Ball lightning: secrets, myths and exposure. Ball lightning Ball lightning mystic
Among all natural phenomena, ball lightning is still the most mysterious. Eyewitnesses of this amazing phenomenon claim that it seems that there is “meaningfulness” in the actions of the flying sphere: choosing targets, maneuvering during the flight, changing speed.
Ball lightning is usually called a spherical luminous object that appears either after a flash/strike of linear lightning, or suddenly materializes inside a closed space, for example: flying out of a socket, telephone handset, electrical panel or vehicle dashboard. Witnesses of the rare phenomenon describe this object as a luminous sphere ranging in size from 5 centimeters to 1 meter in diameter.
If ball lightning flies close, you can hear a crackling and hissing sound. Different eyewitnesses described the glow of the object in different ways: some said that the lightning was white, some saw streaks of blue, and others encountered red ball lightning. There are no barriers to this phenomenon; the luminous ball can fly through walls and glass, and travel along electrical wires as if in its native element.

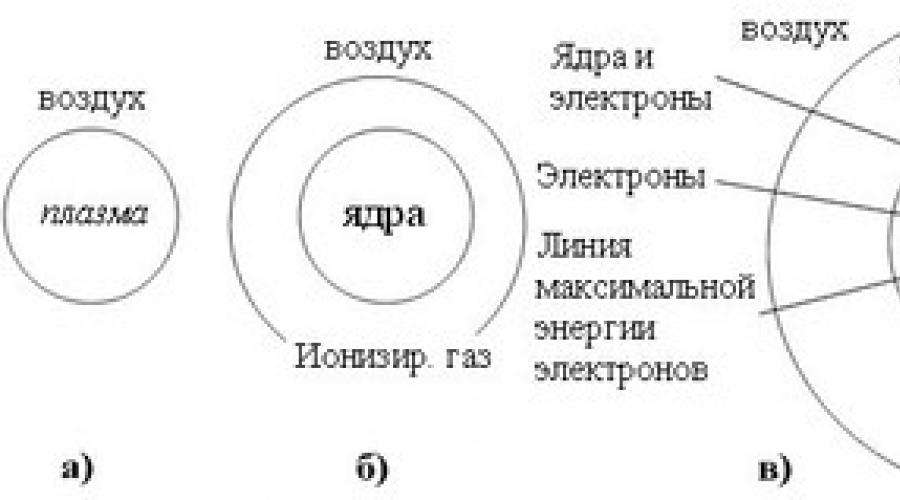
This diagram shows several theories about the structure of ball lightning
Despite many years of work by the best minds on the planet working on the issues of studying the nature of the origin of ball lightning, there is still no answer to the question of what this mysterious phenomenon is, what it consists of and what mechanics of physical laws it is subject to. A lot of hypotheses have been put forward, but none of them can be considered true.
So even in the age of human space flights and the creation of quantum computers, the natural phenomenon that has accompanied humanity throughout history remains hidden in a veil of mystery. According to statistics, more than 500 cases of observation of ball lightning passages are recorded in Russia annually.
According to the analysis, most of the observations occur in the summer, during the daytime, at the time of the onset or shortly before the onset of a thunderstorm. Although this does not mean that ball lightning cannot appear at other times of the year and under other conditions, I repeat that the nature of this phenomenon has not yet been properly studied.
Ball lightning comes to visit
On August 4, 2000, ball lightning flew into the house of a pensioner from the village of Rodniki, located in the Troitsky district of the Chelyabinsk region. According to the recollections of the owner of the house, as soon as it became clear that a thunderstorm would break out in the very near future, all electrical appliances in the house were de-energized, and the owner herself settled down in front of the window to drink tea.
Suddenly there was a crashing sound in the room, and a second later a glowing ball the size of a soccer ball appeared in front of her. For some time, the spherical “something” hung motionless in the air, but then began to rush around the room, flying through walls and objects.
The first target of the lightning was the lamp of the lamp, then the dressing table, after passing through the wall and leaving small traces of charring on it, it evaporated, went into the wiring, and the electrical wiring assembly became unusable. Despite the early blackout, ALL the electronics in the apartment failed.

A mark on the wall from the passage of ball lightning. The incident occurred in 2013, in the village. Small, Simferopol district. This photo clearly demonstrates the traces left in the apartment after the appearance of ball lightning, similar to the described episode.
On August 7, 1958, ball lightning appeared in an apartment in a house located on Kotina Street in Chelyabinsk. According to eyewitnesses, when thunder rumbled outside the window, ball lightning appeared inside the apartment. The flight of the luminous ball was short, but very noisy. After hanging in the air for several seconds, the lightning exploded with an indescribable roar. None of the household members were injured, but the apartment needed repairs: the wallpaper was burnt, the wiring was faulty and the window glass was cracked.
Fiery terror in Yemanzhelinka
In June 2013, an unusual phenomenon caused fires in the village of Yemanzhelinka, which, by the way, became famous throughout the world after the fall of the Chelyabinsk meteorite in February of the same year. On an ordinary summer evening, an ordinary thunderstorm began, which ended in real tragedy.
According to eyewitnesses, before observing the ball lightning, they heard the rumble of thunderclouds a couple of times, after which a strange glow formed in the sky above the village, which instantly transformed into two ball lightning scattered throughout the village. The first one targeted the roof of a two-story house, passing through the slate and attic, landing straight into a residential apartment, after which a fire broke out there.

The photograph from the scene clearly shows damage to the roof.
Most of the room burned out, but the kitchen suffered the most; apparently, lightning, once inside the apartment, was attracted by the largest concentration of electrical appliances, which caused a short circuit in their operation, which led to a fire.


A series of photographs from the damaged apartment
The second ball lightning headed to another part of the village and hit a cottage on Sovkhoznaya Street, where it also provoked the arson of one of the apartments; most likely, events unfolded according to a similar scenario. Luckily, the residents of both apartments were not at home, so no one was injured.
Ball lightning on a tram
On the evening of July 13, 2000, at around 10 p.m., one of the Chelyabinsk trams was struck by ball lightning. The electric transport was approaching the Shoe Factory stop, when suddenly a small ball of lightning flew into the driver’s cab. After flying in the cockpit for several seconds, lightning struck the electrical instrument panel. A fire started.
The tram driver tried to open the doors, but a short circuit that occurred blocked the ability to leave the vehicle in the usual way. The driver herself broke a window in the cabin and was able to get out with minor injuries.
Without succumbing to emotions and rationally assessing the situation, someone remembered a special hammer attached in case of emergency in every public transport salon.
As a result, through the broken window, all the few passengers on the evening route got out safe and sound. By the way, the tram burned out in literally ten minutes and delay or the absence of a small hammer could have ended in tragedy.
Death in an open field: a mystical repetition of tragedy
Cases of observing ball lightning do not always end more or less well. On July 17, 2014, in the vicinity of Chelyabinsk, near the small town of Kopeysk, an extremely tragic and rather mystical story happened. A 16-year-old boy and his grandfather were riding across a field on a motorcycle.
The young man drove the vehicle, and his 64-year-old passenger sat in a stroller. At one point, a luminous ball flew near the motorcycle, blinding both men with a flash of bright light, while a strong roar was heard, as if a thunderbolt had struck literally above their heads. As the 64-year-old man later recalled, he closed his eyes for a few seconds, and when he opened them, he did not find his grandson driving a motorcycle. The motorcycle moved for about ten meters without a driver.
