Examples: multiplication table from 2 to 5. Two-digit multiplication by two-digit
Read also
Tasks on the topic: "Multiplication of numbers. Multiplication table"
Additional materials
Dear users, do not forget to leave your comments, reviews, wishes. All materials have been checked by an antivirus program.
Teaching aids and simulators in the online store "Integral" for grade 2
Mathematics, Russian, computer science for grades 1-4, training simulators "MIR"
"Mathematics is a piggy bank of knowledge", a teaching aid for elementary school
Multiplication of numbers
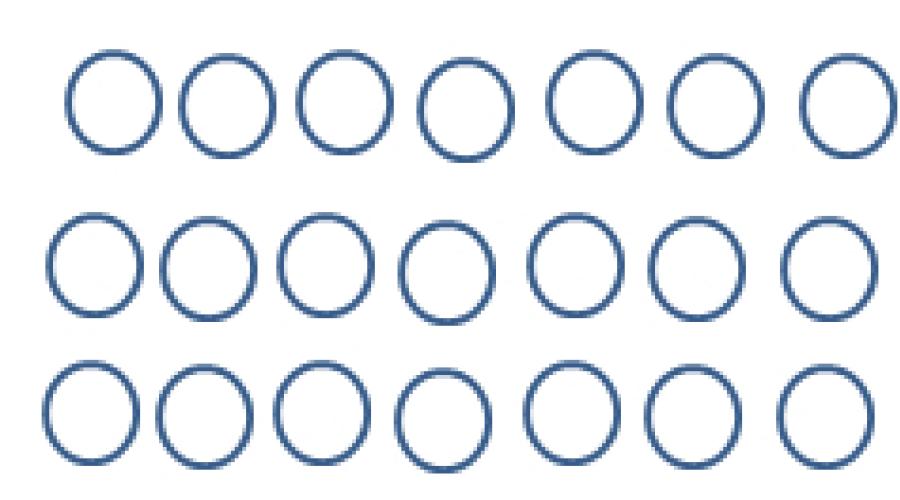
1. Look at the pictures and make examples of addition and multiplication.
B) 
2. Replace addition by multiplication and solve the examples.
| 5 + 5 + 5 = | 6 + 6 = | 8 + 8 + 8 + 8 = | 3 + 3 + 3 = |
| 4 + 4 + 4 = | 5 + 5 + 5 + 5 + 5= | 6 + 6 = | 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3= |
3. According to the picture, compose a text problem, which is solved by multiplication.

Solving problems
1. Mitya lives in a seven-story building. The height of each floor is three meters. Determine the height of the house in which Mitya lives, in meters.
2. The workers put up 6 fence posts. The distance between the posts is four meters. How long is the fence?
3. One package contains 8 handkerchiefs. How many handkerchiefs are there in seven packs?
4. 9 cars arrived at the health camp. There were 4 children in each car. How many children were brought to the camp in total?
5. Raspberry bushes grow in the garden. They are planted in 8 rows with 5 bushes in each row. How many raspberry bushes are there in the garden?
6. There are 8 tables in the school cafeteria. There are 54 chairs around each table. How many chairs are there in the dining room?
7. There are cars in the 8-row parking lot. How many cars are there in the parking lot if 7 cars fit in one row?
8. A column of soldiers is marching across the square. The column consists of nine rows of eight soldiers in each row. How many soldiers are there in the column?
9. Kolya has 7 files of the Murzilka magazine. Each binder contains 6 magazines. How many Murzilka magazines does Kolya have?
10. 7 years old Pasha has been collecting ninja turtles. Every year he collects 5 collections. How many collections does Pasha have?
11. Dad brought 4 bags of apples from the market, each bag contains 11 apples. How many apples did dad bring?
Multiplication table
1. Perform multiplication.
| 9 * 2 = | 7 * 4 = | 8 * 6 = | 3 * 9 = |
| 6 * 5 = | 6 * 7 = | 7 * 4 = | 8 * 2 = |
| 5 * 9 = | 8 * 8 = | 7 * 7 = | 8 * 3 = |
| 8 * 5 = | 4 * 4 = | 6 * 3 = | 5 * 4 = |
2. Replace the product with the sum and solve the examples.
| 4 * 9 = | 5 * 8 = | 6 * 7 = | 7 * 6 = |
| 8 * 5 = | 6 * 4 = | 5 * 3 = | 4 * 2 = |
| 8 * 5 = | 3 * 4 = | 2 * 3 = | 9 * 2 = |
Division is one of the four basic mathematical operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication). Division, like other operations, is important not only in mathematics, but also in everyday life. For example, you will hand over money to the whole class (25 people) and buy a gift for the teacher, but you will not spend everything, there will be change. So you will need to divide the change among all. The division operation comes in to help you solve this problem.
Division is an interesting operation, as we will see with you in this article!
Division of numbers
So a little theory and then practice! What is division? Division is splitting something into equal parts. That is, it can be a bag of chocolates that needs to be split into equal parts. For example, there are 9 sweets in a bag, and the person who wants to get them - three. Then you need to divide these 9 chocolates among three people.
It is written like this: 9: 3, the answer will be the number 3. That is, dividing the number 9 by the number 3 shows the number of three numbers contained in the number 9. The opposite action, a test, will be multiplication. 3 * 3 = 9. Right? Absolutely.
So consider example 12: 6. First, let's name each component in the example. 12 - dividend, that is. a number that can be divided into parts. 6 is the divisor, this is the number of parts by which the dividend is divided. And the result will be a number called "quotient".
Divide 12 by 6, the answer will be the number 2. You can check the solution by multiplying: 2 * 6 = 12. It turns out that the number 6 is contained 2 times in the number 12.

Division with remainder
What is division with remainder? This is the same division, only the result is not an even number, as shown above.
For example, divide 17 by 5. Since the largest number divisible by 5 to 17 is 15, the answer is 3 and the remainder is 2, and it is written like this: 17: 5 = 3 (2).
For example, 22: 7. In the same way, we determine the maximum number divisible by 7 to 22. This number is 21. The answer then will be: 3 and remainder 1. And it is written: 22: 7 = 3 (1).
Division by 3 and 9
A special case of division will be the division by the number 3 and the number 9. If you want to know whether a number can be divided by 3 or 9 without a remainder, then you need:
Find the sum of the digits of the dividend.
Divide by 3 or 9 (whichever you want).
If the answer is obtained without a remainder, then the number will be divided without a remainder.
For example, the number 18. The sum of the digits is 1 + 8 = 9. The sum of the digits is divisible by both 3 and 9. The number 18: 9 = 2, 18: 3 = 6. Divided without remainder.
For example, the number 63. The sum of the digits 6 + 3 = 9. Divisible by both 9 and 3. 63: 9 = 7, and 63: 3 = 21. Such operations are performed with any number to find out whether it is divisible with the remainder 3 or 9 or not.
Multiplication and division
Multiplication and division are opposite operations. Multiplication can be used as a test for division, and division as a test for multiplication. You can learn more about multiplication and master the operation in our article on multiplication. Which describes in detail the multiplication and how to do it correctly. There you will also find the multiplication table and examples for training.
Let's give an example of checking division and multiplication. Let's say the example is 6 * 4. Answer: 24. Then check the answer by division: 24: 4 = 6, 24: 6 = 4. Resolved correctly. In this case, the check is performed by dividing the answer by one of the factors.
Or an example is given for division 56: 8. Answer: 7. Then the check will be 8 * 7 = 56. Right? Yes. In this case, the check is performed by multiplying the answer by the divisor.

Division 3 class
In the third grade, division is just beginning. Therefore, third-graders solve the simplest problems:
Problem 1... A factory worker was given the task of arranging 56 cakes in 8 packs. How many cakes do you need to put in each package to get the same quantity in each?
Task 2... On New Year's Eve at school, children were given 75 sweets for a class of 15 students. How many sweets should each child get?
Problem 3... Roma, Sasha and Misha collected 27 apples from the apple tree. How many apples will each get if they are to be divided equally?
Problem 4... Four friends bought 58 cookies. But then they realized that they could not divide them equally. How many guys need to buy cookies so that everyone gets 15 pieces?
Division 4 class
The division in the fourth grade is more serious than in the third. All calculations are carried out by the method of division into a column, and the numbers that participate in the division are not small. What is long division? You can find the answer below:
Long division
What is long division? This is a method that allows you to find the answer to the division of large numbers. If prime numbers like 16 and 4 can be divided, and the answer is clear - 4. Then 512: 8 in the mind is not easy for a child. And to tell about the technique for solving such examples is our task.
Consider an example, 512: 8.

Step 1... Let's write the dividend and divisor as follows:

The quotient will be written as a result under the divisor, and the calculations under the dividend.
Step 2... We start division from left to right. First, we take the number 5: 
Step 3... The number 5 is less than the number 8, which means that it cannot be divided. Therefore, we take one more digit of the dividend:
Now 51 is more than 8. This is an incomplete quotient.
Step 4... We put a dot under the divider.

Step 5... After 51 there is another number 2, which means there will be one more number in the answer, that is. the quotient is a two-digit number. We put the second point:

Step 6... We start the division operation. The largest number that can be divided without a remainder by 8 to 51 is 48. Dividing 48 by 8, we get 6. Write the number 6 instead of the first dot under the divisor:

7 step... Then we write down the number exactly under the number 51 and put the “-” sign:

Step 8... Then subtract 48 from 51 and get the answer 3.

* 9 step*. We demolish the number 2 and write next to the number 3:

Step 10 Divide the resulting number 32 by 8 and get the second digit of the answer - 4.

So the answer is 64, no remainder. If we were dividing the number 513, then the remainder would be one.
Division of three-digit
Division of three-digit numbers is performed by long division, which was explained in the example above. An example of just the same three-digit number.
Division of fractions
Division of fractions is not as difficult as it seems at first glance. For example, (2/3) :( 1/4). The method for this division is quite simple. 2/3 is the dividend, 1/4 is the divisor. You can replace the division sign (:) with multiplication ( ), but for this you need to swap the numerator and denominator of the divisor. That is, we get: (2/3)(4/1), (2/3) * 4, this equals - 8/3 or 2 integers and 2/3 Let's give another example, with an illustration for better understanding. Consider fractions (4/7) :( 2/5):
As in the previous example, flip the divisor 2/5 and get 5/2, replacing division with multiplication. We get then (4/7) * (5/2). We make the reduction and the answer: 10/7, then we take out the whole part: 1 whole and 3/7.
Dividing a number into classes
Let's imagine the number 148951784296 and divide it by three digits: 148 951 784 296. So, from right to left: 296 - class of units, 784 - class of thousands, 951 - class of millions, 148 - class of billions. In turn, in each class, 3 digits have their own category. From right to left: the first digit is ones, the second digit is tens, the third is hundreds. For example, class of units - 296, 6 - units, 9 - tens, 2 - hundreds.

