How to determine and what is the concept of genre in the literature. Types of literary genres in the form determined and write the name of the literary genre
Genres of literature
Literary genres - Historically folding groups of literary works combined by a set of formal and meaningful properties (in contrast to literary forms, the allocation of which is based only on formal signs). The term is often illegally identified with the term "type of literature".
Births, species and genres of literature do not exist as something unchanged, from the century this and ever existing. They are born, theoretically realizes are historically develop, modified, dominate, freeze or retreating on the periphery depending on the evolution of artistic thinking as such. The most stable, fundamental is, of course, the ultimately general concept of "gene", the most dynamic and volatile - a significantly more specific concept of "genre".
The first attempts of the theoretical justification of the genus make themselves felt in the ancient teaching about Monezis (imitation). Plato in the "state", and then Aristotle in the "poetics" came to the conclusion that poetry is a trojkoy species depending on what, as what means, it imites. In other words, the generic division of fiction is based on the subject, means and methods of imitation.
Separate comments on the methods of organizing art time and space (chronotope) scattered in the "Poets" make up the prerequisites for further division on the species and genres of literature.
The representation of Aristotle about generic signs is traditionally referred to as formal. His successors are representatives of the German aesthetics of the XVIII-XIX centuries. Goethe, Schiller, Aug. Schlegel, Shelling. At about the same time, the principles of the opposite - meaningful approach to the generic division of fiction were laid. His initiator was Hegel, who emanated from the gnoseological principle: the subject of artistic knowledge in the epic serves as an object, in lyrics - subject, in drama - their synthesis. Accordingly, the content of the epic work is generated in its integrity, dominant over the will of people, so the event plan prevails in it; The content of the lyrical work is a mental state, the mood of the lyrical hero, so the events in it retreats to the background; The content of the dramatic work is aspiration towards the goal, the volitional activity of a person manifested in action.
Derivatives from the category of the genus or, or rather, the concepts "species" and "genre" are derived from the concepts that concretize it. By the form of the tradition, we call stable structural formations within the literary genus, grouping even more small genre modifications. For example, the Epos consists of small, medium and large species, such as the story, essay, novel, story, novel, poem, epic. However, they are often called genres, which in strict terminological value specify species or in historical, or in the thematic, or in a structural aspect: the antique novel, the era of the Renaissance, the psychological or production essay or the novel, the lyrical story, the story - the epic ("Fate man "M. Sholokhov). Some structural forms combine species and genre signs, i.e. The types of genre species do not have (such, for example, species and at the same time genres of the medieval theater of Soti and Moralte). However, along with synonymous speculation, the hierarchical differentiation of both terms is relevant. Accordingly, the species are divided into genres on a variety of diverse signs: thematic, stylistic, structural, volume, with respect to aesthetic ideal, real reality or fiction, main aesthetic categories, etc.
Genres of literature
Comedy - kind of dramaturgical work. Displays all the ugly and ridiculous, funny and incomplete, ridicules the flavors of society.
Lyrical poem (in prose) - kind of fiction, emotionally and poetically expressing feelings of the author.
Melodrama - The type of drama, the actors of which are sharply divided into positive and negative.
Fantasy - Podzhanr fantastic literature. The works of this subgenar are written in an epic fabulous manner, use the motives of ancient myths and legends. The plot is usually built on magic, heroic adventures and travel; The plot usually present magic creatures; The action takes place in a fabulous world resembling Middle Ages.
Feature article - The most reliable kind of narrative, epic literature, reflecting facts from real life.
Song, or Song - the most ancient type of lyrical poetry; Pooh, consisting of several verses and chorus. Songs are divided into folk, heroic, historical, lyrical, etc.
Tale - middle shape; The work in which a number of events in the life of the main character is illuminated.
Poem - type of lyroid product; poetic story story.
Story - Small shape, work about one event in the life of the character.
Novel - large form; The work, in the events of which many actors usually take part, whose destinies are intertwined. The novels are philosophical, adventure, historical, family-household, social.
Tragedy - kind of a dramatic work that tells about the unfortunate fate of the main character, often doomed to death.
Utopia - The genre of fiction, close to science fiction, describing the model of the ideal, from the point of view of the author, society. Unlike the anti -topia is characterized by the author faith in the impeccability of the model.
Epic - Work or cycle of works depicting a significant historical era or a large historical event.
Drama- (in a narrow sense) one of the leading genres of drama; Literary work written in the form of dialogue of acting persons. It is intended for execution on the scene. Focusing on entertainment expressiveness. The relationships of people who arise between conflicts between them are revealed through the actions of heroes and get an embodiment in a monologue-dialogic form. Unlike the tragedy, the drama is not completed by catharsis.
For the Millennium of Cultural Development, humanity has created countless literary works, among which some major types can be distinguished, similar to the method and form of reflecting a person's ideas about the world around. These are three kinds of (or species) of literature: Epos, drama, lyrics.
What is the difference between every kind of literature?
Epos like a birth of literature
Epos.(EPOS - Greek, story, story) - this is an image of events, phenomena, processes, external with respect to the author. Epic works reflect the objective course of life, human existence in general. Using various artistic agents, the authors of the epic works express their understanding of the historical, socio-political, moral, psychological and many other problems that the human society lives in general and every representative in particular. Epic works have significant visual capabilities, thereby helping the reader to know the world around him, comprehend the deep problems of human existence.
Drama as a birth of literature
Drama (Drama - Greek., Action, Action) is a genus of literature, the main feature of which is the scenario of works. Pieces, i.e. Dramatic works are created specifically for the theater, for setting on the stage, which, of course, does not exclude their existence in the form of independent artistic texts designed to read. Like the Epos, the drama reproduces the relationship between people, their actions arising between them conflicts. But unlike the epic, which has a narrative nature, the drama has a dialogic form.
Connected with it features of dramatic works :
2) The text of the play consists of conversations of heroes: their monologues (one hero's speech), dialogues (conversation two characters), pollogs (simultaneous exchange of replicas of several participants of the action). That is why the speech characteristic turns out to be one of the most important means of creating a memorable character of the hero;
3) The action of the play, as a rule, develops quite dynamically, intensively, as a rule, it is given 2-3 hours of stage time.
Lyrics like family literature
Lyrics (Lyra - Greek, a musical instrument, which was performed by the accompaniment of the poetic works, songs) is distinguished by a special type of artistic image building - this is an experience of an experience in which the individual emotional-spiritual experience of the author is embodied. Lyrics can be called the most mysterious family of literature, because it is addressed to the inner world of man, his subjective sensations, ideas, ideas. In other words, the lyric work is primarily an individual self-expression of the author. The question arises: why readers, i.e. Other people turn to such works? The thing is that a lyric, speaking of his name and about himself, an amazing way embodies universal human emotions, ideas, hopes, and the more significant personality of the author, the more importantly, its individual experience for the reader.
