What is the hemispheres on the physical map? Scale and conditional signs of physical cards. Conditional signs and designations on geographic maps
Classification
Views:
· Physical
· Political
· Climatic
· Natural zones cards
· Large-scale
· Medium-scale
· Small-scale
· Maps of the world
· Maps of mainland
· Cards of countries and regions
· Totalographic
· Themed.
Classification for purpose:
· Scientific reference
· Training
· Tourist
· Cultural and educational
Content Classification:
· Totalographic
· Thematic
The atmosphere, its structure, composition, value. Heating atmosphere. Water in the atmosphere. The pressure of the atmosphere, its measurement. Wind, speed, strength, direction. Total atmosphere circulation. The protection of the atmosphere.
Atmosphere - The gas shell of the celestial body, held by gravity. Since there is no sharp boundary between the atmosphere and interplanetary space, then usually the atmosphere is considered to be the area around the celestial body, in which the gas medium rotates with it as a whole.
The atmosphere is a mixture of gases consisting of nitrogen (78.08%), oxygen (20.95%), carbon dioxide (0.03%), argon (0.93%), small amount of helium, neon, xenon, crypton (0.01%), ozone and other gases, but their content is negligible (Table 1). The modern composition of the Earth's air has been established over one hundred million years ago, however, the abruptly increased production activity of a person still led to its change. Currently, an increase in CO2 content is about 10-12%.
The protection of the atmosphere.
Careful cleaning of exhaust gases on existing enterprises. In the cities where transport accumulates, expand the area of \u200b\u200bgreen plantings. Trees are not only powerful producers of oxygen, but also significantly reduce the dustiness of the air. 1 hectares of forests within one hour absorbs 2 kg of carbon dioxide. In the forests of dust, 8-10 times less than in flags. Tunnels for machines and underground transitions for pedestrians. Legislative consolidation of legal measures, which provide for violations, administrative, disciplinary, criminal and material responsibility measures.
Observations for clouds.
The nature of the cloudiness and the change in the shape of the clouds is closely related to the change of weather. That the weather will change for the worse, say the types of clouds
Monitoring the color of the sky.
The sky color is also important for weather prediction.
Golden sky color at sunset and lack of clouds in the West - a sign that tomorrow will be good weather.
The sunset of a pale color, even with the apparent absence of clouds in the West - a sign that the weather changes for the worse, since this color of the sky indicates that there is a cluster of the cereal clouds, invisible to the eyes.
Scarlet sunset foreshadows windy weather.
If the sun during the sunset is hidden behind the clouds, it foreshadows bad weather.
Wind observations.
The wind can bring a sharp change in the weather. If the direction of the wind is changing during the day and follows behind the Sun, this is a sign of good weather.
Frequent change in speed and wind direction speaks of the proximity of the cyclone, the arrival of which is accompanied by a sharp decrease in pressure and abundant rains.
If, after a long rain, the wind increases, you can expect the cessation of rain.
If, with good weather, the wind sharply replaces its direction, the weather will deteriorate.
Observation of humidity.
Air humidity during the day changes greatly. It depends on the air temperature, since cold air may contain less water vapor than in heat. For each temperature there is a saturation limit, i.e. such a state when water is condensed in water droplets and falls in the form of dew, and in the form of dew. If the air will cool even more, the fog will appear, then the clouds are formed and the precipitate will fall.
Thus, the decrease in temperature is a necessary condition for the formation of precipitation. Also for the formation of water droplets in the air, the cores are needed condensation the smallest dust or ice crystals. In very clean air, drops are not formed.
Biosphere borders
· Upper border in the atmosphere: 15-20 km. It is determined by the ozone layer, delaying short-wave ultraviolet radiation, destructive for living organisms.
· Lower bound in a lithosphere: 3.5-7.5 km. It is determined by the temperature of the transition of water into steam and the temperature of denaturation of proteins, but mostly the distribution of living organisms is limited to incur into several meters.
· The boundary between the atmosphere and the lithosphere in the hydrosphere: 10-11 km. Determined by the bottom of the World Ocean, including bottom deposits.
Biosphere Structure:
· Live substance - the entire totality of the bodies of living organisms inhabiting land, physico-chemically one, regardless of their systematic affiliation. Biogenic substance is a substance created and processed by a living organism.
· Bone substance - products formed without the participation of living organisms.
· Biocosal substance - a substance that is created simultaneously with alive organisms and oblique processes, representing dynamically equilibrium systems of those and others. These are soil, il, weathered bark, etc. Organisms play a leading role in them.
· Substance in radioactive decay.
· Scattered atoms that are continuously created from all kinds of earth substances under the influence of cosmic radiation.
· Substance of cosmic origin.
Biogeocenosis - A system that includes a community of living organisms and a closely associated combination of abiotic environmental factors within one territory related to the cycle of substances and a stream of energy (natural ecosystem). It is a stable self-regulating environmental system in which organic components (animals, plants) are inextricably linked with inorganic (water, soil). Examples: Pine Forest, Mountain Valley. The teaching about Biogeocenosis was developed by Vladimir Sukachev in 1942.
In 1924, Russian biochemist Alexander Ivanovich Oparin, and later, in 1929, J. Holdane was expressed hypothesis On the occurrence of life as a result of the long-term evolution of carbon compounds, which has formed the basis of modern ideas. Oparin proceeded from the fact that the occurrence of living beings from inanimate nature is impossible in modern conditions. The abiogenous emergence of living matter may have been only under the conditions of an ancient atmosphere.
According to one of the hypotheses, life began in a piece of ice. Although many scientists believe that the carbon dioxide present in the atmosphere ensured maintaining greenhouse conditions, others believe that winter dominated Earth. At low temperature, all chemical compounds are more stable and therefore can accumulate in large quantities than at high temperatures. The fragments of meteorites are brought from space, emissions from hydrothermal sources and chemical reactions occurring during electrical discharges in the atmosphere were ammonia sources and organic compounds such as formaldehyde and cyanide. Finding into the water of the World Ocean, they frozen with her. In the ice thicker, the organic substance molecules closely came closer and joined the interaction, which led to the formation of glycine and other amino acids. The ocean was covered with ice, which defended the newly formed compounds from destruction under the action of ultraviolet radiation. This ice world could melt,
Charles Darwin and his contemporaries believed that life could arise in a reservoir. This point of view, many scientists are also adhered to. In a closed and relatively small reservoir, organic substances, brought by water flowing into it, could accumulate in the required quantities. Then these compounds were further concentrated on the inner surfaces of layered minerals, which could be reaction catalysts.
Excursion
During the excursion, a person has the opportunity to get acquainted with natural objects, touch the history of the edge. The popularity and effectiveness of the excursion form is due to direct acquaintance with genuine objects.
Lecture
Provides or distributing knowledge of the region during lectures or lecture cycles. Lectures are held according to a specific topic.
Archival
In archival documents, old periodicals, a lot of interesting information is contained, often unique data. This form is designed for people who are enthusiastic history requires a lot of accuracy, pain stiffness.
Museum
An acquaintance with the edge in this case is based on the materials of the expositions of local history and other museums. This form also intends to collect materials and the creation of expositions of local history museums.
Directions: Historical (studies the past of the edges, historical monuments), art historical (instilling, respectfulness to the monuments of art, comes to the cultural and artistic population; literary works, etc.), anti-cultural (helps to see and evaluate the beauty of nature, forms ecological skills Cultures), economic (the main objects of economic landmarks are: the territory of the region as a whole, individual industries, enterprises; the population of the region; settlements.
Sakhalin Oblast - The only island region in Russia - includes Sakhalin Island with the islands and seal and two ridges of the Kuril Islands located close to him.
Sakhalin region is located in the seventh time zone (decree time), the North point is located on O. Sakhalin at Cape Elizabeth, South on O. Anunuchi, which is part of the Small Kuril Ridge, Western - on Sakhalin Cape Lah and East - Cape Yaugich on Eastern Outskirts O.Shumsha. According to Laperus, Kunashir, treason and Soviet, the state border between Russia and Japan passes.
The Sakhalin Region Square is 87.1 thousand square meters. km, about 78 thousand square meters. Km occupies Sakhalin. In terms of its size, the area of \u200b\u200bthe region is somewhat more Austria and three times the area of \u200b\u200bBelgium.
Sakhalin is one of the largest islands of Russia. Its length reaches 948 km, the maximum width is 160 km, minimum 26 km. From the mainland, Sakhalin is separated by the Nevelsky Strait, whose width in the narrow part is 7.5 km. From the West and South-West, the ished is washed by the waters of the warm Japanese Sea, from the north and east - the Cold Okhotsk Sea.
The Kuril Island group extends from the southwest to the northeast (from Hokkaido to P-ov Kamchatka), which is separated by two ridges - big and small, separated by South Kuril Strait.
A large Curilian ridge with a length of almost 1200 km has about 30 islands, of which Kunashir, ITUURUP and Paramushir are the largest.
A small Curilian ridge in 105 km long is stretched in parallel to a large Kuril ridge. The ridge includes six islands, the greatest of them - Shikotan.
From the Pacific Ocean along the Kuril Islands there is a deep-water smokylo-Kamchatsky chute.
Geological structure and minerals. Within Sakhalin, large raised lifters are allocated, separated by deflection, intermountain depression and depressions.
S.O. It has significant and a variety of mineral resources: oil and gas, stone and brown coal, black, colored, rare and noble metals, mining and agrochemical raw materials, raw materials for the cement industry and other minerals, as well as the biological resources of sushi and the surrounding seas .
Hydrocarbon resources of Sakhalin and the adjacent shelf, where the main part of the balance sheet and forecast oil and gas reserves is located. A total of 112 deposits, 17 of them on the shelf. There is a sv. 20 promising oil and gas deposits, about 30 deposits are being developed. The main prospects for oil and gas production are associated with the Sakhalin shelf. The explored oil and gas reserves on the shelf exceed stocks on land ten times and constitute CV. 1 billion tons of oil and 3.6 trillion M3 gas.
About 8% of Sakhalin Square occupy coal deposits. Knows sv. 60 coal deposits and promising coaliest areas. The reserves of high-quality coal in them are estimated at 20 billion tons (of which brown coal - 40%, coal - 60%), including coking -1.9 billion tons. For open development, about 8% of total coal reserves are suitable. Forecast coal resources in the Solntsevskoye deposit (2.4 billion tons) are especially large, in most cases their open development is possible.
In the region, 200 peat deposits with total reserves of St. 1.1 billion tons. On the territory of S.O. Numerous manifestations of black, noble and non-ferrous metals have been established. Revealed gold reserves.
On the Kuril O-Wah, the manifestations of polymetallic ores with impurities of rare metals are known. There are about 50 manifestations of native sulfur with its content in ores up to 50-60%. Stocks make up 117.7 million tons. The main volumes are focused on about. Itaruple, where the newly prepared deposit is located with reserves of 5.1 million tons.
At the Schmidt, the stocks of phosphate-containing rocks were revealed. Territory S.O. Rich by building materials, a number of deposits and manifestations of jewelry stones with high artistic value are known.
On the territory of S.O. A variety of types of mineral waters have been revealed. There are sv. 25 groups of mineral springs. Perspective mineral and thermal waters of Kuril O-Great Warm. Their stocks are sufficient to complete the islands of electrical and thermal energy.
Relief The islands are composed of medieval mountains, lowlands and low-lying plains. The southern and central part of the island is characterized by a mountain relief and consist of two meridional oriented mountain systems - West Sakhalin (up to 1327 m height - Onor) and the East Sakhalin Mountains (up to 1609 m, the city of Lopatina), separated by the longitudinal thym Poronian lowland. The north of the island (with the exception of the Schmidt Peninsula) is a canopy hilly plain. The shores of the island are weakly cut; Large bays - aniva and patience (wide open to the south) are respectively in the southern and middle part of the island. Two large bays and four peninsula are distinguished in the coastline.
Orientation on the terrain
1. For nearby local subjects (relief). To do this, you need to orient the card and identify on it and, accordingly, on the area of \u200b\u200b1-2 local items, to determine the eye of its location on the ground relative to these items and it is also an eye on the map.
2. Promder distances. Moving along the road (according to the line in the forest or other line on the ground), marked on the map, measure pairs of steps (by speedometer machine) distance from the nearest reference point. To determine the point of its standing, it is enough just to postpone the measured (passed) distance on the scale on the map in the desired direction.
3. Serfs. When moving along the road (by promoter, along the telegraph line), your location can be determined in local subjects located on the sides of the road. To do this, orient the map in the direction of the road and identify on it and on the area of \u200b\u200bany landmark.
Orientation without a card
It is to define the sides of the horizon (directions to the north, east, south, west) and their location on the area relative to the designated (selected) landmarks and usually applies to a limited territory.
Orientation on the terrain
When determining the side of the horizon on the compass He is given a horizontal position, the arrow brake is released. After the cessation of oscillations, its luminous end will indicate the direction to the north.
To determine the side of the horizon by the Sun. and hours It is necessary to stand face to the sun. Put the clock showing the local time so that the hour arrow is directed in the sun. The line dividing the angle between the clockwise arrow and the direction to the figure "1" in the winter time or on "2" on the summer (only for the territory of the CIS) in half, will show the direction to the south
On the moon and the clock are oriented when the starry sky is poorly visible. In the full moon side of the horizon, it is possible to determine through the moon with the help of hours as well as through the sun.
Types of populations
Populations can occupy different in size and habitat conditions within the habitat of one population can also be not the same. According to this feature, three types of populations are elementary, ecological, geographical. Elementary (local) population is a combination of individuals of one species, occupying a small portion of homogeneous area. Between them is constantly exchanged genetic information. Ecological population is a set of elementary populations, intraspecific groups dedicated to specific bioscenoses. Plants of one type in cenosis are called priceopulation. The exchange of genetic information between them occurs quite often. The geographical population is a set of environmental populations that settled geographically similar areas. Geographical populations exist autonomously, the ranges of them are relatively insulated, the exchange of genes rarely occurs - in animals and birds - during migrations, in plants - with the separation of pollen, seeds and fruits. At this level, the formation of geographical races, varieties, subspecies are distinguished.
Population indicators
Being group associations of individuals, populations have a number of specific indicators that are not inherent in each individual individual. At the same time, two groups of quantitative indicators are distinguished - static and dynamic.
The state of the population is currently characterized static indicators. These include the following.
Number - the total number of individuals on the territory allocated or in this amount. This population indicator is never permanent, it depends on the ratio of the intensity of breeding (fertility) and mortality.
Density The population is the average number of individuals (or biomass) per unit area or volume of the space occupied by the population. Population density also changeable, it depends on the number
Dynamic The population indicators include fertility, mortality, growth and growth rate of the population.
Birthday (Fertility) is the number of new features that appeared per unit of time as a result of breeding. Living organisms have a huge breeding ability. It is characterized by the so-called biotic potential, which is a speed with which with unlimited reproduction (possible only theoretically, with ideal environmental conditions), the individuals of a certain species can be covered with a terrestrial ball with a uniform layer.
Mortality The population is the number of those who died in the population of individuals in a certain period of time. Like fertility, mortality varies depending on the conditions of habitat, age and state of the population; Mortality is expressed as a percentage of initial or more often to its average.
Growth population - difference between fertility and mortality; The increase can be positive, zero and negative.
Growth rate Populations - average increase of it per unit of time.
Types of relationships.
Competition - the struggle for the same environmental conditions between different types or within one species (the plants compete among themselves in the struggle for light, moisture, etc.; predatory birds of forests and predatory animals compete for food - miserable rodents, etc. .)
Predation - One body (predator) produces and eats another (sacrifice). If the organisms of one species are cannibalism (from invertebrate animals: dragonflies and spiders eat flies, butterflies and mosquitoes; from vertebrates: wolves and foxes eaten hares and miserable rodents).
Commminasalism Or cheating - one of the organisms benefits the benefit from the relationship, for another relationship is neutral (fishes-sticky and sharks, giving fishes protection and food; in the nests of birds and nera rodents lives a large number of types of insects that are in nora refuge and food).
Amenzalism - The activity of one species leads to the oppression of others (ate growing in the mixed forest shade birch trees and other deciduous rocks, and the life of fir trees from deciduous trees is practically independent; Mushroom Penicill is distinguished by an antibiotic, overwhelming bacteria).
Neutralism - Different types of organisms have different environmental niches and do not enter into relationships with each other (different types of antelopes in Savannaps Africa eaten plants of different tiers; the giraffe antilope is fed by leaves of trees, antilopa GNU - leaves of shrubs and high herbs, an antilope kuda feeds low herbs).
24. Biogeocenosis, concept, general characteristics.
Biogeocenosis- a system, including a community of living organisms and a closely associated set of abiotic environmental factors within one territory.
Biogeocenosis components.
Biocenosis.The biological part of biogerocenosis is represented by microorganisms, plants and animals and is called biocenosis. Biocenosis consists of plants (phytocenosis), animals (zoecenosis) and microorganisms (microbiocenosis).
The population of various species living in one common area make up the environmental community. Living organisms, being under the influence of other organisms and inanimate nature, in turn, have an impact on them.
Ecotop.The abiotic part of biogeocenosis is part of the sushi or water basin with certain climatic conditions. It is called Ecotop. Ecotops are represented by atmospheric (climatotop) and soil (edafotop) factors.
Classification
Views:
· Physical
· Political
· Climatic
· Natural zones cards
Classification of cards on scale:
· Large-scale
· Medium-scale
· Small-scale
Classification of cards on spatial coverage:
· Maps of the world
· Maps of mainland
· Cards of countries and regions
Classification of maps in content:
· Totalographic
· Themed.
Classification for purpose:
· Scientific reference
· Training
· Tourist
· Cultural and educational
Content Classification:
· Totalographic
· Thematic
Physical map of the world. general characteristics
The study of geography is impossible without a card containing the most objective accurate and concise information on the territory, the placement of natural, economic or social objects and phenomena.
On this map more fully, than on other atlas maps, presented geographical objects (islands, peninsula, bays, sheds, sea, etc.). The physical card gives an idea of \u200b\u200bthe largest form of the relief of sushi and the seabed. It shows the orographic names (the names of the relief shapes): mountains, plains, individual vertices with their absolute height above ocean, as well as the names of the form of the bottom of the ocean bottom - gutters, ridges, kotlovin, etc.
The hydrographic base of the card is represented by fresh and salty lakes, waterfalls on rivers, which makes it possible to draw conclusions about the economic use of sushi water. Thanks to the flow shown, it is possible to draw conclusions about the differences in the climate within the climatic belts. Also shown deserts, wetlands, the spread of salt marshes, sands, acting volcanoes and signed the names of geographic areas (Llanos, Selvas T.P.).
Comparison of this card with political will help make generalizations about the prevailing landscapes (plain or mountain) in a separate country, and the comparison with the map is the disposal of the population will answer the question why some territories are thickly populated, while others are not populated.
Comparing this card with a map of mineral resources, you can trace the relationship of relief forms with the spread of minerals of various origin (sedimentary, igneous, etc.).
This card is useful in drawing up the characteristics of natural resources, as well as in the regional review in evaluating the country's natural resource potential.
On some cards depicts separate relatively small territories, and on others - entire continents or oceans. What is the hemispheres on the physical map? What is its scale? And what information can I "endure" from it? Answers to all these questions you will definitely find in our article.
A few words about the maps
Cartography originated at about the same time as writing. In ancient times, our ancestors painted on the walls of the caves and cliffs primitive plans, on which they denote the important features of the terrain in which they lived. The first world map, according to scientists, was created in Babylon about 3 thousand years ago.
Cartography bloomed in the so-called era of great geographical discoveries. Numerous travelers and navigators were created hundreds of sufficiently detailed and interesting cards. All information obtained during travels to distant and unknown edges were applied.
Despite the course of time, the card did not become archaism and kept its meaning to the present day. In modern science, there is even a special research method - cartographic. Today, geographical maps are used in various sectors of the national economy - urban planning, planning of territories, agriculture, transport, meteorology, tourism, etc.
Maps are different: physical, economic, recreational, climatic, synoptic, geological, political and many more, many others. On physical maps depicted by the mainstream and oceans. You can also see hydrographic objects (rivers, seas, lakes), various forms and sometimes the largest cities.
Back in 150 BC, the ancient Greek scholar Kratty Mallian created the first three-dimensional model of the Earth - Globus. However, it was later that it was not so convenient to use this model in practice. In a long walking expedition, you will not take it, and in the road backpack he will definitely not fit. In addition, when you look at the globe, you see only one half of it. This is also not always convenient.

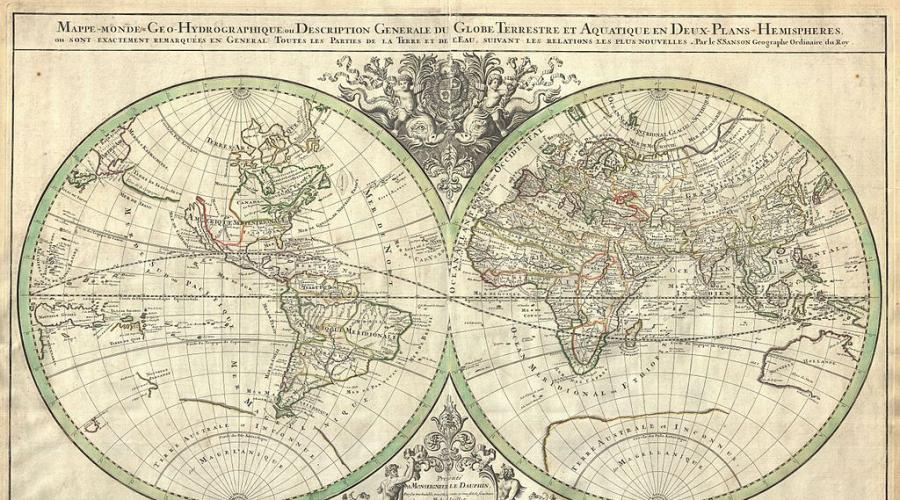
Apparently, therefore, the Hemispheres of the Earth were invented. Without distortion here, of course, do not do. But then such cards make it possible to contemplate the entire picture of the world at once, because two halves of our huge planet are shown on them. If you leave the globe along the equator, then we will get a map of the Northern and South Hemispheres. If you split the planet to zero (Greenwich) meridian, then it turns out, respectively, the map of the Western and Eastern hemispheres.
Scale of a physical card hemisphey
Scale is a purely mathematical concept. This is the ratio of the length of the segment on the geographic map or plan to the real length of the same segment on the ground. For example, we have a topographic map with the following scale: 1: 2000. This means that one centimeter on it corresponds to two thousand centimeters (or twenty meters) on the ground.
Physical maps of hemispheres are reviewed and are used for training purposes (usually in the wall variant). Therefore, they are usually small-scale. The scale of physical cards Hemispheres most often range from 1:15,000,000 to 1:80,000,000. That is, the distance between Kiev and Moscow does not exceed 3-4 centimeters.
What is depicted on the physical card Hemissemi
On a physical map of any scale, various natural objects are displayed primarily. What exactly? What is depicted on the physical hemisphere of the earth specifically? Let's list all these objects.
- Molds of relief of hill, plateaus, mountain ranges).
- Elements of the coastline (island, peninsula, bay, straits, bays, capes).
- Objects of hydrography (sea, oceans, rivers, lakes, canals, large reservoirs, glaciers).
- Elements of underwater relief (basins, oceanic ridges, gutters).
- Capital and largest cities.
The Earth's map shows three continents (North and South America, Antarctica) and three oceans (quiet, Atlantic and northern ice), on the map of Eastern hemisphere - four continents (Eurasia, Africa, Australia and Antarctica) and four oceans (Northern Arctic, Atlantic , Quiet and indian).

How to read a physical card
Any geographical map has its own specific language. Knowing this language, you can learn to read it correctly. First of all, you should pay attention to the map scale. Most often it is placed in the upper left corner of the sheet. The scale is indicated not only in the numerical version, but also in linear so that the process of determining distance distance on the map was as convenient as possible.
The conventions on the physical card of the hemisphere is not too much (as a rule, no more than two dozen). So, the rivers are marked with dark blue lines, lakes and reservoirs - blots of blue. Mainland ice and eternal snow are shown with a series of blue dots parallel to each other. Such a "pattern" is covered by most of Antarctica and Greenland.
On physical maps you can meet some other conditional signs (see photo below). The relief on them is displayed using various shades. It is worth telling about it in more detail below.

Display relief on physical map
Under each physical map, the so-called altitude scale and depths with numeric marks in meters are presented. The shape of the earth's surface is indicated by different colors, depending on the absolute height of the terrain. So, lowlands are shown in green, elevation - yellow, mountain systems and ridges - orange or dark brown.

The same is with depths. The shallow water of the oceanium is marked with a light blue tint. But deep plots are shown more rich in blue. Here the principle is: the deeper - the same darker.
The absolute heights of individual points on the sushi surface are black, and the depths of the seas and oceans are blue.
On one piece of card, a whole world can fit, with all the oceans, continents, mountains and plains, countries, cities, minerals, animals and birds. Just need to be able to correctly read the card. In this lesson, we will find out which cards were in antiquity, and what types of cards are now, what are the advantages of the card in front of the globe, what is the scale, the legend of the card. We will learn how to use the depth scale and heights, determine the coordinates of earth objects.
Subject: Planet on which we live
People began to draw cards even before they thought about the round earth or flat. Scientists have discovered in Kamchatka drawing on the dice depicting the path to a rich prey to the place. This is probably one of the oldest cards. The cards painted on the slices of the bark, cut out on wooden planks, which were convenient to take on the road. Some peoples scratched the cards with an acute subject on raw clay tiles, which, after drying, became durable, with a clear image.
This map of the worldIn the center of which is the city of Babylon, more than 3 thousand years.
Fig. 1. World map of the ancient Babylon ()
Also found rock paintings in the caves, where people lived thousands of years ago.

Fig. 2. Fashionable area of \u200b\u200bterrain ()
With the invention, paper cards began to draw on it. All information received by scientists and travelers was applied to the cards during wanderings on various lands.

Fig. 3. Ancient world map on paper ()
The manufacture of the map was a long process, because all the details were drawn manually, so the cards were very expensive.
The long period of time was present on the maps only four: Eurasia, Africa, North America, South America. Many years passed before the navigators opened Australia and Antarctica.
When you are looking for some country on the globe, you see only one hemisphere. And to see another, the globe must be turned.

On the globe, it is impossible to designate a large number of geographic objects without increasing its size. A large globe is uncomfortable for travel use.
Scale- This is the ratio of the length of the lines on the map or drawing to the actual length. The scale of the physical map of Russia tells us that every centimeter card corresponds to 200 km on the ground.

Fig. 7. Physical map of Russia ()
On the map you can show two half of the earth at once. If we divide the globe on the equator, it will turn out map of the North and South Hemispheres,

Fig. 5. North and South Hemisphere
and if on the line of zero meridian - Western and Eastern Hemispheres.

Fig. 6. Western and Eastern Hemispheres
On the mineral map Special icons marked places of mineral deposits.

Fig. 9. Maintenance map ()
On the habitat animal habitats The habitats of various types of birds and animals are indicated.

Fig. 10. Map of habitat birds and animals ()
On the contour cards No color designations and depicted, but not signed, all kinds of geographical objects. They are convenient for labeling routes.

Fig. 11. Contour map
On the political map. The world is depicted countries and their borders.

Fig. 12. Political map of Eurasia ()
On the synoptic maps Conditional icons showing observations of the weather.

Fig. 13. Synoptic map ()
Different maps are combined into atlasi.

Fig. 14. Geographical Atlas ()
Maps depict various territories. There are cards of districts, cities, regions, states, mainland, oceans, hemispheres and world maps.
Legend The map is the same as on the globe. They're called legendand usually placed at the bottom of the card.

We will find on the physical map of Russia, the West Siberian Plain.

Fig. 16. West Siberian Plain ()
Small horizontal invasses covering a considerable part of its territory, mean swamps.
Here are some of the biggest world of swamps - Vasyugansky. Lines depict rivers, borders and roads, circles - cities.

Fig. 17. Vasyugan Swamot
The sea and mountains have real outlines and paint different colors. Blue and blue - reservoirs, yellow - hills, green - lowlands, brown - mountains.
At the bottom of the card, the depth scales and heights are placed, with which you can see what height or depth means one or another color shade on the map.
The deeper the ocean, the darker color. On the North Ocean map, the darkest shade of blue in the Greenland Sea, where the depth reaches 5 thousand 527 meters; The brightest shade of pale blue color, there is the depth of the sea - 200 meters.

Fig. 18. Physical map of the Arctic Ocean
The higher the mountains, the darker the color they are indicated. So, the Ural Mountains, which are considered relatively low (the highest peaks from 1000 to 2000 m above sea level), on the map painted with light brown color.

Fig. 19. Ural Mountains
Himalayas are the highest mountains in the world (10 vertices with a height of more than 8 km) are denoted by dark brown.

Fig. 20. Himalayan Mountains

In Himalayas, Jomolungma is located (Everest) - the highest peak of the world (8848 m).

Taking advantage of the scale of heights, it is easy to determine the height of the Caucasian mountains.

Fig. 23. Caucasian Mountains
Their brown color indicates that the height of the mountains is more than 5 thousand meters. The most famous vertices - Mount Elbrus (5642 m) and Mount Kazbek (5033 m) are covered with eternal snow and glaciers.


Using a map, you can determine the exact location of any object. For this you need to know it coordinates: latitude and longitude, which are determined by a degree grid formed by parallels and meridians.

Fig. 26. Degree grid
The equator serves as the beginning of the reference - the latitude is equal to it 0⁰. The latitude is counted from 0⁰ to 90⁰ on both sides of the equator and is called northern or south. For example, the coordinate 60⁰ of northern latitude means that this point lies in the northern hemisphere and is at an angle of 60 ° to the equator.

Fig. 27. Geographic latitude
Longitude is counted from 0⁰ to 180⁰ on both sides of Greenwich Meridian and is called Western or Eastern.

Fig. 28. Geographic longitude
Coordinates of St. Petersburg - 60⁰ S.Sh., 30⁰ V.D.
The coordinates of Moscow - 55⁰ S.Sh., 37⁰v.

Fig. 29. Political map of Russia ()
- Vakhrushev AA, Danilov D.D. The world surrounding 3. M.: Ballas.
- Dmitrieva N.Ya., Kazakov A.N. The world around 3. M.: ID "Fedorov".
- Pleshakov A.A.Orrupturing World 3. M.: Enlightenment.
- Academician ().
- Survival ().
- Find a quiet ocean on the physical map of the world. Determine its deepest location, specify its name and depth. Describe how you defined this place.
- Make a short test (4 questions with three answers) on the topic "Geographical Maps".
- Prepare a memo with the rules of work with cards.
Cities - reduced thousands and even in millions of times and shown conditional signs. Many of them are signed. Handling signs and inscriptions on maps are diverse. Be able to break up in the conditional signs, in what is shown on the map, it means to be able to read the card.
Neethes and oceans
On the physical world map, green, yellow and brown shows large parts of the sushi - mainland And small islands. They are surrounded from all sides in the daece and oceans painted in blue and blue. The sea and oceans are interconnected and form single World Ocean An. The continents share the world ocean for individual oceans: Quiet, Atlantic, Indian and Arctic. Seas - These are parts of the World Ocean, walking into the land. On Earth, six continents: Eurasia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica and Australia. The biggest Mate Rick - Eurasia. It consists of two parts of light: Europe and Asia. It happened, because in antiquity people thought it was the owl of various lands, divided Mediterranean Sea. The fact that Euro-P and Asia make up a huge single sushi massif, they learned much later.
Compare Ptolemy card and modern physical-kui map of the world. On the map of Ptolemy, created about 1,800 years ago, the entire surface of the earth, known in the ancient time, is shown. "Antique" translated from Greek - ancient. From the ancient times on all maps North is located at the top of the card, south - downstairs, the East is on the right, the West - on the left. On the map of Ptolemy, we see only the Mediterranean Sea and the Earth, which surround it, - the South of Ev-Ropes, the West Asia and the north of Africa, which in ancient times they called Libya. Europe, Asia, Africa are parts of the old world. Os-altal continents, separating their oceans and the sea, people still had to open. And also open and put on the map the correct borders of Europe, Asia and Africa, which we see on the modern map.
Earth relief
Depth of the seas and oceans are not the same. If it is small, less than 200 m, then on the map we see a pale blue color. The more depth, the darker blue shade. Red arrows in the oceans are shown warm, and blue are cold flows. Water in currents moves like a river flow and is either warmer or colder to surrounding calm water. The si-winding lines on land are shown by rivers, stains -
Here you can look at the physical map of Russia in Super Ultra HD quality and huge resolution of 10350 per 5850 pixels (more than 60 megapixels) - this is the greatest permission of the card you can find on the Internet.
(Map can be enlarged in a new window for detailed consideration)
Attention, the attraction of unheard of generosity is open! This card can be downloaded for free and print.
I know that many users are looking for a physical map of Russia for the whole screen, the map of Russia in good quality close-up, high-resolution cards and the like. Here everyone will find what they expect to see and even more.
Map permission is huge, quality is high. That is why the card is very, very, very detailed. Map scale: 1: 8 000 000 (1 cm - 80 km on the ground). All inscriptions on the map - in Russian.
If you look closely, on this map of the Russian Federation you can see another Ukraine, part of Eastern Europe, Central Asia and other parts of the Eurasian continent.
This generalographic map reports the appearance of the territory and water area. On a physical card, relief and hydrography are shown in detail, as well as sands, glaciers, floating ice, reserves, mineral deposits. Thanks to a large permission on the map you can see cities, towns, towns and other settlements, messages, borders, etc.
I hope that big maps and pictures will bring travelers and ordinary people more benefits.
Something about the resolution of this card
Many know what 4k and Ultra HD is permission. This physical map of the Russian Federation has 2.5 times greater permission in pixels horizontally than 4K. The illustration below shows the comparative dimensions of all HD formats (HD, FULL HD, 2K, 4K) and this physical map of Russia.
Links to the photo galleries of cities and reserves
For those who like to consider photos, not the cards, photos of natural reserves, cities and their attractions are collected on this site. Many photos in the gallery presented below are shown in HD quality.
Even more beautiful photos - in my instagram of the photographer
More different photos can be seen in my instagram.
Subscribe friends. There will be a lot of interesting things.