Cyclic composition. What is the composition in the literature: receptions, species and elements
Style Dominanti
In the text of the work there are always some points in which the style "appears outside." Such points serve as a kind of style "Charton", set up the reader to a certain "aesthetic wave" ... The style is represented as "a certain surface on which a unique trace, a form that issues the presence of one steering force" is designated. (P.V. Paliyevsky)
Here we are talking about style dominants, which in the work performed the organizing role. That is, they, dominants, must be subordinate to all techniques and elements.
Style Dominanti - this is:
Scene, descriptions and psychologism,
Convention and life vessels,
Monologism and dissection,
Verse and prose
Nominative and rhetoricity,
- simple and complex types of composition.
Composition -(from lat. Compositio - drawing up, binding)
Construction of a artistic work due to its content, character, appointment and largely determining his perception.
The composition is the most important organizing element of the artistic form, which gives the work of unity and integrity, with the components of each other and the whole.
In the artistic literature, the composition is a motivated location of the components of the literary work.
The component (unit of the composition) is considered a "segment" of the work in which one image method is preserved (characteristic, dialogue, etc.) or a single point of view (author, narrator, one of the heroes) on the depicted.
The interconnection and interaction of these "" segments "" form a composite unity of the work.
The composition is often identified by both the plot, the image system and the structure of the artistic work.
In the most general form, two types of compositions are distinguished - simple and complicated.
Simple (linear) composition It comes down only to the unification of the parts of the work into a single whole. In this case, there is a direct chronological sequence of events and a single narrative type throughout the entire work.
With a complex (transformation) composition The size of the combination of parts reflects the special artistic meaning.
For example, the author begins not from the exposition, but with some fragment of climax or even a junction. Or the narrative is conducted as it were in two times - the hero "Now" and the hero "in the past" (recalls some events that are currently taking place). Or the twin hero is introduced - in general from another galaxy - and the author plays on comparison \\ opposing episodes.
In fact, the pure type of simple composition is difficult to find, as a rule, we are dealing with complex (to one degree or another) compositions.
Different aspects of the composition:
exterior composition
shaped system
system of characters change points of view,
system of details,
plot and Fabul
conflict art
empty elements
Composite forms:
narration
description
characteristic.
Composite forms and means:
repeat, strengthening, opposition, installation
comparison
"Large" plan, "General" plan,
point of view,
text temporary organization.
Composition reference points:
culmination, junction,
strong text positions
repeats, opposition,
peripetia in the fate of the hero,
spectacular art techniques and means.
The points of the greatest reader voltage are called the support points of the composition. These are peculiar vests who lead the reader in the text, and in them, the ideological problem of the work is most apparent.<…> they are the key to understanding the logic of the composition and, accordingly, the entire internal logic of the work as a whole whole .
Strong text positions:
These include formally dedicated parts of the text, its end and the beginning, including the name, epigraph, prologue, the beginning and end of the text, chapter, part (first and last sentence).
Main types of composition:
ring, mirror, linear, default, retrospection, free, open, etc.
Scene elements:
exposure, Zaguka
development of action
(Peripetia)
culmination, Epilogue, Epilogue
Empty elements
description (landscape, portrait, interior),
putting episodes.
Ticket number 26.
1. Neetic vocabulary
2. Epic, drama and lyricism of the artwork.
3. The volume and content of the stylistics of the work.
Poetic vocabulary
P.L. - one of the most important parties to the artistic text; The subject to study a special section of literary studies. The study of the lexical composition of the poetic (i.e. artistic) works involves the correlation of the vocabulary used in a separate sample of the artistic speech of any writer, with a vocabulary of general, i.e., used by contemporaries of the writer in various household situations. The speech of the Company, which existed in the historical period, refers to the work of the author of the analyzed work, is perceived as a certain norm, therefore, they recognize "natural". The purpose of the research is to describe the facts of deviation of an individual author speech from the norms of speech "Natural". The study of the lexic composition of the speech of the writer (t. N. "Dictionary of the Writer") at the same time turns out to be a private species of such a stylistic analysis. When studying the "Dictionary of the Writer", pay attention to two types of deviations from the "natural" speech: the use of lexical elements, rarely used in "natural", living circumstances, i.e., the "passive" vocabulary to which the following categories of words include archaisms, neologisms, warbarisms, officessels, professionalism, jargonisms (including argotizms) and spacious; The use of words that implement portable (therefore rare) values, i.e. trails. Introduction by the author of the words of the other group to the text determines the image formation, therefore, its artisticness.