Each family of literature also has its own system of genres.
Genre (Genre - Franz. Rod, view) - a historically established type of literary works, which has similar typological devices. The names of the genres help the reader to navigate in the boundless sea of \u200b\u200bliterature: someone loves detectives, the other prefers fantasy, and the third is a fan of memoirs.
How to determine What genre is a specific work? Most often, the authors themselves help us in this, calling their creation by Roman, the story, poem, etc. However, some copyright definitions seem to us unexpected: Recall that A.P. Chekhov emphasized that the "cherry garden" is a comedy, and not the drama at all, and A.I. Solzhenitsyn considered the "one day of Ivan Denisovich" by the story, not the story. Russian literature Some literary critics are called the meeting of genre paradoxes: the novel in verses "Eugene Onegin", the poem in the prose "Dead Souls", the Satyric Chronicle "The Story of one city". A lot of disputes were relative to the "war and the world" L.N. Tolstoy. The writer himself said only about what his book is not: "What is" War and Peace "? This is not a novel, even less poem, even less - the historical chronicle. "War and Peace" is what the author wanted and could express in the form in which it expressed. " And only in the 20th century, literary crowns agreed to call the brilliant creation of L.N. Tolstoy romance-epic.
Each literary genre has a number of sustainable signs, whose knowledge allows us to attribute a specific work in a particular group. Genres are developing, modified, dying and born, for example, literally before our eyes there was a new blog genre (Web Loq English. Network Journal) - a personal Internet diary.
However, for several centuries, there are sustainable (they are also called canonical) genres
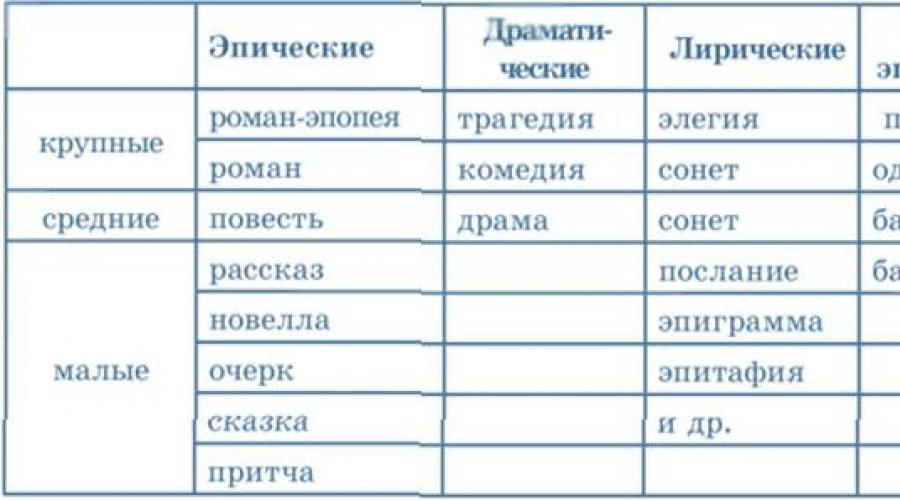
Literary literary literature - see Table 1).
Table 1.
Genres of literary works 
Epic genres of literature
Epic genres primarily differ in volume, they are divided into small ones ( essay, Story, Novel, Tale, Parable ), medium ( tale ), large ( roman, Roman-epic ).
Feature article - A small sketch of nature, the genre at the same time descriptive and narrative. Many essays are created on a documentary, life-based, often they are combined into the cycles: a classic sample - "sentimental journey in France and Italy" (1768) of the English writer Lorenz Stern, in Russian literature - this is a "travel from St. Petersburg to Moscow" (1790) . Radishcheva, "Fregate Pallada" (1858) I. Goncharov "ITALY (1922) B. Zaitseva, etc.
Story - A small narrative genre, in which one episode is usually depicted, an incident, human character or an important case from the Hero's life, which influenced his further fate ("after Bala" L. Tolstoy). Stories are created as on documentary, often autobiographical basis (Matrinin Dvor A. Solzhenitsyn) and thanks to pure fiction ("Mr. from San Francisco" I. Bunin).
The intonation and content of the stories are very different - from comic, curious (Early stories of A.P. Chekhov ") to deeply tragic (" Kolyma stories "V. Shalamov). Stories, like essays, are often combined into the cycles ("Hunter's Notes" I. Turgenev).
Novella (Novella Ial. News) is largely akin to the story and is considered to be a variety, but is distinguished by the special dynamism of the narrative, sharp and often unexpected turns in the development of events. Often, the story in the novel starts from the final, built according to the law of inversion, i.e. reverse order when the disconnection precedes basic events ("terrible revenge" N. Gogol). This feature of the construction of the novel will be later borrowed by a detective genre.
The word "novel" has another meaning that future lawyers need to know. In ancient Rome, the phrase "Novellae Leges" (new laws) called the laws introduced after the official codification of the right (after the release of the Codese of Feodosia II in 438). Novels of Justinian and his successors, who came out after the second edition of the Code of Justinian, amounted to later part of the Roman law (Corpus Iuris Civilis). In modern era, Novella called the law introduced for consideration by Parliament (in other words, the draft law).
Story - The most ancient of the small epic genres, one of the main in the oral work of any people. This is a small work of a magical, adventurous or domestic nature, where fiction is clearly emphasized. Another important feature of the folklore fairy tale is its edification character: "The fairy tale is a lie, yes there is a hint, good young lesson." Folk fairy tales It is customary to divide the Magic ("Tale of the Tsarevne Frog"), domestic ("porridge from the ax") and fairy tales about animals (Zayushkina History).
With the development of written literature there are literary fairy tales in which traditional motives and the symbolic possibilities of the folk fairy tale are used. The classic genre of the literary fairy tale is rightfully considered the Danish writer Hans Christian Andersen (1805-1875), his wonderful "mermaid", "Princess on the pea", "Snow Queen", "Resistant Tin Soldier", "Shadow", "Thumbelina" are loved by many Generations of readers as very young and quite mature age. And this is not by chance, because Andersen's fairy tales are not only unusual, and sometimes the strange adventures of the heroes, they contain deep philosophical and moral meaning imprisoned in excellent symbolic images.
From the European literary fairy tales of the 20th century, the "Little Prince" (1942) of the French writer An-Tuana de Saint Exupery became a classic. And the famous "Chronicles of Narnia" (1950 - 1956) of the English writer CL. Lewis and the "Lord of the Rings" (1954-1955) also Englishman J. R. Tolkina was written in a fantasy genre that can be called modern transformation of an ancient folklore fairy tale.
