A sensational discovery by scientists: The secret of the Russian gene pool is revealed. What peoples are genetically closest to Russians? Top secret or gene of "Russianness"
For a long time, the main method of differentiating different ethnic groups of human civilization was the comparison of languages, dialects and dialects used by those or other populations. Genetic genealogy demonstrates a fundamentally different approach in determining the kinship of certain peoples. It uses information hidden in the Y chromosome, which is passed from father to son almost unchanged.
Thanks to this feature of the male chromosome, a team of Russian scientists from the Medical Genetic Research Center of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, in collaboration with Estonian and British geneticists, was able to identify a significant heterogeneity of the original Russian population of our country and trace the patterns of development of the history of the formation of Russia from prehistoric times to the era of government.
In addition, the scientists were able to show that the differences in the genetic structure of the Y-chromosome of northerners and southerners cannot be explained only by the gradual drift of genes due to the isolation of small populations due to geographic conditions. Comparison of the variability of the male chromosome of Russians with the data of neighboring peoples revealed great similarities between the northerners and the Finnish-speaking ethnic groups, while the inhabitants of the center and south of Russia turned out to be genetically closer to the rest of the peoples communicating in Slavic dialects. While the former often have the "Varangian" haplogroup N3, which is widespread in Finland and northern Sweden (as well as throughout Siberia), the latter are characterized by the R1a haplogroup, which is characteristic of the Slavs of Central Europe.
Thus, another factor determining, according to scientists, the differences between the Russian northerners and our southern population, is the assimilation of the tribes that lived on this land long before our ancestors came to it. The variant of their cultural and linguistic "Russification" without significant genetic mixing is not excluded. This theory is also confirmed by the data of linguistic studies describing the Finno-Ugric component of the northern Russian dialect, which is practically not found among the southerners.
Genetically assimilation was expressed in the presence in the Y-chromosome of the population of the northern regions of the family of N-haplogroups. The same haplogroups are also common for most of the peoples of Asia, however, Russian northerners, in addition to this haplogroup, almost never show other genetic markers that are widespread among Asians, for example, C and Q.
This suggests that there was no significant migration of people from Asian regions in the prehistoric times of the existence of the Proto-Slavic peoples on the territory of Eastern Europe.
Another fact was not surprising for scientists: the genetic variations of the Y-chromosome of the inhabitants of the central and southern regions of Ancient Rus turned out to be not only almost identical to those of the “brothers-Slavs” - Ukrainians and Belarusians, but also very close in structure to the variations of the Poles.
Scientists believe that this observation can be interpreted in two ways. First, such a close genetic structure may mean that the process of the Russians moving eastward was not accompanied by the assimilation of local peoples - at least those that had strong differences in the structure of the male genetic line. Secondly, this may mean that the Slavic tribes had already mastered these lands long before the mass migration to them in the 7th-9th centuries of the main part of the ancient Russians (more precisely, the East Slavic people, which had not yet been divided into Russians and other peoples). This point of view is in good agreement with the fact that the Eastern and Western Slavs demonstrate great similarity and smooth regular changes in the structure of the male genetic line.
"Map" of the genetic proximity of the peoples of Europe and individual populations within ethnic groups // ajhg.org/
It should be noted that in all cases, genetically identified subpopulations do not go beyond the ethnic groups defined from linguistic positions. However, this rule has one very curious exception: four large groups of Slavic peoples - Ukrainians, Poles and Russians, as well as Belarusians not shown in the diagram - demonstrate great similarity both in the genetic structure of the male lineage and in language. At the same time, the Russian northerners are significantly removed from this group on the multidimensional scaling diagram.
It would seem that such a situation should contradict the thesis that geographical factors have a greater influence on the variations of the Y chromosome than linguistic ones, since the territory occupied by Poland, Ukraine and the central regions of Russia extends practically from the center of Europe to its eastern border. ... The authors of the work, commenting on this fact, note that genetic variations, apparently, have much in common even for geographically remote ethnic groups, provided that their languages are close.
Summing up the article, the authors conclude that, despite the widespread opinions about a strong Tatar and Mongolian admixture in the blood of Russians, inherited by their ancestors during the Tatar-Mongol invasion, the haplogroups of the Turkic peoples and other Asian ethnic groups have practically left no trace on the population of the modern northwestern , central and southern regions.
Instead, the genetic structure of the paternal line of the population of the European part of Russia demonstrates a smooth change when moving from north to south, which indicates two centers of the formation of Ancient Russia. At the same time, the movement of the ancient Slavs to the northern regions was accompanied by the assimilation of local Finno-Ugric tribes, while in the southern territories, individual Slavic tribes and nationalities could exist long before the Slavic "Great Migration".
P.S. This article caused a lot of responses from readers, many of which we did not publish because of the unacceptably harsh position of their authors. To avoid inaccuracies in the wording, which could at least partially cause the misinterpretation of the conclusions of scientists, we talked with the lead author of the work on the genetic structure of the Russian ethnos Oleg Balanovsky and, if possible, corrected the wording that could cause ambiguous interpretation. In particular, we excluded the mention of Russians as a "monolithic" ethnic group, added a more accurate description of the interaction between Mongoloids and Caucasians in Eastern Europe, and clarified the reasons for gene drift in populations. In addition, an unsuccessful comparison of mtDNA with DNA of nuclear chromosomes is excluded from the text.
It is also important to note that the “ancient Russians” who moved to the east in the 7th-13th centuries were not yet divided into three East Slavic peoples, so it may not seem entirely appropriate to call them Russians. You can read the full interview with Oleg Balanovsky.
Human haplogroups are transmitted through direct male and female lines. But the information stored in the autosomes of DNA is responsible for the genetics of both men and women. Autosomes are the first 22 pairs of chromosomes in humans, which are passed from both parents after crossing over - the process of recombination. Thus, approximately equal half of the genetic information is transmitted from father and mother to offspring.In this study, more than 80,000 autosomal snips, reference points are used - this is a very high resolution, allowing to capture even relatively small influences at the genetic level in the bulk of the people. The comparative analysis data were taken from an open study by V. Verenich, a specialist in the comparative analysis of genetic components. The genetic calculators themselves are located on the GedMatch service, and allow anyone to find out their comparative position on the genetic graph. To do this, it is enough to have the results of an autosomal test from FTDNA, or 23andMe. At the end of the study, maps of geographic distribution and frequency maxima are provided for the main autosomal components from the MDLP World-22 project.
The graphs below show the main components and their average percentage for each of the populations. One line is the percentage breakdown for one population. Each division (vertical bar) corresponds to 10%, and the names of the autosomal components are in the same sequence from left to right as in the legend from top to bottom. The more similar the percentage of total genetics in different peoples, the more similar the figure in the given graph looks. So let's get started ...
Genetics of Germans, Lithuanians, Russians, Swedes, Finns, etc.
This graph shows the main genetic components for European peoples and is aligned by the decrease in the East European component (North-East-European) in different populations. As you can see, all European peoples are quite different genetically, and having genetic components in their set of the same origin, they are nevertheless in very different percentages. For all Slavs and Balts in general, one of the most significant is this component of Eastern Europe, which is at its maximum for Lithuanians and Belarusians. Probably since the time of the archaeological "Corded Ware culture", the territory of these countries has been the center of origin of this component. It is represented by more than 80% of Lithuanians, and only 20% of Italians.Purple represents the Atlanto-Mediterranean component, and it increases as you move from north-east to south-west. So among the Finns it reaches an average of 15%, and among the Italians 40%. The rest of the components are less pronounced.
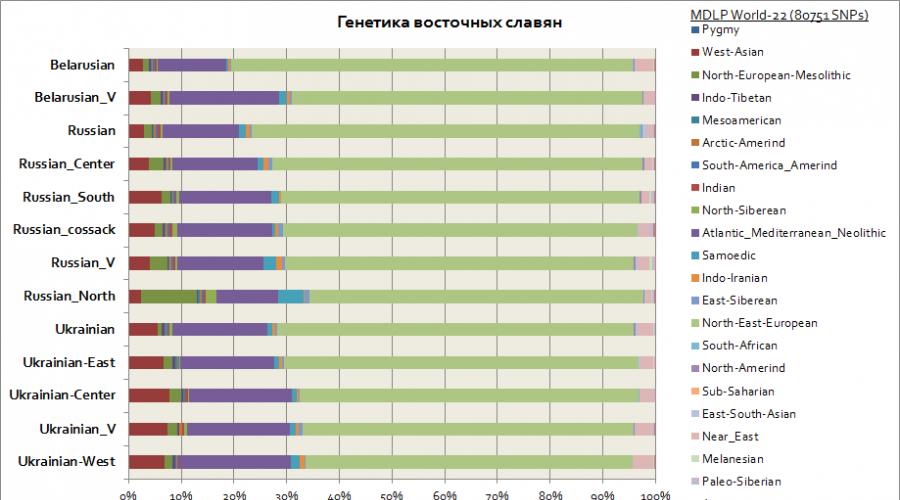
Genetics of Russian Ukrainians Belarusians

This chart shows the Eastern Slavs - Russians, Belarusians, Ukrainians... Attention is drawn to the similarity of the genetic patterns of the three listed peoples, and within the margin of error, they differ quite insignificantly - in the Ukrainians and southern Russians there is a slight increase in the West Asian component, and in the northern Russians there is a slight increase in one of the Siberian components, called conditionally Samoyed, and an increase components of the Mesolithic of Europe to about 10%, which, according to the latter indicator, brings them closer to the German-speaking population of Scandinavia - the Swedes.

This graphic depicts all the Slavs, including Western - Poles and Czechs, as well as southern - Serbs, Bulgarians, Macedonians, etc.
The main components of all Slavs are 2. These are East European and Atlanto-Mediterranean. The first is at the maximum for the Belarusians, and the second for all the southern Slavs - Serbs, Macedonians, Bulgarians. The East European component is more primary in origin among the Slavs, and the Atlanto-Mediterranean is more acquired as the Slavs migrated to the Balkans. Western Ukrainians and Slovaks have a weak increase in the Samoyed component relative to neighboring Slavic peoples - Belarusians, Czechs, Poles; it is probably a genetic trace of the medieval migration of the Huns and Ugrians to Central Europe.
Genetics of Slavs, Russians and Tatars, Germans, Caucasians, Jews, etc.

This graph shows the different origins among the peoples of Russia. As you can see, among the Slavs, the Eastern European component is the main one, and among the peoples of the Volga region, the share of the Siberian components is increasing. While for the Caucasians, the most characteristic is the West Asian component, the Mediterranean and the Middle East.
Genetics of Finns, Ugrians, Udmurts, Hungarians, Sami, etc.

As you can see, the Finns, Vepsians and Karelians are characterized by a similar genetic origin with the Slavs. They also have the highest Eastern European component, decreasing closer to the Urals and the Volga region, with an increase in the Siberian components in this region. Also, all Finno-Ugric peoples have a significant component of the Mesolithic of Europe, which reaches almost 80% among the Sami and is associated with the pre-Indo-European and pre-Neolithic population of Europe. The Hungarians as a whole are characterized by a set of the same genetic components as for other populations of the Carpathian region and Central Europe.

As can be seen, the entire Caucasus is characterized by a relatively similar genetic origin - this is a large share of the West Asian component and the Mediterranean. Only the Nogais are a little knocked out - their share of the Siberian components increases.

As can be seen, the Ashkenazim and Sephardim have a high frequency of the West Asian, Atlanto-Mediterranean and Middle Eastern components. At the same time, the Ashkenazi have a slight increase in the Siberian component, which is probably associated with the Khazar heritage and the growth of up to 30% of the East European component, which, according to this indicator, brings them closer to the countries of southern Europe.
Especially out of their "company" only Ethiopian Jews and Indian Jews. The former have a high proportion of sub-Saharan Africa (up to 40%), while the latter have a high proportion of the South Asian genetic component, conventionally called Indian (up to 50%).
Genetics of Tatars, Bashkirs, Azerbaijanis, Chuvash, etc.

In terms of genetics, the Türks turned out to be one of the most heterogeneous ethnic groups, therefore their genetic components differ significantly. So, given that the primary homeland of the Turks is Siberia, such peoples as the Yakuts, Tuvans, and Khakass have retained the largest percentage of the East Siberian autosomal component, which reaches from 30 to 65%. This genetic component is also the main one among the Kyrgyz and Kazakhs. The rest of the components bring the Turks closer to the peoples from the regions of residence. So, for the Yakuts and Tuvans, these are the North Siberian and Samodian components. In total, these 3 Siberian components among the Yakuts it is up to 90%, among the Tuvinians up to 70%, with an increase up to 20% of the East-South-Asian component, which is connected to a greater extent with the migration flows of the population of East Asia. For the Bashkirs, the share of 3 Siberian components is up to 45%, and the Southeast Asian component is up to 10%. The Tatars have data on 3 Siberian genetic components on average from 25 to 50%. At the same time, the share of components characteristic of the Caucasian population among the Bashkirs is up to 45%, and among the Tatars, on average, from 50 to 70%. The genetics of Azerbaijanis and Turks, within the margin of error, practically does not differ; they, like other peoples of the Caucasus and Transcaucasia region, have a significant Western Asian component (up to 50%) and the Atlantic-Mediterranean (up to 20% on average). The share of 3 Siberian components is presented by Azerbaijanis, Turks and Balkars - at the level of 3-7%.
