Have cylindrical. Support for geometry on the topic "Cylinder"
Read also
The cylinder is a geometric body bounded by two parallel planes and a cylindrical surface. In the article, let's talk about how to find the area of \u200b\u200bthe cylinder and, applying a formula, solve several tasks for example.
 The cylinder has three surfaces: vertex, base, and side surface.
The cylinder has three surfaces: vertex, base, and side surface.
The top and base of the cylinder are circles, they are easy to determine.
It is known that the area of \u200b\u200bthe circle is equal to πr 2. Therefore, the formula of the area of \u200b\u200btwo circles (the vertices and base of the cylinder) will have the form πr 2 + πr 2 \u003d 2πr 2.
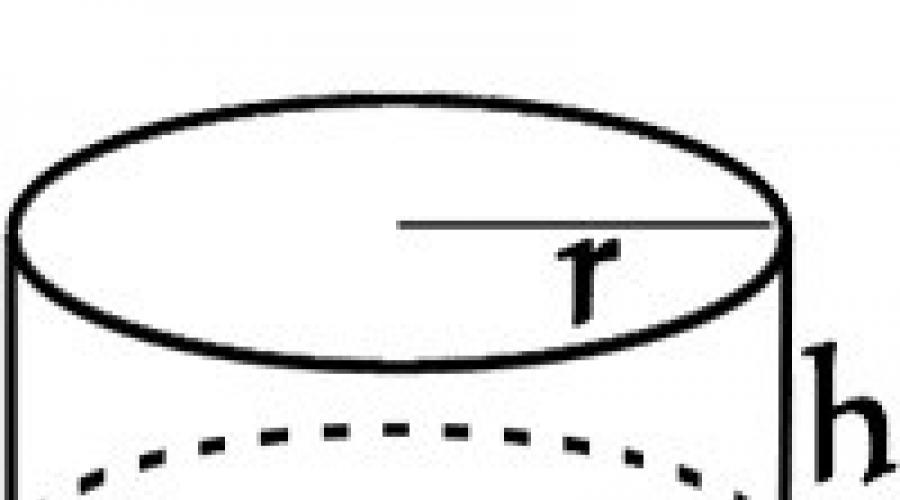
 The third, side surface of the cylinder is a curved cylinder wall. In order to better present this surface, try to convert it to get the recognizable form. Imagine that the cylinder is an ordinary cans, which has no top cover and bottom. We will make a vertical incision on the side wall from the top to the base of the can (step 1 in the figure) and try to reveal (straighten) the resulting figure (step 2).
The third, side surface of the cylinder is a curved cylinder wall. In order to better present this surface, try to convert it to get the recognizable form. Imagine that the cylinder is an ordinary cans, which has no top cover and bottom. We will make a vertical incision on the side wall from the top to the base of the can (step 1 in the figure) and try to reveal (straighten) the resulting figure (step 2).
After the full disclosure of the received bank, we will see a familiar figure (step 3), this is a rectangle. Rectangle area is easy to calculate. But before this will return for a moment to the original cylinder. The top of the source cylinder is a circle, and we know that the circumference length is calculated by the formula: L \u003d 2πr. In the figure it is marked in red.
When the side wall of the cylinder is fully disclosed, we see that the circumference length becomes the length of the obtained rectangle. The parties of this rectangle will be the circumference length (L \u003d 2πR) and the height of the cylinder (H). The area of \u200b\u200bthe rectangle is equal to the product of its sides - s \u003d length x width \u003d L x H \u003d 2πr x H \u003d 2πrh. As a result, we obtained a formula for calculating the area of \u200b\u200bthe side surface of the cylinder.
The formula of the side surface area of \u200b\u200bthe cylinder
S side. \u003d 2πrh
Square of the full surface of the cylinder
Finally, if we fold the area of \u200b\u200ball three surfaces, we obtain the formula of the area of \u200b\u200bthe full surface of the cylinder. The surface area of \u200b\u200bthe cylinder is equal to the area of \u200b\u200bthe top of the cylinder + the area of \u200b\u200bthe base of the cylinder + the area of \u200b\u200bthe side surface of the cylinder or S \u003d πr 2 + πr 2 + 2πrh \u003d 2πr 2 + 2πrh. Sometimes this expression is recorded by an identical formula 2πr (R + H).
Formula of the area of \u200b\u200bthe full surface of the cylinder
S \u003d 2πr 2 + 2πrh \u003d 2πr (R + H)
r - cylinder radius, h - cylinder height
Examples of calculating the surface area of \u200b\u200bthe cylinder
To understand the above formulas, try to calculate the surface area of \u200b\u200bthe cylinder on the examples.
1. The radius of the base of the cylinder is 2, the height is 3. Determine the area of \u200b\u200bthe side surface of the cylinder.
The total surface area is calculated by the formula: s side. \u003d 2πrh
S side. \u003d 2 * 3,14 * 2 * 3
S side. \u003d 6.28 * 6
S side. \u003d 37.68
The area of \u200b\u200bthe side surface of the cylinder is 37.68.
2. How to find the surface area of \u200b\u200bthe cylinder if the height is 4, and the radius 6?
The total surface area is calculated by the formula: S \u003d 2πr 2 + 2πRH
S \u003d 2 * 3,14 * 6 2 + 2 * 3,14 * 6 * 4
S \u003d 2 * 3,14 * 36 + 2 * 3,14 * 24
S \u003d 226,08 + 150.72
The surface area of \u200b\u200bthe cylinder is 376.8.
A limited cylindrical surface and two parallel planes crossing it.
Related definitions
Cylindrical surface - The surface obtained when moving the straight line (forming), parallel to any given, crossing the curve (guide), lying in a non-parallel specified direct plane. Flat figures formed by the intersection of a cylindrical surface with two parallel planes are called bases of cylinder. The cylindrical surface between the base planes is called side surface cylinder. In the case of parallel the foundation plane and the plane of the guide, the base boundary will be coincided with the guide.
Types
In most cases, the cylinder is meant the straight circular cylinder, in which the guide - the circle and the base are perpendicular to the forming. Such a cylinder has a symmetry axis.
Other types of cylinder - (by inclusting forming) oblique or inclined (if the resulting base is not at right angles); (on the basis of the base) elliptical, hyperbolic, parabolic.
Prism is also a type of cylinder - with a base in the form of a polygon.
Cylinder surface area
Side Side Square
 The area of \u200b\u200bthe side surface of the cylinder is equal to the length of the forming multiplied by the perimeter of the cylinder cross section by the plane perpendicular to the forming.
The area of \u200b\u200bthe side surface of the cylinder is equal to the length of the forming multiplied by the perimeter of the cylinder cross section by the plane perpendicular to the forming.
The area of \u200b\u200bthe lateral surface of the direct cylinder is calculated by its depart. Cylinder Runs is a rectangle with a height and length equal to the perimeter of the base. Consequently, the side surface area of \u200b\u200bthe cylinder is equal to the area of \u200b\u200bits expandment and is calculated by the formula:
In particular, for a direct circular cylinder:
, I.
For an inclined cylinder, the side surface area is equal to the length of the generator multiplied by the perimeter of the cross section perpendicular to the forming:
A simple formula expresses the area of \u200b\u200bthe side surface of the oblique cylinder through the base parameters and height, in contrast to the volume does not exist. For an inclined circular cylinder, you can use approximate formulas for the perimeter of the ellipse, and then multiply the resulting value to the length forming.
Full surface area
The area of \u200b\u200bthe total surface of the cylinder is equal to the sum of the area of \u200b\u200bits side surface and its bases.
For a direct circular cylinder:
Cylinder volume
 For an inclined cylinder there are two formulas:
For an inclined cylinder there are two formulas:
- The volume is equal to the length of the forming multiplied by the cylinder cross-section of the plane perpendicular to the forming. ,
- The volume is equal to the ground area multiplied by height (the distance between the planes in which the bases underlie): ,
For a straight cylinder , and and volume is equal:
For a circular cylinder:
where d. - Base diameter.
Write a review about the article "Cylinder"
Notes
Cylinder excerpt
- Paris La Capitale du Monde ... [Paris - the capital of the world ...] - said Pierre, arriving his speech.The captain looked at Pierre. He had a habit in the middle of the conversation to stop and look closely laughing in gentle eyes.
- EH BIEN, SI Vous Ne M "Aviez Pas Dit Que Vous Etes Russe, J" Aurai Parie Que Vous Etes Parisien. Vous Avez Ce Je NE Sais, Quoi, CE ... [Well, if you didn't tell me that you are Russian, I would beat about the mortgage that you are a Parisian. There is something in you, this ...] - and, saying this compliment, he looked silently again.
- J "AI ETE A PARIS, J" Y AI PASSE DES ANNEES, [I was in Paris, I spent there for many years, "said Pierre.
- OH CA SE VOIT BIEN. Paris! .. Un Homme Qui Ne Connait Pas Paris, Est Un Sauvage. Un Parisien, CA SE SENT A DEUX Lieux. Paris, S "Est Talma, La Duschenois, Potier, La Sorbonne, Les Boulevards, - and noticing that the conclusion of the weaker than the previous one, he hastily added: - Il N" Ya QU "Un Paris Au Monde. Vous Avez Ete A Paris et vous Etes Reste Busse. Eh Bien, Je Ne Vous En Estime Pas Moins. [Oh, it can be seen. Paris! .. A person who does not know Paris, - savage. Parisian will find out for two miles. Paris is Talma, Dusheua, Inntidence, Sorbonne, boulevards ... all over the world one Paris. You were in Paris and remained Russian. Well, I do not respect you for that.]
Under the influence of drinking wine and after days spent in solitude with their gloomy thoughts, Pierre felt the invalid pleasure in conversation with this cheerful and good-natured person.
- Pour en Revenir A Vos Dames, On Les Dit Bien Belles. QUELLE FICHUE IDEE D "ALERR S" ENTERRER DANS LES STEPPES EST A MOSCOU. QUELLE CHANCAIS EST A MOSCOU. QUELLE CHANCE ELLES ONT MANQUE CELLES LA. VOS MOUJIKS C "EST AUTRE Chose, Mais Voua Autres Gens Civilises Vous Devriez Nous Connaitre Mieux Que Ca . Nous Avons Pris Vienne, Berlin, Madrid, Naples, Rome, Varsovie, Toutes Les Capitales du Monde ... on No Craint, Mais On Nous Aime. Nous Sommes Bons A Connaitre. ET PUIS L "EMPEREUR! [But they turn to your ladies: they say that they are very beautiful. What kind of stupid thought go to rumble in the steppe, when the French army in Moscow! They missed a wonderful case. Your men, I understand, but you are people Educated - should have been to know us better. We took Vienna, Berlin, Madrid, Naples, Rome, Warsaw, all the capital of the world. We are afraid, but we are loved. It is not harmful to know us closer. And then the emperor ...] - He began, But Pierre interrupted him.
- L "EMPEREUR, - repeated Pierre, and his face suddenly brought a sad and confused expression. - EST CE QUE L" EMPEREUR? .. [Emperor ... what is the emperor? ..]
- L "EMPEREUR? C" EST La Generosite, La Clemence, La Justice, L "Ordre, Le Genie, Voila L" Empereur! C "Est Moi, Ram Ball, Qui Vous Le Dit. Tel Que Vous Me Voyez, J" Etais Son Ennemi Il Y A Encore Huit Ans. MON PERE A ETE COMTE EMIGRE ... MAIS IL M "A VAINCU, CET HOMME. IL M" A EMPOIGNE. JE N "AI PAS PU Resister Au Spectacle de Grandeur et de Gloire Dont Il Couvrait La France. QUAND J" AI COMPRIS CE QU "IL VOULAIT, QUAND J" AI VU QU "IL NOUISAIT UNE LITIERE DE Lauriers Me Suis Dit: Voila Un Souverain, Et Je Me Suis Donne a Lui. Eh Voila! Oh, Oui, Mon Cher, C "Est Le Plus Grand Homme Des Siecles Passes et a venir. [Emperor? These are generosity, mercy, justice, order, genius - that's what is the emperor! This is me, Rambal, I tell you. So what you see me, I was his enemy again eight years old. My father was a graph and an emigrant. But he won me, this man. He took possession of me. I could not resist the spectacle of greatness and glory to which he covered France. When I realized what he wanted when I saw that he was preparing for us Lavrov's bed, I told myself: here is the sovereign, and I gave him. And so! Oh yes, my dear, it is the greatest man of past and future centuries.]
Cylinder (More precisely, the circular cylinder) is called the body, which consists of two circles lying in parallel planes and combined with parallel transfer, and all segments connecting the corresponding points of these circles. Circles are called bases of cylinder, and segments connecting the corresponding points of the circles, - forming.
The cylinder has the following properties, as follows from the fact that the base of the cylinder is combined with parallel transfer:
1. The base of the cylinder is equal.
2. The forming cylinders are parallel and equal.
The cylinder is called direct If its generators are perpendicular to the base planes. In the future, we will consider mainly straight cylinders, therefore, unless otherwise specified, we will understand the direct cylinder under the cylinder.
Radiusthe cylinder is called the radius of its base. Height The cylinder is called the distance between the planes of its bases. For a direct cylinder, the height is equal to the forming. Axis The cylinder is called straight, passing through base centers.
The cylinder is a body of rotation, as it can be obtained by the rotation of the rectangle around its axis.
Tasks
18.1 Cylinder 6, Radius of the base 5. The sections of the segment 10 are lying on the circles of both bases. Find the shortest distance from this segment to the axis of the cylinder.
18.2V with the equilateral cylinder (diameter is equal to the height of the cylinder) the point of the top base circumference is connected to the bottom base circumference. The angle between radius carried out in these points is 60 o. Find the angle between the segment and the axis of the cylinder.
Cone
Definition of cone
Cone (more precisely, the circular cone) is called the body that consists of a circle - bases of cone, points not lying in the foundation plane - vertines cone and all segments connecting the vertex of the cone with points of the base. Segments connecting the vertices of the cone with the points of the base circumference are called forming cone.

Close cone It is called perpendicular, lowered from the vertex of the cone to the base plane. If the base of the height coincides with the center of the circumference of the base, the cone is called direct. Next, under the cone we will usually understand the straight cone.
Axis A direct circular cone is direct, containing its height. Such a cone can be obtained by the rotation of the rectangular triangle around one of the cathets.
Frustum
The plane, parallel to the base of the cone, cuts off from it a similar cone. The remaining part is called truncated cone.

Tasks
19.12Tve the forming cones based on the ends of the base diameter make up an angle of 60 o. The radius of the cone is equal to 3. Find the forming cone and its height.
19.2 Hold the middle of the height of the cone was carried out straight, parallel to forming. Find the length of the length of a straight line enclosed inside the cone.
19.3-forming cone is 13, height 12. The cone is crossed direct, parallel base; The distance from it to base is equal to 6, and to height - 2. Find a straight line, enclosed inside the cone.
19.4radias of the foundations of a truncated cone are 3 and 6, height - 4. Find forming.
Shara definition
Sharh called body, which consists of all points of space located at a distance, no more than a certain point called center of Shara.. This distance is called radius of the ball.

The border of the ball is called ball surface or sphere. Thus, the points of the sphere are all points of the ball, remote from the center of the ball for a distance equal to the radius.
The segment connecting two points of the ball surface and passing through the center of the ball is called the diameter of the ball.
The ball, as well as the cylinder and the cone, is the body of rotation. It turns out when the semicircle is rotated around its diameter.
Tasks
20.1 The surface of the ball is given three points. Straight distances between them 6, 8 and 10. Ball radius 13. Find the distance from the center of the ball to the plane passing through these three points.
20.2 Bowl diameter 25. On its surface there is a point and a circle, all points of which are removed (in a straight line) from 15. Find the radius of this circle.
The 20.3radius of the ball is 7. Two circles that have common chord are given on its surface. 2. Find circles radii, knowing that their planes are perpendicular.
The name of the science "Geometry" is translated as "Measurement of Earth". Originated by the efforts of the very first ancient land routes. And it was like this: during the spills of the sacred Nile, water flows were sometimes washed off the borders of the farmers, and the new borders could not coincide with the old. The taxes of the same peasants were paid in the KazNU Pharaoh proportional to the magnitude of the land. Special people were engaged in the measurement of Pashny space in the new borders after the spill. It is as a result of their activities and a new science emerged, which was developed in ancient Greece. There she also received the name, and acquired a practically modern appearance. In the future, the term became an international name of science on flat and volume figures.
Planimetry is a section of geometry engaged in the study of flat figures. Another section of science is stereometry, which considers the properties of spatial (volume) figures. Such figures refers and described in this article - a cylinder.
There are plenty of examples of the presence of cylindrical objects in everyday life. Cylindrical (much less often - conical) The form has almost all parts of rotation - shafts, sleeves, cervical, axis, etc. The cylinder is widely used in construction: towers, support, decorative columns. And besides the dishes, some types of packaging, pipes of all sorts of diameters. And finally, the famous hats, which have become a long symbol of male elegance. The list can be continued endlessly.
Cylinder definition as a geometric shape
The cylinder (circular cylinder) is customary to call a figure consisting of two circles, which, if desired, are combined with parallel transfer. These are these circles and are the bases of the cylinder. But lines (straight segments) connecting the corresponding points, got the name "forming".
It is important that the bases of the cylinder are always equal (if this condition is not performed, then we are a truncated cone, something else, but not a cylinder) and are in parallel planes. The segments connecting the corresponding points on the circles are parallel and equal.
The combination of an infinite set of generators is nothing but a side surface of the cylinder is one of the elements of this geometric shape. Another important component is the above circles. They are called grounds.
Types of cylinders
The easiest and most common type of cylinder - circular. It forms two right circles acting as grounds. But instead there may be other figures.