In Russian literature unsurpassed, of course, the fairy tales of A.S. Pushkin: "About the dead princess and seven heroes", "About fisherman and fish", "About Tsar Saltan ...", "About the Golden Cockerel", "On the Pop and an employee of his Bald". The substantive storyteller was P. Ershov - the author of the "Skate Gorbunk". E. Schwartz in the 20th century creates the shape of the play-fairy tale, one of them "bear" (another name "ordinary miracle") is well known to many thanks to the wonderful film of the director M. Zakharov.
Parable "Also a very ancient folk genre, but, unlike a fairy tale, parables contained written monuments: Talmud, Bible, Koran, a monument of Syrian literature" Education Akhahar ". Parable is a work of an instructive, symbolic nature, is distinguished by the elevation, seriousness of the content. Ancient parables, as a rule, are small in volume, they do not have a detailed story about the events or psychological characteristics of the character of the hero.
Purpose of parables - edification or, as they said, learning wisdom. In European culture, the most famous are parables from the Gospels: about the prodigal son, about the richer and Lazar, about the wrong judge, about the insane richer and others. Christ often spoke of allegorically with students, and if they did not understand the meaning of parables, explained it.
Many writers appealed to the genre of parables, not always, of course, putting a high religious sense into it, rather trying to express some moralistic ignition in allegorical form, as, for example, L. Tolstoy in his late work. Puli. V. Rasputin - Farewell to the Materia "You can also be called a deployed parable in which the writer with anxiety and sorrow speaks of the destruction of the" ecology of conscience "of man. The story "Old Man and the Sea" E. Hemingway Many critics also classify the tradition of literary parables. The well-known modern Brazilian writer Paulo Coelho in his novels and reports also uses the parable shape (Roman "Alchemik").
Tale - The average literary genre, widely represented in world literature. The story shows several important episodes from the Hero's life, as a rule, one storyline and a small number of actors. The stakes are characterized by a large psychological saturation, the author focuses on the experiences and change of mood of heroes. Very often the main theme of the story is the love of the main character, for example, the "White Nights" of F. Dostoevsky, "Asya" I. Turgenev, Mitina Love I. Bunin. The stories can also be combined into cycles, especially written in autobiographical material: "Childhood", "Defense", Youth L. Tolstoy, "Childhood", "In People", "My Universities" A. Gorky. The initonation and themes of the ABS are distinguished by a huge variety: tragic, addressed to acute social and moral issues ("all flows" by V. Grossman, "House on the Embankment" Y. Trifonova), romantic, heroic ("Taras Bulba" N. Gogol), philosophical , parable ("Kotlovan" A. Platonov), mischievous, comic ("Three in a boat, not counting the dogs" English writer Jerome K. Jerome).
Novel (Gotap Franz. Initially, in later the Middle Ages, any work written in Romanener, as opposed to was written in Latin) - a major epic work, in which the story focuses on the fate of a separate person. Roman is the most complex epic genre, which is distinguished by the incredible number of topics and plots: love, historical, detective, psychological, fantastic, historical, autobiographical, social, philosophical, satirical, etc. It combines all these forms and types of novel its central idea is the idea of \u200b\u200bpersonality, individuality of a person.
The novel is called the epic of private life, because it shows the diverse connections of peace and man, society and personality. Environmental reality is presented in the novel in different contexts: historical, political, social, cultural, national, etc. The author of the novel is interested in how the environment affects the character of a person, as it is formed, how his life develops, whether he managed to find his purpose and realize himself.
The emergence of the genre is many refer to antiquity, it is "Daphnis and Chloe" Long, "Golden Donkey" Apulela, Knight's Roman "Tristan and Isolde".
In the work of the classics of world literature, Roman presented with numerous masterpieces:
Table 2. Examples of the classic novel of foreign and Russian writers (XIX, XX century) 
Famous novels of Russian Writers XIX in
.:
In the 20th century, Russian writers develop and bring the traditions of their great predecessors and create no less wonderful novels:

Of course, none of such enumerations can claim fullness and exhaustive objectivity, especially this refers to modern prose. In this case, the most famous works that glorify both the literature of the country and the name of the writer are named.
Roman-epic.. In antiquity there were forms of heroic epic: folk sagas, runes, epics, songs. This is Indian "Ramayana" and "Mahabharata", the Anglo-Saxon Beowulf, the French "Song of Roland", the German "Song of Nibelunga" and others. In these works, idealized, often hyperbulsed form, the exploits of the hero were extended. Limited epic poems "Iliad" and "Odyssey" of Homer, Shah-Name of Firdusi, while maintaining the mythological nature of the early epic, nevertheless, had a pronounced connection with the real history, and the topic of intertwining the human destiny and the life of the people becomes in them one of major. The experience of the ancients will be in demand in the 19th-20th centuries, when the writers will try to comprehend the dramatic relationship of the era and individual personality, to tell about how morality is subject to, and sometimes the psyche of a person at the time of the greatest historical shocks. Recall the lines of F. Tyutchev: "Blessed, who visited this world in his moments of fatal." The romantic formula of the poet in reality meant the destruction of all the usual forms of life, tragic losses and non-closed dreams.
The complex form of Roman-epic allows writers to artistically explore these problems in their entirety and contradictions.
When we talk about the genre of Roman-epic, of course, immediately remember "War and Peace" L. Tolstoy. Other examples can be called: "Silent Don" M. Sholokhov, "Life and Fate" V. Grossman, "Saga about Forsyites" of the English writer Golsuorussi; The book of American writer Margaret Mitchell "Worked by the Wind" can also be found to this genre with a great basis.
The very name of the genre indicates synthesis, the connection in it of two mains began: romance and epic, i.e. associated with the subject of the life of a separate person and the theme of the history of the people. In other words, in Roman-epic, it is told about the fate of heroes (as a rule, the characters themselves and their fate are fictional, invented by the author) on the background and in close connection with epochal historical events. So, in "War and the World" - these are the fate of individual families (Rostov, Bolkonsky), favorite heroes (Prince Andrei, Pierre Probrazova, Natasha and Princess Mary) in a turning point for Russia and all of Europe, the historical period of the early XIX century, the Patriotic War of 1812 . In the book Sholokhov - the events of the First World War, two revolutions and the bloody civil war are tragically invade the life of the Cossack farmer, the family of Melekhov, the fate of the main characters: Grigory, Aksigni, Natalia. V. Grossman talks about the Great Patriotic War and its main event - the Stalingrad battle, about the tragedy of the Holocaust. In the "life and fate" also intertwined the historical and family topic: the author traces the story of Shaposhnikov, trying to understand why the fate of the members of this family was so differently. Golzouorsi describes the life of the kind of foresites throughout the legendary Victorian era in England. Margaret Mitchell is a central event in the history of the United States, a civil war between the North and South, cool the lives of many families and the fate of the most famous heroine of American literature - Scarlett O. Hara.