Conclusion
The genetics of peoples does not have a direct and significant correlation with the distribution of language families, or with the percentage of homogeneous markers - Y-DNA and mt-DNA haplogroups, represented in a particular population. The greatest correlation can be traced according to the territorial-geographical principle. Thus, the share of the Siberian components characteristic of the Mongoloid race as a whole gradually decreases from East to West, and the share of the components characteristic of the Caucasian race increases accordingly. In the border areas along the line from the north of the Urals to Central Asia, their ratio is approximately equal. In the regions east of Lake Baikal, the genetic components characteristic of the large Caucasian race are practically not represented, at the same time, in the regions west of the Pechora-Volga region, the Siberian components characteristic of the large Mongoloid race come to naught.The spread of the Eastern European genetic component to Siberia took place to a large extent already in the Bronze Age (the culture of the Andronov circle), although individual peaks in the extreme east of Siberia among the Chukchi may have already been associated with the migrations of Russians in the 17th century.
The share of the Sub-Saharan component, characteristic of the Negroid race, is distributed throughout Africa - up to the southern Mediterranean and the northern border of the African continent, reaching a maximum in its equatorial part, and practically never occurs outside of it; light background common on the Arabian Peninsula and the southern part of the Iranian plateau.
Geography of genetic components
Alexey Zorrin
Project
We constantly hear that the Russians are not a people welded by blood, kindred by blood, but a conglomerate of people united by a common culture and territory. Everyone remembers Putin's catchphrases "There are no pure Russians!" and "scrape every Russian, you will certainly find a Tatar."
They say that we are "very different in blood", "did not sprout from one root", but were a melting pot for the Tatar, Caucasian, German, Finnish, Buryat, Mordovian and other peoples who ever came, came, arrived on our land, and we accepted all of them, let them into the house, took them to our relatives.
This has become almost an axiom in use among politicians who dilute the concept of Russian, and at the same time for everyone it has become an entrance ticket to the environment of the Russian people.
This approach, raised to the flag by numerous Russophobic à la "human rights" organizations and Russian Russophobic media outlets, has flooded the airwaves. But, Putin and others like him, sooner or later, will still have to answer for their words of humiliation of the Russian people. The verdict of scientists is merciless:
1) In 2009, a complete “reading” (sequencing) of the genome of a representative of the Russian ethnos was completed. That is, the sequence of all six billion nucleotides in the genome of the Russian man has been determined. All his genetic economy is now in full view.
(The human genome consists of 23 pairs of chromosomes: 23 - from the mother, 23 - from the father. Each chromosome contains one DNA molecule formed by a chain of 50-250 million nucleotides. The genome of a Russian man was sequenced. center "Kurchatov Institute", on the initiative of Corresponding Member of the Russian Academy of Sciences, Director of the National Research Center "Kurchatov Institute" Mikhail Kovalchuk According to information received at the Russian Academy of Sciences, only for the purchase of equipment for sequencing, the Kurchatov Institute spent about $ 20 million. center "Kurchatov Institute" has a recognized scientific status in the world.)
It is known that this is the seventh decoded genome behind the Ural ridge: before that there were Yakuts, Buryats, Chinese, Kazakhs, Old Believers, Khanty. That is, all the prerequisites for the first ethnic map of Russia have been created. But all these were, so to speak, composite genomes: pieces assembled after decoding the genetic material of different representatives of the same population.
The complete genetic portrait of a particular Russian man is only the eighth in the world. Now there is someone to compare Russians with: an American, an African, a Korean, a European ...
“We have not found any noticeable Tatar contributions in the genome of Russian, which refutes theories about the destructive influence of the Mongol yoke,” emphasizes the head of the genomic direction at the Kurchatov Institute, Academician Konstantin Skryabin. - Siberians are genetically identical to Old Believers, they have one Russian genome. There are no differences between the genomes of Russians and Ukrainians - one genome. Our differences with the Poles are scanty. "
Academician Konstantin Skryabin believes that "a genetic map of all peoples of the world will be compiled in five to six years - this is a decisive step towards understanding the susceptibility of any ethnic group to drugs, diseases and foods." Feel what it costs ... Americans in the 1990s gave the following estimates: the cost of sequencing one nucleotide - $ 1; according to other sources - up to $ 3-5.
(The sequencing (spelling of the genetic code) of mitochondrial DNA and DNA of the human Y chromosome is the most advanced DNA analysis method to date. "Got off the tree in East Africa. And the Y-chromosome is only in males and therefore is also transmitted practically unchanged to male offspring, while all other chromosomes, when passed from father and mother to their children, are shuffled by nature, like a deck of cards before being dealt. , unlike indirect signs (appearance, body proportions), sequencing of mitochondrial DNA and DNA of the Y chromosome is indisputable and directly indicative of the degree of kinship of people.)
2) Outstanding anthropologist, researcher of human biological nature, A.P. Bogdanov wrote at the end of the 19th century: “We often use expressions: this is purely Russian beauty, this is a spitting hare, a typically Russian face. One can be convinced that not something fantastic, but real lies in this general expression of Russian physiognomy. In each of us, in the sphere of our “unconscious,” there is a rather definite concept of the Russian type ”(AP Bogdanov“ Anthropological physiognomy ”. M., 1878).
A hundred years later, and now the modern anthropologist V. Deryabin, with the help of the latest method of mathematical multivariate analysis of mixed features, comes to the same conclusion: “The first and most important conclusion is the statement of the significant unity of Russians throughout Russia and the impossibility of identifying even the corresponding regional types, clearly delimited from each other "(" Questions of Anthropology ". Issue 88, 1995). How is this Russian anthropological unity expressed, the unity of hereditary genetic characteristics expressed in the appearance of a person, in the structure of his body?
First of all - hair color and eye color, the shape of the structure of the skull. According to these signs, we, the Russians, differ from both the European peoples and the Mongoloids. And we cannot be compared with the Negroes and Semites at all, the discrepancies are too striking. Academician V.P. Alekseev proved a high degree of similarity in the structure of the skull among all representatives of the modern Russian people, specifying at the same time that the "Proto-Slavic type" is very stable and goes back to the Neolithic era, and possibly the Mesolithic. According to the calculations of the anthropologist Deryabin, light eyes (gray, gray-blue, blue and blue) in Russians are found in 45 percent, in Western Europe, light-eyed only 35 percent. Dark, black hair in Russians is found in five percent, in the population of foreign Europe - in 45 percent. The conventional wisdom about the "snub-nosedness" of the Russians is not confirmed either. In 75 percent of Russians, a straight nose profile is found.
Conclusion of anthropological scientists:
“Russians in their racial composition are typical Caucasians, occupying a central position among the peoples of Europe in most anthropological characteristics and differing in a slightly lighter pigmentation of the eyes and hair. It is also necessary to recognize the significant unity of the racial type of Russians throughout European Russia. "
“A Russian is a European, but a European with physical characteristics peculiar only to him. These signs make up what we call a typical hare. "
Anthropologists have seriously scratched the Russian, and - there is no Tatar, that is, a Mongoloid, in the Russians. One of the typical signs of a Mongoloid is epicanthus - a Mongolian fold at the inner corner of the eye. In typical Mongoloids, this fold is found in 95 percent; in the study of eight and a half thousand Russians, such a fold was found in only 12 people, and in its embryonic form.
Another example. Russians literally have a special blood - the predominance of the 1st and 2nd groups, which is evidenced by the long-term practice of blood transfusion stations. In Jews, for example, the predominant blood group is the 4th, the negative Rh factor is more common. In biochemical blood tests, it turned out that Russians, like all European peoples, have a special PH-c gene, this gene is practically absent in Mongoloids (OV Borisova "Polymorphism of erythrocyte acid phosphatase in various population groups of the Soviet Union." "Questions of anthropology ". Issue 53, 1976).
It turns out, no matter how you scratch a Russian, still not a Tatar, you will not find anyone else in him. This is confirmed by the encyclopedia "Peoples of Russia", in the chapter "The Racial Composition of the Population of Russia" it is noted: "Representatives of the Caucasian race make up more than 90 percent of the country's population, and another 9 percent are representatives of forms mixed between Caucasians and Mongoloids. The number of pure Mongoloids does not exceed 1 million people. " ("Peoples of Russia". M., 1994).
It is easy to calculate that if there are 84 percent of Russians in Russia, then they are all exclusively people of the European type. The peoples of Siberia, the Volga region, the Caucasus, and the Urals are a mixture of the European and Mongolian races. This was perfectly expressed by the anthropologist A.P. Bogdanov in the 19th century, studying the peoples of Russia, he wrote, refuting from his far, far away the today's myth that the Russians poured someone else's blood into their people during the era of invasions and colonization:
“Maybe many Russians married natives and became settled, but most of the primitive Russian colonizers throughout Russia and Siberia were not like that. They were a merchant, industrial people who cared to arrange themselves in their own way, in accordance with their own ideal of prosperity. And this ideal of the Russian man is not at all such as to easily twist his life with some kind of "trash", as now all too often the Russian man honors the Gentile. He will do business with him, will be affectionate and friendly with him, will enter into friendship with him in everything, except to become related, in order to introduce a foreign element into his family. Simple Russian people are still strong for this, and when it comes to the family, to the establishment of his home, here he has a kind of aristocracy. Often the settlers of different tribes live in the neighborhood, but marriages between them are rare. "
Over the millennia, the Russian physical type has remained stable and unchanged, and has never been a cross between different tribes that at times inhabited our land. The myth has been dispelled, we must understand that the call of blood is not an empty phrase, that our national idea of the Russian type is the reality of the Russian breed. We must learn to see this breed, admire it, appreciate it in our near and distant Russian relatives. And then, perhaps, our Russian appeal to completely alien people, but our own people for us - father, mother, brother, sister, son and daughter, will be revived. After all, we are actually all from a single root, from one kind - the Russian kind.
3) Anthropologists were able to identify the appearance of a typical Russian person. To do this, they had to translate into a single scale all the photographs from the photo library of the Museum of Anthropology with full-face and profile images of typical representatives of the population of the Russian regions of the country and, combining them according to the pupils of the eyes, superimposed on each other. The final photographs turned out, of course, blurry, but gave an idea of the appearance of the reference Russian people. This was the first truly sensational discovery. After all, similar attempts by French scientists led to a result that they had to hide from the citizens of their country: after thousands of combinations of the obtained photographs of reference Jacques and Marianne, they looked at gray faceless ovals of faces. Such a picture, even among the French, who are most distant from anthropology, could raise an unnecessary question: is there a French nation at all?
Unfortunately, anthropologists did not go further than creating photographic portraits of typical representatives of the Russian population of different regions of the country and did not superimpose them on each other in order to get the appearance of an absolute Russian man. In the end, they were forced to admit that they could get into trouble at work for such a photo. By the way, the "regional" sketches of the Russian people were published in the general press only in 2002, and before that they were published in small editions only in scientific publications for specialists. Now you can judge for yourself how similar they are to the typical cinematic Ivanushka and Marya.
Unfortunately, mostly black-and-white old archive photos of the faces of the Russian people do not allow to convey the height, physique, color of the skin, hair and eyes of the Russian person. However, anthropologists have created a verbal portrait of Russian men and women. They are of medium build and medium height, light brown-haired with light eyes - gray or blue. By the way, during the research, a verbal portrait of a typical Ukrainian was also obtained. The standard Ukrainian differs from the Russian only in the color of his skin, hair and eyes - he is a dark-skinned brunette with regular facial features and brown eyes. A snub nose turned out to be absolutely uncharacteristic for the Eastern Slav (found only in 7% of Russians and Ukrainians), this sign is more typical for Germans (25%).
4) In 2000, the Russian Foundation for Basic Research allocated about half a million rubles from state budget funds for the study of the gene pool of the Russian people. It is impossible to implement a serious program with such funding. But it was more a landmark than just a financial decision, indicating a change in the country's scientific priorities. For the first time in Russian history, scientists from the Laboratory of Human Population Genetics at the Medical Genetics Center of the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, who received a grant from the Russian Foundation for Basic Research, were able to fully focus on the study of the gene pool of the Russian people, and not small peoples, for three years. And limited funding only spurred their ingenuity. They supplemented their molecular genetic studies with an analysis of the frequency distribution of Russian surnames in the country. This method was very cheap, but its information content exceeded all expectations: a comparison of the geography of surnames with the geography of genetic DNA markers showed that they almost completely coincide.
Unfortunately, the interpretations of the family analysis that appeared in the media after the first publication of the data in a specialized scientific journal could create the wrong impression about the goals and results of the enormous work of scientists. The head of the project, Doctor of Sciences Elena Balanovskaya, explained that the main thing was not that the surname Smirnov turned out to be more common among the Russian people than Ivanov, but that for the first time a complete list of truly Russian surnames was compiled by regions of the country. First, lists were compiled for five conditional regions - North, Central, Central-West, Central-East and South. In total, in all regions there were about 15 thousand Russian surnames, most of which were found only in one of the regions and were absent in others. When regional lists were superimposed on each other, scientists identified only 257 so-called “all-Russian surnames”. Interestingly, at the final stage of the study, they decided to add the surnames of the residents of Krasnodar Territory to the list of the Southern Region, expecting that the predominance of Ukrainian surnames of the descendants of the Zaporozhye Cossacks, evicted here by Catherine II, would significantly reduce the all-Russian list. But this additional limitation reduced the list of all-Russian surnames by only 7 units - to 250. From which the obvious and not for everyone's pleasant conclusion followed that the Kuban was inhabited mainly by Russian people. And where did the Ukrainians go and were there any Ukrainians at all - a big question.
For three years, the participants of the "Russian Gene Pool" project went around with a syringe and a test tube almost the entire European territory of the Russian Federation and made a very representative sample of Russian blood.
However, cheap indirect methods of studying the genetics of the Russian people (by surnames and dermatoglyphics) were only auxiliary for the first study of the gene pool of the titular nationality in Russia. His main molecular genetic results are available in the monograph "Russian Gene Pool" (Publishing House "Luch"). Unfortunately, due to the lack of government funding, scientists had to carry out part of the study jointly with their foreign colleagues, who imposed a moratorium on many of the results until joint publications were published in the scientific press. Nothing prevents us from describing this data in words. So, according to the Y-chromosome, the genetic distance between Russians and Finns is 30 conventional units. And the genetic distance between a Russian person and the so-called Finno-Ugric peoples (Mari, Vepsians, etc.) living on the territory of the Russian Federation is 2-3 units. Simply put, they are genetically almost identical. The results of the analysis of mitochondrial DNA show that the Russians from the Tatars are at the same genetic distance of 30 conventional units, which separates us from the Finns, but between the Ukrainians from Lvov and the Tatars, the genetic distance is only 10 units. And at the same time, Ukrainians from the left-bank Ukraine are genetically as close to Russians as Komi-Zyryans, Mordovians and Mari.
from the blog AEKSEY_RUDKO
Only one male chromosome, Y, does not participate in this lottery; it is entirely passed from father to son like a relay baton. Let me clarify that women do not have this Y chromosome at all.
In each subsequent generation, mutations occur in certain parts of the Y chromosome, called loci, that will be passed on to all subsequent generations through the male gender. It was thanks to these mutations that it became possible to reconstruct the genus. There are only about 1000 loci on the Y chromosome, but only a little more than a hundred are used for comparative analysis of haplotypes and reconstruction of genera.
In the so-called loci, or they are also called STR markers, there are from 7 to 42 tandem repeats, the general picture of which is unique for each person. After a certain number of generations, mutations occur and the number of tandem repeats changes up or down, and thus it will be seen on the common tree that the more mutations, the more ancient the common ancestor for a group of haplotypes.
The haplogroups themselves do not carry genetic information, because genetic information is located in autosomes - the first 22 pairs of chromosomes. You can see the distribution of genetic components in Europe. Haplogroups are just marks of bygone days, at the dawn of the formation of modern peoples.
What haplogroups are most common among Russians?
| Peoples | Qty, Human | R1a1, | R1b1, | I1, | I2, | N1c1, | E1b1b1, | J2, | G2a, |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| East, West and South Slavs. | |||||||||
| Russians(north) | 395 | 34 | 6 | 10 | 8 | 35 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Russians(Centre) | 388 | 52 | 8 | 5 | 10 | 16 | 4 | 1 | 1 |
| Russians(south) | 424 | 50 | 4 | 4 | 16 | 10 | 5 | 4 | 3 |
| Russians (all Great Russians) | 1207 | 47 | 7 | 5 | 12 | 20 | 4 | 3 | 2 |
| Belarusians | 574 | 52 | 10 | 3 | 16 | 10 | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| Ukrainians | 93 | 54 | 2 | 5 | 16 | 8 | 8 | 6 | 3 |
| Russians(together with Ukrainians and Belarusians) | 1874 | 48 | 7 | 4 | 13 | 16 | 4 | 3 | 3 |
| Poles | 233 | 56 | 16 | 7 | 10 | 8 | 4 | 3 | 2 |
| Slovaks | 70 | 47 | 17 | 6 | 11 | 3 | 9 | 4 | 1 |
| Czechs | 53 | 38 | 19 | 11 | 12 | 3 | 8 | 6 | 5 |
| Slovenes | 70 | 37 | 21 | 12 | 20 | 0 | 7 | 3 | 2 |
| Croats | 108 | 24 | 10 | 6 | 39 | 1 | 10 | 6 | 2 |
| Serbs | 113 | 16 | 11 | 6 | 29 | 1 | 20 | 7 | 1 |
| Bulgarians | 89 | 15 | 11 | 5 | 20 | 0 | 21 | 11 | 5 |
| Balts, Finns, Germans, Greeks, etc. | |||||||||
| Lithuanians | 164 | 34 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 44 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Latvians | 113 | 39 | 10 | 4 | 3 | 42 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Finns (east) | 306 | 6 | 3 | 19 | 0 | 71 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Finns (west) | 230 | 9 | 5 | 40 | 0 | 41 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Swedes | 160 | 16 | 24 | 36 | 3 | 11 | 3 | 3 | 1 |
| Germans | 98 | 8 | 48 | 25 | 0 | 1 | 5 | 4 | 3 |
| Germans (Bavarians) | 80 | 15 | 48 | 16 | 4 | 0 | 8 | 6 | 5 |
| The British | 172 | 5 | 67 | 14 | 6 | 0.1 | 3 | 3 | 1 |
| Irish | 257 | 1 | 81 | 6 | 5 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| Italians | 99 | 2 | 44 | 3 | 4 | 0 | 13 | 18 | 8 |
| Romanians | 45 | 20 | 18 | 2 | 18 | 0 | 7 | 13 | 7 |
| Ossetians | 359 | 1 | 7 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 16 | 67 | |
| Armenians | 112 | 2 | 26 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 6 | 20 | 10 |
| Greeks | 116 | 4 | 14 | 3 | 10 | 0 | 21 | 23 | 5 |
| Turks | 103 | 7 | 17 | 1 | 5 | 4 | 10 | 24 | 12 |
Especially noteworthy are the 4 most common haplogroups among Russians:
R1a1 47.0%, N1c1 20.0%, I2 10.6%, I1 6.2%
In simple terms: genetic makeup Russians on the straight male lines of the Y chromosome looks like this:
Eastern Europeans - 47%
balts - 20%
And two haplogroups of native Europeans from the Paleolithic era
Scandinavians - 6%
Balkans - 11%
The names are conditional and given in accordance with the territorial maximums European subclades for haplogroups R1a1, N1c1, I1 and I2. The fundamental point is that the descendants of the Mongols after two hundred years of the Tatar-Mongol yoke did not remain. Or there is still a very small number of direct genetic heirs from such ties. With these words, I do not want to question the historical sources about the Mongols in Russia at all, but only to draw attention to the alleged genetic influence on the part of the Mongol-Tatars on the Russians - it is not there, or it is insignificant. By the way, there is also a large number of carriers in the genome of the Bulgar Tatars haprogroup R1a1(about 30%) and N1c1(about 20%), but they are mostly not of European origin.
