A presentation of the National Program “Digital Economy” took place at Skolkovo. Presentation on the topic: “What is the digital economy? “In the digital world, the main currency is customer data
The program provides for the creation of a National Data Architecture
The second day of the Open Innovations forum, held at the Skolkovo Innovation Center, began with a presentation of the Digital Economy National Program. It was attended by Deputy Prime Minister of Russia Maxim Akimov, who oversees the implementation of digital transformation projects in the Cabinet of Ministers, Minister of Digital Development, Communications and Mass Communications of the Russian Federation Konstantin Noskov, President and Chairman of the Board of Sberbank German Gref, General Director of Yandex in Russia Elena Bunina.
The development of a national program is accompanied by the adoption of new decisions for the development of digitalization. Its success depends, among other things, on technological progress. That is why modern trends are in the constant focus of Russian experts.
During the presentation of the national program, Deputy Prime Minister of the Russian Government Maxim Akimov spoke about the main directions of the digital economy:
“Two key things we will work on are the creation of a National Data Architecture, it must meet the needs of the parties and the state. We also need to work on data regulation. What was once expensive may now be worth nothing, and what we considered insignificant has become valuable. The digital economy has taken place, but what matters is how we manage it.”
As noted by the Minister of Digital Development, Konstantin Noskov, in this regard, the duty of the state is to create such conditions so that every person or organization can connect to broadband Internet. “Within 6 years we will move to providing most government services via the Internet. The national program is the core that ensures the development of other industries. Including healthcare and education.”
German Gref, assessing the Digital Economy program from the point of view of the banking sector, explained that services should be customized as much as possible, because today people do not want to use mass services, they like personal services.
In 2018, the state company “Russian Railways” again acts as an official partner of the International Forum “Open Innovations”.
⠀
Russian Railways is one of the world's largest transport companies and the largest employer in Russia. Today it provides over 45% of cargo turnover and about 25% of passenger turnover of the entire transport system of Russia.
⠀
The company is carrying out comprehensive work to introduce innovative domestic technologies to modernize the industry and increase its efficiency. Among the priority sectors: alternative power sources for rolling stock and infrastructure, unmanned means and technologies for monitoring the condition of infrastructure, IT platforms for customer services in the field of freight and passenger transportation, and others.
⠀
Russian Railways experts became active participants in the VII Moscow International Forum of Innovative Development “Open Innovations”, and company speakers spoke at panel sessions.
What is the digital economy? “In the digital world, the main currency is customer data. Digital companies have significantly more of this currency than others." Konstantin Tsivin, Vice President for Marketing and Business Development, Astro Soft Company 1. The digital economy is an economy based on new business models that combine the physical and digital worlds. 2. She is no better. It is the only possible economy in the next 10 years. For the world is changing rapidly, migrating in the “digital direction”. Russia is still lagging behind; we apparently need a kick in the form of a state program that should support the development and widespread implementation of the digital economy.
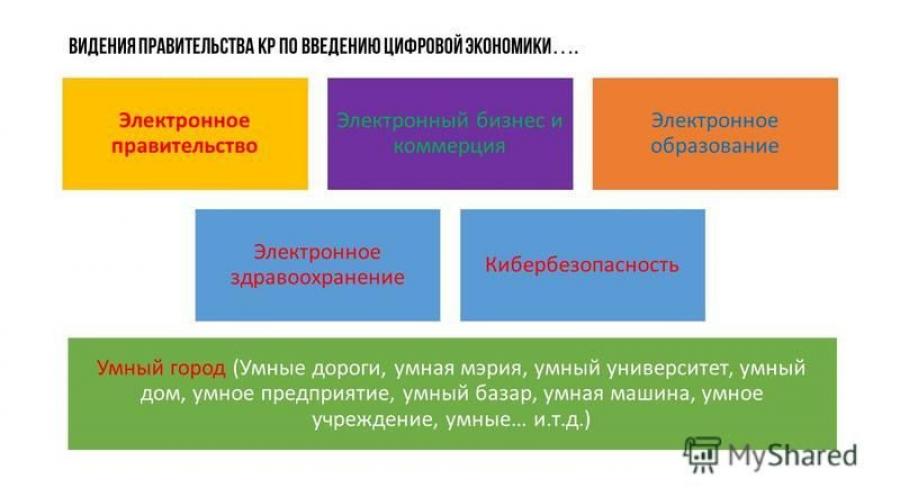
Vision of the Government of the Kyrgyz Republic on the introduction of the digital economy.... E-government E-business and commerce E-education E-health Cybersecurity Smart city (Smart roads, smart city hall, smart university, smart home, smart enterprise, smart bazaar, smart car, smart institution, smart... etc.)