Dramatic genres of literature
Tragedy (Triadia Greek. Goat Song) is a dramatic genre that originated in ancient Greece. The emergence of the ancient theater and tragedy are associated with the worship of the cult of fertility and wine of Dionysis. He was dedicated a number of holidays, during which ritual magic games were played with rich, satiirs that the ancient Greeks were represented in the form of two-legged goat creatures. It is assumed that it is such an appearance of satirs that performed hymns into the glory of Dionysus, gave such a strange name in translating the name of this serious genre. Theatrical action in ancient Greece was attached to magical religious importance, and the theaters built in the form of large open-air arena are always located in the very center of cities and were one of the main public places. The audience spent sometimes spent the whole day: ate, drank, loudly expressed their approval or the censure of the represented spectacle. The heyday of the ancient Greek tragedy is associated with the names of the three great tragics: this is Eschil (525-456 BC) - the author of the tragedy "Chained Prometheus", "Orestea", etc.; Sofokl (496-406 BC) - the author of "Tsar Edipa", "Antihas", etc.; And Eurypid (480-406 BC) - the creator of "Medea", "Troy-Nok" and others. Their creations will remain samples of the genre, they will be attempted to imitate, but they will remain unsurpassed. Some of them ("Antigona", "Medea") are put on stage and now.
What are the main tragedy features? The main one is the presence of an unsolved global conflict: in the ancient tragedy, this confrontation between rock, fate, on the one hand, and a person, his will, free choice - on the other. In the tragedies of later epochs, this conflict gained moral and philosophical character as the confrontation of good and evil, loyalty and betrayal, love and hatred. It is absolute in nature, the heroes embodying the opposing forces are not ready for reconciliation, compromise, and therefore in the final of the tragedy there are often many deaths. So built tragedy of the great English playwright of Villama Shakespeare (1564-1616), remember the most famous of them: "Hamlet", "Romeo and Juliet", "Othello", "King Lear", "Macbeth", "Julius Caesar" and others.
In the tragedies of the French playwrights of the XVII century Cornel ("Horace", "Polyevk") and Racina ("Andromach", "Britanik"), this conflict received a different interpretation - as a conflict of debt and feelings, rational and emotional in the souls of the main characters, i.e . I found the psychological interpretation.
The most famous in Russian literature is a romantic tragedy "Boris Godunov" A.S. Pushkin, created on historical material. In one of his best creations, the poet sharply set the problem of the "real misfortune" of the state of the Moscow - chain reaction of impostations and "terrible villains", for which people are ready for power. Another problem is the attitude of the people to the whole occurring in the country. The image of the "silent" people in the final "Boris Godunova", to this day, continues discussions about what he wanted to say to the most Pushkin. On the tragedy, the Opera M. P. Mussorgsky was written, who became a masterpiece of Russian opera classics.
Comedy (Greek. Komos is a cheerful crowd, Oda - Song) - a genre that originated in ancient Greece a little later than the tragedy (V c. BC). The most famous comedian of that time is Aristophane ("Clouds", "Frogs", etc.).
In comedy with the help of satire and humor, i.e. Comic, moral defects are ridiculous: hypocrisy, stupidity, greed, envy, cowardice, complacency. Comedy, as a rule, isolavous, i.e. Frames to social issues, referring to the deficiencies. Distinguish comedies of positions and comedies of characters. In the first, internally important intrigue, the chain of events ("comedy of mistakes" of Shakespeare), in the second - the characters of the heroes, their absurdity, one-sidedness, as in the Comedy "Lady", D. Fonvizin, "Moborism", Tartuf, belonging to Peru Classics Genre, French Comediography of the XVII century Jean Batista Moliere. In Russian drama, a satirical comedy with its acute social criticism was particularly popular with its acute social criticism, such as "Auditor" N. Gogol, "Bagrous Island" M. Bulgakov. Many wonderful comedies created A. Ostrovsky ("Wolves and Sheep", "Forest", "Mad Money", etc.).
The comedy genre consistently enjoys success among the public, perhaps because the celebration of justice claims: in the final, the vice must certainly be punished, and virtue to triumph.
Drama - A relatively "young" genre, which appeared in Germany in the XVIII century as lesedrama (it) - a play for reading. The drama is addressed to the daily life of man and society, everyday weekdays, family relationships. The drama is primarily interested in the inner world of man, this is the most psychological of all dramaturgical genres. At the same time, it is the most literary of stage genres, for example, A. Chekhov's plays are largely perceived as texts for reading, and not as theatrical productions.
Larine genres of literature
Division on genres in lyrics has no absolute nature, because The differences between genres in this case are conditional and not so obvious as in the epic and drama. More often, we will distinguish lyrical works on their thematic features: landscape, love, philosophical, friendly, intimate lyrics, etc. However, some genres can be called, which have pronounced individual signs: Elegy, Sonnet, Epigram, Message, Epitaph.
Elegy(Elegos Greek. Postal song) - poem of medium length, as a rule, moral and philosophical, love, confessional content.
The genre arose in antiquity, and his main sign was considered an elegic distortion, i.e. division of poems for two hundreds, for example:
MiG Welded: Finished my work many years, so that incomprehensible sadness secretly disturbing me?
A. Pushkin.
In the poetry of the XIX-XX centuries, division on biennium is no longer such a strict requirement, now we are more significant to be semantic signs that are associated with the origin of the genre. Contact Elegy dates back to the shape of ancient burial "ponts", in which, mourning the deceased, simultaneously recalled his extraordinary advantages. Such an origin predetermined the main feature of Elegy - the combination of grief with faith, regret with hope, the benefit of being through sadness. The lyrical hero of Elegy is aware of the imperfection of the world and people, their own sinfulness and weakness, but does not reject life, but takes it in all tragic beauty. Bright example - "Elegy" A.S. Pushkin:
Mad Years Falling Fun
It is hard for me as a vague hangover.
But like wine - sadness of the past days
In my soul, than an older, the stronger.
My way is sad. Promises me work and grief
The coming worried sea.
But I do not want, o'D, dying;
I want to live to think and suffer;
And I know, I will enjoy
Between the sorrows, worries and distill:
Sometimes again harmony I wish,
I will share tears over the fiction
And maybe - on my sunset sad
Liberates love with a smile farewell.
Sonnet (Sonetto Italy. Song) - the so-called "solid" poetic form, having strict rules for constructing. In the sonnet of 14 lines, divided into two quatrains (katro) and two trials (tercet). Only two rhymes are repeated in the katsins, two or three tercets. The methods of rhymes also presented their requirements, which, however, varied.
