Grammar of the Latin language. Tutorial
Read also
1. History of the Latin language
Latin belongs to the group of Italian dead languages. The formation of the literary Latin language took place in the II-I centuries. BC e., and it reached its greatest perfection in the 1st century. BC e., during the period of the so-called classical, or "golden", Latin. He was distinguished by the richest vocabulary, the ability to convey complex abstract concepts, scientific-philosophical, political, legal, economic and technical terminology.
This period is followed by post-classical, or "silver", Latin (I-II centuries AD), when the norms of phonetics and morphology were finally consolidated, the rules of spelling were determined. The last period of the existence of ancient Latin was the so-called late Latin (3rd-6th centuries AD), when the gap between written, bookish, Latin and folk colloquial began to intensify.
In the countries of the Western Mediterranean by the end of the II century. BC e. Latin won the position of the official state language.
Starting from 43 AD. e. and until 407, the Celts (British) who inhabited Britain were also under the rule of Rome.
If in the west of Europe the Latin language in its colloquial form spread, almost without encountering the resistance of tribal languages, then in the depths of the Mediterranean basin (Greece, Asia Minor, Egypt) it encountered languages that had a longer written history and had a level of culture much higher than Latin language of the Roman conquerors. Even before the arrival of the Romans, the Greek language became widespread in these regions, and with it the Greek, or Hellenic, culture.
From the very first cultural contacts between the Romans and the Greeks and throughout the history of ancient Rome, the latter experienced in the economic, state, social and spiritual areas of life the ever-increasing influence of the highly developed Greek culture.
Educated Romans tended to read and converse in Greek. Borrowed Greek words were included in colloquial and literary Latin, especially actively after being under the rule of Rome in the II-I centuries. BC e. Greece and Hellenistic countries were included. From the 2nd century BC e. Rome began to assimilate the vocabulary of Greek science, philosophy and medicine, partially borrowing along with new concepts and terms denoting them, slightly Latinizing them.
At the same time, another process also developed more actively - the formation of Latin words of scientific content, that is, terms.
When comparing the two classical languages, their significant differences are visible.
The Latin language was noticeably inferior in its word-building potential to the Greek language, which had a remarkable ability to clothe in linguistic forms newly discovered, described phenomena, facts, ideas of biological and medical content, to easily create more and more new names, almost transparent in meaning, through various methods of word formation, especially by bases and suffixes.
2. Term and definition
The word "term" (terminus) is Latin in origin and once meant "limit, border". A term is a word or phrase that serves to unambiguously and accurately designate (name) a special, scientific concept in a certain system of special concepts (in science, technology, production). Like any common word, the term has a content or meaning (semantics, from the Greek semantikos - "denoting"), and a form, or a sound complex (pronunciation).
Unlike the rest of the common lexicon, which denotes ordinary, everyday, so-called naive ideas, the terms denote special scientific concepts.
The Philosophical Encyclopedic Dictionary defines the concept as follows: "A thought that reflects in a generalized form the objects and phenomena of reality and the connections between them by fixing general and specific features, which are the properties of objects and phenomena and the relationship between them." The concept has content and scope. The content of a concept is a set of the features of an object reflected in it. The scope of a concept is a set (class) of objects, each of which has features that make up the content of the concept.
Unlike everyday everyday concepts, a special scientific concept is always a fact of a scientific concept, the result of a theoretical generalization. The term, being a sign of a scientific concept, plays the role of an intellectual tool. With its help, scientific theories, concepts, provisions, principles, laws are formulated. The term is often a herald of a new scientific discovery, a phenomenon. Therefore, unlike non-terms, the meaning of a term is revealed in a definition, a definition that is necessarily attributed to it.
Definition(Latin definitio) is a formulation in a concise form of the essence of the concept being terminated, that is, denoted by the term, the concept: only the main content of the concept is indicated. For example: ontogenesis (Greek on, ontos - "existing", "being" + genesis - "generation", "development") - a set of successive morphological, physiological and biochemical transformations of the body from its inception to the end of life; Aerophiles (lat. aёr - "air" + philos - "loving") - microorganisms that receive energy only from the oxidation reaction of oxygen in the environment.
As you can see, the definition does not just explain the meaning of the term, but establishes this meaning. The requirement to determine what this or that term means is tantamount to the requirement to give a definition of a scientific concept. In encyclopedias, special explanatory dictionaries, in textbooks, the concept (term) introduced for the first time is revealed in definitions. Knowledge of the definitions of those concepts (terms) that are included in the curriculum in the disciplines is a mandatory requirement for the student.
3. Medical terminology
Modern medical terminology is a system of systems, or macroterminology. The entire set of medical and paramedical terms, as noted, reaches several hundred thousand. The plan of the content of medical terminology is very diverse: morphological formations and processes characteristic of the human body in normal and pathological conditions at various stages of their development; diseases and pathological conditions of a person; forms of their course and signs (symptoms, syndromes), pathogens and carriers of diseases; environmental factors that positively or negatively affect the human body; indicators of hygienic regulation and evaluation; methods of diagnostics, prevention and therapeutic treatment of diseases; operational accesses and surgical operations; organizational forms of providing medical and preventive care to the population and the sanitary and epidemiological service; devices, devices, tools and other technical means, equipment, medical furniture; medicinal products grouped according to the principle of their pharmacological action or therapeutic effect; individual medicinal products, medicinal plants, medicinal raw materials, etc.
Each term is an element of a certain subsystem, for example, anatomical, histological, embryological, therapeutic, surgical, gynecological, endocrinological, forensic, traumatological, psychiatric, genetic, botanical, biochemical, etc. Each subterminal system reflects a certain scientific classification of concepts adopted in this science. At the same time, terms from different subsystems, interacting with each other, are in certain semantic relationships and connections at the level of the macroterminal system.
This reflects the dual trend of progress: the further differentiation of the medical sciences, on the one hand, and their increasing interdependence and integration, on the other. In the XX century. the number of highly specialized sub-terminal systems has significantly increased, expressing concepts related to the diagnosis, treatment and prevention of diseases that affect mainly individual organs and systems (pulmonology, urology, nephrology, neurosurgery, etc.). Over the past decades, highly specialized dictionaries of cardiology, oncology, radiology, immunology, medical virology, and hygienic sciences have reached an impressive size.
Within the framework of the macroterminal system, the following subsystems play an almost leading role:
1) anatomical and histological nomenclature;
2) a complex of pathological-anatomical, pathological-physiological and clinical term systems;
3) pharmaceutical terminology.
It is these subsystems that are the objects of study in the course of the Latin language and the basics of medical terminology.
4. General cultural humanitarian significance of the Latin language
Studying a Latin language course at a medical institute pursues a purely professional goal - to prepare a terminologically competent doctor.
However, in order to master any language, it is necessary to improve one's cultural and educational level, to broaden one's horizons.
In this regard, Latin aphorisms are useful, sayings that express a generalized, complete thought in a concise form, for example: Fortes fortuna juvat - "Fortune helps the brave"; Non progredi est regredi - "Not to go forward means to go back."
Proverbs like: Omnia mea mecum porto - "I carry everything with me" are also interesting; Festina lente - "Hurry slowly", etc. Many aphorisms are separate lines, statements of famous ancient writers, philosophers, politicians. Of considerable interest are aphorisms in Latin belonging to the scientists of the New Age: R. Descartes, I. Newton, M. Lomonosov, K. Linnaeus and others.
Most of the Latin aphorisms, sayings and proverbs included in the material of individual lessons and presented in a list at the end of the textbook have long become popular expressions. They are used in scientific and fiction literature, in public speaking. Separate Latin aphorisms and sayings deal with issues of life and death, human health, and the behavior of a doctor. Some of them are medical deontological (Greek deon, deonios - "due" + logos - "teaching") commandments, for example: Solus aegroti suprema lex medkorum - "The good of the patient is the highest law of doctors"; Primum noli nocere! - "First of all, do no harm!" (the doctor's first commandment).
In the international vocabulary of many languages of the world, especially European ones, Latinisms occupy a significant place: institute, faculty, rector, dean, professor, doctor, associate professor, assistant, graduate student, laboratory assistant, preparator, student, dissertator, audience, communication, credit, discredit, decree, creed, course, curator, supervise, prosecutor, cadet, ply, competitor, competition, excursion, excursionist, degree, gradation, degradation, ingredient, aggression, congress, progress, regression, lawyer, legal adviser, consultation, intellect, intellectual, colleague, collegium, collection, petition, appetite, competence, rehearsal, tutor, conservator, conservatory, conserve, observatory, reserve, reservation, reservoir, valence, valerian, currency, devaluation, invalid, prevail, equivalent, statue, monument, ornament, style, illustration, etc.
Only in the last few years, on the pages of newspapers and magazines, in the speeches of deputies, words of Latin origin, new to our political life, flashed: pluralism (pluralis - "multiple"), conversion (conversio - "transformation", "change"), consensus (consensus - "consent", "agreement"), sponsor (sponsor - "trustee"), rotation (rotatio - "circular motion"), etc.
5. Alphabet
The Latin alphabet used in modern textbooks, reference books and dictionaries consists of 25 letters.
Table 1. Latin alphabetWith a capital letter in Latin, proper names, names of months, peoples, geographical names and adjectives derived from them are written. In pharmaceutical terminology, it is customary to write the names of plants and medicinal substances with a capital letter.
Notes.
1. Most of the letters of the Latin alphabet are pronounced the same as in various Western European languages, however, some letters in these languages are called differently than in Latin; for example, the letter h is called "ha" in German, "ash" in French, "h" in English, and "ga" in Latin. The letter j in French is called "zhi", in English - "jay", and in Latin - "iot". The Latin letter "c" in English is called "si", etc.
2. It must be borne in mind that the same letter can denote an unequal sound in these languages. For example, the sound indicated by the letter g is pronounced in Latin as [g], and in French and English before e, i - as [g] or [j]; in English j is read as [j].
3. Latin spelling is phonetic, it reproduces the actual pronunciation of sounds. Compare: lat. latina [latina], eng. latin - latin.
The difference is especially noticeable when comparing vowels in Latin and English. In Latin, almost all vowels are always pronounced the same as the corresponding vowels in Russian.
4. As a rule, names not from the Latin language, but from other languages (Greek, Arabic, French, etc.) are latinized, that is, they are drawn up in accordance with the rules of phonetics and grammar of the Latin language.
6. Reading vowels (and consonant j)
In Latin, "E e" is read as [e]: vertebra [ve" rtebra] - vertebra, medianus [media" nus] - median.
Unlike Russians, no Latin consonants soften before the sound [e]: anterior [ante "rior] - front, arteria [arte" ria] - artery.
"I i" reads like [and]: inferior [infe" rior] - lower, internus [inte" rnus] - internal.
At the beginning of a word or syllable, before vowels, i is read as a voiced consonant [th]: iugularis [yugula "rice] - jugular, iunctura [yunktu" ra] - connection, maior [ma" yor] - large, iuga [yu" ha] - elevation.
In these positions, in modern medical terminology, instead of i, the letter J j is used - yot: jugularis [yugula "rice], juncture [yunktu" ra], major [ma" yor], juga [yu" ha].
The letter j is not written only in words borrowed from the Greek language, since there was no sound [th] in it: iatria [ia "tria] - healing, iodum [io "dum] - iodine.
To convey the sounds [ya], [yo], [ye], [yu], combinations of letters ja, jo, je, ju are used.
Y y (upsilon), in French "y", reads like [and]: tympanum [ti "mpanum] - drum; gyrus [gi" Rus] - gyrus of the brain. The letter "upsilon" is used only in words of Greek origin. It was introduced by the Romans to convey the letter of the Greek alphabet upsilon, which was read as German [and]. If the Greek word was written through i (Greek iota), read as [and], then it was transcribed into Latin through i.
In order to correctly write medical terms, you need to know some of the most common Greek prefixes and roots in which "upsilon" is written:
dys- [dis-] - a prefix that gives the term the meaning of a violation, a disorder of function: dysostosis (dys + osteon - "bone") - dysostosis - a disorder of bone formation;
hypo- [hypo-] - "under", "below": hypoderma (hypo + + derma - "skin") - hypodermis - subcutaneous tissue, hypogastrium (hypo- + gaster - "stomach", "stomach") - hypogastrium - hypogastrium;
hyper- [hyper-] - "above", "over": hyperostosis (hyper + + osteon - "bone") - hyperostosis - pathological growth of unchanged bone tissue;
syn-, sym- [syn-, sim-] - "with", "together", "together": synostosis (syn + osteon - "bone") - synostosis - connection of bones through bone tissue;
mu (o) - [myo-] - the root of the word, indicating the relationship to the muscles: myologia (myo + logos - "word", "teaching") - myology - the doctrine of muscles;
phys- [phys-] - the root of the word, indicating in anatomical terms the relation to something growing in a certain place: diaphysis - diaphysis (in osteology) - the middle part of the tubular bone.
7. Diphthongs and features of reading consonants
In addition to simple vowels [a], [e], [i], [o], [i], in Latin there were also two-vowel sounds (diphthongs) ae, oe, ai, her.
Digraph ae reads like [e]: vertebrae [ve" rtebre] - vertebrae, peritonaeum [peritone" mind] - peritoneum.
Digraph oe reads like [e], more precisely, like German o or French oe: foetor [fetor] - a bad smell.
In most cases, the diphthongs ae and oe, found in medical terms, served to render in Latin the Greek diphthongs ai and oi. For example: oedema [ede "ma] - edema, oesophagus [eso" fagus] - esophagus.
If in combinations ae and oe the vowels belong to different syllables, that is, they do not constitute a diphthong, then a separation sign (``) is placed above the "e" and each vowel is pronounced separately: diploё [diploe] - diploe - spongy substance of the flat bones of the skull ; aёr [air] - air.
The diphthong au reads like: auris [ay "rice] - ear. The diphthong eu reads like [eu]: ple "ura [ple" ura] - pleura, neurocranium [neurocra" nium] - brain skull.
Features of reading consonants
A double reading of the letter "C with" is accepted: as [k] or [c].
How [k] is read before the vowels a, o, and, before all consonants and at the end of the word: caput [ka "put] - head, head of bones and internal organs, cubitus [ku" bitus] - elbow, clavicula [curse" kula ] - clavicle, crista [cri "hundred] - crest.
How [c] is read before the vowels e, i, y and the digraphs ae, oe: cervicalis [cervical "fox] - cervical, incisure [incizu" ra] - tenderloin, coccyngeus [koktsinge "us] - coccygeal, coelia [tse" lia ] - abdomen.
"H h" reads like a Ukrainian sound [g] or German [h] (haben): homo [homo] - a person, hnia "tus [gna" tus] - a gap, a crevice, humerus [hume" Rus] - a humerus.
"K k" is very rare, almost exclusively in words of non-Latin origin, in cases where you need to keep the sound [k] before the sounds [e] or [and]: kyphosis [kypho "zis] - kyphosis, kinetocytus [kine" that -citus] - kinetocyte - mobile cell (words of Greek origin).
"S s" has a double reading - [s] or [s]. How [s] is read in most cases: sulcus [su "lkus] - a furrow, os sacrum [os sa" krum] - the sacrum, sacral bone; dorsum [to "rsum] - back, back, rear. How [h] is read in a position between vowels: incisura [incizu "ra] - tenderloin, vesica [wezi" ka] - bubble. Doubled s reads like [s]: fossa [fo "csa] - pit, ossa [o" ss] - bones, processus [proce" ssus] - process. In the position between vowels and consonants m, n in words of Greek origin, s is read as [h]: chiasma [chia "zma] - cross, platysma [fly" zma] - subcutaneous muscle of the neck.
"X x" is called a double consonant, since it represents the sound combination [ks]: radix [ra" dix] - the root, extremitas [extre" mitas] - the end.
"Z z" is found in words of Greek origin and reads like [h]: zygomaticus [zygoma "ticus] - zygomatic, trapezius [trape" zius] - trapezoidal.
8. Letter combinations. Accents. brevity rule
In Latin, the letter "Q q" occurs only in combination with u before vowels, and this combination is read as [kv]: squama [squa" me] - scales, quadratus [quadra" tus] - square.
The letter combination ngu is read in two ways: before vowels as [ngv], before consonants - [ngu]: lingua [li" ngva] - language, lingula [li" ngulya] - tongue, sanguis [sa" ngvis] - blood, angulus [angu" lux] - angle.
The combination of ti before vowels reads like [qi]: rotatio [rota "tsio] - rotation, articulatio [article" tsio] - joint, eminentia [emine" ncia] - elevation.
However, ti before vowels in combinations sti, xti, tti reads like [ti]: ostium [o "stium] - hole, entrance, mouth, mixtio [mi" xtio] - mixture.
In words of Greek origin, there are digraphs ch, ph, rh, th, which are graphic signs for conveying the corresponding sounds of the Greek language. Each digraph is read as one sound:
ch = [x]; ph = [f]; rh = [p]; th = [t]: nucha [well "ha] - neck, chorda [chord] - chord, string, phalanx [fa" lanks] - phalanx; apophysis [apophysis] - apophysis, process; thorax [that" raks] - chest notch, rhaphe [ra" fe] - seam.
The letter combination sch reads like [cx]: os ischii [os and "schii] - ischium, ischiadicus [ischia" dicus] - ischium.
Stress rules.
1. The stress is never placed on the last syllable. In two-syllable words, it is placed on the first syllable.
2. In trisyllabic and polysyllabic words, the stress is placed on the penultimate or third syllable from the end.
The placement of stress depends on the duration of the penultimate syllable. If the penultimate syllable is long, then the stress falls on it, and if it is short, then the stress falls on the third syllable from the end.
Therefore, in order to place stress in words containing more than two syllables, it is necessary to know the rules for longitude or shortness of the penultimate syllable.
Two rules of longitude
Longitude of the penultimate syllable.
1. The syllable is long if it contains a diphthong: peritona "eum - peritoneum, perona" eus - peroneal (nerve), dia "eta - diet.
2. The syllable is long if the vowel comes before two or more consonants, and also before the double consonants x and z. This longitude is called position longitude.
For example: colu "mna - column, pillar, exte" rnus - external, labyri "nthus - labyrinth, medu" lla - brain, medulla, maxi "lla - upper jaw, metaca" rpus - metacarpus, circumfle "xus - envelope.
brevity rule
A vowel before a vowel or h is always short. For example: tro "chlea - block, pa" ries - wall, o "sseus - bone, acro" mion - acromion (shoulder process), xiphoi "deus - xiphoid, peritendi" neum - peritendinium, pericho "ndrium - perichondrium.
9. Cases and types of declensions
The inflection of nouns according to cases and numbers is called declension.
Cases
There are 6 cases in Latin.
Nominativus (Nom.) - nominative (who, what?).
Genetivus (Gen.) - genitive (of whom, what?).
Dativus (Dat.) - dative (to whom, what?).
Accusativus (Acc.) - accusative (of whom, what?).
Ablativus (Abl.) - ablative, creative (by whom, with what?).
Vocativus (Voc.) - vocative.
For nomination, i.e. for naming (naming) objects, phenomena, and the like in medical terminology, only two cases are used - nominative (im. p.) and genitive (gen. p.).
The nominative case is called the direct case, which means the absence of relations between words. The meaning of this case is the actual naming.
The genitive case has a characterizing meaning.
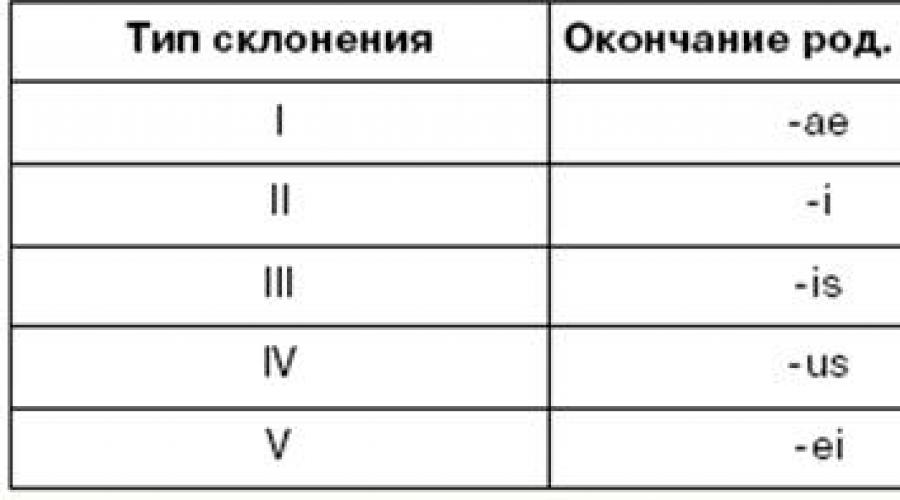
There are 5 types of declensions in Latin, each of which has its own paradigm (a set of word forms).
A practical means of distinguishing declension (determining the type of declension) in Latin is the genitive case of the singular.
Genus forms. p. units hours in all declensions are different.
The distribution of nouns by declension types depending on the gender ending. p. units h.
Genitive endings of all declensions