(household vocabulary, business vocabulary, poetic vocabulary etc.)
Poet of vocabulary. As part of the archaic vocabulary, historians and archaisms are allocated. The historicists include the names of the names of the disappeared objects, phenomena, concepts (Kolchug, Gusar, Oddnodnod, NEP, October (child of younger school age, which is preparing to join Pioneers), Encaughtist (Worker of the NKVD - People's Commissariat of Internal Affairs), Commissioner and T .P.). Historisms can be associated both with very remote epochs and events of relatively recently, however, however, by the facts of history (Soviet power, Partyakitiv, Secretary General, Politburo). Historisms do not have synonyms among the words of the active vocabulary stock, being the only names of the respective concepts.
Archaisms are the names of existing things and phenomena, for some reason those who are displaced in other words belonging to active vocabulary (Wed: Daily - always, comedian - actor, Zlato - Gold, to know - know).
Outdated words are heterogeneous by origin: among them there are original Russians (full, shell), Old Slavonic (glazing, loss, shrine), borrowed from other languages \u200b\u200b(Abside - "resignation", voyage - "Travel").
Of particular interest in stylistic terms, the words of Old Slavic origin, or Slavicama, are of particular interest. A significant part of the Slavs was assimilated in Russian soil and stylistically merged with a neutral Russian vocabulary (sweet, captivity, hello), but there are also such Old Slavonic words that are perceived in modern language as a high-style enemy and retain the solemn, rhetoric color.
With the fate of Slavs in Russian literature, the history of poetic vocabulary associated with antique symbolism and the imagery (so-called poets) is similar. The names of the gods and heroes of Greek and Roman mythology, special poetic symbols (Lira, Ellizius, Parnas, Lavra, Mirates), artistic images of ancient literature in the first third of the XIX century. They constituted an integral part of the poetic dictionary. The poetic vocabulary, like Slavs, strengthened the opposition of an elevated, romantically painted speech - the speech of the budic, prose. However, these traditional means of poetic vocabulary were not long used in fiction. Already the successors of A.S. Pushkin poets archaisisuated. Writers often turn to outdated words as an expressive agent of artistic speech. Interesting the history of the use of Old Slavic vocabulary in Russian artistic literature, especially in poetry. Stylistic Slavicians constituted a significant part of the poetic vocabulary in the works of writers of the first third of the XIX century. The poets found a source of elevated and romantic and "sweet" speech sound in this vocabulary. Slavs, which in Russian, consonant options, first of all, intolerable, were shorter than the Russian words for one syllable and were used in the XVIII-XIX centuries. At the rights of "Poetic Valibilities": poets could choose from two words, which answered the rhythmic rank of speech (I am sigh, and the voice of my Tomny, the harp vote is similar, it will die quietly in the air. - BAT.). Over time, the tradition of "poetic liberties" is overcome, but the obsolete vocabulary attracts poets and writers as a strong means of expression.
Outdated words are performed in an artistic speech of a variety of stylistic functions. Archaisms and historians are used to recreate the color of remote times. In this function, they used, for example, A.N. Tolstoy:
"The land of Motch and Dedich is those shores of full-flow rivers and forest glads, where our Prasrat came to live forever. (...) He disadvantaged his dwelling and looked at the sun in the distance in the distance.
And he studied a lot - heavy and difficult times: the red shields of Igor in the Polovtsy steppes, and the moans of the Russians on the rush, and the dmitry spears mounted under the horsights, and blood flooded Ice of the Lake, and the Grozny king, who spread united, from nowend , the limits of land from Siberia to the Waterproof Sea ... ".
Archaisms, especially Slavicami, give speeches sublime, solemn sound. The Old Slavic vocabulary performed in this function in the Old Russian literature. In the poetic speech of the XIX century. High-grade old-Slavic lexicism was stylistically equal to the ancient Russians, who also began to be involved in creating patter of artistic speech. High, the solemn sound of obsolete words also evaluate the writers of the XX century. During the Great Patriotic War IG Ehrenburg wrote: "By reflecting the blows of predatory Germany, she (the Red Army) saved not only the freedom of our homeland, she saved freedom of peace. In this deposit of the triumph of the ideas of brotherhood and humanity, and I see the world, enlightened by the grief, in which the welcome will excite. Our people showed their military virtues ... "
Outdated vocabulary may acquire ironic color. For example: who from parents do not dream of a dirty, balanced child who grabs everything literally on the fly. But attempts to turn their child in the "miracle" catastrophically end failure (from gas.). An ironic rethinking of obsolete words often contributes to the parody use of high-style elements. In parody-ironic functions, obsolete words often act in fellow, pamphletes, humorous notes. Completely as an example from newspaper publication during the preparation of the President's Entrance Day to the post (August 1996).
The composition is the location of the parts of the literary work in a certain order, the combination of forms and methods of artistic expression by the author, depending on its plan. Translated from the Latin language means "drawing up", "Building". The composition builds all parts of the work into a single finished whole.
It helps the reader deeper to understand the content of works, supports interest in the book and helps in the final to make the necessary conclusions. Sometimes the composition of the book intrigues the reader and he is looking for a continuation of the book or other works of this writer.
Composition elements
Among such elements can be distinguished by story, description, dialogue, monologue, plug-in stories and lyrical deviations:
- Narration - The main element of the composition, the story of the author, revealing the content of the artistic work. It takes most of the volume of all the work. Transmits the dynamics of events, it can be retended or illustrated by drawings.
 Description. This is a static element. During the description of the event, it does not occur, it serves as a picture, background for the work of the work. Description is a portrait, interior, landscape. The landscape is not necessarily an image of nature, it can be a city landscape, a lunar landscape, a description of fantastic cities, planets, galaxies or a description of fictional worlds.
Description. This is a static element. During the description of the event, it does not occur, it serves as a picture, background for the work of the work. Description is a portrait, interior, landscape. The landscape is not necessarily an image of nature, it can be a city landscape, a lunar landscape, a description of fantastic cities, planets, galaxies or a description of fictional worlds.- Dialogue - The conversation of two people. He helps to reveal to Podabul, deepen the characters of the actors. Through the dialogue of two heroes, the reader learns about the events of the last heroes of works, about their plans, it begins to better understand the characters characteristics.
- Monologue - Speech one character. In Comedy, A. S. Griboyedov through the monologues of the Chatsky, the author conveys the thought of advanced people of his generation and the experiences of the hero himself, who learned about the treason beloved.
- System images. All images of the work that interact in connection with the idea of \u200b\u200bthe author. These are images of people, fabulous characters, mythical, toponymic and subject. There are no insurgent images of the image, for example, "nose" from the eponymous story of Gogol. Many images of the authors were simply invented, and their names became commonplace.
- Stick stories, story in the story. Many authors use this technique to tie intrigues in the work or during the junction. There may be several insertion stories in the work, the events in which occurs at different times. Bulgakov in the "Master and Margarita" was used by the reception of a novel in the novel.
 Copyright or lyrical deviations. Many lyrical deviations from Gogol in the work of "Dead Souls". Because of them changed the genre of the work. This is a great prosaic work called the poem "Dead Souls". And "Eugene Onegin" is called novel in verses because of a large number of author's digits, thanks to which the readers appear an impressive picture of the Russian life of the early 19th century.
Copyright or lyrical deviations. Many lyrical deviations from Gogol in the work of "Dead Souls". Because of them changed the genre of the work. This is a great prosaic work called the poem "Dead Souls". And "Eugene Onegin" is called novel in verses because of a large number of author's digits, thanks to which the readers appear an impressive picture of the Russian life of the early 19th century.- Author's characteristic. In it, the author talks about the character of the hero and does not hide his positive or negative attitude towards him. Gogol in his works often gives ironic characteristics to its heroes - such accurate and capacious that its heroes often become nucleating characters.
- Scene narration - This is a chain of events occurring in the work. The plot is the content of artistic text.
- Fabul - All events, circumstances and actions that are described in the text. The main difference from the plot is the chronological sequence.
- Scenery - Description of nature, present and imaginary peace, city, planets, galaxies, existing and fictional. The landscape is a feature, thanks to which the character of heroes is deeper, the nature of the events is revealed. You can remember how the seascape is changing in the Pushkin "fairy tale about fisherman and fish," when the old man is again and again comes to the golden fish with the next request.