List of names of industry models for digitalization of the economy of the Kyrgyz Republic as a whole Address register Agriculture Meteorology Basic spatial data Biodiversity Internal space of buildings Accounting for greenhouse gases Maintaining administrative boundaries Armed forces. Exploration Energy Ecological structures of the Ministry of Emergency Situations. Fire protection Forest cadastre Forestry Geology National GIS (e-gov) Groundwater and wastewater Healthcare Archeology and protection of monuments National security Hydrology International Hydrographic Organization. Irrigation Land cadastre Municipal government Lake navigation State cadastre Oil and gas structures Pipelines Raster storage facilities Bathymetry, lake bed topography Telecommunications Transport Water supply, sewerage, housing and communal services

Why them??? are freely available are not tied to the technology of the “selected” manufacturer are created as a result of the implementation of real projects created with the participation of industry specialists are designed to ensure information interaction between various products and technologies do not contradict other standards and regulatory documents are used in implemented projects around the world are expandable to meet the needs customer without loss of compatibility with other projects and/or models are accompanied by additional materials and examples a large community of participants, while access to the community is open to everyone a large number of references to data models in publications over recent years

Predictions: In 30 years, robots will be able to do almost everything that humans can do, according to Moshe Vardi, professor of computer engineering and director of the Ken Kennedy Institute for Information Technology at Rice University. University). This will lead to more than 50% of the world's inhabitants becoming unemployed. “We are approaching a time when machines will outperform humans in almost every activity,” Vardy said. I believe that society needs to face this problem before it rises to its full height. If machines are able to do almost everything that people can do, what will they be left to do?” Vardy made the announcement at the annual meeting of the American Association for the Advancement of Science, presenting a paper entitled “Intelligent Robots and Their Impact on Society.”

The role of universities in the digital economy... Launch of an international ranking Implementation of the “Digital Education” project program. New requirements of educational standards and programs Introduction of personal learning paths Introduction of online courses that have passed examination into the educational program, etc.... Increasing the practice orientation of educational programs Creation of “Digital Economy Centers”

It is necessary to introduce... 2018 Introduction of the elective course “Fundamentals of the Digital Economy” on the basis of the department “Business Informatics and Mathematics in Economics” at the Faculty of Business and Economics in order to ensure the relevant competencies of bachelors and masters. In the amount of 6-7 credits (hours) Introduction of an elective course “Fundamentals of the Digital Economy” for the university as a whole in order to ensure the relevant competencies of bachelors. In the amount of 3-4 credits (hours) Creation of the “Digital Economy Center” at Osh State University. Organization of internships and training courses according to plan

Svetlana Anurova Public Relations Manager Google Russia There are threats on the Internet, but the last thing we would like to do is leave here saying: “Oh, horror!” The Internet is a place where everyone needs to be. Our main task is to build your life on the Internet so that it is as useful and interesting as possible.


At the CIPR-2017 conference, Minister of Communications and Mass Communications Nikolai Nikiforov spoke about the “Digital Economy of Russia - 2024” program. This is an interesting document with quite correct conclusions. I am publishing the presentation with explanations for each slide.
What is the “digital economy”? This is data that is created using various sensors, data generation sources, stored, protected, processed, and based on it, thoughtful, high-quality decisions are made. Accordingly, new added value is formed.
Russia currently occupies a far from leading position in the global digital market. 38th place in terms of economic results of using digital technologies, 41st place in readiness for the digital economy, 43rd place according to the global competitiveness ranking. This is not even sad, but very bad, since digital is the future.

Accordingly, it was necessary to draw conclusions.
First: that we need to ensure the priority of digitalization in terms of our regulatory framework. We must ensure that the priority and favorable conditions are given to those technologies that are based on this digital long-term approach.
Conclusion two: we must create an environment within which we will encourage innovative processes and investments in innovation and research in every possible way so that the corresponding technological revolution will support this digital transformation.