10. Determination of the practical basis
Nouns are listed in the dictionary and learned in dictionary form, which contains 3 components:
1) the form of the word in them. p. units hours;
2) the end of the genus. p. units hours;
3) gender designation - male, female or neuter (abbreviated as one letter: m, f, n).
For example: lamina, ae (f), sutura, ae (f), sulcus, i (m); ligamentum, i(n); pars, is(f), margo, is(m); os, is(n); articulatio, is (f), canalis, is (m); ductus, us(m); arcus, us (m), cornu, us, (n); facies, ei (f).
Some nouns have the III declension before the ending genus. p. units h. -is is also attributed to the final part of the stem.
This is necessary if the stem of the word is in gender. p. units h. does not coincide with the basis of them. p. units hours:

The full form of the genus. p. units hours for such nouns are found as follows:
corpus, =oris (=corpor - is); foramen, -inis (= fora-min - is).
For such nouns, the practical basis is determined only from the form of the word to the gender. p. units hours by discarding its ending.
If the basics in them. p. units hours and in the genus. p. units h. coincide, then only the ending genus is indicated in the dictionary form. etc., and the practical basis in such cases can be determined from them. p. units hours without ending.
Examples
The practical basis is the basis, to which, during inflection (declension), the endings of oblique cases are added; it may not coincide with the so-called historical basis.
For monosyllabic nouns with a changing stem, the entire word form genus is indicated in the dictionary form. n., for example, pars, partis; crus, cruris; os, oris; cor, cordis.
11. Definition of the gender of nouns
In Latin, as in Russian, nouns belong to three genders: masculine (masculinum - m), feminine (femininum - f) and neuter (neutrum - n).
The grammatical gender of Latin nouns cannot be determined from the gender of Russian words equivalent in meaning, since often the gender of nouns with the same meaning in Russian and Latin does not coincide.

It is possible to determine the belonging of a Latin noun to a particular gender only by the endings characteristic of this gender in it. p. units h.
For example, words in -a are feminine (costa, vertebra, lamina, incisura, etc.), words in -um are neuter (ligamentum, manubrium, sternum, etc.).
A sign of the declension of a noun is the ending of the gender. p. units hours; a sign of the genus - a characteristic ending in them. p. units h.
Determining the gender of nouns ending in the nominative singular in -a, -um, -on, -en, -i, -us
There can be no doubt that nouns in -a belong to the feminine gender, and nouns in -um, -on, -en, -u - to the middle one.
All nouns in -us, if they belong to the II or IV declension, are necessarily masculine, for example:
lobus, i; nodus, i; sulcus, i;
ductus, us; arcus, us; meatus, us, m - masculine.
If a noun with -us belongs to the III declension, then its belonging to a certain gender should be specified with the help of such an additional indicator as the final consonant of the stem in gender. P.; if the final consonant of the stem is r, then the noun is neuter, and if the final consonant is different (-t or -d), then it is feminine.
tempus, or-is; crus, crur is;
corpus, or-is - neuter, juventus, ut-is - feminine.
12. III declension of nouns
Third declension nouns were extremely rare, for example: os, corpus, caput, foramen, dens. This methodological approach was absolutely justified. III declension is the most difficult to master and has a number of features that distinguish it from other declensions.
1. The third declension includes nouns of all three genders ending in gender. p. units h on -is (a sign of the III declension).
2. In them. p. units h. words not only of different genders, but even of the same gender have different endings characteristic of a particular gender; for example, in the masculine gender -os, -or, -o, -eg, -ex, -es.
3. For most nouns, the third declension stems in them. n. and in the genus. items do not match.

With such nouns, the practical basis is not determined by them. n., but by genus. n. by dropping the ending -is.
1. If in the dictionary form of any noun before the ending genus. p. units h. -is the end of the stem is attributed, which means that the stem of such a word is determined by the genus. P.:

2. If in the dictionary form before the end of the genus. p. units h. -is has no postscript, which means that such a word can also have a basis determined by them. p. units h., discarding the ending to them. p.: pubes, is the basis of pub-.
3. Nouns III declension depending on the coincidence or mismatch of the number of syllables in them. n. and genus. p. units hours are equally complex and non-equisyllabic, which is important for the exact definition of the genus in a number of cases. Equosyllabic Nom. pubes canalis rete Gen. pubis canalis retis. Uneven Nom. pes paries pars Gen. pedis parietis partis.
4. For monosyllabic nouns in the dictionary form in gender. n. the word is written in full: vas, vasis; os, ossis.
The genus is determined by the endings of them. p. units h., characteristic of a certain genus within a given declension. Therefore, in order to determine the gender of any noun of the III declension, 3 points must be taken into account:
1) to know that the given word refers specifically to the III declension, and not to any other;
2) know what endings are in them. p. units hours are characteristic of one or another kind of III declension;
3) in some cases, also take into account the nature of the stem of the given word.
13. Adjective
1. Adjectives in Latin, as in Russian, are divided into qualitative and relative. Qualitative adjectives denote a sign of an object directly, i.e., without relation to other objects: true rib - costa vera, long bone - os longum, yellow ligament - ligamentum flavum, transverse process - processus transversus, large hole - foramen magnum, trapezoid bone - os trapezoideum, sphenoid bone - os sphenoidale, etc.
Relative adjectives indicate the sign of an object not directly, but through relation to another object: the spinal column (column of the vertebrae) - columna vertebralis, the frontal bone - os frontale, the sphenoid sinus (the cavity in the body of the sphenoid bone) - sinus sphenoidalis, the sphenoid crest (section anterior surface of the body of the sphenoid bone) - crista sphenoidalis.
The predominant mass of adjectives in the anatomical nomenclature are relative adjectives indicating that a given anatomical formation belongs to a whole organ or to another anatomical formation, such as the frontal process (extending from the zygomatic bone upwards, where it connects to the zygomatic process of the frontal bone) - processus frontalis .
2. The categorical meaning of the adjective is expressed in the categories of gender, number and case. The gender category is an inflectional category. As in Russian, adjectives change by gender: they can be in the form of masculine, feminine or neuter. The gender of an adjective depends on the gender of the noun with which it agrees. For example, the Latin adjective meaning "yellow" (-th, -th) has three gender forms - flavus (m. p.), flava (f. p.), flavum (cf. p.).
3. Inflection of adjectives also occurs according to cases and numbers, i.e. adjectives, like nouns, decline.
Adjectives, unlike nouns, are declined only in I, II or III declension.
The specific type of declension, according to which this or that adjective changes, is determined by the standard dictionary form in which it is recorded in the dictionary and in which it should be remembered.
In the dictionary form of the overwhelming majority of adjectives, the endings characteristic of one kind or another in them are indicated. p. units h.
At the same time, some adjectives have endings in them. n. for each genus are completely different, for example: rectus, recta, rectum - straight, straight, straight; other adjectives for masculine and feminine have one common ending, and for the neuter gender - another, for example: brevis - short and short, breve - short.
Adjectives are given differently in the dictionary form. For example: rectus, -a, -um; brevis, -e.
Ending -us m. is replaced in R. to -a (recta), and cf. R. - on -um (rectum).
14. Two groups of adjectives
Depending on the type of declension according to which adjectives are inclined, they are divided into 2 groups. Membership in a group is recognized by standard dictionary forms.
The 1st group includes adjectives that are declined according to the I and II declension. They are easily recognized by their endings. n. -us (or -er), -a, -um in dictionary form.
The 2nd group includes all adjectives that have a different dictionary form. Their inflection occurs according to the III declension.
Memorizing the dictionary form is necessary in order to correctly determine the type of declension and use the appropriate endings in oblique cases.
Adjectives of the 1st group
In the presence of a dictionary form with endings in them. p. units h. -us, -a, -um or -er, -a, -um adjectives in the form of g. R. inclined according to the I declension, in the form of m. and cf. R. - according to the II declension.
For example: longus, -a, -um - long; liber, -era, -erum - free. In the genus n. they have, respectively, endings:

Some adjectives that have in m. ending -er, the letter "e" drops out in m. p., starting with the genus. p. units h., and in R. and on Wed. R. - in all cases without exception. This is not the case for other adjectives. For example, dictionary forms ruber, -bra, -brum, liber, -era, -erum.
Adjectives of the 2nd group
Adjectives of the 2nd group are declined according to the III declension. Their dictionary form differs from the adjectives of the 1st group.
According to the number of generic endings in the dictionary form, adjectives of the 2nd group are divided into:
1) adjectives of two endings;
2) adjectives of one ending;
3) adjectives of three endings.
1. Adjectives of two endings in anatomical and histological and in general in medical terminology are most common. They have in them. p., unit only two generic endings - -is, -e; -is - common for m. and well. r., e - only for cf. R. For example: brevis - short, short; breve - short.
The prevailing number of adjectives with two endings found in the nomenclature is characterized by the following word-formation model.
2. Adjectives of the same ending have one common ending in them for all genders. p. units h. Such an ending can be, in particular, -x, or -s, etc. For example: simplex - simple, -th, -th; teres - round, -th, -th; biceps - two-headed, -th, -th.
3. Adjectives of three endings have endings: m. - -er, f. p. - -is, cf. R. - e. For example: ce-ler, -eris, -ere - fast, -th, -th; celeber, -bris, -bre - healing, -th, -th.
All adjectives of the 2nd group, regardless of the dictionary form, are declined according to the 3rd declension and have a single stem in oblique cases.
15. Adjective - agreed definition
Another type of subordinating relationship, when the function of definition in a nominal phrase is performed by a non-noun in gender. etc., and the adjective is called agreement, and the definition is agreed.
When agreed, a grammatically dependent definition is likened to gender, number and case with the main word.
As the grammatical forms of the main word change, the forms of the dependent word also change. In other words, as in Russian, adjectives agree with the noun in gender, number, and case.
For example, when agreeing adjectives transversus, -a, -um and vertebralis, -e with nouns processus, -us (m); linea, -ae (f); ligamentum, -i (n); ca-nalls, -is (m); incisura, -ae, (f); foramen, -inis (n) results in the following phrases:

As in Russian, Latin qualitative adjectives have three degrees of comparison: positive (gradus positivus), comparative (gradus comparativus) and excellent (gradus superlativus).
The comparative degree is formed from the basis of a positive degree by adding the suffix -ior to it for m. and well. r., suffix -ius - for cf. R. For example:

1. The main grammatical feature of adjectives in a comparative degree are: for m. and well. R. - suffix -ior, for cf. R. - suffix -ius.
For example: brevior, -ius; latior, -ius.
2. For all adjectives, in a comparative degree, the stem coincides with the form of m. and well. R. in them. p. units hours:

3. Adjectives are declined in a comparative degree according to the III declension. Genus form. p. units hours for all three genera is the same: it is formed by adding the ending -is to the stem.
4. Adjectives are relatively consistent with nouns in gender, number and case, i.e. they are consistent definitions: sutura latior; sulcus latior; foramen latius.
16. Nominative plural
1. Any case endings, including their endings. n. pl. hours, always attached to the base.
2. For the formation of word forms. n. pl. h. different declensions must adhere to the following provisions.
If the noun refers to cf. r., then it declines in accordance with the rule cf. r., which reads: all words cf. R. (both nouns and adjectives of all degrees of comparison), regardless of which declension they belong to, end in it. n. pl. hours on -a. This applies only to the words cf. p., for example: ligamenta lata - wide ligaments, crura ossea - bone legs, ossa temporalia - temporal bones, cornua majora - large horns.
Word endings in m. and well. R. in them. n. pl. hours are easier to remember, taking into account each individual declension. In this case, it is necessary to remember the following correspondences: nouns I, II, IV declensions have in them. n. pl. h. exactly the same ending as in the genus. n. pl. h. The same correspondence is observed for adjectives of the 1st group, because they are declined like nouns of I and II declensions, for example:

Nouns of the III and V declensions, as well as adjectives of the III declension and adjectives in the comparative degree (they also decline according to the III declension) have in them. n. pl. h .. the same ending -es.

Generalization of data on the endings of nouns and adjectives in them. n. pl. h.

17. Genitive plural
Continuing the study of the inflection of nouns and adjectives in the plural, it is necessary to note the genitive case of the plural.
To learn how to quickly and accurately form terms in the form of gender. n. pl. h., you need to be able to:
determine by the dictionary form of a noun its belonging to a certain declension; highlight the base
recognize the gender by their characteristic endings. p. units hours; set according to the dictionary form, an adjective belongs to the 1st or 2nd group; establish which of the three declensions (I-II or III) the given adjective is inclined to, consistent with the noun in gender, number and case.
Genitive plural endings (Genetivus pluralis)
The ending -um has:
1) unequal nouns of all three genders, the stem of which ends in one consonant: tendinum (m), regionum (f), foraminum (n); 2) adjectives in a comparative degree of all three genders (they also have a basis for one consonant): majorum (m, f, n).
The ending -ium has:
1) all other nouns with a stem of more than one consonant; equivalent in -es, -is; nouns cf. R. in -e, -ai, -ar: dentium (m), partium (f), ossium (n), animalium, avium, retium;
2) adjectives of the 2nd group of all three genders: brevi-um (m, f, n).
Notes.
1. Noun vas, vasis (n) - vessel in units. h. declines according to the III declension, and in many others. hours - according to II; Gen. pl. - vasorum.
2. In the term os ilium (ilium), the form genus is used. n. pl. hours from the noun ile, -is (n) (lower abdomen); them. n. pl. hours - ilia (iliac region). Therefore, it is wrong to change the form of ilium to ilii (ossis ilii).
3. The noun fauces, -ium - pharynx is used only in plural. h.
4. Nouns of Greek origin larynx, pharynx, meninx, phalanx end in im. pl. hours on -um.
18. Morpheme analysis
In a linear sequence, the word contains minimal parts that are indivisible neither in form nor in meaning: prefix (prefix), root, suffix and ending (inflection). All these minimal meaningful parts of a word are called morphemes (Greek morphe - form). The core of the meaning lies in the root, for example: sweat, sweat, sweat, sweat, etc. The prefix and suffix, distinguished by their position to the root, are called together word-building affixes (Latin affixus - "attached").
By attaching them to the root, derivatives - new - words are formed. The ending - an affix with a grammatical meaning does not serve for word formation, but for inflection (by cases, numbers, genders). The division of a word into morphemes is called analysis by composition, or morphemic analysis.
The entire unchanging part of the word preceding the ending, which carries the main lexical meaning, is called the basis of the word. In the words vertebr-a, vertebral-is, intervertebral-is, the stems are, respectively, vertebr-, vertebral-, intervertebral-.
The stem can in some cases be represented only by the root, in some others - by the root and word-building affixes, that is, the root, suffix and prefix.
Morpheme analysis shows what minimal meaningful parts (morphemes) the studied word consists of, but does not answer the question of what is the actual mechanism of word formation. This mechanism is revealed with the help of word-formation analysis. The meaning of the analysis is to isolate two direct components in the word: that single segment (generating stem) and that (those) affix(es), due to the combination of which the derivative word is formed.
The difference between derivational and morphemic analyzes can be shown by the following example.
The adjective interlobularis (interlobular) from the standpoint of morphemic analysis consists of five morphemes: inter- (prefix), -lob- (root), -ul-, -ar- (suffixes), -is (end); from the standpoint of word-formation analysis, two direct components are singled out: inter- - between (prefix) + -lobular (is) - lobular (producing stem, or word).
The real formation mechanism: inter- (prefix) + -lobular(is) (generating stem, not divisible in this case into morphemes).
Therefore, the derivative is the one from which another derivative stem, more complex in composition, is formed by attaching affix(s) to it.
The derivative stem is larger than the derivative stem by at least one morpheme.
19. Generating stem of a word
To isolate the generating stem in the word under consideration, it is necessary to compare it with two rows of words:
a) cholecyst-itis, cholecyst-o-graphia, cholecyst-o-pexia;
b) nephr-itis, vagin-itis, gastr-itis, etc. The generating stem is not only the material backbone of the derived word, but also motivates, i.e., determines its meaning. In this sense, one can judge about motivating and motivated words or about motivating and motivated bases. So, for example, derivatives - the names of diseases of the heart muscle - myocarditis, myocardiofibrosis, myocardosis, myocardtodystrophia - are motivated by the motivating basis myo-card (ium).
A motivated word differs from a motivating one in greater semantic (in meaning) complexity, for example: the histological term myoblastus (myoblast), consisting of two root morphemes myo- - "muscle" + blastus (Greek blastos - "sprout", "embryo"), means an undifferentiated cell from which a striated muscle fiber develops. The same word served as a motivating basis for the formation of the motivated word myoblastoma (myoblastoma) - the name of a tumor consisting of large cells - myoblasts.
There are cases when the concepts of generating and motivating words do not completely coincide. This happens if it is not a single word that motivates, but the whole phrase (adjective + noun), and only the adjective is used as a generating basis. Such, for example, are the words-terms choledocho-piastica, chcledocho-tomia, choledocho-scopia, mastoid-itis, mastoido-tomia, for which the phrases ductus choledochus (common bile duct) and processus mastoideus (mastoid process) are motivating, and producing bases - choledoch- (Greek chole - "bile" + doche - "vessel", "receptacle") and mastoid- (Greek mastos - "nipple" + -eides - "similar", "similar"; "mastoid") .
Proper names or surnames of persons who first discovered or described this or that phenomenon are also used as producing bases in clinical and pathological terms. Such "family" terms are called eponymous, or eponyms. Motivating for each such term is usually a phrase - an anatomical name, which includes its own name.
For example: in the term highmoritis (sinusitis), the generating base haimor is from the name of the English physician and anatomist N. Highmore, who described the maxillary sinus, named after him as the maxillary sinus. In the International Parisian Anatomical Nomenclature approved in 1955, all eponyms (names of authors) were removed and replaced by informative terms indicating the main morphological features of the corresponding formation. For example, instead of the eponym "Bartholin's gland", the term glandula vestibularis major was introduced, instead of "Cooper's gland" - glandula bulbourethralis, instead of "wirzung duct" - ductus pancreaticus major, instead of "maxillary sinus" - sinus maxiliaris, etc.
20. Articulation of terms
Partitioned are words, at least one part of which is repeated in any other words that are correlated with the data by meaning. Articulation of different words may be complete or incomplete. Those derivatives are fully segmented, all the constituent parts of which (individual morphemes or a block of morphemes) are repeated in other derivatives. If not every significant part is found in other modern medical terms, then the derivative has incomplete articulation. For example, the following words:
1) with full articulation: pod-algia (Greek pus, podos - "leg" + algos - "pain"), neur-algia (Greek neuron - "nerve"), as well as my-algia (Greek mys, myos - "muscle"), kephal-o-metria (Greek kephalos - "head"), thorac-o-metria (Greek thorax, thorakos - "chest", "chest"), etc.;
2) with incomplete articulation: pod-agra (Greek podagra - "trap"; aching legs; from pus, podos - "leg" + agra - "capture", "attack"). If the first part is singled out, as it is found in a number of modern terms, then the second part - agra - is practically a single one.
Almost all terms - derived words that arose naturally in the ancient Greek and Latin languages or artificially created from morphemes and generating bases of these languages, are completely segmentable. This means that they are also fully motivated in the modern terminology. The remarkable property of complete articulation becomes even more important for those who master the basics of medical terminology due to the fact that a significant number of morphemes and blocks of morphemes are frequent.
Frequency should be considered those morphemes and blocks that are repeated in different words at least 2-3 times. It is clear that the greater the degree of frequency, i.e., the greater the number of uses, parts of derivatives have, the more significant their role in terminology. Some high-frequency morphemes and blocks are involved in the formation of dozens of terms.
Many morphemes of the ancient Greek and Latin languages acquired specific, sometimes new, meanings unusual for them in the ancient source language. Such meanings are called terminological. So, for example, the Greek word kytos (vessel, cavity) in the Latinized form cytus began to be used as a regular root morpheme in the structure of dozens of terms - derived words - in the meaning of "cell". The suffix of ancient Greek adjectives -itis, which gave them the general meaning of "related, belonging", became a regular part of terms - nouns with the meaning "inflammation".
21. Term element
Any part of a derived word (morpheme, block of morphemes) that is regularly reproduced in finished form when using existing or creating new terms and retaining a certain meaning assigned to it in the terminology is called a term element.
term element is a component regularly repeated in a series of terms, which is assigned a specialized meaning. At the same time, it does not matter in principle in the form of which transcription, Latin or Russian, the same international term element of Greek-Latin origin appears: infra- - infra-; -tomia - -tomia; nephro- - nephro-, etc. For example: the term cardiologia - the science of diseases of the cardiovascular system consists of the initial term cardio - heart and the final -logia - science, branch of knowledge.
The division of a term-word into term elements does not always coincide with its division into morphemes, since some term elements represent a whole block - a combination of 2-3 morphemes in one whole: prefix + root, root + suffix, prefix + root + suffix. In such a regular formal and semantic fusion, these blocks of morphemes are distinguished in a number of derivatives of the same type, for example, in terms of asthen-o-spermia - asthen-o-sperm, asthen-opia - asthen-opium, asthen-o-depressivus - asthen-o- depressive, asthen-isatio - asthenization, a block term element asthen (o) - (asthen (o) -), from the Greek. asthenes - "weak": negative prefix a- - "not, without" + sthenos - "strength".
High-frequency term elements tom-ia (-to-miya) (Greek tome - "cut"), rhaph-ia (-raffia) (Greek rhaphe - "seam"), log-ia (-logia) (Greek logos - "science") - the final parts of the derivatives - are two-morphemic in composition: the root + the suffix -ia, which gives the words the general meaning of "action, phenomenon". The high-frequency term element -ectomia (-ectomy) - the final part of the derivatives - consists of three ancient Greek morphemes: the prefix eu- + the root -tome- - "cut" + the suffix -ia - "cutting", "removal".
Term elements of Greek-Latin origin constitute the international "golden fund" of biological and medical terminology.
With the help of frequency term elements, numerous series of terms of the same type in structure and semantics (meaning) are formed. Interacting with each other, the term elements all together form a complex formal semantic term system, which remains open for the inclusion of new term elements and new series of terms, and in which each term element is assigned a specific place and meaning.
A huge number of medical terms are formed by adding bases, combined with suffixation. In this case, the suffix of Greek origin -ia is used more often than others. For example, haemorrhagia in ancient Greek is made by combining two stems: haem - "blood" + rhagos - "broken, torn" + suffix -ia.
22. Greco-Latin doublets
The division of term elements into bound and free should be constantly taken into account. For example, when comparing anatomical values in normal anatomy, on the one hand, with similar values in pathological anatomy and in a complex of clinical disciplines, on the other hand, the following pattern is revealed: the same organ is designated in two ways - different not only in their linguistic origin, but also in grammatical decoration with signs. In the nomenclature of normal anatomy, this is an independent and usually Latin word, and in pathological anatomy, a related term element of Greek origin. Much less often in both disciplines is the same name borrowed from the same source language, for example, the Greek hepar, oesophagus, pharynx, larynx, urethra, thorax, ureter, encephalon and Latin appendix, tonsilla and others that were used even in ancient medicine, as well as complex suffixal derivatives on -turn, created in modern times; for example, myocardium, endothelium, perimetrium, etc. These words are included as free term elements in the structure of compound words in clinical terminology: hepatomegaly, endothelioma, encephalopathy, myocardiopathy, appendectomy. In the anatomical nomenclature, there are designations of the same formation both as an independent Latin root word and as a Greek component as part of a derivative; for example, chin - lat. mentum, but "chin-lingual" - genioglossus (Greek geneion - "chin"); language - lat. lingua, but "sublingual" - hypoglossus; "lingo-pharyngeal" - glossopharyngeus (Greek glossa - "language"), etc. Latin and Greek designations of anatomical structures that have exactly the same meaning are called Greek-Latin doublet designations (or doublets). We can formulate the following fundamental position: as a rule, Greek-Latin doublets are used to designate most anatomical formations (organs, body parts), and in the anatomical nomenclature - mainly Latin words, in clinical terminology - related term elements of Greek origin.
Scope of doublets
23. The meaning and place of term elements in the structure of a derived word
Term elements are mostly unambiguous, but some of them have two or more meanings.
So, for example, the term element onco- (Greek onkos - "heap, mass, volume, swelling") in some compound words has the meaning "volume, mass" (oncogramma - oncogram - a curve reflecting changes in volume; oncometria - oncometry - measurement of volume tissue or organ), in others - "tumor" (oncogenesis - oncogenesis - the process of occurrence and development of a tumor; oncologist - a doctor, a specialist in the treatment and prevention of tumors, etc.).
The final component -lysis (Greek "unleashing, decomposition, dissolution"; luo - "I untie, free") in some compound words means "decomposition, decay, dissolution" (autolysis, karyolysis, hemolysis, etc.), in others - "a surgical operation to release adhesions, adhesions" (cardiolysis, pneumo(no) lysis, etc.).
Usually, the place of a motivating stem in the structure of words does not affect its meaning: whether it is megalo- or -megalia (increase), gnatho- or -gnathia (jaw), blepharo- or -blepharia (eyelid), the meaning of the term elements will remain unambiguous. Some terminological elements, like the above, can act both as the first and final ones. Others may occupy only one permanent place, for example as final ones (-cele, -clasia, -le-psia, -peaia), some may only be the first components (auto-, brady-, bary-, laparo-).
1. It should be borne in mind that, depending both on the specific meaning of another component participating in the addition, and on the place it occupies in the compound word, some shades may arise that affect the general meaning of the motivated word. Thus, the cognate terminological elements haemo-, haemato- and -aemia have the general meaning of "pertaining to blood". At the same time, the final term element -aemia, which is preceded by the designation of a substance, indicates the blood as a medium in which substances are found, the presence and concentration of which in this medium are pathological (azotaemia, uraemia, bacteriaemia, etc.). If the term elements haemo- or haemato- are combined with the designation of an organ, then the general meaning of the compound word is the accumulation of blood in the cavity of the organ, hemorrhage (haematomyelia - hemorrhage into the substance of the spinal cord, haemarthrosis - accumulation of blood in the joint cavity).
2. For a logical understanding of the general meaning of a derivative word, it is advisable to start the semantic analysis of its constituent term elements from the final term element. For example, gastro/entero-logia: logia - "the science of...": gastro- - "stomach", entera- - "intestine".
3. The general meaning of a motivated word is always somewhat more voluminous, fuller, deeper than a simple addition of the meanings of the motivating components: for example, gastrojejunoplastica (Greek gaster - "stomach" + Latin jejunum - "jejunum" + plastike - "formation, plasticity") - surgical replacement of the stomach with a segment of the jejunum.
24. Formal language types of clinical terms
Formal language types of clinical terms are different.
1. Unmotivated simple words:
1) simple root words of Latin or ancient Greek origin: for example, stupor - stupor (numbness), tremor - tremor (trembling), thrombus - blood clot (blood clot), aphthae - aphthae (rashes);
2) simple derivatives (in the source language) - prefix and affix: for example, insultus (lat. insulto - "to attack") - stroke, infarctus (lat. infarcio - "stuff, stuff") - heart attack, aneurysma (Greek aneuryno - "expand") - aneurysm.
The above simple root and simple derivative words and many other clinical terms similar to them turn out to be indivisible within the framework of modern terminology and, therefore, unmotivated. Most often they are not translated, but borrowed, transcribed by means of national languages (Russian, English, etc.) and are internationalisms.
2. Terms-phrases. Nominal phrases occupy a significant place in clinical terminology. For their education, no special knowledge is required, except for grammatical. In each phrase, the core word is the word being defined - the noun in it. p. units or many h. Usually this is a generic term, that is, the name of a higher, more general concept in the classification.
Defining words are most often represented by adjectives. Their role is to clarify in a certain respect the generic (general) concept: for example, pneumonia adenoviralis - adenovirus pneumonia, p. apicalis - apical pneumonia, p. haefflorrhagica - hemorrhagic pneumonia, etc.
The most common meaning of defining words is the localization of the lesion: abscessus appendicis, ab. femoris, ab. parietis arteriae, ab. mesenterii, ab. poliicis, ab. bronchi, ab. peritonealis; ulcus pharyngis, etc.
Some phrases-internationalisms are included in the text in national languages traditionally in Latin grammatical form and transcription, for example, genu valgum (curved knee inside).
3. Fully segmentable motivated terms-words. Among the formal linguistic types of clinical terms, they are of the greatest interest in teaching the basics of medical terminology. Greek or, more rarely, Latin term elements with anatomical meaning act as the first motivating stems in compound words. The final components carry the main semantic load, perform (like suffixes) a classifying function.
Some of them correlate this concept with a certain group, a class of pathological phenomena (signs, conditions, diseases, processes), others with surgical operations or diagnostic techniques, etc. For example, terms with the initial term cardio- (Greek kardia - "heart"): cardiosclerosis, cardioneurosis, cardiomegalia, cardiolysis, cardiotomia, cardiographia, cardiotachometria, cardiovolumometria.
25. Ways of word formation. Deminutives
The main ways of word formation are affixal and non-affixal.
The affixal methods include the methods of forming derivatives by attaching word-forming affixes (prefixes, suffixes) to generating stems.
Non-affix methods are used mainly for the formation of compound words.
A word is complex if it consists of more than one generating stem. A compound word is formed by the method of basic construction.
A word in the structure of which there is only one generating stem is called simple: for example, costoarticularis is a compound word, a costalis and articularis are simple words.
There are also mixed ways of word formation: prefixation + suffixation, addition + suffixation, a way to create compound words, etc.
Deminutives- nouns with a common derivational meaning "diminutive".
A motivated diminutive noun (deminitive) retains the gender of the motivating word from which it is derived. These motivated words are inclined only according to the I or II declension, regardless of which declension the motivating word belongs to: for example, nodus, -i (m); nodulus; vas, vasis (n) vasculum.
1. Some artificially formed terms do not have a diminutive meaning; these are the designations of the stages of embryonic development: gastrula, blastula, morula, organella.
2. The nouns macula (spot), acetabulum (acetabulum) and some others also have a diminutive meaning.

26. Nouns with a common derivational meaning "action, process"
There are nouns in Latin that have certain suffixes with the general meaning "action, process".

1. Nouns of this very productive derivational type denote operations, examination methods, physiological functions, treatments, theoretical concepts in various disciplines: for example, auscultatio - auscultation, listening; percussio - percussion, tapping; palpatio - palpation, feeling.
All three terms refer to methods for examining internal organs.
There are derivatives in -io, denoting not only an action, a process, but also the result of this action, for example, decussatio - a cross (formation in the form of X); impresso - impression; terminatio - ending, end.
2. Among artificially formed words in -io, some do not come from a verb, but from a nominal stem, for example decapsulatio - decapsulation, surgical removal of an organ shell; hepatisatio - hepatization, compaction of lung tissue.
3. Nouns with a general derivational meaning "an object (organ, instrument, device) by which an action is performed; a person carrying out an activity."

4. Nouns with a common derivational meaning "result of action".

27. Suffixes of adjectives
I. Adjectives with a general derivational meaning "characterized or rich in a feature indicated by the generating basis."


II. Adjectives with the general derivational meaning "belonging to or relating to what is called the generative base".
III. Adjectives with a general derivational meaning "similar to what is called the stem of the word."

IV. Adjectives with a general derivational meaning "carrying what is called the generating basis."
V. Adjectives with a general derivational meaning:
1) "generating, producing, causing what is called the basis" (active meaning);
2) "generated, caused, conditioned by what is called the basis" (passive sense).
28. Features of the foundation
1. As the most common word-formation means, with the help of which two or more generating stems are combined into a single word, an interfix, or a connecting vowel, is used. In medical terminology, the most common interfix is -o-, less often -i- is used. In the original words of the ancient Greek language, only the interfix -o- is used, Latin - -i-: for example, lat. aur-i-scalpium (auris - "ear" + scalpo - "scrape, cut") - ear cleaning; viv-i-ficatio (vivus - "live" + facio - "to do") - revival.
However, in artificial neologisms, this linguistic regularity has ceased to be observed. Regardless of origin, the interfix -o- is used (neur-o-cranium, cary-o-lysis, lept-o-meniux, lat. auropalpebraiis, lat. nasolacrimal, etc.). The first addition components are usually indicated in dictionaries and reference books along with the interfix: thoraco-, spondylo-. Non-interfix connection of components usually takes place, although not always, if the first component ends with a vowel or the second component begins with a vowel: for example, the term elements brady- (Greek bradys - "slow"): brady-cardia; brachy- (Greek brachys - "short"): brachy-dactylia; rhin- (Greek rhis, rhinos "nose"): rhin-encephalon.
2. Variation of the generating basis. In Latin and Greek, there are nouns and adjectives (III declension), in which the stems of word forms of the nominative and genitive cases differ: for example, cortex, cortic-is; Greek som-a, somat-os - "body"; Greek meg-as, megal-u - "big"; Greek pan, pant-os - "everything", etc. The basis of the genitive case acts as the generating basis of Latin words: pariet-o-graphia, cortic-o-visceralis; in Greek words, the stem of the genitive case also more often turns out to be the stem. At the same time, sometimes the generating stem appears in a variant form - either nominative or genitive, for example: pan-, pant - "everything" (pan-demia, pant-o-phobia), mega- - "big" (megacolon, megal -o-biastus).
There are also three-variant forms of the same term element: initial - haemo-, haemato-, final -aemia with the general meaning "related to blood" (haemo-globinum, haemato-logia, an-aemia).
3. Phonetic-graphic variation of the bases. Some Greek stems have experienced varying degrees of romanization. In some cases, the pronunciation was preserved, close to the Greek language, in others there was a convergence with the norm of the Latin language. As a result, the same morpheme can be spelled differently: Gr. cheir - "hand" - cheir and chir; Greek koinos - "general", "joint" - coenosis, koino-. Various transcriptions of the Greek word neuron are used - "nerve" in Russian terms: neurology, but neurosurgery; neuritis (axon) and neuritis (inflammation of the nerve).
29. Prefix
Prefixation, i.e., attaching a prefix morpheme (prefix) to the root, does not change its meaning, but only adds to this value a certain component indicating localization (above, below, front, back), direction (approach, distance), flow in time (before something, after something), the absence or denial of something.
Prefixes developed mainly from prepositions, so their direct meanings coincide with the meanings of the corresponding prepositions.
Some prefixes based on direct meanings have developed secondary, figurative ones. So, the Greek preposition-prefix para- (“near, near”) developed a figurative meaning “retreat, deviation from something, inconsistency of external manifestations of the essence of this phenomenon”: for example, para-nasalis - paranasal, but para-mnesia (Greek mnesis - "memory") - paramnesia - the general name for distortions of memories and deceptions of memory.
In descriptive names used in morphological disciplines, prefix term elements have a direct meaning. In terms expressing the concepts of pathological conditions, diseases, impaired organ functions, and the like, prefix term elements are often used with secondary meanings. In various subsystems of medical terminology and in biology, Greek and Latin prefixes are extremely widely used.
As a rule, Latin prefixes are attached to Latin roots, Greek - to Greek roots. However, there are exceptions, the so-called hybrids, for example, in the words epi-fascialis - suprafascial, endo-cervicalis - intra-cervical prefixes are Greek, and the producing stems are Latin. When prefixing, the whole word acts as a generating basis: intra-articularis - intra-articular.
Antonymic prefixes. An important role in the functioning of medical terms is played by antonymous prefixes, i.e. those whose meanings are opposite: for example, lat. intra- - "inside" and extra- - "outside", "outside", etc.
Latin-Greek doublet prefixes. The meanings of a number of Latin prefixes coincide with the meanings of certain Greek prefixes or are very close to them:
lat. media- - Greek. meso- "in the middle", "between".
When prefixes are attached to the stems, changes in the prefix may occur under the influence of the initial sound of the stem.
This is mainly manifested in assimilation (lat. assimilalio - "similarity", "similarity"): the final consonant in the prefix is fully or partially likened to the initial sound of the producing stem. Some Latin prefixes may have elision, that is, the loss of a final consonant. In the Greek prefixes ana-, dia-, cafa-, meta-, para-, and-, epi-, apo-, hypo-, meso-, elision is manifested in the disappearance of the final vowel before the initial vowel of the stem. This eliminates the possible gaping (vowel with vowel).
30. Infinitive
Depending on the nature of the stem - the final sound of the stem - verbs are divided into IV conjugations.

In conjugations I, II, IV, the stems end in a vowel, and in III - most often in a consonant.
The infinitive is an indefinite form. In order to correctly identify the stem and determine by its final sound which of the four conjugations this or that verb belongs to, it is necessary to remember the infinitive of this verb. The infinitive is the original form of the verb; it does not change in persons, numbers, and moods. The sign of the infinitive in all conjugations is the ending -re. In I, II and IV conjugations, it is attached directly to the stem, and in III - through the connecting vowel -e-.
Samples of the infinitive of verbs I-IV conjugations
In II and III conjugations, the vowel [e] differs not only in brevity or longitude: in II conjugation it is the final sound of the stem, and in III it is a connecting vowel between the stem and the ending.
The stem of the verb is practically determined from the infinitive form by separating the ending -re from the verbs of I, II, IV conjugations and -ere from the verbs of the III conjugation.

Unlike the usual complete dictionaries of the Latin language, in educational dictionaries for medical students the verb is given in an abbreviated dictionary form: the full form of the 1st person singular. the present tense of the indicative mood of the active voice (ending -o), then the ending of the infinitive -re is indicated together with the preceding vowel, i.e. the last three letters of the infinitive. At the end of the dictionary form, the conjugation is marked with a number, for example:

31. Imperative and subjunctive
In prescriptions, the doctor's appeal to the pharmacist about the preparation of a medicine has the character of an order, an inducement to a certain action. This meaning of the verb is expressed in the imperative or subjunctive mood.
As in Russian, the order is addressed to the 2nd person. Only the 2nd person singular form of the imperative is used in the recipe. This form completely coincides with the stem for verbs of I, II and IV conjugations, for verbs of III conjugation, -e is added to the stem.
In practice, to form an imperative, one must discard the infinitive ending -re for verbs of all conjugations, for example:

Imperative mood in the form of the 2nd person plural. h. is formed by adding the ending -te: for verbs of I, II, IV conjugations - directly to the stem, for verbs of III conjugation - with the help of the connecting vowel -i-(-ite).
Subjunctive mood
Meaning. The recipe uses only one of the many meanings of the Latin subjunctive mood - an order, a call to action.
The conjunctiva forms with this meaning are translated into Russian by a verb in combination with the word "let" or an indefinite form of the verb, for example: let it be mixed or mixed.
Education. The conjunctive is formed by changing the stem: in conjugation I, -a is replaced by -e, in II, III and IV, -a is added to the stem. Personal endings of verbs are added to the modified stem.
Formation of the basis of the conjunctiva
Latin verbs, like Russian ones, have 3 persons; in medical terminology, only the 3rd person is used. Personal endings of verbs in the 3rd person are shown in the table.

32. Conjunctiva. Accusative
Examples of conjugation of verbs in the conjunctive of the active and passive voices.

Accusative
For competent writing of recipes, it is necessary to learn the endings of two cases - the accusative and the so-called ablative - in five declensions of nouns and adjectives of I, II and III declensions. Accusativus (vin. p.) is the case of the direct object; as in Russian, answers the questions "whom?" So what?" For convenience, the endings of this case are first remembered separately, which have neuter nouns and adjectives, and then the endings of masculine and feminine nouns and adjectives. Middle rules. All neuter nouns and adjectives, regardless of their declension, obey the following rules.
1. End Ass. sing. coincides with the end of Nom. sing. given word: for example, linimentum compositum, semen dulce.
2. End Ass. pl. coincides with the end of Nom. pl. and regardless of the declension, always -a (-ia): for example, linimenta composita, semina dulcia.
Only nouns have the ending -ia cf. R. on -e, -al, -ar (III declension) and all adjectives of the 2nd group (III declension).
Male and female. Masculine and feminine nouns and adjectives in Ass. sing. have a common final element -m, and in Asc. pl. -s; they are preceded by certain vowels depending on the declension.
Ending -im in Asc. sing. accept Greek nouns with -sis like dosis, is (f) and some Latin nouns: pertussis, is (f).
33. Ablative. Prepositions
Ablativus- this is the case corresponding to the Russian instrumental case; answers the questions "by whom?", "what?". In addition, it performs the functions of some other cases.
Ablative endings are shown in the table
Ending -i in Abl. sing. accept:
1) nouns in -e, -al, -ar;
2) adjectives of the 2nd group;
3) equisyllabic nouns of Greek origin with -sis of the dosis type.
All prepositions in Latin are used with only two cases: accusative and ablative. The management of prepositions in Russian does not coincide with Latin.

1. Prepositions used with the accusative case.
2. Prepositions used with the ablative.

3. Prepositions used either with the accusative or with the ablative.
The prepositions in - "in", "on" and sub - "under" govern two cases, depending on the question posed. Questions "where?", "What?" require the accusative case, the questions "where?", "in what?" - ablative.

Examples of the use of prepositions with double control.
34. Form - cyclic, terminological
Pharmaceutical terminology is a complex consisting of a set of terms from a number of special disciplines, united under the general name "pharmacy" (Greek pharmakeia - the creation and use of drugs), which study the discovery, production, use of medicines of plant, mineral, animal and synthetic origin. The central place in this terminological complex is occupied by the nomenclature of medicines - an extensive set of names of medicinal substances and preparations officially approved for use. The pharmaceutical market uses tens and hundreds of thousands of names of medicines. The total number of medicines and their combinations available in different countries exceeds 250,000. Every year, the pharmacy chain receives new and new medicines.
In order to have an idea of how the names of medicines are created, which affects the choice of certain word-formation methods and structural types of names, it is necessary to familiarize yourself at least in the most general terms with some general pharmaceutical terms.
1. Medicinal product (medicamentum) - a substance or mixture of substances permitted by the authorized body of the relevant country in the prescribed manner for use for the purpose of treating, preventing or diagnosing a disease.
2. Medicinal substance (materia medica) - a medicinal product, which is an individual chemical compound or biological substance.
3. Medicinal plant materials - plant materials approved for medical use.
4. Dosage form (forma medicamentorum) - a condition convenient for use to a medicinal product or medicinal plant material, in which the desired therapeutic effect is achieved.
5. Medicinal product (praeparatum pharmaceuticum) - a drug in the form of a specific dosage form.
6. Active substance - a component (s) of a medicinal product that has (s) a therapeutic, prophylactic or diagnostic effect.
7. Combined medicines - medicines containing in one dosage form more than one active ingredient in fixed doses.
35. Trivial names of medicinal substances
Some chemical compounds used as medicinal substances retain the same traditional semi-systematic names that they received in chemical nomenclature (salicylic acid, sodium chloride).
However, in a much larger volume in the nomenclature of medicines, chemical compounds are presented not under their scientific (systematic) names, but under trivial (lat. trivialis - "ordinary") names. Trivial names do not reflect any unified principles of scientific classification adopted by chemists, do not indicate the composition or structure. In this respect, they are completely inferior to systematic names. However, the latter are unsuitable as the names of medicinal substances due to their bulkiness and complexity for use in prescriptions, on labels, and in the pharmacy trade.
Trivial names are short, convenient, accessible not only for professional, but also for ordinary communication.
Examples of trivial names
Ways of word formation of trivial names
Trivial drug names are derivatives of various word-formation structures. A word or a group of words, which are often systematic names of chemical compounds or names of sources for their production, is used as a producer. The main "building" material for the formation of trivial names is words, word-forming elements, roots and simply the so-called verbal segments of ancient Greek and Latin origin. So, for example, a drug from the herb Adonis spring (Adonis vernalis) is called Adonisidum - adonizide; a substance (glycoside) obtained from some species of the digitalis plant (Digitalis) is called Digoxinum - digoxin. The name Mentholum - menthol is assigned to a substance derived from mint oil (oleum Menthae).
Among the various methods of word formation used to create trivial names, the most productive is abbreviation (lat. brevis - "short") - reduction. This is a way of creating complex abbreviated words, the so-called abbreviations, by combining word segments arbitrarily selected from the corresponding producing words or phrases. As such, the systematic names of chemical compounds are often used.
With the help of abbreviation, the names of combined drugs are also formed. Instead of listing the names of all active substances contained in one dosage form, the drug is assigned a complex abbreviated name. It is placed in quotation marks and is an appendix to the name of the dosage form.
36. General requirements for the names of medicines
1. In Russia, the name of each new drug is officially approved in the form of two mutually translatable equivalents in Russian and Latin, for example: solutio Glucosi - glucose solution. As a rule, the Latin names of medicinal substances are nouns of the II declension, cf. R. The Russian name differs from the Latin only in transcription and the absence of the ending -um, for example: Amidopyrinum - amidopyrine, Validolum - validol. Trivial names of combined drugs, which are inconsistent applications to the name of the dosage form, are also nouns of the II declension cf. R.: for example, tabulettae "Haemostimulinum" - tablets "Hemostimulin".
2. The name of medicines should be as short as possible; easy to pronounce; have a clear phonetic-graphic distinction. The last requirement is especially important in practice.
Each name should be noticeably different in its sound composition and graphics (writing) from other names.
After all, it is enough to memorize the sound complex at least a little inaccurately and write it incorrectly in Latin letters in the recipe for a serious mistake to occur. A large number of drugs under the original brand names enter the domestic market. They are spelled out and grammatically most often in any national language, that is, they do not have a Latin grammatical design. Often the names do not have the ending -um completely (German) or partially (English) or the ending -um is replaced by -e (English and French), and in some languages (Italian, Spanish. , Rum.) - on -a.
At the same time, firms also assign names to their drugs with the traditional Latin ending -um. In domestic prescription practice, in order to avoid discrepancies, commercial names of imported drugs should be conditionally latinized: substitute the last vowel instead of the last vowel or add the ending -um to the final consonant, for example: instead of Mexase (mexase) - Mexasum, instead of Lasix (lasix) - Lasixum, etc. .
Exceptions are allowed only for names ending in -a: Dopa, Nospa, Ambravena. They can be read and considered by analogy with the nouns of the first declension.
In modern commercial names, the traditional scientifically approved transcription of word-forming elements (word segments) of Greek origin is often neglected; their graphic simplification is cultivated; to facilitate pronunciation, ph is replaced by f, th by t, ae by e, y by i.
37. Frequency segments in trivial names
A huge number of abbreviations, as noted, are formed by a combination of segments arbitrarily selected from the composition of generating words - systematic names.
At the same time, there are many such names in the nomenclature, the sound complexes of which include repeating frequency segments - a kind of pharmaceutical terminological elements.
1. Frequency segments, very conditionally and approximately reflecting information of anatomical, physiological and therapeutic nature.
For example: Corvalolum, Cardiovaienum, Valosedan, Apressinum, Angiotensinamidum, Promedolum, Sedalgin, Antipyrinum, Anaesthesinum, Testosteronum, Agovirin, Androfort, Thyrotropinum, Cholosasum, Streptocidum, Mycoseptinum, Enteroseptolum.
2. Frequency segments that carry pharmacological information. Over the past decades, the recommendation of the World Health Organization (WHO) has become widespread to include in the trivial names of medicinal substances (namely substances!) Frequency segments that carry not a random and vague characteristic, like the above segments, but stable information of a pharmacological nature.
For this purpose, it is recommended to include frequency segments in the names indicating that the medicinal substance belongs to a certain pharmacological group. To date, several dozen such frequency segments have been recommended. For example: Sulfadimezinum, Penicillinum, Streptomycinum, Tetracyclinum, Barbamylum, Novocainum, Corticotropinum, Oestradiolum, Methandrostenolonum.
Trivial names of vitamins and multivitamin combination medicines
Vitamins are known both under their trivial names and under letter designations, for example: Retinolum seu Vitaminum A (also known under another name - Axerophtholum); Cyanocobalaminum seu Vitaminum B12; Acidum ascorbinicum seu Vitaminum C. The names of many multivitamin preparations include the frequency segment -vit- - -vit-, for example, Tabulettae "Pentovitum" (contains 5 vitamins), Dragee "Hexavitum" (contains 6 vitamins), etc.
Trivial names of enzyme preparations
Often the names contain an indication that the drug affects the enzymatic processes of the body. This is evidenced by the presence of the suffix -as- - -az-. Such names are usually latinized according to the general rule, that is, they receive the ending -um. However, there are deviations from this rule: for example, Desoxyribonucleasum (or Desoxyribcnucleasa) is a deoxyribonuclease, Collagenasum is a collagenase.
38. Dosage forms
Aerosolum, -i (n)- aerosol - dosage form, which is a dispersed system obtained using special packaging.
Granulum, -i (n)- granule - a solid dosage form in the form of grains, grains.
Gutta, -ae (f)- drop - a dosage form intended for internal or external use in the form of drops.
Unguentum, -i (n)- ointment - a soft dosage form having a viscous consistency; designed for outdoor use.
Linimentum, -i (n)- liniment - liquid ointment.
Pasta, -ae (f)- paste - ointment with a content of powdery substances over 20-25%.
Emplastrum, -i (n)- patch - a dosage form in the form of a plastic mass, softening at body temperature and sticking to the skin; designed for outdoor use.
Suppository, -i (n)- suppository, suppository - a dosage form that is solid at room temperature and expands or dissolves at body temperature; injected into body cavities. If administered per rectum (through the rectum), it is called a suppository. If the suppository has the shape of a ball for insertion into the vagina, then it is called globulus vaginalis - a vaginal ball.
Pulvis, -eris (m)- powder - a dosage form intended for internal, external or injection (after dissolution in an appropriate solvent) use.
Tabuletta, -ae (f)- dosage form obtained by pressing medicinal
substances or mixtures of medicinal and excipients; intended for internal, external or injection (after dissolution in an appropriate solvent) use.
tabuletta obducta- coated tablet - a coated tablet designed to localize the site of action, taste; persistence, improved appearance.
Dragee (French)- dragee (not folded) - a solid dosage form obtained by layering medicines and excipients on granules.
Pilula, -ae (f)- pill - a solid dosage form in the form of a ball (weight 0.1-0.5 g) containing drugs and excipients.
Species, -ei (f)(usually in the plural Species, -erum) - a collection - a mixture of several types of crushed or whole medicinal raw materials for the preparation of infusions and decoctions.
C. amylacea seu oblate- a dosage form, which is a drug enclosed in a shell (made of gelatin, starch or another biopolymer); intended for internal use.
Seu Lamella ophthalmica- eye film - a dosage form in the form of a polymer film that replaces eye drops.
39. Liquid dosage forms. Name of drugs
Solutio, -onis (f)- solution - a dosage form obtained by dissolving one or more medicinal substances; intended for injection, internal or external use.
Suspensio, -onis (f)- suspension - a liquid dosage form, which is a dispersed system in which a solid substance is suspended in a liquid; intended for internal, external or injection use.
Emulsum, -i (n)- emulsion - a liquid dosage form, which is a dispersed system consisting of mutually insoluble liquids; intended for internal, external or injection use.
Tinctura, -ae (f)- tincture - dosage form, which is an alcohol, alcohol-ether, alcohol-water transparent extract from medicinal plant materials; Designed for indoor or outdoor use.
Infusum, -i(n)- infusion - dosage form, which is an aqueous extract from medicinal plant materials; Designed for indoor or outdoor use.
Decoctum, -i (n)- decoction - infusion, characterized by the mode of extraction.
Sirupus, -i (m) (medicinalis)- syrup - a liquid dosage form intended for internal use.
Extractum, -i (n)- extract - dosage form, which is a concentrated extract from medicinal plant materials; designed for indoor or outdoor use.
Names of drugs.
1. If the dosage form given to a medicinal substance or herbal raw material is indicated in the name of the preparation, then the name begins with its designation, followed by the name of the medicinal substance or raw material.
Tabulettae Analgini - analgin tablets, Pulvis Ampicillini - ampicillin powder, etc.
2. The name of the combined medicinal product accompanying the designation "dosage form" is a noun in it. etc., placed in quotation marks as an inconsistent application to the designation "dosage form", for example: Tabulettae "Urosalum" - tablets "Urosal", Unguentum "Calendula" - ointment "Calendula", etc.
3. In the names of infusions and decoctions, between the designations "Dosage form" and "Plants" is in the genus. n. name of the type of raw material (leaf, herb, bark, root, flowers, etc.), for example: Infusum florum Chamomillae - infusion of chamomile flowers, Infusum radicis Valerianae - infusion of valerian root, etc.
4. An agreed definition characterizing the dosage form takes the last place in the name of the drug: for example, Unguentum Hydrargyri cinereum - gray mercury (mercury) ointment, Solutio Synoestroli oleosa - solution of sinestrol in oil (oily), Solutio Tannini spirituosa alcohol tannin solution, Extractum Belladonnae siccum - extract of belladonna (belladonna) dry.
40. Recipe
Recipe(receptum - "taken" from recipio, -ere - "take", "take") - this is a written prescription from a doctor to a pharmacist, drawn up in a certain form, about the manufacture, issuance and method of using a medicine. A prescription is an important legal document that must be drawn up in accordance with official rules. Prescriptions are written on a standard form with a size of 105 x 108 mm clearly and legibly, without blots and corrections, in ink or a ballpoint pen. Doctors who have the right to issue prescriptions are required to indicate their position and rank in them, sign and certify it with a personal seal.
The following parts are usually distinguished in the recipe.
1. Inscriptio - a stamp of a medical institution and its code.
2. Datum - the date the prescription was issued.
3. Nomen aegroti - surname and initials of the patient.
4. Aetas aegroti - the age of the patient.
5. Nomen medici - the surname and initials of the doctor.
6. Praescriptio - "prescription" in Latin, which consists of invocatio - a standard address to a doctor, Rp .: - Recipe - "take" and designatio materiarum - designations of substances indicating their quantity.
7. Subscriptio - "signature" (lit. "written below" the designation of substances) - a part in which some instructions are given to the pharmacist: about the dosage form, the number of doses, the type of packaging, about issuing the medicine to the patient, etc.
8. Signature - a designation, a part that begins with the verb signa or signetur - "to designate", "to designate". Then follows in Russian and (or) the national language an indication to the patient about the method of taking the medicine.
9. Nomen et sigillum personaie medici - the signature of a doctor, sealed with a personal seal.
Each drug is prescribed on a separate prescription line and with a capital letter. The names of medicinal substances and plants inside the line are also written with a capital letter.
The names of medicinal substances or preparations grammatically depend on their dose (amount) and are put in the gender. P.
Prescription rules
41. Use of the accusative case when prescribing tablets and suppositories
There are various approaches to naming tablets and suppositories.
1. Medicinal preparations of a combined composition are assigned a trivial and most often abbreviated name, placed in quotation marks: for example, tabulettae "Codterpinum" - tablets "Codterpin"; suppositoria "Neo-anusolum" - candles "Neo-anusol".
The trivial names of tablets or suppositories are in them. p. units hours and are inconsistent applications. The dose, as a rule, is not indicated, since it is standard.
2. If the suppositories consist of one active medicinal substance, then its name is attached to the name of the dosage form using the preposition cum and put in the ablative indicating the dose; for example: Suppositoria cum Cordigito 0.0012 - candles with cordigite 0.0012.
3. If the tablets consist of one active medicinal substance, then after indicating the dosage form, its name is put in the genus. n. with the designation of the dose; for example: Tabulettae Cordigiti 0.0008 - Cordigita tablets 0.0008.
4. When prescribing tablets and suppositories in prescriptions in an abbreviated way, the name of the dosage form is put in wines. n. pl. hours (tabulettas, tabulettas obductas, suppositoria, suppositoria rectalia), since it is grammatically dependent on the Recipe, and not on the dose.
In a similar way (in win. p. pl.) eye films (lamellae ophthalmicae) are prescribed: the name of the medicinal substance is introduced using the preposition cum and put in the ablative, for example: Recipe: Lamellas ophthalmicas cum Florenalo numero 30.
5. With an abbreviated way of prescribing tablets and suppositories with one ingredient, you can put the name of the dosage form in Asc. sing. (tabulettam, suppository). In this case, the prescription ends with the standard wording Da (Dentur) tales doses numero... For example:
Recipe: Tabulettam Digoxini 0.0001
Da tales doses numero 12
Recipe: Suppositorium cum Ichthyolo 0.2
Da tales doses numero 10.
6. A prescription for tablets is also common, in which the name of the medicinal substance and its single dose are indicated, ending with the designation of the number of tablets in the standard formulation Da (Dentur) tales doses numero ... in tabulettis. - Give out such doses in number ... in tablets, for example:
Recipe: Digoxini 0.0001
Da tales doses numero 12 in tabulettis.
42. Name of chemical elements
Names of acids
Latin semi-systematic and trivial names of acids consist of the noun acidum, -i (n) - "acid" and the adjective of the 1st group agreed with it. The suffix -ic-um or -os-um is added to the basis of the name of the acid-forming element.
The suffix -ic- indicates the maximum degree of oxidation and corresponds in Russian adjectives to the suffixes -n-(aya), -ev-(aya) or -ov-(aya), for example: acidum sulfur-ic-um - ser-n-aya acid; acidum barbitur-ic-um - barbituric acid; acidum fol-ic-um - folic acid.
The suffix -os- indicates a low degree of oxidation and corresponds to the Russian adjective with the suffix -ist-(aya); for example: acidum sulfur-os-um - sulfuric acid; acidum nitr-os-um - nitrogen-ist acid.
Adjectives in the names of anoxic acids include the prefix hydro-, the basis of the name of the acid-forming element, and the suffix -ic-um.
In the Russian nomenclature of drugs, this corresponds to the adjective with endings -hydrogen (acid), for example: ac. hydro-brom-ic-um - hydrobromo-ic-hydrogen acid.
Names of oxides
The names of oxides consist of two words: the first is the name of the element (cation) in the genus. n. (inconsistent definition), the second - the group name of the oxide (anion) in them. pad. (inclined).
The segment -oxy- indicates the presence of oxygen, and the prefixes specify the structure of the compound: oxydum, -i (n) - oxide; peroxydum, -i (n) - peroxide; hydroxydum, -i (n) - hydroxide. The Russian name also uses the same word order as in the international (Latin).
Names of salts
The names of salts are formed from two nouns: the name of the cation, which comes first in the genus. etc., and the name of the anion, which is in second place in them. n. Some names of ethers are formed in the same way.
The names of anions are formed by adding the standard suffixes -as, -is, -idum to the roots of the Latin names of acids.
With the suffixes -as and -is they form the names of anions in salts of oxygen acids, and with the suffix -id-um - in salts of oxygen-free acids. The names of anions with suffixes -as, -is - nouns of the III declension m. (an exception to the gender rule), and the names of anions with the suffix -id-um are nouns of the second declension cf. R.
Names of anions
The names of anions of basic salts are formed with the prefix sub-, and the names of anions of acid salts are formed with the prefix hydro-, for example: subgallas, -atis (m) - basic gallate; hydrocarbonas, -atis (f) - hydrocarbonate.
43. Numerals and numeral prefixes
Numerals
In Latin, cardinal numbers do not affect the case of their nouns. Of the cardinal numbers, only unus, a, um are declined; duo, duae, duo; tres, tria. A number of medical terms are formed with the help of prefixes. Numerals prefixes of Latin origin prevail in the anatomical nomenclature, and Greek - in clinical terminology and in the nomenclature of medicines.
Numerals-prefixes
44. Adverbs and pronouns
Adverbs are of 2 types according to the way they are formed:
1) independent adverbs, for example: statim - immediately, saepe - often;
2) derivatives from adjectives.
Adverbs from adjectives I-II are formed by adding the suffix -e to the stem, for example: asepticus, a, um - aseptice - aseptically (under aseptic conditions). From adjectives III declension adverbs are formed by adding the suffix -iter to the stem, and from adjectives on -ns - the suffix -er, for example: siertlis, -e - steriliter - sterile; recens, -ntis - recenter - fresh (fresh-).
Some adjectives in the form of wines are also used as adverbs. p. units h. wed R. or in the form of an ablative with the ending -o, for example: multus, a, um - multum - a lot; facilis, with - facile - easy; citus, a, um - ciro - quickly, soon.
As adverbs of the comparative degree, the form cf. R. adjectives of this degree. Superlative adverbs are formed from the superlative degree of an adjective with the suffix -e: citius - faster, citissime - fastest.
Adverbs used in the recipe.
1. If you need to urgently issue a medicine at the top of the prescription form, the doctor writes: Cito! - Fast! or Statim! - Immediately! Immediately!
2. If two (or more) ingredients are prescribed in a row in the same dose, then this dose is indicated only once with the last of them, and Greek is placed before the figure. ana (aa) - equally.
3. When prescribing suppositories in a detailed way, the amount of cocoa butter can be indicated exactly in grams or by means of the expression quantum satis - "how much" - the pharmacist himself must calculate the right amount.
Pronouns
Personal pronouns:
1st person: ego - I, nos - we;
2nd person: tu - you, vos - you.
There are no personal pronouns of the 3rd person in Latin; instead of them, demonstrative pronouns is, ea, id are used - that, that, that or he, she, it.
Usually, there is no personal pronoun as a subject for a Latin verb, and when translated into Russian, it is added, for example: homo sum - I am a person.
The reflexive pronoun sui - itself, as in Russian, does not have the form im. n. and is used only in relation to the 3rd person.
Professional expressions with pronouns:
1) with a personal pronoun in Abl.: pro me - for me;
2) with a reflexive pronoun in Ass.: per se - in its purest form.
Possessive pronouns: mens, a, um - mine; tuns, a, um - yours; noster, tra, trum - ours; vester, tra, trum - yours.
Relative pronouns: qui, quae, quod - which, -th, -oe; what, -th, -th; something that is often found in aphorisms, for example: Qui scribit, bis legit. - Who writes - reads twice. Quod licet Jovi, non licet bovi. - What is allowed to Jupiter is not allowed to the bull.
45. Active participle
Active Present Participle
Unlike Russian, Latin has only one participle for each tense: the present participle of the active voice and the past participle of the passive voice. Most of the participles used in medical terminology act only as definitions for nouns. These are adjective participles, for example: dentes permanentes - permanent teeth, cysta congenita - congenital cyst, aqua destiilata - distilled water, etc.
Present participles of the active voice are formed from the stem of the present tense verb by adding the suffix -ns in I, II conjugations, and the suffix -ens in III, IV conjugations. In the genus p. units h. all participles end in -ntis (-nt-end of stem).
For example, the formation of participles:

Present participles of the active voice are declined according to the III declension, like adjectives of the 2nd group with one ending like recens, -ntis.
They have endings in Nom. pl. -es for m, f; -ia for n; in Gen. pl. - -ium for all three genders, for example: communicare - to connect.
Passive past participles
In Latin, as well as in Russian, such participles are verbal adjectives.
They are formed from the stem of the so-called supine (one of the main forms of the verb ending in -urn) by adding the generic endings -us, -a, um to it.
Forming the Past Participles of the Passive Voice
The basis of the supine is determined by discarding the ending -um from the form of the supine. The base of the supine usually ends in -t, -x, -s. In philological dictionaries, Latin verbs are given in four main forms: 1st person singular. h. vr.; 1st person singular h. perfect (perfect past tense); supine; infinitive, for example: misceo, mixi, mixtum, ere (II); solvo, solvi, solutum, ere (III).
46. Latin-Russian dictionary А-В
abductor, -oris, m (m. abductor) - abductor muscle
accessorius, -a, um - additional
acetabulum, -i, n - acetabulum
acusticus, -a, -um - auditory
oris m (m. adductor) - adductor muscle
adhaesio, -onis, f - fusion
adiposus, -a, um - fatty
aditus, -us, m - input
adnexa, -orum, n - appendages
afferens, -ntis, - bringing
affixus, -a, -um, - attached
ala, -ae, f - wing
apex, -icis, m - apex
arachnoideus, -a, -um - gossamer
arcus, -us, m - arc
balneum, -i, n - bath
balsamum, -i, n - balm
basis, -is, f - base, base
benignus, -a, -um - benign
biceps, cipitis - two-headed
bilateralis, -e, - bilateral
biliaris, -e, - bile
bilifer, -era, -erum - bile (bile)
bilis, -is, f - bile
bolus, -i, f - clay
brachium, -i, n - shoulder
brevis, -e - short
bronchus, -i, m - bronchus
bubo, -onis, m - bubo (a lymph node enlarged as a result of inflammation)
bucca, -ae, f - cheek
bursa, -ae, f - bag
47. Latin-Russian Dictionary C-D
caecum, -i, n - caecum
callosus, -a, -um - calloused
caput, -itis, n - head; head
cartilago, -inis, f - cartilage
cavernosus, -a, -um - cavernous
cavitas, -atis, f - cavity
cellula, -ae, f - cell
cerebrum, -i, n - big brain
cervix, -icis, f - neck; neck
circumferentia, -ae, f - circumference
clavicula, -ae, f - clavicle
coccyx, -ygis, m - coccyx
commissura, -ae, f - spike
concha, -ae, f - shell
cor, cordis, n - heart
costa, -ae, f - rib
cranium, -i, n - skull
dens, dentis, m - tooth
depuratus, -a, -um - cleaned (by mechanical means)
descendens, -ntis - descending
dexter, -tra, -trum - right
digestio, -onis, f - digestion
digitus, -i, m - finger
dilatatus, -a, -um - extended
diploe, -es, f - diploe (spongy substance of the bones of the cranial vault)
discus, -i, m - disc
dolor, -oris, m - pain
dorsum, -i, n - rear, back, back
dubius, -a, -um - doubtful
ductulus, -i, m - groove, tubule
ductus, -us, m - duct
duplex, -icis, - double
durus, -a, -um - hard
dysuria, -ae, f - dysuria (urination disorder)
48. Latin-Russian Dictionary E-F
ejaculatorius, -a, -um - ejaculatory
embolicus, -a, -um - embolic
embryo, -onis, m - embryo
eminentia, -ae, f - eminence
emissarius, -a, -um - emissary (issuing, withdrawing)
enamelum, -i, n - enamel
encephalon, -i, n - brain
epididymis, -idis, f - epididymis
epiglottis, -idis, f - epiglottis
eponychium, -i, n - supranail plate
epophoron, -i, n - ovarian epididymis
equinus, -a, -um - horse
ethmoidals, -e, - ethmoid
excavatio, -onis, f - deepening
extensor, -oris, m (m. extensor) - extensor muscle
externus, -a, -um - external
extremitas, -atis, f - end
facialis, -e - facial
fades, -ei, f - face; surface
falx, falcis, f - serp
fasciculus, -i, m - bundle
fauces, -ium, f - pharynx
femina, -ae, f - woman
femur, -oris, n - thigh, femur
fenestra, -ae, f - window
fibra, -ae, f - fiber
flexor, -oris, m (m. flexor) - flexor muscle
flexura, -ae, f - bend
fonticulus, -i, m - fontanel
foramen, -inis, n - hole
fornix, -icis, m - vault
fossa, -ae, f - fossa
fovea, -ae, f - fossa
funiculus, -i, m - cord
49. Latin-Russian Dictionary G-H
galactocele, -es, f - galactocele, milk cyst
ganglion, -i, n - ganglion, (nerve) node
gaster, -tris, f - stomach
gastralgia, -ae, f - gastralgia (stomach pain)
gemma, -ae, f - bud (plants)
geniculatus, -a, -um - cranked
genu, -us, n - knee
gingiva, -ae, f - gum
glandula, -ae, f - gland
glomus, -eris, n - glomus (tangle)
gluteus, -a, um - gluteal
granulosus, -a, -um - granular
granulum, -i, n - granule
gravida, -ae, f - pregnant
gutta, -ae, f - drop
gyrus, -i, m - gyrus
habenula, -ae, f - leash (paired formation of the epithalamus connecting the epiphysis with the diencephalon)
haema, -atis, n - blood
hallux, -ucis, m - big toe
helix, -icis, f - curl
hemispherium, -i, n - hemisphere
hernia, -ae, f - hernia (pathological protrusion of an organ)
hiatus, -us, m - cleft, gap, hole
hilum, -i, n - gate
humeroulnaris, -e - humerulnar
humerus, -i, m - humerus
humor, -oris, m - moisture
hymen, -enis, m - hymen
hyoideus, -a, -um, - sublingual
hypochondrium, -i, n - hypochondrium
hypogastrium, -i, n - hypogastrium
50. Latin-Russian Dictionary I-J-K
impressio, -onis, f - impression
imperfectus, -a, um - imperfect
incisivus, -a, -um - incisive
incisura, -ae, f - tenderloin
inclinatio, -onis, f - inclination
incus, -udis, f - anvil
index, -icis, m - index finger
infans, -ntis, m, f - child, child
inferior, -ius, - lower
infraspinatus, -a, -um - subacute
initialis, -e, - initial
intentio, -onis, f - tension
interstitialis, -e - intermediate
intestinum, -i, n - gut
iris, idis, f - iris
ischium, -i, n - seat
isthmus, -i, m - isthmus
jejunalis, -e - jejunal
jejunum, -i, n - jejunum
jugularis, -e - jugular
jugum, -i, n - elevation
junctio, -onis, f - connection
juvans, -ntis, - helping, auxiliary
juvenilis, -e, - youthful
juventus, -utis, f - youth
keloidum, -i, n - keloid (tumor-like growth of the connective tissue of the skin, mainly scars)
keratitis, -idis, f - keratitis (inflammation of the cornea)
keratoma, -atis, n - keratoma (tumor-like thickening of the stratum corneum of the epidermis)
keratomalacia, -ae, f - keratomalacia (melting of the cornea)
keratoplastica, -ae, f - keratoplasty (corneal plastic surgery)
keratotomia, -ae, f - keratotomy (cornea dissection)
Khellinum, -i, n - khellinum
kinesia, -ae, f - kinesia (motor activity)
kyematogenesis, -is, f - kyematogenesis (the process of intrauterine development of the organism)
51. Latin-Russian Dictionary L-M
labium, -i, n - lip
lacrima, -ae, f - tear
lamella, -ae, f - film
larynx, -ngis, m - larynx
latens, -ntis - latent, hidden
lateralis, -e - lateral, lateral
lemniscus, -i, m - loop
lens, lentis, f - lens
liber, -era, -erum - free
lien, -enis, m - spleen
ligamentum, -i, n - ligament
limen, -inis, n - threshold
lingua, -ae, f - language
lobus, -i, m - share
longitudinalis, -e - longitudinal
lumbi, -orum, m - waist
lunula, -ae, f - lunula
magnus, -a, -um - large (posit. degree)
major, -jus - large (comparative degree)
mandibula, -ae, f - lower jaw
manus, -us, f - brush
margo, -inis, m - edge
mastoideus, -a,um - mastoid
maxilla, -ae, f - upper jaw
meatus, -us, m - pass
medius, -a, -um - medium
medulla, -ae, f - brain, medulla
membrana, -ae, f - membrane
membrum, -i, n - limb
minor, -us - small (comparative degree)
morbus, -i, m - disease
mors, mortis, f - death
mucilago, - inis, f - mucus
musculus, -i, m - muscle
52. Latin-Russian Dictionary N-O
naevus, -i, m - nevus, birthmark
narcosis, -is, f - anesthesia
nasalis, -e - nasal
nasofrontalis, -e - nasofrontal
nasolabialis, -e - nasolabial
nasolacrimalis, -e - nasolacrimal
nasus, -i, m - nose
natura, -ae, f - nature
naturalis, -e - natural
neonatus, -i, m - newborn
nervosus, -a, -um - nervous
nervus, -i, m - nerve
neuralgia, -ae, f - neuralgia (pain along the nerve)
neuronum, -i, n - neuron
nodus, -i, m - node
nomen, -inis, n - name, denomination
nuchalis, -e - out
numerus, -i, m - number
nutricius, -a, -um - nutritious
obductus, -a, -um - coated
obliquus, -a, -um - oblique
oblongatus, -a, -um - oblong
occiput, -itis, n - back of the head
oculus, -i, m - eye
oedema, -atis, n - edema
oesophagus, -i, m (esophagus, -i, m) - esophagus
omentum, -i, n - omentum
ophthalmicus, -a, -um - eye
orbita, -ae, f - eye socket
organum, -i, n - organ
or, oris, n - mouth
os, ossis, n - bone
os coccygis, n - coccyx
os sacrum, n - sacrum
ossiculum, -i, n - bone
ovarium, -i, n - ovary
53. Latin-Russian Dictionary P-Q
palatum, -i, n - palate
palpebra, -ae, f - eyelid
pancreas, -atis, n - pancreas
papilla, -ae, f - nipple, papilla
papula, -ae, f - papule, nodule
paries, -etis, m - wall
partus, -us, m - childbirth
parvus, -a, -um - small (positive degree)
pecten, -inis, m - comb
pedunculus, -i, m - leg
pelvis, -is, f - pelvis; pelvis
persistens, -ntis, - persistent
pes, pedis, m - foot
phalanx, -ngis, f - phalanx
pharynx, -ngis, m - pharynx
pilus, -i, m - hair
planus, -a, -um - flat
plexus, -us, m - plexus
pons, pontis, m - bridge
porta, -ae, f - gate
posterior, -ius - rear
primus, -a, -um - first, primary
protuberantia, -ae, f - ledge
pubes, -is, f - pubis
pupilla, -ae, f - pupil
quadrangularis, -e - quadrangular
quadratus, -a, -um - square
quadriceps, cipitis - four-headed
quantum - how much
quartus, -a, -um - fourth
Quercus, -us, f - oak
quintus, -a, -um - fifth
53. Latin-Russian Dictionary R-S
radius, -i, m - radius
radix, -icis, f - root, spine
ramus, -I, m - branch
reconvalescentia, -ae, f - recovery
rectum, -i, n - rectum
regio, -onis, f - region
ren, renis, m - kidney
renalis, -e - renal
resectio, -onis, f - resection (removal of part of an organ with the connection of its saved parts)
retina, -ae, f - retina
retinaculum, -i, n - retainer
retroflexus, -a, -um - backward curved
rhinalis, -e - nasal
rostrum, -i, n - beak
rotationatio, -onis, f - rotation
rotundus, -a, -um - round
ruber, -bra, -brum - red
ruga, -ae, f - fold
ruptura, -ae, f - gap
saccus, -I, m - bag
saliva, -ae, f - saliva
salpinx, -ngis, f - fallopian tube
sanguis, -inis, m - blood
scapula, -ae, f - scapula
sectio caesarea - caesarean section
segmentum, -i, n - segment
sella, -ae, f - saddle
semen, -inis, n - seed
sensus, -us, m - feeling, feeling
septum, -i, n - partition
siccus, -a, -um - dry
simplex, -icis - simple
sinister, -tra, -trum - left
55. T-U Latin-Russian Dictionary
tabuletta, -ae, f - tablet
tardus, -a, -um, - slow
tarsus, -i, m - tarsus; eyelid cartilage
tegmen, -inis, n - roof
temporalis, -e - temporal
tempus, -oris, n - time
tendo, -inis, m - tendon
tensor, -oris, m (m. tensor) - tensing muscle
tenuis, -e - thin
teres, -etis - round
terminatio, -onis, f - ending
testis, -is, m - testicle
tetraboras, -atis, m - tetraborate
Tetracyclinum, -i, n - tetracycline
textus, -us, m - cloth
thoracicus, -a, -um - chest
thorax, -acis, m - chest, chest
thymus, -i, m - thymus, thymus gland
thyroideus, -a, -um - thyroid
tibia, -ae, f - tibia
tinctura, -ae, f - tincture
tonsilla, -ae, f - tonsil
traumaticus, -a, -um - traumatic
tremor, -oris, m - tremor
trochlearis, -e - block
truncus, -us, m - trunk, torso
tuba, -ae, f - pipe
tubarius, -a, -um - trumpet
tuber, -eris, n - hillock
ulcus, -eris, n - ulcer (festering or inflamed wound on the surface of the skin or mucous membrane)
ulna, -ae, f - ulna
ulnaris, -e - elbow
umbilicalis, -e - umbilical
umbo, -onis, m - navel
uncus, -i, m - hook
unguis, -is, m - nail
ureter, -eris, m - ureter
urethra, -ae, f - urethra, urethra
urina, -ae, f - urine
56. Latin-Russian Dictionary V-X-Z
vagina, -ae, f - vagina
valva, -ae, f - valve
valvula, -ae, f - damper, valve
vas, vasis, n - vessel
vena, -ae, f - vein
venenum, -i, n - poison
venter, -tris, m - abdomen (muscles)
ventriculus, -i, m - ventricle; stomach
venula, -ae, f - venule (small vein)
vermiformis, -e - worm-like
vermis, -is, m - worm
vertebra, -ae, f - vertebra
vertex, -icis, m - top; crown
verus, -a, -um - true
vesica, -ae, f - bubble
vestibulum, -i, n - vestibule
via, -ae, f - path
vinculum, -i, n - bunch
viscera, -um, n - internal organs
visus, -us, m - vision
vita, -ae, f - life
vitium, -i, n - vice
vitrum, -i, n - bottle, test tube
vivus, -a, -um - alive
vomer, -eris, m - coulter
vortex, -icis, m - curl
xanthoerythrodermia, -ae, f - xanthoerythrodermia (yellowish-orange coloration of the skin due to the deposition of cholesterol or lipids in it)
xiphosternalis, -e - xiphosternal
zonula, -ae, f - girdle
zoster, -eris, m (herpes zoster) - herpes zoster
zygomaticomaxillaris, -e - zygomaticomaxillary
zonularis, -e - girdle
The Latin language, despite the fact that it is dead, is still of great interest in various fields of human activity, including for linguists.
About Latin
Latin belongs to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Despite the fact that Latin is a dead language, interest in its history and study does not fade in our time.
The languages of the Italic branch included Faliscan, Oscan, Umbrian and Latin, but over time the latter supplanted the rest. The people who spoke Latin were called Latins, and their region of residence was called Latium. Its center in 753 BC. e. was Rome. Therefore, the Latins called themselves Romans, the founders of the great Roman Empire and its culture, which later had an impact on all spheres of life in Europe and the world.
Grammar Feature
All parts of speech in Latin are divided into changeable and unchangeable. Variables include noun, adjective, verb, participle, pronoun, gerund, gerund. Invariables include adverbs, particles, conjunctions and prepositions. For inflected parts of speech, there is a declension system in Latin.
Invariable parts of speech
The invariable parts of speech are conjunction, particle, preposition and interjection.

Inflected parts of speech
The inflected parts of speech are declined by gender, number, and case, and conjugated by person, number, tense, voice, and mood.
Language learners should know that Latin has three genders (masculine, feminine, and neuter), two numbers (singular and plural), six cases (nominative, genitive, dative, accusative, instrumental, and vocative) and five declensions.
Let's take a closer look at the declension system in Latin. Declension changes the form of the word, that is, the ending changes.
Cases and declension
What is interesting about the declension system in Latin? There are five declension forms for nouns, and three for adjectives.
The first declension includes feminine nouns and adjectives ending in -a in the nominative and ending in -ae in the genitive. For example, agua - aguae (water).
The second declension includes masculine nouns and adjectives with the ending -us and the neuter with -um in the nominative case and the ending -i in the genitive. For example, albus-albi (white), oleum-olei (oil).
The third declension includes nouns and adjectives, the endings of which are not listed above, not below. This is the largest group of words, as it includes nouns and adjectives of all three genders.
So, in the nominative case of the ending in the words y:
- masculine - -er, -os. oe, or.
- feminine - -x, -io, -is;
- neuter --ur, -n, -ma, -i, -c, -e.
In the genitive case they all end in -ips, -icis, -tis, -cis, -inis, -is, -eris, -oris, onis.
The fourth declension includes masculine nouns that end in -us and do not change in the genitive case. For example, spiritus (spirit).
The fifth declension includes feminine nouns ending in -es in the nominative case and ending in -ei in the genitive. For example, species-speciei (collection).
The adjective, pronoun and noun in Latin change in 6 cases:
- nominative (who? what?) - in the sentence takes the role of the subject or nominal part of the predicate;
- genitive (whom? what?) - in the sentence is an inconsistent definition, addition or logical subject;
- dative (to whom? What?) - in the sentence it takes the role of an indirect object, an object or a person contributing to the action;
- accusative (whom? what?) - in the sentence is an object;
- instrumental and prepositional (by whom? by what?) - in the sentence they take on the role of circumstance;
- vocative - does not have a question, does not take on the role of any member of the sentence in the sentence.