Motherland Soneta - Italy, this genre is also represented in English and French poetry. The Italian poet of the XIV century Petrarch is considered to be the Coriferation of the genre. He dedicated all his sonnets with his beloved - Donne Laura.
In Russian literature, Sonnets A.S Pushkin remain unsurpassed, beautiful sonnets also created the poets of the Silver Age.
Epigram (Epigramma Greek, inscription) - a short mockery poem, usually addressed to a specific person. The epigrams write many poets, sometimes increasing the number of their ill-wishers and even enemies. The epigram on Count Vorontsov turned around for A.S. Pushkin hatred of this Veelmazby and, ultimately, sent out of Odessa to Mikhailovskoye:
Pop Milord, Semi-merchant,
Semi-sage, semi-ignorant,
Semi-scoundrel, but there is hope,
What will be full finally.
Mocking poems can be devoted not only to a specific person, but also a generalized addressee, as, for example, in the epigram A. Akhmatova:
Could beat Dante Dante
Should Laura's feather love to reclaim?
I taught women to talk ...
But, God, how to silence them!
Also known even cases of peculiar duels of epigram. When the famous Russian lawyer A.F. Konsi were appointed in the Senate, the unfriendlies spread to him the evil epigram:
In the Senate Konia Kaligula led,
It is located, removed and in the velvet, and in the chant.
But I will say, we have the same arbitrariness:
In the newspapers I read that the horses are in the Senate.
To which A.F. Horses, distinguished by an extraordinary literary talent, answered:
(Epitafia Greek, gravestone) - Farewell poem with a deceased person intended for a tombstone monument. Initially, this word was used in the literal sense, but in the future it was mostly figuratively. For example, I. Bunin has a lyrical miniature in the prose "Epitaph", dedicated to the farewell from a dear for a writer, but forever leaving the past Russian manor. Gradually, epitaph is transformed into a dedication poem, a farewell poem ("Wreath of the Dead" A. Akhmatova). Perhaps the most famous poem of this content in Russian poetry is "death of the poet" M. Lermontov. Another example is "epitaph" M. Lermontov, dedicated to the memory of Dmitry Venerevitinova, the poet and the philosopher, who deceased at the age of twenty-two years.
Laro-epic literature genres
There are works in which some features of lyrics and epics have connected, as the name of this group of genres itself. Their main feature is the substitution of the story, i.e. Status of events, with the transfer of feelings and experiences of the author. It is customary to the lyrol-epic genres poem, ODU, Ballad, Bass .
Poem (PoEo Greek. I create work) - a very famous literary genre. The word "poem" has many values, both direct and portable. In antiquity, poems called large epic works, which today are considered epic (already mentioned above the poems of Homer).
In the literature of the XIX-XX centuries of the poem, this is a large poetic work with a deployed plot, for which it is sometimes called poetic story. The poem has characters, the plot, however, their destination is somewhat different than in Prosaic Tale: In the poem, they help the lyrical self-expression of the author. Probably, so this genre of romance poets ("Ruslan and Lyudmila" of the Early Pushkin, "MTSI" and "Demon" M. Lermontov, "Cloud in the pants" V. Mayakovsky).
Oh yeah (ODA Greek. Song) - Genre, presented mainly in the literature of the XVIII century, although also has an ancient origin. Oda goes back to the ancient genre of Diffiram - the hymn, glorifying the folk hero or the winner of the Olympic Games, i.e. man outstanding.
The poets of the XVIII-XIX centuries created ODD for various occasions. It could be an appeal to the monarch: M. Lomonosov devoted his ODD to Empress Elizabeth, G. Derzhavin-Katerina P. glorifying their acts, poets simultaneously passed the empress, inspired them with important political and civil ideas.
Significant historical events could also be the subject of glorifying and admirable in Ode. G. Derzhavin after taking the Russian army under the command of A.V. Suvorov Turkish fortress Ishmael wrote OED "Thunder Victory, distribute!", Which was the unofficial anthem of the Russian Empire for some time. There was a kind of spiritual OD: "Morning thinking about God's magnitude" M. Lomonosov, "God" of Derzhavin. Civilians, political ideas could also become the basis of ODD ("liberty" by A. Pushkin).
This genre has a pronounced didactic nature, it can be called a poetic sermon. Therefore, it is characterized by the solemnity of the syllable and speech, the famous passage from "ODD for the Day of Eden to the All-Russian throne of Her Majesty of the Empress of the Empress Elizabeth Petrovna Petrovna, M. Lomonosov, written in the year, as Elizabeth approved the new charter of the Academy of Sciences, significantly Increased funds for its content. The main thing for the Great Russian Encyclopedist is a young generation education, the development of science and education that will be, on the conviction of the poet, the key to the prosperity of Russia.
Ballad (Balare Provence - dance) enjoyed extremely popular at the beginning of the XIX century, in sentimental and romantic poetry. This genre arose in French Provence as a folk dance love content with mandatory repetitions. Then the ballad moved to England and Scotland, where new features acquired: now it is a heroic song with the legendary plot and heroes, for example, the famous ballads about Robin Hood. The constant sign remains only the presence of refrains (repetition), which will be important for ballads written later.
The poets of the XVIII and the beginning of the 19th centuries fell in love with the ballad for its special expressiveness. If you use an analogy with epic genres, a ballad can be called poetic novel: an unusual love, legendary, heroic plot that captures imagination is required in it. Often in ballads are used fantastic, even mystical images and motives: remember the famous "Lyudmila" and "Svetlana" V. Zhukovsky. No less famous "Song of the meaning of Oleg" A. Pushkin, Borodino M. Lermontov.
In the Russian lyrics of the XX century, the ballad is a love romantic poem, often accompanied by a musical accompaniment. Ballads in the "bard" poetry, anthem, whose anthem you can call the favorite Ballad of Yuri Vyborribor.
Fable (Basnia Lat. Story) - a short story in verses or prose didactic, satirical character. The elements of this genre from ancient times were present in the folklore of all nations as fairy tales about animals, and then transformed into jokes. The literary fables took shape in ancient Greece, her founder is Ezop (V c. BC), according to his name, allegorizing speech began to call "Ezopov language". In the bass, as a rule, two parts: plot and moral. The first contains a story about a funny or ridiculous case, the second - morality, teaching. The heroes of the Bassen often become animals, under the masks of which are completely recognizable moral and social defects that are subject to ridicule. Great Basinople were Lafontiton (France, XVII century), Lessing (Germany, XVIII century) In Russia, the Coriferation of the genre will remain forever I.A. Wings (1769-1844). The main advantage of his Bassen is a living, popular language, a combination of the author's intonation of the lucavia and wisdom. Plots and images of many Bassen I. Krylov look quite recognizable in our day.