Another important point, the southern Russians, within the margin of error, do not differ from the Ukrainians, and the northern Russians, having one of the predominant haplogroups R1a1, also have a higher percentage of the N1c1 haplogroup. But the% of N1c1 haplotypes is on average 20% in Russians.
Emperors. Nikolay 2
The first known ancestor of the Grand Ducal House of Oldenburg was, mentioned in the annals for 1091, Egilmar, Count of Lerigau (d. 1108).
Nicholas II turned out to be a carrier of the haplogroup R1b1a2- a representative of the Western European line, from the Holstein-Gottorp dynasty. This Germanic dynasty is characterized by the terminal snip U106, which is most widespread in northwestern Europe in the places of settlement of Germanic tribes. This is not quite typical for Russian people DNA marker, but its presence among Russians could also be associated with early contacts between Germans and Slavs.
Natural princes. Rurikovich
Vladimir Monomakh and his descendants, called "Monomashiches" belong to the haplogroup N1c1-L550 which is widespread in the South Baltic region (subclade L1025) and in Fennoscandia (subclades Y7795, Y9454, Y17113, Y17415, Y4338). The terminal snip Y10931 is characteristic of the Rurik dynasty.
Some of those whom historians call the Olgovichi (named after Oleg Svyatoslavich - the main rival of Vladimir Monomakh in the feudal struggle - and, as all sources assure, his cousin) have no kinship with the Rurikovichs from the Monomashic family (in the direct male line). These are the descendants of Yuri Tarusky
Russians, Slavs, Indo-Europeans and haplogroups R1a, R1b, N1c, I1 and I2
In ancient times, about 8-9 millennia ago, there was a linguistic group that laid the foundation for the Indo-European family of languages (at the initial stage, most likely these are haplogroups R1a and R1b). The Indo-European family includes such linguistic groups as Indo-Iranians (South Asia), Slavs and Balts (Eastern Europe), Celts (Western Europe), Germans (Central, Northern Europe). Perhaps they also had common genetic ancestors, which about 7 thousand years ago, as a result of migrations, ended up in different parts of Eurasia, some went to the south and east (R1a-Z93), laying the foundation for the Indo-Iranian peoples and languages (largely taking part in the ethnogenesis of the Turkic peoples), and some remained in Europe and laid the foundation for the formation of many European peoples (R1b-L51), including the Slavs and Russians in particular (R1a-Z283, R1b-L51). At different stages of formation, already in antiquity, there were intersections of migration flows, which was the reason for the presence of a large number of haplogroups in all European ethnic groups.Slavic languages emerged from the once united group of Balto-Slavic languages (presumably the archaeological culture of the late Corded Ware). According to the calculations of the linguist Starostin, this happened about 3.3 millennia ago. Period from the 5th century BC to IV-V century A.D. can be considered conditionally Proto-Slavic, tk. The Balts and the Slavs were already divided, but the Slavs themselves were not yet there, they will appear a little later, in the 4-6 centuries AD. At the initial stage of the formation of the Slavs, probably about 80% were haplogroups R1a-Z280 and I2a-M423. At the initial stage of the formation of the Balts, probably about 80% were haplogroups N1c-L1025 and R1a-Z92. The influence and intersection of the migrations of the Balts and Slavs was from the very beginning, therefore, in many respects, this division is conditional, and in general reflects only the main trend, without details.
Iranian languages belong to Indo-European, and their dating is as follows - the most ancient, from the 2nd millennium BC. to IV century BC, middle - from IV century BC until the 9th century A.D., and a new one - from the 9th century A.D. Until now. That is, the most ancient Iranian languages appear after the departure of a part of the tribes who spoke Indo-European languages from Central Asia to India and Iran. Their main haplogroups were probably R1a-Z93, J2a, G2a3. The Western Iranian group of languages appeared later, around the 5th century BC.
Thus, the Indo-Aryans, Celts, Germans and Slavs in academic science became Indo-Europeans, this term is the most appropriate for such a vast and diverse group. This is completely correct. In the genetic aspect, the heterogeneity of the Indo-Europeans is striking, both in Y-haplogroups and in autosomes. The Indo-Iranians are characterized to a greater extent by the Near Asian genetic influence of BMAC.
According to the Indian Vedas, it was the Indo-Aryans who came to India (to South Asia) from the north (from Central Asia), and it was their hymns and legends that formed the basis of the Indian Vedas. And, continuing further, we will touch on linguistics, because this is the Russian language (and its related Baltic languages, for example, Lithuanian as part of the once existing Balto-Slavic linguistic community) is relatively close to Sanskrit along with Celtic, Germanic and other languages of the large Indo-European family ... But genetically, the Indo-Aryans were already to a greater extent the Near Asians, and as they approached India, the Veddoid influence also intensified.
So it became clear that haplogroup R1a in DNA genealogy - this is a common haplogroup for a part of the Slavs, a part of the Turks and a part of the Indo-Aryans (since naturally there were representatives of other haplogroups in their midst), a part haplogroup R1a1 during migrations across the Russian Plain, they became part of the Finno-Ugric peoples, for example, the Mordovians (Erzya and Moksha). Part of the tribes (for haplogroup R1a1 this is a subclade Z93) during migrations brought this Indo-European language to India and Iran about 3500 years ago, that is, in the middle of the 2nd millennium BC. In India, by the works of the great Panini, it was made into Sanskrit in the middle of the 1st millennium BC, and in Persia-Iran, the Aryan languages became the basis of the group of Iranian languages, the oldest of which date back to the 2nd millennium BC. These data are confirmed by: DNA genealogy and linguistics are correlated here.
Extensive part haplogroup R1a1-Z93 even in antiquity they joined the Turkic ethnic groups and mark today in many respects the migrations of the Turks, which is not surprising in view of the antiquity haplogroup R1a1, while representatives haplogroup R1a1-Z280 were part of the Finno-Ugric tribes, but during the settlement of the Slavic colonists, many of them were assimilated by the Slavs, but even now, among many peoples, for example, Erzya still has the dominant haplogroup R1a1-Z280.
All this new data was able to provide us DNA genealogy, in particular, the approximate dates of migrations of carriers of haplogroups on the territory of the modern Russian Plain and Central Asia in prehistoric times.
So scientists to all Slavs, Celts, Germans, etc. gave the name of the Indo-Europeans, which corresponds to reality from the point of view of linguistics.
Where did these Indo-Europeans come from? In fact, Indo-European languages existed long before migrations to India and Iran, throughout the Russian Plain and up to the Balkans in the south, and up to the Pyrenees in the west. Later, the language was spread to South Asia - and to Iran and India. But genetically, there are much fewer correlations.
"The only justified and accepted in science at present is the use of the term" Aryans "only in relation to tribes and peoples who spoke Indo-Iranian languages."
So in which direction did the Indo-European flow go - to the west, to Europe, or vice versa, to the east? According to some estimates, the Indo-European language family is about 8,500 years old. The ancestral home of the Indo-Europeans has not yet been determined, but according to one version, it could be the Black Sea region - southern or northern. In India, as we already know, the Indo-Aryan language was introduced about 3500 years ago, presumably from the territory of Central Asia, and the Aryans themselves were a group with different genetic Y-lines, like R1a1-L657, G2a, J2a, J2b, H, etc.
Haplogroup R1a1 in Western and Southern Europe
Analysis of 67 marker haplotypes haplogroup R1a1 from all European countries made it possible to determine the approximate migration path of the R1a1 ancestors in the direction of Western Europe. And calculations showed that almost all over Europe, from Iceland in the north to Greece in the south, the common ancestor of the haplogroup R1a1 was one about 7000 years ago! In other words, the descendants, like a baton, passed on their haplotypes to their own descendants from generation to generation, diverging in the process of migrations from the same historical place - which, presumably, turned out to be the Urals or the Black Sea lowland. On the modern map, these are the countries of mainly Eastern and Central Europe - Poland, Belarus, Ukraine, Russia. But the area of more ancient haplotypes of the haplogroup R1a1 leads to the east - to Siberia. And the lifetime of the ancestor, which is indicated by the most ancient, most mutated haplotypes, is 7.5 thousand years ago. In those days, there were still no Slavs, no Germans, no Celts.Lack of method
If you have made the test, and you are greatly pleased with it, then I hasten to bring in my ladle of tar. Yes, the Y chromosome is passed from father to son practically unchanged, but there is actually no genetically useful information in it, in other pairs of chromosomes there are much more genes.
And these other 22 are shuffled in a very random way, with no traces left on Y of such a mixing.
Imagine. Anglo-Saxon seafarers took over the Negro state. Women are not accepted on such trips, and one has to establish contact with the local population. What are the possible options?
1) The Anglo-Saxons have children from black women, but the nationality is passed on only to boys. In this case, the Y chromosome will be transferred to the European one, but the proportion of actually significant European genes will decrease. The first generation will be half blacks and the former "aristocracy" in such a case will quickly dissolve, although Y will be from this ethnic group. Only there will be little sense from it. Perhaps something similar happened with the Finns and Indians. The Yakuts and Finns have the highest percentage of their characteristic haplogroup N1c1, but genetically they are completely different peoples with different subclades of haplogroup N1c1 with their own unique history, separated more than 6 millennia ago. Conversely, Indians - having a high percentage haplogroup R1a1 genetically they have very little in common with the European representatives of this haplogroup, because also various subclades with their own history separated more than 6 millennia ago.
2) Indo-Aryans arrange a caste system. The first generation will also be semi-black, but then, if the aristocracy interbreeds only with each other, then the percentage of the original genetics will float around 50%. But in practice, marriages will be mainly with local women, and even more so it will be impossible to get the initial gene pool of the conquerors. And similar things happened in the history of the Earth. The highest castes of Hindus from 20% to 72% have haplo group R1a1(on average 43%), but genetically they have very little in common with European or Turkic representatives of the same haplogroup R1a1, and again the reason is different subclades with their own special history.
A similar situation probably happened in Cameroon, a Central African country where Y haplogroup R1b-V88, but at the same time among the typical anthropologically African Negroid population.
It can be concluded that the presence of a marker and a haplogroup is an important condition for determining nationality, but not sufficient. To determine the national-territorial origin of a person, Family Tree DNA has an autosomal test called Family Finder
Alexey Zorrin 
The Pentagon has recognized the experiments with biomaterials of Russian citizens
The apocalyptic assumption about the possible development of biological weapons by the Americans has received strong confirmation. The Pentagon has recognized the fact of collecting biomaterials from Russian citizens.
According to Pentagon spokesman Bo Downey, the 59th Air Force Medical Group's Molecular Research Center is conducting musculoskeletal studies to identify various biomarkers associated with injury. Samples of Russian origin are required only because the first batch of them was from Russia, and now an identical one is needed for control.
Recall that the American Air Force intends to purchase 12 samples of the RNA molecule and 27 samples of the synovial (joint) fluid of the Russians. This announcement was posted on the US government procurement portal. At the same time, the contract emphasizes that among all residents of Russia, the customer is only interested in Europioids, and people from, for example, from Ukraine will not be considered.
The issue of collecting biomaterials from Russians began to be discussed in society after a public statement by Vladimir Putin. According to him, biomaterials are collected "for different ethnic groups and people living in different geographic points of the Russian Federation." "The question is, why are they doing this?" the president asked rhetorically at a meeting with human rights activists.
Later Dmitry Peskov explained that it was about information received through the special services.
Putin’s words have caused caustic ridicule from part of Russian society. “The ancient Incas were also afraid of such dirty tricks, so the supreme ruler even had special maids whose task was to eat hair, spitting, nail clippings and other biomaterial left over from the Great, in order to avoid the trash from falling into the wrong hands,” the media quoted the teacher Andrei Nikulin.