Division of natural numbers
Division of natural numbers is the simplest division described in this article. It can be with or without a remainder. The divisor and divisible can be any non-fractional, whole numbers. 
Take the course "Speeding Up Verbal Counting, NOT Mental Arithmetic" to learn how to quickly and correctly add, subtract, multiply, divide, square numbers and even extract roots. In 30 days, you will learn how to use easy tricks to simplify arithmetic operations. Each lesson has new techniques, clear examples, and helpful assignments.
Division presentation
Presentation is another way to visually show the topic of division. Below we will find a link to a great presentation that explains well how to divide, what division is, what is the dividend, divisor and quotient. Don't waste your time, but consolidate your knowledge!
Division examples
Easy level
Average level
Difficult level
Games for the development of oral counting
Special educational games developed with the participation of Russian scientists from Skolkovo will help improve the skills of oral counting in an interesting way.
Guess the operation game
The game "Guess the operation" develops thinking and memory. The main point of the game is to choose a mathematical sign for the equality to be true. There are examples on the screen, look carefully and put the desired "+" or "-" sign, so that the equality is correct. The sign "+" and "-" are located at the bottom of the picture, select the desired sign and click on the desired button. If you answered correctly, you collect points and keep playing.

Simplification game
Simplify develops thinking and memory. The main point of the game is to quickly perform a mathematical operation. On the screen, a student is drawn at the blackboard, and a mathematical action is given, the student needs to calculate this example and write an answer. Below there are three answers, count and click the number you need with the mouse. If you answered correctly, you collect points and keep playing.

Fast Add Game
The Fast Addition game develops thinking and memory. The main point of the game is to choose numbers, the sum of which is equal to a given number. This game is given a matrix from one to sixteen. A given number is written above the matrix, you need to select the numbers in the matrix so that the sum of these numbers is equal to the specified number. If you answered correctly, you collect points and keep playing.

Visual Geometry Game
The game "Visual Geometry" develops thinking and memory. The main point of the game is to quickly count the number of painted objects and select it from the list of answers. In this game, blue squares are shown on the screen for a few seconds, they must be quickly counted, then they are closed. Below the table there are four numbers written, you need to select one correct number and click on it with the mouse. If you answered correctly, you collect points and keep playing.

Piggy bank game
The game "Piggy bank" develops thinking and memory. The main point of the game is to choose which piggy bank has more money. In this game you are given four piggy banks, you need to count which piggy bank has more money and show this piggy bank with the mouse. If you answered correctly, then you collect points and continue to play further.

Fast Add Reload Game
The Fast Addition Reloading game develops thinking, memory and attention. The main point of the game is to choose the correct terms, the sum of which will be equal to a given number. In this game, three numbers are given on the screen and a task is given, add the number, the screen indicates which number needs to be added. You select the desired numbers from three digits and press them. If you answered correctly, then you collect points and continue to play further.

Developing phenomenal oral counting
We've just covered the tip of the iceberg, to get a better understanding of math - sign up for our course: Speed up verbal counting - NOT mental arithmetic.
From the course, you will not only learn dozens of techniques for simplified and quick multiplication, addition, multiplication, division, percent calculation, but also work them out in special tasks and educational games! Verbal counting also requires a lot of attention and concentration, which are actively trained when solving interesting problems.

Speed reading in 30 days
Increase your reading speed by 2-3 times in 30 days. From 150-200 to 300-600 words per minute or from 400 to 800-1200 words per minute. The course uses traditional exercises for the development of speed reading, techniques that speed up the work of the brain, the method of progressively increasing the speed of reading, the psychology of speed reading and the questions of the course participants are discussed. Suitable for children and adults reading up to 5000 words per minute.
Development of memory and attention in a child 5-10 years old
The course includes 30 lessons with helpful tips and exercises for child development. Each lesson contains useful advice, several interesting exercises, an assignment for the lesson and an additional bonus at the end: an educational mini-game from our partner. Course duration: 30 days. The course is useful not only for children, but also for their parents.
Super memory in 30 days
Memorize the necessary information quickly and for a long time. Wondering how to open a door or wash your hair? I am sure not, because this is part of our life. Easy and simple exercises to train your memory can be made part of your life and done little by little during the day. If you eat the daily ration of food at a time, you can eat in portions throughout the day.

Brain fitness secrets, train memory, attention, thinking, counting
The brain, like the body, needs fitness. Exercise strengthens the body, mental exercises develop the brain. 30 days of useful exercises and educational games to develop memory, concentration, intelligence and speed of reading will strengthen the brain, turning it into a tough nut to crack.

Money and Millionaire Mindset
Why are there problems with money? In this course, we will answer this question in detail, look deeper into the problem, consider our relationship with money from a psychological, economic and emotional point of view. From the course you will learn what you need to do to solve all your financial problems, start accumulating money and invest it in the future.
Knowledge of the psychology of money and how to work with it makes a person a millionaire. 80% of people with an increase in income take more loans, becoming even poorer. On the other hand, self-made millionaires will make millions again in 3-5 years if they start from scratch. This course teaches competent distribution of income and cost reduction, motivates to learn and achieve goals, teaches to invest and recognize a scam.

And multiplication. The multiplication operation is what will be discussed in this article.
Multiplication of numbers
Multiplication of numbers is mastered by children in the second grade, and there is nothing complicated about it. We will now look at multiplication with examples.
Example 2 * 5... This means either 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2, or 5 + 5. Take 5 twice or 2 five times. The answer, respectively, is 10.
Example 4 * 3... Likewise, 4 + 4 + 4 or 3 + 3 + 3 + 3. Three times 4 or four times 3. Answer 12.
Example 5 * 3... We do it in the same way as in the previous examples. 5 + 5 + 5 or 3 + 3 + 3 + 3 + 3. Answer 15.
Multiplication formulas
Multiplication is the sum of the same numbers, for example, 2 * 5 = 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 + 2 or 2 * 5 = 5 + 5. The formula for multiplication is:
Where, a is any number, n is the number of terms a. Suppose a = 2, then 2 + 2 + 2 = 6, then n = 3 multiplying 3 by 2, we get 6. Consider in the reverse order. For example, given: 3 * 3, that is. 3 multiplied by 3 - this means that the three must be taken 3 times: 3 + 3 + 3 = 9.3 * 3 = 9.
Abbreviated multiplication
Abbreviated multiplication - abbreviated multiplication in certain cases, and especially for this, formulas for abbreviated multiplication have been derived. Which will help to make calculations the most rational and fastest:
Abbreviated multiplication formulas
Let a, b belong to R, then:
The square of the sum of the two expressions is the square of the first expression plus twice the product of the first expression by the second plus the square of the second expression. Formula: (a + b) ^ 2 = a ^ 2 + 2ab + b ^ 2
The squared difference of the two expressions is the square of the first expression minus twice the product of the first expression by the second plus the square of the second expression. Formula: (a-b) ^ 2 = a ^ 2 - 2ab + b ^ 2
Difference of squares two expressions is equal to the product of the difference between these expressions and their sum. Formula: a ^ 2 - b ^ 2 = (a - b) (a + b)
Sum cube of two expressions is equal to the cube of the first expression plus three times the square of the first expression and the second plus three times the product of the first expression and the square of the second plus the cube of the second expression. Formula: (a + b) ^ 3 = a ^ 3 + 3a (^ 2) b + 3ab ^ 2 + b ^ 3
Difference cube two expressions is equal to the cube of the first expression minus three times the square of the first expression and the second plus three times the product of the first expression and the square of the second minus the cube of the second expression. Formula: (a-b) ^ 3 = a ^ 3 - 3a (^ 2) b + 3ab ^ 2 - b ^ 3
Sum of cubes a ^ 3 + b ^ 3 = (a + b) (a ^ 2 - ab + b ^ 2)
Difference of cubes two expressions is equal to the product of the sum of the first and second expressions by the incomplete square of the difference of these expressions. Formula: a ^ 3 - b ^ 3 = (a - b) (a ^ 2 + ab + b ^ 2)
Take the course "Speeding Up Verbal Counting, NOT Mental Arithmetic" to learn how to quickly and correctly add, subtract, multiply, divide, square numbers and even extract roots. In 30 days, you will learn how to use easy tricks to simplify arithmetic operations. Each lesson has new techniques, clear examples, and helpful assignments.

Multiplication of fractions
Considering addition and subtraction of fractions, the rule was sounded, bringing fractions to a common denominator in order to perform the calculation. When multiplying this do no need! When multiplying two fractions, the denominator is multiplied by the denominator, and the numerator by the numerator.
For example, (2/5) * (3 * 4). Let's multiply two thirds by one quarter. We multiply the denominator by the denominator, and the numerator by the numerator: (2 * 3) / (5 * 4), then 6/20, we make a reduction, we get 3/10.

Multiplication class 2
The second grade is just the beginning of the study of multiplication, so second graders solve the simplest problems to replace addition by multiplication, multiply numbers, learn the multiplication table. Let's consider the problems of multiplication at the level of the second grade:
Oleg lives in a five-storey building, on the top floor. The height of one floor is 2 meters. What is the height of the house?
The box contains 10 packs of cookies. There are 7 of them in each package. How many cookies are in the box?
Misha arranged his toy cars in a row. There are 7 of them in each row, and there are only 8 rows of them. How many cars does Misha have?
The dining room has 6 tables and 5 chairs are pushed back at each table. How many chairs are in the dining room?
Mom brought 3 bags of oranges from the store. The packages contain 22 oranges. How many oranges did Mom bring?
There are 9 strawberry bushes in the garden, and 11 berries grow on each bush. How many berries are there on all the bushes?
Roma put 8 pipe parts one after the other, the same size, 2 meters each. How long is the full pipe?
Parents brought their children to school on September 1. 12 cars arrived, each with 2 children. How many children did the parents bring in these cars?

Multiplication grade 3
In the third grade, more serious tasks are given. In addition to multiplication, Division will also be traversed.
Among the tasks for multiplication will be: multiplication of two-digit numbers, multiplication by a column, replacing addition by multiplication and vice versa.
Column multiplication:
Long multiplication is the easiest way to multiply large numbers. Consider this method using the example of two numbers 427 * 36.
![]()
Step 1... Let's write the numbers under each other, so that 427 is at the top, and 36 is at the bottom, that is, 6 under 7, 3 under 2.

Step 2... We start multiplication from the rightmost digit of the bottom number. That is, the order of multiplication is as follows: 6 * 7, 6 * 2, 6 * 4, then the same with a triple: 3 * 7, 3 * 2, 3 * 4.
So, first multiply 6 by 7, the answer is 42. We write it like this: since it turned out 42, then 4 are tens, and 2 are ones, the recording is similar to addition, which means we write 2 under the six, and add 4 to the number 427.

Step 3... Then we do the same with 6 * 2. Answer: 12. The first ten, which is added to the four of 427, and the second - one. Add the resulting two and four from the previous multiplication.

Step 4... Multiply 6 by 4. Answers 24 and add 1 from the previous multiplication. We get 25.
So, multiplying 427 by 6, the answer is 2562

REMEMBER! The result of the second multiplication must begin to be written under SECOND the number of the first result!
Step 5... We perform similar actions with the number 3. We get the multiplication answer 427 * 3 = 1281

Step 6... Then we add up the received answers during multiplication and get the final answer of multiplication 427 * 36. Answer: 15372.

Multiplication grade 4
The fourth class is the multiplication of only large numbers. The calculation is performed using the column multiplication method. The method is described above in accessible language.
For example, find the product of the following pairs of numbers:
- 988 * 98 =
- 99 * 114 =
- 17 * 174 =
- 164 * 19 =

Multiplication presentation
Download a multiplication presentation with simple exercises for second graders. The presentation will help children to better navigate this operation, because it is composed in a colorful and playful style - in the best way for teaching a child!
Multiplication table
The multiplication table is learned by every student in the second grade. Everyone should know it!

Take the course "Speeding Up Verbal Counting, NOT Mental Arithmetic" to learn how to quickly and correctly add, subtract, multiply, divide, square numbers and even extract roots. In 30 days, you will learn how to use easy tricks to simplify arithmetic operations. Each lesson has new techniques, clear examples, and helpful assignments.
Multiplication examples
Multiplication by one-to-one
- 9 * 5 =
- 9 * 8 =
- 8 * 4 =
- 3 * 9 =
- 7 * 4 =
- 9 * 5 =
- 8 * 8 =
- 6 * 9 =
- 6 * 7 =
- 9 * 2 =
- 8 * 5 =
- 3 * 6 =
Two-digit multiplication
- 4 * 16 =
- 11 * 6 =
- 24 * 3 =
- 9 * 19 =
- 16 * 8 =
- 27 * 5 =
- 4 * 31 =
- 17 * 5 =
- 28 * 2 =
- 12 * 9 =
Two-digit multiplication by two-digit
- 24 * 16 =
- 14 * 17 =
- 19 * 31 =
- 18 * 18 =
- 10 * 15 =
- 15 * 40 =
- 31 * 27 =
- 23 * 25 =
- 17 * 13 =
Multiplication of three-digit numbers
- 630 * 50 =
- 123 * 8 =
- 201 * 18 =
- 282 * 72 =
- 96 * 660 =
- 910 * 7 =
- 428 * 37 =
- 920 * 14 =

Games for the development of oral counting
Special educational games developed with the participation of Russian scientists from Skolkovo will help improve the skills of oral counting in an interesting way.
Game "Quick Counting"
A quick score game will help you improve your thinking... The essence of the game is that in the picture presented to you, you will need to choose the answer "yes" or "no" to the question "are there 5 identical fruits?" Follow your goal, and this game will help you with this.

Game "Mathematical matrices"
"Mathematical matrices" great exercise for the brain of children, which will help you develop his mental work, oral counting, quick search for the right components, attentiveness. The essence of the game lies in the fact that the player has to find a pair from the offered 16 numbers that will add up to the given number, for example, in the picture below, the given number is “29”, and the desired pair is “5” and “24”.

Numeric Reach Game
The number coverage game will strain your memory as you practice this exercise.
The essence of the game is to memorize a number, which takes about three seconds to memorize. Then you need to reproduce it. As you progress through the stages of the game, the number of numbers increases, you start with two and further.

Guess the operation game
The game "Guess the operation" develops thinking and memory. The main point of the game is to choose a mathematical sign for the equality to be true. There are examples on the screen, look carefully and put the desired "+" or "-" sign, so that the equality is correct. The sign "+" and "-" are located at the bottom of the picture, select the desired sign and click on the desired button. If you answered correctly, you collect points and keep playing.

Simplification game
Simplify develops thinking and memory. The main point of the game is to quickly perform a mathematical operation. On the screen, a student is drawn at the blackboard, and a mathematical action is given, the student needs to calculate this example and write an answer. Below there are three answers, count and click the number you need with the mouse. If you answered correctly, you collect points and keep playing.

Fast Add Game
The Fast Addition game develops thinking and memory. The main point of the game is to choose numbers, the sum of which is equal to a given number. This game is given a matrix from one to sixteen. A given number is written above the matrix, you need to select the numbers in the matrix so that the sum of these numbers is equal to the specified number. If you answered correctly, you collect points and keep playing.

Visual Geometry Game
The game "Visual Geometry" develops thinking and memory. The main point of the game is to quickly count the number of painted objects and select it from the list of answers. In this game, blue squares are shown on the screen for a few seconds, they must be quickly counted, then they are closed. Below the table there are four numbers written, you need to select one correct number and click on it with the mouse. If you answered correctly, you collect points and keep playing.

Game "Mathematical Comparisons"
The game "Mathematical Comparisons" develops thinking and memory. The main point of the game is to compare numbers and mathematical operations. In this game you have to compare two numbers. At the top, a question is written, read it and answer correctly to the question posed. You can answer using the buttons below. There are three buttons "left", "equal" and "right" drawn. If you answered correctly, you collect points and keep playing.

Developing phenomenal oral counting
We've just covered the tip of the iceberg, to understand math better - sign up for our course: Speeding Up Verbal Counting.
From the course, you will not only learn dozens of techniques for simplified and quick multiplication, addition, multiplication, division, percent calculation, but also work them out in special tasks and educational games! Verbal counting also requires a lot of attention and concentration, which are actively trained when solving interesting problems.

Speed reading in 30 days
Increase your reading speed by 2-3 times in 30 days. From 150-200 to 300-600 words per minute or from 400 to 800-1200 words per minute. The course uses traditional exercises for the development of speed reading, techniques that speed up the work of the brain, the method of progressively increasing the speed of reading, the psychology of speed reading and the questions of the course participants are discussed. Suitable for children and adults reading up to 5000 words per minute.
Development of memory and attention in a child 5-10 years old
The course includes 30 lessons with helpful tips and exercises for child development. Each lesson contains useful advice, several interesting exercises, an assignment for the lesson and an additional bonus at the end: an educational mini-game from our partner. Course duration: 30 days. The course is useful not only for children, but also for their parents.
Super memory in 30 days
Memorize the necessary information quickly and for a long time. Wondering how to open a door or wash your hair? I am sure not, because this is part of our life. Easy and simple exercises to train your memory can be made part of your life and done little by little during the day. If you eat the daily ration of food at a time, you can eat in portions throughout the day.

Brain fitness secrets, train memory, attention, thinking, counting
The brain, like the body, needs fitness. Exercise strengthens the body, mental exercises develop the brain. 30 days of useful exercises and educational games to develop memory, concentration, intelligence and speed of reading will strengthen the brain, turning it into a tough nut to crack.

Money and Millionaire Mindset
Why are there problems with money? In this course, we will answer this question in detail, look deeper into the problem, consider our relationship with money from a psychological, economic and emotional point of view. From the course you will learn what you need to do to solve all your financial problems, start accumulating money and invest it in the future.
Knowledge of the psychology of money and how to work with it makes a person a millionaire. 80% of people with an increase in income take more loans, becoming even poorer. On the other hand, self-made millionaires will make millions again in 3-5 years if they start from scratch. This course teaches competent distribution of income and cost reduction, motivates to learn and achieve goals, teaches to invest and recognize a scam.

Learning fast with the best free game. Check it out for yourself!
Learn multiplication table - game
Try our educational e-game. Using it, you will be able to solve math problems in the classroom at the blackboard without answers tomorrow, without resorting to a sign to multiply the numbers. One has only to start playing, and in 40 minutes you will have an excellent result. And to consolidate the result, train several times, not forgetting to take breaks. Ideally, every day (save the page so you don't lose it). The play shape of the simulator is suitable for both boys and girls.
Result: 0 point.
See the full cheat sheet below.
Multiplication directly on the site (online)
*| × | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 |
| 2 | 2 | 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 16 | 18 | 20 | 22 | 24 | 26 | 28 | 30 | 32 | 34 | 36 | 38 | 40 |
| 3 | 3 | 6 | 9 | 12 | 15 | 18 | 21 | 24 | 27 | 30 | 33 | 36 | 39 | 42 | 45 | 48 | 51 | 54 | 57 | 60 |
| 4 | 4 | 8 | 12 | 16 | 20 | 24 | 28 | 32 | 36 | 40 | 44 | 48 | 52 | 56 | 60 | 64 | 68 | 72 | 76 | 80 |
| 5 | 5 | 10 | 15 | 20 | 25 | 30 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 50 | 55 | 60 | 65 | 70 | 75 | 80 | 85 | 90 | 95 | 100 |
| 6 | 6 | 12 | 18 | 24 | 30 | 36 | 42 | 48 | 54 | 60 | 66 | 72 | 78 | 84 | 90 | 96 | 102 | 108 | 114 | 120 |
| 7 | 7 | 14 | 21 | 28 | 35 | 42 | 49 | 56 | 63 | 70 | 77 | 84 | 91 | 98 | 105 | 112 | 119 | 126 | 133 | 140 |
| 8 | 8 | 16 | 24 | 32 | 40 | 48 | 56 | 64 | 72 | 80 | 88 | 96 | 104 | 112 | 120 | 128 | 136 | 144 | 152 | 160 |
| 9 | 9 | 18 | 27 | 36 | 45 | 54 | 63 | 72 | 81 | 90 | 99 | 108 | 117 | 126 | 135 | 144 | 153 | 162 | 171 | 180 |
| 10 | 10 | 20 | 30 | 40 | 50 | 60 | 70 | 80 | 90 | 100 | 110 | 120 | 130 | 140 | 150 | 160 | 170 | 180 | 190 | 200 |
| 11 | 11 | 22 | 33 | 44 | 55 | 66 | 77 | 88 | 99 | 110 | 121 | 132 | 143 | 154 | 165 | 176 | 187 | 198 | 209 | 220 |
| 12 | 12 | 24 | 36 | 48 | 60 | 72 | 84 | 96 | 108 | 120 | 132 | 144 | 156 | 168 | 180 | 192 | 204 | 216 | 228 | 240 |
| 13 | 13 | 26 | 39 | 52 | 65 | 78 | 91 | 104 | 117 | 130 | 143 | 156 | 169 | 182 | 195 | 208 | 221 | 234 | 247 | 260 |
| 14 | 14 | 28 | 42 | 56 | 70 | 84 | 98 | 112 | 126 | 140 | 154 | 168 | 182 | 196 | 210 | 224 | 238 | 252 | 266 | 280 |
| 15 | 15 | 30 | 45 | 60 | 75 | 90 | 105 | 120 | 135 | 150 | 165 | 180 | 195 | 210 | 225 | 240 | 255 | 270 | 285 | 300 |
| 16 | 16 | 32 | 48 | 64 | 80 | 96 | 112 | 128 | 144 | 160 | 176 | 192 | 208 | 224 | 240 | 256 | 272 | 288 | 304 | 320 |
| 17 | 17 | 34 | 51 | 68 | 85 | 102 | 119 | 136 | 153 | 170 | 187 | 204 | 221 | 238 | 255 | 272 | 289 | 306 | 323 | 340 |
| 18 | 18 | 36 | 54 | 72 | 90 | 108 | 126 | 144 | 162 | 180 | 198 | 216 | 234 | 252 | 270 | 288 | 306 | 324 | 342 | 360 |
| 19 | 19 | 38 | 57 | 76 | 95 | 114 | 133 | 152 | 171 | 190 | 209 | 228 | 247 | 266 | 285 | 304 | 323 | 342 | 361 | 380 |
| 20 | 20 | 40 | 60 | 80 | 100 | 120 | 140 | 160 | 180 | 200 | 220 | 240 | 260 | 280 | 300 | 320 | 340 | 360 | 380 | 400 |
How to multiply numbers with a column (video on math)
To practice and learn quickly, you can also try column-multiplying numbers.
Topic: Multiplication and division table by 2. (Lesson reinforcement)
Purpose: to consolidate the computational skills of the multiplication and division tables.
Lesson Objectives:
1. To consolidate knowledge of the multiplication and division tables; to develop the ability to solve complex problems; continue to build computational skills.
2. Develop logical and economic thinking; the ability to draw conclusions, generalize.
3. Working in groups, cultivate such personality traits as cooperation, mutual assistance, tolerance; respect for work and people of work.
Lesson type : a lesson in improving and consolidating skills.
During the classes.
1. Organizational moment. The psychological attitude of students.
The bell rang, the lesson begins.
- Guys,Imagine that your palms are a small mirror, look into it, smile at yourself - you see how cute and smart you are! Look at each other, smile, and your mood will be cheerful and upbeat, you will want to learn new things, because it is so interesting!
There was a sage who knew everything. One man decided to prove that the sage does not know everything. Clutching the butterfly in his palms, he asked: "Tell me, sage, which butterfly is in my hands: dead or alive?" And he himself thinks: "The living one will say - I will kill her, the dead one will say - I will release her." The sage, thinking, replied: "Everything is in your hands."
Your knowledge is also in your hands. Let us prove it with our work in the lesson.
(Slide 1)
II. Updating basic knowledge.
To work quickly and dexterously
We need training for the mind.
a) What number is superfluous?(Slide 2)
What task do you need to complete with numbers? (Remove extra number)
7 14 21 27 28 35 42 49
5 10 11 15 20 25 30 35
4 8 12 16 17 20 24 28
Knowing what did you need to complete the task? (Multiplication Talks)
Assessment.
b) Name the word.
I invite you to ask questions about the topic of today's lesson.
1. An action that can replace the sum of identical terms (multiplication)
2. The number to be divided by (divisor)
3. The number that is divided (dividend)
4. Result of the action during multiplication (product)
5. Result of an action when dividing (quotient)
6. Component of multiplication action (multiplier)
Slide 3. Assessment.
III. Independent formulation of the topic and purpose of the lesson. Target setting for the lesson.
Who guessed what the topic of the lesson was?
Multiplication and division table.
Guys, what is the goal we set for ourselves?
Slide 4
Today we will consolidate our knowledge of the multiplication and division tables, we will use the table to solve problems, equations, and find the value of an expression.
Problematic question.
What do you think, is it possible to learn something new by repeating and reinforcing? We need to figure it out.
4. Verbal counting
1. Statement of the problem. Mystery.
To find out what will be discussed today, you will have to guess the Russian folk riddle “There is a bunch of pigs lying down, whoever touches them will screech”. Doubt the answer? And now we will solve this problem by performing the calculations.
Slide 5
What is in front of us? (block diagram)
How will we do the calculations? (by algorithm)
What is an Algorithm? (performing actions in order)
Write down the written numbers 13, 4, 8, 17, 5 in ascending order (4, 5, 8, 13, 17)
Slide 6
What word came out? (bees)
Who else will we talk about in the lesson?
Assessment.
Slide 7
Guys, bees are tireless workers. And the agricultural sector is beekeeping. What is this industry doing? (bee divorce)
Man, what profession is engaged in breeding bees? (beekeeper).
Guys, do you have a beekeeper in your village?
Do you think he knows everything about bees? (Yes)
The main thing in this profession is that the beekeeper must know everything about bees.
What do you know about bees?
Unfortunately, we cannot know everything about bees, but we will try to find out as much as possible. I'm sure you will succeed.
Today one of the bees will accompany us in the lesson. So, let's go for the bee.
Work in pairs. Finding the value of expressions with variables.
- Our road starts from the hive. There are usually many hives in the apiary. Each hive has its own entrance - a summer entrance. In order to open the entrance, we need to complete the task. What goal will we set by completing this task? (execute variable expressions) -What is a variable expression?
| from: 2 |
| C * 2 |
Assessment. Mutual and self-test against the reference.
Slide 8
You know very well the multiplication and division table, the entrance in the hives is open and it is no coincidence that our hives turned out to be of exactly those colors. (Yellow, blue, white). The bee simply does not distinguish between other colors. But on the other hand, she sees ultraviolet rays that are beyond our eyes.
IV. Logical task.
Do you know how many eyes a bee has? (No)
Let's count orally.
The bee has as many eyes as you have, again as many, and half that. (The bee has 5 eyes. 2 large, consisting in turn of 10 thousand eyes, and located on the sides of the head and 3 small ones on the forehead between them)
V. Work on consolidation of the passed material.
1. Mathematical dictation. Work in notebooks.
Beekeepers usually assign their own numbers to the beehives in the apiary. There are such numbers in our apiary. - But we will recognize them when we complete the task. Record only responses.
1) Product of numbers 2 and 4
2) Increase 2 by 9 times
3) How many times is 14 more than 2
4) 1 multiplier 2, the second is the same. Work?
5) Reduce 20 by 2 times
6) What number was reduced by 2 if you got 5
7) By how many multiplied 8, if you got 16
Slide 9
8 18 7 4 10 10 2
Assessment. Cross-check from the slide.
2. Speech on bees. (Ruban Vanya.)
Hello guys! I am a worker bee. We produce wax, propolis, the most valuable medicine - honey and bee bread. Perga is a bee bread made from pollen and nectar. We bees eat it.
What do you know about the bee colony? (The main in the bee family is the queen - she is the queen. The rest of the bees are workers. They do the work of watchmen, cell cleaners, ventilators, nectar collectors, cell builders. Drones also live with them, who do nothing, but are needed to procreate.)
3. Writing expressions and finding their values. Slide 10
It's time for the bee to go to work. What time does a student's working day start? (8 hours) How do you determine the time? (by the hour)
The bee is well versed in time. For this, she does not need a watch or the sun. She needs flowers. She flies out whenthe flower clock starts working.
How do you understand my words?
So we will work with colors and find the values of the expressions. The first number in mathematical expression shows the time when the flower “wakes up”, the answer you found is when it “falls asleep”.
What is important to know in order to complete this task? (procedure)
Rosehip 2 * 7-10: 2 =
Poppy 5+ 7 * 2 - 11 =
Assessment. Mutual verification.
4. The task of finding the perimeter of the rectangle. Slide 11
What do we see on the slide? (frame)
Why does the beekeeper need it?
What kind of work can we do? (find the sides and perimeter of the rectangle).
S - 12 dm2
Length - 3 dm
What formulas helped?
Formulas for finding the perimeter, area.
What else helped?
Multiplication and division table.
5. Differentiated work.
Work on the textbook number 2 (strong students) Mutual check.
Work on cards (weak students) Self-test.
5. Work on the task. (Cards)
Bees are so hard workers! And we will solve the problem about them.
Read the problem, there are several solutions to it. You need to choose one correct solution, mark it with a plus. Explain your choice.
Task ... Uncle Vitya pumped out 7 kg of honey from one hive, and twice as much from the other. How many kg of honey did Uncle Vitya pump out from two hives?
Slide 12
Vii. Lesson summary.
Our lesson is coming to an end. At the beginning of the lesson, I asked you if you can learn something new in the revision and reinforcement lesson. What conclusion have you come to?
What new have you learned in the lesson? (the industry is beekeeping, the profession is a beekeeper. The more bees fly out to work, the more harvest we get, the more beautiful our Earth will be from fragrant flowers.) - What did you learn?
Our bee thanks you for your work.
Did you enjoy collaborating, working in pairs, collectively?
Today you also worked like bees, and I really enjoyed working with you.