Once representatives of the kind of man belong to the presented. The main stages of the evolution of man
Anthropogenesis (from Greek. Anthropos - man + genesis - origin) - the process of historical formation. Today there are three main theories of anthropogenesis.
Creation Theory, the most ancient of the existing, argues that a person is the creation of a supernatural being. For example, Christians believe that the person was created by God in a one-time act "in the image and likeness of God." Similar ideas are present in other religions, as well as in most myths.
Evolutionary theory It claims that a person has occurred from monkey-like ancestors in the process of long-term development under the influence of the laws of heredity, variability and natural selection. The foundations of this theory for the first time proposed an English scientist Charles Darwin (1809-1882).
Space theory It claims that a person has extraterrestrial origin. He is a direct descendant of alien creatures, or the fruit of extraterrestrial reason experiments. According to the majority of scientists, it is the most exotic and least likely of the main theories.
Stages of the evolution of man
With all the diversity of points of view on anthropogenesis, the overwhelming majority of scientists adhere to evolutionary theory, which is confirmed by a number of archaeological and biological data. Consider the stages of the evolution of a person from this point of view.
Australopithek (Australopithecus) is considered the closest to the anestick form of a person; He lived in Africa 4.2-1 million years ago. The body of Australopithek was covered with thick hair, and in appearance he was closer to the monkey than to man. However, he has already walked on two legs and enjoyed different objects as an instruments, which contributed to the estimated thumb. The volume of its brain (with respect to the volume of the body) was less than human, but more than that of modern human monkeys.
Man skillful (Homo Habilis) is considered the very first representative of the human race; He lived 2.4-1.5 million years ago in Africa and was named so because of the ability to manufacture the simplest stone guns. His brain on a third was superior to the brain of Australopithek, and the biological peculiarities of the brain testify to the possible reaches of speech. The rest of the person skilled more was like Australopithek than on a modern man.
Strong man (Homo Erectus) settled 1.8 million - 300 thousand years ago in Africa, Europe and Asia. He did complex guns and was already able to use the fire. His brain is close to the brain of a modern man, which allowed him to organize collective activities (hunting for large animals) and use speech.
In the period from 500 to 200 thousand years ago, a transition from a person sparkling to a reasonable person (Homo Sapiens) took place. It is quite difficult to detect the border when one species replaces the other, so representatives of this transition period are sometimes called Ancient man intelligent.
Neanderthal (Homo Neanderthalensis) lived 230-30 thousand years ago. The brain volume of Neanderthal corresponded to the modern (and even a little surpassed it). Excavations also testify to a sufficiently developed culture, which included rituals, fuzz of art and morality (concern for tribesmen). Earlier it was believed that the neandertalets - the direct ancestor of a modern man, but now scientists are inclined to the version that he is a dead-end, "blind" branch of evolution.
Reasonable new (Homo Sapiens Sapiens), i.e. A modern type man appeared about 130 thousand (perhaps more) years ago. Fossil "new people" at the place of the first find (Cro-Manon in France) was called Cromanons. Cryanonians outwardly differed little from a modern person. After them, numerous artifacts remained, which make it possible to judge the high development of their culture - cave painting, miniature sculpture, engraving, decoration, etc. Man is intelligent thanks to his abilities of 15-10 thousand years ago, settled all the land. In the course of improving labor tools and accumulation of life experience, a person moved to the producing farm. During the Neolithic period, large settlements arose, and humanity in many areas of the planet entered into the era of civilizations.
The phylogenetic man of a sensible man is built only in general terms. The main stages of the evolution of a person are characterized in the table:
| Anthropoids | Gominids | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dryoitek | Australophec (Australopita) | Man skillful | Ancient people (Peteitront, Sinantrophop) | Ancient people (Neanderthals) | New people (Cryanonets, man) |
| Age, years | |||||
| 18 million | 5 million | 2-3 million | 2 million - 200 thousand | 250-35 thousand | 50-40 thousand |
| Appearance | |||||
| Small animals with a rounded skull, binocular vision, well-developed brain; may be vertical | Weight up to 50 kg, height up to 150 cm, hands are free, straight | Falangie fingers are flattened, the first finger of the foot is not assigned to the side | Growth of about 160 cm, massive bony, hematic body position | Height 155-165 cm, County people, went somewhat bent | Growth of about 180 cm, physical type of modern man |
| Brain volume, see 3 | |||||
| — | 550-650 | 750 | 700-1200 | Up to 1400. | About 1400. |
| Skull | |||||
| Skull is close in structure to the skull of man-shaped monkeys | Massive jaws, small cutters and fangs | Teeth of the human type | Skull bones massive, forehead sloping, Absorbral rollers are expressed | Beveled forehead and headings, a large superlord roller, the chin protod is poorly developed | The brain skull prevails above the facial, the solid superlordable roller is absent, the chin protod is well developed |
| Tools | |||||
| Manipulation with surrounding objects | Systematic use of natural items | Making primitive labor instruments | Production of well-selected stone tools of labor | Making a variety of stone workers of labor | Production of complex tools of labor and mechanisms |
| Lifestyle | |||||
| Studied lifestyle | Study Lifestyle, Hunting, Gathering | Cooperation during hunting and group protection | Public Lifestyle, Maintaining Fire, Primitive Speech | Collective activities, care for neighbors, developed speech | True speech, abstract thinking, development of rural and industrial economy, technology, science, art |
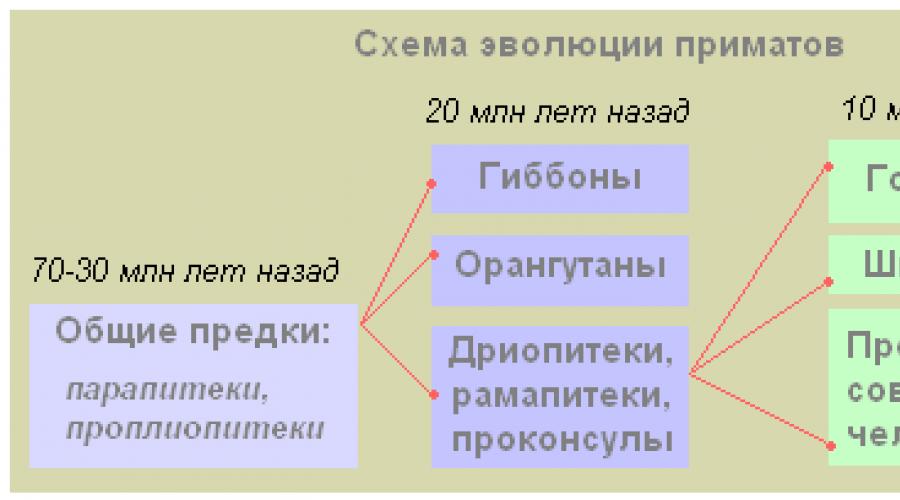
According to modern data of paleontology, the predecessors of man are the ancient primitive insectivorous mammals, which have granted parapichecans.
Parappitecia Around about 35 million years ago. These were wood monkeys from which modern gibbons, Orangutans and Driopiteki occurred.
Dryoitek Around about 18 million years ago. These were half impess, midnight monkeys who gave the beginning of modern gorillas, chimpanzees and Australopithecks.
Australopitetse There were about 5 million years ago in the flanned steppes of Africa. These were highly developed monkeys that moved on two hind limbs in a half-woven position. Their growth was 120-150 cm, the mass of the body is 20-50 kg, the volume of the brain is about 600 cm 3. They could take sticks, stones, other items and use them for hunting and protection against enemies. Manufacturing tools of labor Australopithekami is not installed. They lived with groups, used both plant and animal food. Australopitets may have gave rise to a person skillful. This question remains discussion.
Man skillful Formed 2-3 million years ago. Morphologically, he was very different from Australopites, but it was at this stage that the monkey was turned into a person, since the man skillful made the first primitive workers of the labor. From that moment on, the conditions for the existence of man's ancestors have changed, as a result of which the advantages in survival received individuals with signs that contribute to directly, ability to work, improving the upper limbs and cognitive activity of the brain. The person skillful is considered the ancestor of Archantropov.
Ancient people (archangets)
These include, in particular, Peteitroantropra and Synantroprop, belonging to in one species - Strong man. Remains peteitrop were discovered in 1891 on the island of Java; remains sinantropropa - In 1927 in the cave near Beijing. Peteitrocks and synanthops were more similar to Australopitek than with modern people. They had an increase of up to 160 cm, the brain volume is 700-1200 cm 3. They lived 2 million - 200 thousand years ago, mainly in the caves and were a herd lifestyle. The tools manufactured by them were more diverse and perfect than the person skillful. They believe that they had a rush of speech. They used fire, which made food easier to be digested, defended from predators and cold, contributed to the expansion of the range.
Ancient people (Paleoanthropes)
Related to them neanderthasev. For the first time, their remains were found in the valley of the river. Neandertal in Germany in 1856 Neanderthals were widely resets in Europe, Africa and Asia in the ice era of 250-35 thousand years ago. The volume of their brain reached 1400 cm 3. They still survived the abnormal rollers, a relatively low forehead, a massive lower jaw with the desire of a chiffer protrusion. They lived in the caves groups of 50-100 people, kneel how to extract and maintain fire, fed on plant and animal food, made a variety of stone, bone and wooden tools (knives, scrapers, chop, stick, etc.). They had a division of labor: men hunted, made tools of labor, women treated animal carcasses, gathered edible plants.
Modern people (Neoantropips)
Neanderthals changed the people of modern physical type - cryanonians - The first representatives of the species are reasonable. They appeared about 50-40 thousand years ago. For some time, Paleoanthropes and Neoantropips existed together, but then the Neanderthals were ousted by Cryanonians. Cryanonians possessed all physical characteristics of the living people: high growth (up to 180 cm), a large brain volume (about 1400 cm 3), a high forehead, smoothed outbreak rollers, a developed chin. The latter indicates a developed self-partition. Kroanonians built dwellings, made clothes from the skins, cross-bone needles, made products from horns, bones, silica and decorated them with carvings. Cryanonians learned to grind, drill, knew a pottery. They lived by the genital communities, tamed animals, engaged in agriculture. They had the primitives of religion and culture.
Taxon - classification unit in the systematics of plant and animal organisms.
The main evidence of human origin from animals is the presence of rudiments and atavisms in his body.
Rudiment - These are organs incurred in the process of historical development (evolution) of their meaning and function and remaining in the form of underdeveloped formations in the body. They are laid during the development of the embryo, but do not develop. Examples of rudiments in humans can be: Copter vertebrae (the remains of the skeleton of the tail), Appendix (the process of the blind intestine), the hair cover; Ear muscles (some people can stir ears); Third eyelid.
Atavisms - This is a manifestation, in individual organisms, signs that existed in individual ancestors, but were lost during evolution. A person has this - the development of the tail and hair cover on the whole body.
Historical past people
First people on earth. The name of the monkeyeequel - Petetecantropropa received one of the earliest finds, made in the 19th century on Java. For a long time, this discovery was considered a transitional link from the monkey to a person, the first representatives of the family of hominids. These views were facilitated by morphological features: a combination of modern in the form of the bones of the lower limb with a primitive skull and intermediate Brain mass. However, Java's pytecans are a rather late group of hominids. Starting from the 20s of the twentieth century and to the present, an important discovery was made in South and East Africa: the remains of two-legged Plio-Pleistocene primates were found (from 6 to 1 million years old). They laid the beginning of a new stage in the development of paleontology - reconstruction of these stages of the evolution of hominids on the basis of direct paleontological data, and not on the basis of various indirect comparative anatomical and embryological data.
Epoch of two-legged manobazyan Australopites. The first Australopita of East Africa - Zindjanthrope was found by the spouses L. and M. Liki. The brightest distinguishing feature of Australopitets is a strain. This is evidenced by the structure of the pelvis. Stirry belongs to the oldest acquisitions of a person.
The first representatives of the human race in East Africa. Together with massive Australopita in East Africa, 2 million years ago lived and other creatures. For the first time, it became known when the next year after the opening of the Zindjanthropa, the remains of a miniature hominid were found, the volume of the brain of which was no less (and even more) than the Australopithek. Later it turned out that he was a contemporary Zindjantrophop. The most important discoveries are made in the lowest layer dating back 2-1.7 million years. Its maximum thickness is 40 meters. The climate, when this layer was laid, was a more humid and its inhabitants were Zindjanthrop and the congregation. The latter existed not long. In addition, stones with traces of artificial processing were found in this layer. Most often it was a pebble size of walnut to 7-10 cm, with a few chips of the working edge. It was originally assumed that this was able to do zinjanthropes, but after new discoveries it became obvious: or the guns made a more advanced crepage, or both of the inhabitants were capable of such initial processing of stone. The occurrence of the clamp with a full oppression of the thumb should be preceded by a period of predominance of power grip, when the object was brought into a handful and clamped in his hand. Moreover, the nail phalanx of the thumb was experiencing a particularly strong pressure.

Background AnthropogenesisSupportless ancestors of man-like monkeys and man were herd cloth monkeys who lived on trees in tropical forests. The transition of this group to a terrestrial lifestyle, caused by climate cooling and the dysfunction of forests by the steppes, led to straightening. The straightened position of the body and the transfer of the center of gravity caused the replacement of the arcuate spinal column S-shaped, which gave it flexibility. A vaulted spring stop was formed, the pelvis was expanded, the chest became wider and shorter, the jaw apparatus is easier, and the main thing - the forefinders were released from the need to maintain the body, their movements became more free and diverse, the functions were complicated. The transition from the use of items to the manufacture of guns is the line between monkey and man. The evolution of the hand went along the path of natural selection of mutations, useful for work. Along with straightening, the most important prerequisite of anthropogenesis was a stadium lifestyle, which, as labor activity, and exchange the signals led to the development of a self-regulatory speech. Specific ideas about the surrounding subjects and phenomena were summarized in abstract concepts, mental and speech abilities developed. The highest nervous activity was formed, and a self-regulation was developed.
Stages of formation of man. In the evolution of a person there are three stages: the most ancient people, ancient people and modern (new) people. Many populations of a sensible person did not replace each other consistently, and lived at the same time, conducting the struggle for existence and destroying weaker.
| Ancestors of man | Progressive features in appearance | Lifestyle | Tools |
| Parappiete (found in Egypt in 1911) | Walked on two legs. Low forehead arcs, hairproof | Considered as the oldest man monkey | Tools of labor in the form of a baton; Closed stones |
| Dryoitek (bone residues found in Western Europe, South Asia and East Africa. Antiquity from 12 to 40 million years old) | According to the majority of scientists, dripiteki are considered as a common alert group for modern man-like monkeys and a person. | ||
| Australopites (bone residues of antiquity of 2.6-3.5 million years found in South and East Africa) | There were a small body (for 120-130 cm), a mass of 30-40 kg, the volume of the brain - 500-600 cm 2, moved on two legs. | They consumed vegetable and meat food, dwell in open areas (such as Savanne). Australopites are considered as a stage of the evolution of a person who directly preceded the emergence of the most ancient people (archantropov). | As a gun used sticks, stones, animal bones |
| Peteicantrop (ancient man, remains found - Africa, Mediterranean, Oh. Java; 1 million years ago) | Height 150 cm; the volume of the brain is 900-1,000 cm 2, the forehead is low, with a survering roller; Jaws without chores | Public lifestyle; We lived in the caves, enjoyed fire. | Primitive Stone Tools, Sticks |
| Sinantrophop (China et al., 400 thousand years ago) | Height 150-160 cm; The volume of the brain is 850-1 220 cm 3, the forehead is low, with a surplus roller, there is no chifferent | Lived herds, built primitive dwellings, enjoyed fire, dressed in skins | Means from stone and bones |
| Neanderthals (ancient man); Europe, Africa, Asia; about 150 thousand years ago | Height 155-165 cm; Brain volume 1 400 cm 3; SOZOROVAL; The forehead is low, with a surprise roller; The chin protrusion is developed weakly | Public lifestyle, construction of foci and dwellings, the use of fire for cooking, dressed in the skins. Used gestures and primitive speech to communicate. There was a division of labor. First burials. | Tools of labor from wood and stone (knife, scraper, multifaceted island, etc.) |
| Cryanonets - the first modern person (everywhere; 50-60 thousand years ago) | Height up to 180 cm; Brain volume - 1 600 cm 2; forehead high; gyrus are developed; Lower jaw with a chiffering protrusion | Generic community. Relevant to the mind is reasonable man. Construction of settlements. The appearance of rites. The emergence of art, pottery, agriculture. Developed. Developed speech. Taming animals, planting plants. Have fading painting. | Diverse tools of labor from bone, stone, wood |
Modern people. The emergence of people of modern physical type occurred relatively recently (about 50 thousand years ago), which were called Cromanons. Increased brain volume (1,600 cm 3), well-developed self-partition; Construction of housing, the first primitives of art (rock painting), clothes, decorations, bone and stone tools of labor, the first tamed animals - everything indicates that the real man finally addressed from his animal ancestors. Neanderthals, Cryanonians and modern people form one species - a reasonable man. Many years passed before people from the assigning farm (hunting, gathering) moved to the manufacturing farm. They learned how to grow plants and tame some animals. Social factors were of great importance in the evolution of Cryanonians, the role of education, the transfer of experience increased immeasurably.
Races of man
All modern humanity belongs to the same type - Homo Sapiens.. The unity of mankind follows from the generality of origin, the similarity of the structure, unlimited crossing of representatives of various races and the fertility of the offspring from mixed marriages. Inside the type - Homo Sapiens. - Allocate five large races: a non-corrosive, europeoid, mongoloid, Australoid, American. Each of them is divided into small races. Differences between races are reduced to the features of the color, hair, eye, lip nose form, etc. These differences arose in the process of adapting human populations to local natural conditions. It is assumed that black leather absorbed ultraviolet rays. Narrow eyes protected from a sharp solar effect in the conditions of open spaces; A wide nose fasterly cooled inhaled air by evaporation from the mucous membranes, on the contrary, the narrow nose was better warming cold inhaled air, etc.
But a person thanks to the work quickly came out of the influence of natural selection, and these differences quickly lost an adaptive value.
The races of a person began to form began to form, as believed, about 30-40 thousand years ago in the process of settling the man of the Earth, and then many racial signs had an adaptive importance and were fixed by natural selection in a certain geographic environment. All human races are peculiar to the general features of a person reasonable, and all races are absolutely equal in biological and mental relations and are at the same level of evolutionary development.
There is no sharp border between the main races, and there are a number of smooth transitions - small races, from which representatives are smoothed or mixed by the traits of the main masses. It is assumed that in the future the differences between races will completely disappear and humanity in a racial attitude will be homogeneous, but with many morphological options.
The races of a person should not be mixed with the concepts nation, people, language group. Different groups can be part of one nation, and the same races are part of different nations.
Completeness of classification
It would seem that no problems with the classification of the animal type, known as Homo Sapiens Sapiens (intelligent person), should not arise. It would seem that it's easier? It belongs to the chord (vertebral subtype), to the mammal class, the detachment of primates (humans). If more detail, then his family is hominids. So, the genus him is a man, the species is reasonable. But the question arises: how does it differ from others? At least from the same Neanderthals? Did you have extinct views of people so unreasonable? Is it possible to call Neanderthal far, but the direct ancestor of a person of our time? Or maybe these two species existed in parallel? Did they cross the joint offspring? Until the work on the study of the genome of these Mysterious Homo Sapiens NEANDERTHalensis, there will be no answer to this question.
Where did the look "reasonable man" appeared?
Most scientists believe that the overall ancestor of all people both modern and disappeared Neanderthals appeared in Africa. There in the Miocene era (this is approximately six or seven million years ago) a group of species separated from hominids, subsequently evolving to the genus Homo . First of all, the foundation of such a point of view was the discovery of the oldest remains of a person called Australoptecom. But soon other finds were discovered by the most ancient people - Sinantropra (in China) and Homo Heidelbergensis (in Europe). Were these varieties of the same kind?

Have they all the ancestors of modern people or dead-end branches of evolution development? One way or another, a man is a reasonable appeared later - forty or forty-five thousand years ago, in the time of Paleolithic. And the revolutionary honors from the homo sapiens from other hominids moving on the hind limbs was that he made the tools of labor. The ancestors of it, however, like some modern monkeys, only used the remedies.
Secrets of the generic tree
Another 50 years ago, the school was taught that the person was intelligible from Neanderthal. It was often represented in the image of a hairy semi-boring, with a beveled skull and a protruding jaw. And Homo Neandert Poles, in turn, evolved from Peteitrontrop. His Soviet science portrayed almost a monkey: on semi-bent legs, fully covered with wool. But if everything is more or less clear with this ancient ancestor, then the relationship of homo Sapiens Sapiens and Neanderthal is much more confusing. It turns out that both of these types have existed at the same time and even in some territories. Thus, the hypothesis of the origin of a person intelligent from Neanderthals requires additional evidence.

Does Homo Neanderthalensis belonged to the mind "reasonable man"?
A more careful study of the burials of this species has shown that the Neanderthals was completely well. In addition, these people had ai-graduated speech, the tools of labor (stone chisel), religious cults (including funeral), primitive art (decorations). However, a number of features distinguished him from a modern person. For example, the lack of chores, which makes it possible to judge that the speech of such people was not well developed. Finds are confirmed by the following facts: Neanderthals arose hundred and fifty thousand years ago and flourished to 35-30 thousand years before our era. That is, this happened at that time when it was already appeared and clearly took shaped the appearance of "Man Reasonable Sapirens". Fully disappeared "Neanderthals" only in the era of the last glaciation (Vurm). What was the cause of his death (after all, the change of climatic conditions was touched by Europe), it is difficult to say. Perhaps the legend of Cain and Avele has deeper roots?
Anthropogenesis (Greek Anthropos Man, Génesis Origin), biological evolutionwhich led to the appearance of the type of Homo Sapiens, separated from the other hemp. persons
monkey I. placental mammals. This is the process of historical and evolutionary formation of a physical standard, the initial development of its labor activity, speech, and also the company.
Stages of the evolution of man
Scientists argue that a modern person did not occur against modern human monkeys, for whom a narrow specialization is characterized (adaptation to a strictly defined lifestyle in tropical forests), and from extincting several million years ago of high-organized animals - dripitecs.
According to the paleontological finds (fossil residues), about 30 million years ago, the ancient primates of parapiratios, who lived in open spaces and trees appeared on Earth. Their jaws and teeth were like the jaws and teeth of man-like monkeys. Parappiratios gave rise to modern gibbons and orangutans, as well as extinct branches of dripitecs. The latter in its development was divided into three lines: one of them led to a modern gorilla, the other to chimpanzees, and the third to the Australopitek, and from him - to the person. Rodality of Driopitec with a person is established on the basis of studying the structure of its jaws and teeth found in 1856 in France. The most important stage on the path of transformation of monkey-like animals in the oldest people was the appearance of straightening. In connection with the climate change and the progress of forests, a transition came from wood to a terrestrial lifestyle; To better overlook the locality, where there were many enemies in the ancestors, they had to get up on the hind limbs. In the future, natural selection has developed and secured the strain, and, as a result, the hands were released from the functions of support and movement. So there were Australopitets - the genus, to which the hominids are related (family of people).
Australopitetse
Australopitseki - Highly developed two-legged primates used objects of natural origin as a tool (consequently, Australopithecans can not be considered people). The bone residues of Australopites were first discovered in 1924 in South Africa. They were tall with chimpanzees and a mass of about 50 kg, the volume of the brain reached 500 cm3 - on this basis of Australopita stands closer to man than any of the fossil and modern monkeys.
The structure of the pelvic bones and the position of the head was similar to such a person, which indicates a straightened position of the body. They lived about 9 million years ago in the open steppes and fed on plant and animal food. The tools of their work were stones, bones, sticks, jaws without traces of artificial processing.
Man skillful
Not possessing a narrow specialization of the general structure, Australopitets began a more progressive form, called Homo Habilis - a skillful man. Bone residues were discovered in 1959 in Tanzania. Their age is determined by about 2 million years. The growth of this creature reached 150 cm. The brain volume was 100 cm3 more than that of Australopites, the teeth of the human type, the phalange of the fingers as in humans, are flattened.
Although it combined signs like monkeys and a person, the transition of this creature to the manufacture of pebble guns (well-selected stone) indicates the appearance of labor activity. They could catch animals, throw stones and perform other actions. Heaps of bones, who, together with the fossil residues of a person skillful, testify that the meat has become a permanent part of their diet. These hominids used rude stone worms of labor.
Strong man
Homo Erectus - man strapping. The view from which the modern person believed happened. His age is 1.5 million years old. His jaws, teeth and abnormal arcs still remained massive, but the volume of the brain in some individuals was the same as a modern person.
Some bones of Homo Erectus are found in the caves, which makes it possible to assume its constant dwelling. In addition to the bones of animals and fairly well-isolated stone tools, in some caves, piles of charcoal and burnt bones were found, so, apparently, at that time Australopitets had already learned how to produce fire.
This stage of the evolution of the hominid coincides with the population of other cold regions from Africa. Withstand the cold winters, without working out complex behaviors or technical skills, it would be impossible. Scientists suggest that the Homo Erectus daughter brain was able to find social and technical solutions (fire, clothing, stock and joint living in the caves) problems associated with the need to survive in winter struran.
Thus, all fossil hominids, especially Australopitseki, are treated as human predecessors.
The evolution of the physical characteristics of the first people, including a modern person, covers three stages: ancient people, or archangets;ancient people, or Paleoanthop;modern people, or Neoantrips.
Archantrip
The first representative of Archantropov - Peteitroprop (Japanese man) - monkeys, straight. His bones found on about. Java (Indonesia) in 1891. Initially, its age was determined equal to 1 million years, but, according to a more accurate modern assessment, a little more than 400 thousand years. The height of Peteitront was about 170 cm, the scral box volume is 900 cm3. Somewhat later there is a social dancer (Chinese man). Numerous remnants were found in the period 1927 to 1963. In the cave near Beijing. This creature used the fire and made stone tools. The heidelberg man is also attributed to this group of the most ancient people.
Paleoanthropes
Paleoanthropes - Neanderthals appeared to replace the archangelts. 250-100 thousand years ago they were widely resettled in Europe. Africa. Front and South Asia. Neanderthals made a variety of stone tools: handproof, scraper, pointers; We used fire, coarse clothing. The volume of their brain has grown 1,400 cm3.
The features of the structure of the lower jaw show that they had a swap. They lived with groups of 50-100 individuals and during the onset of glaciers used caves, which traveled wild animals from them.
Neoantrops and a reasonable person
Neanderthals replaced the people of modern type - Cryanonians - or Neoantrops. They appeared about 50 thousand years ago (bone residues were found in 1868 in France). Cryanonians form the only genus Homo Sapiens - a reasonable man. They were completely smoothed by monkey features, on the lower jaw there was a characteristic peer protrusion, pointing to their ability to a self-parting speech, and on the art of manufacturing a variety of guns from stone, bones and horns, Comanonians went far ahead compared to Neanderthals.
They tamed animals and began to master agriculture, which allowed to get rid of hunger and produce a variety of food. In contrast to the predecessors, the evolution of Cryanonians took place under the great influence of social factors (collective cohesion, mutual support, improvement of work, a higher level of thinking).
The emergence of Cryanonians is the final stage of the formation of a modern man . The first generic system came to replace the primitive human flock, which completed the formation of human society, the further progress of which began to be determined by socio-economic laws.
18) Evidence of the origin of man from animals. Atavisms and rudiments in humans.
TO it is traditionally referred to him Comparative anatomical, embryological, physiological-chemical, molecular genetic, paleontological.
1. Comparative anatomical.
The general body structure of the human body is similar to the structure of the body of chordan animals. The skeleton consists of the same departments as other mammals. The body cavity is separated by a diaphragm on the abdominal and thoracic departments. Nervous tubular type system. In the middle ear, there are three auditory bones (hammer, anvil, rapidly), there are ear sinks and associated ear muscles. In man's skin, like other mammals, there are moss, greasy and sweat glands. The blood system is closed, there is a four-chamber heart. The confirmation of the animal origin of a person is the presence of rudiments and atavisms.
2. Embryology.
In human embryogenesis, there are basic stages of development, characteristic of vertebrate animals (crushing, blastuly, gastrol, etc.) in the early stages of embryonic development in the human embryo appear signs characteristic of the lower vertebrates: chord, gill groats in the cavity of the throat, the hollow nervous Tube, bilateral symmetry in the structure of the body, the smooth surface of the brain. Further development of the embryo show features characteristic of mammals: several pairs of nipples, the availability of hair on the body surface, like all mammals (except for single-pass and silent), the development of a young inside the body of the mother and the power of the fetus through the placenta.
3. Physiole biochemical.
The man and human monkeys are very close to the structure of hemoglobin and other organism proteins. There is similarity in blood groups. Blood dwarf chimpanzees (bonobo) of the corresponding group can be overflowed and man. There is a man and antigen rezes-factor (for the first time he was revealed from Macaque Rus). Man-like monkeys are close to a person in the duration of pregnancy, period of puberty.
4. Molecular genetic.
In all human-like monkeys, the diploid number of chromosomes 2 n \u003d 48. It has 2 N \u003d 46 (it has been established that chromosome 2 in hummic is formed by a merger of two chromosomes, homologous to chimpanzees). There is a high degree of homology on the primary structure of genes (more than 90% of human and chimpanzee genes are similar to each other).
5. Paleontological.
Numerous fossil residues (individual bones, teeth, skeleton fragments, guns, etc.) were found, which make it possible to draw up an evolutionary range of the ancestral forms of a modern person and explain the main directions of their evolution.
The difference of man from animals
In the course of evolution, hereditary changes under the control of natural selection contributed to the emergence of a person of straightening, exemption of hands, development and an increase in the brain skull, and a decrease in its facial part. At the same time, a person has developed a need for systematic making tools, which contributed to the improvement of the structure and function of the hand, brain, speech apparatus, mental activity and the emergence of speech. A significant role for the development of a brain and hand was binocular (stereoscopic) vision, which was in the ancestors of man.
Atavisms and rudiments in humans.
Rudiments are called bodies that have lost their main importance in the process of evolutionary development of the body.
Many rudimentary organs are not perfectly useless and perform any secondary functions with the help of structures obviously intended for more complex purposes.
Atavism is called the appearance of individuals in individuals inherent in remote ancestors, but those absent from the nearest.
The appearance of atavisms is explained by the fact that the genes responsible for this feature have been preserved in DNA, but do not function, since the action of other genes is suppressed.
Rudiment in humans:
∙ tail vertebrae;
∙ some people have an EXTENSOR CoccyGis rudimentary muscle, identical to the muscles moving the tail from other mammals. It is attached to the smokehouse, but because the cochter in a person practically can not move, this muscle is useless for a person;
∙ hair cover torso;
∙ the special muscles of the Arrectores Pilorum, which our ancestors served to "raise the wool end," (this is useful for thermoregulation, and also helps animals look large - to intimid the predators and competitors). People have a reduction in these muscles leading to "goose skin", which can hardly have some adaptive value;
∙ three ear muscles that allowed our ancestors to move the ears. There are people who know how to use these muscles. It helps animals with big ear sinks to determine the direction to the source of the sound, but a person can only be used for fun;
∙ morganiev Golden Golden;
∙ celebration of a blind intestine (Appendix). Perennial observations have shown that the removal of appendix does not have a significant impact on the lifespan and health of people, except for the fact that after this operation, people are on average with a little more raising colitis;
∙ grass reflex in newborns (a young monkeys he helps hold on to mother's wool);
∙ iKOTA: This is a reflex movement we inherited from their distant ancestors - amphibians. The headstuffs this reflex allows you to quickly skip the portion of water through the gill slots. Both in humans, and the headstoves, this reflex is controlled by the same brain department and can be suppressed by one and the same means (for example, inhalation of carbon dioxide or breast resolution);
∙ lanugo: hair cover, developing in a human embryo, almost all body, except palms and feet, and disappearing shortly before birth (premature children are sometimes born with Lano).
Examples of atavisoms:
∙ tail-shaped appendage in humans;
∙ solid hair cover on the human body;
∙ additional pairs of mammary glands;
nineteen . The aging of the body. Theories of aging. Geriatry and gerontology.
Old age is a stage of individual development, upon reaching which in the body there are natural changes in physical state, external form, the emotional sphere. Staff changes are becoming apparent and increasing in the postproinder period of ontogenesis. However, the beginning of the extinction of the reproductive function or even its complete loss cannot serve as the lower border of old age. Indeed, menopause in women, consisting in the termination of the release of mature eggs from the ovary and, accordingly, stopping the monthly bleeding, determines the end of the reproductive period of life. At the same time, by the time of menopause, most of the functions and external signs are far from reaching the state characteristic of old people. On the other hand, many changes that we associate with old age begin to reduce the reproductive function. This applies to both physical signs (habits, the development of hyperopias) and the functions of various organs. For example, men reducing the release of men's sex hormones with gender glands and increase the release of gonadotropic hormones by the pituitary gland, which is characteristic of the old organism, starts from about 25 years.
Distinguished chronological and biological (physiological) age.
According to a modern classification based on the assessment of many averages of the body's condition, people, whose chronological age reached 60-74 years, is called the elderly, 75-89 years old, over 90 years old - long-livers. The exact definition of biological age is difficult in that the individual signs of old age are manifested in different chronological age and are characterized by different rates of increasing. In addition, age changes of even one feature are subject to significant sexual and individual fluctuations.
Consider such a sign as the elasticity (elasticity) of the skin. The same biological age is achieved in this case by a woman about 30 years old, and a man - in 80. That is why, first of all, women need competent and constant skin care. In order to determine the biological age, which is necessary for judgment about the speed of aging, use batteries of tests, conducting an aggregate assessment of simultaneously many signs, naturally changing in the course of life.
The basis of such batteries constitutes complex functional indicators, the state of which depends on the agreed activity of several systems of the body. Simple tests are usually less informative. For example, the speed of propagation of a nerve impulse, which depends on the state of the nervous fiber, is reduced in the age range of 20-90 years by 10%, while the life capacity of the lungs, determined by the coordinated operation of the respiratory, nervous and muscular systems, is 50%.
The state of old age is achieved through changes that make up the content of the aging process. This process captures all levels of the structural organization of individuals - molecular, subcellular, cellular, tissue, organ. The total result of numerous private manifestations of aging at the level of a holistic organism is increasing with age reducing the viability of individuals, reducing the effectiveness of adaptive, homeostatic mechanisms. It is shown, for example, that young rats after immersion in ice water for 3 minutes restore the body temperature for about 1 hour. Animals of the middle age for it is required to be 1.5 hours, and the old - about 2 hours.
In general, aging leads to a progressive increase in the likelihood of death. Thus, the biological meaning of aging is that it makes the inevitable death death. The latter is a universal way to limit the participation of a multicellular organism in reproduction. Without death, there would be no change of generations - one of the main conditions of the evolutionary process.
Age changes in the process of aging are not in all cases in reducing the adaptability of the body. The person and higher vertebrates in the process of life are acquired by experience, the ability to avoid potentially dangerous situations. Interesting in this regard and system of immunity. Although its effectiveness after reaching the body of maturity as a whole decreases, thanks to "immunological memory" with respect to some infections, old individuals may be more protected than young.
Hypotheses explaining aging mechanisms
Gerontology knows at least 500 hypotheses explaining the root cause, and the mechanisms of aging the body. The overwhelming majority of them could not register the test of time and represents purely historical interest. In particular, there are hypotheses that bind aging with the spending of a special substance of cellular cores, the fear of death, the loss of some of the substances of the substances obtained by the body at the time of fertilization, self-denial of the products of life, the toxicity of products formed under the action of the microflora of the large intestine. Hypotheses representing scientific value today correspond to one of the two main directions.
Some authors consider aging as a stochastic process of age-related accumulation of "errors", inevitably occasionally occurring in the course of conventional processes of life, as well as damage to biological mechanisms under the influence of internal (spontaneous mutations) or external (ionizing irradiation) of factors. Stochasticity is determined by the random character of changes in time and localization in the body. In various versions, the hypotheses of this direction a primary role is allocated to different intracellular structures, from the primary damage of which functional disorders on cellular, tissue and organ levels depend. First of all, this is a genetic device of cells (hypothesis of somatic mutations). Many researchers associate initial changes in the aging of the body with changes in the structure and, consequently, the physicochemical and biological properties of macromolecules: DNA, RNA, chromatin proteins, cytoplasmic and nuclear proteins, enzymes. Also highlight lipids of cell membranes, often targets for free radicals. Failures in receptors, in particular cell membranes, violate the effectiveness of regulatory mechanisms, which leads to the mismatch of the processes of life.
The considered direction includes hypotheses that examine the primary aging in the increasing wear of structures in the range from macromolecules to the body as a whole, leading in the end to a state that is not compatible with life. Such an idea, however, is too straightforward.
Recall that the emergence and accumulation of mutational changes in DNA is opposed by natural antimutation mechanisms, and harmful effects of formation of free radicals
reduced due to the functioning of antioxidant mechanisms. Thus, if the "concept of wear" of biological structures correctly reflects the essence of aging, the result in the form of a greater or lower rate of senile changes of age, in which these changes are becoming obvious, is a consequence of the imposition of destructive and protective processes. In this case, the hypothesis of wear with inevitability includes
the factors such as genetic predisposition, conditions and even lifestyle, from which the speed of aging depends on how we have seen.
The second direction is represented by genetic or program hypothesis, according to which the aging process is under direct genetic control. The specified control, according to one views, is carried out with the help of special genes. In other views, it is associated with the presence of special genetic programs, as is the case with respect to other stages of ontogenesis, such as embryonic.
In favor of the programming of aging, there are evidence, many of which are already considered in Section. 8.6.1. Usually also refer to the presence of species in the nature, which, after the reproduction, the changes are rapidly growing, leading animals to death. A typical example is Pacific salmon (society, pink salmon), dying after spawning. The starting mechanism in this case is associated with a change in the mode of secretion of sex hormones, which should be considered as a feature of the genetic program of individual development of salmon, reflecting their ecology, and not as a universal aging mechanism.
It is noteworthy that the nestred pink salmon does not spawn and lives 2-3 times longer. It was in these additional years of life that the signs of aging in cells and tissues should be expected. Some program hypothesis are based on the assumption that biological clocks function in the body, in accordance with which age changes occur. The role of "clock" is attributed, in particular, the fork gland, which stops functioning in the transition of the body into mature age. Another candidate is a nervous system, especially some of its departments (hypothalamus, sympathetic nervous system), the main functional element of which are primary age-aging nervous cells. Suppose that the termination at a certain age of the functions of the thymus, which is undoubtedly under genetic control, is a signal of the beginning of the aging of the body. This, however, does not mean genetic control of the aging process. In the absence of thymus, immunological control over autoimmune processes weakened. But in order for these processes to make, either mutant lymphocytes (DNA damage), or proteins with a modified structure and antigenic properties.
Gerontology and Geriatry
Gerontology (from Greek. Gerontos is an elder) - section of biology and medicine that studies the patterns of aging of living beings, including a person. The main directions of gerontology include the study of the main causes, mechanisms and conditions of aging, the search for effective means of increasing the life expectancy and extension of the period of active working capacity.
Geriatry (from Greek. IATREIA - treatment) - the area of \u200b\u200bclinical medicine, which studies the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of diseases of the elderly and senile people.