Conjugation and tenses
The verb in Latin has the following characteristics:
- The mood is imperative, subjunctive and conditional.
- Time - past, past (perfect and imperfect types), present, future and future.
- Voice - real (active) and passive (passive).
- Number is singular and plural.
- Face - first, second and third.
- Conjugation, determined by the final sound of the stem. There are 4 conjugations in total - I - -ā, II - -ē, III - -ĭ, -ŭ, consonant, IV - -ī. The exception is the verbs esse, velle, ferre, edere, nolle, which have their own conjugation features.
The past tense tells about an event that happened before an action that happened in the past. For example, Graeci loco, quo hostem superaverant, trophaea statuebant. - The Greeks erected trophies (monuments) in the place where they defeated the enemy.
The future tense tells about an event that will happen earlier than the one that the person is talking about. For example, Veniam, quōcumque vocāveris. - I'll go wherever you call me.
When determining the conjugation of a verb, the infinitive form in the present tense of the active voice is used, having the ending -re and the letter that comes before the indicated ending determines the conjugation of the verb. For example, laborare refers to the first conjugation because the -re is preceded by the letter a.
numeral
The numeral in Latin can be ordinal, quantitative, dividing and adverbial. The endings of ordinal chimes are the same as those of adjectives and agree with nouns in gender, numbers and cases.
The Latin language has its own system of numbers, which are denoted by letters of the alphabet.
Pronouns
In Latin, pronouns are divided into:
- personal;
- returnable;
- possessive;
- index;
- relative;
- interrogative;
- indefinite;
- negative;
- defining;
- pronoun adjectives.
Adverbs
Adverbs in Latin are divided into independent and derivatives and show the features of a process or action.

Latin in medicine
Latin is required for study at any medical university, as it is the basic language of medicine throughout the world. Why? The fact is that in Greece, before the conquest by the Romans, there was a developed medical system with its own terminology, the basis of which was laid by Hippocrates. These terms have survived unchanged to our time. The words derma, gaster, bronchus, dispnoe, diabetes are familiar to any Greek person. But over time, there was a latinization of medical terminology and today it is pure Latin, but a mixture with Greek. There are several objective reasons why Latin is not losing ground:

Nouns denote objects and phenomena.
Genus
Every noun in Latin belongs to one of three genders:
- Male (genus masculinum)
- Female (genus femininum)
- Medium (genus neutrum)
Animated nouns are classified by gender according to their biological sex.
Besides
TO masculine include the names of months, mountains, winds, large rivers, peoples, professions.
TO feminine include the names of countries, cities, islands, gems, trees.
TO neuter traditionally include the names of metals, elements, fruits, as well as indeclinable words.
The gender of a noun is indicated in the dictionary, it is indicated by one of three letters: " m "(male)," f "(female)," n " (average).
Number (numerus)
In Latin, nouns can be used in the singular or plural.
Singular number (numerus singularis) - to designate one object,
Plural (numerus pluralis) - to refer to many objects.
In dictionary and reference entries, the number of a noun is indicated by two letters: Sg (singular) or pl (plural).
Case (casus)
A noun can be in one of six cases:
Nominative case (casus nominativus) - answers the questions: "Who?" “What?”, in the sentence in the nominative case is the subject or the nominal part of the predicate. Denoted by the letter " N " or combination " Nom ".
Genitive case (casus genetivus) - answers the questions: “Whom?” “What?”, in a sentence in the genitive case, there is an inconsistent definition for another noun. Identified by the letter " G " or " Gen ".
Dative case (casus dativus) - answers the questions: “To whom?” “What?”, in the sentence in the dative case there is an indirect object that accompanies the action. Designated with a capital letter " D " or combination " Dat ".
Accusative case (casus accusativus) - answers the questions: "Whom?" “What?”, in the sentence in the accusative case there is a direct object to which the action is directed. Denoted " AC " or " acc ".
Separative or deferred case (casus ablativus) - answers the questions: "By whom?" “What?”, in the sentence in the deferred case there is a circumstance. Indicated by the letters " Ab " or " Abl ".
The vocative case (casus vocativus) is an appeal to a person or object, which is not a member of the sentence. Denoted by the letter " V " or combination " Voc ".
Declension
Every noun in Latin belongs to one of the 5 declensions. The declension is determined by the end of the genitive singular.
- I declension -ae
- II declension -i
- III declension -is
- IV declension -us
- V declension -ei
There are also disparate words "vesper" (II or III), "domus" (II or IV).
Often they talk about types of declension and equate them to 5 declensions. Strictly speaking, this is not true. There are much more types of declension in Latin than there are declensions. It should be noted that in Latin, knowledge about the belonging of a noun to a particular declension gives only an approximate idea of the end of a word in a particular case. It is the types of declension that give an accurate idea of the endings. The declension type system in Latin is more branched than the declension system, because it takes into account the variability within 5 declensions, and therefore it is easier to use it to solve a practical problem - the declension of words.
Many textbooks have a very strange attitude towards the types of declension. There is no general system of declension types and different sources can contain different versions, but, as already mentioned, it is customary to talk about 5 declensions or 5 types of declension, and then make a reservation that there is, for example, declension IIIa, which is somewhat different from declension IIIb .
Here we will not indicate the specific names of the types, since different authors call them differently, but we will try to describe the most detailed classification. So:
IN I declension 2 types of nouns:
- male
- female
(declension paradigm is the same).
In II declension- 6 types:
- ending in -us (in N.Sg.) masculine and feminine,
- ending in -ius (in N.Sg.) masculine,
- ending in -ir (in N.Sg.) masculine,
- ending in -er (in N.Sg.) masculine,
- ending in -um (in N.Sg.) neuter,
- ending in -ius (in N.Sg.) neuter.
The declension of all types is different.
A special type of declension is formed by the noun "deus" - god.
In the III declension- 6 types:
- 2 consonants:
- masculine and feminine,
- neuter.
- 2 vowels:
- ending in -e, -al, -ar of the neuter gender (equisyllabic and equally syllabic);
- equal syllables ending in -is feminine.
- 2 mixed:
- equally syllable ending in -es, -is (masculine and feminine);
- unequal with different endings (masculine and feminine).
Almost all types are in small things, but they differ.
Separate types of declension form the words "vis" - strength, "bos" - bull, Iuppiter - Jupiter.
IN IV declination- 2 types:
- ending in -us masculine and feminine,
- ending in neuter -u.
IN 5th declension types are not distinguished.
It is somewhat more difficult to determine whether a word belongs to one or another type of declension than to determine the declension itself. To determine the type of declension, a slightly more subtle analysis of the word is needed, but over time this becomes a very useful habit.
A separate article will be devoted to the types of declension, which is now (unfortunately) under development.
Dictionary form of a noun
In the dictionary (with the exception of educational dictionaries, they are generally a separate topic) the noun is in the nominative singular. Immediately after, through a comma, the ending of the genitive case of the singular is indicated (the same one by which the declension of the noun is determined), but if the stem of the nominative and genitive cases differ, then the whole word can be indicated in second place. After a space (usually in italics), the noun belongs to one of the 3 genders (m, f or n).
For example:
ramus, i m branch
Nominative - ramus,
Genitive - rami(II declension),
Genus - m- male.
lanx, lancis f cup
Nominative - lanx,
Genitive - lancis(hence III declension)
Genus - f- female.
Noun endings in declension
| case | I | II | III | IV | V | ||
| male gender | neuter gender | in agreement | on i | ||||
| Singular | |||||||
| N | -a | -us, -er, -ir | -um | -e, -al, -ar | -us, -u | -es | |
| G | -ae | -i | -i | -is | -is | -us | -ei |
| D | -ae | -o | -o | -i | -i | -ui | -ei |
| AC | -am | -um | -um | -em | -e | -um | -em |
| Ab | -a | -o | -o | -e | -i | -u | -e |
| V | = N | -e | = N | = N | = N | = N | = N |
| Plural | |||||||
| N | -ae | -i | -a | -es | -ia | -us | -es |
| G | -arum | -orum | -orum | -um | -ium | -uum | -erum |
| D | -is | -is | -is | -ibus | -ibus | -ibus | -ebus |
| AC | -as | -os | -a | -es | -ia | -us | -es |
| Ab | -is | -is | -is | -ibus | -ibus | -ibus | -ebus |
| V | = N | = N | = N | = N | = N | = N | = N |
Latin Grammar
Latin, like Russian, is predominantly synthetic. This means that grammatical categories are expressed by inflection (declension, conjugation), and not by function words.
There are 6 cases in Latin:
Nominative (nominative, nominativus)
Genitive (genitive, genitivus)
Dative (dative, dativus)
Accusative (accusative, accusativus)
Delay (ablative, ablativus)
Vocal (vocative, vocativus)
Three genders, as in Russian:
Male (genus masculinum)
Female (genus femininum)
Medium (genus neutrum)
Divided into 5 declensions.
Latin verbs have 6 tenses, 3 moods, 2 voices, 2 numbers and 3 persons.
Latin verb tenses:
Present tense (praesens)
Past tense imperfective (imperfectum)
Past perfect tense (perfectum)
Plusquamperfect, or pre-past (plusquamperfectum)
Future tense, or future first (futurum primum)
Pre-future tense, or future second (futurum secundum)
Inclinations:
Indicative (modus indicativus)
Imperative (modus imperativus)
Subjunctive (modus conjunctivus)
Valid (activum)
Passive (passivum)
singular (singularis)
Plural (pluralis)
First (persona prima)
Second (persona secunda)
Third (persona tertia)
In Latin, there are nouns (lat. Nomen Substantivum), numerals and pronouns, declined according to cases, persons, numbers and genders; adjectives, except for the listed ones, changeable according to degrees of comparison; verbs conjugated by tenses and pledges; supin is a verbal noun; adverbs and prepositions.
Latin and science
The Latin language is also of great general educational importance, as it helps to better and deeper analyze the Russian language, into which many Latin roots have passed, creating a number of new words, for example: communism, presidium, council, quorum, university, etc.
Many Greek words entered the Latin language, which have survived to this day, mainly in medical names - anatomical, therapeutic, pharmacological, etc. Greek terms, while retaining their basis, were latinized and gradually gained international recognition and distribution, for example: arteria - artery, aorta - aorta, etc.
For more than one and a half thousand years, the Latin language was the language of culture and writing, the only language of science and philosophy in Western Europe. In Latin, the foundations of scientific terminology in almost all disciplines were laid. Even after the national languages gradually replaced the Latin language from scientific literature, it remained for a long time as the main language in certain branches of knowledge.
This unity of terminology, which underlies the modern scientific terminology of a number of sciences, facilitates the understanding and communication of people in the field of science, the translation of scientific literature from one language to another, and the Latin language has not lost this meaning to this day. The preservation of scientific Latin terminology attaches particular importance to the study of the Latin language, as necessary in practical work, and not only as the language of one of the most ancient cultures. Therefore, although the Latin and Greek languages \u200b\u200bare commonly called “dead”, however, for medical workers they are living languages necessary for everyday work.
In Russia, Latin has long been the language of science. In Moscow, at the Slavic-Greek-Latin Academy, the first scientific institution in Russia, all sciences were studied in Latin. Many scientific works of M. V. Lomonosov, as well as some works of N. I. Pirogov, M. Ya. Mudrov and other Russian scientists were written in this language.
The Latin language in biology can be considered as an independent scientific language, descended from the Latin language of the Renaissance, but enriched with many words borrowed from Greek and other languages. In addition, many words of the Latin language are used in biological texts in a new, special sense. The grammar in the Latin biological language is noticeably simplified. The alphabet has been supplemented: unlike classical Latin, the letters "j", "u", "w" are used.
Modern Codes of Biological Nomenclature require that the scientific names of living organisms be Latin in form, that is, written in the letters of the Latin alphabet and subject to the rules of Latin grammar, regardless of which language they are borrowed from.
A reference book on the main sections of the grammar of the Latin language (phonetics, morphology, syntax) is intended for classical philologists, philologists-novelists, students of classical and non-specialized departments of higher educational institutions.
Grammar information is collected in tables, which allows you to quickly find the necessary data and easily understand the difficult history of the language of the ancient Romans.
The original Romanesque period (IV-VIII centuries).
The formation of Romance languages from vernacular Latin dates back to the weakening of Rome around the 4th century AD. Provinces become more and more independent, communication between different parts of the empire and the Eternal City is less and less constant. Differences accumulate, dialects are formed. In phonetics, these are all kinds of consequences from the disappearance of longitude and shortness of vowels (see Table 15). There is a forceful impact. Stressed and unstressed vowels develop according to different laws (see Table 16i). Changes in combinations that have been outlined in folk Latin are significantly intensifying (see Table 17i). It was during this era that the foundations for differences in the sound of the Romance languages were laid (see Table 18i).
Folk Latin changes continued in the declension system, which led to the complete destruction of the paradigm. From 5 classical Latin declensions with 4 cases in each, barely distinguishable 3 classes remain, having no cases at all (see Table 19i). Pronouns form articles (ibid. - Table 19i).
In the verb system, the mixing of paradigms continues, the replacement of commonly used classical verbs with colloquial ones. The number of descriptive forms of different tenses is increasing (see Table 20i).
This period, covering the 4th-8th centuries AD, ends with the mature Middle Ages - the time of the appearance of writing in the Romance languages.
Free download e-book in a convenient format, watch and read:
Download the book Latin in tables, Grammar guide, Makhlin P.Ya., 2008 - fileskachat.com, fast and free download.
- Latin language, Reference book on verbs, Bogatyreva I.I., 2011
- Lingua Latina, Latin textbook, 36 lessons to complete the course
- Textbook of the Latin language for non-philological humanitarian faculties of universities, Kozarzhevsky A.Ch., 1981
The following tutorials and books:
- English modal verbs, Handbook, Mitroshkina T.V., 2012 - Handbook English modal verbs is a practical guide to the use of modal verbs in modern English. Addressed to students of secondary schools, ...
- English pronouns, Handbook, Mitroshkina T.V., 2012 - Everything you need to know about the peculiarities of the use of pronouns in modern English is presented in a systematic way in the handbook. He is … English Dictionaries, Vocabularies
- English articles, Educational reference book, Mitroshkina T.V., 2011 - Reference book English articles contains detailed information about the system of English articles. Addressed to students of secondary schools, lyceums and gymnasiums, students and teachers, ... English Dictionaries, Vocabularies
- Non-finite forms of the English verb, Infinitive, Participle, Gerund, Handbook, Mitroshkina T.V., 2012 - The handbook contains a detailed description of the rules for the functioning of non-finite forms of the English verb in modern English. Addressed to those who have mastered the main sections ... English Dictionaries, Vocabularies