Nevertheless, the country is preparing at the legislative level to counter the new threat. It is expected that in December a law on the protection of biomaterials will be submitted to the State Duma. "Today we have many laboratories that conduct clinical research, these are foreign laboratories, for example, Invitro. We allowed them to the most intimate," explained the problem of the first deputy head of the State Duma Committee on Education and Science Gennady Onishchenko.
In "Invitro" their involvement in the export of biomaterials denied. In turn, the SP Institute of General Genetics of the Russian Academy of Sciences reported that this institution was involved in the collection of biomaterials. “The scientific director of our institute, academician Nikolai Yankovsky, has just organized and headed the program for the collection of biomaterials,” said Ilya Zakharov-Gezehus, an employee of the institute. It was not possible to promptly contact the Yankovsky "SP" itself.
Alexei Kulikov, senior researcher at the Genetics Laboratory at the Institute of Developmental Biology, Russian Academy of Sciences, is inclined to justify his American colleagues.
You have to understand what the Americans were doing. They looked at how genes work in patients with an affected musculoskeletal system and looked at the composition of the synovial fluid. They initially purchased biomaterials somewhere in Eastern Europe from sick representatives of the Slavic nation, and therefore they also need control samples of people whose musculoskeletal system is normal from representatives of the Slavic nation: Russians, Ukrainians, Belarusians, etc.
"SP": - Well, how ?! The tender explicitly states that biomaterials from Ukraine will not be considered. It is the Russians that they need ...
All the same, it is not connected with any intentions there. Genetic weapons are all nonsense. This is unrealistic, since people in the world are too polymorphic - very diverse. It is difficult to think of something that would work on some and not work on others. I think this is just about the conditions of the experiment. There is scientific experience and there is control. Control materials must be from the same region.
"SP": - Everything is so, if these "scientific research" were not carried out by the military, the Pentagon ...
Scientific research can also be carried out by the military. We also have specific medical tasks that are being addressed by representatives of the security forces. Perhaps we are talking about the low mobility of the pilots. They have to sit for a long time. Therefore, it is fundamentally important that there are no problems with the musculoskeletal system. Therefore, Americans are interested in these diseases and what genes are responsible for it.
In turn, head of the laboratory at the Institute of General Genetics of the Russian Academy of Sciences Sergei Kiselev believes that creating genetic weapons is too risky and it is easier to kill people using traditional methods.
Biomaterials have been and are being transferred from Russia. At least, as Onishchenko said, within the framework of clinical trials. Because over the past 25 years, dozens of foreign companies have been conducting clinical trials of drugs in Russia. Biomaterials are needed to understand how drugs work.
Of course, any such sample can be used both for the above purposes, and for some others. Because he still remains a national biological model. The main thing is how the information obtained with the help of the sample will be subsequently used. Genetic information can be used for a variety of purposes, including for selfish purposes.
"SP": - Which ones?
Today's technologies make it possible to determine the genome of each person in detail. That is, taking a DNA sample from a spoon in the canteen of the CIA building, you can determine whether the intelligence officer really comes from the state of Minnesota, as he wrote when he was hired, or he is from Eastern Siberia. That is, you can very accurately tie a person to a place.
But for this, you must first create a genetic map of the territories. I think that interested special services of many countries of the world have been making such maps of territories for a long time. To be able to identify people in different circumstances.
For example, people of dangerous professions. If one of them is torn to pieces, it is possible, using the genetic map, to establish who he is, where he came from and pay tribute to him. That is, within the country. But if this information falls into third hands, it can be used to their advantage.
"SP": - In this case, we are interested in the likelihood of creating genetic, ethnic weapons ...
In my opinion, it makes no sense to create such a weapon. First, in order to kill a person, you need to influence vital functions such as respiration, blood circulation, etc. There are not many of them, and they are the same for all people. Finding an ethnically important vital function is hardly possible.
And second, who are the Americans? They do not have a titular nation. Everyone was mixed up there, including Russians, Chinese, Anglo-Saxons. Therefore, if you create a weapon against the Russians, some of the Americans will fall under its effect, since they are either Russians or their descendants.
Therefore, the more people spread across the planet, the mixing of genomes, the less likely it will be possible to create a genetic weapon. It is not cost effective. Easier, cheaper and more efficient to soak in another way.
"SP": - Nevertheless, the Pentagon conducts such research, and today its representative directly admitted it ...
I looked at the terms of the tender. This Air Force base has requested RNA samples. But RNA is a subgenetic material. It is an intermediary between the human genome and the functional state of the cell. RNA reflects the specialization of each individual cell at one time or another. That is, the genome - DNA in every cell of the body is always the same. And the RNA in each cell is different, because it is a portrait of how the genome works at every minute. Therefore, the RNA sample taken from the big toe will be different from the RNA from any other organ. The Americans did not indicate where exactly they needed RNA.
The second thing they asked for was synovial fluid from the joint capsule. Moreover, in the terms of the tender, it was agreed that the liquid can be taken from another donor, not the one from whom the RNA was taken. That is, Americans do not need any connection between RNA and synovial fluid. It looks like they were taking samples for various studies that are not related to each other.
"SP": - However, this did not add clarity ...
Maybe they laundered money there in this way. Or students learned to write bids for a tender.
Igor Nikulin, a former member of the UN biological weapons commission, has no doubts about the aggressive plans of the Pentagon.
Of course, this is an attempt by the Americans to conduct research for military purposes. The Pentagon is not a charitable or humanitarian organization dedicated to the benefit of humanity. Rather, the opposite is true. It is possible to use viruses that will act selectively.
Such viruses still exist. For example, Ebola, Lassa, Marburg. The hemorrhagic fevers that they cause act mainly on the Negroid race, the bird flu - on the Mongoloid, SARS on the Indo-Europeans.
"SP": - In the conditions of the competition, for some reason, an exception is made for Ukraine ...
In Ukraine, the American program was carried out 5-7 years ago. And now they have only epidemics. Either measles, then rubella, then tuberculosis, then tetanus, then cholera, etc. And then the Americans offer them vaccines against this. Very comfortably.
Over the past ten years, the United States has spent tens of billions of dollars, has created more than four hundred laboratories around the world, which are developing new types of biological weapons and vaccines for them. About forty laboratories are located in the countries of the former USSR. These are Ukraine, Moldova, Georgia, Armenia, Azerbaijan, Uzbekistan, Kyrgyzstan and Kazakhstan. Such is the controlled chaos.
"SP": - But our Russian geneticists are skeptical about the possible development of weapons aimed at one or another ethnic group ...
What else can they do? Many of them are on grants. If I sat on a grant, I would also be silent. But, since the Americans will not offer me any grants, I can speak on these topics freely.
Rate the news
Partners news: