How to log in with an Administrator account in Windows XP. Account Administration in Windows XP Log in xp as administrator
Read also
In all versions of Windows that were born after Windows XP, logging in with Admin rights is not so easy. This is easily explained by the fact that an account with Administrator rights is set to be blocked. Why was she blocked? In fact, the answer is simple - users who log in under this account put the entire system at undue risk. Having made meaningless changes, the user can “put the system on the shoulder blades”, or severely harm it.
Let's take a closer look at why you should not log in as Admin while working on a computer. In the hands of the Administrator is the entire operating system, that is, he is able to influence the system through various settings. Curious or inexperienced users, without realizing it, can harm the operating system. For example, reconfigure the registry.
Sometimes there are situations in which it is extremely important to log in to the system under the Administrator. I don't think it's worth dwelling on the question, why do this? As mentioned earlier, from the Administrator's record, the settings for everything your heart desires are concentrated in your hands.
So, we gradually approached the consideration of the procedure itself, after which it is not difficult to log in with Administrator rights to the Windows 7 system. The account itself must be part of the administrator account group
There are several ways to log in as Administrator.
1. Using the Computer Management utility:
2. Using the "Command line":
Instead of the word administrator, you should write the name of the system administrator.
How to log in as administrator Windows 8?
With regards to the Windows 8 system, the previous two methods for logging in under the Administrator account apply to this version as well.
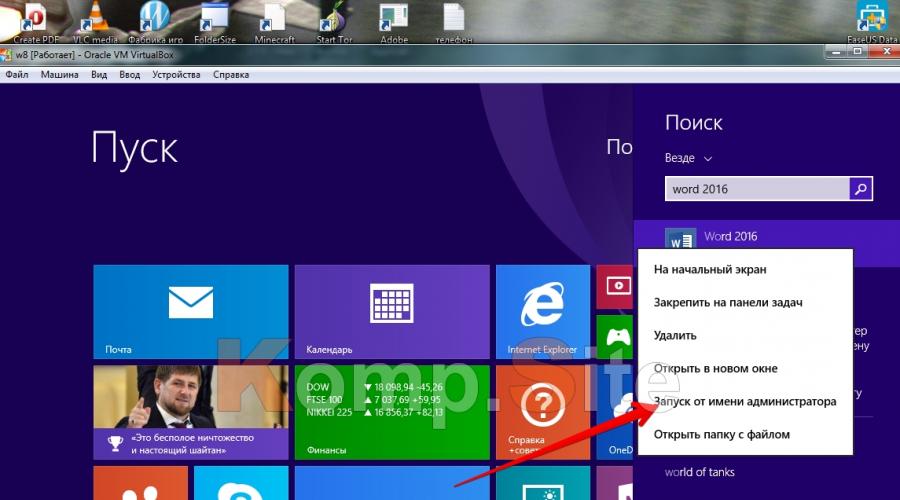
Windows 8 also allows you to run software as Administrator. Here you need to right-click on the shortcut of the program that you want to open as Administrator. This brings up the menu at the bottom of the monitor. Among the list of the menu that appears, find "Run as administrator", run it, and a program opens that gives you Administrator rights.

You can also make a certain program run constantly by applying Administrator rights. In this regard, on the shortcut of the desired program, click on the right functional mouse button, selecting "Properties". Next, select the "Compatibility" tab and in it put a check mark next to the entry "Run the program using administrator rights." Accordingly, click "OK". After such actions, the program will always open with Admin rights.

You can do the same thing in a different way. Right-click on the shortcut, select "Properties" and the "Shortcut" tab. Then click on "Advanced" and check the box next to the entry "Run as administrator". Click "OK" in each open window.
Each account in Windows 10 has its own access rights. Privileges can be given as a regular user or a user with extended rights, as well as an administrator. If you log in with administrator privileges, you can do everything: changing UAC, setting up and administering a local network, installing any applications - in general, really everything you want to do in the operating system.
Method number 1 - using the command line
How to use it? We launch the cmd mode on behalf of the admin by any method convenient for you (for example, right-click on the start button "Start" and select the item "Command line (administrator)" in the menu).
Now that you are logged in, enter the following command at the prompt: and quietly log in to the system with maximum access rights.

This is the most accessible, simple and clear way to log in as an administrator, since it does not require special knowledge and skills, and all the necessary administration skills are reduced to a banal right-click on a menu item.
Method number 2 - using the "Local Security Policies" snap-in
The above snap-in is a great tool for OS administration. More details can be found in the article. If you haven't used it before, it's time to join. This mechanism is incredibly functional and capable of quite a lot, so you will use its services more than once if you want to make your work in Windows 10 more comfortable and enjoyable.
We enter it using the key combination Win + R and entering the command "secpol.msc". An alternative way is "Start" -> "System Tools - Windows" -> "Control Panel" -> "Security and System" -> "Administrative Tools".
Finally, if you are logged into this tool, open the Local Policies -> Security Settings folder and select the Accounts: Administrator account status option from the list of options on the right.

Double click on the parameter and activate the presented option.

We save all the changes, and now you can log in under the current active account with admin rights.
Method number 3 - using the utility "Local groups and users"
Again we resort to the key sequence "Win + R" and set the command "lusrmgr.msc". The equipment we need opens. We open the “Users” branch in detail and study the list of users who have access to the system.

We select the user we need and double-click the mouse. The form of user access parameters to the OS opens. Go to the second tab "Group Membership", and here we add the "Administrators" group to the privileges of the active user. How to do it? First, click on the "Add" button.

Next, in the text field of the new form that opens, enter the name of the group - "Administrators". After that, click on the "Check Names" button. The group must be identified and its full name must appear in the same form. We click OK, and the group is added to the privileges of the active user.

Method number 4 - using Windows 10 settings
We go to the "Settings" menu of the system and select the "Accounts" section in it. Next, we need the category "Family and other users." Here, in the section of the form we need, we perform one click on the user's name. The Change Account Type button appears. Click on it.

As a result of such simple manipulations, a mini-form appears on the screen with a choice of account type. Select "Administrator" from the list and confirm your decision by clicking OK.

Now all that remains for us is to log into the system under this user and enjoy all the benefits of extended superuser rights.
In this article, I described several practical ways to log in as an administrator to Windows 10. In fact, such rights may be needed if you often install new applications, clean the registry, change operating system settings. In all other cases, normal user rights may be sufficient, and you can work successfully without administrator privileges.
Hi all. In today's article, I want to show you the easiest way to how to login as administrator windows 7. But for this we will need you, you will learn how to turn it on at the link.
Open the start menu, move the mouse cursor over the arrow next to the “shut down” button and select “change user” in the context menu that opens.
Next, the monitor screen will turn off and after a few seconds all the accounts registered on your computer will appear on it, you need to select the one with the signature "Administrator" and double-click on it with the left button.

Now the computer will successfully start the system as an administrator and from that moment absolutely all windows 7 settings will be available to you.
If you are not an experienced computer user, which I am 100% sure of (otherwise you would know how to log in with administrator rights), then I do not recommend staying in the system for a long time with this profile.
Because with careless use, windows 7 can start to fail and then you have to.
How to log in with a regular account?
To log in with a regular account, you need to do everything that I showed above, but with the only difference that in the menu that opens you must select not the “change user” item, but the “log out” item.
Since when you select the first one, the administrator account will not be disabled, as a result, when you turn off the computer, you will receive a warning that shutting down windows can lead to data loss.

If you saved all the data before exiting, then this problem is easily solved, just click the "yes" button.
I also want to advise you on one of my latest articles about. Perhaps you will need it.
And that's all for today. Now you know how to login as administrator windows 7. I hope you liked this post and share it using the buttons below or subscribe to my RSS feed.
The admin account gives the user full control over the computer. In this case, there are all system folders, files that are located on the computer. It becomes possible to make changes that will affect other users of the computer. You can change security settings, install software and hardware.
By default, in Windows 10, this account is not active and is not displayed when you select a user. To sign in with these rights, you must have an account of this type on your computer. You can check your account type after logging in.
If your account type is not admin, you won't be able to log in as admin if you don't know the username and password of the account on the computer.
How to log in as an administrator

How to login to windows 10 as administrator
You can use the Local Security Policy utility. For a quick login, you can use the command line by typing "secpol.msc". You can open it in the standard way by clicking the Start menu, selecting the "Control Panel" section, then "Administrative Tools".
In the window that opens, you need to open the "Local Policies" branch, select the "Security Settings" item and on the right, in the policies, select the following item: "Accounts: Status "Administrator". You will need to double-click on it and enable the account. The rights will be granted and at startup it will be possible to log in as an administrator.

How to log in as an administrator to a computer
You can log into the system with administrator access with unlimited capabilities through the Local Users and Groups utility. You will need to run the "lusrmgr.msc" command at the command prompt. Then expand the "Users" section to see all the users that are on the PC. 
What to do if a user with rights is deleted?
If the admin account has been deleted, then it will not be possible to restore it using the described methods. These recovery methods are only suitable if you do not have access to your account, for example, you forgot your password. Then you can give your current account admin rights.
In this case, it is recommended to use "System Restore".
The first method is to open the "Control Panel" through the Start menu. Then select the "Recovery" section, then "Start System Restore". After the done actions, the "System Restore" window will open, where you need to click "Next". All possible restore points will become available to which you can return / roll back, including the one where the admin account was still.
If this method does not help, then you can try another method.
To do this, you need a disk or flash drive with the desired OS. When the system boots, enter Safe Mode (by pressing "F8"), then select "Troubleshoot your computer". The Windows 10 System Recovery Options window will open. You will need to boot from the drive and select "System Restore". After which the OS will be updated, the administrator account will be created again. In this case, the files will not be affected, they will remain in their places.
The Administrator account gives the user full control over the computer, including full access to all system folders. However, while using this account, UAC is disabled and does not display warning messages.
By default, in Windows 10, the Administrator account is not active and does not appear when you select a user. In this article, we'll show you how to activate this account and how to use it to sign in to Windows 10 as an Administrator.
Step #1: Launch Command Prompt with Administrator rights.
In order to log into Windows as an Administrator, you first need to activate an Administrator account. And for this you need.
To do this, first press the key combination Windows+X and in the menu that opens, select "Command Prompt (Admin)".
After that, a pop-up window with a warning from User Account Control (UAC) will appear. In this window, click on the "Yes" button.

Thus, you will launch a command prompt with Administrator rights. Now, using this command line, you can run a command that activates the Administrator account in Windows 10.
Step #2: Activate the Administrator account.
So, after the command line is open, you can activate the Administrator account. To do this, on the command line, you need to run the command " net user administrator /active:yes". If you have an English version of Windows 10, then this command will look like this “net user administrator / active: yes”.

After the message "Command completed successfully" appears in the Command Prompt, you can close the Command Prompt.
Step number 3. We enter Windows 10 as Administrator.
Once the Administrator account is activated, it can be logged on like any other account on the computer. To do this, click on the "Start" button, and then click on the username in the upper left corner of the "Start" menu and select "Administrator".

After that, a standard screen for logging into your account will appear, and in order to log into Windows 10 as an Administrator, you just have to click on the "Login" button.
Some notes about using the Administrator account:
- Do not use the Administrator account all the time. Perform the operations you need with the system and disable this account using the “net user administrator / active: no” command;
- If you plan to regularly log into Windows 10 as an Administrator, then set a password for this account;
- The Administrator account is local, and when using this account, you will not be able to use new applications for Windows 10;
- The Administrator account can be enabled and disabled through "Local Users and Groups", for this you need to run the "usrmgr.msc" command;
Today's article is devoted to the extensive topic of protecting a PC running Windows XP from the inept actions of a novice user. The actions that I am going to describe can be useful both in an enterprise where there is a large amount of computer equipment, and there are very few specialists who can correct the changes made by users to the system settings , or it can come in handy at home when a small child or grandmother works with a computer, which is almost the same thing. I ask grandmothers not to be offended! The reason for writing this article was - ending patience. I mean endless fixes for common user errors in the enterprise I work for. So often the following happens:
accidentally turn off a network device;
accidentally disable anti-virus programs;
remote desktop programs (Remote Administrator, etc.);
remove keyboard layouts;
install unnecessary applications (games, etc.);
there were cases when the applications necessary for the work were deleted;
change system parameters;
There is also a theoretical possibility that the prohibition on changing system settings under a user who does not have the right to change those same settings can protect the system from some virus programs.
So my decision to limit these actions and others (see the text) is final and not subject to change. Getting started, let's do the basic steps.
1. Getting Users
1. If you are using Windows builds (Zver, Best Xp and the like)
You know, many smart people can start criticizing me now. To say that screw builds are complete garbage ... but I think that for a simple user it is very convenient.
So this is what I mean, if you have a similar Windows XP installed, then you probably have an additional applet in the control panel called "Win2K User Accounts"
If it is available, this will make it easier for you, go to the menu "Start"? "Setting" ? "Control Panel" ? "Win2K User Accounts"
First, let's look at the system administrator settings.
Here we can change the administrator name. What is it for? The fact is that if you change the administrator's name, then for those who try to hack into your computer this will be one of the additional obstacles, because the standard name admin or administartor will not work. Of course, this will not stop a professional cracker, but still.
Since in this case we are protecting the computer not from hackers, but to a greater extent from the actions of ordinary users, I did not change the administrator's name. Go ahead.
In the next tab "Group Membership" we look to select a group from the drop-down menu Administrators.
Everything, we figured out the computer administrator, we move on to adding a new user. We give it a name, you can set a description, then move on.
For the user, I would set a password. In any case, this will only be an additional, albeit a small, brick in ensuring the security of the computer.
After creating a password, the setup utility will take you to a menu in which we will set the rights for this user "Limited access"
We save the settings and you're done. To check, you can do a change of user and make sure that by registering under the name of a new user you will not be allowed much of what was said above.
Now consider what to do if this utility is not available.
2. If you are using regular standard Windows XP
First, let's go to the menu. user accounts
:"Start"? "Setting" ? "Control Panel" ? "User accounts"and create a new user.
In the next window, select Limited entry and press the button Create an account.
Congratulations! You have created a limited user account.
Computer user rights management
Create then we created the user, but Windows also provides for more fine-grained user settings. This menu is located in:"Start"? "Setting" ? "Administration"?"Local Security Policy".In the window that opens, find"Local Policies"?"Assigning Rights to Users".
This menu allows you to configure permission or prohibition to perform certain actions for users of this computer. There is nothing complicated there .... Good luck!(jcomments on)(odnaknopka)
A small instructive article from which you will learn how you can find out what rights your account has, what other users are present in the system and how to log into the OS as an administrator.
So, let's start the excursion with the most basic and paramount.
How to find out under which profile (account) you are in the system?
IN Windows XP it is enough that you open Start menu and see the account name in the title.
IN Windows 7 need to go to Control Panel And user accounts.
IN Windows XP right click on to my computer, choose Properties, go to the tab Additionally and click the button Options in field User profile:
A window will appear in which you can see all user profiles and, if necessary, "play around" with them. But it's up to whoever wants it.

In Windows 7 we follow the path: Control Panel -> All Control Panel Items -> User Accounts -> Manage Accounts

Now let's find out What rights does the account (profile) have?.
In XP and 7, this is done the same way - right-click on to my computer(in the Start menu or on the Desktop) and select Control.

Next, we need an item Local groups and users and in it Users

If you click on the user, then you can also "cheat" with his rights and password, which we will do now.
IN Windows XP You can only edit and add a profile using administrator rights. They can be obtained, in most cases, if you log into the system in .
IN Windows 7 it's more interesting. The fact is that even if you have an Administrator account, then he is, as it were, not a full Admin. In the "seven" there is already a built-in SuperVisor or SuperAdministrator, and to enter the OS under it, you just need to uncheck Disable account V Admin Properties.

After that, we reboot and a new account will appear when loading:

There is still a small nuance here. In Windows 7 Home Basic (Home Basic) and Starter (Initial / Starting) there are no Local Policies, which means you will not be able to uncheck the item.
But it's okay, you just need to run (console) (right-click on it and select Run as administrator), then enter in the field
net user Administrator /active:yes
and reboot.
It is worth warning you that when you log in as an Administrator, all programs (including those located in) are launched with his privileges. This can give the green light to all sorts of viruses and malware.
And yet, it is desirable to set a password for the Administrator account.
Article content:
In any enterprise where computers/software are maintained by adequate people, ordinary computer users do not have any administrative rights behind them, which greatly reduces the risk of deleting important system files, installing incomprehensible software, and other miracles. However, some programs stubbornly refuse to work without administrator rights - and what to do if there is no desire to give the user computer administrator rights, but there is a need to run the application?
The article will discuss how to give a regular user the ability to run the application, and not give him administrator rights on the computer. We will talk about two methods - more or less safe (Issuing rights to the folder with the program), and less secure (the method using the RunAs program).
Granting rights to the folder with the program
Often, administrator rights are required for a program to perform any operations with files in its folder - for example, a certain Programm "e needs to write data to its configuration file in the folder where it is installed (let's say this directory C:\Program Files (x86)\Programma). You can try to give the right users full rights to this folder. This is done as follows:
- Right click on the folder, open Properties
- In Properties, open the tab Safety.
- Depending on your computer settings, you may see either " Add"or" Change". In the first case, you need to press the button " Add", in the second - " Change", after which you will most likely need to enter administrator account information. After that, a window will appear with a button" Add", which you will need to press.
- After pressing the button " Add" add all the necessary users. To check the correctness of the username entered, you can use the button " Check names".
- Then we give full rights to the added user - for this you need to check the box " Permissions for....", paragraph " Full rights".
Running the program under an administrator account from a regular user account
For this purpose, the RunAs program, which comes with Windows, will do. For the convenience of using it, the easiest way is to create a cmd file in which you should put the following:
C:\WINDOWS\system32\runas.exe /user:\ /SAVECRED
Instead of User Domain and User, enter the data of a user account that has administrator rights in the domain or on the computer (in this case, instead of the User Domain, write the computer name). Instead of the Path to the program, respectively, write the path to the desired exe file.
Requirements.
The article applies to Windows XP.
Information
Typically, if a computer has multiple local administrator accounts, Windows automatically hides the built-in Administrator account. But there is a need to log into Windows under this account. This can be done in three ways, with the choice of envy depending on your system settings.
Method number 1. If you are using the Welcome screen.
1. Wait for the screen " Greetings", where you will be prompted to select the desired account from the list;
2. Hold down the two buttons "Ctrl" and "Alt" on the keyboard, without releasing the pressed buttons, press the "Del" button on the keyboard twice;
3. The screen should display the " Login to Windows" with two fields "User", "Password" and three buttons "OK", "Cancel", "Parameters >>";
4. In the "User" field, enter Administrator and password (if any) and click the "OK" button;
If you have an automatic login to Windows, i.e. If you are not prompted for a username and password, then follow these steps.
Ending a session
<имя Вашего пользователя>
";
3. In the "Exit Windows" window, click the " Exit". We draw your attention once again "Exit" button;
4. Wait for the session to end and the " Greetings";
5. Then follow steps 2 - 4 indicated in method No. 1;
Method number 2. If you are not using the Welcome screen.
If you do not use the "Welcome" screen, but instead you have a window " Login to Windows", which has two fields "User", "Password" and three buttons "OK", "Cancel", "Parameters >>", then:
1. In the "User" field, enter Administrator
2. In the "Password" field, enter the password (if any) and click the "OK" button;
If you have an automatic login to Windows, i.e. If you are not prompted for a username and password, then follow these steps.
1. Wait for the desktop to load;
2. Click the "Start" button and select " Finishing work...";
3. In the window " Shutdown Windows", in the "Select the desired action" field, select " Ending a session <имя Вашего
пользователя>
" and click the "OK" button;
4. Then follow the steps indicated in method No. 2;
Method number 3. Using safe mode.
1. Turn on the computer;
2. As soon as letters and / or numbers appear on the screen, periodically (2 times per second) press the "F8" button on the keyboard;
3. A menu should appear on the screen. In this menu, select " Safe mode";
4. If a window appears prompting you to click "Yes" or "No", click the " Yes";
5. The "Administrator" account will appear automatically, you will only have to select it and enter the password (if any);