Then to:
a) learn mastery in its genre;
b) to know exactly how to offer a manuscript;
c) learn your target audience and offer a book not "In general, everyone", namely, people who may be interested in it.
What is fiction?
Under artistic literature, all works that have a fictional plot and fictional heroes are understood: novels, stories, stories and plays.
Memoirs belong to the poor literature, because we are talking about unseen events, but they are written through the canons of fiction - with the plot, heroes, etc.
But poetry, including lyrics, is fiction, even if the author recalls the former love, which actually happened.
Types of fiction for adults
Artistic works are divided into genre literature, mainstream and intellectual prose.
Genre literature
In the genre literature, the first violin plays the plot, while he fits into certain, in advance known framework.
This does not mean that all genre novels must be predictable. The mastery of the writer is precisely that in the given conditions to create a unique world, unforgettable heroes and an interesting way to get from the point "A" (tie) to the item "B" (omission).
As a rule, the genre work ends on a positive note, the author does not deepen into psychology and other high matters and tries to just entertain readers.
Basic scene schemes in genre literature
Detective: The crime is the investigation - the expulsion of the criminal.
Love story: Heroes meet - fall in love - fight for love - connect hearts.
Thriller: The hero lived his usual life - the threat arises - the hero is trying to escape - the hero gets rid of danger.
Adventures: The hero sets the goal and, overcoming many obstacles, is achieved.
When we are talking about fiction, fantasy, historical or modern novel, we are not so much about the plot as about the scenery, therefore, when determining the genre, two or three terms are used, which allow you to answer questions: "What happens in the novel?" And "where is it going?". If we are talking about children's literature, then the corresponding mark is made.
Examples: "Modern love romance", "Fantastic fighter" (a fighter is an adventure), "Historical Detective", "Children's Adventure Tale", "Tale for Junior School Age."
Genre prose is usually published by the series - either by copyright or common.
Mainstream
In mainstream (from English. mainstream - Main flow) Readers are waiting for the author of unexpected decisions. For this type of books, the most important thing is the moral development of heroes, philosophy and ideology. Requirements for the mainstream author are much higher than to writers working with genre prose: it should be not only an excellent storyteller, but also a good psychologist and a serious thinker.
Another important feature of mainstream - such books are written at the junction of genres. For example, it is impossible to unambiguously say that "the wind gone" is only Love novel or only Historical drama.
By the way, the drama itself, that is, the story about the tragic experience of heroes, is also a sign of mainstream.
As a rule, novels of this type are produced outside the series. This is due to the fact that serious works are written for a long time and form a series of them is quite problematic. Moreover, the mainstream authors are so different from each other that their books are difficult to group on any sign, except for the "good book."
When specifying the genre in the mainstream-novels, it is usually done not so much on the plot, how many distinctive signs of the book: a historical drama, a novel in letters, fantastic saga, etc.
The emergence of the term
The term "mainstream" himself arose thanks to the American writer and criticizing William Dina Howells (1837-1920). Being the editor of one of the most popular and influential literary logs of its time, The Atlantic Monthly.He gave an obvious preference to works written in a realistic key and focusing on moral and philosophical problems.
Thanks to Howells, realistic literature entered the fashion, and for some time it was her mainstream. The term entrenched in English, and from there switched to Russia.
Intellectual Prose
In the overwhelming majority of cases, the intelligent prose has a gloomy mood and is released outside the series.
The main genres of fiction
Approximate classification
When applying for publishing house, we must specify the genre - so that our manuscript will send the appropriate editor.
Below is an exemplary list of genres, as they are understood in publishing houses and bookstores.
- Avant-garde literature. It is characterized by violation of canons and linguistic and plot experiments. As a rule, the avant-garde comes out very small circulations. Closely intertwined with intellectual prose.
- Action. Oriented mainly on the men's audience. The basis of the plot - fights, chase, salvation of beauties, etc.
- Detective. The main storyline is the disclosure of the crime.
- Historical novel. The time of action is the past. The plot is usually tied to significant historical events.
- Love story. Heroes take love.
- Mystic. The basis of the plot is supernatural events.
- Adventures. Heroes are binding to the adventure and / or go to a risky journey.
- Thriller / Horror. The heroes threatens the deadly danger from which they are trying to get rid of.
- Fiction. The plot is spinning in the hypothetical future or in the parallel world. One of the varieties of fiction is an alternative story.
- Fantasy / fairy tales. The main signs of the genre are fabulous worlds, magic, unprecedented creatures, speaking animals, etc. often based on folklore.
What is non-grateful literature?
Eldly books are classified on topics (for example, gardening, history, etc.) and types (scientific monograph, collection of articles, photo album, etc.).
Below is the classification of non-Fikshn books, as is done in bookstores. When submitting an application to the publisher, specify the topic and type of book - for example, a textbook on writing skill.
Classifications of non-counselible literature
- autobiographies, biographies and memoirs;
- architecture and art;
- astrology and esoteric;
- business and finance;
- armed forces;
- education and education;
- house, garden, garden;
- health;
- history;
- career;
- computers;
- regionalism;
- love and family relationships;
- fashion and beauty;
- music, movies, radio;
- science and technology;
- food and cooking;
- gift editions;
- politics, economics, right;
- travel Guides and Travels;
- religion;
- self-development and psychology;
- agriculture;
- dictionaries and encyclopedias;
- sport;
- philosophy;
- hobby;
- school textbooks;
- linguistics and literature.
Literature is called the works of human thought, enshrined in writing and possess an ordinary meaning. Any literary product, depending on how the writer depicts reality in it, belong to one of the three literary birth: Epos, lyrics or drama.
Epos. (from Greek. "Nattery") - a generalized name of works, in which external events are depicted in relation to the author.
Lyrics (from Greek. "Performed under LIRA") - the generalized name of works is usually poetic, in which there is no plot, and the thoughts, feelings, the experiences of the author (lyrical hero) are reflected.
Drama (from Greek. "Action") - the generalized name of works in which life is shown through conflicts and collisions of heroes. Dramatic works are designed not so much to read as for the stage. In drama, it is not an external action in the drama, and the experience of the conflict situation. In the Epos Drama (narration) and lyrics are merged together.
Within each kind of literature allocate genres - Historically established types of works characterized by certain structural and meaningful features (see the genres table).
| Epos. | LYRICS | DRAMA |
| epic | oh yeah | tragedy |
| novel | elegy | comedy |
| tale | anthem | drama |
| story | sonnet | tragicomedy |
| story | message | vaudeville |
| fable | epigram | melodrama |
Tragedy (From Greek. "Goat Song") - a dramatic work with an insurmountable conflict, where a stress struggle of strong characters and passions, the end of the death of the hero is depicted.
Comedy (With Greek. "Funny song") is a dramatic work with a fun, a funny plot, usually ridiculeling public or household defects.
Drama - This is a literary work in the form of a dialogue with a serious plot, depicting a person in her dramatic relations with society.
Vaudeville - Easy comedy with singing of couplets and dancing.
Farce - Theatrical play of a lung, playful character with external comic effects, designed for a rough taste.
Oh yeah (from Greek. "Song") - a choral, solemn song, a work that is punched, praising any significant event or a heroic personality.
Anthem (from Greek. "Praise") - a solemn song on a verses of a software character. Initially, the hymns were dedicated to the gods. Currently, the anthem is one of the national symbols of the state.
Epigram (Since Greek. "Inscription") is a short satirical poem of a mocking nature that emerged in the 3rd century BC. e.
Elegy - The genre of lyrics dedicated to sad thoughts or a lyrical poem, imbued with sadness. Belinsky called Elegy "Summer Song Content." The word "Elegy" is translated as "Reed Flute" or "File Song". Elegy originated in ancient Greece in the 7th century BC. e.
Message - A poetic letter, appeal to a specific person, request, wish.
Sonnet (from Provence. "Song") - poem from 14 lines with a certain rhyme system and strict stylistic laws. Sonnet originated in Italy in the 13th century (the creator is the poet of Jacopo and Lentini), in England appeared in the first half of the 16th century (Sarry), and in Russia - in the 18th century. The main types of Soyeta are Italian (from 2 katrenoes and 2 tercets) and English (from 3 katrenins and final two-bending).
Poem (With Greek. "I do, doing") - a lyrol-epic genre, a large poetic work with a narrative or lyrical plot usually on a historical or legendary topic.
Ballad - Laro-epic genre, plot song of dramatic content.
Epic - Large artwork, telling about significant historical events. In antiquity - narrative poem of heroic content. In the literature of 19-20 centuries, the genre of Roman-epic appears - this is a work in which the formation of the characters of the main characters occurs during their participation in historical events.
Novel - A large narrative artwork with a complex plot, in the center of which is the fate of the person.
Tale - Artistic work that occupies a middle position between the novel and the story in terms of the volume and complexity of the plot. In antiquity the story was called any narrative work.
Story - The artwork of a small size, based on the episode, the case of the Hero's life.
Story - The work of fictional events and heroes, usually with the participation of magical, fantastic forces.
Fable - This is a narrative product in poetic form, small size, moral or satirical nature.
Each literary genus is divided into genres, which are characterized by a common manner for a group of works. Spots epic, lyrical, limier genres, genres of dramaturgy.
Epic genres
Story(literary) - a work in prosaic or poems, based on folk traditions of the folk fairy tale (one storyline, fiction, image of the struggle of good and evil, antithesis and repeat as leading principles of composition). For example, satirical fairy tales M.E. Saltykov-Shchedrin.
Parable(From the Greek Parabole - "located (placed) behind") - a small epic genre, a small narrative product of an outfit character, containing moral or religious teaching, based on a broad generalization and use of the allegory. Russian writers often used the parable as a plug-in episode in their works to fill the story with a deep meaning. Recall the Kalmyk Tale, told by Pugacheva Peter Greenyava (A. Pushkin "Captain's Daughter") - In fact, it is a climax in the disclosure of the image of Emelyan Pugacheva: "Than three hundred years to eat Padalu, it's better to drink alive blood, and there it will give!". Scene parables about the resurrection of Lazarus, who read the Sonechka Marmeladov Rodion Raskolnikov, tells the reader about the possible spiritual revival of the main character of the Roman F.M. Dostoevsky "Crime and Punishment". In the play M. Gorky "At the bottom", the wanderer Luka tells the parable of "on the righteous land" to show how dangerous is the truth for weak and desperate people.
Fable- Small epic genre; The plugly complete, having an allegorical meaning, the fable is an illustration for known everyday or moral rules. The primacy of fables is characterized by the completion of the plot, the unity of action, the compression of the presentation, the absence of detailed characteristics and other elements of the defiative nature, which are inhibited by the development of Fabul, are characteristic of the fastener. Usually, the fable consists of 2 parts: 1) a story about an event, concrete, but easy to generalize, 2) moraling, following the story or the preceding story.
Feature article- Genre, a distinguishing sign of which is "Scripture from Nature." The role of the plot is weakened in the sketch, because The fiction here has an insignificant value. The author of the essay, as a rule, leads a first-person narrative, which allows it to include its reflections in the text, to compare and the analogies - i.e. Use the means of journalism and science. A sample of use in the literature of the essay genre are "Hunter's Notes" I.S. Turgenev.
Novella(Ital. Novella is news) - this is a type of story, an epic islar product with an unexpected junction, differing in brevity, neutral style of presentation, the absence of psychologism. The case, the intervention of fate plays a major role in the development of the actions of themella. A typical example of Russian novels is the cycle of stories I.A. Bunin "Dark Alleys": the author psychologically does not draw the characters of his heroes; The whim of fate, the blind case drives them for a while and is separated forever.
Story- Epic genre of small volume with a small number of heroes and short-lived events. In the center of the narration - an image of a event or life phenomenon. In Russian classical literature, recognized masters of the story were A.S. Pushkin, N.V. Gogol, I.S. Turgenev, L.N. Tolstoy, A.P. Chekhov, I.A. Bunin, M. Gorky, A.I. Kubrin et al.
Tale- Prose genre that has no sustainable volume and occupying an intermediate place between the novel, on the one hand, and the story and the novel with the other, which is a physical plot that reproduces the natural course of life. The story and novel the story is characterized by the volume of text, the number of heroes and raised problems, complexity of conflict, etc. The test is important not so much the plot movement, how many descriptions: the heroes, the place of action, the psychological state of the person. For example: "Enchanted Wanderer" N.S. Leskova, "Steppe" A.P. Chekhov, "Village" I.A. Bunin. In the story, episodes are often followed by one after another on the principle of the chronicles, there is no internal connection between them, or it is weakened, so the story is often built as a biography or autobiography: "Childhood", "Defense", Youth L.N. Tolstoy, "The Life of Arsenyev" I.A. Bunina, etc. (Literature and language. Modern illustrated encyclopedia / ed. Prof. A.P. Gorkina. - M.: Rosman, 2006.)
