Hired work and trade unions. Labor collectives and trade unions
1. Hired work
Rather's relationship
The overwhelming part of the country's population to provide themselves with the necessary means of existence is forced to offer their work on labor for a certain monetary remuneration called wage. This part of the population sells special goods - labor. For trade, it has a special market - the labor market. The latter is directly related to the legal freedom of labor of labor and their economic coercion: a "free" person who has no means of production, no means of existence, is forced to join the relationship of hiring. But the methods of violence (the use of legislation, police and even the army against workers) did not immediately disappear, and were widely used to force employees to accept the workforce for them unprofitable for them, which contribute to the growth of employers' profits. This, naturally, caused resistance, which was intensified as the number of employees of employees and the enrichment of the arsenal of their struggle for their rights. New in relations between labor and capital was the formation of trade unions representing the interests of employees in negotiations with entrepreneurs.
Hired work and trade unions
Professional unions are associations of employees of one profession, a branch or enterprises created to protect their interests when agreeing with employers and wages. Trade unions have turned employees to organized in the labor market, which forced employers to reckon with their interests. In general, this contributed to the fact that the confrontation of the two sides ceased to take extreme forms.
In most countries of the world, two main ways of buying and selling labor are used: individual labor contracts and collective agreements (agreements). The collective agreement records the coordination of the positions of the parties to the widest range of issues. At the national level, general agreements are signed. They are documents that determine the overall conditions for the sale of labor. The General Agreement signs the government, associations of employers and trade unions following the negotiations.
The labor market covers ways, public mechanisms and organizations that allow sellers (employees) to find the work they need, and buyers (employers) - to hire workers who are required to conduct production, commercial or other activities.
Turning to the analysis of the labor market, it is necessary to remember that it is not soulless goods, but people who form organic unity with the workforce that is the object of sale. Therefore, psychological, social, national, cultural, spiritual and other aspects of human behavior in the labor market should be taken into account.
Labor cost
Wages are a monetary expression of the cost of goods, which is the workforce, or the price of labor. The cost of labor, as we already know, is determined by the value of the existence of the existence necessary for the reproduction of labor.
The cost of labor depends on a number of factors, including climatic and other natural conditions of a country. Besides
the natural needs of a person in food, clothes, the dwelling there are still cultural and professional inquiries that must be satisfied, and, therefore, they are also included in the workforce. The overwhelming part of life needs, as well as methods of their satisfaction depend on the achieved scientific and technical, socio-economic and cultural level of development of a country.
The cost of the workforce includes the cost of the vital funds necessary for the content of the employee's family, as the indispensable condition for the natural reproduction of labor.
Factors of influence on the cost of labor
The factors that determine the decrease in the cost of labor include the increase in the performance of social labor, since it is associated with a decrease in the cost of existence. In this direction, there is an involvement in the process of the production of women and children, since the content of the family is carried out in this case income received not only by the head of the family, but also its members.
The factors causing an increase in the cost of labor should include primarily the advancement of the qualifications of employees, expanding the needs in new products and services of their families. This is directly related to increasing the requirements for general education and special training of workers who are imposed on it from all types of economic activity as a result of the implementation of the achievements of science, technology, culture. As a result, new material and spiritual requests arise, constantly introducing adjustments to the volume and structure of the needs of the population.
In the direction of increasing the cost of the workforce, an increase in labor intensity is also valid, which causes an increase in energy costs by man and requires additional expenses for maintaining it
health. This is not only possible, perhaps not so much about physical, how much about nervous, mental exhaustion. Therefore, sometimes the visible "lightness" of the work is conjugate with the colossal neuropsychiatric loads, the moral responsibility of the employee who require not only greater material compensation, but also compensation for free times, the recreation of the body.
Labor efficiency and employee income
It should be noted that in all concepts to stimulate labor activity, the price of hours of work is of particular importance, which makes dependent on labor from spent working time. Consequently, wages appear as a monetary remuneration paid by the employee for the implementation of a certain task, the scope of work or official duties during the set time. In this connection, the value of the limit product created by the additional work involved (1 hour of labor, an additional worker, or a group of workers) acquires the value. Consequently, the limit product of labor is the criterion of effectiveness involved in the additional labor force. A positive moment in such an approach is that the worker receives one or another wage not only because it must reproduce its workforce, but also because it depends on the number of hours worked with a certain degree of labor efficiency.
2. Wages
Lower wage border
Are there any borders of wages? The answer to this question identifies different approaches to the definition of the essence of this category. Thus, the concept of a "minimum means of existence", which originates from D. Ricardo and T. Malthus, makes wages to the physically necessary minimum of the means of existence. However, the cost of labor cannot only be reduced to this minimum, but includes the needs generated by economic, social, cultural conditions in which the army of wage labor is formed. At the same time, determining the lower boundary of the cost (price) of the labor force to the minimum means of existence and approval about the desire of an entrepreneur to reduce wages to the lower border is hardly legitimate and economically justified. As the economic practice of developed countries shows, the average level of real wages is installed on a much higher level than the cost of a minimum of existence.
Living wage
The subsistence minimum is the level of income required to acquire food by the person in the lower border of physiological norms, as well as to meet at least minimal needs for clothing, shoes, pay for housing and transport services, in sanitation and hygiene subjects. At the modern labor market, the subsistence minimum actually serves only the lowest border of wages. This circumstance today is clearly stipulated by the legislation of many countries, directly defining the minimum wage and its obligation for all employers.
Nominal and real salary
It is important not only what salary receives an employee, but and some of the goods and services can be purchased for it. It is necessary to distinguish between the nominal wages, its money size, and the real wages under which the number of goods and services purchased for this remuneration is understood. All other things being equal, it is possible to derive the ratio of these values:
where zp. R - real wages; Zp. N. - nominal wages; C - prices for consumption and services.
Salad factors
As you know, the employer is committed to the benefit, and it is embodied in profits (in the difference between the sale price of the goods and the sum of all expenses for its manufacture and implementation). Wages always constitute a weighty part in production costs. We must not forget that the interests of the employer and the hired worker are opposite. With the same amount of revenue from the sale of goods produced, wage increases means a reduction in the profit, which is assigned to the entrepreneur, and on the contrary, the increase in profits leads to a reduction in remuneration.
Another component of the factor is labor productivity. The salary movement and changes in labor productivity are inextricably linked. If the growth in performance lags behind the increase in wages, efficiency falls and the profitability of production decreases. And on the contrary, if the productivity of labor overtakes in its increasing wages, production becomes more profitable and more profitable. Therefore, for a separate enterprise, and for the country as a whole, there is always the upper limit of the increase in wages, it is determined by the growth rate of labor productivity.
Often, the statistical documents appear the value of the average wage. The average salary is also afflicted as the average worker. The fact is that there are various types of work, various qualifications, various working conditions. To incline people to perform an unavailable work, the salary rate rises. Attractive types of work attract more willing, in connection with which their wages are installed at a lower level than is required. Possessing various abilities, various predisposition to the acquisition of one or another qualifications, finally, talent, people cannot receive equal wages. In particular, in a salary of talented musicians, poets, athletes there is a kind of economic rent for unique abilities.
The factors determining the differences in wages include the level of education and training. And this is true, since, for example, doctors, lawyers, engineers are investing in the acquisition of education a lot of effort and funds that can be called investments in human capital. These investments and bring revenues in the future.
Many payroll differences arise due to the presence of so-called non-competitive groups. For example, doctors and mathematics are non-competitive groups, since it is difficult and almost impossible for a representative of one profession to enter another group of employees. The workers change professions with smaller losses, so they can move from one group to another, which leads to an equilibrium system of differences in wages from various categories of workers.
Differences in wages between population groups will always exist. But often they arise because of such characteristics, which do not have any relation to the labor process: nationality, gender, religion. These phenomena are already related to another assessment system called "discrimination". So, the labor market is committed to such an equilibrium system of differences in wages, in which the demand for each category of labor will be exactly equal to the proposal of this category of labor. Therefore, the task of the labor market is the necessary proportional distribution of labor between various sectors and the spheres of the national economy.
3. Demand and labor offer
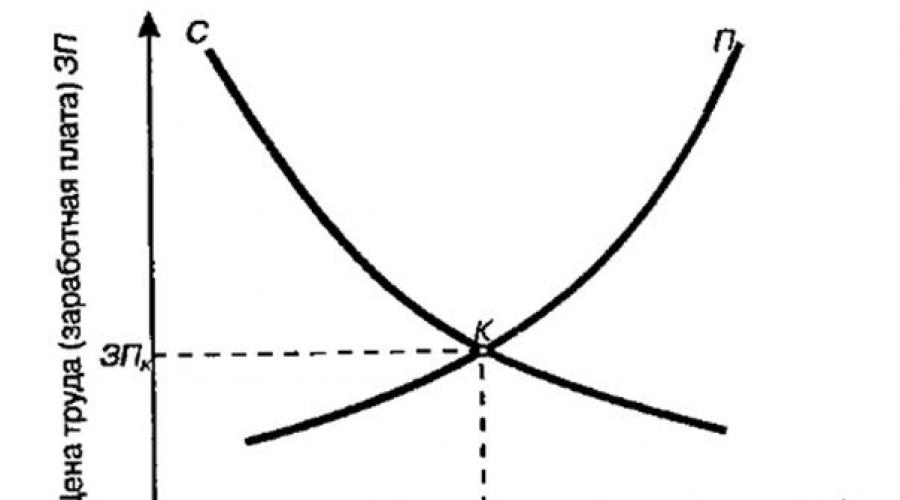
The dynamics of wages has an impact in both the demand and supply of labor. The dependence of the latter on the labor price can be expressed already familiar to us by the schedule, only the object of supply and supply is now the amount of labor, which depends on its price, wages (Fig. 15.1).

Fig. 15.1. Equilibrium market state
All other things being equal, the higher the fee that workers require for their work, the less fewer their number will agree to hire employers (the law of demand). And on the other hand, the higher the fee offered by employers for the performance of a certain type of work, the larger the number of people are ready to engage in this type of work (the law of proposals). At the intersection of these interests and the equilibrium price of the workforce is born - the salary, in which the number of people who are ready to engage in certain work, and the number of available workplaces coincide. It should be noted that, along with the salary, the choice of work is influenced by such factors as labor safety, its creative character, a friendly atmosphere, professional growth, career.
Proposal of labor
The supply of labor depends on the population, its age-age structure, the average number of working hours per week, the level of qualifications and quality of labor, culture, religion, national traditions. The supply of labor is constantly changing. Young people comes to the labor market, the increasing number of women are drawn into it. Some find work, others are in her search, others lose hope and are out of workforce.
The proposal of labor depends on the level of wages. However, this dependence is not so straightforward and unambiguous, as it may seem at first glance. The fact is that in one case the increase in wage rates can cause increasing the supply of labor, in another - reduction. It depends on the material well-being of the employee.
Recognition effect
The proposal of labor increases under the influence of the effect of replacement of free time by working time. According to the effect of substitution, every hour of free time, the employee is assessed as a missed possibility of obtaining additional earnings. It occurs with insufficient saturation of the needs of the employee. Therefore, with an increase in wages, the employee tends to perform a larger amount of work, which is reflected in the lower from the point to part of the curve of the workforce, presented in Fig. 15.2.
Effect of income
At the same time, the proposal of labor can decline, despite the growth of payroll rates. This situation occurs when the effect of revenue comes to change the effect of substitution. The income effect begins to act in conditions when a high degree of saturation of the needs of the employee and the value of free time is raised above the additional income. With the achievement of a certain level of wealth, a change in the relationship to free time is associated. If earlier it was considered as a loss of the potential possibility of obtaining additional income, now it acquires increased value as a leisure where a person does not think about material supply (this is already achieved), and about meeting its needs related to requests and elements of personality self-realization outside the sphere basic work. This employee behavior is reflected in Fig. 15.2. At the top of the point to the curve of the supply of labor.

Fig. 15.2. Manifestation of the effect of substitution and effect of income in the labor market
However, the level of wages is determined not only by economic interest, but also ethics, mentality of the nation. In particular, the fracture point to the effect of substitution and the effect of income is largely determined by the fact that a person is focused on the values \u200b\u200bof a consumer society imposing money, wealth, material wealth, or society in which spiritual values \u200b\u200bprevail, stay in harmony With nature and preferred the principle of necessary sufficiency of material well-being.
It is quite obvious that, in essence, the effects of substitution and income is another, along with the pyramid of the oil, the testimony of a scientific way of imposing a market method of thinking to a person and a society, which allows capital (bourgeois) to achieve its goals by suggesting the population of primary values, secondaryness and secondary spiritual. This veiled of labor subordination is capital, which complements such consumer injection means, as advertising, fashion, demonstrative and prestigious consumption. It is the consumerism - a prerequisite, condition and fact of prosperity and establishing the rule of capital of capital.
Demand for work
The demand for labor is determined primarily by the utmost product created by labor, the level of technical equipment of production, as well as the ratio of labor and machines. In the latter case, either low wages does not stimulate the use of machines, or replacement machines do not differ in high technical level and sufficient economic efficiency. The demand for labor, as well as the proposal, undergoes changes. In some cases, this is caused by changes in the structure of consumption of goods and services, and therefore in the structure of jobs, in others - the emergence of new types of industries with the relevant professions, in third - by extinction and dying of entire industries and types of industries.
As a result, the situation in the labor market is characterized by the presence of redundant, ready-to-use goods - labor, as well as the presence of a significant number of free jobs that cannot be occupied by the inhomogeneity of the proposed and required structure of labor. This obstacle can not be overcome by any wage, nor by increasing the aggregate demand. Because there were no miners or weaver cases in view of the coagulation of production in the respective industries, the demand is impossible to satisfy demand, for example, on computer operators. Decisions of this problem, or rather, it can be achieved by conducting a policy that stimulates the flexibility of the labor market, which is achieved through the implementation of a whole system of activities: retraining, retraining of personnel, material support, issuing benefits and lifting, clear work of labor exchange, perfect information system.
Solidarity salary
Considering that the labor market consists of a variety of sectors, each of which is set by its wage level, the problem of selecting its degree of differentiation occurs. In recent years, the policy of solidarial wages has been obtained, which is based on the principle of "equal wage for equal labor", leading actually to reduce the gap in the wage levels.
In particular, the study of the labor market revealed the following important points. First, a smoother salary structure leads to many comparable jobs. And this helps or, in any case, does not interfere with structural changes in the economy.
Secondly, the payment of relatively equal wages in all enterprises, despite the level of profitability, leads to the exacerbation of the competitive struggle on the basis of production costs. The fact is that inefficiently working enterprises in this case are forced to either pull up, or faster to stop their activities than if they continued to compete, paying low wages. On the contrary, highly profitable enterprises can use the ever-increasing part of the profit on expansion and improvement, avoiding additional costs of salary increases.
Thirdly, this study revealed the similarity between equalizing and increasing the wage difference, which manifested itself in the smaller movement of labor (especially young people) in the labor market. On the one hand, the wage leveling has little stimulates the regional and sectoral migration of labor. On the other hand, the workforce, which will be recruited into developing areas or to areas experiencing a shortage of labor resources, with high wages, is unlikely to leave them if there is even a decrease in labor demand.
Differentiation of labor
At the same time, differentiation in paying from the profession, depending on the profession, plays an important role in the orientation of employees to those markets, where it is well paid, where specialists with higher qualifications are required. For clarity, you can take two specialized labor market: miners and operators of computing equipment (Fig. 15.3, a, b).

Fig. 15.3. The ratio of two specialized markets under the conditions of free wage formation.
Suppose that the equilibrium has been established in these markets, which correspond to the equilibrium labories of ZP A and ZP B. Suppose also that many industries are equipped with computational technology, while part of the mines are closed due to coal non-competitiveness compared to other energy carriers. In the first case, an additional and increasing demand for computer operators is presented, in the second case, demand for miners is reduced. As a result of the changed demand on both specialized markets, the salary movement occurs in opposite directions: in the labor market of the operators, it grows to the level of ZP A (see Fig. 15.3, a), in the labor market of miners, it decreases to the ZP b (see rice . 15.3, b). This forces the labor force to leave the mining market of labor to the EMM operator market.
However, this is in theory, everything is clearly and simply, in reality there are a lot of problems with retraining, a change in the well-minded lifestyle, possible relocation. Therefore, it is necessary to restore balance on these two specialized markets, and considerable. And as it were, neither a gap in wages, overnight, Shakhtar will not become an operator if he is generally able to become. Therefore, the equilibrium will be achieved only for a long period of time. The idea of \u200b\u200bthe high differentiation in the wage levels as a labor market regulator is very simplified and does not find sufficient confirmations in economic practice, although it should not be fully neglected.
4. Employment and unemployment
Changes in the labor market
Knowledge of the labor market requires careful and careful study of structural shifts in labor activity due to the trends in the development of NTP and changes in the public division of labor. These processes find their manifestation in the rapid change of work activities. Currently, in the industrialized countries of the world, about 70% of work activities are among them, which were not at all at the beginning of the twentieth century. Other factors that have a significant impact on the labor market is, on the one hand, the elongation of the person's labor activity period is about twice, on the other - later entry into labor activities (from 16, 18 years, and even 21 years), due to the increasing terms Training and training. At the same time, if earlier a person acquired the specialty enough for the rest of his life, then he is currently forced to change occupations at least 2-3 times for his career activities.
Finally, it should be noted that the problem of employment and unemployment is inextricably linked with occurring structural shifts in the national economy and world economy, demographic and cultural and educational and other processes, as well as the deformations and inertia of the labor market. The study of long-term trends in the labor market shows that they occur annually as a significant flow of labor and noticeable changes in the structure of free jobs.
Mobility of labor
Everything indicates the high demands of the labor market to labor mobility, which implies the flexibility and adjustability of working professions, freedom of movement in labor field. We are talking about sectoral, professional and qualifying mobility, which cannot be provided without a fairly complete general education base, without broad professional training. Requirements for the implementation of NTP achievements cause the need to revaluate the role of education, including higher, in the system of priorities for the socio-economic development of any country, seeking not falling back in the development of NTP.
In many cases, as we have already seen, the salary is not able to quickly and in a timely manner to eliminate the imbalance in the labor market, and above all between its individual sectors. This requires time and means. Therefore, we must not forget about a number of factors that have a significant regulatory impact on the labor market.
First of all, we are talking about the general educational training of future workers at the level of both the general and secondary special and higher vocational education. It is working force with such a preparation in a state quickly and with less damage to itself and for society as a whole to respond to the requirements that scientifically progress makes it. This is the basis on which rapid advanced training can occur, and retraining on such specialties for which the lack of labor is experienced.
Employment and capital
Another factor affecting the efficiency of the labor market differentiation is capital. The fact is that it is far from always possible and it is necessary to carry out migration flows of labor into remotely incomplete areas, while you can try to bring jobs to the unemployed. To do this, in places with excessive strength it is necessary to create a favorable economic climate for the application of capital. For this purpose, a whole system of benefits and various target subsidies can be used. Therefore, the problem of the effective functioning of the labor market comes far beyond the framework of the Institute of Labor and becomes a nationwide problem of socio-economic development.
The next factor affecting the flexibility of the labor market is the tax system. Income tax and social contributions create a difference between wages after tax deductions, on the one hand, and the total cost of employers on wages on the other. An increase or decrease in this difference is affected accordingly in an increase or reducing the cost of entrepreneurs, which are conjugate with the motivation to migrate labor or change profile. In all likelihood, high income tax rates and entrepreneurs contributions reduce labor mobility in the labor market.
Labor market infrastructure
An important meaning in the mobility of the labor market has the development of its infrastructure, designed to ensure full and reliable information on the availability of free jobs and the structure of the existing unemployed labor force. We are talking about labor exchanges, employment bureau, the organization of the work of which depends on the speed and clarity of the functioning of the labor market. However, it should not be simplified and limited the labor market of the labor exchange and other employment institutions. In connection with the specifics of the labor market, with a high degree of its regulation, bargaining begins much earlier at all levels of recruitment.
First, at the level of general and sectoral agreements between trade unions and unions of industrialists and entrepreneurs with the participation of the government. Secondly, at the level of enterprises carrying out employees with or without trade union participation. Thirdly, at the level of directly jobs, where the relief of labor agreements on hiring is carried out in connection with advanced training, professional retraining, promotion on the service staircase. Therefore, labor exchange is an important infrastructure link of the labor market, but only one of the institutions of the R & D Relations system.
In general, the functioning of the labor market can be schematically represented in the form of flow streams of the workforce (Fig. 15.4).

Fig. 15.4. Block of the labor market scheme (labor flows)
5. Employment models
Special place is occupied by the problem of unemployment. Unemployment is characterized by such a position in the economy, when a part of people capable and wanting to work for hiring people cannot find a job in their specialty or employed at all. Explanation of unemployment is based on several models, each of which requires its mechanism for regulating the labor market.
Classic model
The most simple model of the labor market is represented by the classic economies, for which the labor market is the same as any other market, and, therefore, the balance between supply and supply of labor is achieved exclusively by establishing the equilibrium price - wages. If the salary is higher than the equilibrium value, the supply of labor exceeds demand. As a result, unemployment occurs, the main reason for which is considered a high level of wages. The unemployment growth causes an increase in labor supply, which objectively leads to a decrease in the level of wages until the equilibrium price is established.
If the abscissa axis is given the number of occupied, and on the ordinate axis - the price of the workforce (wage), the relationship between them can be expressed graphically, as shown in Fig. 15.5.

Fig. 15.5. Voluntary unemployment
At an equilibrium price for the labor force (zp a), demand and proposal coincide at a point A, which corresponds to the employment of the workforce, equal to the value of Q A. However, if the salary rises to the ZP b, then the demand for it will be reduced to the value of Q b, then As the supply of labor under this wage will be the value of Q. The value, the difference between the value of the supply of labor and the real value of demand for it, and will personify unemployment, or the excess of the supply of labor over demand for it.
Consequently, the classical model implies that unemployment arises due to the requirements of the employees themselves too high wages. The elimination of unemployment is seen in the mechanism of pressure supply of labor at the level of wages until it decreases to the equilibrium labor price. However, if the salary does not fall, and holds at the level of the ZPD, the proposal curve takes the horizontal position of P, indicating that the decline in wages cannot occur so much to increase employment. Therefore, it is believed that employees themselves, choosing an increased level of wages, thereby cause unemployment. From here it is concluded about the voluntary nature of unemployment, since the hired workers themselves made a choice in favor of high wages, and not in favor of full employment.
Solidarity of female labor, combining them into professional unions to protect their income is estimated as manifestations of a monopoly, which violates the normal action of the market mechanism. However, there are living people interested in certain stability for the work of labor. Employers are also interested in the lastness, since the predictability of wage dynamics allows them to anticipate production costs, choose more optimal variants of its development. In addition, it contributes to the establishment of suspended and smooth relations with hired personnel, which undoubtedly create a favorable atmosphere for higher productivity, which is also in the interests of entrepreneurs.
Keynesian model
Within the framework of the Keynesian model, the theoretical position of the classical school is not denied, expressing the relationship between wages and employment. However, the ability to fight unemployment is skeptical by decreasing wages.
First, the strategy for a decrease in wage is difficult to relate. Secondly, even if it becomes possible to implement this strategy, it will not be particularly effective against
unemployment. Of course, the decline in the overall level of wages opens up the prospect for hiring a larger number of employees on the same value of advanced variable capital. However, this is fraught with a reduction in aggregate demand from female labor.
In the Keynesian model, a decisive role is given to the aggregate demand in society, which manages the volume of production, and therefore, and demand for labor. Consequently, the main cause of unemployment seems to be insufficient demand in the markets of goods and services. Therefore, as a main means, with the help of which the state can withstand unemployment, an active financial policy is allocated. It is primarily about reducing tax pressure and increasing income that will cause the growth of aggregate demand, which will stimulate production, and therefore, an increase in the number of jobs.
At the same time, within this model, production and employment are linked to a certain level of wages. Employment growth without increasing capital, technology leads to a fall in the labor productivity of the limit worker, and from here - to a decrease in real wages. In this regard, it is proposed to use moderately regulated information as a means of promoting employment growth. The growth of nominal wage growth is considered as a prerequisite for increasing profitability, expansion of production, an increase in investment and, therefore, employment growth.
Marxova model
Marxova Employment Concept is based on the law of capitalist accumulation, which, causing the development of scientific and technological progress, leads to a gradual increase in organic capital (C / V). This growth causes a fall in the share of variable capital (V) in the total mass of capital (C + V). Due to the fact that labor demand
determined by the value of alternating capital, advanced to the purchase of labor, the decrease in its share determines the relative reduction in demand for labor, while its proposal increases. The supply growth also occurs at the expense of both the natural growth of the population and the ruin of small commodity producers, forced to seek hiring work.
At the same time, the presence of unemployed, or, as K. Marx said, the industrial reserve army of labor, is the objective need and the need for capitalist reproduction. The fact is that when the economy is in the lifting phase or new directions of economic activity are formed, the availability of the workforce provides it with the necessary additional labor resources.
In general, on the basis of the action of the universal law of capitalist accumulation, it is concluded that the increasing of antagonistic contradictions between labor and capital is concluded. Attaching the importance of research trends in the development of technical progress and public division of labor, K. Marx turned out to be right in the growth of the organic capital building in the areas of material production, which led to unprecedented displacements of workers from agriculture and industry. However, he was unable to predict the emergence and development of labor-intensive areas of economic activity - trade and services, which acted as the excretion of the released labor, from which the organic structure of capital in general has undergone not so radical change. However, at present, employment problem is again increasing due to a surge of the growth of the organic structure of capital under the influence of the technical re-equipment of these labor-intensive spheres of social production and the upcoming technological revolution.
Rather's relationship
The overwhelming part of the country's population to provide themselves with the necessary means of existence is forced to offer their work on labor for a certain monetary remuneration called wage. This part of the population sells special goods - labor. For trade, it has a special market - the labor market. The latter is directly related to the legal freedom of labor of labor and their economic coercion: a "free" person who has no means of production, no means of existence, is forced to join the relationship of hiring. But the methods of violence (the use of legislation, police and even the army against workers) did not immediately disappear, and were widely used to force employees to accept the workforce for them unprofitable for them, which contribute to the growth of employers' profits. This, naturally, caused resistance, which was intensified as the number of employees of employees and the enrichment of the arsenal of their struggle for their rights. New in relations between labor and capital was the formation of trade unions representing the interests of employees in negotiations with entrepreneurs.
Hired work and trade unions
Many payroll differences arise due to the presence of so-called non-competitive groups. For example, doctors and mathematics are non-competitive groups, since it is difficult and almost impossible for a representative of one profession to enter another group of employees. The workers change professions with smaller losses, so they can move from one group to another, which leads to an equilibrium system of differences in wages from various categories of workers.
Differences in wages between population groups will always exist. But often they arise because of such characteristics, which do not have any relation to the labor process: nationality, gender, religion. These phenomena are already related to another assessment system called "discrimination". So, the labor market is committed to such an equilibrium system of differences in wages, in which the demand for each category of labor will be exactly equal to the proposal of this category of labor. Therefore, the task of the labor market is the necessary proportional distribution of labor between various sectors and the spheres of the national economy.
Demand and supply of labor
All other things being equal, the higher the fee that workers require for their work, the less fewer their number will agree to hire employers (the law of demand). And on the other hand, the higher the fee offered by employers for the performance of a certain type of work, the larger the number of people are ready to engage in this type of work (the law of proposals). At the intersection of these interests and the equilibrium price of the workforce is born - the salary, in which the number of people who are ready to engage in certain work, and the number of available workplaces coincide. It should be noted that, along with the salary, the choice of work is influenced by such factors as labor safety, its creative character, a friendly atmosphere, professional growth, career.
Proposal of labor
The supply of labor depends on the population, its age-age structure, the average number of working hours per week, the level of qualifications and quality of labor, culture, religion, national traditions. The supply of labor is constantly changing. Young people comes to the labor market, the increasing number of women are drawn into it. Some find work, others are in her search, others lose hope and are out of workforce.
However, the level of wages is determined not only by economic interest, but also ethics, mentality of the nation. In particular, the fracture point to the effect of substitution and the effect of income is largely determined by the fact that a person is focused on the values \u200b\u200bof a consumer society imposing money, wealth, material wealth, or society in which spiritual values \u200b\u200bprevail, stay in harmony With nature and preferred the principle of necessary sufficiency of material well-being.
It is quite obvious that, in essence, the effects of substitution and income is another, along with the pyramid of the oil, the testimony of a scientific way of imposing a market method of thinking to a person and a society, which allows capital (bourgeois) to achieve its goals by suggesting the population of primary values, secondaryness and secondary spiritual. This veiled of labor subordination is capital, which complements such consumer injection means, as advertising, fashion, demonstrative and prestigious consumption. It is the consumerism - a prerequisite, condition and fact of prosperity and establishing the rule of capital of capital.
Demand for work
The demand for labor is determined primarily by the utmost product created by labor, the level of technical equipment of production, as well as the ratio of labor and machines. In the latter case, either low wages does not stimulate the use of machines, or replacement machines do not differ in high technical level and sufficient economic efficiency. The demand for labor, as well as the proposal, undergoes changes. In some cases, this is caused by changes in the structure of consumption of goods and services, and therefore in the structure of jobs, in others - the emergence of new types of industries with the relevant professions, in third - by extinction and dying of entire industries and types of industries.
Secondly, the payment of relatively equal wages in all enterprises, despite the level of profitability, leads to the exacerbation of the competitive struggle on the basis of production costs. The fact is that inefficiently working enterprises in this case are forced to either pull up, or faster to stop their activities than if they continued to compete, paying low wages. On the contrary, highly profitable enterprises can use the ever-increasing part of the profit on expansion and improvement, avoiding additional costs of salary increases.
Thirdly, this study revealed the similarity between equalizing and increasing the wage difference, which manifested itself in the smaller movement of labor (especially young people) in the labor market. On the one hand, the wage leveling has little stimulates the regional and sectoral migration of labor. On the other hand, the workforce, which will be recruited into developing areas or to areas experiencing a shortage of labor resources, with high wages, is unlikely to leave them if there is even a decrease in labor demand.
Differentiation of labor
At the same time, differentiation in paying from the profession, depending on the profession, plays an important role in the orientation of employees to those markets, where it is well paid, where specialists with higher qualifications are required. For clarity, you can take two specialized labor market: miners and operators of computing equipment (Fig. 15.3, a, b).

Fig. 15.3. The ratio of two specialized markets under the conditions of free wage formation.
Suppose that the equilibrium has been established in these markets, which correspond to the equilibrium labories of ZP A and ZP B. Suppose also that many industries are equipped with computational technology, while part of the mines are closed due to coal non-competitiveness compared to other energy carriers. In the first case, an additional and increasing demand for computer operators is presented, in the second case, demand for miners is reduced. As a result of the changed demand on both specialized markets, the salary movement occurs in opposite directions: in the labor market of the operators, it grows to the level of ZP A (see Fig. 15.3, a), in the labor market of miners, it decreases to the ZP b (see rice . 15.3, b). This forces the labor force to leave the mining market of labor to the EMM operator market.
However, this is in theory, everything is clearly and simply, in reality there are a lot of problems with retraining, a change in the well-minded lifestyle, possible relocation. Therefore, it is necessary to restore balance on these two specialized markets, and considerable. And as it were, neither a gap in wages, overnight, Shakhtar will not become an operator if he is generally able to become. Therefore, the equilibrium will be achieved only for a long period of time. The idea of \u200b\u200bthe high differentiation in the wage levels as a labor market regulator is very simplified and does not find sufficient confirmations in economic practice, although it should not be fully neglected.
Employment and unemployment
Changes in the labor market
Classic model
Keynesian model
Within the framework of the Keynesian model, the theoretical position of the classical school is not denied, expressing the relationship between wages and employment. However, the ability to fight unemployment is skeptical by decreasing wages.
First, the strategy for a decrease in wage is difficult to relate. Secondly, even if it becomes possible to implement this strategy, it will not be a particularly effective means against unemployment. Of course, the decline in the overall level of wages opens up the prospect for hiring a larger number of employees on the same value of advanced variable capital. However, this is fraught with a reduction in aggregate demand from female labor.
In the Keynesian model, a decisive role is given to the aggregate demand in society, which manages the volume of production, and therefore, and demand for labor. Consequently, the main cause of unemployment seems to be insufficient demand in the markets of goods and services. Therefore, as a main means, with the help of which the state can withstand unemployment, an active financial policy is allocated. It is primarily about reducing tax pressure and increasing income that will cause the growth of aggregate demand, which will stimulate production, and therefore, an increase in the number of jobs.
At the same time, within this model, production and employment are linked to a certain level of wages. Employment growth without increasing capital, technology leads to a fall in the labor productivity of the limit worker, and from here - to a decrease in real wages. In this regard, it is proposed to use moderately regulated information as a means of promoting employment growth. The growth of nominal wage growth is considered as a prerequisite for increasing profitability, expansion of production, an increase in investment and, therefore, employment growth.
Marxova model
Marxova Employment Concept is based on the law of capitalist accumulation, which, causing the development of scientific and technological progress, leads to a gradual increase in organic capital (C / V). This growth causes a fall in the share of variable capital (V) in the total mass of capital (C + V). Due to the fact that the demand for labor is determined by the value of alternating capital, advanced to the purchase of labor, the decrease in its share determines the relative reduction in demand for labor, while its proposal increases. The supply growth also occurs at the expense of both the natural growth of the population and the ruin of small commodity producers, forced to seek hiring work.
At the same time, the presence of unemployed, or, as K. Marx said, the industrial reserve army of labor, is the objective need and the need for capitalist reproduction. The fact is that when the economy is in the lifting phase or new directions of economic activity are formed, the availability of the workforce provides it with the necessary additional labor resources.
In general, on the basis of the action of the universal law of capitalist accumulation, it is concluded that the increasing of antagonistic contradictions between labor and capital is concluded. Attaching the importance of research trends in the development of technical progress and public division of labor, K. Marx turned out to be right in the growth of the organic capital building in the areas of material production, which led to unprecedented displacements of workers from agriculture and industry. However, he was unable to predict the emergence and development of labor-intensive areas of economic activity - trade and services, which acted as the excretion of the released labor, from which the organic structure of capital in general has undergone not so radical change. However, at present, employment problem is again increasing due to a surge of the growth of the organic structure of capital under the influence of the technical re-equipment of these labor-intensive spheres of social production and the upcoming technological revolution.
Unemployment, wages and inflation
General view of unemployment
In conclusion, it can be concluded that the Phillips curve takes the type of vertical direct. As can be seen, the concept of maintaining the natural level of unemployment gives the interpretation of the Phillips curve from the Keynesian interpretation.
Types of unemployment and form of their manifestation
Natural unemployment
Voluntary unemployment includes a contingent of unoccupied able-bodied people, who in their will self-made out of employment, i.e. Just does not want to work.
Institutional unemployment is caused by the functioning of the labor market infrastructure, as well as factors deforming demand and supply in this market. Relatively large unemployment allowance can provoke the elongation of job search periods, which has a tangible impact on the supply of labor. This can then manifest itself in the adaptive effect of unemployment, when people who have experienced an idleness, accompanied by the receipt of unemployment benefits, in the future, often resorted from time to time to use this form of income generation.
The system of providing a guaranteed minimum wage, which has a negative impact on the flexibility of the labor market has a certain impact on unemployment. On the one hand, a guaranteed minimum wage will exclude employment with a lower rate, which causes an increase in unemployment. On the other hand, this minimum has a positive effect on the restriction of inefficiently working enterprises, since, establishing the minimum permissible value of the wage, the state thus indirectly establishes the lower limit of the profitability of enterprises that should not make a profit due to the inclination of the value of one of the factors of production - labor.
In the direction of reducing the proposal of labor, there are also high income tax rates, significantly reduce the amount of income remaining at the disposal of the employee. This reduces the interest of hired labor to the proposal of their workforce.
Institutional unemployment should include the unemployment of labor, conjugate with the imperfection of the work of information systems, tracking the volume and structure of both available free jobs and free labor.
Forced unemployment
Structural unemployment is due to the release of labor as a result of changes in the structure of the National Economy. In the conditions of accelerated NTP, large-scale structural shifts in public production are occurring, which entail significant changes in the structure of employment of labor. The structural restructuring of the national economy is accompanied by coagulation of investments, production and employment in some industries and their expansion in others. It should be noted that the greatest social tension in society is generated by this unemployment (if not take into account the unemployment caused by repeating cyclic decosions or crises).
Despite the entire objectivity and predetermination of the structural changes in the national economy, countering the coagulation of certain types of work is associated with economic, social, psychological and other factors. In this regard, the problem of structural unemployment should constantly be in the focus of attention of the socio-economic policy of the state, and above all those institutions that are directly involved in the labor market and are directly related to structural changes.
Regional unemployment is associated with a whole complex of factors of historical, demographic, cultural and national, socio-psychological nature. Therefore, in solving this problem, there should be close interaction of local administrative-national-territorial authorities with the central, federal government, without excluding interaction with the governments of neighboring states.
A special place in the structure of forced unemployment occupies a hidden unemployment, characterized by part-time employment during the working day,
working week, month, year. It includes and that part of the workforce, which performs noticeably incomplete work. The colossal scale has reached a hidden unemployment in Russia in 1992-1998, which was due to the consequence of the erroneous policy in the transition to a market economy, which did not lead to the structural restructuring of the national economy, and to the socio-economic crisis unprecedented in their depth.
Stagnant unemployment covers that part of the able-bodied population, which lost the work, has lost the right to receive unemployment benefits, desperate to find jobs, has already adapted to live on social servants of society and has lost all interest in active work. It can be characterized and lacking opportunities to find work in regions affected by the economic downturn, when even the total number of free jobs is less than the number of unemployed.
Independent significance has a cyclic unemployment, which is predetermined by the cyclical nature of public reproduction and occurs at the stage of decline in production or in the phase of the economic crisis. Employment level fluctuations are depending on the stage that the economy passes: at the lifting stage, employment is growing, at the stage of recession - it is sharply reduced, at the stage of depression - is held at a low level and at the stage of revival occurs intensive "resorption".
Law OUCEN
In this regard, the pattern of relationship between production and employment, identified by the American economist A. Ouchen, acquires particular importance in this regard. According to the OUCEN law, the annual increase in the real gross national product at about 2.7% holds the share of the unemployed at a stable level. Oaken's law reads: Each additional two percentage points of the GNP increase reduces the share of the unemployed to one percentage point. Reduction of the GNP, respectively, leads to an increase in unemployment in the same ratio. The use of this pattern allows government agencies to navigate in investment policies, economic growth policies in order to solve employment problems arising from a certain stage of the development of the national economy.
As a result of unemployment, the society carries enormous economic losses. When people remain without work, this means that production is reduced compared to the existing real possibilities. As a result, it is complicated by the solution to the problem of improving well-being.
Social implications of unemployment
Social costs of unemployment are primarily connected with the loss of professional and human communication, involvement in the general case. The resulting income is not easy and not only a remuneration for work, but also evidence of the significance of what people are busy. Work provides social status, prestige and vocational suitability, and if you want, pride. In addition, work mobilizes a person, creates conditions for the right lifestyle.
Unemployment is not only a decrease in income, but also gradually professional degradation, infringement of human dignity. The unemployed begins to feel a feeling of his cloth. Many unemployed become alone, prone to alcohol or drug abuse. Therefore, we must not forget that the growth of unemployment is fraught with a deterioration in the health of the nation. All this leads to the social bundle of society and causes an increase in social tensions. Therefore, only a socially oriented market economy, in which the state actively supports the development of competition, contributes to the weakening of conflicts between employees and employers, is implementing extensive programs to support socially unprotected populations, avoids socio-political cataclysms.
conclusions
1. The vast majority of people to exist are forced to enter the employment relationship. The hiring is the economic form of coercion to work, since the hired employee does not have the means of production. Entering the relationship of hiring, the employee sells a special product - labor (ability to work), which has a consumer value and cost.
2. The cost of labor is in the form of its price - wages. Distinguish the nominal and real wages. The first is determined by the value of the received income, the second value of the nominal wage and the level of prices for consumption items, i.e. It is measured by the number of goods and services that can be purchased on a nominal wage.
3. The specificity of the labor market is that the goods are the workforce inherently from the employee itself. Therefore, in order to protect their interests as a labor resource sellers, employees are united in professional unions. Industrialists and entrepreneurs are also united in alliances to defend their interests as labor buyers. In this regard, it becomes obvious that in this market the laws of demand and proposals are subject to public strength.
4. The demand for labor is imposed by employers. Work (labor) is offered employees. Two factors affect the offer of labor: the effect of substitution and the effect of income. The first is associated with a higher cost of working time compared with free time. The second is due to the achievement of such a position when free time is valued above working time. Therefore, the increase in wages may be accompanied by an increasing, but a reduction in the supply of labor.
5. For the labor market, not only employment, but also unemployment, which, on the one hand, can be assessed negatively - "intact" resource, on the other - as good, for it testifies to the availability of free workers, which if necessary, may immediately Join the production process and ensure its extended scale.
6. There are three approaches to the explanation of the phenomenon of unemployment. The classic labor market model links unemployment in a high level of wages. The Keynesian labor market model treats unemployment as a result of insufficient aggregate demand, which implies the need for a policy of effective demand. Marxova, the model explains the unemployment with the accumulation of capital, with which the growth of organic capital is associated, and therefore the displacement of living labor (employees) of emitted labor (machines). It is necessary to raise the presence of "rational grains" in all three approaches explaining unemployment.
7. By nature, unemployment is divided into natural and forced. Natural unemployment is estimated as an objective inevitability of the existence of its forms such as frictional (current), voluntary and institutional. Forced unemployment manifests itself in the following forms: technological, structural and cyclic.
8. The unemployment rate is directly associated with the production of GDP (GNP). This interconnection was reflected in the OUCEN law, according to which the reducing unemployment for one percentage point in relation to its natural levels causes an increase in GDP (GNP) by more than two percentage points and, on the contrary, an increase in unemployment for one percentage point causes a reduction in GDP (GNP ) More than two percentage points.
Federal Agency for Education
State educational institution of higher
Vocational education
"Ural State Economic University"
department National Economics
Hired work
Course work on labor law
Artist: Marina Anatolyevna
Taktaiev
Student
Center for remote education
c. EPB-09Ant.
(signature)
Scientist Slyusarenko T.V.
_______________________________
(signature)
Preliminary estimate________
Date of protection __________________
Evaluation _______________________
Yekaterinburg, 2010.
Introduction ....................................................................................... ... 3
1. Theoretical foundations of the study of hired labor ........................ ..6
1.1. The concept of hired labor ..........................................................6
1.2. Hired work as a subject of legal regulation ..................... 8
2. Features of the regulation of hired labor ...................................15
2.1. Requirements for attracting hired labor ........................... .... 15
2.2. Characteristic of hired labor ...............................................16
2.3. Principles of creating a system of stimulating employees.19
3. Features of the use of hired labor on the example of OJSC ARTINSKY FACTORY ...............................................................................................
3.1. General characteristics of the enterprise .......................................... 28
3.2. Attraction and use of hired labor at the enterprise .... ... 30
Conclusion .................................................................................... .33
Bibliographic list ................................................................36
Attachment 1
Appendix 2.
Introduction
The study of hired labor is relevant in the conditions of expanding market relations and is one of the most important general economic problems. This is due to the fact that it is the social and labor sphere that acts as the most sensitive element of the life of society, because the tensions of the relations underlying it can cause a social explosion, the consequences of which are mainly predictable in a negative plan.
In the conditions of economic transformations, issues of hired labor have gained a priority due to a number of difficulties that negatively affect the socio-labor sphere. This is a systemic crisis accompanied by the increase in social tensions in society, the fall in the standard of living of a significant part of the country's population; and the arbitrary employers of the commercial sector as a result of the imperfection of the legislative base and the indifference of the executive branch; and numerous violations in the public sector of the economy, dictated by the time and irresponsibility of a number of modern leaders.
The priority of the problems of socio-labor relations is also due to the increased dynamics of negative trends in the field of hired labor, such as: the expansion of the zone of the shadow economy, whose employees are generally deprived of the opportunity to protect their labor rights; exacerbation of the contradictions between the labor force and the administration of enterprises expressed in significant differentiation in wages and conscious desire to enrich individual managers; in the deterioration of the situation of enterprises in order to further bankruptcy and acquire property rights with minimal cost; as well as the tightening of labor legislation, indicating the strengthening of the differentiation of the rights of various participants in the labor relations system.
Reform conducted in modern conditions requires the rethinking of many well-established ideas about the employee labor and its essence, which recently do not meet the economic realities of society's life. Full labor in conditions of market relations acts as a multifaceted phenomenon, the economic essence of which is developing in close relationship with the diversity of property and management and many other factors that have a significant impact on its dynamics. However, many views and judgments or do not take into account these features of the employment of hired type of labor relations, or they look so unconvincing that there was a need for their serious revaluation, the synthesis of new ideas that determine the place of socio-labor sphere in the modern economy. The need for a new concept of hired labor, reflecting its essence, able to show the variety of its modern forms of manifestation in economic practice, and allowing the use of those of them that would ensure the optimal performance of work activities, the security of employees in the field of social labor relations and the prospects for the function of hired Labor of all categories of labor resources, regardless of their competitiveness in a market economy.
The goal of the course work is to study the wage labor as a subject of legal regulation, as well as forms of manifestation of wage labor, the features of its use at various levels under conditions of economic transformations.
The subject of the study is a combination of production
relations about the functioning of hired labor in its various forms of manifestation.
In the course of achieving the following tasks:
1) to explore the development of wage relations in modern conditions;
2) allocate the features of the regulation of wage labor;
3) determine the features of the use of hired labor.
The object of the study is the Open Joint-Stock Company "Arthnsky Plant", which operates in the conditions of economic transformations.
The course work is based on the works of domestic authors such as, E.A. Sukhanova, O.S. Belokrylova, E.V. Mikhalkin, N.A. Brilliantov and others, materials of the seminar "Practice of contractual relations with employees of the company. Features of attracting, design and use of hired labor. " The information base of the study was a collective agreement and local regulatory acts of the enterprise, the Civil Code and the Labor Law of the Russian Federation. As an actual material, examples of hired labor in OJSC ARTINA FACTORY.
1.Toretical foundations for wage research
1.1. After hired labor
Hired work - The historical form of labor for which the following features are characteristic:
1) the prerequisite for the work of the labor process is the purchase and sale of goods "Workforce" in the labor market;
2) the labor process is performed under the supervision of the employer or their personnel hired;
3) Product Labor belongs to the employer, contains a newly created value consisting of the cost of the necessary product, which compensate for the cost of labor and surplus value.
Getting the surplus value is the purpose of the employer that buys the labor and the organizing process of production.
Historically, the hired work came to replace the natural work characteristic of the primitive communal, slave-owner and feudal societies. Natural work, with all the differences in its data "of production, was characterized by the fact that the worker was not the owner of his workforce, there was no conditions for its sale. The emergence and distribution of the system of wage labor is a qualitatively new stage of the development of society, forming the historical era, ongoing and currently.
The conditions for the emergence of hired labor:
1) market relations;
2) the emergence of the "labor force" on the market.
A developed system of hired labor involves a formed system of rights and obligations for employees, including ownership of its labor; Competition Right with other workforce sellers in determining the payment level, requirements for the quality of workforce, etc.; creating trade unions to defend their interests; The right to choose the buyer of its workforce, choosing the place of sale of labor force (freedom of movement); The right to choose life products and ways to meet life needs, etc. All forms of freedom, in which the hired worker has been delivered, are associated with his personal responsibility for themselves, for the decision on the choice of employer, compliance with the terms of employment, maintaining its workforce in good condition etc. In contrast to all forms of natural (donated) labor, where a significant part of the responsibility for the state of the employee, its existence, work was entrusted with the owner (slave owner, landlord), a developed system of waged labor forms an employee as a person who fully responsible for itself , your choice, decision making.
Concept as " work », « hired work "It is important for studying the problems of labor at the present stage of development of market relations, their correct decision. Labor is the basis of the life of human society. There is practically no such economic problem in any field of human activity, which would not be associated with his interests and work.
Labor issues in the present conditions have acquired so acute character that their nonreolence is increasingly causes social conflicts that need to be solved in the shortest possible time. Therefore, a deeper understanding of the economic essence of hired labor allows it to be used in the process of practical transformation of labor, improvement of labor activities and labor relations.
Work - This is an objectively inherent activity aimed at meeting the needs of society and the transformation of the disposable person.
1.2.Fast work as a subject of legal regulation
Under the influence of labor law norms, public relations, developing in the process of applying and organizing labor, are lifted in the legal form and become legal relations. At the same time, it is important to note that public relations in the field of labor do not always function in legal form, that is, in the form of legal relations, although it is predominant. In some cases, these relations are regulated by the customs, norms of corporate organizations, moral norms. However, public relations on the use of wage labor always require the legal form of regulation.
The labor law of Russia in the situation of market relations must be consistent with the idea of \u200b\u200ba social state enshrined in the Constitution of the Russian Federation (Article 7), whose policy is aimed at creating conditions that provide a decent life and free development primarily.
In the conditions of market relations, the labor price is determined by the Agreement of the Parties, since free work as a product becomes a source of revenue receiving, profits both for a hired employee who sells their ability to work and for an employer who uses acquired labor to obtain surplus value.
The interaction of the two main participants in the labor market - an employee and an employer who joined the contractual relationship about the use of the employee's ability to fulfill a certain work for a fee is characterized by the resistance of relations between them. Being settled law rules, these relationships become legal relations, legal model of the behavior of the parties to the employment contract. The objects of such relations on which the interests of the parties of the employment contract are focused, are the ability and obligation of the employee to perform labor function and wages needed for the employer, i.e. The ability and obligation of the employer in a timely manner and fully pay for the work of the hired employee, pay him wages.
Hired work organized by the employer with the participation of the employee, in contrast to the work of the individual or individually-group, i.e. Labor "on themselves", receives social and public importance, becomes public labor, by virtue of which the social importance of such labor increases sharply and it becomes the object not only to jointly regulate the agreement of the parties to the part-based contract between the employer and the employee, but also of state-legal regulation.
The state, participating in the regulation of the application and use of hired labor in the interests of society, as well as an employee and an employer, accepts legal norms that establish the legal borders of the legal freedom of participants in labor relations, within which they independently determine the working conditions, their rights and obligations by entering into an employment contract. , guided by the current legislation, which in the mechanism of labor regulation the central place takes exactly the employment contract.
But after the entry of the employer and the employee to the contractual relations, after determining the main conditions of use and remuneration, the state is not eliminated from control over forms and measures by its use, since public labor, unlike the individual, affects the interests of not only the employee and the employer, But both society. Therefore, the state cannot regulate labor relations fully on the Contracting Parties.
The state cannot eliminate the regulation of labor and control over the conclusion and execution of the employment contract and because its parties are an employer and employee - are in an unequal position, they do not have actual nor legal equality.
The unequal position of the parties to the employment contract seems that the Labor Code of the Russian Federation empowers the employer with disciplinary power in relation to the employee, provides him with the right to make mandatory requirements for it, apply to the employee of the promotion and recovery (Article 191, 192 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation ), without asking for this agreement. In order to limit the employer's opportunities to abuse its leading position in labor relations, in the normalization and remuneration of the employee, in providing him with benefits, creating the necessary conditions for work, as well as to guarantee the rights of employees, the state establishes the rules for the conclusion, execution, changes and termination of the employment contract, Principles of legal regulation of labor relations, the estimated list of which is provided in Article 2 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
He heads this list of labor freedom principle, which includes the right to work, which every freely chooses or which freely agrees, and prohibit forced labor, labor without relevant fair payment. The principle of labor freedom is fundamental to the entire mechanism of legal regulation of labor. After all, only work is free and compensated, implies fair payment for its use, may be the object of legal and contractual regulation.
Among the significant number of industrial colors regulating the compensated use of free labor, a lot of share amounts to civil law agreements for work or provision of services (contracts of contract, storage, transportation, instructions, to carry out research and other), which are concluded and executed In order governed by civil law. Parties in them are persons interested in obtaining such work or services (customers), and persons, such work or service providing (performers, contractors).
The second large group of contracts for paid use and the use of hired labor is the contracts (contracts), concluded with persons entering the state (federal or regional) service (civil, military or law enforcement) or municipal service to fulfill work on a particular position. Official relations arising on this basis are governed by the standards not working, but the constitutional (state), administrative, municipal and other branches of law. While in organic unity and having a general subject of regulation, these legal norms of different sectoral affiliation in their totality form an intersectoral integrated institute, which in the legal literature of recent times is often called official law.
The third group of contracts for free and compensated use of labor of employees is labor contracts. They are directly directly by employees and employers on the basis of and in the manner prescribed by labor law.
In the economy, the hired employee and the employer interact at two levels:
1) in the labor market, where the payroll rate is determined and the collective agreement is concluded;
2) inside the enterprise where the payment systems are established, which are fixed for specific jobs, groups, works, professions, positions and activities, the specific relationship between the payment of workers and the results of their labor.
Inside the enterprise, the relationship between employees and employers is based on labor standards, which establish a working day, labor intensity.
The employer provides employee scope of work and provides him with safe working conditions. An employee in turn should effectively and qualitatively carry out the volume of work provided to him within the existing norms.
Thus, the stimulation of employees at the enterprise is closely related to the scientific organization of labor, which includes the rationing of labor, which represents a clear definition of the circle of labor duties of the employee and those qualitative and quantitative results of labor that are required from it.
Speaking about stimulating employees, it is necessary to take into account such a concept as a motivation of labor. Motivation is determined by two concepts: the need and reward.
Needs are primary and secondary.
The primary human physiological needs are: food, water, clothing, dwelling, leisure, etc. Secondary needs are in their character psychological: the need for attachment, respect, success.
When stimulating labor as a remuneration worker for the work, which he uses to meet his needs, it must be borne in mind that different people are somewhat approaching this issue, determining various values \u200b\u200bfor themselves. So, for a person of high material wealth, an extra time for rest may be more significant than additional earnings, which he would get for overtime. For many people, for example, workers engaged in intellectual labor, more significant will be respected from colleagues and interesting work than the additional money that he could get, proceed by trade or becoming a commercial agent.
Forms and methods for the use of hired labor and bringing labor on the basis of an employment contract do not remain unchanged, once and forever data. Calculated changes in the socio-economic sphere of society have a significant impact on them, which are especially noticeable in the modern period, which is characterized by the transition of the country's economy to market regulation, to a market economy, the meaning and purpose of which is the maximum profit, which, in turn, pushes users hired work, especially in the field of entrepreneurial activity, to find new ways to obtain high-performance and highly qualified labor in the labor market for the smallest fee, using it with the greatest return, with minimal costs of its content.
At the same time, the state proceeds from the fact that the degree of protection of the rights and interests of employees as major labor carriers, the effectiveness of social labor will be the higher, the better the process of using the workforce, the labor process will be organized. And in this dominant role belongs to employers as the side of the employment contract, which not only hires workers and uses their work in its production in accordance with the terms of the employment contract, but also performs an important social function - creates jobs, ensures people with work, promotes ultimately Enhance the welfare of workers and the material well-being of the whole society.
Therefore, in the labor contract, the work of a hired employee who took the duty to fulfill a certain work in the interests of the employer, and the work of the employer who performs the important and necessary work to create the conditions for the worker to organize the work of the work process itself is merged. Taking into account this, the employment contract is intended to carry out not only the role of the regulator of the relations of workers with employers, but also to achieve the goal proclaimed by the Constitution - to ensure a decent life and free human development. And this suggests that not only the hired employee must have real guarantees for the implementation of its rights and freedoms, but also an employer. Performing a duty to ensure the necessary level of labor rights and guarantees of employees, the employer should be able to satisfy and its interests in obtaining profits from business, organizational and other activities.
Consequently, the subject of legal regulation within the framework of the employment contract is not only the labor of the employee, but also the work of the employer, who speaks no less important and socially significant figure than the hired worker.
The combination of labor and otherwise related interests of the employee and the employer within the framework of the employment contract creates favorable conditions for social partnership in the field of labor, the legal basis for the implementation of the objectives of labor legislation on the establishment of state guarantees of the rights, freedoms and interests of workers and employers (Article.1stkrf).
2. Output of the regulation of hired labor
2.1. Requirements for hire labor
The current legislation clearly defines the requirements that should be observed by employers in the event of hired employees. As the employment legislation implies, the employment contract must be concluded with each employee. It must be decorated in writing.
However, the employment contract will be considered concluded and in the event that the employee has begun to work with the knowledge or on behalf of the employer or its representative. At the same time, the employer is obliged to issue an employment contract within three days from the date of the actual assumption of the employee to fulfill its duties (part 2 of Article 67 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation). For non-compliance with the obligation, an authorized representative of the employer can be attracted to administrative responsibility.
Due to the fact that in the employment contract two parties: an employee and an employer, the contract is in two copies, one of which must be transferred to the employee, and the other is stored at the employer.
When concluding an employment contract, the employer has the right to demand the following documents from the employee:
Passport or other document certifying;
An employment record, except when the employment contract is for the first time or an employee comes to work on a part-time environment;
Insurance certificate of state pension insurance, except in cases where the employment contract is for the first time;
Military accounting document - for military-ridic and persons subject to military service;
Document on education, qualifications or availability of special knowledge or special training.
Documents not included in this list, including those provided by the Decrees of the President of the Russian Federation or the Resolutions of the Government of the Russian Federation, must be prohibited.
When concluding an employment contract it should be borne in mind that some restrictions are established by law. The main ones are the limitations associated with:
Age of the employee;
The need to comply with the form of the contract;
The need to pass a medical examination;
Establishing a test for an employee;
Reasons for refusal to conclude a contract.
All employers are obliged to fulfill their obligations towards employees in accordance with the legislation.
2.2. Characteristic of hired labor
As a peculiar antipode, independent work can be called inspitable or hired work. The basis of division into these two categories is the attitude of the employee to its products used during the labor process, or labor tools (mechanisms, tools, etc.). The belonging of such funds by the worker, as we found out, gives rise to the effect of direct or directly connected by the human labor force with its own means of production. The connection of the workforce of the worker with the means of production, the owner of which it is not, is not carried out directly, and indirectly: the owner of the relevant labor force and the owner of the means of production must first agree on the conditions of working on the basis of these funds, i.e. enter into a contract.
The first element of the public organization of hired labor is the nature of wage labor, since the nature of the wage labor to a certain extent reflects the qualitative state of the productive forces of society. So, if it does not require a division of labor to produce this or that type of products, it is the nature of the individual, regardless of the existing historical period of production relations. If, in order to increase and reduce the cost of production, there is a need to divide wage labor, each operating operation is allocated to an independent activity, organically and inseparable associated with all others, i.e. Labor acquires the character of the joint.
The separation of hired labor is necessary only where its implementation is necessary for the growth of labor productivity, increasing its production rates. In the history of mankind, many examples when the production of violent division of labor and the socialization of the means of production gave the opposite effect and the pace of production has greatly fell.
The division of labor, which occurs naturally, is gaining its fixation in production, making its internal structure only if it leads to an increase in productivity of its quality. This indispensable condition for any division of work acquires a property of a decisive criterion during its in-depth division, since the second party in-depth divided (joint) labor is the coordination of joint work, which causes the objective need to create a production process authorities, and the cost of holding management personnel includes an integral part of the production cost .
Therefore, an in-depth division of labor should bring very useful fruits. It is necessary that due to its implementation, the costs of the content of the control apparatus did not exceed the cost of final products produced on the basis of unrequited labor.
The next element in the characteristic of workers' work is forms of attraction to work. Fashing social and labor relations is based on the freedom of concluding an employer's labor contract with a hired employee. Freedom of concluding a contract follows from the legal equality of the employer and the hired employee, which is extremely unambiguous and exhaustively found its expression and consolidation in the norms of Art. Art. 17, 18, 19, 34, 35, 36, 37 and other Constitution of the Russian Federation, including in the norm of imperative nature: work is free, forced labor is prohibited.
Freedom of Labor - In addition to the ideological aspect that is currently the ideological aspect - a person who consumes, may not work at all, meaning by anyone is not limited to the possibility of choosing the form of working out every person - in free form or by employment. It is the possibility of an independent choice that makes a really free conclusion of an employment contract, since the legal equality of the parties is only their formal equality in relation to each other, in no way affecting their real economic situation in public production, which is based on the objectively determined inequality of the owner of the production and carrier work force. And if the employee has a certain alternative to work for someone or work on itself with its own means of production, while receiving the support of the state (loans, benefits, etc.), or does not work at all, which is enshrined in the Constitution, this will be the real Freedom of choice, and not just formal equality in relations between the employee and the employer.
The next element of the characteristics of the public organization of labor is a way to maintain labor discipline and labor management. With any form of labor, if labor is carried out jointly, it needs coordination. Otherwise, it is not possible to achieve the actual purpose of the production itself: creating a specific type of product or product. That is, the main reason for establishing a certain order of management is the objective need for its coordination.
This condition has a different impact on the will of participants in collaboration. After all, the owner of the means of production that has invested its capital in the means of production, technology, labor and organizing production, expects to make a profit from the sale of manufactured products or goods. And the workers do not need employees. After all, they pass their opportunity to work as an employer, and they do not carry economic responsibility for the result of labor.
2.3. Principles of creating a system for stimulating employees
The current stage of economic reforms in Russia is characterized by the fact that enterprises work in the situation of growing demands of various public groups. In this regard, the creation of an effective system of stimulating employees is particularly relevant.
Consider some directions for solving this task.
When creating a stimulation system, principles developed in the theory of management and used in the market economy are designed:
Complexity;
Systemability;
Regulation;
Specialization;
Stability;
Targeted creativity.
Let us dwell on the essence of these principles.
The first principle is complexity. The complexity suggests that a comprehensive approach is needed, taking into account all possible factors: organizational, legal, technical, material, social, moral and sociological.
Organizational factors are the establishment of a certain procedure for carrying out work, delimitation of powers, formulating goals and objectives. As already mentioned, the correct organization of the production process lays the foundation for further efficient and high-quality work.
Legal factors are closely interacting with organizational factors that serve the goals of ensuring the compliance of the rights and obligations of the employee in the process of labor, taking into account the functions assigned to it. This is necessary for the correct organization of production and further fair incentive.
Technical factors involve the provision of personnel with modern means of production and office equipment. As well as organizational, these aspects are fundamental in the work of the enterprise.
Material factors determine specific forms of material incentives: wages, premiums, surcharges, etc. and their size.
Social factors involve increasing the interest of employees by providing them with various social benefits, providing social assistance, the participation of employees in the management team.
Moral factors represent a set of activities, the purpose of which is to ensure a positive moral and moral climate in the team, the correct selection and placement of personnel, various forms of moral incentives.
Physiological factors include a set of activities aimed at maintaining health and improving employees. These activities are carried out in accordance with sanitary and hygienic, ergonomic and aesthetic requirements that contain the rules for the equipment and the establishment of rational regimes of labor and recreation. Physiological factors play an equally important role in improving the efficiency and quality of work performed than the rest.
All listed factors should be applied separately, but in the aggregate, which gives a guarantee of obtaining good results. It was then that will become a reality to a significant increase in efficiency and quality of work.
The principle of complexity is already in its title determines the conduct of these activities not in relation to one or several employees, but in relation to the entire team of the enterprise. This approach will give a significantly greater effect at the level of the entire enterprise.
The second principle is systemic. If the principle of complexity involves the creation of a stimulation system, taking into account all its factors, the principle of systemicity involves identifying and eliminating contradictions between factors, their linking together. This makes it possible to create a stimulating system that is internally balanced by mutual harmonization of its elements and is able to work effectively for the benefit of the organization.
An example of systemicity can be a system of material and moral incentives for hired workers, based on the results of quality control and evaluation of the employee's contribution, that is, there is a logical relationship between the quality and efficiency of work and the subsequent remuneration.
The third principle is regulatory. Regulation involves the establishment of a certain order in the form of instructions, rules, standards and control over their implementation. In this regard, it is important to distinguish between the areas of activity of workers who require harsh compliance with instructions and control over their implementation, from those areas in which the employee must be free in their actions and can manifest the initiative. When creating a system of stimulating, regulatory objects should be the specific responsibilities of one or another employee, the specific results of its activities, labor costs, that is, each employee must have a complete picture of what is included in his duties and what results are waiting for it. In addition, regulation is necessary and in the matter of estimating the final work, that is, those criteria for which the ultimate work of the employee will be evaluated clearly established. Such regulation, however, should not exclude a creative approach, which in turn should also be taken into account in the subsequent remuneration of the employee.
Regulation of the content of the work performed by the company's employees should solve the following tasks:
1) the definition of work and operations to be assigned to employees;
2) providing employees with the necessary information entrusted to them;
3) distribution of works and operations between enterprise divisions on the principle of rationality;
4) establishing specific job responsibilities for each employee in accordance with its qualifications and level of education.
Regulation of labor content serves as an increase in the effectiveness of the work performed.
From the point of view of stimulating the work performed, a very important role is played by the regulation of the results of the work performed. It includes:
1) the definition of a number of indicators characterizing the activities of enterprise units and each employee separately, which would be given to the contribution of divisions and individual workers in the overall result of the enterprise;
2) definition of a quantitative assessment for each of the indicators;
3) the creation of a general assessment system of the employee's contribution to the achievement of general results of activities, taking into account the effectiveness and quality of work performed.
Thus, it can be said that regulation in stimulating issues plays a very important role, organizing the system of stimulating in the enterprise.
The fourth principle is specialization. Specialization is the consolidation of certain functions and work in accordance with the principle of rationalization for enterprise divisions and individual employees. Specialization is an incentive to increase labor productivity, increase efficiency and improving the quality of work.
The fifth principle is stability. Stability involves the presence of a current collective, the absence of fluidity of frames, the presence of certain tasks and functions facing the team and the procedure for their execution. Any changes occurring in the work of the enterprise should take place without violating the normal functions of the functions of this or another division of an enterprise or employee. Only then will not reduce the effectiveness and quality of work performed.
The sixth principle is targeted creativity. Here it is necessary to say that the system of stimulating in the enterprise should contribute to the manifestation of the creative approach. This includes the creation of new, more advanced products, production technologies and structures of used equipment or types of materials, and the search for new, more efficient solutions in the field of production and management organization.
Based on the results of the creative activity of the enterprise as a whole, the structural unit and each individual employee, measures of material and moral incentives are envisaged. The employee who knows that the proposal put forward by him will bring him additional material and moral benefits, a desire to think creatively appears. It is especially serious to approach the stimulation of a creative process in scientific and design teams.
When organizing a stimulation system in the enterprise, it is necessary to take into account the proportions in the payment between simple and difficult labor, between employees of various qualifications.
When creating a system of stimulating in the enterprise, it is necessary to adhere to the principle of system flexibility. Flexible stimulating systems allow the entrepreneur, on the one hand, to provide employee certain guarantees for obtaining wages in accordance with his experience and professional knowledge, and on the other hand, to pay the wage of the employee dependent on its personal indicators in the work and on the results of the enterprise's work as a whole .
Flexible stimulation systems today have been widespread in foreign countries with developed economies. Moreover, the flexibility in wages is manifested not only in the form of additional individual surcharges to wages. The spectrum of flexible payments is quite wide. These are individual surcharges for the experience, experience, level of education, etc., and collective premium systems calculated, first of all, on workers, and profit participation systems, designed for specialists and managers, and flexible social benefits. Only the use of all forms of stimulation designed to be applied to all employees of the organization can give the necessary effect.
As experience shows, in Russian enterprises now the main problems in the mechanism of stimulating employees are:
1) the insufficient flexibility of the mechanism for the formation of remuneration, its inability to respond to changes in the efficiency and quality of labor of a separate employee;
2) the absence of any assessment or a biased by the entrepreneur with an assessment of individual labor rates of employees;
3) the lack of equitable remuneration of managers, specialists and employees; the presence of unreasonable relationships in paying their labor;
4) the negative attitude of the staff to the amount of payment of their labor and to the existing payment system.
All these challenges that are facing enterprises in solving issues on wages are overcome using Russian and foreign experiences.
Thus, insufficient flexibility in remuneration is solved by the introduction of modern forms of remuneration, depending on the results of work. Such forms are flexible payment systems, where, along with a constant part of earnings, there is a variable part in the form of participation in profits, collective premiums, etc.
Issues of the biased assessment of the results of employees are associated again with an outdated remuneration mechanism that do not take into account the individual achievements of the employee and the result of the enterprise's activities as a whole. The fair assessment system can be created based on the description of the workplace and employee job duties to determine the permanent part of wages. And on the basis of participation in profits in relation to the flexible part of earnings.
Fair payment of managers, specialists and employees should also be based on the same principles, but using the specifications specific for these categories that take into account the complexity of the tasks solved, the level of responsibility, the number of subordinates and others.
It is using flexible wage systems, using a reasonable assessment of the workplace and official duties and the subsequent participation of employees in profits and collective prizes for reducing the share of labor costs in the cost of production, the negative attitude of the organization's staff to the existing system of payment of their labor and size of this payment.
The result of the system of stimulating the enterprise should be improving the efficiency of the enterprise, which can be achieved, in turn, by increasing the efficiency and quality of labor of each employee of the enterprise. At the same time, the entrepreneur must be guided by the need to attract and preserve for long term highly qualified workers, improving labor productivity and improving the quality of products, increasing the return on investments in personnel, increasing the interest of workers not only in personal success, but also in the success of the entire enterprise in general, Finally, raising the social status of employees.
Therefore, both material and intangible forms of staff stimulating, which include wages, various profit participation systems, collective bonuses, individualization of wages, moral incentives, stimulating workers engaged in creative labor, by applying free work schedule, social benefits for employees.
The employer, solving the issue of creating a system of stimulating employees at the enterprise, should take into account such a macro-frame, independent of the efficiency and quality of labor of workers and the team of the enterprise as a whole as the consumer price index. Accordingly, the presence of such an indicator makes it necessary to automatic wage indexing, taking into account the change in price index for a certain period.
The incentive system in the enterprise should clearly define its goals, to establish the types of stimulation in accordance with the results achieved, determine the evaluation system, the period and timing of remuneration.
Any types of stimulation should be targeted and vowels, because you can expect from employees to improve the efficiency and quality of work performed only when they know that their work is paid fairly.
The stimulation system must comply with the principle: payment must match the work.
Speaking about the system of stimulating employees, it is necessary to highlight the basic requirements for it. To those can be attributed:
1) clarity and specificity of the stimulation system as a whole, the provisions on wages and additional payments;
2) a clear statement of employee's labor duties;
3) the creation of an objective assessment system of workers and the exclusion of subjectivity in the assessment;
4) the dependence of the size of wages from the complexity and responsibility of the work;
5) the possibility of unlimited wage growth with an increase in the individual results of the employee;
6) accounting in the payment of the level of significance of certain works for the enterprise;
7) Equal payment of workers with the same complexity and responsibility of work performed in various enterprise units (refers to basic payment without taking into account additional payments on the results).
Thus, when creating a stimulation system, it is necessary to take into account the full range of issues, including the state regulation of the wage.
3. Features of the use of hired labor on the example
OJSC "Arthnsky Plant"
3.1. General characteristics of the company
The art plant is the oldest enterprise of the Urals, it was founded in 1787 as a ferrous plant on imported raw materials.
The plant is located in P.G.T. Arti, in the south-west of the Sverdlovsk region, 180 km from Yekaterinburg and 60 km from Krasnoufimsk Station.
Organizational and legal form - Open Joint Stock Company, whose founders are legal entities and individuals. Open Joint-Stock Company "Arthnsky Plant" is an independent society with its legal address and independent balance.
The purpose of creating an enterprise is the implementation of financial and economic activities in order to profit.
In 1827, the plant issued the first braids for agricultural work, hardened according to the technology of the Creator of the Russian Boutique of the Great Metallurg P.P.Anosov. Since that time, braids have become the main products of the plant.
In a modern period, the main activities of ARTINA Factory OJSC are:
1) Production and sale of consumer goods (KOST sets in the assortment depending on the purpose and size; agricultural sickles; sets of gardening "Dachnik"; stairs; chains.); production and technical products and component parts; Building materials, services to the population.
2) carrying out and implementing research and development work;
3) capital construction, repair and maintenance: industrial facilities; residential buildings; social objects; Transfer devices.
4) Organization and exercise of forest work, sawmills, production of containers and wood products.
5) participation in exhibitions, fairs, various kinds of bidding, including investment.
The sales markets of the ARTINA Factory OJSC are divided by regions - Federal Districts of the Russian Federation. Also buyers are enterprises of neighboring countries (Lithuania, Latvia, Ukraine, Belarus, Azerbaijan) and Far (Hungary, Bulgaria, Slovakia, Turkey, Iran) abroad. Export supplies occupy a significant proportion in the total volume of product sales.
The main buyers of the company's products are large wholesale firms specializing in the sale of haberdashery goods, gardening equipment, as well as sewing, shoe industry.
Consumers of services are mainly local organizations and the population.
Currently, the braids of the Arthnical Plant are exported to Germany, Slovakia, Turkey, Iran, Hungary, Bulgaria, Latvia, Estonia and CIS countries.
For 57 years of production, the plant has been mastered by about 500 sizes of needles for sewing, knitwear, shoe and leather goods industry. The company expands the range of gardening inventory, haberdashery products.
The general leadership of the company is carried out by the Director General. He coordinates the work of directors in areas of activity: technical, financial, personnel director, director of marketing, director of quality, security director. In submission of each of the directors there are functional divisions and services.
The main priorities at Arytinsky Plant OJSC are an increase in sales and raising the quality of basic goods and services. In all areas of production in 2010, it is planned to grow due to an increase in the range of products manufactured, improve their quality, as well as by increasing the provision of services and create a modern organization organization system. The priority direction for 2010, as in previous years, is to improve the quality of manufactured (traditional) products, an annual development (implementation) of at least ten new products.
3.1. Attraction and use of wage labor at the enterprise
In the ARTINA Factory OJSC, the hired labor of Russian citizens is used, the average number in March 2010 is 845 people. For each employee, in accordance with the legislation, an employment contract is drawn up, as well as a personal employee card.
Under the labor relations, the parties take relations between people, due to the social, legal and functional aspects of work. Among them are relations:
Between the employee and the employer (regulated by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and the employment contract)
Between the administration and the trade union (regulated by the Federal Law "On Trade Unions", the Labor Code of the Russian Federation and the collective agreement)
Between the boss and subordinates (regulated by job descriptions)
Between labor collectives (regulated by internal local regulatory acts, internal labor regulations (Appendix 1).
Labor relations at the enterprise arise when an employee arrives at work as a result:
Election to address the meeting of shareholders - general director, according to constituent documents
Appointment for a position or approval in the new position of persons relevant qualifications or education
Acceptance of job seekers for vocational training (retraining) under the student agreement
Attracting an employee to fulfill a certain work in accordance with the Civil Code of the Russian Federation under the terms of the contract
When admitting work, labor relations are made by concluding an employment contract in writing in two copies - one for each side (Appendix 2). The employment contract can be concluded as an indefinite period, for a certain period (urgent contract). The urgent contract is in cases where labor relations cannot be established for an indefinite period, taking into account the nature of the upcoming work or the conditions for its implementation.
The employer and employees undertake to fulfill the terms of the employment contract. In this regard, the employer is not entitled to demand from workers to fulfill work, not caused by the employment contract. Transfer to another work without the consent of the employee is allowed only in cases provided for by Art. 74 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
In the conditions of the employment contract, the test may be included in order to verify the conformity of the employee of the commissioned work. The test condition should be indicated in the employment contract, the lack of testing conditions in the labor contract means that the worker is accepted without testing. The test term cannot exceed three months (for managers, chief accountants and their deputies - no more than six months).
Tests when taking work are not established for individuals defined by Article 70 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
In the unsatisfactory result of the test, the employer has the right before the expiration of the test expires to terminate the employment contract with the employee, who warn him about this in writing no later than three days, indicating the reasons that served as the basis for the recognition of this employee who could not withstand the test.
Each newly adopted employee establishes an adaptation period for a period of not more than two months, during which the sentences for omission in work will not be applied to it, except in cases of deliberate disruption of labor and production discipline.
When applying for a job, the employer is obliged to familiarize the employee with the Organization of the Internal Labor Regulations operating in the organization, other regulatory acts related to the employment of the employee, the collective agreement.
Conclusion
As a result of the study, the following conclusions were made.
Hired work is an integral element of a market economy, due to the excessive extensity of this topic, it is impossible to consider in detail all parties to this problem in one work. However, based on the foregoing, it is possible to submit employees in the Russian Federation as a dynamic system, which is based on the relationship and supply of labor, the relationship between employment and unemployment, the factors of formation and operation of labor, its competitiveness and mobility.
The labor market formed in Russia has a complex structure. It is the deepening of its segmentation for a number of criteria: forms of ownership, labor-intensity of production, peculiarities of production technology, qualifications of employed, level of separation and public utterance, historically established forms of organization and stimulation of labor, traditions in the motivational behavior of workers. It is better to understand the structure of the market, to identify its steady segmentation and, accordingly, develop differentiated methods for its regulation will allow an integrated analysis of the action of the factors that determine segmentation.