The bases of cylinders can form (except for circles) ellipses, other closed figures. But the cylinder may not necessarily be closed. For example, the base of the cylinder can serve as a parabola, hyperbole, another open function. Such a cylinder will be open or deployed.
At the angle of inclination, the cylinders may be straight or inclined. At the direct cylinder forming strictly perpendicular to the base plane. If this angle differs from 90 °, the cylinder is inclined.

What is the surface of rotation
A straight circular cylinder, no doubt - the most common surface of the rotation used in the technique. Sometimes technical indications are used conical, spherical, some other types of surfaces, but 99% of all rotating shafts, axes, etc. Made precisely in the form of cylinders. In order to better understand what the surface of rotation is, it is possible to consider how the cylinder itself is formed.
Suppose there is some straight a.located vertically. ABCD - a rectangle, one of the sides of which (Cut AB) lies on a straight line a.. If you rotate the rectangle around the straight line, as shown in the figure, the volume that it will take, rotating, and it will be our own body of rotation - a direct circular cylinder with a height H \u003d AB \u003d DC and R \u003d AD \u003d BC radius.

In this case, as a result of rotation of the figure - a rectangle - the cylinder is obtained. Rotating a triangle, you can get a cone, rotating a semicircle - a ball, etc.
Cylinder surface area
In order to calculate the surface area of \u200b\u200bthe usual direct circular cylinder, it is necessary to calculate the base areas and the side surface.

First, consider how the side surface area is calculated. This is a product of the circumference of the cylinder height. The length of the circle, in turn, is equal to the twin product of the universal number P On the radius of the circle.
The area of \u200b\u200bthe circle, as is known, is equal to the work. P On the square of the radius. So, folding the formula for the area of \u200b\u200bdetermining the side surface with a double expression of the base area (therefore, two) and producing simple algebraic transformations, we obtain the final expression to determine the surface area of \u200b\u200bthe cylinder.
Definition of the volume of the figure
The volume of the cylinder is determined according to the standard scheme: the surface area of \u200b\u200bthe base is multiplied by height.

Thus, the final formula looks like this: the desired is defined as a piece of body height on a universal number Pand on the square of the base radius.
The resulting formula must be said, applies to solve the most unexpected tasks. In the same way as the volume of the cylinder is determined, for example, the volume of wiring. This is necessary to calculate the mass of wires.

Differences in the formula is only that instead of the radius of one cylinder, it is worth a divided dying diameter of the conductors of the wiring and in the expression the number emerges in the wire N.. Also, instead of height, the length of the wire is used. Thus, the volume of the "cylinder" is calculated not one, but by the number of wiring in the overall.
Such calculations are often required in practice. After all, a significant part of water capacities is made in the form of a pipe. And calculate the volume of the cylinder is often needed even in the household.
However, as already mentioned, the shape of the cylinder may be different. And in some cases it is required to calculate what is equal to the volume of the cylinder of the inclined.
The difference is that the surface area of \u200b\u200bthe base is multiplied by the length of forming, as in the case of a direct cylinder, and by the distance between the planes - perpendicular segment, built between them.

As can be seen from the figure, this segment is equal to the length of the length of the angle of inclination forming to the plane.
How to build a cylinder rave
In some cases, it is required to carve a cylinder debug. The figure shows the rules on which the billet is built for the manufacture of a cylinder with a given height and diameter.

It should be borne in mind that the drawing is shifted without taking into account the seams.
Differences of the beveled cylinder

Imagine a certain straight cylinder, limited on one side by the plane perpendicular to the generators. But the plane limiting the cylinder on the other side is not perpendicular to the forming and not parallel to the first plane.

The figure shows a bevelled cylinder. Plane but Under a certain angle, different from 90 ° to the forming, crosses the figure.
Such a geometric form is more common in practice in the form of pipelines (knee). But even there are buildings built in the form of a beveled cylinder.
Geometrical characteristics of the bevelled cylinder

The slope of one of the planes of the beveled cylinder slightly changes the procedure for calculating both the surface area of \u200b\u200bsuch a figure and its volume.