- Portrait - This is a description of not only the appearance of the hero, but also its inner world. Thanks to the talent of the author, the portrait is so accurate that all readers are equally representing the appearance of the hero read book: what Natasha Rostov looks like, Prince Andrei, Sherlock Holmes. Sometimes the author attracts the attention of the reader to some characteristic character of the hero, for example, the mustache at Poiro in the books of Agatha Christie.

Do not miss: in the literature, examples of use.
Composite techniques

Scene composition
In the development of the plot there are its own stages of development. In the center of the plot, it is necessary to conflict, but the reader does not know about it immediately.

The plot composition depends on the product genre. For example, the bass necessarily ends with morality. The dramatic works of classicism had their own laws of the composition, for example, they had to have five acts.
The composition of the works of folk folklore differs in its unshakable features. Songs, fairy tales, epics were created in their laws of construction.
The composition of the fairy tale begins with the promotion: "As at sea-ocean, yes on the island of Buyan ...". The surcharge often composed in the poetic form and sometimes was far from the content of the fairy tale. The storyteller attracted the attention of the listeners and waited when he would not be distracted. Then he said: "This surcharge, not a fairy tale. The fairy tale will be ahead. "
Then followed the stained. The most famous of them begins in words: "lived," or "in some kingdom, in the thirtieth of the state ...". Then the storyteller passed to the tale itself, to her heroes, to wonderful events.
Takers of a fabulous composition, a triple repetition of events: Bogatyr is fighting three times with the snake of Gorynych, three times the princess sits at the Terema window, and Ivanushka on horseback comes to it and breaks the ring, three times the king experiences a daughter in the fairy tale "Tsarevna-Frog".
The ending of the fairy tale is also traditional, about the heroes of the fairy tales say: "Live - and we are doing well." Sometimes the ending hints towards a treat: "You have a fairy tale, and I have a branch of a knitting."
 The literary composition is the location of the parts of the work in a certain sequence, this is a holistic system of forms of an artistic image. The means and techniques of the composition deepen the meaning of the depicted, disclose the characteristics of the characters. Each artwork has its own unique composition, but there are traditional laws that are respected in some genres.
The literary composition is the location of the parts of the work in a certain sequence, this is a holistic system of forms of an artistic image. The means and techniques of the composition deepen the meaning of the depicted, disclose the characteristics of the characters. Each artwork has its own unique composition, but there are traditional laws that are respected in some genres.
In the times of classicism, the rule system existed that the authors had prescribed certain rules for writing texts, and they could not be disturbed. This is a rule of three unity: time, places, plot. This is a five-act construction of dramatic works. These are talking surnames and a clear division on negative and positive heroes. Features of the composition of the works of classicism went into the past.
Composite techniques in the literature depend on the genre of the artwork and from the talent of the author, which has in stock species, elements, adoption of composition, knows its features and is able to use these artistic ways.
Any literary creation is an artistic whole. This can be not only one product (poem, story, novel ...), but also a literary cycle, that is, a group of poetic or prosaic works, united by a common hero, common ideas, problems, etc., even a common place of action (for example , A L.Gogol's Age Time Cycle on the farm near Dikanka, "Tale of Belkin" A. Pushkin; Roman M.Lermontova "Hero of Our Time" - also the cycle of individual novel, united by a common hero - Pechorin). Any artistic integer is essentially a single creative organism having its special structure. As in the human body, in which all independent organs are inextricably linked with each other, in the literary work all elements are also independent, and are interrelated. System of these elements and the principles of their relationship and are called Composition:
Composition (from lat. Compositio, writing, compilation) -building, structure of artwork: selection and sequence of elements and visual techniques of works that create an artistic integer in accordance with the copyright.
The elements of the composition of the literary work include Epigraphs, Dedications, Prologies, Epilogues, Parts, Heads, Acts, Phenomena, Scenes, Preface and Previewing "Publishers" (created by the author's fantasy of outworking images), Dialogues, monologues, episodes, plug-in stories and episodes, letters, songs (for example, sleep Oblomov in the novel of Goncharov "Oblomov", a letter to Tatiana to Onegin and Onegin to Tatiana in the novel of Pushkin "Evgeny Onegin", the song "The sun is booming and comes ..." in the Drama of Gorky "at the bottom"); All artistic descriptions are portraits, landscapes, interiors are also composite elements.
the action of the work can begin from the end of events, and subsequent episodes will restore the time stroke and explain the causes of what is happening; such a composition is called reverse (This technique applied N. Chernyshevsky in the novel "What to do?");
the author uses framing composition, or ring, At which the author uses, for example, the repetition of stanf (the latter repeats the first), artistic descriptions (the work begins and ends with a scenery or interior), the events of the beginning and the final occur in the same place, the same heroes are participating in them. d.; Such a reception is found in both poetry (Pushkin, Tyutchev, A.Blok, in the "verse about the beautiful lady"), often resorted to him, and in prose ("Dark Alleys" I. Bunina; "Song about Sokol", "old woman Izergil" M. Gorky);
the author uses receiving retrospection, that is, returning actions in the past, When the causes of what is happening at the moment of the narrative (for example, the author of the author about Pavel Petrovich Kirsanov in the Roman Turgenev "Fathers and Children"); Often, when using retrospection in the work there is a plug-in story of the hero, and this kind of composition will be called a "story in the story" (Confession of Marmaladov and the letter of the Pulcheria Alexandrovna in "Crime and Punishment"; Chapter 13 "Hero's Phenomenon" in Master and Margarita; " After the ball "Tolstoy," Asya "Turgenev," Gooseberry "Chekhov);
often the organizer of the composition is an artistic image, eg, the road in the poem Gogol "Dead Souls";pay attention to the scope of the author's narration: the arrival of Chichikov to the city of NN - the road to Manilovka - Manilov's manor - the road - arrival to the box - the road is a restaurant, meeting with Nozdrey - the road - arrival to Nosdreva - road - etc.; It is important that the first one is expensive; So the image becomes the leading structure-forming element of the work;
the author may prevail the main exposure,write will, for example, the entire first chapter in the novel "Eugene Onegin", and can start the action immediately, sharply, "without acceleration", How it does Dostoevsky in the novel "Crime and Punishment" or Bulgakov in the "Master and Margarita";
the composition of the work can be based on symmetrywords, images, episodes (or scenes, heads, phenomena, etc.) and will be a mirroras, for example, in the poem of A. Blok "Twelve"; the mirror composition is often combined with the framing (such a principle of the composition is characteristic of many poems by M.TSvetaeva, V. M. Markovsky et al.; Read, for example, the poem of Mayakovsky "From the street to the street");
often the author uses receiving a composite "gap" of events: breaks down the story in the most interesting place at the end of the chapter, and the new chapter begins with a story about another event; For example, it is used by Dostoevsky in "Crime and Punishment" and Bulgakov in the "White Guard" and "Master and Margarita". Such a reception is very fond of the authors of adventure and detective works or works, where the role of intrigue is very large.
The composition is an aspect of the form of a literary product, but its content is expressed through the features of the form. The composition of the work is an important way to embody the author's idea. Read my own poem A. Block "Stranger" completely, otherwise our reasoning will be incomprehensible to you. Pay attention to the first and seventh stains, listening to their sound:
1st stanza
In the evenings above restaurants
Hot air dick and deaf
And ruled by drunk
Spring and tweeted spirit.
7th stanza
And every evening, an hour appointed
(Ile it only dreams to me?),
Devichy Still, grated silks,
In the foggy moves the window.
The first stanza is sharply and disharmoniously sound - due to abundance [P], which will be, like other disharmonious sounds, can be repeated in the following stanza until the sixth. Otherwise, it is impossible, because the block here draws a picture of the disgusting philistine vulgarity, the "terrible world", in which the soul of the poet is. So presents the first part of the poem. The seventh stuff marks the transition to a new world - dreams and harmony, and the beginning of the second part of the poem. This transition of the plan, accompanying his sounds pleasant and soft: [A:], [NN]. So in the construction of the poem and with the help of the intake of so-called sounding, the block expressed its idea of \u200b\u200bopposing the two worlds - harmony and disharmony.
The composition of the work may be thematic, At which the mainstream of the relationship between the central images of the work becomes the mainstream. This type of composition is more characteristic of lyrics. There are three kinds of such compositions:
consistent representing a logical reasoning, the transition from one thought to another and the subsequent conclusion in the final of the work ("Cicero", "Silentium", "Nature - Sphinx, and that it is more faithful ..." Tyutchev);
development and transformation of the central image:the central image is considered by the author from various sides, its bright features and characteristics are revealed; Such a composition involves the gradual increase in the emotional stress and the culmination of experiences, which often falls on the final of the work ("Sea" Zhukovsky, "I came to you with greetings ..." Feta);
comparison of 2 images entered into an artistic interaction ("stranger" of the block); Such a composition is built At the reception of antithesis, or opposition.
There are three levels of the literary work:
Subject image - Life material
Composition - organization of this material
Art language - speech system of the literary work, at all four levels of the artistic language: Fonika, vocabulary, semantics, syntax.
Each of these layers has its own difficult hierarchy.
The apparent complexity of the literary work is created by the difficult labor of the writer at all three levels of artistic integer.
We will get acquainted with several definitions of this concept and various classifications, when the text composition is revealed by different signs and indicators.
Artistic text is a communicative, structural and semantic unity, which manifests itself in its composition. That is, this is the unity of communication - structures - and meaning.
The composition of artistic text is "mutual relationship and location units of the pictured and artistic and speech funds. " Units depicted here mean: theme, problem, idea, characters, all aspects of the depicted external and inner world. Artistic and speech facilities are the entire form of a language system at the level of its 4-layers.
The composition is a construction of a work that defines its integrity, completeness and unity.
Composition - is "System connections » All his elements. This system has an independent meaningful, which should be disclosed in the process of philological analysis of text.
Composition, or structure, or architectonics - this is the construction of an artistic work.
The composition is an element of the form of an artistic work.
The composition contributes to creating a work as an artistic integrity.
The composition combines all components and subordinates their idea, the plan of the work. Moreover, this connection is so close that it is impossible to remove or rearrange in places by any component from the composition.
Types of composite organization Works:
Scene view - that is, PodaBuli (Epos, Lyrics, Drama)
Navigable species - Besfabul (in lyrics, in epic and drama created by the creative method of modernism and postmodernism)
The scene view of the composition of the composition of the work is two types:
Event (in Epos and Drama)
Descriptive (in lyrics)
Consider the first type of scene composition - event. It has three forms:
Chronological form - events develop in a straight line of time, the natural temporal sequence is not disturbed, there may be time intervals between events.
Retrospective form - a retreat from a natural chronological sequence, a violation of a linear order of passage of events in life, interrupting the memories of the heroes or the author, familiarize the reader with the prehistory of events and the life of the characters (Bunin, "Light Breathing")
Free or assembly form - a significant violation of spatial-temporal and causal relationships between events; Communication between individual episodes is an associative-emotional, and not logical-sense ("Hero of Our Time", "Process" of Kafki and other works of modernism and postmodernism)
Consider the second type of composition - descriptive:
It is present in lyrical works, they are mainly missing clearly limited and connectedly detailed action, the experience of the lyrical character or character is put forward to the fore, and the whole composition is subordinate to the objectives of its image, this is a description of thoughts, impressions, feelings, paintings by experiences of the lyrical hero .
The composition is external and internal
Exterior composition (Architectonics): chapters, parts, sections, paragraphs, books, volumes, their location may be different depending on how to create a plot selected by the author.
Exterior composition - This is a selection of text characterized by continuity to discrete units. The composition, therefore, is the manifestation of significant intermittentness in continuity.
External composition: The boundaries of each composite unit allocated in the text are clearly specified, are determined by the author (chapters, the heads, partitions, parts, epilogs, phenomena in drama, etc.), it organizes and directs the perception of the reader. The architectonics of the text serves as the way "portioning" meaning; With the help of ... composite units The author indicates the reader to the union, or, on the contrary, the dismemberment of the elements of the text (and therefore its content).
External composition: No less significant and lack of membership of the text or its deployed fragments: it emphasizes the integrity of the spatial continuum, the principal non-compliance of the organization of the narrative, non-differentiation, the flow of the painting of the world of the narrator or character (for example, in the literature "Consciousness flow").
Inner composition : This is a composition (building, location) of images - characters, events, action of action, landscapes, interiors, etc.
Internal (Sustainable) The composition is determined by the system of form-character, features of the conflict and the scene originality.
Not to be confused: the plot is elements the plot, the composition is - there receivers(internal composition) and parts (external composition) composition.
The composition includes, in its construction, both all the elements of the plot are scene elements and extra-wedge elements.
Internal compositions:
Prologue (often attribute it to the plot)
Epilogue (often refer to the plot)
Monologue
Portraits of characters
Interiors.
