Change in wages in 1s. Accounting info
Program "1C: Salary and HR Management 8" ed. 3 contains new (relative to previous editions) tools for recording labor and working time: wages depending on the place of work and depending on the type of time. In the article, 1C experts consider the use of these mechanisms using the example of solving the problem of automating the calculation of wages for theater actors.
Before we move on to the description of the new possibilities for recording labor and working time in “1C: Salary and Personnel Management 8” edition 3, we will define the conditions that the theater considered in the solution options is not a government institution; this article will not pay attention to the peculiarities of salary calculation "state employees". In accordance with Chapter 16 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, to record the labor of actors, as well as for all other citizens, working hours are planned according to schedules.
Connecting the ability to use functionality
To start using the guide Places of work and be able to manage Changes in places of work, use different Types of time, you need to configure the appropriate functionality of “1C: Salaries and HR Management 8” edition 3.
When initially setting up the program or in the future, you need to set the appropriate flags in the menu Settings —> Salary calculation (Fig. 1):
Rice. 1. Setting up functionality
1. Uses short-term changes in wages depending on the work performed provides access to the directory Places of work and the ability to display changes in the type of work performed by the document Changing jobs.
2. allows you to schedule different types of work within one working day.
3. Several tariff rates are used for one employee(flag enabled Several types of time are used in the work schedule) allows you to set different wages depending on the type of time.
Automation of payroll calculation for a theater actor in “1C: Salary and Personnel Management 8” (ed. 3)
According to the terms of the task of automating the calculation of salaries of actors, they work on a five-day schedule, only the weekends fall on Monday and Tuesday. Thus, according to the norm in October 2016, you need to work 22 working days. Actors' salaries consist of rehearsals and performances. Rehearsals are paid at the employee’s basic rate - salary per day. In this case, the standard time is considered to be a full month worked according to the schedule (in October - 22 days). Each performance has its own salary. It is paid in addition to the basic one. If the actor was sick or was on vacation, this is registered in the “1C: Salary and Personnel Management 8” program, edition 3, with standard absence documents, and the salary is calculated for the time worked.
A solution to the problem using short-term changes in wages
Short-term changes in wages depending on the work performed(see Fig. 1), considering performances as short-term changes, and rehearsals as a permanent place of work.
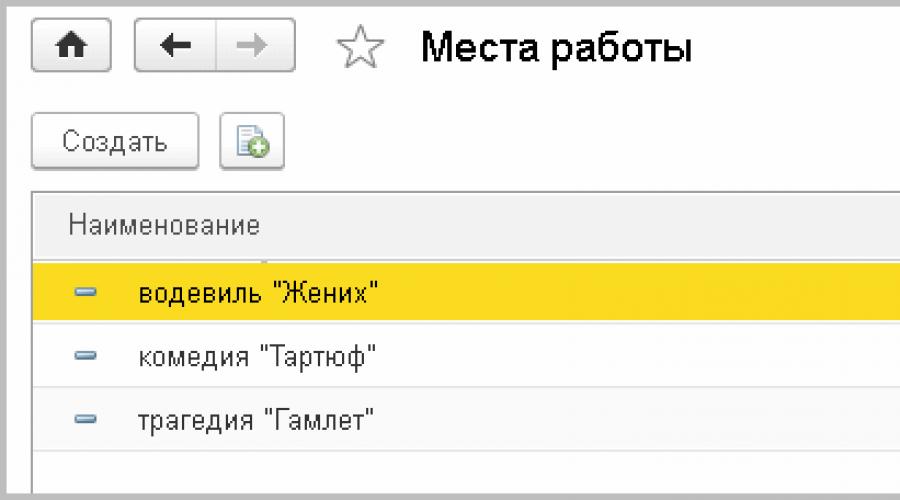
1. Filling out the directory Places of work(menu Settings -> Places of work) (Fig. 2).

Rice. 2. Directory “Places of Work”
Since wages depend on the performance, the directory also contains Places of work performances will be indicated: comedy, tragedy, vaudeville. For each place of work (for each performance) you need to indicate Per-performance payment(Fig. 3).

Rice. 3. Per-performance payment
2. Every working day, when there is no performance, the actor is busy at rehearsal. There is no need to perform any actions in the program. A working day is paid in accordance with the work schedule based on the employee’s base salary, recorded in the personnel document.
3. The day on which the actors perform the play is registered with a document Change of place of work(Fig. 4) in the menu Payroll -> Changing employee pay by button Create.

Rice. 4. Document “Changing places of work”
This document indicates the date of the performance and lists the employees involved in it. The total tariff rate for each employee is calculated automatically as the sum of the employee’s base salary and tariff Per-performance payment selected performance.
When filling out the document the actor is paid a base salary for all days he is scheduled to work, provided there are no absences. For the days when the performance took place, you will also be charged Per-performance payment based on the salary indicated for each performance ( Places of work).
Features of the solution option. Solving the problem of salary automation using a mechanism Places of work implies that Place of work is set for the whole day, and wages in this place are the same for all employees. Distribution of costs by place of work is not provided, therefore, in the case when it is necessary to take into account the costs of wages depending on performances, you need to use the document Distribution of basic earnings. In the report all performances and rehearsals will be reflected equally - Turnout.
A variant of solving the problem using several types of time in the schedule
To automate payroll calculation we will use Several types of time in the work schedule And Several tariff rates for one employee for each type of time(see Fig. 1). Each performance from the theater's repertoire must be assigned Type of time, and to each employee in personnel documents ( Recruitment, Personnel transfer) indicate all possible payment options in the column Add. Tariffs, odds... on the bookmark Salary.
1. Setup Types of time produced in the classifier Types of working time(menu Settings) (Fig. 5). The Main Time for all performances will be indicated Turnout. In this case, for each type of time you can specify your own alphabetic and digital code. As a result, the report Time sheet (T-13) it will be clear on what days and in what performance the actor participated, or whether he was busy at rehearsal.

Rice. 5. Setting up “Types of use of working time”
2. Payment types must be set up in terms of payment types Accruals, creating for each performance (Type of time) your own type of calculation (see Fig. 6).

Rice. 6. Setting up “Accruals”
On the bookmark Basics in field Accrual performed, you should select the option Only if a type of time recording is entered and specify this type of time. When setting up a formula, you need to enter a new Constant indicator(for each type of time), which determines the tariff rate at which the salary will be calculated for the selected type of time (in the example - Constant indicator per-performance rate 1 for time type Tragedy).
You can add a new indicator when editing a formula in the accrual card by clicking the button Create indicator. By indicating Name - Performance rate should be determined Indicator purpose - For employee. Select indicator type Monetary(the flag is available Is the tariff rate and the choice of clarification is possible: Daily tariff rate) Next, use the switch to set the order and frequency of how this indicator Used: permanently or one-time. The newly created indicator can be added to the formula.
The formula in the example will look like this: Newly created indicator (per-performance rate 1) x Predetermined indicator of the number of days worked in the calculated period for the selected type of time (TimeInDays), that is
per-performance rate 1 x TimeInDays
Note, that you need to fill out all the bookmarks that define the accrual and indicate that it is included in the base for calculating average earnings, is income for personal income tax purposes with code 2000, determine the accrual accounting item, etc.
3. Individual working time schedules for employees should be created, indicating not only the number of hours per day, but also the types of time corresponding to performances on the days when the employee participates in performances (Fig. 7).

Rice. 7. Setting up a work schedule
When filling out the document Calculation of salaries and contributions The actor is paid a separate salary for the days worked for each type of work, according to the schedule.
Features of the solution option. It is recommended to use this solution in cases where the variety of performances is limited.
Application of methods to solve other problems
Using a mechanism for accounting for changes in places of work can be useful, for example, in tasks where cashier salespeople work for a month in different stores, and salaries or additional payments depend on the store; boiler house operators, working for a month in different boiler houses, receive a bonus, but the percentage of the bonus depends on the place of work, etc. The use of different types of time and several tariff rates is recommended when solving such automation problems as, for example, calculating the salary of a driver who independently repairs a car at the tariff rate of a mechanic or machine tool adjuster, if the tariff depends on the type of machine, and several different machines are serviced per day.
About the author: Elena Lobyntseva - certified 1C specialist in the field of building automated systems for management and regulated payroll accounting in application solutions "1C: Enterprise 8". Head of a number of large automation projects for Russian and transnational corporations.
Payroll calculation at manufacturing enterprises and in budgetary institutions is a rather complex process. At the same time, it is possible and necessary to automate this process, taking into account the modern level of software. Automation of payroll calculations should provide for possible changes in the field of remuneration and comply with current standards. However, this is not always the case. The number of errors and questions regarding payroll calculations grows along with the number of personnel in the enterprise. The variety of allowances, bonuses and additional payments, on the one hand, is a stimulating factor for employees and motivates them to work, and, on the other hand, is a headache for many accountants. This challenging accounting task raises many questions. How to take into account and quickly calculate all kinds of accruals to employees? How to competently build an error-free accrual system so that both the employee and the employer are satisfied? And at the same time, we must not forget to always monitor and take into account changes in Russian legislation. All this variety of tasks associated with accrual accounting and payroll calculation leads us on the right path to the idea of automating this process.
Based on our experience in constructing payroll calculations in the Energy Service of the State Unitary Enterprise "Mosgortrans", we propose to consider in this article the features of multi-level, volume and multi-stage accruals, as well as complex cases of calculation using the program "1C: Salary and Personnel Management 8" (rev. 2.5 ).
The basis of remuneration is the salary of employees (the main type of accrual predefined in the configuration “1C: Salary and Personnel Management 8”), as well as bonuses, allowances and additional payments. Budgetary institutions use this remuneration scheme to the greatest extent. What is the difference between a supplement and a surcharge? The bonus is an incentive payment, the additional payment is a compensatory one. The bonus is paid for merit, length of service, class, and additional payment - for work on weekends, holidays, night time, for combining positions, for work in difficult working conditions. Exceptions are bonuses for work in the Far North and equivalent areas and for shift work, which in essence are more reminiscent of compensation payments. These incentive and compensation payments are calculated, among other things, based on salary.
Salary
The basis of the salary of any employee is the salary, which can be set individually for each employee or can be implemented in the form of a tariff rate. The tariff rate and its size can be assigned to several employees.
Therefore, with a large number of employees, it is more convenient to use Tariff categories. When increasing salaries in an organization, it will be enough to indicate in the 1C: Salary and Personnel Management 8 program a new rate for each tariff category in the Tariff Classes directory. Using the salary system requires entering an individual amount of accruals for each employee in the documents “Entering information about planned accruals for employees of an organization”, “Hiring to an organization”, “Personnel transfer of organizations”.
Having opened the Plan of calculation types “Basic accruals of organizations”, open the predefined element “Salary by day” or “Salary by hour”. In the first case, the formula is used:
Monthly tariff rate / Monthly time limit in days * Time worked in days;
In the second case, the formula is as follows:
Monthly tariff rate / Monthly time standard in hours * Time worked in hours
In the Plan of calculation types, it is possible to select the type of calculation according to tariff rates, available for selection if the calculation method is regulated “By monthly tariff rate”.
If you need to use an individual salary for each employee, then you must select the type of calculation based on tariff rates “Tariff rate is specified in monetary units.”
If you need to use one for several employees, then you must select the type of calculation for tariff rates “Requires entering a tariff category”.

Tariff rates are entered into the “Tariff Levels” directory. The reference book must indicate from what date this rate is valid and its size.
Tariffs are assigned by the documents “Hiring to an organization” or “Entering information on planned accruals to employees of an organization” by selecting a Tariff category from the “Tariff categories” directory.
Bonus system
In this article we will look at several motivation schemes for the bonus system. The size and conditions of the bonus are established by separate orders. At the discretion of the organization's management, various types of financial incentives are used to motivate employees. Premiums may be paid in a lump sum or may be paid over a specified period, may be calculated as a percentage, or may be paid as a fixed amount.
Implementation in the program “1C: Salary and Personnel Management 8”
One-time bonuses in the program are specified in the Plan of calculation types “Additional accruals of organizations”, and planned ones in the Plan of calculation types “Basic accruals of organizations” according to predefined formulas:
Amount formula: Fixed amount.
Formula for percentage: Percent * Calculation base.
The calculation base is set on the “Other” tab in the “Base accruals” section by selecting the required accruals.
One-time bonuses on the form of the element of the plan of calculation types “Additional accruals of organizations” on the “Use” tab are marked as a bonus. One-time bonuses are introduced by the document “Bonuses for employees of the organization.” And planned bonuses are assigned by the document “Entering information about planned accruals to employees of the organization.” If the bonus is assigned for a specific period (quarter, half-year, work in winter or summer), then it is important to indicate not only the start date, but also the end date.
Premiums calculated as a percentage can be assigned based on the calculation base, both for the current month and a month later. On the “Other” tab, you can specify the period for selecting the calculation base (for the previous month or for the period of validity of the accrual).
Benefits
Benefit is a gratuitous monetary payment paid at the expense of the state.
Benefits paid at the expense of the Social Insurance Fund are assigned by the document “Accrual of one-time benefits at the expense of the Social Insurance Fund.” In this document, by selecting the type of benefit (at the birth of a child, when registering in the early stages of pregnancy, in connection with death, upon adoption of a child) and the date of the event, when you click the “Calculate” button, the amount of the benefit will be automatically displayed.
Allowances
The organization may establish allowances for certain categories of employees (incentives: for skill, team management, maintaining trade secrets; compensatory - for harmful/difficult working conditions)
Implementation in the program “1C: Salary and Personnel Management 8”
Allowances in the system are specified in the Plan of calculation types “Basic accruals of organizations”
Formula: Percent * Calculation base.
The calculation base includes such types of accruals as salary by day, salary by hour. Assigned by the document “Entering information on planned accruals to employees of the organization,” which indicates the percentage .
Additional loads
In any business, workers may be subject to additional workloads. And these additional loads can be calculated both from the salary (salary at the tariff rate) of the employee, and from the salary assigned according to the staffing table (the minimum or maximum value determined by the order). Additional payments for overtime work are made in accordance with Articles 149, 152, 119 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Implementation in the program “1C: Salary and Personnel Management 8”
The above additional payments are implemented using the Plan of calculation types “Basic charges of organizations”
When calculating additional payments for additional workloads from an employee’s salary, the following formula is used:
Percent * Calculation base.
The calculation base is set on the “Other” tab in the “Base accruals” section. In this case, it is salary/salary at the tariff rate. The percentage is assigned by the document “Entering information on planned accruals of organizations.”
In turn, we propose to calculate payments from salary at the rate according to the staffing table using the following formula:
Percentage * Salary according to staff schedule * Number of days worked / standard days.

The parameter “Salary according to staffing table” was created with the following indicators:
The rate and percentage, which are determined by the Order, are assigned by the document “Entering information on planned accruals of organizations.” The number of days worked is determined according to the timesheet.
Combination of professions
Often, an enterprise is faced with a shortage of qualified personnel or temporary absence of an employee. In such cases, an employee can combine several professions. Additional payments for combining professions due to an absent employee or in cases of shortage are stipulated in Articles 149 and 151 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
Implementation in the program “1C: Salary and Personnel Management 8”
Additional payments for combining professions are implemented using the Plan of calculation types “Basic charges of organizations”.
If the combination can take place for quite a long time (there are no plans to occupy this position in the near future), then we propose to calculate this accrual using the formula: Salary of combined position * Percentage * Number of days worked / standard days
The percentage is assigned by the document “Entering information on planned accruals to employees of the organization.” The number of days worked is determined again according to the report card.
If the combination is short-term in nature, i.e. for an incomplete month (for example, working for a sick employee or an employee who went on vacation), the formula is used:
Salary of the combined position * Percentage * Number of days the employee is absent according to the time sheet / Standard time in days.
The percentage and salary of the combined position, the number of days the employee is absent are assigned by the document “Entering information on planned accruals to employees of the organization.”
Temporary replacement
Another example is temporary substitution. That is, performing duties for a temporarily absent employee (usually a superior), caused by production needs. It is usually assigned by order.
Implementation in the program “1C: Salary and Personnel Management 8”
Payment for temporary substitution is reflected in the Plan of types of calculation “Basic accruals of organizations”. We propose to introduce a new type of calculation with the addition of the following formula:
Formula: (Salary of the person being replaced – salary of the deputy) * Number of days of absence of the person being replaced according to the time sheet / Standard time in days.

The indicator “Time in days for manual entry” was created with the following parameters:

Assigned by the document “Entering information on planned accruals to employees of the organization,” which indicates the salary of the person being replaced, the salary of the deputy, and the number of days the person being replaced is absent according to the timesheet.
Premium for class
A bonus for excellence (for example, after completing advanced training courses) can be assigned in the form of a bonus in the amount of the rate per day worked. A bonus for classy drivers is very common. This allowance established by local acts of the organization, labor and (or) collective agreement; in budgetary organizations it is established by the Government of the Russian Federation, government bodies of the corresponding constituent entity of the Russian Federation, and local government bodies (Article 144 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation).
Implementation in the program “1C: Salary and Personnel Management 8”
The Plan of calculation types “Basic accruals of organizations” uses the following formula:
Fixed amount * Days worked in a month.
The fixed amount is set as a tariff category in the Tariff categories directory, days worked - according to the timesheet. Let's consider another case. For example, the premium for drivers is:
For 2nd grade – 10%
For 1st grade – 21%
Let's assume that the employee has a second class qualification, and his salary is 20,000 rubles. Let’s say he worked not all the required 184 hours a month, but 160, and the remaining 24 for reasons beyond his control (for example, a breakdown) he participated in other work at the enterprise. Then his bonus will be 1,739 rubles: 20,000 (tariff rate) * 160 (production in hours) * 10% (percentage of premium for class) / 184 (standard hours per month). Thus, in the case where the premium is expressed as a percentage, the following formula is used:
Salary/hours*hours worked per month*Percentage
The percentage and salary are assigned by the document “Entering information on planned accruals to employees of the organization.” The number of hours worked (days can also be used) is determined according to the timesheet.
Order matters
When calculating wages, it is important to adhere to a certain chronology for creating accruals. Since many types of accruals are based on others, it is necessary that when entering them, slave accruals can be assigned leading ones, which should already exist. Experience suggests the following procedure for creating accruals: 1. Entering information about planned accruals,
2. Entering information about one-time charges,
3. Bonuses for the organization’s employees,
4. Accrual of vacation to employees of the organization,
5. Payment for sick leave,
6. Entering time sheets/ Absence for unknown reasons. After entering all of the above documents into the program “1C: Salary and Personnel Management 8” (rev. 2.5), you can use the document “Payroll for employees of the organization” to correctly and quickly calculate all accruals for the month, as well as correctly calculate the personal income tax due, taking into account deductions. And then quickly and accurately calculate the unified social tax and generate labor costs.
We continue to study the configuration of “1C: Salaries and HR Management 3.0” on the “1C: Enterprise 8.3” platform. In the previous article we looked at the organization, and in this and the next article we will analyze the payroll settings. Let me remind you that this article uses the configuration “1C: Salaries and HR 8. Basic version” as an example. You can read about its differences from the PROF version in the following.
So, we launch the application, go to the “Settings” section, select the “Payroll” item and see that we already have certain settings here - we specified them during the initial configuration using the wizard. Now we will look at each point in detail and I will tell you what they are all responsible for.
First of all, let's look at the settings available on the main page of the section. The first item is “Perform automatic recalculation of documents when editing them.” Please note that when we filled out the initial settings, we did not see this item. It is activated automatically and you can change its settings here.
This function is used to automatically recalculate the result when changes are made to the document. If it is not activated, then recalculations will have to be carried out manually using the “Recalculate” button. Of course, this is not very convenient and it is better to use automatic recalculation. Therefore, developers enable this option by default.
Why might you need to turn it off? This may be necessary if the performance of the computer or server is not enough for stable operation of the configuration and automatic recalculations slow down the work with the program.
But if you encounter such a problem, it is better to think about upgrading your computer hardware. In enterprises, such problems are less common, since system administrators usually initially take into account the system requirements necessary for stable operation and select equipment based on this data.
The option “Employee earnings are being indexed” allows you to index salaries at the enterprise. If this setting is activated, the “Earnings Indexation” document will appear in the “Salary” section, and if the organization maintains a staffing table, the “Staffing Table Indexation” document will be added to the “Personnel” section. Also, in the settings of the calculation type, the item “Accrual is indexed” will appear, which is used when calculating average earnings.
The option “Loans are issued to employees” adds documents to the configuration that allow you to manage such loans.
The function “Payments under civil contracts are registered” allows you to maintain documents on agreements. If such an agreement is concluded with an employee who permanently works at the enterprise on the basis of an employment contract, there is no need to create him as a separate contractual employee. I'll show you how to do this when we get to the relevant topic.
The “Rate groups are used” function in earlier versions of the configuration was called “Rate scales are used” and this is exactly how it is described in the reference literature that is relevant at the moment. It is also absent from the starting assistant and can be activated here if necessary. If you activate it, the “Tariff groups” directory will appear in the program and you can use these groups and qualification categories of employees when calculating salaries.
The option “Several types of time are used in the work schedule” is needed if schedules with several planned types of work are used and with hourly payment, when several different types of planned time are used for an employee during one working day.
The setting “Other income of individuals not related to wages is registered” is required when there is a need to keep records of the income of individuals who are not employees of the organization and are not associated with it in any labor relations. Such income may include, for example, vehicle rental or any prizes given out as part of ongoing promotions. This setting activates the “Other Income” document.
The “Income is paid to former employees of the enterprise” setting is needed if the organization makes some payments to former employees. For example, it provides financial assistance to retirees who previously worked at the enterprise. Activating this setting will make the “Payments to Former Employees” document available.
The item “Gifts and prizes are given to employees of the enterprise” should be noted if employees sometimes receive some valuable gifts. For example, as a reward in competitions. Accounting for gifts is maintained in the document “Prizes, gifts”. This document uses a special reference book for its work, and its activation does not entail the addition of a new type of calculation.
The last setting in this section specifies how to calculate the time standard if it has changed due to the fact that the work schedule has not changed since the first day of the month. The options “Based on work schedules before and after the change” and “Based on individual work schedules” are available.
Now let’s look at other salary calculation settings, for which we’ll follow the link of the same name at the very bottom of the screen.
The very first setting we see in the new section is “Use a payroll program.” If the user of the “1C: Salary and Personnel Management 3.0” configuration only needs personnel records and staffing from the program, he should uncheck this box. In this case, payroll tools will become unavailable. Only those that are necessary for the above tasks will remain.
The “Use accounting by funding item” option allows non-profit organizations and unitary enterprises to divide salary expenses by funding source and draw up reports for each of them. She adds to the program the directory “Items of Financing”, which already includes two types of them - “Budget financing” and “Entrepreneurial activity”. The adjacent option “Social Sphere Enterprise” also becomes active, in which you can more precisely specify the scope of the enterprise’s activities: healthcare, culture, research and development, education and social services.
The program has the ability to calculate salaries both for the entire organization and for its individual divisions. The next setting in line is responsible for this, which is called “Calculation and payment of salaries is carried out for the organization as a whole.” If you uncheck it, salaries will be calculated by department.
The option “Use multiple tariff rates for one employee” is mainly used if different types of working hours are used in the work schedule. It allows you to use the “Accrual for full/part-time shift work within normal time limits” setting, while simultaneously calculating different types of time for an employee within one working day.
The option “Several types of time are used in the work schedule” located right there simply duplicates the option of the same name from the main settings screen, discussed a little higher. If you need to activate it, it doesn't matter which page you do it on. Perhaps they forgot to remove it from one section during the next configuration update. Or maybe it was intended that way.
At the end of the section there are settings for recalculating the employee’s tariff part into the cost of an hour or day. Here the user can specify how the number of hours will be calculated and note the indicators that determine the composition of the total tariff schedule.
We'll stop there for now. In the next article we will look at, thereby closing the topic of setting up payroll calculations in the “1C: Salaries and Personnel Management 3.0” configuration.
In situations where your company employs a small number of people, you can maintain both personnel records and documents in this program. We paid attention to the number of employees for a reason. The reason is that you can only use some functionality if you have no more than 60 people working for you.
In later releases of 1C 8.3 Accounting 3.0, the configuration interface has changed slightly, but the functionality essentially remains the same. You can find it in the “Administration” program menu - “”. In the form that appears, click on the “Salary Settings” link.
The interface of the settings we are interested in is quite simple, because now everything is arranged in one window. Below we will describe all sections in detail.

First of all, we need to indicate that payroll and personnel records will be kept in this 1C Accounting. Without this, other settings will be unavailable. If it is carried out in an external program, it often means ZUP, but it can be any other.
To set up payroll accounting, click on the link as shown in the image below.

If you plan to keep records for several organizations at once, then this setup will need to be done for each one separately.
On the “Salary” tab, it is indicated, which is selected from a special directory. We will consider filling it out later. It also indicates the account to which the costs will be posted. We will also indicate from what period the changes will take effect.
This tab indicates the date of payment of wages, reflection in the accounting of depositors and the procedure for paying sick leave. Please note that personal income tax and fear. contributions are adjusted separately. You can access them by clicking on the corresponding hyperlink at the bottom of the form.

If your company must provide for the formation of a vacation reserve, go to the second tab of this window.

Some companies have some special surcharges for territorial conditions, for example, northern surcharge, regional coefficient, indicate this information on the “Territorial conditions” tab.

Salary calculation
In the “Payroll calculation” section, you can make available the functionality of keeping records of sick leave, vacations and executive documents. As mentioned earlier, this functionality is only available to companies with fewer than sixty employees. It is also recommended to set the flag on the second item. This is necessary for the convenience of working with payroll documents.
From the section we are considering, you can go to the list of types of accruals and deductions using the hyperlinks of the same name. As shown in the image below.

These lists initially already have some elements, but you can change and add your own. For example, a special bonus can be included in the accruals, and payments for the rental of company property by employees can be included in the deductions.

Reflection in accounting
Above we described setting up salary accounting. Accounting methods can be changed in the “Reflection in accounting” section using the link shown in the figure below.
In our example, the default accrual reflection is used. We will charge all costs to account 26 with the cost item “Payment”.

Personnel accounting
For more complete and convenient work with the program, it is better to make personnel records complete. In this case, personnel department employees will be able to enter data on admissions, transfers and dismissals of employees.

After making all the necessary settings in 1C 8.3, you will be able to maintain both personnel records and calculation of employee accruals. Of course, the functionality in the 1C:Accounting program is inferior to 1C:ZUP, but for small companies it is more than enough.
Accounting for the movement of personnel Personal data Accounting for working hours Accounting for vacations Military registration Salaries and reporting Accruals and deductions Salary calculation process Regulated accounting Payment of wages Transfer to personal income tax and contributions Personalized accounting Pilot project Social Insurance Fund Statistical reportingCalculations of accruals and deductions in 1C: ZUP
The 1C Salary and Personnel Management 8 (1C ZUP) program provides for the calculation of accruals for all forms of remuneration:
- time-based (using monthly, daily and several hourly tariff rates);
- piecework;
- using a bonus system.
They correspond to such time-based and piece-rate accruals as:
- salary payment;
- payment by salary (hourly);
- payment at an hourly rate;
- piecework earnings.
The size of any tariff rate is set in rubles with the accuracy that was specified during the initial setup of the program.
The size of the rates can be determined by the tariff scale in accordance with the categories of personnel. In this case, the grid can be described in the staffing table, and in the program its changes can be reflected in special documents for indexing earnings.
Several tariff rates can be applied to each employee at the same time.
A cumulative tariff rate can be applied to set up charges. By default, the employee’s tariff rate during recalculation is the rate of his “basic” (time-based) accrual, for example, salary by day. The total tariff rate takes into account not only the employee’s salary, but also any other charges, for example, percentage or bonus amount.
During the initial setup, you can specify the option of the company’s bonus system in the form:
- one-time bonus - amount or percentage;
- monthly premium - amount;
- monthly bonus - percentage of employee salary:
- for the current month;
- for the past month;
- bonuses for the quarter - percentage or amount - can be paid:
- when calculating the month in which the percentage or amount is entered;
- during the inter-settlement period when the “Premium” document is registered;
- in the same preset months. The amount of the bonus is specified in personnel documents;
- bonuses for the year - amount;
- bonuses for the year as a percentage - by default, the calculation is based on the salary for the year, but in the annual bonus card you can indicate the period for which the employee’s earnings are used in the calculation.
Each accrual in the 1C ZUP information system must be described by certain properties:
- Purpose of charges in the form:
- time wages and allowances;
- remuneration in kind;
- income in kind;
- compensation payments;
- bonuses;
- vacation pay;
- vacation compensation;
- vacation without pay;
- absences for unknown reasons;
- absenteeism;
- business trip payments;
- payment of maintained average earnings;
- payment of sick leave;
- payment for days to care for disabled children;
- child care benefits up to 1.6 years;
- child care benefits up to 3 years old;
- severance pay;
- illness without pay;
- maternity leave;
- material assistance;
- vacations at the expense of the Social Insurance Fund for sanatorium and resort treatment;
- time off;
- other charges and payments.
- Calculation frequency:
- monthly;
- in the months listed;
- according to a separate document:
- "Awards";
- “One-time accrual”;
- another document, independently configured in the program;
- provided that you have entered:
- indicator value;
- type of time tracking;
- time falling on holidays.
- The method for calculating the result, which is selected from the following options:
- the result is entered as a fixed amount;
- the result is calculated based on a combination of any data;
- from those available in regulated calculation methods, as well as based on the values of own calculation indicators using various formulas, including mathematical functions max and min.
- Dependence of this accrual on other accruals.
- Reflection in working time recording:
- for work within the norm/exceeding the norm/for an incomplete shift/for already paid time;
- types of experience for SZV/PFR.
- The relationship of accrual to social benefits or vacations, to the calculation of average earnings.
- Classification of accruals for calculating personal income tax.
- Classification of charges for calculated insurance premiums.
- Method of reflecting accruals in accounting.
- A list of “crowding out” accruals (for example, an employee cannot be sick and work at the same time).

In the 1C Salary and Personnel Management 8 (1C ZUP) program, you can calculate deductions:
- Depending on the purpose in the form:
- union dues;
- writ of execution;
- payment agent remuneration;
- deductions for unworked vacation days;
- voluntary contributions to non-state pension funds;
- additional insurance contributions for the funded part of the pension;
- deductions for settlements on other transactions;
- other deductions in favor of third parties.
- Every month or only when the indicator value is entered.
- The following ways to calculate the result:
- fixed amount;
- a formula based on a combination of any data available in regulated calculation methods, as well as on the basis of the values of its own calculation indicators using various formulas, including mathematical functions max and min.
As a result, in the 1C Salary and Personnel Management 8 (1C ZUP) program for all accruals and deductions, you can record and save all the characteristics necessary for its use in calculating wages, personal income tax calculations and contributions. This will allow all calculations to be carried out in accordance with the company's accounting policies.