What is asphyxia in medicine? Species, symptoms and consequences
The term "asphyxia" - ancient Greek origin. They were characterized by a state in which the human body stopped "fluid", "pulsate". The term was described as the absence of breathing oscillations of the chest and the absence of heart rhythm and pulse.
Asphyxia is a symptom of some cardiovascular, oncological diseases, respiratory disease diseases, arises as a result of accidents or causes intentionally.
In contact with
What is asphyxia in medicine?
In modern medicine, as well as forensic, the word "asphyxia" in the general sense denote the suffocation, i.e. The state of total oxygen starvation caused by cell death.
When they say that such asphyxia of the respiratory tract is, in most cases they mean situations under which there is a mechanical obstacle to air movement paths. In a medical sense, this concept is consumed wider. It is used to describe the states of oxygen starvation arising from the violations of gas exchange, paralysis of the respiratory center and other reasons.
What is the difference between asphyxia from hypoxia?
Recall that the oxygen molecules, falling into the lungs, penetrate the blood, are attached to hemoglobin in red blood cells, and further transported along the circulatory system to all cells. In the same way, but in the opposite direction, carbon dioxide is transferred. This is how the process of breathing each cell and the entire body occurs. 
At the biochemical level, the suffocation is accompanied by two multidirectional processes:
- Hypoxia;
- hypercup.
Hypoxia denote a simultaneous decrease in the amount of erythrocytes carrying oxygen.
Hypercapnia is a single increase in the number of erythrocytes carrying carbon dioxide.
Asphyxia pathogenesis
To understand what asphyxia in medicine is, it is necessary to have an idea of \u200b\u200bthe fundamental role of breathing in the life of a living organism.
The longer the breaking disorder continues, the greater the blood of the carbon dioxide and the level of oxygen increases. Despite the fact that metabolic processes are characterized by a high degree of inertia, the most important organs react to the formative hypoxia / hypercupnia almost instantly.
Asphyxia Stages:
- Stage of respiratory failure - for 1 min.
- The stage began to extract respiratory and cardiac activity - for 1 min.
- Short-term respiratory stop - for 1 min.
- Terminal stage - up to 10 minutes.
With complete mechanical asphyxia or stopping respiration, irreversible changes in the nervous system and in the heart muscle begin to occur already at the first stage of asphyxia. Depending on the state of health, age and other factors, death occurs 3-5 minutes after the start of the suffocation.
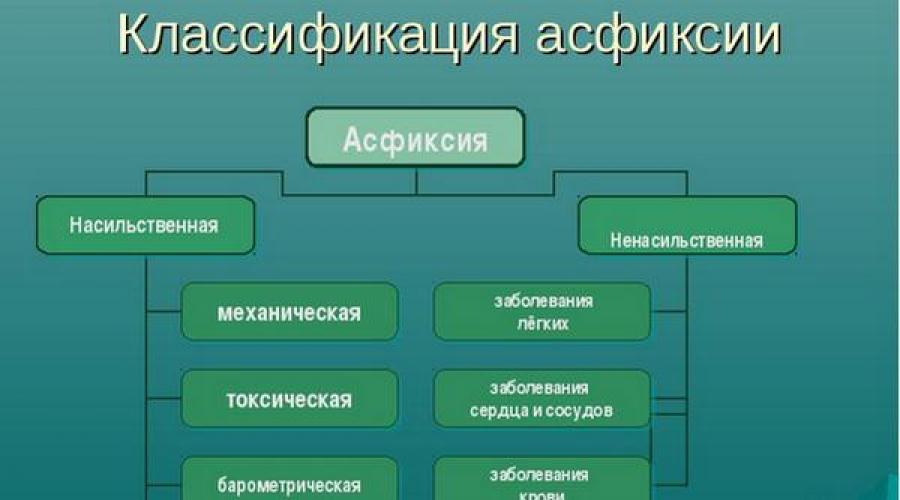
Types of asphyxia
Classical cases are related to states with, i.e., to the resulting respiration from the mechanical overlap. However, today this concept is consumed in a broader sense. 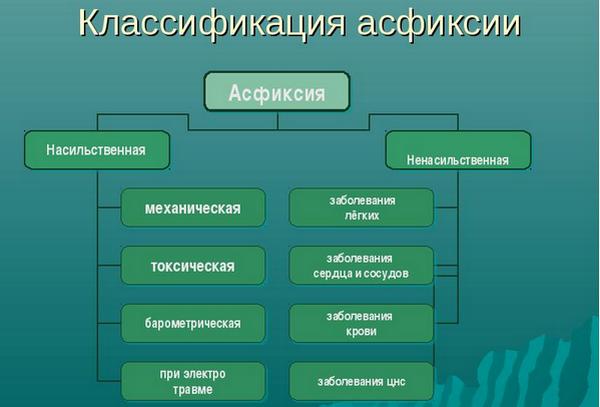
Compression
There arises from squeezing the neck (hands, rope, etc.), chest (eg, while under the root). The second name of this species is the stagnation asphyxia. It is always heavy asphyxia.
