Asphyxia of newborns - 4 options for the development of events and their consequences for the child
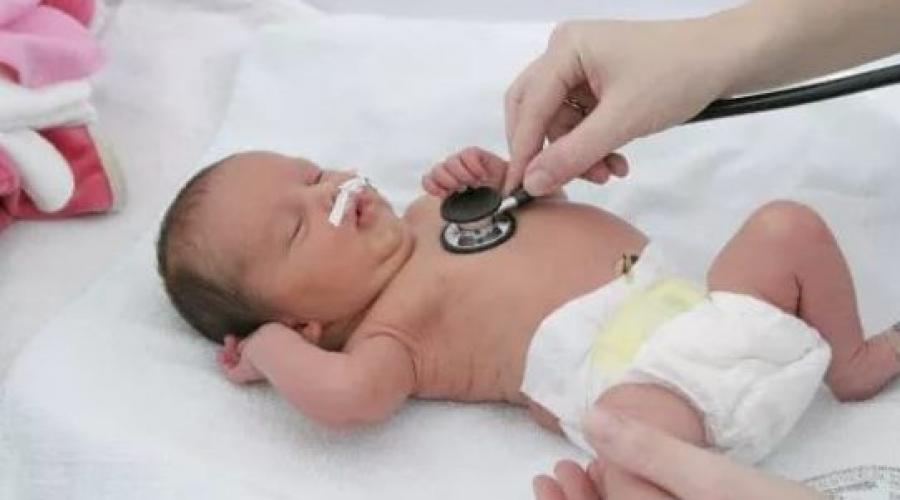
Asphyxia Newborns - Complication developing in the early postpartum period. This pathology is accompanied by a violation of the process of respiration and the work of the cardiovascular system in the infant. Consider more such a state, we will determine its causes, types, find out: what is the difference in the hypoxia of the fetus and the asphyxia of the newborn.
What is asphyxia in a newborn baby?
The asphyxia of newborns is the condition of the small organism, in which the respiratory disorder is observed. At the same time, there is a difference between the pathology and the definition of "hypoxia of the newborn". Oxygen starvation () is developing in the process of pregnancy or childbirth (the detachment of the placenta, the pressing of the umbilical cord), and is accompanied by an insufficient intake of oxygen. In this case, the process of respiration is not violated. Asphyxia (stroke) is characterized by a temporary cessation of respiration and requires resuscitation activities.
The causes of asphyxia of newborns
Asphyxia in a child during childbirth can be provoked by numerous factors. At the same time, the causes that cause pathology can be associated directly with the process of root separation and with the peculiarities of the intrauterine development of the fetus. Among the main pathological factors causing asphyxia, doctors identify:
- Sharp, sudden failures in the bloodstream and in umbilical cord -, the formation of a node on the umbilical cord, hauling.
- The violation of the gas exchange process in the royal-placental system is the wrong preservation of the kindergarten, premature and partial.
- Failure in the process of blood circulation in the placenta caused by the mother.
- Reducing the level of oxygen in the blood of the feminine -, cardiovascular diseases, diseases of the respiratory system.
- The difficulty of the respiratory process at the fetus - the abnormalities of the development of the lungs, chronic infectious processes, the consequence of medications taken.
These reasons provoke primary asphyxia of newborns, which develops in the process of the delivery. However, asphyxia can be both secondary in nature when the violation occurs immediately after the appearance of the baby to the light. Among the reasons for secondary asphyxia must be called:
- aspiration of respiratory tract - fluid getting into the lungs;
- violation of the process of cerebral circulation;
- the immaturity of the lungs is the body is not able to perform respiratory movements;
- congenital brain defects, hearts, lungs.
The degrees of asphyxia of newborns
Depending on the clinical picture and severity of violations, doctors allocate several degrees of pathology. The rating is carried out directly after the birth of the baby on the first minute. The classification of asphyxia of newborns looks like this:
- easy degree;
- average;
- heavy;
- clinical death.
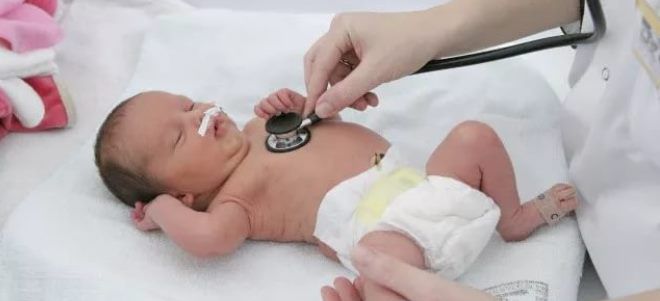
Asphyxia of newborn mild
Asphyxia is a light degree characterized by the lack of a cry, but the reaction of the baby is present on touch. Breathing newborn independent, but slow and irregular. Legs and handles have a blue shade, cardiac activity is not broken. After cleaning the upper respiratory tract from mucus and liquid, carrying out tactile stimulation (stroking on the back, patting on the heels) and oxygen therapy through the mask, the state of the newborn is normalized.
The child born in a state of moderate asphyxia, in the future there is no problem with breathing. At the same time, small neurological disorders are possible, in the form:
- increase muscle tone;
- Handles, legs, lower jaws.
Asphyxia of medium severity in a newborn
This degree of violation is also characterized by the absence of a scream during birth. At the same time, the reaction to tactile stimuli of touch is not observed. A characteristic feature of this form is the change in the color of the skin, so it is often referred to as the blue asphyxia of newborns. Respiratory movements are part of a part, but cardiac activity is not violated.
The average asphyxia of newborns requires ventilation of the lungs. For this, more often use a special bag, occasionally an oxygen mask. The transferred form of pathology always leaves an imprint on the health of the baby, provoking neurological changes:
- increased excitability - unless shouts, long-term tremor handles and legs;
- the oppressed state is sluggish breast sucking, low motor activity (movements with handles and legs are practically not carried out).
Asphyxia of severe in newborns
A severe pathology is accompanied by a complete absence of breathing at the moment of birth. Skin covers due to insufficient blood circulation become pale. Because of this, this form of pathology is denoted as white asphyxia of a newborn. When carrying out a tactile dough, the baby does not respond in any way to touch. There is a violation of the work of the cardiovascular system - when listening to the tone of the heart is strongly muffled or completely absent. Strong bradycardia develops.

This asphyxia of newborns requires urgent resuscitation activities. The actions of the doctors at the same time are aimed at restoring the respiratory and cardiac activity of the newborn. The child is connected to an artificial respiration apparatus. At the same time, medicines are introduced into the umbilical cord, which stimulate cardiac activity. Such kids for a long time are on hardware respiration, and later severe neurological disorders are developing, neurochical development is possible.
Clinical death of the newborn
The clinical death of the baby occurs when doctors fix the complete absence of signs of life. In this case, after birth, the baby does not make one independently inhale, the heart activity is absent, the reaction to stimuli too. The correct and timely start of resuscitation measures gives hope for a favorable outcome. At the same time, the severity of neurological consequences for the health of the kid depends on how long there was no breathing. In such situations, the brain is strongly damaged.
Newborn Asphyxia - Symptoms
In order to evaluate the severity of this pathology, the doctors use a scale of apgar. The method is based on the scores in points at once several indicators:
- reflex excitability;
- breath;
- cardiac activity;
- muscular tone;
- color skin.
For each parameter, points are charged, which are summed up and output overall rating. The results look like this:
- easy degree - 6-7 points;
- average - 4-5;
- heavy - kid picks 1-3 points;
- clinical death - 0 points.
When exposing the degree of asphyxia, obstetres are evaluating the symptoms of violations. The pulse during asphyxia in newborns is reduced and is less than 100 shots per minute. For easy asphyxia characteristic:
- the first breath occurs on 1 minute;
- muscle tone is reduced slightly;
- nasolabial triangle blue;
- breathing is weakened.
At a moderate severity of asphyxia, doctors fix:
- weave breathing
- legs and handles become blue;
- the amount of heart abbreviations is reduced;
- muscular tone is reduced;
- there is a pulsation of cord vessels.
A severe degree of this pathology is manifested by the following symptoms:
- breathing is absent;
- strong bradycardia;
- atonia muscles;
- pallor skin;
- development of adrenal insufficiency;
- strong ripple veins of umbilical cord.

Asphyxia newborns - consequences
Talking about what is dangerous asphyxia in newborns, doctors note that in severe violation, the death of a baby is possible. It happens in the first hours of life. With medium and easy degree, the forecast is favorable. The outcome depends on the time to start resuscitation, the presence of related violations. The consequences of pathology developed during the neonatal period may arise as in the first hours of life and in older age.
Asphyxia in a newborn after childbirth - consequences
The heavy asphyxia of newborns, the consequences of which depend on the correctness and timeliness of the initial therapy, does not pass without a trace for the body. Complications may arise as in the early stages of perinatal development and in high age. Complete brain atrophy after asphyxia in newborns is rare. Among the frequent complications of the early recovery period:
- convulsive encephalopathy;
- hydrocephalus;
- hypertensive syndrome;
- hypo- or hyperoportability.
Asphyxia of newborns - consequences at older age
Asphyxia and hypoxia newborns belong to those complications of pregnancy, which are reflected on the health of the kid after his birth. Problems may appear in a few months, and sometimes years. Among the late complications:
- meningitis;
- pneumonia;
- sepsis.
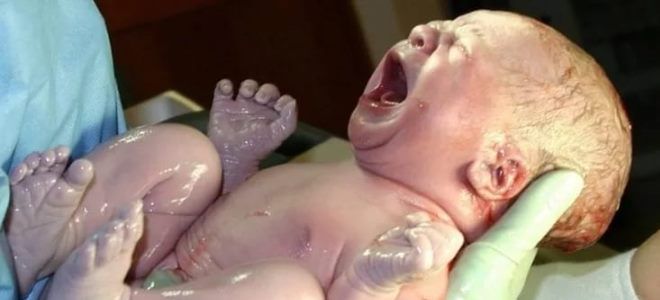
The treatment of asphyxia in newborns
When evaluating the apgar 4 score and less conducted on the first minute, resuscitation activities are required. Resuscitation of the newborn during asphyxia is carried out in 4 stages:
- Liberation of the respiratory tract, ensuring their passability. It is carried out with the help of catheter and electrics. If asphyxia occurs intrauterine, cleaning manipulation is carried out immediately after the appearance of the head.
- Maintaining the respiratory process. Auxiliary ventilation is carried out using a respiratory bag, and with ineffectiveness - the intubation is carried out and the device of artificial ventilation of the lungs is connected.
- Restoring the process of blood circulation. For this purpose, a closed body massage is carried out, even if there are cuts (in bradycardia 60-70 beats per minute). It is carried out by pressing on the sternum by two thumbs, with a frequency of 100-120 times per minute. When cardiac activity is not restored for a minute, go to the next step.
- The introduction of drugs. At this stage of therapy, doctors use the following means to treat asphyxia of newborns: