Brief history of the symphony orchestra. Brief history of the orchestra, from ancient times to Beethoven Orchestra
Read also
Marina Rzheva
Abstract Node "Symphony Orchestra"
Abstract classes
« Symphony Orchestra»
for children 5 -6 years
Prepared: Music leader
Razheva Marina Anatolyevna
takikovo 2015
purpose: Promotion of preschoolers for classical music
Tasks. To form in children aesthetic perception of the surrounding world.
Promotion to musical culture.
To form the need for the perception of music.
Develop cognitive and creative abilities.
Enrich the dictionary.
Education area - "Artistic and aesthetic upbringing"
Organization form - joint activities of the teacher with children.
Type of activity of children: Cognitive, Communicative, Music and Artistic.
Materials and equipment: Music center for listening to music, children's musical instruments, presentation.
Preliminary work: At musical classes, children should get acquainted with the main tools symphony orchestra, their real sound, timbre color. Discerge groups of instruments: Strings, wind, drums, single.
Software content.
1. Expand the knowledge of children about the characteristics of the sound of musical instruments.
2. To educate interest, desire to listen to the sound tool.
3. Continue to develop the skills of the game on dmi (children's musical instruments)
4. Develop the timber ear of children.
Planned result.
Formation of the representation of O. symphony orchestra.
Strengthening the ability to distinguish the sound tool symphony orchestra.
Take an active part in the game on dmi.
Experience the need for the perception of music performed symphony orchestra.
Travel course.
Children enter the hall and perform an ordinary complex of musical and rhythmic movements, then calmly pass on chairs.
M. r. Hello with children using a speaker "Hello!", author ...
M. r. Draws the attention of children to the screen where children see a large group of musicians.
M. r. Guys, what you see in this photo.
Responses of children.
M. r. Yes this orchestra - group of musiciansthat perform one musical work together. Each musician plays his batch on notes, which is called score. Partitions are on special stands - consoles.
And now, I want to guess you a riddle. Try to guess it.
It orchestra controls,
Joy for people delivers.
Only a wand wave,
Music sound starts.
He is not a doctor and not a driver.
Who is it?. (Conductor)
Children. Conductor.
M. r. To orchestra It sounded simply and harmoniously - the conductor is managed. He stands face to musicians. The conductor can make orchestra play and fast, and slowly, and quietly, and loudly - as you like! But at the same time does not say a single word. He enjoys only his magic conductor. Before the conductor is thick-fat notes, in which the parties of all musicians are painted. They are called such notes - the key.
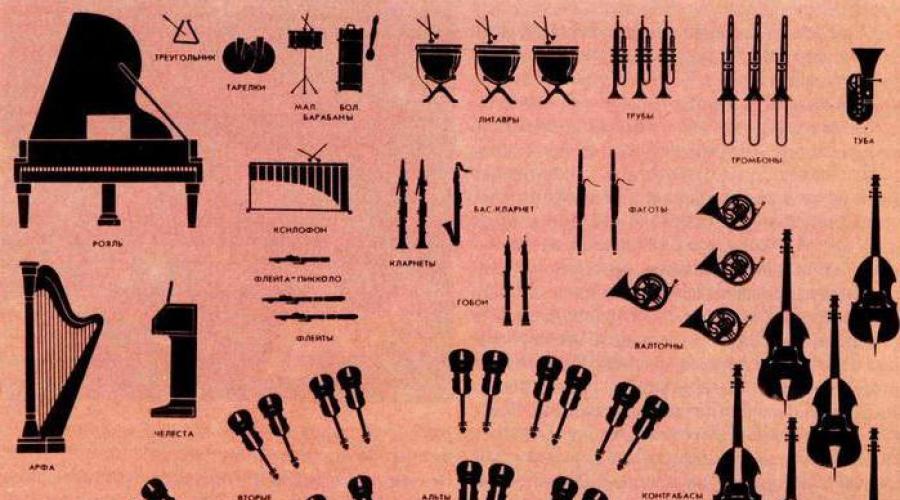
Violin - 4-String Bed tool, the highest sound in its family and the most important orchestra.
Cello is a big violin on which sitting sitting. Cello has a rich low sound.
Double bass - the lowest sound and the largest in size (up to 2 meters) Among the family of strings of brook tools. Play on it standing or on a special chair. This is a bass foundation (the foundation) Total orchestra.
Flute refers to the group of wooden wind instruments. But modern flutes are very rarely from wood, more often from metal, sometimes of plastic and glass. The most virtuoso and technically mobile tool in the wind family. Flute often charges orchestral solo.
M. r. Guys, why are the tools are called wind?
Responses of children.
M. r. Yes, they really blow in them. And it is more correct to say that the wind instruments sound when air is blown in them.
And now you see and hear the pipe from the group of copper wind instruments. The pipe has a high clean sound, very suitable for fanfar. Fanfares are used to supply signals - solemn or militant at festive celebrations, military parades.
Before you - Trombone. Trombone performs more bass line than melodic. From other copper tools it is distinguished by the presence of mobile scenes, moving forward and back the musician changes the sound tool.
French horn. Initially happened from hunting horn. French horn can be soft and expressive or sharp and creaking.