Novel(Franz. Roman - a work written on one of the "living" romance languages, and not on the "dead" Latin) - the epic genre, the subject of the image in which is a certain period or a whole person's life; Roman what is it? - Roman is characterized by the duration of the events described, the presence of several storylines and systems of the acting persons entering the groups of equivalent characters (for example: the main characters, secondary, episodic); The work of this genre covers a large range of life phenomena and a wide range of socially significant problems. There are different approaches to the classification of novels: 1) according to structural features (novel-parable, novel-myth, novel-antiutopia, romance, romance in verses, etc.); 2) on issues (family-household, social and household, socio-psychological, psychological, philosophical, historical, adventurous, fantastic, sentimental, satirical, etc.); 3) by the era in which one or another type of novel (knightly, educational, Victorian, Gothic, modernist, etc.) dominated. It should be noted that the exact classification of genre varieties of the novel has not yet been established. There are works, ideological and artistic peculiarity of which does not fit into the framework of any one classification method. For example, the work of MA Bulgakov "Master and Margarita" contains both acutely social and philosophical issues, in it in parallel the events of biblical history (in the author's interpretation) and the modern author of the Moscow life 20-30s of the 20th century, scenes, full of drama, are interspersed Satirical. Based on these features of the work, it can be classified as a socio-philosophical satirical novel-myth.
Roman-epic. - This is a work in which the subject of the image is not a story of privacy, but the fate of the entire people or a whole social group; The plot is based on nodes - key, turning historical events. At the same time, the fate of the people and, on the other hand, the picture of the people's life is reflected in the destinies of the people and, on the other hand, the picture of the people's life is made up of individual destinies. An integral accessory of epic is mass scenes, thanks to which the author creates a generalized picture of the flow of folk life, the movement of history. When creating an epic, the artist requires the highest skill in the adhesion of episodes (scenes of private life and mass scenes), psychological reliability in the drawing of characters, historicism of artistic thinking - all this makes the epic of the vertex of literary creativity, which is not every writer. That is why only two works created in the epic genre are known in Russian literature: "War and Peace" L.N. Tolstoy, "Quiet Don" M.A. Sholokhov. Genres lyrics
Song- Small poems lyrical genre, characterized by the simplicity of musical and verbal construction.
Elegy(Greek. Elegeia, Elegos is a plaintive song) - a poem of meditative or emotional content dedicated to philosophical meditation caused by the contemplation of nature or deeply personal experiences about life and death, about unrequited (usually) love; The prevailing mood of Elegy - sadness, light sadness. Elegy - a favorite genre of V.A. Zhukovsky ("Sea", "Evening", "Singer", etc.).
Sonnet(Ital. Sonetto, from Ital. Sonare - sounded) - a lyrical poem from 14 lines in the form of complex stanza. Sonyet rows can be located in two ways: two cores and two tercets or three miles and distorts. There may be only two rhymes in the rhymes, and in Terectets - two or three.
Italian (Petrarkovsky) Sights consists of two katrenins with ABBA ABBA ABBA or Abab ABAB and two tercets with a CDC DCD or CDE CDE rhyme, less commonly CDE EDC. French Sonet Form: Abba ABBA CCD EED. English (Shakespearean) - with ABAB CDCD EFEF GG rhyme scheme.
Classic Sonnet involves a certain sequence of development of thought: thesis - antithesis - synthesis - an omission. Judging by the name of this genre, there is no particular importance to the sonnet musicality, which is achieved by alternating male and female rhymes.
European poets have developed many original types of sonnets, as well as a wreath of sonnets - one of the most difficult literary forms.
Russian poets treated the genre of the sonnet: A.S. Pushkin ("Sonnet", "Poet", "Madonna", etc.), A.A. Fet ("Sonnet", "Date in the Forest"), poets of the Silver Century (V.Ya. Bryusov, K.D. Balmont, A.A. Blok, I.A. Bunin).
Message(Greek Epistole - Epistole) - a poetic letter, during the time of Horat - philosophical and didactic content, later - any character: narrative, satirical, love, friendly, etc. The mandatory sign of the message is to have an appeal to a specific addressee, the motives of the wishes, requests. For example: "My Penates" K.N. Batyushkova, "Pushchina", "Message of Czensor" A.S. Pushkin and others.
Epigram(Greek. Epgramma is an inscription) - a short satirical poem, which is a teaching, as well as a direct response to topical events, often political. For example: epigrams A.S. Pushkin on A.A. Arakcheeva, F.V. Bulgarine, the epigram Sasha black "in the Bryusov album" and others.
Oh yeah(from Greek. ōdḗ, Latin. ODE, ODA - Song) - a solemn, pathetic, glorifying a lyrical work devoted to the image of large historical events or persons talking about the significant topics of religious-philosophical content. The ODA genre was distributed in Russian literature of the XVIII - early XIX centuries. In the work of M.V. Lomonosov, G.R. Derzhavina, in the early work of V.A. Zhukovsky, A.S. Pushkin, F.I. Tyutchev, but at the end of the 20s of the XIX century. Other genres came to change Ode. Separate attempts of some authors to create an ODU do not correspond to the canons of this genre ("Ode Revolution" by V.V. Mayakovsky et al.).
Lyrical poem - a small poetic product in which there is no plot; The author's focus is the inner world, intimate experiences, reflections, the mood of the lyrical hero (author of the lyrical poem and the lyrical hero is not the same person). Laroepic genres
Ballad(Provencal Ballada, from Ballar - dance; ITAL. - Ballata) - a plot poem, that is, a story of a historic, mythical or heroic character, set out in poetic form. Typically, the ballad is based on the character dialogue, while the plot does not have an independent value - this is a means of creating a certain mood, subtext. So, "Song about Oleg" A.S. Pushkin has a philosophical subtext, "Borodino" M.Yu. Lermontov - social and psychological.
Poem(Greek. Poiein - "Create", "Creation") - a major or secondary poems with a narrative or lyrical plot (for example, "Copper Horseman" A.S. Pushkin, "MTSY" M.Yu. Lermontov, "Twelve" a .A. Bloka, etc.), the poem may include a lyrical hero (for example, "Requiem" Akhmatova).
Pooh in prose - A small lyrical product in prosaic form, distinguished by increased emotionality, expressing subjective experiences, impressions. For example: "Russian language" I.S. Turgenev. Genres of Dramaturgia
Tragedy- a dramatic work, the main conflict of which is caused by exceptional circumstances and insoluble contradictions, leading the hero to death.
Drama- Piece, the content of which is associated with the image of everyday life; Despite the depth and seriousness, the conflict, as a rule, concerns privacy and can be resolved without a tragic outcome.
Comedy- a dramatic work, in which the action and characters are presented in funny forms; The comedy is distinguished by the rapid development of the action, the presence of complex, tangled plot strokes, a prosperous ending and simplicity of style. There are a comedy of provisions based on ingenious intrigue, a special coincidence of circumstances, and comedies of morals (characters) based on ridicule of human defects and shortcomings, a high comedy, domestic, satirical, etc. For example, "grief from the mind" A.S. Griboedova is a high comedy, "inexpensive" D.I. Fonvizin - satirical.