawing, student, tongue.
Exercise 22, p. 12
22. Read. What rule is we talking about? Why are the consonants so called?
Paired consonants - The most dangerous!
In the root you check them -
Near the vocal substitution!
We are talking about the rule of spelling words with pairs of deaf-belling by consonant sound in the root of the word. Such consonants are called "dangerous" because we can choose an incorrect letter denoting the pair by deaf-belling the consonant sound in the root of the word in front of other pairwise consonants. These are "mistake" places, or orphogram.
Exercise 23, p. 12
23. Read. Insert the missing letters.
1. Will be chle b, there will be a lunch. 2. There would be a cake, there is a meal. 3. Who is lazy, that and son. 4. Untrect face, it's good. 5. The bear clumsion, and dyzhe.
- Orally pick up test words to words with missed letters.
Chle b (bread), lunch (lunch), cake (pies), eater (consuming), lazy (lazy), drone (dried), ugly (ugly), good (good), bear (bears), clumsy (clumsy) .
Exercise 24, p. 12
24. Read.
Creep crep. Grind frost.
And the snow is dry and stuck.
And Elm Ozheb, and Oak Oakz.
Through the Obrogly trees.
G. Volzhina
- Choose for each word the correct letter from the brackets, emphasize it. Write down these words.
Moro. s, snow, elm, chillure, oak, frozen, up.
Exercise 25, p. 13
25. Read the lines from the American songs, which Leonid Yakhnin translated.
Pyro g bake old woman phogg
In the kitchen at the slab
And dog bulldog on nickname e dog
Walking flowers.
Takes the cake of the old woman Fogg
And tea with milk,
And the dog is a Bulldog on the nickname e dog -
In it near the table.
- What do you think in these rows is true?
Truth:
Cake bake old woman phogg
In the kitchen at the stove ...
Takes the cake of the old woman Fogg
And tea with milk ...
Strits about Bulldog - Nonbylitsa.
- Stress in the words of the spell on the rules studied.
Exercise 26, p. 13
26. Read. Write the words, replacing the selected sounds with letters.
chá [Sh] Ka - Chá ш ka uká [s] ka - ukaz ka
ló [sh] ka - lók ká [s] ka - kác ka
lá [f] ka - lounter [k] T - ló
Kó [F] TA - Kóf TA [K] TI -
shá [n] ka - shhap ka ló [t] ka - lice
Шý [П] Ка ка коль каски [t] ka
- Prepare to prove that you correctly recorded words.
Cha ш ka (cup), lies ka (spoon), lava ka (shop), kofa - vocabulary word, you need to remember, ka support (cap), fur coats (fur coats), decree ka (pointer), cas ka (kassochka) , Lock TI (dowels), cogging (claws), Lod ka (boat), ka (brush).
Exercise 27, p. fourteen
27. Read. Emphasize the consonants, whose writing must be checked.
Nó g., Zagda, Skolz Kiy, Moroccal, Mork, Row, Rod, Strong, Rifle, Slip, Nost, Watch, Turn.
- Find for each test word verification. Write down the sample.
(Ró b.oK) ró b.cue, (storo j.iT) Store j.ka, (knife d.tange) d.ka, (nó g.oh) nó g.tee, (how many z.iT) z.cue, (smelting in) Morocca inka
Exercise 28, p. fourteen
28. Read. Name fairy tales.
1. Z Olushk A., running out of the palace, lost the crystal shoe.
2. B ELO SELL A Very made friends with family dwarves.
- Insert the missed words. Stress in them letters that are marked by the deaf-belling, consonant sounds.
Exercise 29, p. fifteen
29. Select a single test word for each word. Write down the sample.
D. bi - oaks, berries ka - berries.
Loose cues, close - close.
LOUR FRIENDS, BULARS KA - Bully.
Continued - ask, stuffing ka - watching.
Holiday is indulgent, Horoch - Horce.
- Emphasize the letters whose writing you checked.
Exercise 30, p. fifteen
30. Read the riddle. Insert the missed letters and the word. Draw a gifue.
I'm round, I'm glad to
And the taste is pleasantly sweet.
Knows every carpus,
What is your name.

Exercise 31, p. fifteen
31. Read. Insert the missing letters.
1. SALE inki, goal b.tsy, Pyro j.ki, water vehicle z.
.
2. Vdru g. , blý. z.ka, sap j.ki, rubá. shka
Unnecessary words - diver, suddenlySince the spell at the end of the word, and in the rest - in the root of the word.
- Emphasize the unnecessary word in each group of words. Explain your answer.
Exercise 32, p. sixteen
32. Read. Select the desired letter and insert it into words.
B? P?
Oak, Screw, error, button, G. Kiy.
G? TO?
Iceberg, circus, leng cue, south, soft cue.
IN? F?
Island, Giraffe, Cofa, Lovoch, beak.
D? T?
Iodine, view, cell, zagad ka, mole.
Well? Sh?
Chizh, Varezh Ka, Yersh, Flagush, books.
S? FROM?
Cargo, sauce, salad, Mas ka, tale.
Exercise 33, p. sixteen
33. Read. Insert the missing letters.
1. Each tree has its own d.. On the river floats the root t..
2. In the hands of the boy Pru t.. In the village Deep Pru d..
3. Beautiful summer blooming lu g.. Green Lou has grown on the garden to.
4. On the Klumbe Ro from Kush Alich Ro. z..
- What is interesting words with missed letters? In the last offer, emphasize the main members.
In each pair, the words are pronounced equally, and they are written differently.
Exercise 34, p. 17.
34. Read. Perform tasks data in the table.
- Explain how you picked up test words for words with unstressed vowels and for words with pair by deaf-belling consonant sound in the root of words.
We picked up such verification words for words with unstressed vowels, so that the unknown vowel sound in the root became percussion. For a word with a pair of deaf-belling, the consonant sound in the root of the word we picked up a single word so that the pair consonant sound in the root was in front of a vowel sound.
Exercise 35, p. 17.
35. Read the riddles. Insert the missed letters in the deposits.
1. Hu himself d, go lo va with powders, how to hit - firmly. (M. about l about t about to)
2. It's not snow, not ice, but the sulfur broma de ver willing kill riv. (AND not th)
- Stress in the words of the spell.
Exercise 36, p. eighteen
36. Read. Casting text.
January
I love you, I Nvar!
For me, you too i C best -
M. aboutl. aboutdoy, B. aboutlHEO, SKR andbumpy
Z. aboutl. about Tyish like Yantian b!
Sun, Sing g., aboutgon, M. about roses -
White B. Flame e. Ryu. z.!
S. Kozlov
- Do you agree with the opinion of the author? What does the word amber mean?
Amber - petrified resin, yellow-brown or golden color.
- Which of the selected spells can you not explain? Why? Stress these orphograms.
Underlined spells We cannot explain because it is unstressed vowels in the root that cannot be checked. The spelling of such words must be either memorized or check by spelling dictionary.
Exercise 37, p. eighteen
37. Read. Insert the missing letters.
LE. g cue Mo Roses, Bo's snowdrift, sulfur british isna, a dream Gurochka, a dream eopa, grandfather Mo Roses, Puffy a lot of sleep, Skye Snow, nickname, glad cue ice, dream gosch.
- What topic binds these words and combinations of words?
The subject of the winter binds these words and combinations of words.
- Make an oral text on this topic.
On the street stood Light Frost. Yesterday's snowfall looked at the city with soft snow, the roofs of the houses sparkled from silver Iney. The blizzard has large drifts.
Children could not stop at home. Nading new skates, from the morning painted patterns on smooth ice. The kids played snowballs and sculpt the snowman.
Fluffy snowflakes have fun around, like children in a New Year's dance with Santa Claus and Snow Maiden.
Ring and deaf consonants
4.7 (94%) from 10 votesAll consonant sounds in Russian are divided into several features, including on the principle of deaf bellivity. This spoke characteristic affects whether the voice is used if the voice is used or not. The study of this topic is very important for understanding the basic principles of the function of the phonetic system, because the deaf consonants are very important part of it.
What is a deaf consonant sound
Deaf consonants are made only by noise, without voting. If they are pronouncing, voice ligaments are completely relaxed, the larynge do not vibrate.
Pair and unpaired deaf consonants
Most sounds that belong to this category have a ringing couple. What are these sounds, you can learn from the table "Deaf consonants in Russian".
Thus, in Russian there are 11 deaf consonants having a ringing couple. But there are not the unpaired - these are sounds such as [x], [x '], [h'] and [sh '].
They cannot be ringing regardless of the position.
Remember all the deaf consonants, which are in Russian, helps a special mnemonic phrase: "Stepka, do you want a helmet? - Fu! ". But it will not help to remember their steady firmness in hardness, since the deaf consonants, having a pair, are represented in it only in one variety - or solid, or soft.
The rule of stunning agree
In Russian, there are often cases when the writing is written in the letter, and in speech it turns into a deaf consonant sound. This happens, for example, when the ringing letter turns out to be at the very end of the word, as in the word mushroom, the transcription of which will look like [the hype].
Due to the fact that the ringing consonants at the end are stunned, often arise difficulties when playing such words in the letter. However, there is an easy way to check what the letter to use: you need to change the word so that the consonant turned out to be in front of the vowel, for example, a mushroom - mushroom. Then it will immediately become clear what to write. The same applies to cases where at the end there is a deaf consonant, and in the letter it is spinning "as a general rule." Check which letter is written, it is possible in the same way: a cry - a cry, lot - lot.
Also might be stunned by ringing consonants, located in the position at the beginning and in the middle of the word, if after them is a deaf consonant. It is easy to understand by the example: Buddes [Butka].
What did we know?
The deaf consonants are such sounds, when the larynx does not vibrate, that is, the voice does not participate. They are only from noise. Most deaf consonants have a vapor steam, however there are four unpaired sound of this type - this is [x], [x '], [h'] and [sh ']. Because of the rules of stunning consonants, those consonants, which in writing are ringing, are moving into their deaf pair. This happens if they turn out to be in the end of the word, as well as when there is another deaf consonant in front of them.
In Russian, not all sounds of speech are indicated, but only basic. In Russian, 43 main sound - 6 vowels and 37 consonants, whereas the number of letters is 33. The number of basic vowels (10 letters, but 6 sounds) and consonants (21 letters, but 37 sounds) do not coincide. The difference in the quantitative composition of the main sounds and letters is determined by the peculiarities of the Russian letter. In Russian, a solid and soft sound is indicated by the same letter, but the sounds are soft and solid are considered different, therefore it turns out the consonant sounds more than the letters that they are designated.
Ringing and deaf consonants
The consonants are divided into ringing and deaf. Calls consist of noise and voices, deaf - only from noise.
Ring consistent sounds: [b] [b "] [in] [in"] [g] [g "] [d] [d] [z] [z] [z] [l] [l] [ M] [M "] [N] [N"] [p] [p "] [th]
Deaf consonants: [P] [P] [F] [F "] [K] [K"] [T] [T "] [C] [C"] [Ш] [x] [x "] [ h "] [sh"]
Paired and unpaired consonants
Many consonants form a couple of bell and deaf consonants:
Ringing [b] [b "] [in] [in"] [g] [g "] [d] [d] [z] [z]] [w]
Deaf [P] [P "] [F] [F"] [K] [K "] [T] [T"] [s] [C "] [Ш]
Do not form couples following ringing and deaf consonants:
Bezov [l] [l] [m] [m] [n] [n "] [p] [p"] [th]
Deaf [x] [x "] [h"] [sh "]
Soft and hard consonants
The consonants are also divided into solid and soft. They differ in the position of language when pronouncing. When pronouncing soft consonants, the middle back of the language is raised to a solid nebu.
Most of the consonants forms a pair of solid and soft consonants:
Keywords: [b] [in] [g] [d] [z] [k] [l] [m] [n] [p] [p] [s] [t] [f] [x]
Soft [b "] [in"] [g "] [d"] [z "] [k"] [l] [m] [n "] [p"] [p "] [s"] [ T "] [f"] [x "]




Do not form steams the following solid and soft consonants:
Solid [z] [sh] [C]
Soft [h "] [sh"] [th "]
Hissing consonants
Sounds [F], [Ш], [ch '], [sh'] are called hissing.

[F] [sh] [h "] [sh"]
Whistling consonants

[s] [z] [s] [s "] [C]
Whistling sounds sch, z-ze front-band, slotted. With the articulation of solid ss, the teeth are naked, the tip of the language concerns the lower teeth, the back of the tongue is slightly curved, the side edges of the language are pressed to the upper indigenous teeth, which is formed in the middle a groove. Air passes through this groove creating friction noise.
When pronouncing soft C, s articulation is the same, but additionally the back of the tongue rises to a solid nebu. When pronouncing the sounds of the Z-Z, bonds closed and vibrate. The root curtain is raised.