What is asphyxia newborns: pulmonary and extrapileous causes of development, medical tactics
The asphyxia of newborns is a suffocation, manifested by a breakdown, or a lack of self-breathing in the presence of heartbeat and other signs of life. In other words, the child is not capable, can not breathe himself immediately after birth or it breathes, but his breath is inefficient.
40% of premature and 10% of the docking babies need medical care due to violation of independent respiration. Asphyxia of newborns is more common in premature babies. Among all the newborn, children born in asphyxia occupy 1 - 1.5% of the total.
A child born in asphyxia is a serious problem for doctors providing assistance in the maternity hospital. Worldwide every year about a million children die from asphyxia and approximately the same children arise serious complications subsequently.
The asphyxia of the fetus and the newborn flows with hypoxia (decrease in oxygen concentration in tissues and blood) and hypercapnia (increasing carbon dioxide content in the body), which is manifested by heavy respiratory disorders, blood circulation and disorders of the child's nervous system.
The causes of asphyxia of newborns
Factors contributing to the development of asphyxia
The antenatal and intranatal factors distinguish.

Antenatal affects the developing fruit intrauterine and are a consequence of the lifestyle of a pregnant woman. Antenatal factors include:
- mother diseases (diabetes mellitus, hypertension, diseases and vices of the heart and blood vessels, kidneys, lungs, anemia);
- problems of previous pregnancies (miscarriage, stillbirth);
- complications for real pregnancy (threat of miscarriage and bleeding, multi-way, lowland, misunderstanding or rejunction, multiple pregnancy);
- receiving the mother of some drugs;
- social factors (admission of narcotic substances, lack of medical observation during pregnancy, pregnant women under 16 and older than 35 years).
Intranatal factors act on the child in the process of childbirth.
The intranatal factors include various complications arising directly at the time of birth (rapid or protracted childbirth, premature or premature detachment of placenta, native anomalies).
All of them lead to the hypoxia of the fetus - to reduce the flow of oxygen to the tissues and to oxygen starvation, significantly improving the risk of birth of a child with asphyxia.
Causes of asphyxia
Among numerous reasons, five main mechanisms are distinguished, which lead to asphyxia.
- Insufficient purification from the toxins of the motherboard placenta as a result of low or high pressure in mothers, excessively active bouts or for other reasons.
- Reducing the oxygen concentration in the blood and the organs of the mother, the cause of which may be heavy anemia, the insufficiency of the respiratory or cardiovascular system.
- Various pathology on the part of the placenta, as a result of which gas exchange through it is violated. Among them, calcinates, predatory or premature detachment of the placenta, inflammation of the placenta and hemorrhage into it.
- Interrupt or violation of blood flow to the fetus through the umbilical cord. It is found when the UPU is tightly winds the neck of the baby, when squeezing the cord during the passage of the child through the generic paths, when the umbilical cord.
- Insufficient respiratory efforts of a newborne with the oppressing effects of drugs on the nervous system (a consequence of mother's treatment with various drugs), as a result of severe developmental defects, with prematurity, due to the immaturity of the respiratory organs, due to violation of air intakes in the respiratory tract (blockage or surveillance), As a result of generic injuries and severe intrauterine infections.
A special group of risk on the development of asphyxia is premature babes, who have a body weight at birth extremely low, transferred and children who have a delay of intrauterine development. Such children have the risk of asphyxia.
Most children who are born with asphycia are observed a combined effect of the ante and intranatal factors.
Today, among the causes of chronic intrauterine hypoxia, not the last place is occupied by drug addiction, toxicizing and mother's alcoholism. The number of smoking pregnant women increases progressively.
Smoking of pregnant catches:
- the narrowing of the uterine vessels, which continues for another half an hour after the buried cigarette;
- suppression of the respiratory activities of the fetus;
- increased in the blood of the fetus concentration of carbon dioxide and the appearance of toxins, which increases the risk of prematurity and premature labor;
- hypermatural syndrome after birth;
- damage to the lungs and the delay in the physical and mental development of the fetus.


With short-term and moderate hypoxia (reducing oxygen level in the blood) of the fetus, the body is trying to compensate for the lack of oxygen. This is manifested by an increase in blood volume, heartbeat, breathing, increasing the motor activity of the fetus. Such adaptive reactions lack of oxygen is compensated.
With long and severe hypoxia, the fetal body cannot compensate for the lack of oxygen, tissues and organs suffer from oxygen starvation, because oxygen is delivered, first of all, to the brain and heart. The motor activity of the fetus decreases, the heartbeat is replenished, breathing becomes less often, and its depth increases.
The result of severe hypoxia is the insufficient intake of oxygen to the brain and the violation of its development, which can be drained to break the breath at birth.
Easy docking fetus in front of childbirth is distinguished by a liquid that enters the oily water. The breath of the fetus shallow and voice gap is closed, so with normal development, the accumulate water can not get into the lungs.
However, the pronounced and long-term hypoxia of the fetus may cause irritation of the respiratory center, as a result of which the depth of breathing increases, the disclosure of the voice slot and the ingress of the oil-free waters into the lungs occurs. So the aspiration occurs. The substances that are available in the ocoplodic waters cause inflammation of the lung tissue, make it difficult to disrupt the lungs at the first breath, which leads to a breath disruption. Thus, the outcome of the aspiration by the accumulating waters is asphyxia.
Breathing disorders in newborns can be caused not only to impaired gas exchange in the lungs, but also the result of damage to the nervous system and other organs.
The reasons for respiratory disorders not related to the lungs include the following states:
- Disorders of the nervous system: anomalies for the development of the head and spinal cord, the effect of drugs and drugs, infection.
- Violation of the cardiovascular system. These include malformations of heart and blood vessels, fetal waterfront.
- The defects of the gastrointestinal tract: the atresia of the esophagus (blindly ending the esophagus), the fistula between the trachea and the esophagus.
- Violations of metabolism.
- Violation of the function of the adrenal glands and the thyroid gland.
- Blood diseases such as anemia.
- Incorrect development of respiratory tract.
- Congenital malformations of the bone system development: variables of the development of sternum and ribs, as well as rib injuries.
Types of asphyxia of newborns
- Acute asphyxia caused by the impact of only intranatal factors, that is, arising during childbirth.
- Asphyxia, which developed against the background of long-term intrauterine hypoxia. The child developed in conditions of lack of oxygen month and more.
According to gravity distinguish:
- light asphyxia;
- asphyxia of medium severity;
- heavy asphyxia.
Neonatologists assesses the state of the child born, using the apart scale, which includes an assessment of breathing, heartbeat, muscle tone, skin painting and newborn reflexes. An assessment of the state of the newborn is carried out on the first and fifth minute of life. Healthy kids are gaining 7 - 10 balls on the scale of apgar.
A low estimate suggests that the child has problems either with breathing or heartbeat and requires immediate help of physicians.
Easy asphyxia
Cardioresis depression is manifested. This is the oppression of breathing or heartbeat as a result of stress, which the child feels in the transition from the intrauterine life into the outside world.
![]()
Birth for a child is a colossal stress, especially if any complications arose. At the same time, on the first minute of life, Kroch receives 4 -6 points on apgar. As a rule, for such children it is enough to create optimal conditions for the surrounding world, heat and temporary support for breathing and after five minutes the child is restored, it is put on 7 points and higher.
Asphyxia of medium severity
The state of the baby at birth is estimated as a medium. The kid is sluggish, poorly reacts to inspection and stimuli, but spontaneous movements of the hands and feet are observed. Screaming the child is weak, little and easily shrinks. Child's skin is blue, but quickly pose after inhalation of oxygen through the mask. The heartbeat is rapidly, reflexes are reduced.