Landscapes
Extrapty elements in the composition
Classification of composite techniques for the selection of individual elements:
Each composite unit is characterized by methods of extension that provide selection the most important meanings of the text And the reader's attention is activated. It:
geography: various graphic isolations,
reversals: Repeats of language units of different levels,
strengthening: strong positionstext or its composite part - the position of the extension associated with the establishment of a hierarchy of meanings, focusing on the most important, enhancement of emotionality and aesthetic effect, the establishment of significant links between elements of adjacent and distant, belonging to one and different levels, the provision of connecting text and its memories. Strong text positions are traditionally related title, epigraphs, beginningandendworks (parts, chapters, mastergua). With their help, the author emphasizes the most significant elements of the structure and at the same time determines the main "semantic milestones" of a particular composite part (text as a whole).
Wide distribution in Russian literature of the end of the XX century. Installation and collage techniques, on the one hand, has led to strengthening text fragment, on the other hand, it opened the possibilities of new combinations of "semantic plans".
Composition in terms of its connectivity
In the peculiarities of the text architectonics, such a most important feature is manifested as connectivity.The text selected as a result of the segment (parts) correspond to each other, "curb" based on common elements. Two types of connectedness differ: cohesion and coherence (terms are offered by V. Dressler)
Kegezia (from lat. - "be connected"), or local connectivity, - Linear type connected, expressed formally, mainly by language means. It is based on the location of the substitution, lexic repetitions, the availability of unions, the correlation of grammatical forms, etc.
Coherence(from lat. - "Clutch"), or global connectivity, - connectedness, nonlinear type, combining elements of different levels of text (for example, title, epigraph, "text in the text" and the main text, etc.). The most important means of creating coherence - repetitions (primarily words with common semantic components) and parallelism.
In the artistic text, semantic chains arise - rows of words with common seeds, the interaction of which generates new semantic communications and relationships, as well as the "increment of meaning."
Any artistic text is permeated by semantic rolls, or repetitions. Words associated on this basis may occupy a different position: to be located at the beginning and at the end of the text (the annular semantic composition), symmetrically, to form a gradation series, etc.
Consideration of the semantic composition is the necessary stage of philological analysis. It is especially important for the analysis of "unustool" texts, texts with weakened causal relationships of components, texts saturated with complex images. The identification of semantic chains and the establishment of their connections is the key to the interpretation of the work.
Empty elements
Plug-in episodes
Lyrical retreats
An artistic advance
Art framing
Dedication
Epigraph,
Title
Putting episodes - These are part of the narrative, which are not directly related to the plot, events that are only associated and recall in connection with the current events of the work ("Tale of Captain Copekin" in the "Dead Souls")
Lyrical deviations - There are lyrical, philosophical, journalistic, express the thoughts and senses of the writer directly, in direct author's word, reflect the author's position, the attitude of the writer to the characters, some elements of the theme, problems, ideas of the work (in the "dead souls" - about youth and old age , about Russia as a bird - Troika)
Artistic advance -image of scenes that are ahead of the further course of events (
Art Framing -the scenes begins and ends with an artistic work, most often this is the same scene given in development, and creating ring composition("The Fate of Man" M. Sholokhov)
Dedication -short description or lyrical product having a specific addressee, which is addressed and dedicated to the work
Epigraph -aphorism or quote from another known work or folklore, located in front of the whole text or in front of its individual parts (Proverb in the "Captain Daughter")
Title- The name of the work that always contains the topic, problem or idea of \u200b\u200bthe work, a very brief formulation, which has a deep expressiveness, imagery or symbolism.
Object of literary analysis in the study of the composition Can be different aspects of the composition:
1) architectonics, or the external composition of the text, - it is membership in certain parts (chapters, subpower, paragraphs, stanzas, etc.), their sequence and relationship;
2) system of patterns of artwork characters;
3) shift points of view in the structure of the text; So, according to B.A. Supenssky, it is the problem of the point of view amounts to "Central Production Problem»; consideration in the structure of the text of different points of view in the ratio with the architectonics of the work allows you to identify the dynamics of the deployment of artistic content;
4) the system of parts presented in the text (part composition); Their analysis makes it possible to reveal the ways of deepening the depicted: how it was finely noticed by I.A. Goncharov, "Details that appear in the long run of common plan and separately", in the context of the whole "merge in general, ... as if thin invisible threads act or, perhaps, magnetic currents;
5) correlation with each other and with the other components of the text of its extra-wing elements (inserted novels, stories, lyrical deviations, "scenes on stage" in the drama).
Analysis of the composition, therefore, takes into account the different aspects of the text.
The term "composition" in modern philology turns out to be very multivalued, which makes it difficult to use it.
To analyze the composition of the artistic text, you must be able to:
To allocate in its structure to interpret the work repeats, which serve as the basis of cohesion and coherence;
Identify semantic roll calls in parts of the text;
Select markers - dividers of different composite parts of the work;
Relate the peculiarities of the design of the text with its content and determine the role of discrete (individual parts) of composite units in the composition of the whole;
To establish the connection of the narrative text structure as its "deep composite structure" (B.A. Uspensky) with its external composition.
Determine all the techniques of the outer and inner composition in the poem F. Tyutchev "Silentium" (namely: parts of the composition, the type of plot - non-sales, event - descriptive, cutting individual elements, type of their connectivity, - NB
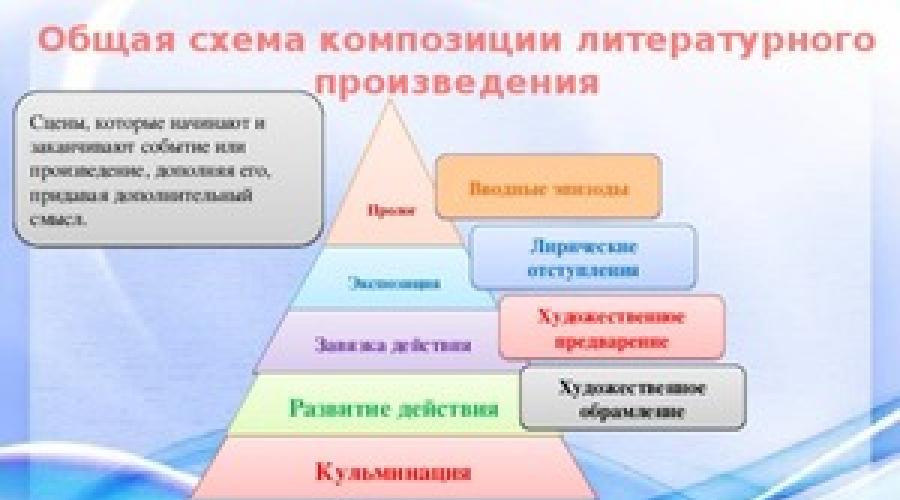
Prologue is called the introductory part of the work. She either precesses the storyline or the main motifs of the work, or is the events preceding the pages described on the pages.The exposition in something is akin to the Prologue, however, if the Prologue does not have much influence on the development of the plot of the work, then directly introduces the reader into the atmosphere. It gives the characteristic time and place of action, central characters and their relationship. The exposure may be both at the beginning (direct exposure) and in the middle of the work (delayed exposition).
With a logically clear construction behind the exposure, the tie is an event that begins and provokes the development of the conflict. Sometimes the tie is preceded by exposure (for example, L.N. Tolstoy "Anna Karenina"). In detective novels, which are distinguished by the so-called analytical construction of the plot, the cause of events (i.e. zag) is usually opened by the reader after it generated by it.
Behind the risk traditionally, the development of action, consisting of a number of episodes, in which the characters seek to resolve the conflict, but it only exacerbates.
Gradually, the development of action is suitable for its highest point, which is called the climax. Culmination is called a clash of characters or a turning point in their fate. After the climax, the action is uncontrollabically moving towards the junction.
An exposure is completed or at least conflict. As a rule, the junction occurs at the end of the work, but sometimes appears at the beginning (for example, I.A. Bunin "Light breathing").
Often, the work is completed with an epilogue. This is the final part in which the events followed after the completion of the main plot, and the further fate of the characters. These are epilogs in Romanov I.S. Turgenev, F.M. Dostoevsky, L.N. Tolstoy.
Lyrical deviations
Also, the compositions may be present elements, for example, lyrical retreats. In them, he appears in front of the reader, expressing its own judgments on various issues that are not always directly related to action. Of particular interest are lyrical deviations in Evgenia Onegin A.S. Pushkin and in the "Dead Souls" N.V. Gogol.All listed allow us to give artistic integrity, logicality and fascination.