The program was divided into nine main areas.

And three layers: environment, platform and technology, markets and economic sectors. The program's task is to focus on the first two layers. The environment, the legislative regulatory environment, personnel, infrastructure, information security and the management system that ties it all together are those institutional conditions without which it is impossible to create the necessary foundation for development. Platform and technologies are those technological elements that ensure the creation of a kind of digital foundation, a fulcrum on the basis of which the further process of digital transformation will take place.

From the point of view of legislation and the regulatory environment, it is necessary to create such legal groundwork that will provide priority for the digital approach to activities in key sectors of the economy and create a special legal regime.

The next section is staffing. We need to reconsider traditional approaches to organizing labor relations, create a variable certification system in order to harmonize professional standards, take into account new challenges, the transformations that occur in traditional sectors of the economy, and thus take this into account throughout the entire educational environment.

Research and development. The goal is to coordinate the efforts of the main players, to form a mode of full-fledged network interaction between them, to make the necessary connections between enterprises, universities, and research centers in order for it all to work. In addition, it is an incentive to attract private investment in research and development, since the state should only play the role of a catalyst. All direct implementation of digitalization should remain with private business.

Information infrastructure. From the point of view of the size of our country, despite the optimistic indicators about high 3G speed and LTE penetration at 70%, we still have a lot, a lot to do. Very often we see in the media attention to the so-called fifth generation of communication technologies – 5G. It is directly related to digitalization and the point of 5G is that per square kilometer we will be able to serve a significantly larger number of connected devices. If today we mainly consider our smartphone or some familiar electronic device as a connected device, then almost all objects that surround a person in his usual life will become connected. The density of such connections will increase dramatically and completely different speeds of these connections will be required. This is why fifth-generation technologies are needed, which will be deployed at least in cities with a population of over a million, where their maximum concentration will be observed.

Information Security. Especially in the context of various ongoing events, including in the Russian Federation, related to various virus attacks, failures in the operation of individual communication networks, we all understand how dependent we become on the reliable uninterrupted operation of the relevant digital telecommunications and other types of information systems. Our task is to ensure that we respect the rights and freedoms of citizens, guarantee them in the same way as we guarantee from the point of view of our traditional law. All this must be transferred to the digital environment and the necessary legal regime must be ensured. We must ensure that the jurisdiction of the Russian Federation is one of the most favorable in the world for the implementation of the most advanced modern technologies.

Public administration. A real revolution is currently taking place in the Russian Federation in terms of procedures for obtaining government services. More than half of citizens - this is shown by the official report of Rosstat - receive services electronically. But public administration is not only the provision of public services, it is also an increase in the efficiency of the state as a large hierarchical structure, which also manages quite serious resources: property, finances, and many other aspects. Here it is necessary to create a number of conditions, including such infrastructural aspects as, for example, a unified system of trust, a cross-border system of trust, so that businesses can carry out relevant transactions in a digital format.

Smart city. It is the urban environment, as the living environment of millions of our fellow citizens, that should become a powerful pilot zone for the introduction of the most modern technologies.

Digital health. This is an example of an industry that has certainly been identified by experts as key in terms of the need for accelerated digital transformation. There will be appropriate discussion and elaboration of these goals and objectives in detail.

Thanks for reading! Follow me on social networks
Description of the presentation by individual slides:
2 slide
Slide description:
In 1995, American computer scientist Nicholas Negroponte coined the term “digital economy.” Now this term is used all over the world; it has come into use not only by politicians, entrepreneurs, journalists and ordinary citizens. In general, the term digital economy is vague. According to the definition of Doctor of Economics Vladimir Ivanov: “The digital economy is a virtual environment that complements our reality.”
3 slide

Slide description:
The economic evolution plan “The Program for the Development of the Digital Economy in Russia” was adopted in July 2017 economics system of public administration business Social sphere 2005 2010 2015 2020 Singapore To assess the readiness of countries for the digital economy, the international network readiness index is used Japan 41st place Russia Putin V.V. . emphasized that the digital economy is not a separate industry, but “essentially it is a way of life, a new basis for the development of the United States
4 slide

Slide description:
The theoretical postulates for creating a digital economy belong to Anatoly Ivanovich Kitov (07/9/1920 -10/14/2005) - Soviet scientist, developer of electronic computer technology in the USSR, Doctor of Technical Sciences, professor, Honored Worker of Science and Technology, Academician of the Russian Academy of Sciences, engineer-colonel, manager 1st computer center of the Ministry of Defense in 1954.
5 slide

Slide description:
In the USSR, cybernetics was considered a “bourgeois reactionary pseudoscience.” Only in 1958 Norbert Wiener's work "Cybernetics" was officially translated. Kitov A.I. in 1958 he wrote the article “Basic Features of Cybernetics” and the book “Electronic Digital Machines” - the first publicly available book on computers and programming. Also in 1958, Kitov put forward an innovative idea to connect all the country's computers into a single network.
6 slide

Slide description:
In January 1959, Kitov created the “Red Book” project and handed it over to N.S. Khrushchev. with fundamental proposals for the development of VT in the country and the creation of the Unified State Computer and Information Center, that is, an automated control system for the country’s economy. Kitov believed that the presence of such a network in a planned economy would make it possible to quickly collect and process statistical information about the state of individual enterprises and use the processing results for planning and managing the national economy." These projects were not destined to come true.
7 slide

Slide description:
This is what his follower, Academician V.M. Glushkov believed. Viktor Mikhailovich Glushkov honestly said: the total costs of implementing the “Red Book” project should exceed the costs of the atomic and space programs combined. Under the leadership of Glushkov, a preliminary design of the Unified State Medical Center was developed, which included about 100 centers. The leadership of the country considered that “this is such a revolutionary transformation that it is difficult for us to implement it now.” The reaction of the Western press is a quote from the English newspaper The Guardian: “The Tsar of Soviet cybernetics, Academician V.M. Glushkov proposes to replace Kremlin leaders with computers.”
8 slide

Slide description:
In 1960 - 1970, the iceberg of scientific thought was believed that computers would take on the role of universal stabilizers of world markets. A project similar to Kitov’s was carried out on the other hemisphere in Chile. The government, represented by S. Allende, turned to the famous English cyberneticist Stafford Beer for help. The scientist believed that the economy is a complex, constantly changing system. Effective governance throughout the country is based only on a transparent planned economy. In Chile, in 1972, most of the industrial enterprises that could have been combined into one system were nationalized.
Slide 9

Slide description:
In a country where there were no computers or programmers, a unique system called “Cybersyn” was deployed. Telex communication was used to input and output information. It was telex - the same teletype - that saved the project, allowing the exchange of data throughout the country, uniting 500 enterprises. The system control center was located in the presidential palace, where information about the activities of these enterprises flowed in real time and management decisions were made.
10 slide

Slide description:
Scientist Beer and Allende assumed that the management system should be free from bureaucratic structure, especially the absence or weakness of the feedback system. The point was to build not just a system of industrial management, but to create a system of state management in accordance with the interests of the people.
11 slide

Slide description:
When there was a truck owners' strike in Chile, the Cybersyn system, which was not fully deployed, was able to mobilize all the government's resources and distribute them effectively. After Pinochet's coup, the Chilean cybernetic miracle was destroyed. If in the USSR the implementation of such a system was prevented by complete misunderstanding, then in Chile the rebellion of conservative forces supported by the United States turned out to be important.
12 slide

Slide description:
Currently, humanity lives in the era of the fourth industrial revolution - during artificial intelligence (AI), the transfer of large amounts of information and the Internet of things. The scale of changes that the digital era will cause and its impact on all aspects of people’s lives will be colossal, A. Shalaginov, an expert in the field of information and communication technologies and an ex-employee of Huawei, is sure of this.
Slide 13

Slide description:
Digital technologies will gradually lead to the transformation of government, business, everyday life and other things. IoT - Internet of Things with sensors, sensors and devices capable of collecting large amounts of digital heterogeneous data Artificial intelligence fifth generation mobile networks 5G which will analyze and use this data to control these same devices; through which a colossal amount of data will be transmitted. The main drivers will be:
Slide 14

Slide description:
An example of IoT affecting road safety, 23.5 million cars manufactured with Internet connection (panic button, navigator). Some car models can even recognize a pedestrian accidentally running into the road.
15 slide

Slide description:
Many computers and robots already have elements of AI. A prime example of such machine learning is self-driving cars.
16 slide