Breathing after its restoration rhythmic, but weakened, can be mounted intercostal intervals. After medical care in the maternity hospital, children require oxygen therapy for some time. With timely and adequate medical care, the condition of children is improved quickly and they are restored by 4 - 5 days of life.
The condition of the baby at birth is severe or extremely heavy.
With severe asphyxia, the child reacts poorly to the inspection or does not react at all, while the tone of the muscles and the movement of the child weak or they are not at all. Skin skin color and pale or just pale. Poses after breathing oxygen slowly, the skin restores its color for a long time. The heartbeat is muffled. Breathing is nehydramic, irregular.
With very heavy asphyxia, the skin is pale or has a hortal shade. Pressure is low. The child does not breathe, does not react to the inspection, the eyes are closed, there are no movements, there are no reflexes.
As the asphyxicia of any gravity flows, directly depends on the knowledge and skills of medical personnel and good fitting, as well as the child has developed the intrauterine and from the available concomitant diseases.
Asphyxia and hypoxia. Differences in manifestations in newborns
The picture of acute asphyxia and asphyxia in children who have undergone hypoxia intrauterine has some differences.
Features of children born in asphyxia, which transferred long-term hypoxia intrauterine, are presented below.
- Significantly pronounced and long continuing disorders of metabolism and hemodynamics (blood movement in the organism vessels).
- Often, various bleeding occurs as a result of the inhibition of blood formation and reduce the content of microelements in the blood, responsible for stopping bleeding.
- It is more common to develop severe lung damage as a result of aspiration, a shortage of a surfactant (this substance prevents the lungs falling) and inflammation of the pulmonary fabric.
- Often there are disorders of metabolism, which is manifested by a decrease in blood sugar and important trace elements (calcium, magnesium).
- Neurological disorders that arose as a result of hypoxia and due to brain edema, hydrocephaliya (watering), hemorrhages are characteristic.
- Frequently combined with intrauterine infections, bacterial complications are often joined.
- After transferred asphyxia, remote consequences remain.
Among the complications, the early, the development of which occurs in the first hours and day of the life of the baby, and the late, which arise after the first week of life.
Early complications include the following states:
- Defeating the brain, which is manifested by an edema, intracranial hemorrhage, filling the brain sites due to the lack of oxygen.
- Violation of blood flow through the organism vessels, which is manifested by a shock, pulmonary and heart failure.
- Kidney defeat manifested by renal failure.
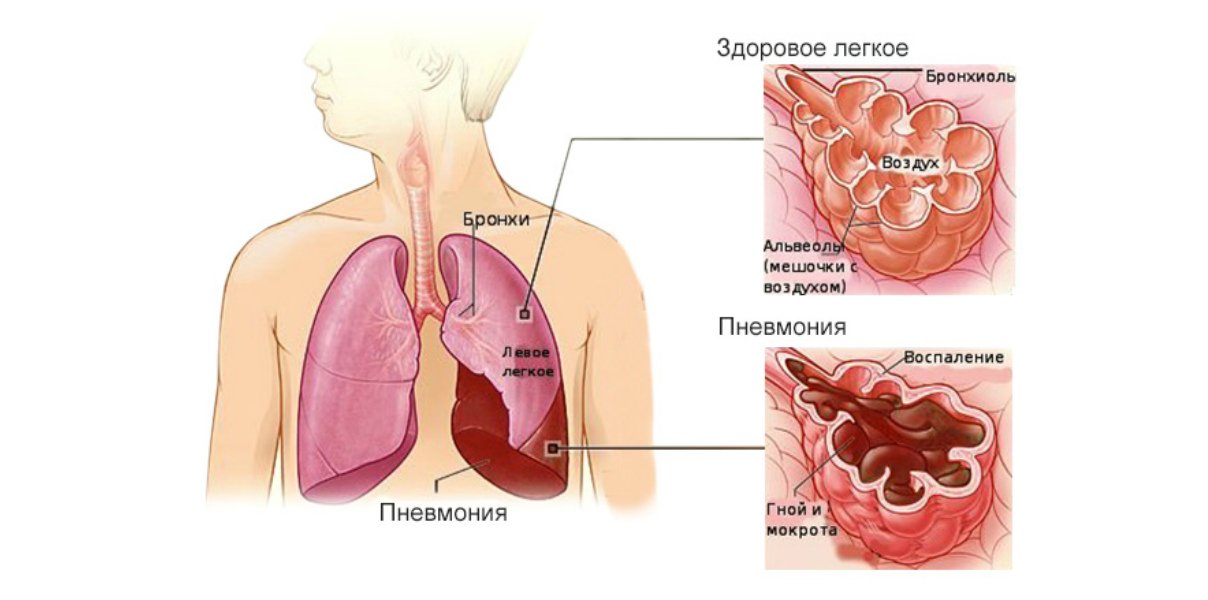
- Light defeat, manifested by edema of the lungs, pulmonary bleeding, aspiration and pneumonia.
- Defeat of digestive organs. The intestine is most of all, his motility is disturbed, as a result of insufficient blood supply, some intestinal sites die out, inflammation develops.
- The defeat of the blood system, which is manifested by anemia, a decrease in platelets and bleeding from various organs.
Late complications include the following states:
- The addition of infections, develops meningitis (brain inflammation), pneumonia (inflammation of the lungs), enterocolit (inflammation of the intestine).
- Neurological disorders (hydrocephalus, encephalopathy). Lekomolation is considered to be the most serious neurological complication - damage (melting) and the motion of the brain sections.
- The consequences of excessive oxygen and therapy: bronchopheral dysplasia, damage to the retinal vessels.
Resuscitation of newborns during asphyxia
The state of children born in asphyxia requires resuscitation. Resuscitation is a complex of medical measures aimed at reviving, resuming respiration and heart abbreviations.
Resuscitation is carried out on the ABC system developed back in 1980:
- "A" means the provision and maintenance of respiratory tract;
- "B" means breathing. It is necessary to restore the breath with the help of artificial or auxiliary ventilation of the lungs;
- "C" means to restore and maintain the reductions in the heart and blood flow by vessels.
Resuscitation events of newborns have their own characteristics, their success largely depends on the readiness of medical personnel and the correct assessment of the child's condition.
- Preparedness of medical personnel. Ideally, two people should have assistance who own the appropriate skills and know how pregnancy and childbirth proceeded. Before the start of childbirth, the medical staff should check whether equipment and medicines are ready to assist.
- The readiness of the place where the child will help. It should be specifically equipped and located right in the maternity hospital or in close proximity to it.
- Reanimation in the first minute of life.
- The stage of resuscitation by "ABC" is a system with an assessment of the effectiveness of each stage.
- Care in carrying out infusion therapy.
- Observation after the relief of asphyxia.
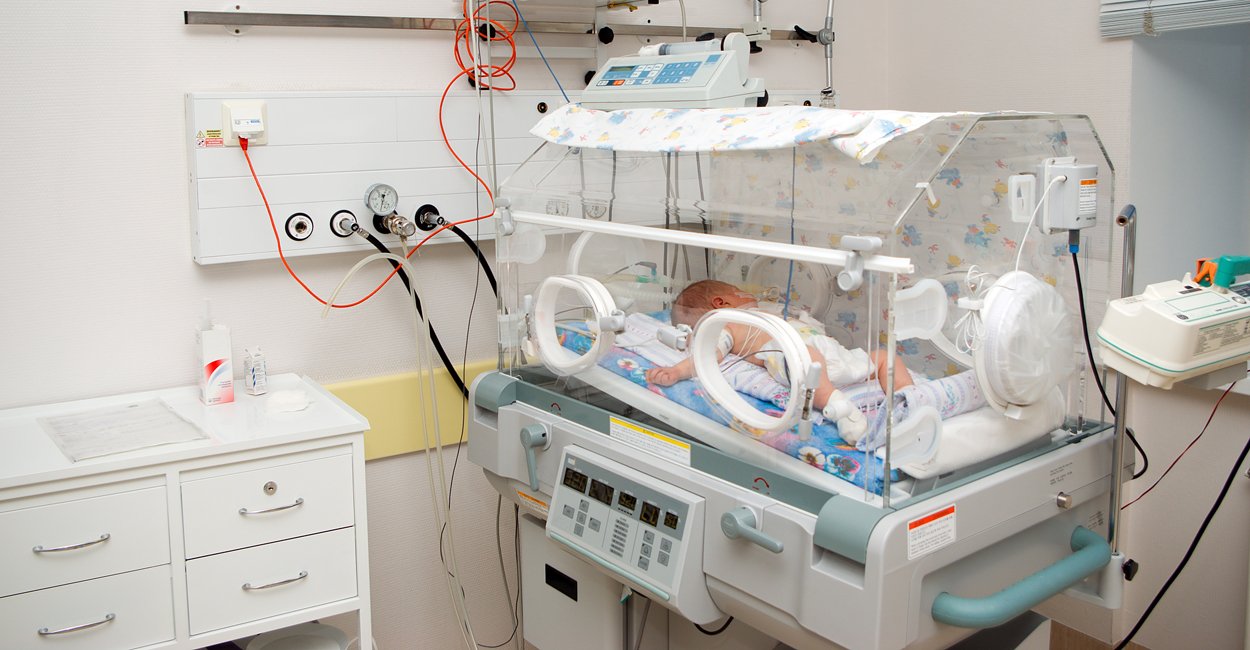
The restoration of breathing begins, as soon as the head of the generic paths appears, with suction of mucus from the nose and mouth. As soon as the child was born completely, it must be warm. For this, it is wipe it, wrapped in heated diapers and put under radiant heat. In the maternity hospital should not be through, the air temperature should not be reduced less than 25 ºС.
And supercooling, and overheating oppress their breath, so it is impossible to allow them.
If the child shouted, he is laid out on the mother's belly. If the baby does not breathe, breathing stimulates, wiping the back and patting the soles of the child. With medium and heavy asphyxia, respiration stimulation is ineffective, so the child is rapidly transported under radiant heat and begin artificial ventilation of the lungs (IVL). After 20 - 25 seconds, they see if there was a breath. If the child's breath restored and the heart rate above 100 per minute, resuscitation stopped and observed for the child's condition, trying to feed the child with maternal milk as soon as possible.
If there is no effect from IVL, again suck the contents of the oral cavity and renew the IVL. In the absence of breathing on the background of IVL for two minutes, the trachea intubation is carried out. A hollow tube is introduced into the trachea, providing air intake to the lungs, the child is connected to the artificial respiration apparatus.
In the absence of heartbeat or reducing the frequency of abbreviations less than 60 per minute, the impermanent of the heart massage, continuing the IVL. Massage is stopped if the heart begins to fight independently. In the absence of heartbeat, a duration of more than 30 seconds, the heart is stimulated with drugs.
Prevention of asphyxia in newborns
All measures for the prevention of asphyxia are reduced to the timely identification and elimination of pregnant causes causing hypocyses of the fetus.
Each pregnant woman should be observed by a gynecologist throughout the pregnancy. It is necessary to register on time, to pass tests, to undergo consultations of doctors and treatment, which is appointed if necessary.
Mother's lifestyle has a significant impact on the development of the fetus.
Conclusion
Treatment of children who suffered asphyxia, until complete recovery is quite a long time.
After the events held in the maternity hospital, children are transferred to children's resuscitation or to the department of the pathology of newborns. In the future, if required, assign rehabilitation therapy in specialized departments.
The forecast largely depends on the severity of damage to the brain under the action of hypoxia. The stronger the brain suffers, the greater the likelihood of a deadly outcome, the risk of developing complications and a longer period of full recovery. In premature babies, the forecast is worse than in children born on time.