To begin to effectively solve problems in the wage market, you must first reform all areas of the economic, political and social life of society.
For the regulation of hired labor at the enterprise, effective management of the workforce and maintenance of labor discipline is necessary.
Stimulating employees is ensured by increasing profits by increasing the efficiency and quality of work. "Labor efficiency" and "quality of labor" are key factors in increasing the company's profits in the long term.
At stimulation of hired workers is influenced by an entrepreneur social policy.
Social benefits are the form of participation of employees in the economic success of the enterprise.
It is advisable to proceed from the following principles of building a system of social benefits for employees:
1) it is necessary to identify the material and intangible needs of employees;
2) it is necessary to fully inform employees about the social benefits provided by them, as well as their additional, excess of state benefits;
3) Social benefits provided should be economically justified and applied only with the budget of the enterprise;
4) social benefits that have already been granted to state employees should not be applied at the enterprise;
5) Social benefit system must be understandable to employees and each employee must know what kind of merit should be or not allowed for it or other benefits.
To enhance the stimulating role of wages, it is advisable to comply with the following principles:
1) the dependence of wages from the efficiency, productivity and quality of work performed in order to ensure the interest of employees in the results of their work;
2) the introduction of flexible payment systems based on the registration of the final results of the organization and the individual contribution of the employee, including participation in profits;
3) the exclusion of equation in paying for employees;
4) When creating a system for paying hired workers to provide an increase in its unifying role, excluding confrontation between employees.
At the enterprise ARTINA Factory, labor relations are governed by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, a collective agreement, internal local regulatory acts. When an employee arrives at work, labor relations are made by concluding an employment contract in writing in two copies. At the same time, the employer complies with labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts, containing the rules of labor law, local regulations, collective agreement conditions, agreements and employment contracts; ensures safety and working conditions that meet the state regulatory requirements of labor protection; Perfect other obligations provided for by labor laws and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law standards, collective agreement, agreements, local regulatory acts and employment contracts
Bibliographic list
Regulations
1. Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation dated June 30, 2004 N 324 "On approval of the Regulation on the Federal Service for Labor and Employment". Meeting of the legislation of the Russian Federation, 2004, No. 28, Art. 2901).
2. Labor Code of the Russian Federation. M., 2006.
3. Resolution of the Government of the Russian Federation dated June 30, 2004 No. 324 "On approval of the Regulations on the Federal Service for Labor and Employment" (Meeting of the legislation of the Russian Federation, 2004, No. 28, Art. 2901).
Main literature
4. Civil law: in 2 tons: Textbook / Ed. E. A. Sukhanova. M.: Publishing House "Beck", 2000. T. 1. - 816 p.
5. Belokrylova O. S, Mikhalkina E. V. Labor Economics: Summary of Lectures. - Rostov-on Don: Phoenix, 2002. - 154c.
6. Vorogoreikin I. E. Labor and entrepreneurship. Tutorial. - M.: Gau, 1995. - 56c.
7. Roof A, I., Zhukov A. L. Theoretical foundations of the economy of sociology of labor: a textbook. - M.: Mick, 2005. - 254С.
8. Roof A. I., Zubysko B. G., Ishin V. V. Labor market, employment of the population, the economy of resources for labor. - M., 2000. - 111c.
9. Labor law: studies. / ON THE. Brilliantov; Ed. O.V. Smirnova, I.O. Snegier. - 4th ed., Pererab. And add. - M.: Prospekt, 2009. - 624c
Additional sources
10. Legal portal "LAVVMIX" (WWW. LAVVMIX.RU).
11. WWW site. BBEST.RU.
12. WWW site.
ATTACHMENT 1
internal labor regulations for employees of OJSC ARTINA FACTORY
1. GENERAL PROVISIONS
1.1. Rules of domestic labor regulations of the open joint stock company
"Arthnsky Plant" - a local regulatory act regulating in accordance with the Labor
Code of the Russian Federation and other federal laws of admission and dismissal
employees, basic rights, responsibilities and responsibilities of workers and employer, regime
work, resting time applied to employees to promote and recovery measures, as well as other
Issues of regulation of labor relations in the organization.
These rules, as well as all changes and additions to them, are approved by the Director-General of the Organization, taking into account the opinion of the representative body of the organization's employees.
Compliance with these Rules is mandatory for all employees of the organization.
An employee of the organization gets acquainted with these Rules before signing the employment contract.
2. The procedure for the reception and dismissal of employees
2.1. When admission to work with the employee is an employment contract.
2.2 When concluding an employment contract, the employer is obliged to demand from the incoming:
Passport or other document certifying;
An employment record, except when the employment contract is for the first time or an employee comes to work on a part-time environment;
Insurance certificate of state pension insurance;
Military accounting documents - for military-ridden and persons subject to military service;
Document on education, on qualification or availability of special knowledge - when admitting work requiring special knowledge or special training;
Insurance medical policy of mandatory insurance of citizens;
Conclusion about the passage of medical examination;
persons under the age of 18 are accepted only after a preliminary compulsory medical examination (survey).
Acceptance of specialists can be made on a competitive basis. The Regulations on the Competition is approved by the administration of the enterprise and the trade union.
When concluding an employment contract for the first time, the employment record and the insurance certificate of state pension insurance are issued by the employer.
When concluding an employee of an employment contract in it, under the Agreement of the Parties, a condition for testing an employee may be envisaged in order to verify its compliance of the ordered work. The absence in the labor contract the test conditions means that the worker is hired without a test. The test term for admission to work is set from 3 to 6 months, depending on the post. During the test, the periods of temporary disability of the employee and other periods, when he actually absent at work is not counted. For
the unsatisfactory result of the test employer has the right before the expiration of the test expires to terminate the employment contract with the employee who warn him about it in writing
form no later than 3 days indicating the reasons that served as the basis for the adoption of such a decision. Employer's decision The employee has the right to appeal in court. In the unsatisfactory result of the test, the termination of the employment contract is made without taking into account the opinion of the relevant trade union organ and without paying the output benefit. If the test term is expired, and the employee continues to work, then it is considered to be withstrone the trial period and the subsequent termination of the contract is allowed only on general reasons. If in the test period, the employee decides that the proposed work is not suitable for him, he has the right to terminate the employment contract on his own willing of this employer in writing in writing for 3 days.
2.3.Trudovaya agreement is in writing to an indefinite or definite
term. The document is drawn up in two copies, each of which is signed by the parties.
One copy of the employment contract is transferred to the employee, another is stored with the employer.
The acquisition of an employee of an employment contract must be confirmed by the employee's signature at an instance of an employment contract stored at the employer.
2.4. Just at work is issued by the order, which is announced by the employee under the painting in
Three-day period from the date of the actual start of work.
An employment contract not decorated in writing is considered to be concluded if the employee | I started working with the knowledge or on behalf of the Director General of the Organization. In this case, the written design of the employment contract must be made no later than three working days from the date of the actual assumption of the employee to work.
2.5. The change in the working contract defined by the parties is carried out by agreement between the employee and the employer, with the exception of the cases provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. Agreement on the change in certain parties: the conditions of the employment contract lies in writing.
2.6. When receiving an employee to work or transfer it in the prescribed manner to another job, the host head of the structural unit introduces an employee with the rules of the internal labor regulations in force in the enterprise, other regulatory acts related to the employment function of the employee, a collective agreement.
2.7. Transfer to another constant work in the same organization at the initiative of the employer, that is, changes in the labor function or the change in the essential conditions of employment contract, transfer to a permanent job to another organization, or to another locality, together with the organization is allowed only with the written consent of the employee. Worker who needs
according to the medical conclusion in the provision of other work, the employer is obliged to transfer to another work that is not contraindicated by him for health. If the employee fails to fail, or the absence of an agreement on the organization of relevant work is terminated. Is not a translation to another permanent job and not
requires the consent of the employee to move it in the same organization of it to another workplace, in
Another structural unit of this organization in the same locality, the commissioning of the work on another mechanism or unit, if it does not entail a change in the labor function and
changes in essential conditions of employment contract.
2.8. For reasons related to a change in organizational or technological conditions of labor, it is allowed to change the significant conditions of the employment contract defined by the parties under the initiative of the employer when the employee continues without changing the labor function.
On the introduction of these changes, the employee must be notified by the employer in writing no later than 2 months before their introduction. If the employee does not agree to continue working in the new conditions, the employer is obliged to offer him a different work available in the organization that meets his qualifications and health status, and in the absence of such a job - a vacant substrait position or the lower job that the worker can perform with By consideration of its qualifications and health status. In the absence of the specified work, as well as in the event of a refusal of an employee from the proposed work, the employment contract is terminated.
If the circumstances may entail a massive dismissal of workers, the employer in order to preserve jobs has the right to consider the opinion of the elected trade union body of the Organization to introduce incomplete working time for up to 6 months. If the employee refuses to continue working on the conditions of the relevant modes of working time, the employment contract is terminated with the provision of appropriate guarantees and compensation. Cancellation of the regime of incomplete working time is made by the employer, taking into account the opinion of the representative body of employees of the organization.
2.9. In the case of industrial necessity, the employer has the right to translate an employee to work in the same organization with the work of work on the work performed, but not lower than the average earnings for the previous work. Such a translation is allowed to prevent disasters, an industrial accident or natural disaster; To prevent accidents, downtime (temporary exposure of work for reasons of economic, technical or organizational nature), destruction or damage to property, as well as for replacing the missing employee. At the same time, the employee cannot be translated into work contraindicated by him for health. The duration of transfer to another job to replace the missing employee cannot exceed one month in. Calendar Year's flow (from January 1 to December 31). With written consent, the employee can be transferred to work that requires lower qualifications.
2.10. When admission to work, translation to another work in other cases established by labor law, as well as in the event of the need, a specialist in the protection of the organization of the organization introduces all employees with labor protection requirements.
Instructions for safety in the workplace of each employee conducts; The receiving head of the structural unit with the enlarging of the results of the safety instruction on the workplace of employees of the organization.
When fulfilling its employment duties, the employee must comply with the appropriate
Security Instructions.
2.11. The employer is obliged to remove from work (not allowed to work) an employee:
Appeared at work in a state of alcoholic, narcotic or other toxic intoxication;
Not held in the prescribed manner training and verification of knowledge and skills in the field of labor protection;
Mandatory preliminary or periodic medical examination in the prescribed manner;
When identifying in accordance with the medical conclusion of contraindications to fulfill the employee of the work due to the employment contract;
The employer removes from work (does not allow for work) an employee for the entire period of time before eliminating the circumstances that were the basis for removing work or preventing work;
In other cases, provided for in Article 76 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
2.12 Termination of an employment contract may take place only on the grounds provided for by labor law.
2.13Theternal contract may be terminated at any time by agreement of the parties to the employment contract.
2.14 Thermal career has the right to terminate the employment contract, writing in writing about this employer no later than two weeks, unless otherwise established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation or other federal law. After the expiration of the warning about the dismissal, the employee has the right to stop working.
2.15 Working employment contracts with employees are terminated in compliance with the rules established by Article 79 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation.
2.16 The extension of the employment contract on the initiative of the employer is made on the grounds provided for in Article 81 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. The employee is not allowed to dismiss the employee at the initiative of the employer (with the exception of the case of the elimination of the organization) during its temporary disability and during the stay on vacation.
2.17 The proceedings of the employment contract is issued by the order subscribed by the Director General of the Organization or the person who are authorized. With this order, the employee meets under the painting.
2.18 The end of the work of the employment contract in all cases is the last day of the employee, except when the employee actually did not work, but for him, in accordance with the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, or other federal law, the place of work was maintained.
2.19 On the day of termination of the employment contract, a specialist of the personnel personnel department issues an employee a labor book, as well as on a written statement of the employee, a properly certified copy of documents related to work. On the estimated day, the department of the organization produces a final calculation with the employee. Records to the labor book on the basis and reason for the termination of the employment contract are made in accurately in accordance with the formulations of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation or other Federal Law and with reference to the appropriate, article, part of the article, the article of these documents.
3. Basic rights, duties and responsibilities of employees
3.1. The worker has the right to:
Conclusion, change and termination of the employment contract in the manner and under the conditions established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, other federal laws;
Providing him with work due to the employment contract;
Workplace conforming to the state regulatory requirements of labor protection and conditions provided for by the collective agreement;
Timely and in full payment of wages in accordance with its qualifications, complexity of labor, the number and quality of work performed;
Rest, provided by the establishment of a normal duration, working time, reduced working time for individual professions and categories of workers, the provision of weekly weekend days, non-working holidays paid for annual holidays.
Other rights of employees are established by Article 21 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, and may also be provided for by a collective agreement, local regulatory acts of the organization and employment contract.
3.2. The worker is obliged:
Conscientiously performing your employment responsibilities assigned to it by the employment contract and the job description;
Comply with these Rules, other local regulatory acts of the organization;
Observe labor discipline;
Perform established labor standards;
Take care of the property of the employer (including the property of third parties who have an employer if the employer is responsible for the safety of this property) and other employees;
Immediately report to the employer, or the immediate leader about the emergence of situations representing the threat of life and health of people, the safety of the employer's property (including the property of third parties at the employer, if the employer is responsible for the safety of this property).