Dislocation
It is formed as a result of the traumatic displacement of the jaws, larynx, language, a soft sky that impede the process of respiration.
Stenotic
It occurs during stenosis (squeezing) trachea tumor, inflammation, edema.
Aspirational (Obstructive)
Overlapping the respiratory tract resulting from aspiration, i.e. From inhalation of finely dispersed structures, ingress of liquid content (vomit, water, blood, etc.), as well as food particles ("suppressed").
A special appearance manifested in the absence of breathing or its incomplete and insufficient character. It is a frequent cause of death of newborns.
Reflex
Spasm of the respiratory tract, as a result of which a person cannot do inhale. There is in response to the impact of chemicals, low / high temperatures.
Amphibotropic
 Difficulty breathing occurring on a wall of angina or heart failure. According to tradition, these states call "chest toas." Amphibiotropic - means "similar amphibian" or "like a tob."
Difficulty breathing occurring on a wall of angina or heart failure. According to tradition, these states call "chest toas." Amphibiotropic - means "similar amphibian" or "like a tob."
Amphibiotropic asphyxia occurs in response to the overload of the heart, the increase in pressure, in particular, in the artery leading to the easy. The lungs begin to swell, in connection with which the exchange of oxygen / carbon dioxide deteriorates - the person begins shortness of breath.
Autoerotic (sexy, erotic)
There is a targeted squeezing of the neck at the time preceding orgasm. Artificially caused by the condition of oxygen starvation, in all likelihood, leads to additional sensations, but often ends with disabilities or death.
Other species
Not mechanical asphyxia can manifest itself against the background of internal pathologies, to be the result of drug poisoning. You can hear about this form as "Puffed Asphyxia". Naturally, gas formation in the process of digestion of food cannot lead to suffocation. On the contrary, he always observes such a voltage of the entire body, as a result of which feces, gases, urine and sperm is involved.
Classification for the flow and degree of complication of respiratory activities
The following form of the flow of asphyxes is distinguished:
- Acute;
- gradual compensated.
A sharp form arises sharply, develops quickly with well-manifested symptoms.
A gradual protracted form is a phenomenon that is more common in medical practice. The internal cause aggravating the passage of air can develop for a long time. A person gets used to compensate for the poor performance of the respiratory tract, taking a certain pose, tilting his head - that is, to find a natural way to increase the amount of inhaled air.
According to the degree of complication of respiratory activities, mechanical asphyxia is divided:
- Partial overlap of breathing;
- complete overlap of breathing.
Symptoms
The attack of the suffocation with partial air access overlap is characterized by the following initial features:
- Noisy difficulty inhaling with a whistle;
- acceleration and deepening breathing;
- the inclusion in the breathing process of all the muscles of the chest, back, abdomen.
With complete mechanical asphyxia, the main initial symptoms:
- Inability to breathe;
- "The grabbing" of air lips;
- convulsive movements with hands and legs.