M. r. Please call percussion instruments.
Children. Drum, tambourine, maraakas, triangle, metallophone, cassattags, bells, ratchets, bubrels.
M. r. That's right guys. Shock tools are very much, but not all of them can serve in symphony orchestra.
Name the tools that you see on the slide.
Drums, plates, xylophone.
Slide 14.15.
And also guys, in orchestra Single tools are used. And you have to learn and call
they are correct.
Children. Piano. Harp.
M. r. Right. This is a concert piano and ancient tool - harp.
And you guys want to feel like a big musicians orchestra? Then I suggest you take tools and play one very beautiful musical play.
Performed "Rondo in Turkish style" - V. Mozart or
"Naughty Polka" - A. Filippenko.
M. r. Thanks guys. I like it.
What do you think guys, such tools like balalaika or saxophone, can play in orchestra. And what? The fact is that these tools are part of others orchestras.
Look carefully on these illustrations. Besides symphony orchestra There are other species orchestras: Spirit, folk, pop, jazz. They differ in the composition of the tools and by the number of musicians. IN symphony orchestra, on average, about 60-70 people, but it happens - 100 or more. Musicians are located in a definite order. They are combined into groups of similar to the timbre of tools.:
string, wooden-brazovaya, copper-well and shock. The musicians of the same group are sitting nearby to better hear each other. And it creates a consistent sound.
And now, I want to suggest you play the game.
Find out the tool.
Slide 17, 18, 19.
M. r. We wonderfully spent time. Did you like it? What is the name of orchestrawith whom we met today? What tool did you like? (Children answer one at will). I prepared for you a card with a mystery, which you will try to solve with my mother or dad and draw a gifue. (on the circulation silhouette - points).
Please come to me, I want to thank and say goodbye (the children close their eyes, the music leader strokes them on the head)
Orchestra (from Grech.Orhestra) is a large team of instrumental musicians. Unlike chamber ensembles, in the orchestra, some of its musicians form groups playing unison, that is, playing the same parties.
The idea of \u200b\u200bsimultaneous musitizing a group of instrumental executive groups is leaving in deep antiquity: in ancient Egypt, small groups of musicians played together on various holidays and funerals.
The word "orchestra" ("Orheztra") comes from the title of a round site before the scene in an ancient Greek theater, where an ancient Greek choir, a member of any tragedy or comedy, was located. In the era of rebirth and then inXVII the century of Orhestra was transformed into the orchestral pit and, accordingly, gave the name of the team of musicians placed in it.
There are many different types of orchestra: military consisting of brass - copper and wooden - tools, orchestras of folk instruments, string orchestras. The most rich in its capabilities is the symphony orchestra.
Symphonythe orchestra is called from several heterogeneous groups of instruments - the family of strings, wind and drums. The principle of such an association has developed in Europe inXVIII century. Initially, the symphony orchestra included a group of bow tools, wooden and copper brass instruments, which were adjacent to a few shock musical instruments. Subsequently, each of these groups expanded and diversified. Currently, among a number of varieties of symphony orchestras, it is customary to distinguish between a small and large symphony orchestra. A small symphony orchestra is an orchestra mainly classic composition (playing music of the end of the 18th - early XIX century, or modern stylization). In its composition 2 flutes (rarely small flute), 2 oboe, 2 clarinet, 2 Baby, 2 (rare 4) French horn, sometimes 2 pipes and litales, string group no more than 20 tools (5 first and 4 second violins, 4 viola, 3 cello, 2 double bass). The big symphony orchestra (BSO) includes mandatory trombones in the copper group and can have any composition. Often, wooden tools (flutes, baroes, clarinets and baggages) reach 5 instruments of each family (clarinets sometimes and more) and include varieties (small and alcohol flutes, Amur-Oboe and English Oboe, small, altove and bass clarinets, counterphagot). The copper group may include up to 8 horn (including special wagner tubes), 5 pipes (including small, alt, bass), 3-5 trombones (tenor and tenorbasy) and tube. Saxophones are very often used (in the jazz orchestra all 4 species). String group reaches 60 or more tools. Shock instruments are numerous (although Litavra, bells, small and large drums, triangle, plates and Indian tammes make up their backbone), harp, piano, harpsichine are often used.
To illustrate the sound of the Orchestra, I will use the entry of the final concert of the "Youtube Symphony Orchestra". The concert took place in 2011 in the Australian city of Sydney. In the live broadcast, it was observed on television millions of people all over the world. The Youtube Symphony Orchestra project is dedicated to raising love for music and demonstrating a huge creative diversity of mankind.
The concert program included well-known and little-known works of famous and little-known composers.
Here is his program:
Heector Berlioz - Roman Carnival - Overture, Op. 9 (Featuring Android Jones - Digital Artist)
MEET Maria Chiossi - Harp
Percy Grainger - Arrival On A Platform Humlet From In A Nutshell - Suite
Johan Sebastian Bach - Toccata in F Major for Organ (Featuring Cameron Carpenter)
MEET PAULO CALLIGOPOULOS - ELECTRIC GUITAR AND VIOLIN
Alberto Ginastera - Danza Del Trigo (Wheat Dance) And Danza Final (Malambo) from the Ballet Estancia (ConduCed by Ilyich Rivas)
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart - "Caro" Bell "IDOL MIO" - Canon in Three Voices, K562 (Featuring The Sydney Children "S Choir and Soprano Renee Fleming Via Video)
MEET XIOMARA MASS - OBOE
Benjamin Britten - The Young Person "S Guide to the Orchestra, Op. 34
William Barton - Kalkadunga (Featuring William Barton - Didgeridoo)
Timothy Constable - Suna
MEET Roman Riedel - Trombone
Richard Strauss - Fanfare for the Vienna Philharmonic (Featuring Sarah Willis, Horn, Berlin Philharmoniker and ConduCed by Edwin Outwater)
* Premiere * Mason Bates - Mothership (Specially Composed for the YouTube Symphony Orchestra 2011)
MEET SU CHANG - GUZHENG
Felix Mendelssohn - Violin Concerto in E Minor, Op. 64 (Finale) (Fefan Jackiw and ConduCed by Ilyich Rivas)
MEET OZGUR BASKIN - VIOLIN
Colin Jacobsen and Siamak Aghaei - Ascending Bird - Suite for String Orchestra (Featuring Colin Jacobsen, Violin, and Richard Tognetti, Violin, and Kseniya Simonova - Sand Artist)
Meet Stepan Grytsay - Violin
Igor Stravinsky - The Firebird (Infernal Dance - Berceuse - Final)
* Encore * Franz Schubert - Rosamunde (Featuring Eugene Izotov - Oboe, and Andrew Mariner - Clarainet)
HISTORY OF SIMPONIC ORCHESTRATION
The symphony orchestra was formed during the centuries. Its development for a long time occurred in the depths of the opera and church ensembles. Such teams B.XV - XVII explosive were small and heterogeneous. They included lute, violis, flutes with hobs, trombones, harp, drums. Gradually, the dominant position won stringed bow tools. Viol's place was taken by violin with their more juicy and singeling sound. By topXVIII in. They had already reinforced in the orchestra. Combined a separate group and brass (flutes, baroes, bassotes). From the church orchestra, they moved to the symphony tube and the Litavra. An indispensable participant in the instrumental ensembles was Clausing.
Such a composition was characteristic of I. S. Baha, Handel, A. Vivaldi.
From the middleXVIII in. The genres of symphony and instrumental concert begin to develop. The departure from the polyphonic style led to the desire of composers to the timbre diversity, the relief dissection of orchestral votes.
The functions of new tools are changed. Clausing with its weak sound gradually loses its leading role. Soon composers completely refuse him, relying mainly on the string and brand group. By the endXVIII in. The so-called classic composition of the orchestra has been formed: about 30 strings, 2 flutes, 2 oboy, 2 lags, 2 pipes, 2-3 French horn and litavra. Soon the wind joined the clarinet. For such a composition, J. Gaidn wrote, V. Mozart. This is the orchestra in the early writings of L. Beethoven. INXIX. in.
The development of the orchestra was mainly in two directions. On the one hand, increasing in the composition, it is enriched with the instruments of many species (in this great merit of composer-romantics, primarily Berlioz, Sheet, Wagner), on the other hand, developed the internal capabilities of the orchestra: the sound paints became cleaner, the texture is clearer, Expressive resources - economy (such an orchestra Glinka, Tchaikovsky, Roman-Korsakov). Significantly enriched orchestral palette and many end composersXIX - 1st Half XX in. (R. Strauss, Malener, Debussy, Row, Stravinsky, Barkok, Shostakovich, etc.).
Composition of symphony orchestra
The modern symphony orchestra consists of 4 major groups. The foundation of the orchestra is the string group (violins, alta, cello, double bass). In most cases, strings are the main carriers of the melodic principle in the orchestra. The number of musicians playing strings is approximately 2/3 of the entire team. The group of wooden wind instruments includes flutes, baroes, clarinets, baggage. Each of them is usually an independent batch. Landing the scum in the timbre saturation, dynamic properties and diversity of the game techniques, the winds have a lot of power, sound compactness, bright colorful shades. The third group of orchestra instruments are copper brass (French horn, pipe, trombone, tube). They contribute to the orchestra new bright paints, enriching its dynamic capabilities, give the sound and glitter, also serve as a bass and rhythmic support.
Percussion instruments are increasingly acquired in the symphony orchestra. Their main function is rhythmic. In addition, they create a special sound-checked background, complement and decorate the orchestral palette with coloristic effects. By the nature of the sound, the drums are divided into 2 types: some have a certain height of sound (litwords, bells, xylophone, bells, etc.), others are devoid of accurate soundness (triangle, tambourine, small and large drum, plates). Of the tools that are not included in the main groups, the role of the harp is the most significant. Epizodically composers include Cheeset, Piano, Saxophone, Organ and Other Tools in Orchestra.
Read more about the tools of the symphony orchestra - a string group, wooden wind, copper brass and drums can be read on site..
I can not get around the attention of another useful site, "children about music", which discovered during the preparation of the post. No need to scare that this is a site for children. It has quite serious things, only told by a simpler, understandable language. Here linkon him. By the way, it has a story about the symphony orchestra too.
The word "orchestra" is familiar to every schoolchild. This is the name of a large team of musicians who jointly fulfill the musical work. Meanwhile, in ancient Greece, the term "Orhestra" (from which the modern word "Orchestra" was subsequently formed) denoted the platform before the scene, where the choir was located, is an indispensable participant of the ancient Greek tragedy. Later, a group of musicians began to be located on the same platform, and it was called "orchestra."
Passed century. And now the word "orchestra" itself does not have a certain meaning. Nowadays, there are different orchestras: brass, folk, orchestras of bayanists, chamber orchestras, pop-jazz, etc. But none of them can withstand competitions with the "sound miracle"; So often, of course, the symphony orchestra is completely called.
The capabilities of the symphony orchestra are truly limitless. At its disposal - all the shades of the soundness of barely audible oscillations and rustles to the powerful bulwed risks. And it's not even in the very latitude of dynamic shades (they are generally available to any orchestra), and in that conquering expressiveness, which always accompanies the sound of genuine symphonic masterpieces. Here come to the rescue and timbre combinations, and powerful wave-like increments and decals, and expressive solo replicas, and the fusion "organ" layers of sound.
Listen to some samples of symphonic music. Recall the fabulous picture of the famous Russian composer A. Lyadov "Magic Lake" by their heartfelt silence. The subject of the image serves here nature in its intact, static condition. It emphasizes the composer in his statement about the "Magic Lake": "How it is picturesque, purely, with stars and mysteriousness in the depths! And most importantly - without people, without their requests and complaints - one dead nature is cold, angry, but fantastic, as in a fairy tale. " However, Lyadovsky score can not be called dead or cold. On the contrary, she is a warm lyrical feeling, - trembling, but restrained.
The famous Soviet musicologist B. Asafiev wrote that in this "poetic contemplative musical picture ... Lyadov's creativity seizes the sphere of lyric symphony landscape." The colorful palette of "Magic Lake" is made up of veiled, muted sounds, from rustles, rustles, barely notable splashes and oscillations. Thin openwork strokes are dominated here. Dynamic increments are minimized. All orchestral voices carry an independent visual load. Melodic development in the true sense of this word is not; Like flickering glare, separate short phrases-motifs ... Lyadov, who sacraged to "hear silence," silent, painting a picture of the enchanted lake - a picture of the smoky, but inspired, full of fairy-tale fragrance and clean, chaste beauty. A similar landscape could be "drawing" only with the help of a symphony orchestra, for no tool and no other "orchestral organism" are not able to portray such a visual picture and find such thin timbre paints and shades for it.
But an example of the opposite type - the final of the famous "Ecstasy Poems" by A. Scriabin. The composer shows in this product a manifold of human states and actions in steady and logically thoughtful development; Music sequentially transfers inertia, waking will, a collision with threatening forces, fighting them. Culmination follows climax. By the end of the poem, the tension is growing, preparing a new one, an even more ambitious rise. Epilogue "Ecstasy Poems" turns into a dazzling picture of the colossal scope. At sparkling, overflowing with all the colors, the organ) is also connected to the huge orchestra) eight horn and the pipe joyfully proclaim the main musical theme, whose temptation is to the end reaches inhuman power. There can be no other ensemble for such power and majestity. Only the symphony orchestra is capable of so richly and at the same time to organizely express delight, ecstasy, frantic lifting of feelings.
The Lyad "Magic Lake" and Epilogue "Ecstasy Poems" is, if you can express, extreme sound and dynamic poles in the richest sound palette of the symphony orchestra.
Now let's turn to the example of another kind. The second part of the eleventh symphony of D. Shostakovich has a subtagolo wok - "9th of January". In it, the composer tells about the terrible events of the "bloody Sunday". And at that moment, when the cries and moans of the crowd, rifle salts, the iron rhythm Sol Danish steps merge into the striking and powerful of the sound picture, - a deafening squall suddenly obras ... and in the coming silence, in the "whistling" whisper of string tools It is clearly heard by the quiet and sorrowful singing of the choir. By a member of the definition of the musicologist of Orlov, the impression is created, "as if the air of the Palace Palace groaned from grief at the sight of the sulled atrocities." Possessing an exceptional timbre of alarm and brilliant skill of instrumental letter, D. Shostakovich managed to create a pure orchestral means to create an illusion of choral sound. There were even cases when on the first executions of the eleventh symphony, the listeners were listened to themselves from their places, thinking that there was a choir at the orchestra ...
The symphony orchestra is able to transmit a wide variety of naturalistic effects. So, an outstanding German composer Richard Strauss in the symphony poem "Don Quixote", illustrating the famous episode from the Roman Servantes, surprisingly "visually" portrayed the flue of the herd of the rams in the orchestra. In the suite of the French composer K. Saint-Sansa "Carnival of Animals" and cries of Oslov, and the clumsy gait of an elephant, and the restless roll call chicken with roosters. The Frenchman's Frenchman in the Symphonic Screezo "Student of Correction" (it is written based on the ballads of the V. Goethe's named) brilliantly painted the picture of the roaring water element (in the absence of an old wizard, the student decides to turn a prayer in the servant: he makes it wear water that gradually floods the whole house ). Do not have to talk, how many sound-resistant effects are scattered in the music of the opera and ballet; Here, they are also transferred to the means of the symphony orchestra, but are suggested by a direct stage situation, and not a literary program, as in the compositions of symphony. It is enough to recall such operas as the "tale of the Tsar Saltan" and "Snow Maiden" N. Rimsky-Korsakov, ballet I. Stravinsky "Petrushka" and others. Excerpts or suits from these works are often performed in symphony concerts.
And how many excellent, almost visual paintings of the marine element can be found in symphonic music! Suite N. Rimsky-Korsakov "Shehherazada", "Sea" K. Debussy, Overture "Sea Tish and Happy Swimming" F. Mendelssohn, Symphony Fantasies "Storm" P. Tchaikovsky and "Sea" A. Glazunov - a list of such writings is very large . For the symphony orchestra, many works depicting pictures of nature or containing landscape sketches are written. I will call at least sixth ("pastoral") Symphony of L. Beethoven with a striking image of the image by the picture of a suddenly broken thunderstorm, the symphony picture of A. Borodin "in Central Asia", the symphonic fantasy of A. Glazunov "Forest", "scene in the fields" from fantastic Symphony of Berlioz. However, in all these works, the nature of nature is always associated with the emotional world of the composer itself, as well as the idea that determines the nature of the composition as a whole. And in general, the moments are descriptive, naturalistic, sound-resistant occupy a very small proportion in the symphonic canvases. Moreover, actually software music, that is, the music that conveys any literary plot consistently, also does not occupy the leading place among the symphony genres. The main thing that the symphony orchestra can be proud is a rich palette of the diverse means of expressiveness, these are colossal, still not exhaustable possibilities of various combinations and combinations of tools, these are the richest timbre resources of all components of the band orchestra.
The symphony orchestra differs sharply from other instrumental teams as the composition of it is always strictly defined. To take at least numerous pop-jazz ensembles, existing in abundance almost in all corners of the globe. They are not at all like one at all: different tools and the number of tools (from 3-4 to two dozen or more), and the number of participants. But the most important thing is that these orchestras are not similar to their sound. In some, string, in others - saxophones and copper brass instruments; In some ensembles, the leading role is performed by piano (supported by shock and double bass); The pop orchestras of various countries include national instruments, etc. Thus, in almost every pop orchestra or jazz, there are no strictly defined tool composition, but freely use combinations of various tools. Therefore, the same product sounds differently from different pop-jazz teams: each of them offers its specific processing. And this is understandable: because jazz is art, based on its improvisational.
There are also brass bands. Some consist exclusively of copper tools (with mandatory inclusion of drums). And most of them do not cost without wooden winds - flutes, braes, clarinets, scenes. Orchestras of folk instruments are different: the Russian People's Orchestra is not similar to Kyrgyz, and Italian - on the folk orchestras of the Scandinavian countries. And only the symphony orchestra is the largest musical organism - has a long-established, strictly defined composition. Therefore, a symphonic work written in one country can be fulfilled by any symphony team of another country. Therefore, the language of symphonic music is a truly international language. They have been used for more than two centuries. And he does not age. Moreover, nowhere is so many interesting "internal" changes, how many of them happen in the modern symphony orchestra. On the one hand, often causing new timber paints, the orchestra becomes everything richer every year, on the other - everything is more clearly evacuated by his main core, which formed in the XVIII century. And sometimes composers of our time, referring to such an "old-fashioned" composition, once again prove how great his expressive opportunities are ...
Perhaps, so many wonderful music has been created for one of the music teams! In the brilliant pleiad, composers-symphonists shine the names of Hydena and Mozart, Beethoven and Schubert, Mendelssohn and Shumanan, Berliosa and Brahms, Sheet and Wagner, Griga and Noborik, Glinka and Borodin, Roman Corsakov and Tchaikovsky, Rakhmaninov and Scriabin, Glazunov and Taneyev, Male and Brookner, Debussy and Ravel, Sibelius and R. Strauss, Stravinsky and Bartok, Prokofiev and Shostakovich. In addition, the symphony orchestra, as is known, is an indispensable participant in opera and ballet performances. And therefore, those fragments from the operas and ballets should be added to the hundreds of symphonic works, in which the orchestra (and not soloists, choir or just a stage action) plays a paramount role. But that's not all. We are watching hundreds of movies and most of them "voiced" with a symphony orchestra.
The radio, television, CDs, and through them - and symphonic music are firmly entered into our lives. In many cinemas, small symphony orchestras play in front of sessions. Create such orchestras and in amazing. In other words, from the huge, almost the immense ocean of music surrounding us, a good half of one way or another is associated with symphonic sound. Symphony and oratorios, operas and ballets, instrumental concerts and suite, music for theater and cinema - all these (and many others) genres simply cannot do without a symphony orchestra.
However, it would be wrong to believe that any musical essay could sound in the orchestra. After all, it would seem that knowing the principles and laws of the instrumentation, each competent musician can orchest the piano or some other product, that is, put it in a bright symphony outfit. Meanwhile, in practice, this is relatively rare. It is not by chance that N. Rimsky-Korsakov said that the instrumentation is "one of the soul of the soul of the essay itself." Therefore, already thinking about the plan, the composer calculates on a certain instrumental composition. Therefore, light, unassicuating plays, and ambitious, large-scale canvases can be written for the symphony orchestra.
True, cases where the essay receives a second life in a new, symphonic version. It happened to the genius piano cycle M. Mussorgsky "Pictures from the exhibition": his masterfully orchestrated M. Ravel. (There were other, less successful attempts to orchestra's "pictures from the exhibition.") Opera M. Mussorgsky Opera, Boris Godunov and Hovanshchina, rebel to D. Shostakovich, who carried out their new orchestral edition. Sometimes two versions of the same work are peacefully in the creative heritage of the composer - solo-instrumental and symphonic. Such examples are a bit, but they are rather curious. "Pavana" Ravel exists in the piano, and in the orchestral version, and both live an equal concert life. Prokofiev orchestrated slow part of his fourth piano sonata, making it an independent, purely symphonic work. Leningrad composer S. Slonimsky wrote the vocal cycle "Wolnitsi songs" on folk texts; This essay also has two equivalent on its artistic significance of the option: one goes accompanied by piano, the other in the orchestra. However, most often the composer, bearing for the work, well represents not only the idea of \u200b\u200bthe writings, but also his timbre embodiment. And such genres like symphony, instrumental concert, symphonic poem, suite, rapeseed, etc., are always closely connected with the sound of the symphony orchestra, you can even say, are inseparable from it.
Music is, first of all, sounds. They can be loud and quiet, fast and slow, rhythmic and not very ...
But each of them, each sounding note, somehow definitely affects the consciousness of a person who listens to music, on his mental state. And if it is orchestral music, then leave someone else, she will definitely can't!
Orchestra. Types of orchestras
The orchestra is called the combined musicians playing on musical instruments of works that are designed specifically for these tools.
And on what this composition, the orchestra has various musical abilities: on the timbre, dynamics, expressiveness.
What types of orchestras exist? The main one is:
- symphonic;
- instrumental;
- orchestra of folk instruments;
- wind;
- jazz;
- pop.
There is also a military orchestra (performing military songs), school (as part of which schoolchildren) and so on.
Symphony Orchestra
This type of orchestra in its composition contains string, brass and percussion instruments.
There is a small symphony orchestra and big.
Small is the one that plays the music of composers of the end of the XVIII - early XIX centuries. In its repertoire there may be modern variations. The big symphony orchestra differs from the small amount of more tools into its composition.

As part of the small necessarily present:
- violins;
- alto;
- cello;
- double bass;
- lays;
- french horn;
- pipes;
- litavra;
- flutes;
- clarinet;
- oboe.
The following tools are included in the big:
- flutes;
- goboes;
- clarinets;
- contraneagotes.
By the way, in its composition it may be up to 5 instruments of each family. And also in the Big Orchestra are present:
- french horn;
- pipes (bass, small, alte);
- trombones (tenor, tenorbasy);
- tuba.
And, of course, percussion instruments:
- litavra;
- bells;
- small and large drum;
- triangle;
- plate;
- indian tames;
- harp;
- piano;
- harpsichord.
A feature of a small orchestra is the fact that string instruments in it about 20, while in the big - about 60.
Manages the Symphony Orchestra conductor. He artistically interprets the work performed by the orchestra with the help of the score - a complete note record of all parties of each instrument of the orchestra.
Tool orchestra
This type of orchestra is different in its form that it does not have a clear number of musical instruments of certain groups. And he can perform any music (in contrast to the symphony orchestra, which performs exceptionally classical).
There are no specific types of tool orchestras, but it is conventionally related to the pop orchestra, as well as an orchestra performing the classics in modern processing.

According to the historical reference, instrumental music began to actively develop in Russia only under Peter the first. She, of course, had a western influence on himself, but she was no longer under such a ban, as in earlier times. And before it came to such that it was not forbidden to play, but burned musical instruments. The church believed that they had no soul, no heart, and therefore they could not glorify God. And therefore instrumental music developed mainly among the simple people.
Play in the instrumental orchestra on flute, lyre, kifara, swirls, pipe, bobbin, tambourine, trombone, drawing, rim and other musical instruments.
The most popular instrumental orchestra of the 20th century is the Orchestra of the Moria field.
He was his conductor, head, arranger. His orchestra played a lot of popular musical works of the 20th century, as well as its own essay.
People's Orchestra
In such an orchestra, the main tools are folk.
For example, for the Russian national orchestra, the most typical are: domra, balalaiks, huslies, accordions, harmonics, pranks, swirls, the horns of Vladimir, tambourines. Also, additional musical instruments for such an orchestra have a flute and oboe.

For the first time, the People's Orchestra appeared at the end of the XIX century, the organizer of which V.V. became Andreev. This orchestra toured a lot and was widely popular in Russia and beyond. And at the beginning of the 20th century, folk orchestras began to appear everywhere: in clubs, with cultural palaces, and so on.
Brass band
This type of orchestra assumes that its composition includes various brass and percussion instruments. It happens: small, medium and large.

Jazz orchestra
Another orchestra of this species was called Jazz Band.
It includes such musical instruments: saxophone, piano, banjo, guitar, drums, pipes, trombones, double bass, clarinets.

In general, Jazz is a direction in music that has developed under the influence of African rhythms and folklore, as well as European harmony.
For the first time jazz appeared in the south of the United States at the beginning of the XX century. And soon spread in all countries of the world. In Motherland, this musical direction developed and supplemented with new characteristic features that appeared in a particular region.

At one time in America, the terms "Jazz" and "Popular Music" had the same semantic meaning.
Jazz orchestras began to actively form in the 1920s. And those of them remained up to the 40s.
In these musical groups, the participants came, as a rule, in adolescence, by performing their specific batch - bored or notes.
The peak of the glory of jazz orchestras is considered to be the 1930s. The leaders of the most famous jazz orchestras were: Arti Shaw, Glenn Miller, and others. Their musical works sounded at that time everywhere: on the radio, in dance clubs, and so on.
Currently, jazz orchestras and melodies, written in the style of "Jazz" are also very popular.
And although species of musical orchestras there are more, the article considers the main ones.
, Cello, double bass. Collected together, in the hands of experienced musicians, subordinate the will of the conductor, they form a musical instrument capable of expressing and passing any musical content, any image, any idea. Many combinations of the orchestra tools give a practically an inexhaustible set of diverse sounds - from a bulk-like, deafening to barely heard, from a sharp cutting rumor to caressing-soft. And multi-storey chords of any complexity, and patterned-winding plexus of heterogeneous melodic ornaments, and a cellular-thin fabric, small sound "fragments", when, according to the figurative expression S. S. Prokofiev, "from the orchestra as if dust", and powerful uninsions of many Tools simultaneously playing the same sounds - all this is subject to the orchestra. Any of orchestral groups - string, brave, shock, plug, keyboards - can be separated from others and lead their musical narration in the remaining silence; But all of them completely, partially or one or individual representatives, merging with another group or part of it, form a complex timber alloy. For more than two centuries, the most cherished thoughts of composers, the brightest milestones of the history of the art of sounds are associated with the music conceived, written, and sometimes overlapped for the symphony orchestra.
The scheme of the arrangement of musical instruments of the symphony orchestra.
Everyone who loves music knows and remembers the names of J. Gaidna, V. A. Mozart, F. Schubert, R. Shuman, I. Brams, Berlioz, F. Sheet, S. Frank, J. Bizeta, J. Verdi, P. I. Tchaikovsky, N. A. Rimsky-Korsakov, A. P. Borodin. M. P. Mussorgsky, S. V. Rakhmaninova, A. K. Glazunova, I. F. Stravinsky, S. S. Prokofiev, N. Ya. Meakovsky, D. D. Shostakovich, A. I. Khachaturian, K. Debussy, M. Ravel, B. Bartok and other masters, whose symphonies, suite, overtures, symphonic poems, paintings, fantasies, instrumental concerts, accompanied by orchestra, finally, cantata, oratoria, operas and ballets are written for a symphony orchestra or involve its participation . The ability to write for it is the highest and most complex region of art of a musical composition, requiring deep special knowledge, greater experience, practitioners, and most importantly - special musical abilities, giftedness, talent.
The history of the emergence and development of the symphony orchestra is the history of the gradual restructuring of the old and the invention of new tools, an increase in its composition, the history of improving ways to use combinations of instruments, i.e. the history of the area of \u200b\u200bmusical science, which is referred to as the orchestration or tool, and, finally, the story of symphonic Opera, oratorical music. All these four terms, four sides of the concept of "Symphony Orchestra", are closely related. There was a diverse and remain their influence on each other.
The word "ORCHESTRA" meant in ancient Greece a semicircular platform before the scene of the theater, where the choir was located - an indispensable participant of dramatic ideas in the era of Eschila, Sofokla, Euripid, Aristofan. Around 1702, this word for the first time was marked by a small space, intended for the ensemble of the instrumentalist opera. So called instrumental groups in chamber music. In the middle of the XVIII century. The difference is introduced decisive for the history of the orchestra - the numerous orchestra was opposed to small chamber music - an ensemble. Until that time, the clear face between the music chamber and orchestral was not conducted.
The concept of "Symphony Orchestra" appeared in the era of classicism, when they lived and created K. V. Glitch, L. Bokkerini, Gaidn, Mozart. It has already arisen after the composers have become accurately discharged in the notes of the name of each tool playing one or another voice, one or another musical line. Even at the beginning of the XVII century. K. Monteverdi in "Orphey" before each number only listed tools that could perform it. The question of who should play, remained open. Therefore, in any of the 40 opera theaters of his native Venice, one execution of "Orpheus" could be unlike another. J. B. Lully, composer, violinist, conductor, was probably the first to write for a certain composition of the tools, for the so-called "24 scripts of the king" - a string ensemble formed at the yard of Louis XIV and led by the Rully. He has a top voice of the string band, and the gobies also were supported, and the bottom - Fagotami. Goby and lamps without string, contrasting with the full composition, participated in the middle sections of its compositions.
Throughout the XVII century. And the first half of the XVIII century. The initial basis of the orchestra is formed - the string group. Gradually add representatives of the Family of Winds - Flutes, Goboes and Fags, and then French Horn. The clarinet penetrated the orchestra significantly later due to its extremeness of the then imperfection. M. I. Glinka in his "instrumentation notes" calls the sound of clarinet "goose". All the same spirit group consisting of flutes, braes, clarinets and horn (all two) appears in the "Prague Symphony" of Mozart, and in front of his French contemporary - F. Gossek. In London Symphony, Haidna and Early Symphony L. Beethoven appear two pipes, as well as Litales. In the XIX century The brass group in the orchestra is even more intensified. For the first time in the history of orchestral music, there are participating in the final of the 5th Symphony of Beethoven Flute Piccolo, counterfeit, as well as three trombone, before the operations used only in operations. R. Wagner adds a tuba and brings the number of pipes up to four. Wagner is a composer for the benefit of the opera, but at the same time it is rightfully considered an outstanding symphony and reformer of the symphony orchestra.
The desire of composers of the XIX-XX centuries. Enrich the sound palette led to an introduction to the orchestra of a number of instruments with special technical and timber capabilities.
By the end of the XIX century. The composition of the orchestra is communicated to the impressive, and sometimes to gigantic sizes. So, the 8th Symphony of the Mahler is not accidentally called the "symphony of thousands of participants." In the symphonic canvases and operations of R. Strauss, numerous varieties of windows appear: alte and bass flutes, baritone oboe (hekkelphone), small clarinet, double bass clarinet, alte and bass pipes, etc.
In the XX century The orchestra is replenished mainly by shock instruments. Prior to this, the usual participants of the orchestra were 2-3 liters, plates, large and small drums, a triangle, less often tambourine and tames, bells, xylophone. Now composers apply a set of orchestral bells, giving chromatic gamut, Cheeset. They are introduced into the orchestra such tools like Flexton, Bubrentes, Spanish Kastagniques, Warning Casting Wooden Box, Ratchet, Beach Clapper (her blow is similar to Shot), Siren, Wind and Thunder Machine, Even the singing of the nightingale recorded on a special plate (it is used In the symphony poem of the Italian composer O. Respigi "Ponya Rome").
In the second half of the XX century. From jazz to the symphony orchestra, such percussion, like a vibraphone, tomtomas, bongs, combined percussion, come from jazz, and "Hai-Hat"), Maracasi.
As for the string and overall groups, their formation by 1920 was mainly completed. The composition of the orchestra is sometimes introduced separate representatives of a group of saxophones (in the works of Visa, Rowel, Prokofiev), the brass orchestra (Cornets at Tchaikovsky and Stravinsky), harpsichine, domra and balalaikas, guitar, mandolin, etc. Composers are increasingly creating works for partial The compositions of the symphony orchestra: for some strings, for stringed and copper, for the brass group without stringed and drums, for stringed with shock.
Composers XX century. Many music writes for chamber orchestra. In its composition, 15-20 strings, one wooden wind, one or two French horses, a group of drums with one performer, harp (instead there can be a piano or harpsichine). Along with these, works for the ensemble of soloists, where there is one representative from each variety (or from some of them). These are chamber symphones and plays A. Schönberg, A. Webern, Suite Stravinsky "History of Soldier", Composition of Soviet composers - our contemporaries M. S. Weinberg, R. K. Gabicwadze, E. V. Denisov and others. Increasingly, the authors turn to the compositions unusual, or, as they say, emergency. They need unusual, rare sounds, as the role of the timbre in modern music has increased, more than ever.
And yet, so that there is always the opportunity to perform music and old, and the new, and the newest, the composition of the symphony orchestra remains stable. The modern symphony orchestra is divided into a large symphony orchestra (about 100 musicians), medium (70-75), small (50-60). On the basis of a large symphony orchestra, it is possible for each work to select the composition necessary for its execution: one for the "eight Russian folk songs" by A. K. Lyadova or "String Serenada" Tchaikovsky, the other - for the Grand Towns of Berlioz, Scriabin, Shostakovich, for Parsley "Stravinsky or Fiery" Bolero "Ravel.
How are Musicians on stage? In the XVIII-XIX centuries. The first violins were sitting on the left of the conductor, and the right - the second, behind the first violins, the altas was sat down, and behind the second - cello. At the string group, the rows were sitting: a wooden brass group ahead, and behind it the copper brass. Double bass were located in the background on the right or left. The rest of the space was assigned to the harp, the chase, piano and shock. In our country, the musicians are seated according to the scheme introduced in 1945 by the American conductor L. Shkye. According to this scheme, instead of the second violins to the right of the conductor in the foreground, cello placed; Their former place is now occupied by second violins.
The symphony orchestra is managing the conductor. It combines the orchestra musicians and directs all their efforts to implement its executive plan in the rehearsal process and at the concert. Conducting is based on a specially designed system of hand movement. In his right hand, the conductor usually holds a wand. The most important role is played by his face, a look, Mimica. The conductor must be a highly educated person. He needs knowledge of music of various eras and styles, instruments of the orchestra and their capabilities, a thin rumor, the ability to deeply penetrate the composer's idea. The talent of the artist must be combined with him with organizational and pedagogical abilities.