Protect the property of the employer, effectively use equipment, tools, materials, saving heat, electricity, fuel and other energy resources;
take measures to immediately eliminate the causes and conditions of preventing or impellent labor production (downtime, breakdowns, accidents), in case of the impossibility of eliminating these reasons to immediately report the administration of the site, workshop, plant;
The circle of responsibilities that each employee must fulfill in their qualifications, specialty, position is determined by the employment contract, tariff-qualification directories, technical rules, job descriptions and provisions approved in the prescribed manner.
4. Basic rights, duties and responsibility of the employer
4.1. The employer has the right:
Conclude, change and terminate labor contracts with employees in the manner and under the conditions established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, other federal laws;
Lead collective negotiations and conclude collective agreements;
Encourage workers for conscientious effective labor;
Require employees of the work of labor duties and respect for the property of the employer (including the property of third parties from the employer, if the employer is responsible for the safety of this property) and other employees, compliance with this Regulation;
Attract workers to disciplinary and material responsibility in the manner established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, other federal laws;
Take local regulations;
Create associations of employers for the purpose of representation and protect their interests and join them.
4.2. The employer must:
Comply with labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law norms, local regulations, collective agreement conditions, agreements and employment contracts;
Provide employees work due to labor contracts;
Ensure safety and working conditions that meet the state regulatory requirements of labor protection;
Provide workers with equipment, tools, technical documentation and other means necessary for the performance of labor duties;
Fulfill other obligations provided for by labor legislation and other regulatory legal acts containing the norms of labor law, a collective agreement, agreements, local regulatory acts and employment contracts;
To pay in the full amount due to employees wages within the deadlines established by the TC RF, collective agreement, the rules of the internal labor regulation of the organization, employment contracts;
Ensure the labor needs of employees related to the performance of labor duties;
Carry out compulsory social insurance of employees in the manner prescribed by federal laws;
Compensate for the harm caused to employees in connection with the performance of labor duties, as well as compensate for moral harm in the manner and under the conditions established by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, federal laws and other regulatory legal acts;
To fulfill other obligations provided for by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, federal laws and other regulatory legal acts containing labor law standards, a collective agreement, agreements and employment contracts.
Legal status (legal status) of trade unions is determined by the Constitution of Ukraine (1996), which citizens of Ukraine are guaranteed the right to associate in political parties and public organizations for the implementation and protection of their rights and freedoms and the satisfaction of political, economic, social, cultural and other interests (Article 36 ).
Employees based on the content of Art. 36 of the Constitution of Ukraine, have the right to unite into trade unions in order to protect their labor and socio-economic rights and interests.
Professional unions —
These are the most massive public organizations in accordance with their charters and represent the interests of employees in the field of production, labor, life, culture, etc. Trade union bodies
It has the right to carry out supervision and control over compliance with labor legislation, rules for labor protection and exercise other powers in the field of labor, housing and domestic service of workers, etc. Wide powers
The trade union bodies provided for by the Constitution of Ukraine find a specific implementation in such basic legal norms: the Code of Labor Law on Ukraine (ch. XVI); The Law of Ukraine "On Professional Unions, their Rights and Guarantees of Activities" of September 15, 1999, with significant changes from December 13, 2001 and the Charters (provisions) of specific trade union organizations, which are accepted at congresses, conferences, founding or general meetings of the trade union members. According to these norms, commercial unions, and more precisely, their trade union bodies carrying out their work in the field of labor in two main directions. First - This is the protection of the interests of workers, and the second - the trade union authorities are entitled to speak on behalf of the trade union as an employer, that is, to use hired labor. With respect to the first direction of activity of trade unions as a defender of the interests of workers in the field of labor, their powers have a wide scope of application. This, in particular, in case of labor legal relations, the test term for employment, in some cases, can be established, besides harmonizing the parties to the employment contract, in coordination with the relevant trade union committee for up to six months, whereas with the overall test for employees he is not May exceed three months.
However, the most fully carried out by trade union authorities protection of the interests of workers
In the process of work, that is, when the employment contract is concluded. Almost this applies to both the conclusion and control over the implementation of the collective agreement. Together with the owner, the electoral trade union authority of the enterprise solves the issue of introducing, revising or changing the norms of labor, it takes part in solving the wage of workers, in establishing a form and wage system, the introduction of premiums, additional payments, premiums and other incentive payments. Together with the trade union authorities, the owner solves the issues of working time, the rest time, coordinates the schedules of replacement and the provision of vacations. Trade union organ
gives permission to carry out overtime works, work on weekends, etc. The real defense of the trade union authority of the interests of workers is occurring at the termination of labor relations. So, when dismissing an employee, on the initiative of the owner, on the grounds, as the identification of the inconsistency of the employee of the position or work performed due to insufficient qualifications or health status, the commission, the systematic non-fulfillment of the employee without the valid causes entrusted with the employment contract and in other cases provided for in other cases Labor legislation, the owner can realize his right, that is, to dismiss the employee only having received the preliminary agreement of the trade union organ of the primary organization, the member of which is a worker (Article 43 of the Kzot of Ukraine).
Along with the specified, trade union bodies, like any other legal entity, are entitled to act as an employer, that is, to use hired labor. This applies primarily by elected trade union permanent bodies, which for the implementation of their powers use the hired labor of different categories of employees - employees, engineering and technical workers, service personnel and other, concluding an employment contract with them. Feature of trade union bodies As employers lies in a harmonious combination of the use of hired labor in order to protect the interests of employees in the process of realizing the right to work, with the existence of labor relations, when they change or terminate them. In other words, all trade union authorities: the Federation of Trade Unions of Ukraine, regional trade union councils, city councils of trade unions (Kiev and m. Sevastopol), industry trade union bodies, district trade union committees and primary trade union bodies in enterprises, organizations, institutions using hired work How employers are aimed at protecting the interests of workers in the process of their work.
Ministry of Education and Science, Youth and Sports of Ukraine
Gvuz "Priazovsky State Technical University"
Department of Economic Theory
Lecture number 8.
At the rate of the foundation of the economy theory
"Labor relations and wages"
Compiled by: k.e.n. Dyakova M.S.
Mariupol, 2014.
Topic 8. Labor relations and wages
1. Labor teams and trade unions.
2. The cost of labor and workplace
3. Salary of its shape and function
4. Influence of state and trade unions on wages and labor market
Labor collectives and trade unions.
First of all, we note that the combination of labor with the means of production occurs in society at the level of individual enterprises, when individual labor is included in the composition of the labor collective.
At the same time, the organizational and economic essence of this compound comes down to the direct use of the employee of certain funds and labor items, regardless of their belonging (property). The main thing in this process is rational to organize a workplace, work; achieve the highest results with a minimum of labor costs and means of production (SP).
The socio-economic side of this compound indicates its nature and method. Those. If the means of production belong to the labor team or a separate individual, the compound is of direct nature, it is based on its own work. If they (SP) belong to the capitalist (individual, associated), then the compound is carried out directly, i.e. Through the purchase and sale of labor and is based on the work of hired workers. However, the joint activities of employees in modern conditions are carried out with the formation of labor collectives.
Labor team is the socio-economic form of the organization of workers. According to the Law of Ukraine "On the Enterprise", it includes all citizens who take part in its activities on the basis of an employment contract (contract, agreements) or other forms that regulate the labor relations of workers and enterprises.
In a political economy understanding, a labor collective is a subject of economic relations, primarily property relations, as well as a cumulative worker, which ensures the rational use of cash in order to create and assigning income.
However, if the employment team refers to an enterprise belonging to private capital, it is only a subject of organizational and economic relations (specialization, cooperation, etc.).
Depending on the ownership of the means of production, the functions of the labor collective are formed.
The main function of the labor collective is production and labor (i.e. associated with the main task - to produce goods and services in order to meet the need for them).
The next function of the labor collective is production and financialwhich is associated with measures to improve production efficiency (intensification, resource saving) in order to obtain greater income and profits.
Further, socio-educational function. It is aimed at the preparation of a highly qualified, initiative employee; the formation of a stable, disciplined labor collective, creating favorable conditions for high-performance labor; Implementation of the principle of social justice in the distribution of income, social benefits.
Contradictions that arise between the state and the labor collective, as well as the last and capitalist arise on the basis of the distribution of income created by him, as well as working conditions. So, in the former union from the incomes of labor collectives in the state budget (closed) more than 70%, i.e. The so-called "nationwide interests" prevalted, and collective were secondary.
In order to defend its interests, employees of the enterprise are combined into trade unions.
Initially, trade unions grew from workers' clubs, temporary strike committees. Formed trade unions began to defend: wage increase; reduction of the working day; an increase in the duration of vacations; improving working conditions; Providing additional insurance assistance.
The first trade unions arose in the middle of the XVIII century. In England, and at the end of the XVIII - in France and the United States.
At the same time, in England, trade unions were prohibited by a parliamentary act of 1799, in France - the decision of the National Assembly of 1791.
However, under pressure from the labor movement, these laws were abolished (in England - 1825, in France - 1864, in Germany - 1869). Later in other countries.
Of course, combined into trade unions, the workers sought their requirements if not completely, then at least partially (in increasing wages, improving working conditions, reduction of the working day).
The largest success of the trade unions was achieved in the post-Betyabrs (1917) and after World War II.
During this period, the basics of labor law were laid, which became a guideline for trade unions in the struggle for improving labor legislation.
In the future, the system of collective agreements between trade unions and employers, entrepreneurs gradually enacted.
And the subject of negotiations at the conclusion of contracts were:
The size of the hourly salary rate;
Duration of the day;
Conditions for determining pensions and insurance in case of illness, injuries;
Procedure for appealing cases of dismissal of employees.
The conclusion of such contracts (agreements) is a large socio-economic conquest of workers and trade unions, which has a positive effect on the overall development of a person.
However, entrepreneurs defended their right to dismissal workers, which in modern conditions is included in the collective contracts, but imposing certain compensation for dismissal (for the I-36 weeks after the dismissal of 100% wages as it takes place in the automotive industry).
At the same time, trade unions are not only struggling for the rights of workers, but also pay more attention to improving and strengthening the discipline of the work of workers in the enterprise, an increase in their experience, qualifications, initiatives.
Moreover, the collective agreements began to include items on additional material interest in highly efficient, initiative work of employees. The practice of redemption of part of capital is expanding, the acquisition of shares by employees. It was assumed that by 2000 the co-owners of enterprises will be a quarter of all working Americans. And this is largely promoted by trade unions.
All this could not but affect the decline in the activity of the labor movement in the 80s (the number of strikes decreases by 3 times compared with the 70s.).
Such a tactic of national trade unions coincides with the main activities of the International Labor Organization (ILO), acting in the UN.
A member of this organization were trade unions of the former Union since 1934. Over the years of its existence, the ILO adopted 172 of the Convention, the regulatory act, which should have regulated socio-labor agreements (the Union ratified 43 of them).
The ILO Council is seeking social partnership between workers and entrepreneurs.
As for the trade unions in the former USSR, their leaders have grown with representatives of the party-state management system and defended the interests, above all, elites.
Therefore, such an unsightly existence of workers was in a number of industries (coal, chemical, metallurgical, etc.). From 20 to 26% worked under conditions degrading person, and they continue to work, say, in the same coal industry.
The result of such a relationship of trade unions to its functions was the fact that strike movements began to turn away from official trade unions, creating their own, independent strike committees. This process was especially common in mid-1989, when the wave of the strike movement covered 40 regions of the former Union.
At the same time, in the conditions of reforming the economic economy and strikes, it is not the best means of settling their rights, although necessary. Everything is connected with those losses that they are applied by the national economy as a whole (in 1989, only in Ukraine through the strikes of miners and metallurgists, there were no products for 187.3 million kb.).
In this regard, the conclusion of collective labor contracts is played to reduce the confrontation between the owner of the production and working contracts. In developed countries, this system of establishing employment relations received official status at the beginning of the XX century. Residually admitted this system and ILO in 1949, 1951. In its Convention on the recognition of the principles of the right to the organization and conclusion of collective agreements.
For the first time, this system was used successfully during the NEP. Then after its folding, it acquired a purely formal character (in the form of a ritual). And only in recent years she began to revive.
Thus, in the Law of Ukraine "On Enterprises" it is said that a collective agreement should be to be in all industries where hired labor is used between the owner and the labor team or the authority authorized by it.
The collective agreement is regulated by the production, labor and economic relations of the labor collective with the administration of the enterprise, the issues of labor protection, social development, the participation of employees in the use of the company's profits, if this is provided for by the Company's charter.
As for the trade unions, the advice of sectoral trade unions of federations, independent and other trade unions is granted the right to conclude labor agreements with the government of the republic or another authority. So, in 1991-1993 Such an agreement was concluded between the Government of Ukraine and the Council of the Federation of Independent Trade Unions of the Republic.
In addition, republican associations of trade unions have the right to legislative initiative. Regarding the workforce, which is the main object in the activities of trade unions, then it will be discussed in the next question.