 For several minutes to several hours or days, the following symptoms are developing consistently:
For several minutes to several hours or days, the following symptoms are developing consistently:
- Overexcitation state;
- redness, finedness, face tension;
- the skin and mucous membranes are pale, a blue or grayish shade appears;
- pulse is accelerated or slowed;
- confused heart rhythm;
- convulsions;
- loss of consciousness;
- extended pupils;
- stop breathing;
- stop heart and death.
If you suffer is compensated, it is often: it is often:
- Acceptance of patients with specific poses, which allows him to breathe as efficiently as possible;
- wide opening of the mouth;
- proving language;
- pulling neck.
The reasons
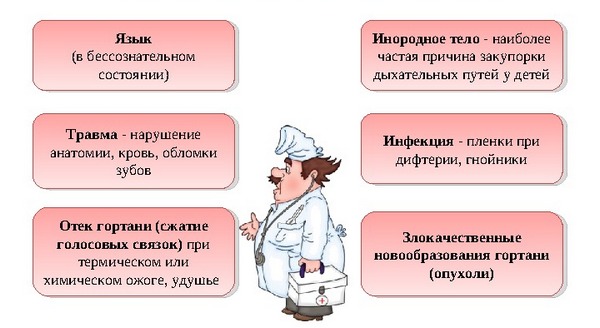
Asphyxia may be the result of a wide set of events:
- Chest injury, neck, head;
- cepen-orpinal injuries;
- stroke / drowning;
- foreign bodies in respiratory tract;
- tumors of respiratory tract, esophagus;
- stroke;
- the narrowing of the respiratory tract due to asthma, bronchitis, tracheitis, when burning the pharynx and larynx, etc.;
- violation of gas exchange in the lungs against the background of thromboembolism of the pulmonary artery, pneumothorax, pleuritis, pneumonia, pulmonary edema.
- paralicity of respiratory muscles as a result of infectious diseases (tetanus, poliomyelitis, etc.);
- an overdose of substances depressing the activity of the nervous system, including the respiratory center;
- long inhalation of toxic substances, such as combustion products in case of fire.
As can be seen from the above list, in most cases asphyxia arises regardless of the will of the person. However, a person can reduce the risk of suffocation. Asphyxia prevention includes:
- Timely treatment of diseases;
- eating, not in a hurry;
- promotive behavior in places and situations with an increased probability of trauma.
Treatment
Medical assistance when choking is reduced to the elimination of a factor that impedes the normal ventilation of the lungs:
- Removal of foreign objects;
- aspiration of fluid;
- bleeding vessels;
- surgical reposition of jaws;
- stitching soft tissues of the tongue of the sky, pharynx;
- creating an artificial exit from trachea to the environment;
- drainage of pulmonary pleura by puncture;
- therapy of concomitant diseases and states that led to the occurrence of suffocation (thrombolytic therapy, the introduction of antidotes, etc.).
Effects
Frequent consequence of asphyxia in adults -.
Long oxygen fasting can be felt in perspective. In the period of asphyxia, the cells, first of all, nervous, begin to die. In the young age of their functions to some extent compensated by other cells. However, as age changes occurred, degenerative changes in the nervous system will be accelerated.
The consequences of asphyxia in newborns depend on the duration of oxygen starvation. In general, the children's body has significant compensation abilities. With timely resuscitation measures for the health of the child, nothing threatens.
Conclusion
 At the household level, under the choke, they understand the stagnation asphyxia, i.e. Compression, most often neck, in the style of detective or suicidal stories.
At the household level, under the choke, they understand the stagnation asphyxia, i.e. Compression, most often neck, in the style of detective or suicidal stories.
However, in medical practice, the main part of cases is the consequences of injuries, drug overdoses, infectious and noncommunicable diseases, oncologies and allergies.
Asphyxia always implies radical struggle, often requires operational intervention. A separate problem is asphyxia in newborns, but it is successfully solved in modern maternity hospitals. The effects of asphyxia are often postponed in time and depend on timeliness.
The video provides an analysis of the reasons for the development of asphyxia, and the first aid recommendations will help preserve life at the first signs of suffocation