Slide description:
Many fear that AI will be smarter than humans and replace us. It’s just that “machine intelligence” will do certain operations for a person better. Artificial intelligence is already superior to most doctors in diagnosing diseases. AI is better at analyzing laws than most criminologists and lawyers. He can make decisions for financial institutions better than many market analysts. At the same time, AI does in seconds the work that would take a human weeks or months to complete.
In April 2017, at the RIF+KIB 2017 forum, the Association of Electronic Communications (RAEC) presented “Russian Digital Economy. Analytics. Numbers. Data". The presentation has few differences from the RAEC studies of 2013–2015, which analyzed the narrow sector of the economy of Internet services and content. As before, in RAEC research, the main indicator of the digital economy is its contribution to the country’s GDP. Estimates of the contribution of the digital economy in the presentation range from 2.4% to 5.7% of GDP. In a study presented by RAEC in December 2016, the figure was estimated at 2.4% of GDP. The share of GDP formed by Internet-dependent markets remained unchanged (19% of GDP).
The presentation compares the contribution of the digital economy to the economies of different countries: China - 6.9%, USA - 5.4%, India - 5.4% and Russia - 5.7%. Based on a comparison of these figures, it is concluded that Russia has formed its own digital economy.
In 2017, RAEC for the first time divided the digital economy ecosystem into 8 hubs (sectors): state and society, marketing and advertising, finance and trade, infrastructure and communications, media and entertainment, cybersecurity, education and personnel, startups.
The content of the presentation is characterized by poor elaboration of the issue of the formation of a digital economy in Russia. The assessment of the digital economy does not include the most important indicators of the sustainability and security of its development, such as: whose digital technologies are being introduced in Russia, whether a system for the reproduction of domestic technologies has been created, which country’s budget receives funds from the sale of digital goods in the country, whether standards are being developed, regulations and methodologies that subsequently allow the promotion of Russian digital goods and services in foreign markets, etc.
For the hubs (sectors) of the digital economy, 9 sections have been identified (the most significant technologies and conditions for the development): development and design, analytics and data, AI (artificial intelligence) and Big Data, hardware, business models, Internet of things, mobile, platforms and regulation.
The list of hubs does not include the most important sectors for assessing the digital economy: industry, transport, energy, and agriculture. The presentation does not address the issue of the influence of science and education on the development of the digital economy.
This year, the RAEC study for the first time highlighted the mobile economy - an economy in which mobile technologies play a major role. To assess its size, RAEC, with the support of Google, entered into a partnership agreement with the Turkish company OC&C Consulting, which has experience in conducting similar studies in emerging markets.
According to the results of a joint study, the contribution of the mobile economy to Russia’s GDP is estimated at 3.7% of GDP. The presentation does not answer the question of how the mobile economy depends on the digital economy. Information was found on the RAEC website that the assessment of the mobile economy includes a direct contribution – “IT sector”, an additional contribution – “service of the IT sector” and an indirect contribution – “dependent technologies of the economic sector”.
The slide about the “Society and State” hub reports a sharp decrease in the number of legislative initiatives in the first quarter of 2017. This is presented as an achievement of the RAEC, although the reason is most likely related to the formation of the State Duma of a new convocation and the traditional low activity of deputies at the beginning of the year. The same slide shows figures characterizing the attitude of experts to the bills: positive assessment - 18% (over the year decreased by 2%), negative assessment - 35% (increased by 2% over the year), neutral or ambiguous assessment - 47% (for year increased by 10%).
The “What We Want” section of the presentation lists the goals for the development of the digital economy: smart cities and autonomous transport, protection from cyber attacks and responsible handling of personal data, eliminating the digital divide, telemedicine and smart agriculture, trust mechanisms on the Internet, “so that copyright goes to about the Internet, and not vice versa,” “so that regulation does not interfere with the development of new models,” “to consolidate the status of the Internet as a national treasure.”
From the way the goals, main indicators and structure of the digital economy are formulated, we can conclude that RAEC experts consider the country’s territory only as a promising market for international IT companies to sell their products and services.
In its current form, the RAEC study cannot adequately assess the success of Russian business in the domestic and foreign markets, and, accordingly, will not help formulate recommendations for accelerating the development of the digital economy in Russia.