Having stopped the vehicle, the man got out of the stroller and, a few meters from the motorcycle, in the bushes on the side of the road, discovered the lifeless body of his grandson. The guy died instantly, probably, he didn’t even have time to understand what happened.
As medical experts later established, ball lightning hit the young man squarely in the head; the potential energy from the impact was so powerful that even the cap on the guy’s head was torn to shreds. Abrasions and burns characteristic of victims of electrical discharges were found throughout the body. As it later turned out, several years ago, under similar circumstances, the young man’s uncle died. The man was making hay when a suddenly appeared ball lightning struck him in the head.
The very fact of death from a lightning strike, according to statistics, is estimated at a probability of 1 in 83,930 cases; there are no analysts at all on deaths from ball lightning. Such a strange coincidence, when years later ball lightning kills a second member of the family, can only be called mystical.
What to do if you see ball lightning?
If you have witnessed ball lightning, then you should remember the extreme danger of this phenomenon. Under no circumstances should you try to swat away a ball that approaches you or try to run - in both cases, attempts are obviously doomed to failure.
All your actions should be smooth and not create unnecessary air vibrations. Despite all its mystery, ball lightning is still a physical phenomenon and moves in the air not along a meaningful trajectory, but under the influence of air currents.
So if suddenly a clot of energy flew into your home, the only right decision would be to slowly approach the window and open the window - the draft will pull the lightning out. Remember that ball lightning is deadly.
In recent years, researchers have become increasingly inclined to believe that ball lightning is not just a natural phenomenon, but also something intelligent.
Over the history of mankind, more than 10 thousand eyewitness accounts of encounters with “intelligent balls” have accumulated. But scientists began studying this natural phenomenon only 150 years ago. But so far science cannot boast of great achievements in the study of these objects.
Today there are more than a hundred different theories about the origin and “life” of ball lightning. From time to time, in laboratory conditions, it is possible to create objects that are similar in appearance and properties to ball lightning - plasmoids. However, no one was able to provide a clear picture and logical explanation for this phenomenon.
There was a time when scientists simply did not believe in the existence of ball lightning, not believing the stories of eyewitnesses who happened to see it. For them, ball lightning was like a flying saucer for modern science. But as time passed, the number of observations of ball lightning increased, and now it is a natural phenomenon generally recognized by scientists.
One of the first mentions of the observation of ball lightning dates back to 1718, when on one April day during a thunderstorm in Couennon (France), eyewitnesses observed three fireballs with a diameter of more than 1 meter. And in 1720, in one of the French cities, a fireball fell to the ground during a thunderstorm, bounced off it, hit a stone tower, immediately exploded and destroyed it.
In the 19th century A French writer described a curious incident in which a fireball flew into the kitchen of a residential building in the village of Salagnac. One of the cooks shouted to the other, “Get that thing out of the kitchen!” But he was afraid, and this saved his life. Ball lightning flew out of the kitchen and headed into the pigsty, where a curious pig decided to sniff it. But as soon as she brought her snout to it, it exploded. The pig died instantly, and the entire pigsty suffered severe damage.
In 1936, the British Daily Mail newspaper reported on a case in which an eyewitness saw a hot ball descend from the sky. The ball first hit the house, damaging telephone wires and setting a wooden window frame on fire. And the ball ended its journey in a barrel of water, which immediately began to boil.
Ball lightning also flew into airplanes. In 1963, British professor R. S. Jennison, who was traveling on a New York-Washington flight, witnessed such an incident. According to him, the plane was first struck by ordinary lightning, and then ball lightning flew out of the cockpit. She slowly floated along the cabin, quite frightening the passengers. The ball lightning did not emit heat; the ball had an ideal spherical shape and looked like a “solid body” to Jennison.
Typically, ball lightning moves in the air above the earth's surface at a height of about 1.5 meters, its average lifespan does not exceed several minutes. The diameter ranges from a few centimeters to the size of a soccer ball. Ball lightning is usually characterized by a white color, but there are lightning of red, yellow, green and, according to eyewitnesses, even gray and black.
The fireball is able to maneuver and fly around various obstacles in its path. He also has the ability to pass through solid objects. As it moves, ball lightning often makes a sound reminiscent of high-voltage lines crackling, buzzing, or hissing.
All this, according to researchers of anomalous phenomena and ufologists, confirms that ball lightning is not just a natural formation, but an intelligent plasmoid. In support of the hypothesis that this phenomenon is controlled by some extraterrestrial intelligence, numerous examples of the “selectivity” of lightning are given.
In this series, the contacts of ball lightning with a person look especially strange. They are simply amazing in their illogicality. In some cases, fireballs easily overturn tractors, in others they explode upon slight contact with cars, but in others they allow a motorcyclist to run over them, and in others they very selectively... hit parts of the human body.
Here is just one such case. It happened in Kazakhstan. One day, a shepherd, as usual, drove a flock of sheep to pasture. But the weather suddenly changed sharply, and lightning began to flash. The shepherd did not have time to get to the village - he was struck by ball lightning, which he met on his way.
The man died on the spot. And this is where the most mysterious and incomprehensible things begin. The fact is that the temperature of ball lightning is so high that in seconds it can burn not only a person, but everything around.
Of course, this is a property of especially powerful balls. But in this case, as the meteorological center experts assured, there was just such lightning. So, the clothes, shoes, even the whip in the shepherd’s hand were not damaged at all after his death. The body itself was not damaged. The internal organs were also intact - everything except the heart, only it turned into coal. Neither doctors nor scientists could explain what it was.
“Eyewitness accounts of encounters with ball lightning, like pieces of a mosaic, put together, create the image of an amazing creature with an incomprehensible mind and logic - a kind of plasma clot that formed in a place of local concentration of energy and absorbed part of this energy, self-organized and evolved to an awareness of the surrounding the world and yourself in it,” sums up the famous ufologist Maxim Karpenko.
Well, it seems that ball lightning will present many more surprises to researchers.
Ball lightning is a unique natural phenomenon. There are about 400 theories that explain it, but none of them have received absolute recognition. Some even believe that this phenomenon is associated with hallucinations, others with aliens.
Ball lightning can appear in clear weather, fly out of the ground, glow in different colors, and pass through glass. American astronauts saw similar phenomena on the Moon during the Apollo 11 mission. Unknown balls were recorded by spacecraft on Mars. There are people who have suffered from lightning who claim that plasmoids have intelligence and can “mock” the victim.
The first written evidence of the observation of ball lightning dates back to 1638, when a two-meter ball lightning flew into a church in England, which killed and injured many parishioners, and caused serious damage to the building. Several centuries have passed since then, thousands of observations have been recorded, but there is still no clarity regarding ball lightning. Hundreds of hypotheses have been put forward for the formation and structure of this object, but none of them can explain all the amazing properties of ball lightning. Only the famous Nikola Tesla at one time knew how to make and publicly demonstrate ball lightning, but he never revealed this secret. You can read about amazing experiments at the link:
NIKOLA TESLA – A MADNESS OR A GENIUS?

Appearance
It is very easy to recognize ball lightning, despite the variety of its types. It usually has the shape of a ball that glows like a 60-100 watt light bulb. Much less common are lightning that looks like a pear, mushroom or drop, or such an exotic shape as a pancake, donut or lens. But the variety of colors is simply amazing: from transparent to black, but shades of yellow, orange and red are still in the lead. The color can be uneven, and sometimes ball lightning changes it like a chameleon.
 But once in Moscow, as well as in Canada, completely transparent ball lightning was observed at dusk, in which only the circumference of the shell was slightly visible. It is clear that during the day or in bright light such lightning would be completely invisible.
But once in Moscow, as well as in Canada, completely transparent ball lightning was observed at dusk, in which only the circumference of the shell was slightly visible. It is clear that during the day or in bright light such lightning would be completely invisible.
The size of the plasma ball ranges from several centimeters to several meters. But usually people encounter ball lightning with a diameter of 10-20 centimeters.
According to scientists, the temperature of this clot can range from 100 to 1000 degrees Celsius. Surprisingly, people who encountered ball lightning at arm's length rarely noticed any heat emanating from them, although, logically, they should have received burns. The same mystery is with mass: no matter what size the lightning is, it weighs no more than 5-7 grams.
 Behavior of ball lightning
Behavior of ball lightning
The behavior of ball lightning is unpredictable. They refer to phenomena that appear when they want, where they want and do what they want.
According to statistics, about 20 percent of observations of ball lightning occur in clear weather. During earthquakes, flights of ball lightning are often observed.
 It was also believed that lightning is, as it were, “attracted” to places of high voltage with a magnetic field - electric wires. But there have been cases recorded when they actually appeared in the middle of an open field...
It was also believed that lightning is, as it were, “attracted” to places of high voltage with a magnetic field - electric wires. But there have been cases recorded when they actually appeared in the middle of an open field...
They either hang calmly in one place at a short distance from the ground, or rush somewhere at a speed of 8-10 meters per second. Having met a person or animal on their way, lightning can stay away from them and behave peacefully, they can circle around curiously, or they can “attack” and burn or kill, after which they either melt away as if nothing had happened, or explode with a terrible roar.
 There have also been many unexplained cases where ball lightning is “tied” to a specific place or person and appears regularly. Moreover, in relation to a person, they are divided into two types - those that attack him every time they appear and those that do not cause harm or attack people nearby. There is another mystery: ball lightning, having killed a person, leaves absolutely no trace on the body, and the corpse does not become numb and does not decompose for a long time...
There have also been many unexplained cases where ball lightning is “tied” to a specific place or person and appears regularly. Moreover, in relation to a person, they are divided into two types - those that attack him every time they appear and those that do not cause harm or attack people nearby. There is another mystery: ball lightning, having killed a person, leaves absolutely no trace on the body, and the corpse does not become numb and does not decompose for a long time...
Some scientists say that lightning simply “stops time” in the body.
 Ball lightning from a scientific point of view
Ball lightning from a scientific point of view
There are a lot of disparate theories about the origin and “life” of ball lightning. From time to time, in laboratory conditions, it is possible to create objects that are similar in appearance and properties to ball lightning - plasmoids. In 1999-2001, employees of the St. Petersburg Institute of Nuclear Physics of the Russian Academy of Sciences (St. Petersburg, Gatchina), Anton Ilyich Egorov and Gennady Dmitrievich Shabanov, obtained a compact spherical plasmoid with a lifetime of up to half a second and with a diameter of 12-15 cm. However, there is a harmonious picture and a logical explanation No one could provide this phenomenon.
It has been noticed that sometimes thunderstorm linear lightning generates ball lightning. At the initial point of motion of the charge and at each break in the trajectory, a vortex component of the electromagnetic field is created, which breaks away from the general field and begins an independent life.
 The most famous and developed earlier than the others is the theory of Academician P. L. Kapitsa, which explains the appearance of ball lightning and some of its features by the emergence of short-wave electromagnetic oscillations in the space between thunderclouds and the earth's surface. However, Kapitsa was never able to explain the nature of those very short-wave oscillations. In addition, as noted above, ball lightning does not necessarily accompany ordinary lightning and can appear in clear weather. However, most other theories are based on the findings of Academician Kapitsa.
The most famous and developed earlier than the others is the theory of Academician P. L. Kapitsa, which explains the appearance of ball lightning and some of its features by the emergence of short-wave electromagnetic oscillations in the space between thunderclouds and the earth's surface. However, Kapitsa was never able to explain the nature of those very short-wave oscillations. In addition, as noted above, ball lightning does not necessarily accompany ordinary lightning and can appear in clear weather. However, most other theories are based on the findings of Academician Kapitsa.
A hypothesis different from Kapitza’s theory was created by B. M. Smirnov, who claims that the core of ball lightning is a cellular structure with a strong frame and low weight, and the frame is created from plasma filaments.
D. Turner explains the nature of ball lightning by thermochemical effects occurring in saturated water vapor in the presence of a sufficiently strong electric field.
However, the theory of the New Zealand chemists D. Abrahamson and D. Dinnis is considered the most interesting. They found that when lightning strikes soil containing silicates and organic carbon, a tangle of silicon and silicon carbide fibers is formed. These fibers gradually oxidize and begin to glow. This is how a “fire” ball is born, heated to 1200-1400 °C, which slowly melts. But if the temperature of the lightning goes off scale, it explodes. However, this harmonious theory does not confirm all cases of lightning occurrence.
For official science, ball lightning still continues to be a mystery. Maybe that’s why so many pseudo-scientific theories and even more fictions appear around it.
Pseudo-scientific theories about ball lightning
 At a minimum, ball lightning is considered a device for exploring our world. At the most, by energy entities that also collect some information about our planet and its inhabitants.
At a minimum, ball lightning is considered a device for exploring our world. At the most, by energy entities that also collect some information about our planet and its inhabitants.
An indirect confirmation of these theories can be the fact that any collection of information is work with energy.
And the unusual property of lightning to disappear in one place and appear instantly in another. There are suggestions that the same ball lightning “dives” into a certain part of space - another dimension, living according to different physical laws - and, having dumped information, appears again in our world at a new point. And the actions of lightning in relation to living creatures on our planet are also meaningful - they do not touch some, they “touch” others, and from some they simply tear out pieces of flesh, as if for genetic analysis!
The frequent occurrence of ball lightning during thunderstorms is also easily explained. During bursts of energy - electrical discharges - portals from a parallel dimension open, and their collectors of information about our world enter our world...
Incidents with ball lightning
 Thunderstorm at Widecombe Moor
Thunderstorm at Widecombe Moor
On October 21, 1638, lightning appeared during a thunderstorm in the church of the village of Widecombe Moor, Devon County, England. Eyewitnesses said that a huge fireball about two and a half meters in diameter flew into the church. He knocked several large stones and wooden beams out of the church walls. The ball then allegedly broke benches, broke many windows and filled the room with thick, dark smoke that smelled of sulfur. Then it split in half; the first ball flew out, breaking another window, the second disappeared somewhere inside the church. As a result, 4 people were killed and 60 were injured. The phenomenon was explained by the “coming of the devil”, or “hell fire” and was blamed on two people who dared to play cards during the sermon.
Death of Georg Richmann
 In 1753, Georg Richmann, a full member of the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences, died from a strike by ball lightning. He invented a device for studying atmospheric electricity, so when at the next meeting he heard that a thunderstorm was approaching, he urgently went home with an engraver to capture the phenomenon. During the experiment, a bluish-orange ball flew out of the device and hit the scientist directly in the forehead. There was a deafening roar, similar to the shot of a gun. Richman fell dead, and the engraver was stunned and knocked down. He later described what happened. A small dark crimson spot remained on the scientist’s forehead, his clothes were singed, his shoes were torn. The door frames were shattered into splinters, and the door itself was blown off its hinges. Later, M.V. Lomonosov personally inspected the scene of the incident.
In 1753, Georg Richmann, a full member of the St. Petersburg Academy of Sciences, died from a strike by ball lightning. He invented a device for studying atmospheric electricity, so when at the next meeting he heard that a thunderstorm was approaching, he urgently went home with an engraver to capture the phenomenon. During the experiment, a bluish-orange ball flew out of the device and hit the scientist directly in the forehead. There was a deafening roar, similar to the shot of a gun. Richman fell dead, and the engraver was stunned and knocked down. He later described what happened. A small dark crimson spot remained on the scientist’s forehead, his clothes were singed, his shoes were torn. The door frames were shattered into splinters, and the door itself was blown off its hinges. Later, M.V. Lomonosov personally inspected the scene of the incident.
The case of the USS Warren Hastings
One British publication reported that in 1809 the ship Warren Hastings was “attacked by three fireballs” during a storm. The crew saw one of them go down and kill a man on the deck. The one who decided to take the body was hit by the second ball; he was knocked off his feet and had minor burns on his body. The third ball killed another person. The crew noted that after the incident there was a disgusting smell of sulfur hanging over the deck.
The tragedy of the climbers
The most tragic story happened to five climbers on August 17, 1978. Having overcome the most difficult climb to Trapezium Peak in the North Caucasus, the athletes were unable to descend on the same day due to heavy snowfall and fog. They decided to stop for the night just below the peak, at an altitude of 3900 meters above sea level. With difficulty, the entire group accommodated themselves in one small tent, leaving all their metal equipment a few meters away in the snow. Suddenly, in the middle of the night, screams and moans were heard. At times, people were shaken by convulsions, accompanied by severe pain. Miraculously, the uninjured climber called rescuers on the radio.
Already at the Moscow Burn Center it turned out that a few seconds before the attack, one of the climbers saw some yellow flashes. He suggested that it was ball lightning, although, as an additional survey showed, no one visually saw the fireball. However, doctors were puzzled by the fact that on the bodies of some climbers there were huge third- and fourth-degree burns (up to 25 centimeters in length). In some places, human flesh was simply scorched and charred. One of the athletes died due to shock, as his spleen was burned out. He was the only one who slept that night on a rug that isolated him from the ground. The survivor, V. Kavunenko, an international master of sports in mountaineering, said something strange: “It was not simple ball lightning... The fireball mocked us for a long time and relentlessly...”
 After the climbers were discharged from the hospital, an additional examination of their equipment showed that there were some strange holes on the tent and in the sleeping areas, the diameter of which increased from 5 millimeters to 10 centimeters as they approached the human bodies. The origin of these holes remains unclear, although the ends of the threads of one of the climbers' sweaters indicated that they had been burned through by something!
After the climbers were discharged from the hospital, an additional examination of their equipment showed that there were some strange holes on the tent and in the sleeping areas, the diameter of which increased from 5 millimeters to 10 centimeters as they approached the human bodies. The origin of these holes remains unclear, although the ends of the threads of one of the climbers' sweaters indicated that they had been burned through by something!
Be that as it may, numerous stories about “dates” with ball lightning testify far from the peaceful qualities of her “character.” Based on a thorough study of the characteristics of the mysterious “fire lady,” basic safety rules were formulated when encountering ball lightning.
 What to do when encountering ball lightning?
What to do when encountering ball lightning?
The main rule when ball lightning appears - whether in an apartment or on the street - is not to panic and not to make sudden movements. Don't run anywhere! Lightning is very susceptible to air turbulence that we create when running and other movements and which pull it along with us. You can only get away from ball lightning with a car, but not under your own power.
Try to quietly move out of the lightning's path and stay away from it, but do not turn your back on it. If you are in an apartment, go to the window and open the window. With a high degree of probability, lightning will fly out.
And, of course, never throw anything into ball lightning! It can not just disappear, but explode like a mine, and then serious consequences (burns, injuries, sometimes loss of consciousness and cardiac arrest) are inevitable.
 If ball lightning touched someone and the person lost consciousness, then he must be moved to a well-ventilated room, wrapped warmly, given artificial respiration and be sure to call an ambulance.
If ball lightning touched someone and the person lost consciousness, then he must be moved to a well-ventilated room, wrapped warmly, given artificial respiration and be sure to call an ambulance.
In general, technical means of protection against ball lightning as such have not yet been developed. The only “ball lightning rod” that currently exists was developed by the leading engineer of the Moscow Institute of Heat Engineering B. Ignatov.
Ignatov's ball lightning rod has been patented, but only a few similar devices have been created; there is no talk of actively introducing it into life yet.
Ball lightning is a phenomenon of natural electricity, lightning that has a spherical shape and an unpredictable trajectory. To this day, the phenomenon remains poorly understood and provides grounds for speculation. There are currently about 200 theories of origin.
What types of ball lightning are there?
It is very easy to recognize ball lightning, despite the variety of its types. Usually it has, as you can easily guess, the shape of a ball, glowing like a 60-100 Watt light bulb. Much less common are lightning that looks like a pear, mushroom or drop, or such an exotic shape as a pancake, donut or lens. But the variety of colors is simply amazing: from transparent to black, but shades of yellow, orange and red are still in the lead. The color can be uneven, and sometimes ball lightning changes it like a chameleon.
There is also no need to talk about a constant size of the plasma ball; it ranges from several centimeters to several meters. But usually people encounter ball lightning with a diameter of 10-20 centimeters.
The worst thing about describing lightning is its temperature and mass. According to scientists, the temperature can range from 100 to 1000 oC. But at the same time, people who encountered ball lightning at arm's length rarely noticed any heat emanating from them, although, logically, they should have received burns. The same mystery is with mass: no matter what size the lightning is, it weighs no more than 5-7 grams.
If you've ever seen an object from afar that looked like what was described, congratulations - it was most likely ball lightning.
Behavior of ball lightning
Ball lightning inexplicably erupts from electrical sockets in the house and “leaks” through the slightest cracks in the walls and glass, turning into “sausages” and then again taking on its usual form. The behavior of ball lightning is unpredictable. They refer to phenomena that appear when they want, where they want and do what they want. Thus, it was previously believed that ball lightning is born only during thunderstorms and always accompanies linear (ordinary) lightning. However, it gradually became clear that they can appear in sunny, clear weather. It was believed that lightning is, as it were, “attracted” to places of high voltage with a magnetic field - electric wires. But there have been cases recorded when they actually appeared in the middle of an open field...
Ball lightning inexplicably erupts from electrical sockets in the house and “leaks” through the slightest cracks in the walls and glass, turning into “sausages” and then again taking on its usual shape. In this case, no melted traces remain... They either calmly hang in one place at a short distance from the ground, or rush somewhere at a speed of 8-10 meters per second. Having met a person or animal on their way, lightning can stay away from them and behave peacefully, they can circle around curiously, or they can attack and burn or kill, after which they either melt away as if nothing had happened, or explode with a terrible roar. However, despite frequent stories of those injured or killed by ball lightning, their number is relatively small - only 9 percent. Most often, lightning, after circling around the area, disappears without causing any harm. If it appears in the house, it usually “leaks” back out onto the street and only melts there.
There have also been many unexplained cases where ball lightning is “tied” to a specific place or person and appears regularly. Moreover, in relation to a person, they are divided into two types - those that attack him every time they appear and those that do not cause harm or attack people nearby. There is another mystery: ball lightning, having killed a person, leaves absolutely no trace on the body, and the corpse does not become numb and does not decompose for a long time...
Some scientists say that lightning simply “stops time” in the body.
Ball lightning from a scientific point of view
In 1999-2001, employees of the St. Petersburg Institute of Nuclear Physics of the Russian Academy of Sciences (St. Petersburg, Gatchina), Anton Ilyich Egorov and Gennady Dmitrievich Shabanov, obtained a compact spherical plasmoid with a lifetime of up to half a second and with a diameter of 12-15 cm. Ball lightning is a unique and peculiar phenomenon. Over the history of mankind, more than 10 thousand evidence of meetings with “intelligent balls” has accumulated. However, scientists still cannot boast of great achievements in the field of research of these objects. There are a lot of disparate theories about the origin and “life” of ball lightning. From time to time, in laboratory conditions, it is possible to create objects that are similar in appearance and properties to ball lightning - plasmoids. However, no one was able to provide a coherent picture and logical explanation for this phenomenon.
The most famous and developed earlier than the others is the theory of Academician P. L. Kapitsa, which explains the appearance of ball lightning and some of its features by the emergence of short-wave electromagnetic oscillations in the space between thunderclouds and the earth's surface. However, Kapitsa was never able to explain the nature of those very short-wave oscillations. In addition, as noted above, ball lightning does not necessarily accompany ordinary lightning and can appear in clear weather. However, most other theories are based on the findings of Academician Kapitsa.
A hypothesis different from Kapitza’s theory was created by B. M. Smirnov, who claims that the core of ball lightning is a cellular structure with a strong frame and low weight, and the frame is created from plasma filaments.
D. Turner explains the nature of ball lightning by thermochemical effects occurring in saturated water vapor in the presence of a sufficiently strong electric field.
However, the theory of the New Zealand chemists D. Abrahamson and D. Dinnis is considered the most interesting. They found that when lightning strikes soil containing silicates and organic carbon, a tangle of silicon and silicon carbide fibers is formed. These fibers gradually oxidize and begin to glow. This is how a “fire” ball is born, heated to 1200-1400 °C, which slowly melts. But if the temperature of the lightning goes off scale, it explodes. However, this harmonious theory does not confirm all cases of lightning occurrence.
For official science, ball lightning still continues to be a mystery. Maybe that’s why so many pseudo-scientific theories and even more fictions appear around it.
Pseudo-scientific theories about ball lightning
At a minimum, ball lightning is considered a device for exploring our world. At the most, energy entities that also collect some information about our planet and its inhabitants. We will not tell here stories about demons with burning eyes, leaving behind the smell of sulfur, hell dogs and “fire birds”, as the spherical ones were sometimes imagined lightning. However, their strange behavior allows many researchers of this phenomenon to assume that lightning “thinks.” At a minimum, ball lightning is considered a device for exploring our world. At the most, by energy entities that also collect some information about our planet and its inhabitants.
An indirect confirmation of these theories can be the fact that any collection of information is work with energy.
And the unusual property of lightning to disappear in one place and appear instantly in another. There are suggestions that the same ball lightning “dives” into a certain part of space - another dimension, living according to different physical laws - and, having dumped information, appears again in our world at a new point. And the actions of lightning in relation to living creatures on our planet are also meaningful - they do not touch some, they “touch” others, and from some they simply tear out pieces of flesh, as if for genetic analysis!
The frequent occurrence of ball lightning during thunderstorms is also easily explained. During bursts of energy - electrical discharges - portals from a parallel dimension open, and their collectors of information about our world enter our world...
What to do when encountering ball lightning?
This photo of ball lightning was taken by a student from Nagano, Japan in 1987. The main rule when ball lightning appears - whether in an apartment or on the street - is not to panic and not to make sudden movements. Don't run anywhere! Lightning is very susceptible to air turbulence that we create when running and other movements and which pull it along with us. You can only get away from ball lightning with a car, but not under your own power.
Try to quietly move out of the lightning's path and stay away from it, but do not turn your back on it. If you are in an apartment, go to the window and open the window. With a high degree of probability, lightning will fly out.
And, of course, never throw anything into ball lightning! It can not just disappear, but explode like a mine, and then serious consequences (burns, injuries, sometimes loss of consciousness and cardiac arrest) are inevitable.
If ball lightning touched someone and the person lost consciousness, then he must be moved to a well-ventilated room, wrapped warmly, given artificial respiration and be sure to call an ambulance.
In general, technical means of protection against ball lightning as such have not yet been developed. The only “ball lightning rod” that currently exists was developed by the leading engineer of the Moscow Institute of Heat Engineering B. Ignatov. Ignatov's ball lightning rod has been patented, but only a few similar devices have been created; there is no talk of actively introducing it into life yet.
Therefore, take care of yourself, and if you encounter ball lightning, do not forget about the recommendations
From time to time, nature presents us with such riddles, the answers to which researchers have been unsuccessfully searching for for centuries. These phenomena also include ball lightning - certain luminous spheres that appear and quickly disappear, plunging eyewitnesses into horror and dismay.
Everything happens so instantly that witnesses sometimes do not have time not only to see, but also to understand what happened. Are ball lightning, as once thought, intelligent beings or, on the contrary, are we talking about a natural object whose behavior can be explained in terms of normal science?
For now, one thing can be said: neither science, nor parascience, nor more or less ingenious hypotheses and theories have fully explained this phenomenon...
This phenomenon has been known since ancient times. In the 6th century, Saint Gregory of Tours was attending a church ceremony when suddenly a glowing ball of fire appeared in the air above the heads of the priests and parishioners. According to the chronicles, his appearance made such a strong impression that the participants in the service fell to the ground in fear. There is nothing strange in the fact that these ordinary people thought that a miracle had happened. The behavior of current witnesses to the appearance of ball lightning is often not much different from the actions of our distant ancestors.
“At the end of July 1979, we were caught in a thunderstorm in the forest,” says T. Meteleva from the Amur region. “Suddenly, right in front of me, on the ground, I saw a golden fireball. Out of surprise, I froze with my arm and leg raised for the next step, and at that moment the ball exploded. It was as if a fire had flared up under my feet. I felt that my arm and leg, which were above the explosion site, began to go numb and lose their strength. This went on for about four hours, then it all went away.”
Whether it was a miracle or not, one thing is clear: church observers were luckier than others, one might say, less qualified in this kind of matter. Why? Yes, for one simple reason: thanks to the reputation of the priests, no one dared to dismiss their evidence, calling it a hallucination or even a deliberate lie.
And this was precisely the fate that befell the messages of many others at first - ridicule, caustic criticism, but for the most part - Olympian indifference. The same applied to stories about falling stones engulfed in flames; the possibility of this was rejected by the maxims of celebrities like the one uttered by the French scientist Lavoisier: “Rocks cannot fall from the sky, because there are no stones in the sky.” It seems that the fireballs had no less right to exist; however, they dared to fly over the heads of priests of very high rank with impunity.
Speaking of qualified observers - at least from the point of view of their social significance - one cannot help but recall the history of which such a special person as Pedro II of Alcántara, who served as Emperor of Brazil for almost fifty years, became the hero. Once he found himself at a meeting of the French Academy of Sciences, dedicated to the consideration of a lot of evidence of fireballs that woke up in a real shower in 1890. Observers, who came mainly from peasants, said that they had seen such objects many times. Their testimonies even included stories of how the balls entered homes through chimneys and windows, hung around the house for a short time, and then left it or exploded inside with violent force.
Having examined and heatedly discussed some of the statements of eyewitnesses, one of the academicians came to the categorical conclusion that all these observations, as carried out by ordinary villagers, have no scientific value. And then Don Pedro, who was an honorary member of the Academy, rose from his seat and told his illustrious opponent that he himself had seen such balls with his own eyes - exactly the same as those that the peasants talked about!
Although he was an emperor, it seems that the scientific views of the academicians only slightly wavered after the words of Don Pedro. After all, as a certain scientist, whose name it is better to prudently forget, put it on another occasion: “If the facts do not correspond to my theory, the facts must be changed.” And this is not just about an anecdote. For example, it is enough to refer to the story of the Canadian scientist Edward Argyle. This gentleman dealt with fireballs like this. He simply classified them as “optical illusions,” which supposedly occur when an observer looks at ordinary lightning at close range. The flash turns out to be so bright that it confuses the observer, and he begins to believe that he saw a round luminous object. But what can we say about those phenomena that occurred over a considerable period of time, so that the balls even managed to burn those who came into physical contact with them? Yes, you can simply ignore them! “If the glowing ball is in fact an optical illusion,” says Argyle, “then it does not seem to me that it would be unreasonable to characterize all such reports as “unreliable.” Based on similar arguments, the “Procrustean bed” was activated in Greco-Roman mythology. If someone's legs protruded beyond the edge of the bed, there was no need to bother making the furniture bigger: it was enough to just trim a little at the top or bottom of the person himself.
But nevertheless, there is no need to exaggerate when talking about the distrust of scientists who lived in those days. Perhaps the simplest explanation for this is based on this: both meteorites and fireballs are extremely rare phenomena in nature; consequently, the number of their eyewitnesses is also small. Fortunately, in the subsequent era there were witnesses who deserved the same confidence as in the old days. Including scientists.
Examples? In 1867, Russian chemist M. T. Dmitriev observed a fireball on the Onega River. In 1933, Dr. Stanley Singer, an expert in assessing the damage caused by storms, accidentally photographed “spherical lightning” while recording various electrical discharges during a storm (his book “The Nature of Ball Lightning” was published in Russian translation by the Mir publishing house in 1973 year). Even in the prestigious journal Nature in 1991, a work by British physicist Brian Pippard appeared, in which he claimed that, together with other scientists, he had seen various types of these luminous balls. These are just a few examples out of many.
It is obvious, however, that no one has yet understood the nature of this phenomenon, and the best confirmation of this is that no one has been able to reproduce it in the laboratory, although three or four years ago a group of Japanese scientists obtained similar “objects.” The only thing that can be stated with certainty today is that the nature of this phenomenon is electrical and in most cases - but not in all - it accompanied a storm. Most observations describe luminous spheres of small diameter - from 10 to 30 cm - white, red, orange and, slightly less often, green or blue. Some theoretical physicists also talk about “ball lightning” and resort to the concept of plasma to explain its origin. This plasma, often defined as the fourth state of matter—neither solid, liquid, nor gas—occurs as a sphere of ionized gas at very high temperatures. Plasma is the main component of stars, and plasma also consists of those smallest and most powerful dazzling balls that are formed in thermonuclear reactors for a fraction of a second, when oxygen nuclei, when merging with each other, release huge quantities of energy: in short, stars in miniature. It is clear that if these shining spheres are related to plasma, then a scientific problem of no small magnitude arises. After all, if we do not yet have the inexhaustible energy that the thermonuclear reaction provides us, then we cannot know how to maintain a fireball within the physical boundaries of the reactor. You cannot place it in any container of the substance without the container itself evaporating. In fact, the researchers keep it suspended in space using powerful magnetic fields of such current strength—a so-called “magnetic coupling device”—that their work takes up a good portion of the energy generated by the reactor itself. But ball lightning seems to float through the air without any worries or external sources of energy. Where did plasma get such audacity to exist outside of an appropriately equipped laboratory?
The selectivity of ball lightning remains unclear and inexplicable to science. One of them, for example, entered the house of a certain Kononov from Kolpin through the kitchen window. She flew inside, spun around in a cast iron with water standing on a hot stove, and flew out of the same window without touching anyone in the room. And on the street she killed two people, a horse and melted a piece of rail.
Why do the fiery spheres wander impudently, fearing nothing when violating both physical laws and the air borders of states?
In 1960, a US Air Force KC-97 cargo plane was flying at an altitude of almost six kilometers when an uninvited guest showed up on board: a luminous sphere almost a meter in diameter that entered the cabin, flew back and forth between crew members, and then departed back to sky, without causing the slightest harm to both people and instruments and the aircraft body.
This story is also good for illustrating another interesting characteristic of the phenomenon traditionally attributed to souls in purgatory: fireballs are also able to pass through walls and any other material obstacles that get in their way. If, as it seems, this is indeed the case, then they have some kind of “insight” at the atomic level. An object passes through matter without colliding with subatomic particles. But let's not be too surprised: radioelectric waves do the same thing, and at the same time they are not aliens from another dimension.
Can we include in the category of fireballs those mysterious spheres of light known as “foo-fighters” that have been talked about so much lately? Without entering into a discussion of all UFO sightings, it may be assumed that some of these objects do indeed belong to our natural wonders, the whole operation of which, as we have already seen, seems to consist only of a calm supernatural passage, and which in no way intend to harm their frightened observers.
Scientific hypotheses
The fact that their flight is calm does not mean that it is so harmless and safe for observers. After all, physicists believe that with such a superconcentration of energy, the temperature can reach 30 thousand degrees Celsius. Then the question is: if the temperature is really so high, then why, instead of rising like jets of hot air, do these balls fly both vertically and horizontally? And for what reason does this intense heat not immediately spread around? In addition, it may be recalled that these fireballs were sometimes observed for an unusually long time. The latest interpretation of the nature of the origin of this phenomenon was put forward by Antonio Fernandez-Rañada, a famous Spanish scientist from the Complutene University of Madrid, and appeared on the pages of the Nature magazine. Fernandez-Rañada's hypothesis is based on the theory of the electromagnetic node, which he developed five years ago. It is difficult to retell it without resorting to mathematical formulas, but we are talking about a formation similar to a ball, only consisting not of threads of yarn, but of magnetic field lines. As the name implies, this is a combination of magnetic and electric fields, ensuring the continuation of one of them while the other exists, and so on. When these fields combine and mutually reinforce each other, a strong pressure is generated within them, holding the entire structure. In short, a type of “magnetic bottle” similar to what we have already described when talking about a thermonuclear reactor. Energy accumulates inside for an unusually long time for this type of phenomenon. If this is the case, all that remains is to reproduce something similar in the laboratory.
So-called ball lightning - BL - often appears naturally during a storm. They have also been observed to be associated with tornadoes in circumtropical latitudes, more often in the United States than in Europe. Therefore, most observations were carried out in the USA. And at the same time, so-called technological phenomena were recorded, such as, for example, electrical discharges of high strength but low voltage. The shape of the CMM, apparently, is not spherical, but similar to a pretzel or donut with a very small central hole. The light of ball lightning is blinding, which makes it difficult to determine the shape, especially when the “doughnut” is compressed from the sides and its “pipe hole” is flattened. Then it really looks a lot like a ball. This is a “ring-shaped vortex plasmoid”, in which a semblance of internal rotational motion occurs. It maintains its shape, adhesion and stability for a relatively long time.
This is the same type of phenomenon as the smoke rings that clever smokers can produce, which anyone can produce by blowing it through a hole in a cardboard box and then shaking it.
The movement of such a ring of smoke depends not on the force of the smoker's initial blow, but on the further rotation of this blow in the air. Let us imagine the rotation of such a “pipe closed on itself” and we will see that its outer part has a much larger surface than the inner one. In BLs, slowly moving along bizarre trajectories, something similar happens.
The most amazing thing about ball lightning is its ability to penetrate, without losing its shape, into military aircraft, whose cockpits consist mostly of crystalline structures of plastics united by metal “veins”, that is, a “tunnel effect” occurs. In non-thunderstorm times, such phenomena in airplanes can begin with “St. Elmo’s fire,” which, under certain humidity conditions, takes on the following form: the edges, under the influence of internal pressure, trying to avoid external compression, curl up, and a semblance of a vortex is obtained. And it is precisely this vortex that makes up the core of the BL, which in this case does not need a thunderstorm at all as a current generator. During a storm, a spark that reaches the aircraft punches a micro-hole in it and forms a BL in the fuselage, just like the smoke rings that escape from the pores in a cardboard box.
In submerged submarines, equipped with batteries of enormous capacity and currents of thousands of amperes (sometimes up to 100 thousand), these spark plugs are likely formed when switches malfunction, when the current is abruptly interrupted to reverse the ship. These smaller BLs, even natural ones, used to wander inside the hull for about 30 seconds, penetrating into different compartments before exploding. They were green, perhaps because they carried copper atoms from the switches that produced them. Commander Stuart Albert managed to photograph one of these in the submarine's engine room.
Even the brilliant electromechanic Nikola Tesla accidentally observed BL in large induction coils with a spherical electrode, which received his name. Lightning originated in these coils of high voltage and absolutely insignificant current. Other researchers have used cathodes on a disk or similar conical tube. Magnetic fields of opposite polarity are also associated with BL, and Tesla himself could generate them on his coils.
The Japanese, like T. Matsumoto, who were busy studying the mechanisms of energy release while working on the “cold thermonuclear”, obtained microscopic plasmoids-BL with a diameter of 9.5 microns on the surface of the electrodes of galvanic cells and were even able to photograph them.
We thus find ourselves faced with BLs of various sizes, from microscopic to those formed in tornadoes, 15 m in size, and medium ones, which were observed in airplanes and submarines.
If we turn to the largest BLs that occur during such natural phenomena as tornadoes, it turns out that the main problem of their study is that most people who had the misfortune of finding themselves inside did not survive, and those who were lucky enough were not prepared for scientific observations. This happened with the Silverton tornado, which killed 20 people in Texas on May 15, 1957.
An observer who found himself at its center said that he saw light in the form of a huge ring, from 12 to 15 m in diameter, 12 meters above the ground. Luckily for science, there has been at least one case where two meteorologists managed to survive being inside a tornado; it seems that their professional curiosity outweighed their fear, and they were able to make interesting observations.
The commander of the Il-18M airliner M. Matyushin says:
The plane took off from Riga to Moscow. Two minutes after takeoff, at an altitude of 600 meters, an orange ball half a meter in diameter suddenly appeared in front of the car. Seeing him, I said: “Look, ball shiya! Now it will hit us." Before I could say these words, a bright blue flash blinded the crew of the plane.
According to an eyewitness standing on the ground, after 10-15 seconds, when the plane disappeared into the low dark clouds, a white bright ball flew at an altitude of 50-100 meters. There was a long, foggy trail behind him. Three seconds later there was a roar of thunder.
Many residents of Riga also saw walking lightning at this time. According to them, it was about a meter long, had the colors of the rainbow with a predominance of yellow, and was surrounded by white fog. But, as meteorologists claimed, there was no thunderstorm in Riga that day...
Most tornadoes do not glow. The column or trunk that descends from the clouds may be dark due to the industrial waste carried along with it, but its black, like a firebrand, color indicates that some strange phenomenon is happening, during which all the light from the outside is absorbed. However, in all cases there is an inner light, although most often the dark outer layer prevents it from being seen.
It is known that there are also glowing tornadoes, and this can be especially noticeable in those rare cases when it occurs at night. F. Montgomery; One of those meteorologists who visited the Black Well tornado in Oklahoma on May 25, 1955, described plasmoids 120 m wide, and located 250 m above the ground, blinding like a blowtorch and spinning dizzyingly. The inner part of the tornado's trunk was torn off the ground by its roots, which began to rotate and scatter smaller ball lightning. Another meteorologist, R. Hall, who was inside the 1948 Texas tornado, saw a column of light that was separated from transparent, dark walls. This column was formed by rings, which, when lowered, turned into ball lightning.
The formation of BL in the lower part of the tornado, where they break off the trunk, is a phenomenon observed by many, since it is clearly visible from the outside. Measurements of electric and magnetic fields recorded near the tornadoes showed the release of an inexplicably large amount of energy, greater than that of a major storm, as evidenced by the immediate rise in temperature in their vicinity by as much as three degrees Celsius.
Another unexplained phenomenon that suggests strange curvatures of space-time along with gravitational anomalies is the lifting of people and cars into the air without any wind, as if attracted by ball lightning several meters in diameter. Dr. Pettier noted that he was experiencing some kind of pressure from above and at the same moment he found himself above the ground, although there was no wind - as if lifted by an invisible hand. During the same tornado, round holes in glass similar to those photographed by Matsumoto were photographed. Some publications on “cold thermonuclear fusion” included references to “luminous tornadoes,” which is nothing strange from the point of view of experts.
Other strange phenomena associated with tornadoes and BLs are the penetration of matter. For example, one car tire ended up stuck on trees whose branches were not touched. Such phenomena confirm, although they do not explain, the conduction of BL through solid objects. In August 1924, in the village of Gvozdki, Valdai district, Novgorod region, an incident with lightning occurred. Around two o'clock in the afternoon it began to rain heavily with gusty winds. There were two people in the Savushkins’ house: the owner’s adult daughter Anna and 10-year-old son Alyosha. The boy sat on a bench and looked out the window. Near the stove stood a kneading bowl covered with a tablecloth.
Anna went out into the hallway, and then a loud crash was heard. She fell and, waking up, ran into the hut. An incredible picture appeared before her eyes: there was no one on the windows, no boy either! In fright, Anna ran to the window and saw: Alyosha was sitting by the fence behind the road, and three frames were lying nearby and there was a kneading bowl with dough! Alyosha escaped with minor bruises, and the dough didn’t even spill.
As a result, what had until now been a meteorological curiosity began to be studied seriously. Tornadoes themselves, in their more familiar form, even without the appearance and abilities of a BL, are one of the most mysterious natural phenomena. But when tornadoes find themselves in the state of plasma and in the form of a BL, as we have already seen, they acquire almost magical properties. The more interesting it is to study them. Well, that's all we have left. For only one thing is reliably known about the nature of ball lightning - we know little reliably. Now let’s speak to Doctor of Physics and Mathematics Boris Smirnov:
Ball lightning is a mysterious natural phenomenon, observations of which have been reported for several centuries. Great progress in the study of this phenomenon has been achieved in the last ten to fifteen years. Currently, we have several independent sets of descriptions of ball lightning, which allows us to provide reliable quantitative information about its parameters. Although the fundamental laws of its nature are clear, the problem of ball lightning cannot be considered solved, because there are no specific ways to create it in laboratory conditions. However, the study of the mysterious phenomenon is progressing due to the development of related fields of physics and chemistry.
Research into ball lightning in attempts to understand its nature has been ongoing for several centuries. The mystery of this phenomenon, combined with the unexpectedness of the appearance of ball lightning and the strong emotional impression it makes, can lead to extreme conclusions about this phenomenon. Suspicious people claim that ball lightning is controlled by a higher intelligence, that it is a creature or is associated with aliens from outer space. Transformed into science, these extreme views explain the nature of ball lightning based on cosmic radiation, antimatter and other exotic elements that, as in the first case, cannot be reproduced. And although a sober mind cannot take such points of view seriously, they will disappear only when a sufficiently natural and convincing explanation for this phenomenon can be found. And it will become convincing when they learn to reproduce it in laboratory conditions.
The question arises: what will understanding the nature of ball lightning give us? Let's turn to fantastic works. In one of them, ball lightning is used as a source of energy. One ball lightning powers a tractor for a year, you just need to make sure that it remains dry: as soon as the ball lightning gets wet, it explodes.
In another work, ball lightning is used for military purposes: controlled lightning brings a lot of trouble to the enemy. In the third, ball lightning is used as a radiation source - a lamp without wires that can be hung anywhere.
However, I believe that the main interest in ball lightning research lies elsewhere. It is natural to assume that the nature of ball lightning is based on known physical laws, but their combination leads to a new quality that we do not understand. Having understood this, we will find real what previously seemed exotic, and we will provide qualitative ideas that may have analogues in other physical processes and phenomena. Gaining such insights enriches science and is valuable in the research at hand. This is the logic of the development of science in general, and the accumulated experience in studying the nature of ball lightning confirms this.
Despite the difficulties in understanding the nature of tent lightning, this problem is in a more favorable position than the study of a number of other atmospheric phenomena (for example, “flying saucers”, or UFOs). This is due to the fact that there are clear signs by which ball lightning can be separated from other phenomena.
Along with the information obtained from processing reports of observations of ball lightning, monographs that provide a comprehensive analysis of this phenomenon are of scientific value. S. Singer’s book “The Nature of Ball Lightning” contains a description of various theoretical models of ball lightning; J. Barry’s book “Ball Lightning and Bead Lightning” presents laboratory studies of phenomena that model individual properties of ball lightning, photographs are collected and analyzed, and a large bibliography, which includes about two thousand publications. In general, all this scientific literature allows us to create a reliable image of ball lightning and determine the numerical parameters characterizing its properties.
The research carried out allows us to unambiguously answer the question of whether ball lightning exists. At one time it was suggested that it could be an optical illusion. This hypothesis is repeated in our time. Its essence is that a strong flash of linear lightning, due to photochemical processes, can leave a mark on the retina of the eye, which remains on it in the form of a spot for 2-10 seconds. This spot is perceived as ball lightning.
This statement is rejected by all authors of reviews and monographs on CMM, who have processed a large number of observations. Firstly, each of the numerous descriptions of observations of ball lightning, used as evidence in favor of the reality of its existence, contains a lot of detail. These details could not have arisen in the brains of observers as an aftereffect of a flash of linear lightning. Secondly, there are a number of reliable photographs of ball lightning, which objectively proves the reality of its existence. Thirdly, in some cases, ball lightning leaves behind traces that cannot be associated with linear lightning. Thus, based on the totality of data on observations of ball lightning and their analysis, we can say with complete confidence that it is a very real phenomenon.
The next question to consider is: what is the reliability of the reported observations of ball lightning? There are a number of examples when one can compare the description of an observed fact by an eyewitness and a report about it in the press. A very illustrative case of this kind is given in the book by I. M. Imyanity and D. Ya. Tikhoy. In the newspaper “Komsomolskaya Pravda” dated July 5, 1965, it published an article “Fiery Guest”, which describes the behavior of ball lightning with a diameter of approximately 30 cm, observed in Armenia, the article, in particular, says: “After circling the room, the fireball penetrated through the open door to the kitchen and then flew out the window. Ball lightning hit the ground in the yard and exploded. The force of the explosion was so great that the adobe house that stood about fifty meters collapsed. Fortunately, no one was hurt." Regarding the behavior of ball lightning, a request was sent to the Department of Hydrometeorological Service of the Armenian SSR. The answer says that ball lightning was actually observed. The nature of the movement of lightning in the apartment is described, which had nothing to do with the text of Komsomolskaya Pravda. At the end of the answer it is said: “As for the adobe house described in the newspaper, this half-ruin has nothing to do with ball lightning.” Unfortunately, this did not end there. The correspondent's report formed the basis for estimating the energy of ball lightning, which was approximately 10 to the 9th power of kcal (a ton of explosives!). This estimate was taken into account in many publications on the energetics of ball lightning, including books by Singer and Barry. It is clear that such misinformation is harmful, especially since we have few cases where, based on the consequences of ball lightning, its energy parameters can be restored.
There are a number of other newspaper reports, verification of which showed that the facts stated are not entirely true. This is understandable - reports of ball lightning can be classified as sensational, and the associated haste can lead to distortion of information. Therefore, newspaper publications about CMM should be treated with some caution.
How often does ball lightning occur and what is the probability of an individual observing it? Experience shows that it is not so small. For example, a survey conducted by Raleigh found that among 4,400 NASA employees, 180 had encountered ball lightning. I. Stakhanov, based on the data he received, believes that the average probability for a person to see ball lightning during his life is approximately 10 to the power of minus 3. J. Barry estimates the probability of the appearance of ball lightning by saying that on average 100-1000 ball lightning should exist on the globe every hour. This figure is average over time and space. In thundery weather, the likelihood of ball lightning occurring is higher. It also depends on the geography of a particular area.
Let us consider the nature of the decay of ball lightning. Observations show that its existence can end with an explosion or it can quietly go out. Moreover, according to McNally, in those observations of ball lightning when its end was recorded, 309 explosions and 112 cases of slow decay were observed. According to Raley, in 54 cases the lightning quietly died out, in 24 it exploded, and according to W. Charman, in 25 cases it quietly died out, and in 26 it exploded. I. Stakhanov reports 610 observations of ball lightning, when the end of its life occurred in front of eyewitnesses. In 835 cases it exploded, in 78 it fell apart, and in 197 it quietly died out.
As can be seen, slightly different terminology and data processing make it difficult to compare these messages. From them we can conclude that most often the existence of ball lightning ends with an explosion, and the likelihood of its slow extinction is somewhat less likely. However, it is not uncommon for ball lightning to break into pieces.
Most often, a ball lightning explosion occurs without consequences. I. Stakhanov selected 335 reports of explosions, among which only 34 were accompanied by damage. Most often this is the splitting of trees, wooden poles, piles (19 cases). Sometimes it pierces light walls and partitions. If there were people in the explosion zone, then in most cases it ended well. Nevertheless, according to Stakhanov, out of 1000 descriptions of ball lightning he processed, five resulted in human casualties, although this was not always the result of its mediocre impact. The most tragic of the known ones was the explosion of ball lightning, described in the Literary Gazette on December 21, 1983, which said: “Twenty-three women and one man were working in Sunny Valley. The valley was surrounded by mountains. Suddenly a cloud appeared in the sky. The cloud was unwieldy. As if illuminated from within. Whip blind rain. People rushed to the mulberry tree for shelter! Ball lightning was already here.”
The note is dedicated to the courage and nobility of the people who came to the aid of the victims. However, this note does not say what the ball lightning was that exploded and scattered the people hiding under the tree. Most of them lost consciousness. Help was prompt, but three people died without regaining consciousness.